9fa15c92ae855ed810b6deb3e62e1fd7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Ethics of Software Testing Thomas La. Toza CS 210 Final Presentation 12 / 2002
Ethics of Software Testing Thomas La. Toza CS 210 Final Presentation 12 / 2002
 Overview l l Background - facts of testing and bugs Education, training, best practices, and a commitment to reliability l l l All help to improve reliability Don’t solve the problem and still leave Research How much to spend on testing When to release software Most organizations should spend more on testing © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Overview l l Background - facts of testing and bugs Education, training, best practices, and a commitment to reliability l l l All help to improve reliability Don’t solve the problem and still leave Research How much to spend on testing When to release software Most organizations should spend more on testing © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Facts of Testing l Testing is an activity to evaluate quality and find bugs l Testing only proves presence of bugs l Testing NEVER proves absence of bugs l l (unless you could run every line of code for all possible inputs for all possible states in all possible environments with an oracle that knows the correct output and state) Testing is underappreciated l None of the top 5 CS departments offer an undergraduate course on testing or building software systems for reliability (other than formal verification) – only taught as part of a software engineering course l Often not perceived as challenging and fun l Admission of failure – people make mistakes © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Facts of Testing l Testing is an activity to evaluate quality and find bugs l Testing only proves presence of bugs l Testing NEVER proves absence of bugs l l (unless you could run every line of code for all possible inputs for all possible states in all possible environments with an oracle that knows the correct output and state) Testing is underappreciated l None of the top 5 CS departments offer an undergraduate course on testing or building software systems for reliability (other than formal verification) – only taught as part of a software engineering course l Often not perceived as challenging and fun l Admission of failure – people make mistakes © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Finding Bugs Not all bugs are equal. Bugs may be l Easier to find than other bugs l More important than other bugs (bugs that crash or destroy data vs. bugs that make the interface look bad) l Invisible until other bugs are fixed © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Finding Bugs Not all bugs are equal. Bugs may be l Easier to find than other bugs l More important than other bugs (bugs that crash or destroy data vs. bugs that make the interface look bad) l Invisible until other bugs are fixed © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Fixing Bugs l l Fixing a bug always has a chance of introducing new bug(s) which may be worse Overall effect of testing depends on ratio of bugs fixed to bugs introduced © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Fixing Bugs l l Fixing a bug always has a chance of introducing new bug(s) which may be worse Overall effect of testing depends on ratio of bugs fixed to bugs introduced © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Bugs aren’t cheap For users l Bugs and glitches cost the economy $59. 5 Billion a year (NIST estimate) For software projects l Testing cost can easily be 25 – 50% cost of project and can be much more for certified systems © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Bugs aren’t cheap For users l Bugs and glitches cost the economy $59. 5 Billion a year (NIST estimate) For software projects l Testing cost can easily be 25 – 50% cost of project and can be much more for certified systems © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
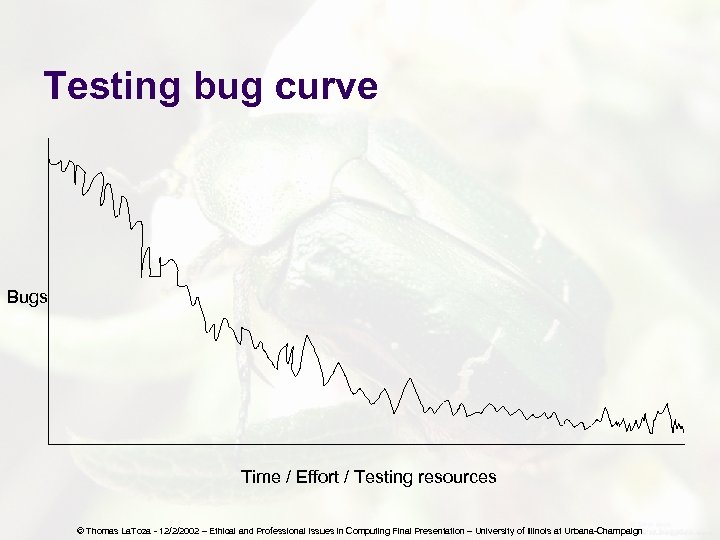 Testing bug curve Bugs Time / Effort / Testing resources © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Testing bug curve Bugs Time / Effort / Testing resources © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Overview l l Background - facts of testing and bugs Education, training, best practices, and a commitment to reliability l l l All help to improve reliability Don’t solve the problem and still leave Research How much to spend on testing When to release software Most organizations should spend more on testing © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Overview l l Background - facts of testing and bugs Education, training, best practices, and a commitment to reliability l l l All help to improve reliability Don’t solve the problem and still leave Research How much to spend on testing When to release software Most organizations should spend more on testing © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Engineering practices can help prevent bugs l Code reviews – highly effective l l Writing for readability l l Team members proof read the code and discuss There are two ways of constructing a software design; one way is to make it so simple that there are obviously no deficiencies, and the other way is to make it so complicated that there are no obvious deficiencies. The first