2b8f91a4595d820c0b54f7aa67f9758c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 75
 Ethnicity Chapter 7
Ethnicity Chapter 7
 Introduction § As citizens of the US, we are Americans § Our nationality § Many Americans also identify with an ethnicity § A group that they share a common culture with § Ethnicity is a source of pride to many
Introduction § As citizens of the US, we are Americans § Our nationality § Many Americans also identify with an ethnicity § A group that they share a common culture with § Ethnicity is a source of pride to many
 continued § Ethnicity- identity with a group of people who share the cultural traditions of a particular homeland or hearth § Not the same as race § Identity with a group of people who share a biological ancestor § Geographers are interested in where ethnicities are distributed across space
continued § Ethnicity- identity with a group of people who share the cultural traditions of a particular homeland or hearth § Not the same as race § Identity with a group of people who share a biological ancestor § Geographers are interested in where ethnicities are distributed across space
 Distribution of Ethnicities in the United States § 2 most important are Hispanics (Latinos) at 14% of pop. and African Americans at 12% of pop. § Also have about 4% Asian American and 1% American Indian
Distribution of Ethnicities in the United States § 2 most important are Hispanics (Latinos) at 14% of pop. and African Americans at 12% of pop. § Also have about 4% Asian American and 1% American Indian
 Clustering of Ethnicities § 1. 2. Clustering occurs on two scales Particular regions of a country Particular neighborhoods of cities
Clustering of Ethnicities § 1. 2. Clustering occurs on two scales Particular regions of a country Particular neighborhoods of cities
 Regional Concentrations of Ethnicities § African Americans are clustered in the SE, Hispanics in the SW, Asian Americans in the West, and American Indians in the SW and Plains states
Regional Concentrations of Ethnicities § African Americans are clustered in the SE, Hispanics in the SW, Asian Americans in the West, and American Indians in the SW and Plains states
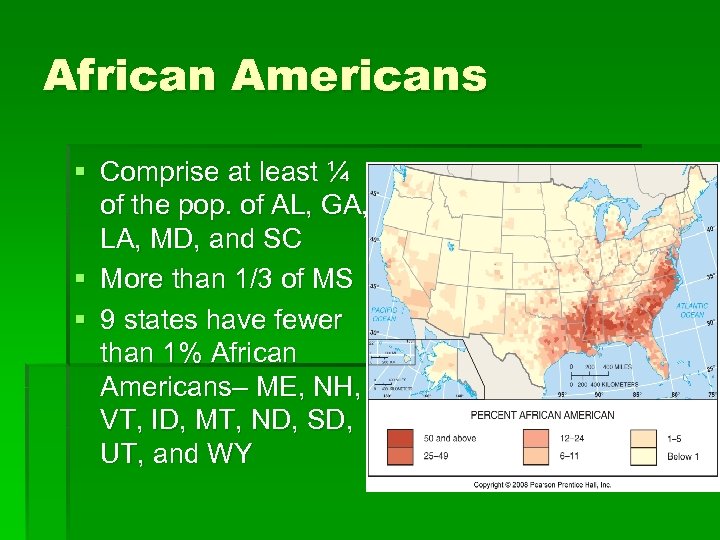 African Americans § Comprise at least ¼ of the pop. of AL, GA, LA, MD, and SC § More than 1/3 of MS § 9 states have fewer than 1% African Americans– ME, NH, VT, ID, MT, ND, SD, UT, and WY
African Americans § Comprise at least ¼ of the pop. of AL, GA, LA, MD, and SC § More than 1/3 of MS § 9 states have fewer than 1% African Americans– ME, NH, VT, ID, MT, ND, SD, UT, and WY
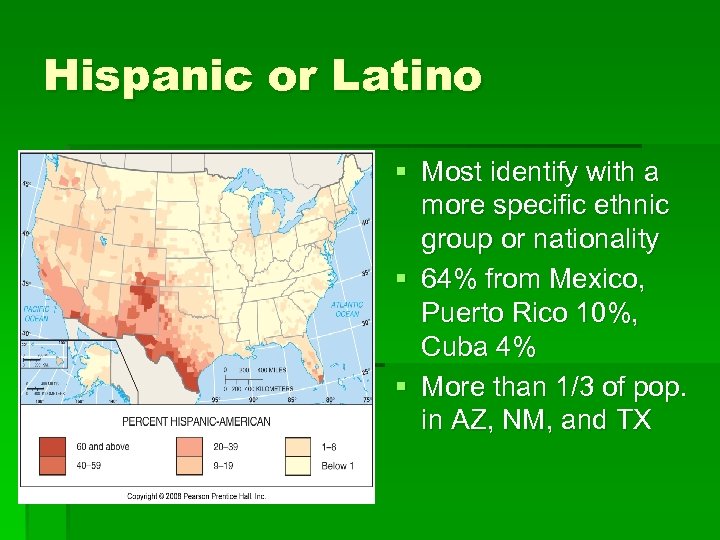 Hispanic or Latino § Most identify with a more specific ethnic group or nationality § 64% from Mexico, Puerto Rico 10%, Cuba 4% § More than 1/3 of pop. in AZ, NM, and TX
Hispanic or Latino § Most identify with a more specific ethnic group or nationality § 64% from Mexico, Puerto Rico 10%, Cuba 4% § More than 1/3 of pop. in AZ, NM, and TX
 continued § CA is home to 30% of all Hispanics in the US § Hispanics are more than ¼ pop. of CA § TX home to 20% § FL and NY home to about 15% each of all Hispanics in the US
continued § CA is home to 30% of all Hispanics in the US § Hispanics are more than ¼ pop. of CA § TX home to 20% § FL and NY home to about 15% each of all Hispanics in the US
 Asian Americans § Chinese account for 23% of Asian Americans § 19% are Indian § 18% Filipino § Korean 10% § Vietnamese 10% § Japanese 7%
Asian Americans § Chinese account for 23% of Asian Americans § 19% are Indian § 18% Filipino § Korean 10% § Vietnamese 10% § Japanese 7%
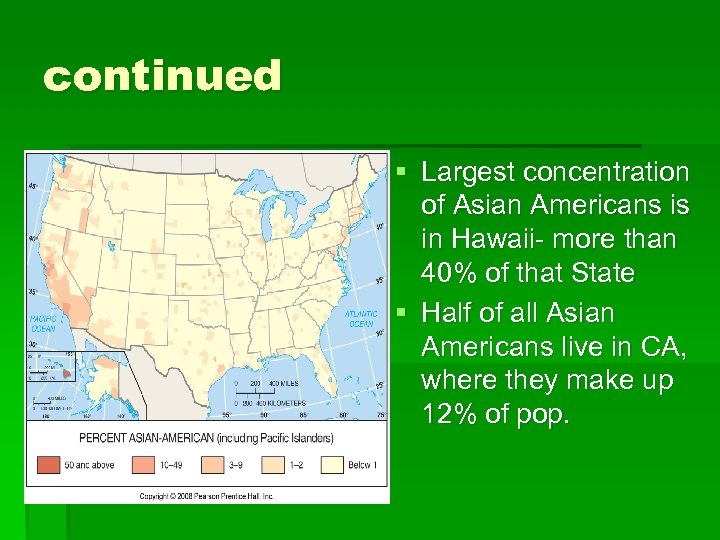 continued § Largest concentration of Asian Americans is in Hawaii- more than 40% of that State § Half of all Asian Americans live in CA, where they make up 12% of pop.
continued § Largest concentration of Asian Americans is in Hawaii- more than 40% of that State § Half of all Asian Americans live in CA, where they make up 12% of pop.
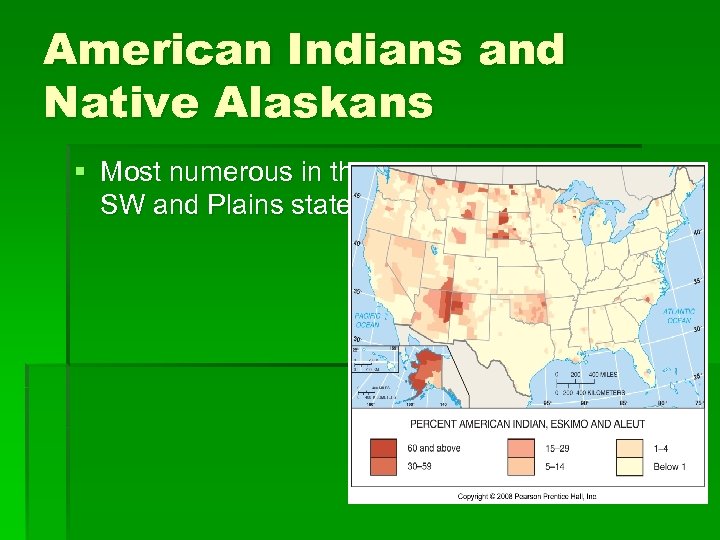 American Indians and Native Alaskans § Most numerous in the SW and Plains states
American Indians and Native Alaskans § Most numerous in the SW and Plains states
 Concentration of Ethnicities In Cities § African Americans are highly clustered within cities § Only ¼ of all Americans live in cities, but more than ½ of African Americans do § African Americans make up 7% of state of Michigan, but 85% of Detroit § Chicago is more than 1/3 African American, state of Illinois only 1/12
Concentration of Ethnicities In Cities § African Americans are highly clustered within cities § Only ¼ of all Americans live in cities, but more than ½ of African Americans do § African Americans make up 7% of state of Michigan, but 85% of Detroit § Chicago is more than 1/3 African American, state of Illinois only 1/12
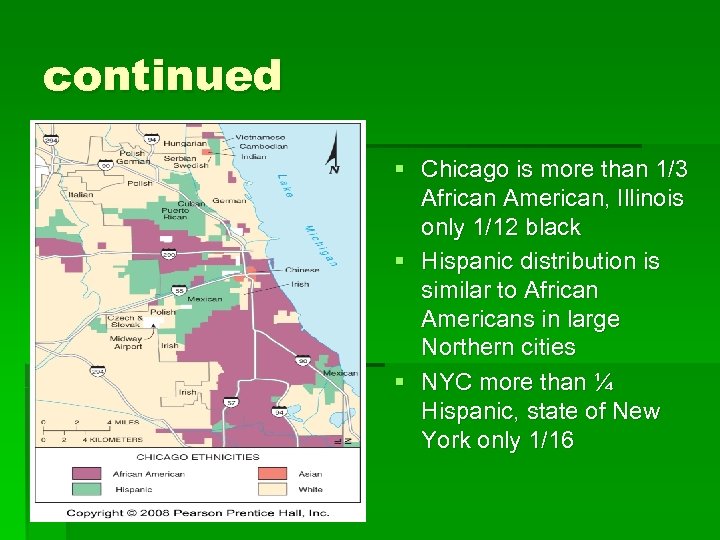 continued § Chicago is more than 1/3 African American, Illinois only 1/12 black § Hispanic distribution is similar to African Americans in large Northern cities § NYC more than ¼ Hispanic, state of New York only 1/16
continued § Chicago is more than 1/3 African American, Illinois only 1/12 black § Hispanic distribution is similar to African Americans in large Northern cities § NYC more than ¼ Hispanic, state of New York only 1/16
 continued § Clustering of ethnicities is especially pronounced on the scale of neighborhoods within cities § Chicago, Cleveland, and Detroit attracted ethnic groups from Southern and Eastern Europe to work in steel and auto industries during the early 1900 s § Their children and grandchildren moved out of original inner-city neighborhoods during the 20 th century
continued § Clustering of ethnicities is especially pronounced on the scale of neighborhoods within cities § Chicago, Cleveland, and Detroit attracted ethnic groups from Southern and Eastern Europe to work in steel and auto industries during the early 1900 s § Their children and grandchildren moved out of original inner-city neighborhoods during the 20 th century
 continued § An abundance of ethnic restaurants are the only visible signs of what was once an ethnic neighborhood § Today, African Americans, Latin Americans, and Asian Americans increasingly make up ethnic concentrations at the neighborhood level § In many cases they have moved into neighborhoods once dominated by European ethnicities
continued § An abundance of ethnic restaurants are the only visible signs of what was once an ethnic neighborhood § Today, African Americans, Latin Americans, and Asian Americans increasingly make up ethnic concentrations at the neighborhood level § In many cases they have moved into neighborhoods once dominated by European ethnicities
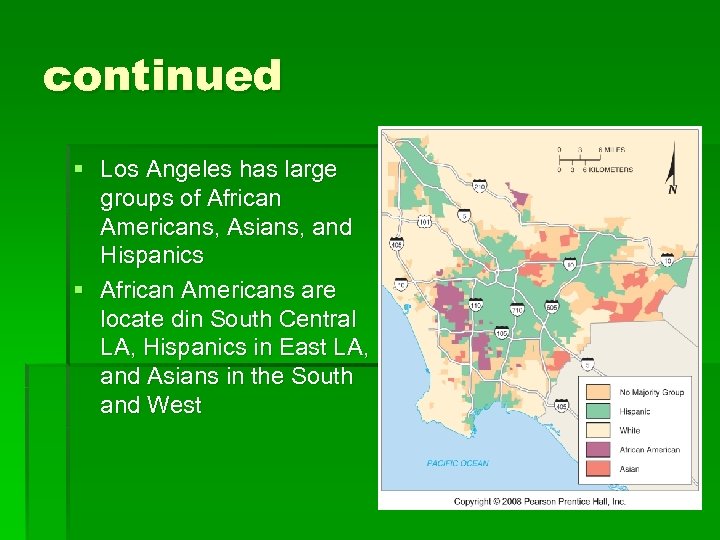 continued § Los Angeles has large groups of African Americans, Asians, and Hispanics § African Americans are locate din South Central LA, Hispanics in East LA, and Asians in the South and West
continued § Los Angeles has large groups of African Americans, Asians, and Hispanics § African Americans are locate din South Central LA, Hispanics in East LA, and Asians in the South and West
 African American Migration Patterns § § 1. 2. 3. The clustering of ethnicities in the United States is partly a function of migration Three migration flows have shaped the current distribution of African Americans in the US Forced immigration from Africa in the 18 th century Immigration from the Us South to northern cities during the first half of the 20 th century Immigration from inner-city ghettos to other urban neighborhoods during the second half of the 20 th century and first decade of the 21 st
African American Migration Patterns § § 1. 2. 3. The clustering of ethnicities in the United States is partly a function of migration Three migration flows have shaped the current distribution of African Americans in the US Forced immigration from Africa in the 18 th century Immigration from the Us South to northern cities during the first half of the 20 th century Immigration from inner-city ghettos to other urban neighborhoods during the second half of the 20 th century and first decade of the 21 st
 Forced Migration From Africa § Most African Americans are descended from slaves § The first African slaves arrived in Jamestown in 1619 § In 1700 s 400, 000 African slaves were brought to the American colonies § In 1808 the US banned the importation of new African slaves, but it is estimated 250, 000 more were brought in illegally
Forced Migration From Africa § Most African Americans are descended from slaves § The first African slaves arrived in Jamestown in 1619 § In 1700 s 400, 000 African slaves were brought to the American colonies § In 1808 the US banned the importation of new African slaves, but it is estimated 250, 000 more were brought in illegally
 continued § The large-scale slave trade was a response to a shortage of labor in the sparsely inhabited Americas § b/w 1710 and 1810 more than 10 million Africans were sold into slavery in the Western Hemisphere § The British and Portuguese each shipped about 2 million during this period § Most British went to Caribbean Islands, most Portuguese to Brazil
continued § The large-scale slave trade was a response to a shortage of labor in the sparsely inhabited Americas § b/w 1710 and 1810 more than 10 million Africans were sold into slavery in the Western Hemisphere § The British and Portuguese each shipped about 2 million during this period § Most British went to Caribbean Islands, most Portuguese to Brazil
 continued § Triangular slave trade- practice of European ships transported slaves from Africa to Caribbean islands, molasses from the Caribbean to Europe, and trade goods from Europe to Africa § “Middle passage” was middle leg where slaves were transported to the Americas
continued § Triangular slave trade- practice of European ships transported slaves from Africa to Caribbean islands, molasses from the Caribbean to Europe, and trade goods from Europe to Africa § “Middle passage” was middle leg where slaves were transported to the Americas

 continued § In the American colonies, the need for large scale agricultural labor was greatest in the South § Mostly for cotton and tobacco § After the Emancipation Proclamation, the Civil War, and the 13 th Amendment slavery was outlawed
continued § In the American colonies, the need for large scale agricultural labor was greatest in the South § Mostly for cotton and tobacco § After the Emancipation Proclamation, the Civil War, and the 13 th Amendment slavery was outlawed
 continued § Most freed slaves remained in the South during the late 19 th century working as sharecroppers § Farmer who works land owned by someone else, turning over a portion of proceeds for use of the land § Sharecroppers had to get a line of credit to buy seeds, tools, living quarters, etc. from the landowner § The debt was to be repaid with more crops
continued § Most freed slaves remained in the South during the late 19 th century working as sharecroppers § Farmer who works land owned by someone else, turning over a portion of proceeds for use of the land § Sharecroppers had to get a line of credit to buy seeds, tools, living quarters, etc. from the landowner § The debt was to be repaid with more crops
 continued § Sharecropping burdened African Americans with a large amount of debt and high interest rates § They were forced to grow cash crops instead of food they could eat
continued § Sharecropping burdened African Americans with a large amount of debt and high interest rates § They were forced to grow cash crops instead of food they could eat
 Immigration to the North § Sharecropping declined in early 20 th century with the introduction of farm machinery § Got pushed off the farms § Pulled to Northern cities and the prospect of jobs § Migration happened in 2 main waves
Immigration to the North § Sharecropping declined in early 20 th century with the introduction of farm machinery § Got pushed off the farms § Pulled to Northern cities and the prospect of jobs § Migration happened in 2 main waves
 continued 1. 2. § 1910 s-1920 s before and after WWI 19402 -1950 s before after WWII Factories had a huge demand for labor to produce war materials and the increase in demand for consumer goods after the wars
continued 1. 2. § 1910 s-1920 s before and after WWI 19402 -1950 s before after WWII Factories had a huge demand for labor to produce war materials and the increase in demand for consumer goods after the wars
 Expansion of the Ghetto § Most immigrants to big cities clustered in the one or two neighborhoods were African Americans were already living § Ex. 500, 000 African Americans lived in a 3 sq. mile ghetto in Chicago § Ghettos were small and overcrowded and African Americans began to push into areas adjacent to the Ghettos
Expansion of the Ghetto § Most immigrants to big cities clustered in the one or two neighborhoods were African Americans were already living § Ex. 500, 000 African Americans lived in a 3 sq. mile ghetto in Chicago § Ghettos were small and overcrowded and African Americans began to push into areas adjacent to the Ghettos

 Differentiating Ethnicity and Race § Asian is recognized as a race by US Census Bureau– therefore Asian as a race and Asian American ethnicity pretty much mean the same thing § African American and black are diff. groups– some American blacks trace back their heritage to places other than Africa § Hispanic or Latino in not a race– on the census they may choose any race they wish
Differentiating Ethnicity and Race § Asian is recognized as a race by US Census Bureau– therefore Asian as a race and Asian American ethnicity pretty much mean the same thing § African American and black are diff. groups– some American blacks trace back their heritage to places other than Africa § Hispanic or Latino in not a race– on the census they may choose any race they wish
 continued § The traits that characterize race are those that can be transmitted genetically from parents to children § Biological classification by race can lead to racism § Belief that race is the primary determinant of human traits and capacities and that racial differences produce an inherent superiority of a particular race
continued § The traits that characterize race are those that can be transmitted genetically from parents to children § Biological classification by race can lead to racism § Belief that race is the primary determinant of human traits and capacities and that racial differences produce an inherent superiority of a particular race
 continued § Contemporary geographers reject the entire biological basis of classifying humans into a handful of races because these features are not rooted in specific places § Only one feature of race matters to geographers § The color of skin § Matters because in many societies it helps determine where you live, attend school, recreate, and perform many activities of daily life
continued § Contemporary geographers reject the entire biological basis of classifying humans into a handful of races because these features are not rooted in specific places § Only one feature of race matters to geographers § The color of skin § Matters because in many societies it helps determine where you live, attend school, recreate, and perform many activities of daily life
 Race in the United States § 2000 census listed 14 races for respondents to choose from § 75% indicated they were white § 12% black § 4% Asian § 1% American Indian § 6% other § 2% checked more than 1
Race in the United States § 2000 census listed 14 races for respondents to choose from § 75% indicated they were white § 12% black § 4% Asian § 1% American Indian § 6% other § 2% checked more than 1
 “Separate But Equal” Doctrine § A distinctive feature if US race relations has been the history of discouragement of spatial interaction b/w races § In the past thru legal means, today thru cultural preferences or discrimination § Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) § Led to “Jim Crow” laws and legalized segregation
“Separate But Equal” Doctrine § A distinctive feature if US race relations has been the history of discouragement of spatial interaction b/w races § In the past thru legal means, today thru cultural preferences or discrimination § Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) § Led to “Jim Crow” laws and legalized segregation
 “White Flight” § Segregation laws were eliminated in the 1950 s and 1960 s after Brown v. Board of Education (1954) § Rather than integrate, many whites moved into area that African Americans could not afford to live (white flight) § Helped spur the growth of the ghetto § Ex. Detroit § 1950 1. 7 million whites, 300 thousand blacks § 2000 200 thousand whites, 800 thousand blacks
“White Flight” § Segregation laws were eliminated in the 1950 s and 1960 s after Brown v. Board of Education (1954) § Rather than integrate, many whites moved into area that African Americans could not afford to live (white flight) § Helped spur the growth of the ghetto § Ex. Detroit § 1950 1. 7 million whites, 300 thousand blacks § 2000 200 thousand whites, 800 thousand blacks
 continued § Blockbusting encouraged white flight § A process by which real estate agents convince white property owners to sell their houses at low prices because of fear that persons of color will soon move into the neighborhood § The agents would then sell the home at a higher price to black families hoping to escape the ghetto § Neighborhoods went from all white to all black in a matter of months
continued § Blockbusting encouraged white flight § A process by which real estate agents convince white property owners to sell their houses at low prices because of fear that persons of color will soon move into the neighborhood § The agents would then sell the home at a higher price to black families hoping to escape the ghetto § Neighborhoods went from all white to all black in a matter of months
 Division b Race in South Africa § While the US was repealing segregation laws South Africa was enacting them § Done thru a legal system known as apartheid § The physical separation of diff. races into diff. geographic areas § Laws were repealed in 1990 s, but policies are still impacting South Africa
Division b Race in South Africa § While the US was repealing segregation laws South Africa was enacting them § Done thru a legal system known as apartheid § The physical separation of diff. races into diff. geographic areas § Laws were repealed in 1990 s, but policies are still impacting South Africa
 Apartheid
Apartheid
 continued § § § 4 classifications of race White, black, colored (mixed), Asian 75% black, 14% white, 8% colored, 3% Asian § Each group had a different legal status § Laws determined where you could live, go to school, work, shop, and own land based upon your race
continued § § § 4 classifications of race White, black, colored (mixed), Asian 75% black, 14% white, 8% colored, 3% Asian § Each group had a different legal status § Laws determined where you could live, go to school, work, shop, and own land based upon your race
 continued § Blacks were only allowed to do certain jobs and could not vote or run for office § Read page 228+229 for the colonial history of South Africa to learn the origin of apartheid § Many nations cut off relations with South Africa in the 1970 s and 1980 s because they opposed apartheid
continued § Blacks were only allowed to do certain jobs and could not vote or run for office § Read page 228+229 for the colonial history of South Africa to learn the origin of apartheid § Many nations cut off relations with South Africa in the 1970 s and 1980 s because they opposed apartheid
 continued § Ford and GM closed factories in South Africa § However, neighboring nations were sill compelled to trade with them, Why? ? ? § Needed to use their ports to ship goods, and needed some of heir natural resources as well– chromium, platinum, and manganese
continued § Ford and GM closed factories in South Africa § However, neighboring nations were sill compelled to trade with them, Why? ? ? § Needed to use their ports to ship goods, and needed some of heir natural resources as well– chromium, platinum, and manganese
 continued § Trying to further separate the races the gov. created 10 “homelands” for blacks § The white gov. expected every black to become a citizen of a homeland move there § Only got around to making 4 homelands § If it had been fully implemented, the homelands would have been 19% of the land mass, but 44% of the pop.
continued § Trying to further separate the races the gov. created 10 “homelands” for blacks § The white gov. expected every black to become a citizen of a homeland move there § Only got around to making 4 homelands § If it had been fully implemented, the homelands would have been 19% of the land mass, but 44% of the pop.
 Dismantling of Apartheid § Laws repealed in 1991 § The African National Congress, was legalized and its leader Nelson Mandela, was released from prison after 27 years § 1994 all citizens were allowed to vote for first time and Mandela was elected President § Blacks have achieved political equality, but are still much poorer than whites
Dismantling of Apartheid § Laws repealed in 1991 § The African National Congress, was legalized and its leader Nelson Mandela, was released from prison after 27 years § 1994 all citizens were allowed to vote for first time and Mandela was elected President § Blacks have achieved political equality, but are still much poorer than whites
 Rise of Nationalities § Nationality- identity with a group of people who share legal attachment, cultural tradition, and personal allegiance to a particular country § Cultural traditions are different form than those of ethnicities § Thinks like voting, civic duties, and obtaining a passport
Rise of Nationalities § Nationality- identity with a group of people who share legal attachment, cultural tradition, and personal allegiance to a particular country § Cultural traditions are different form than those of ethnicities § Thinks like voting, civic duties, and obtaining a passport
 continued § Every citizen of the US is a member of the American nationality and a member of a race, but not all Americans identify with an ethnicity
continued § Every citizen of the US is a member of the American nationality and a member of a race, but not all Americans identify with an ethnicity
 Nation-States § Self-determination- the concept that ethnicities have the right to govern themselves § Wanted so they can preserve and enhance distinctive cultural characteristics § Modern political leaders have tried to support the right of self-determination and have attempted to organize Earth’s surface into a collection of nation-states
Nation-States § Self-determination- the concept that ethnicities have the right to govern themselves § Wanted so they can preserve and enhance distinctive cultural characteristics § Modern political leaders have tried to support the right of self-determination and have attempted to organize Earth’s surface into a collection of nation-states
 continued § Nation-states- a state whose territory corresponds to that occupied by a particular ethnicity that has been transformed into a nationality § Despite these efforts the territory of a state rarely corresponds to the territory occupied by an ethnicity
continued § Nation-states- a state whose territory corresponds to that occupied by a particular ethnicity that has been transformed into a nationality § Despite these efforts the territory of a state rarely corresponds to the territory occupied by an ethnicity
 Nation-States in Europe § During the 19 th century, ethnicities were transformed into nationalities in Europe § By 1900, most of Western Europe was made up of nation-states § They had boundary disagreements and competed to control Asia and Africa § Eastern Europe did not fit this pattern until the fall of the Ottoman Empire and the Austro. Hungarian Empire at the end of WWI
Nation-States in Europe § During the 19 th century, ethnicities were transformed into nationalities in Europe § By 1900, most of Western Europe was made up of nation-states § They had boundary disagreements and competed to control Asia and Africa § Eastern Europe did not fit this pattern until the fall of the Ottoman Empire and the Austro. Hungarian Empire at the end of WWI
 continued § The boundaries of Eastern Europe were redrawn according to the principles of nation-states § In the 1930 the Nazis used the same idea to claim that all German speaking peoples should be united into one state
continued § The boundaries of Eastern Europe were redrawn according to the principles of nation-states § In the 1930 the Nazis used the same idea to claim that all German speaking peoples should be united into one state
 Denmark: There are No Perfect Nation-States § Territory occupied by Danish ethnicity closely matches the state of Denmark § However, the southern boundary with Germany does not divide Danish and German nationalities precisely § Area is known as Schleswig-Holstein § Historically part of Denmark, taken by Germans in 19 th century, voted to return to Denmark after WWI
Denmark: There are No Perfect Nation-States § Territory occupied by Danish ethnicity closely matches the state of Denmark § However, the southern boundary with Germany does not divide Danish and German nationalities precisely § Area is known as Schleswig-Holstein § Historically part of Denmark, taken by Germans in 19 th century, voted to return to Denmark after WWI
 continued § Now some native German speakers live in Denmark and some native Danish speakers live in Germany § Denmark also controls two territories that are not populated heavily with Danes § Faeroe Islands and Greenland
continued § Now some native German speakers live in Denmark and some native Danish speakers live in Germany § Denmark also controls two territories that are not populated heavily with Danes § Faeroe Islands and Greenland
 Nationalism § A nationality must hold the loyalty of its citizens to survive § Politicians and governments use nationalism to do this § Loyalty and devotion to a nationality § Promotes a sense of national consciousness that promotes that nation over all others § Mass media is used in many states to foster nationalism
Nationalism § A nationality must hold the loyalty of its citizens to survive § Politicians and governments use nationalism to do this § Loyalty and devotion to a nationality § Promotes a sense of national consciousness that promotes that nation over all others § Mass media is used in many states to foster nationalism
 continued § In the US, an independent news media is used § Most countries regard independent news sources as a risk to the stability of gov. § States also foster nationalism by promoting symbols of the nation-state, such as flags and songs
continued § In the US, an independent news media is used § Most countries regard independent news sources as a risk to the stability of gov. § States also foster nationalism by promoting symbols of the nation-state, such as flags and songs
 continued § Nationalism is an important example of centripetal force § An attitude that tends to unify people and enhance support for a state
continued § Nationalism is an important example of centripetal force § An attitude that tends to unify people and enhance support for a state
 Multinational States § Multi-ethnic state- a state that contains more than one ethnicity § sometimes all ethnicities can contribute cultural features to the formation of a single nationality § Ex. Belgium – Flemish and Walloons § Multi-national states- state that contains two or more ethnic groups with traditions of selfdetermination that agree to coexist peacefully by recognizing each other as distinct nationalities
Multinational States § Multi-ethnic state- a state that contains more than one ethnicity § sometimes all ethnicities can contribute cultural features to the formation of a single nationality § Ex. Belgium – Flemish and Walloons § Multi-national states- state that contains two or more ethnic groups with traditions of selfdetermination that agree to coexist peacefully by recognizing each other as distinct nationalities
 continued § In some multi-national states one nationality tries to dominant another (often when they have greater numbers of people, and in some multi-national states everyone gets along peacefully § The people of one nation are sometimes assimilated into another, but in some cases the 2 nationalities remain distinct
continued § In some multi-national states one nationality tries to dominant another (often when they have greater numbers of people, and in some multi-national states everyone gets along peacefully § The people of one nation are sometimes assimilated into another, but in some cases the 2 nationalities remain distinct
 continued § The UK is a multi-national state § 4 main nationalities– England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland § Today they hold little independent power § Even though Scotland Wales have separately elected gov. ’s § Main element of distinct national identity comes from sports § Each have their own national soccer team
continued § The UK is a multi-national state § 4 main nationalities– England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland § Today they hold little independent power § Even though Scotland Wales have separately elected gov. ’s § Main element of distinct national identity comes from sports § Each have their own national soccer team
 Former Soviet Union: The Largest Multinational State § Its 15 Republics were based on the 15 largest ethnicities § Smaller ethnicities were not given enough recognition to get a republic § Some of the smaller ethnicities are now divided into more than one state
Former Soviet Union: The Largest Multinational State § Its 15 Republics were based on the 15 largest ethnicities § Smaller ethnicities were not given enough recognition to get a republic § Some of the smaller ethnicities are now divided into more than one state
 continued § Former Soviet Republics are broken into f different group § Three Baltic: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania § Three European: Belarus, Moldova, and Ukraine § Five Central Asian: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan § Three Caucasus: Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Georgia § Russia
continued § Former Soviet Republics are broken into f different group § Three Baltic: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania § Three European: Belarus, Moldova, and Ukraine § Five Central Asian: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan § Three Caucasus: Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Georgia § Russia

 continued § Reasonably good examples of nationstates have been created in the Baltic, European, and Central Asian states § But the Caucasus states have not been so lucky, and Russia itself has a difficult time keeping all its diff. ethnicities happy
continued § Reasonably good examples of nationstates have been created in the Baltic, European, and Central Asian states § But the Caucasus states have not been so lucky, and Russia itself has a difficult time keeping all its diff. ethnicities happy
 New Baltic Nation-States § All had been independent b/w the end of WWI until 1940 when they were annexed into the Soviet Union with an agreement with Nazi Germany § Lithuania is the closet to a true nationstate— 83% of pop. are ethnic Lithuanians
New Baltic Nation-States § All had been independent b/w the end of WWI until 1940 when they were annexed into the Soviet Union with an agreement with Nazi Germany § Lithuania is the closet to a true nationstate— 83% of pop. are ethnic Lithuanians
 continued § The three Baltic states have distinct cultural differences § Most Estonians are Lutherans, Lithuanians are mostly Catholic, and Latvians are Lutheran with a large Catholic Minority § Estonians speak a Uralic language, while Lithuanians and Latvians speak languages within the Balto-Slavic branch of Indo. European
continued § The three Baltic states have distinct cultural differences § Most Estonians are Lutherans, Lithuanians are mostly Catholic, and Latvians are Lutheran with a large Catholic Minority § Estonians speak a Uralic language, while Lithuanians and Latvians speak languages within the Balto-Slavic branch of Indo. European
 Russia: Now the Largest Multinational State § Officially recognizes 39 nationalities, many eager for independence § 20% of pop. is non-Russian § Chechens have been a big problem § They are Sunni Muslims § Brought under Russian control in the 1800 s after a 50 year fight § They declared independence in 1991 with the fall of the Soviet Union, but Russians sent in the military to prevent it from happening § Areas contains important petroleum deposits § Also didn’t want other groups to get any ideas
Russia: Now the Largest Multinational State § Officially recognizes 39 nationalities, many eager for independence § 20% of pop. is non-Russian § Chechens have been a big problem § They are Sunni Muslims § Brought under Russian control in the 1800 s after a 50 year fight § They declared independence in 1991 with the fall of the Soviet Union, but Russians sent in the military to prevent it from happening § Areas contains important petroleum deposits § Also didn’t want other groups to get any ideas
 Revival of Ethnic Identity § Europeans believed that ethnicity was a thing of the past and that nationalism could always be used to unite people § In the late 20 th century ethnic identity once again became more important than nationality
Revival of Ethnic Identity § Europeans believed that ethnicity was a thing of the past and that nationalism could always be used to unite people § In the late 20 th century ethnic identity once again became more important than nationality
 Ethnicity and Communism § Until they lost power in the late 1980 s and early 1990 s communists used centripetal forces to discourage ethnicities from expressing their cultural uniqueness § Thought differences would serve as an obstacle for unified support for communist ideology § Russian language was promoted as a unifying force in Soviet Union and taught as a second language n other communist countries
Ethnicity and Communism § Until they lost power in the late 1980 s and early 1990 s communists used centripetal forces to discourage ethnicities from expressing their cultural uniqueness § Thought differences would serve as an obstacle for unified support for communist ideology § Russian language was promoted as a unifying force in Soviet Union and taught as a second language n other communist countries
 Ethnic Competition to Dominate Nationality § Sub-Saharan Africa is a region plagued by conflicts among ethnic groups competing to become dominant within the various countries § The Horn of Africa and central Africa are two regions where conflicts have been brutal
Ethnic Competition to Dominate Nationality § Sub-Saharan Africa is a region plagued by conflicts among ethnic groups competing to become dominant within the various countries § The Horn of Africa and central Africa are two regions where conflicts have been brutal
 Ethiopia and Eritrea § Both were Italian colonies at one time § After WWII Ethiopia was granted independence and given control of Eritrea § Italians thought Ethiopia would give Eritrea local authority, but they didn’t § Actually banned their language and dissolved its legislature
Ethiopia and Eritrea § Both were Italian colonies at one time § After WWII Ethiopia was granted independence and given control of Eritrea § Italians thought Ethiopia would give Eritrea local authority, but they didn’t § Actually banned their language and dissolved its legislature
 continued § Led to civil war that lasted 30 years (1961 -1991) § Eritrean rebels defeated Ethiopians in 1991 and became independent § 1998 disputes broke out again over the location of the border § In 2000 Ethiopia won, and took the territory in dispute
continued § Led to civil war that lasted 30 years (1961 -1991) § Eritrean rebels defeated Ethiopians in 1991 and became independent § 1998 disputes broke out again over the location of the border § In 2000 Ethiopia won, and took the territory in dispute
 Sudan § Civil war has been raging since 1980 s § Christian and animist rebels in the south vs. Arab-Muslim dominated forces in the North § Southerners are resisting gov. attempts to make Sudan a totally Muslim state § Gov. has instituted many sex segregation laws
Sudan § Civil war has been raging since 1980 s § Christian and animist rebels in the south vs. Arab-Muslim dominated forces in the North § Southerners are resisting gov. attempts to make Sudan a totally Muslim state § Gov. has instituted many sex segregation laws
 continued § More than 2 million died during the war § 2005 peace accords called for autonomy for southern Christians and sharing power in the national gov. § As the religion based civil war was winding down an ethnic war erupted in the western Darfur region § Gov. has killed more than 450, 000 and more than 2. 5 million are living in refugee camps
continued § More than 2 million died during the war § 2005 peace accords called for autonomy for southern Christians and sharing power in the national gov. § As the religion based civil war was winding down an ethnic war erupted in the western Darfur region § Gov. has killed more than 450, 000 and more than 2. 5 million are living in refugee camps
 Somalia § Somalia is overwhelmingly Sunni Muslim and they speak the same language, Somali § On surface they should get along § However, there are six major ethnic groups or clans that make up the population § 1991 the gov. fell apart and since then the clans have been fighting for power
Somalia § Somalia is overwhelmingly Sunni Muslim and they speak the same language, Somali § On surface they should get along § However, there are six major ethnic groups or clans that make up the population § 1991 the gov. fell apart and since then the clans have been fighting for power
 Ethnic Competition in Lebanon § 4 million people living in 4000 sq. miles § Since 1970 s country has been damaged by religious fighting § Estimated that Lebanon is 60% Muslim, 30% Christian, and 10% other § Became independent in 1943, the constituion required that each religion be represented in the Chamber of Deputies according to percentage from 1932 census
Ethnic Competition in Lebanon § 4 million people living in 4000 sq. miles § Since 1970 s country has been damaged by religious fighting § Estimated that Lebanon is 60% Muslim, 30% Christian, and 10% other § Became independent in 1943, the constituion required that each religion be represented in the Chamber of Deputies according to percentage from 1932 census
 continued § Chrisitians were the majority when the gov. was created § But now Muslims are the majority § War broke out in 1975 and each religious group formed a private army to guard its territory § Israel and the US sent troops into Lebanon to try to restore peace several times unsuccesfully
continued § Chrisitians were the majority when the gov. was created § But now Muslims are the majority § War broke out in 1975 and each religious group formed a private army to guard its territory § Israel and the US sent troops into Lebanon to try to restore peace several times unsuccesfully