method is far more difficult. - C. A. R. Hoare Design by test l Write the interface and test case first, then write the functionality Statistical testing l Commercial off the shelf software / Open Source / Components l Separate Quality Assurance team l Betas But none of these replace testing… l © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Engineering practices can help prevent bugs l Code reviews – highly effective l l Writing for readability l l Team members proof read the code and discuss There are two ways of constructing a software design; one way is to make it so simple that there are obviously no deficiencies, and the other way is to make it so complicated that there are no obvious deficiencies. The first method is far more difficult. - C. A. R. Hoare Design by test l Write the interface and test case first, then write the functionality Statistical testing l Commercial off the shelf software / Open Source / Components l Separate Quality Assurance team l Betas But none of these replace testing… l © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Research Problem has (recently) sparked great research interest l Recovery Oriented Computing l Formal Methods l Program Comprehension l Software Engineering © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Research Problem has (recently) sparked great research interest l Recovery Oriented Computing l Formal Methods l Program Comprehension l Software Engineering © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Testing Review It’s expensive and time consuming Doesn’t guarantee lack of bugs Developers often don’t like doing it But it’s really important… © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Testing Review It’s expensive and time consuming Doesn’t guarantee lack of bugs Developers often don’t like doing it But it’s really important… © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Overview l l Background - facts of testing and bugs Education, training, best practices, and a commitment to reliability l l l All help to improve reliability Don’t solve the problem and still leave Research How much to spend on testing When to release software Most organizations should spend more on testing © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Overview l l Background - facts of testing and bugs Education, training, best practices, and a commitment to reliability l l l All help to improve reliability Don’t solve the problem and still leave Research How much to spend on testing When to release software Most organizations should spend more on testing © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Review – Applying Ethical Theories 1. 2. 3. 4. Evaluate information Consider how decision may affect stakeholders Consider what ethics [ethical values] are relevant to situation Determine the best course of action that takes into account relevant values and stakeholders’ interests. (from Lockheed Martin Decision Making Model) © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Review – Applying Ethical Theories 1. 2. 3. 4. Evaluate information Consider how decision may affect stakeholders Consider what ethics [ethical values] are relevant to situation Determine the best course of action that takes into account relevant values and stakeholders’ interests. (from Lockheed Martin Decision Making Model) © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 How much to spend on testing (1. Evaluate Information) l l Most organizations should spend more on testing But have to stop somewhere – can’t spend all of your budget on testing Question of where on the curve is best There advantages for being further left and advantages for being further right © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
How much to spend on testing (1. Evaluate Information) l l Most organizations should spend more on testing But have to stop somewhere – can’t spend all of your budget on testing Question of where on the curve is best There advantages for being further left and advantages for being further right © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 More testing / Less bugs (2. Consider how decision may affect stakeholders) Advantages l Developers / Customers – less time working around bugs l Customers – less frustration dealing with software l Managers – know more about bugs in product and can deliver a higher quality product l Company – quality makes software more valuable to customer l Company – sooner bugs can be fixed the cheaper they are to fix Disadvantages l Customers – more expensive products l Company – less features, less compelling reasons for customer to spend money upgrading © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
More testing / Less bugs (2. Consider how decision may affect stakeholders) Advantages l Developers / Customers – less time working around bugs l Customers – less frustration dealing with software l Managers – know more about bugs in product and can deliver a higher quality product l Company – quality makes software more valuable to customer l Company – sooner bugs can be fixed the cheaper they are to fix Disadvantages l Customers – more expensive products l Company – less features, less compelling reasons for customer to spend money upgrading © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
![How much to spend on testing (3. Consider what ethics [ethical values] are relevant How much to spend on testing (3. Consider what ethics [ethical values] are relevant](https://present5.com/presentation/9fa15c92ae855ed810b6deb3e62e1fd7/image-16.jpg) How much to spend on testing (3. Consider what ethics [ethical values] are relevant to situation) (4. Determine best action based on relevant values and stakeholders) Utilitarian – maximize cost / benefit for company and / or customers Value – have a responsibility to provide a quality product by setting a quality standard and sticking to it Libertarian – just enough that it helps company the most (customer fends for himself) Altruism – so that it is best for the customer © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
How much to spend on testing (3. Consider what ethics [ethical values] are relevant to situation) (4. Determine best action based on relevant values and stakeholders) Utilitarian – maximize cost / benefit for company and / or customers Value – have a responsibility to provide a quality product by setting a quality standard and sticking to it Libertarian – just enough that it helps company the most (customer fends for himself) Altruism – so that it is best for the customer © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 When to release (1. Evaluate Information) l l Would like to have a higher quality product But have to stop somewhere – may not ever find all of the bugs Again question of where on the curve is best There advantages for being further left and advantages for being further right © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
When to release (1. Evaluate Information) l l Would like to have a higher quality product But have to stop somewhere – may not ever find all of the bugs Again question of where on the curve is best There advantages for being further left and advantages for being further right © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Release later / Less bugs (2. Consider how decision may affect stakeholders) Advantages l All of the advantages of more testing / less bugs l Managers – know more about quality of the product being delivered l Company / customers – higher quality product Disadvantages l All of the disadvantages of less testing / more bugs l Company – may lose marketshare to competitors l Company – no income from product l Customer – can’t use product at all l Company – may lose credibility for missing deadline © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Release later / Less bugs (2. Consider how decision may affect stakeholders) Advantages l All of the advantages of more testing / less bugs l Managers – know more about quality of the product being delivered l Company / customers – higher quality product Disadvantages l All of the disadvantages of less testing / more bugs l Company – may lose marketshare to competitors l Company – no income from product l Customer – can’t use product at all l Company – may lose credibility for missing deadline © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
![When to release (3. Consider what ethics [ethical values] are relevant to situation) (4. When to release (3. Consider what ethics [ethical values] are relevant to situation) (4.](https://present5.com/presentation/9fa15c92ae855ed810b6deb3e62e1fd7/image-19.jpg) When to release (3. Consider what ethics [ethical values] are relevant to situation) (4. Determine best action based on relevant values and stakeholders) Utilitarian – maximize cost / benefit for company and / or customers Value – set quality standard vs. keeping a ship date vs. money for company Libertarian – whenever the most customers will buy it Altruism – so that customer will have optimum balance of most time to use it and the best product © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
When to release (3. Consider what ethics [ethical values] are relevant to situation) (4. Determine best action based on relevant values and stakeholders) Utilitarian – maximize cost / benefit for company and / or customers Value – set quality standard vs. keeping a ship date vs. money for company Libertarian – whenever the most customers will buy it Altruism – so that customer will have optimum balance of most time to use it and the best product © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Conclusions l Many other ethical questions l l Should a bug be fixed? How much information about testing to release? Do developers and testers have professional standards to uphold? Expectations for quality – too high or too low? © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Conclusions l Many other ethical questions l l Should a bug be fixed? How much information about testing to release? Do developers and testers have professional standards to uphold? Expectations for quality – too high or too low? © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Further Reading l Economics of Software Verification l http: //cm. bell-labs. com/cm/cs/who/gerard/gz/paste 01. pdf © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Further Reading l Economics of Software Verification l http: //cm. bell-labs. com/cm/cs/who/gerard/gz/paste 01. pdf © Thomas La. Toza - 12/2/2002 – Ethical and Professional Issues in Computing Final Presentation – University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign


