bcb190c9d8c6341fb0bd49a0b1b35156.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

ESTMD System -- A Web-based EST Model Database System Yinghua Dong 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 1

Outline n Project Review n Architecture Design n Formal Requirement Specification n Test Plan n Formal Technical Inspection n Project Status n References n Acknowledgments 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 2

Project Review Objective Build a web-based, user-friendly Expressed Sequence Tags model database (ESTMD) system to help biologists search expression sequences and related information to make further decisions 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 3
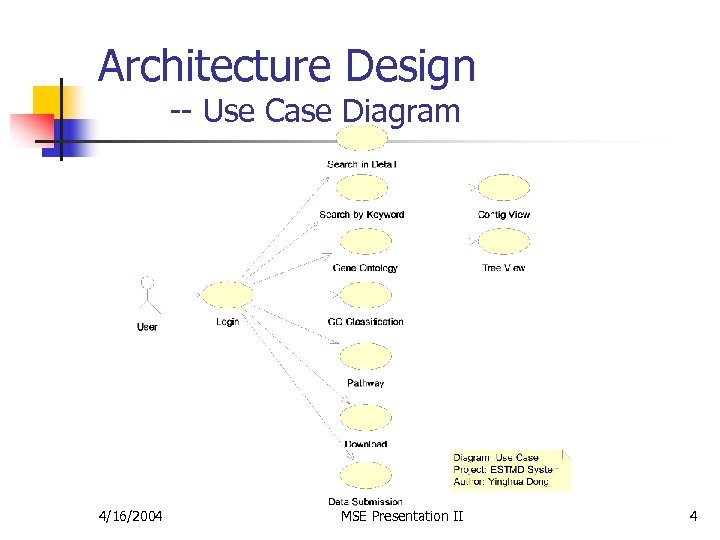
Architecture Design -- Use Case Diagram 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 4
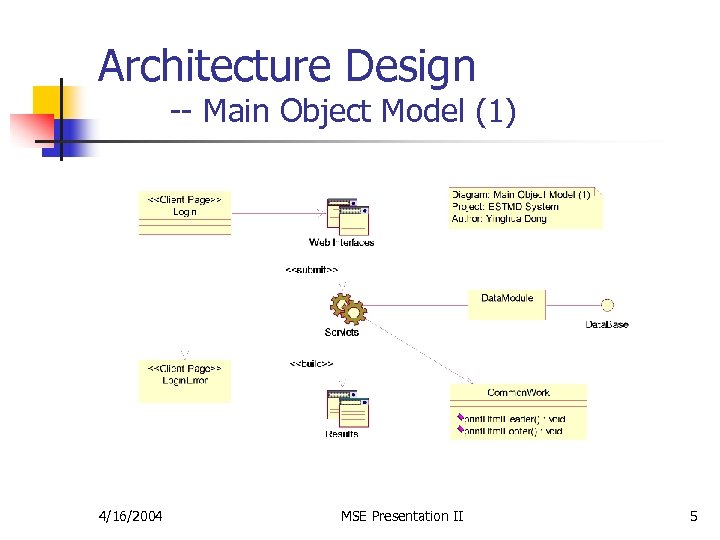
Architecture Design -- Main Object Model (1) 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 5
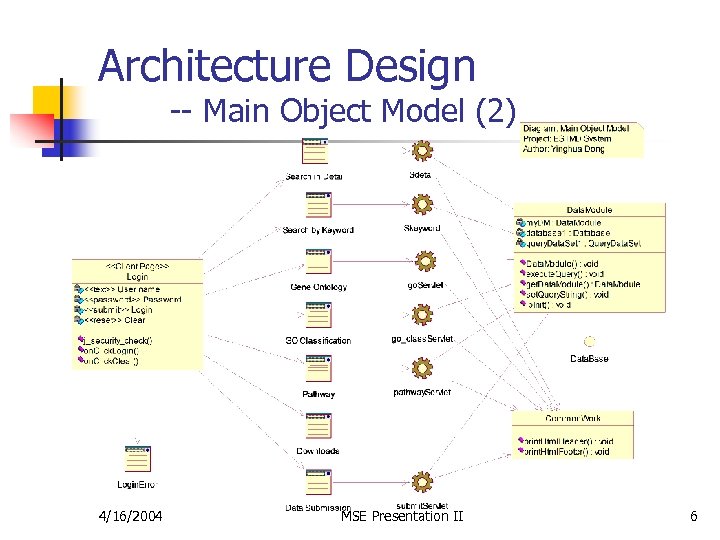
Architecture Design -- Main Object Model (2) 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 6
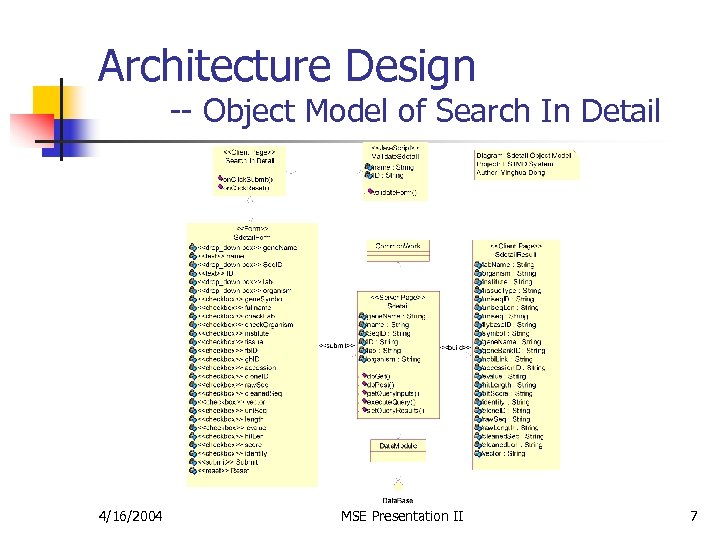
Architecture Design -- Object Model of Search In Detail 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 7
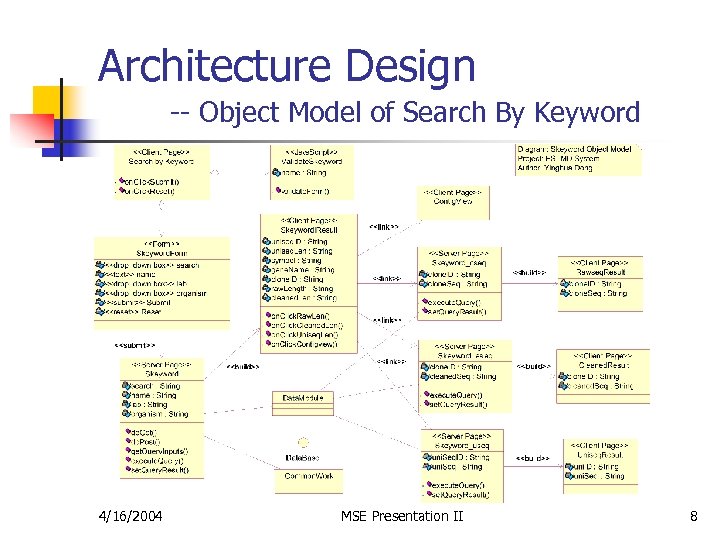
Architecture Design -- Object Model of Search By Keyword 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 8
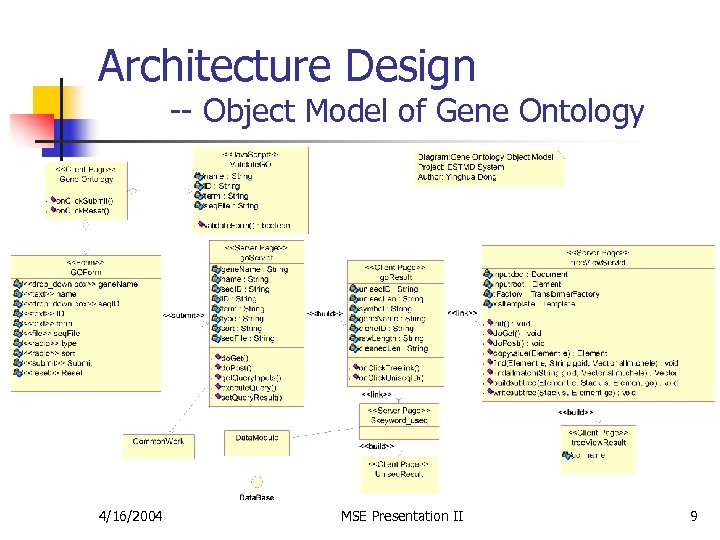
Architecture Design -- Object Model of Gene Ontology 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 9
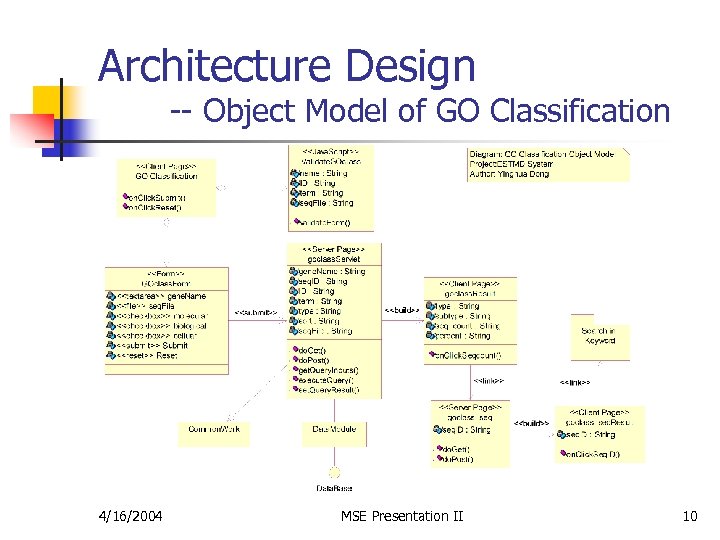
Architecture Design -- Object Model of GO Classification 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 10
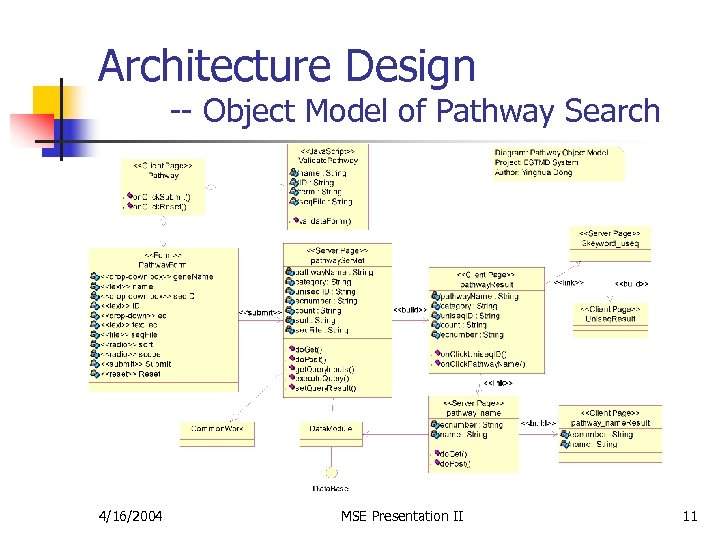
Architecture Design -- Object Model of Pathway Search 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 11
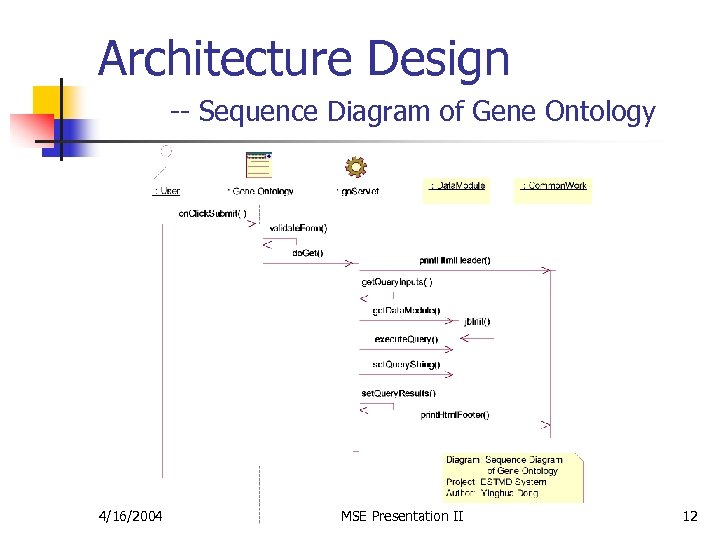
Architecture Design -- Sequence Diagram of Gene Ontology 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 12
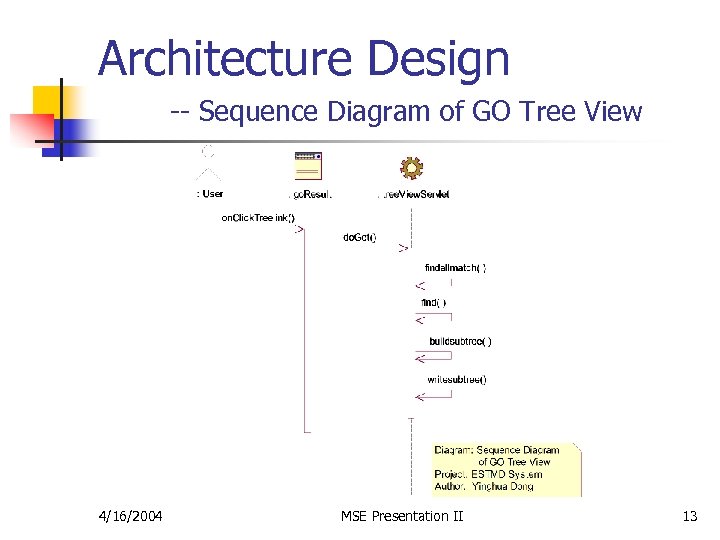
Architecture Design -- Sequence Diagram of GO Tree View 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 13
Formal Requirement Specification -- Overview n Language: Alloy 1. 1 -- a structural modeling language based on first-order logic n Tool: ACA (Alloy Constraint Analyzer) n Purpose: explore abstract software designs, simulate execution of operations (even defined implicitly), and check user-specified properties of a model n Scopes: Gene Ontology Query and Gene Ontology Tree Generation n References: Dr. John Hatcliff, CIS 771 Lectures Alloy web site, http: //sdg. lcs. mit. edu/alloy 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 14
FRS (cont’d) -- For Gene Ontology Query n n n The user who submits a form is the user who gets the form's query result. all f : Form | f. who. Put = f. query. who. Get. Rule The link belongs to the result which its corresponding output item belongs to. all l : Link | l. linked. By in l. link. Belong. To. include. Output. Item The input item is written by the user who put the corresponding query form. all ii: Input. Item | ii. belong. To. User=ii. belong. To. Form. who. Put 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 15
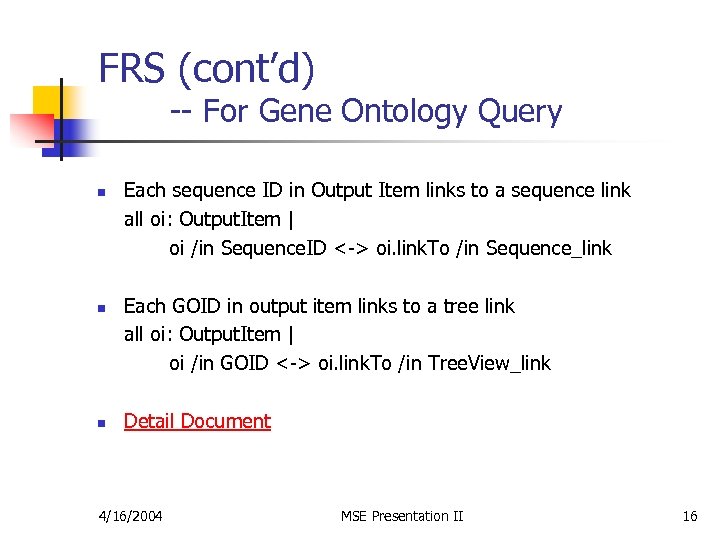
FRS (cont’d) -- For Gene Ontology Query n n n Each sequence ID in Output Item links to a sequence link all oi: Output. Item | oi /in Sequence. ID <-> oi. link. To /in Sequence_link Each GOID in output item links to a tree link all oi: Output. Item | oi /in GOID <-> oi. link. To /in Tree. View_link Detail Document 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 16

FRS (cont’d) -- For Gene Ontology Tree Generation n n n No Item is its own ancestor. no i: Item | i in i. +parents There is exactly one Root in each tree. one i: Item | i /in Root Each item except Root is Root's descendant. all i: Item - Root | Root in i. +parents Root has no parents or ancestor all r: Root | no r. +parents Leaf has no children or descendant all l: Leaf | no l. +children Non. Leaf. Item must have at least one parent and at least one child. all nl: non. Leaf. Item | some nl. parents && some nl. children 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 17
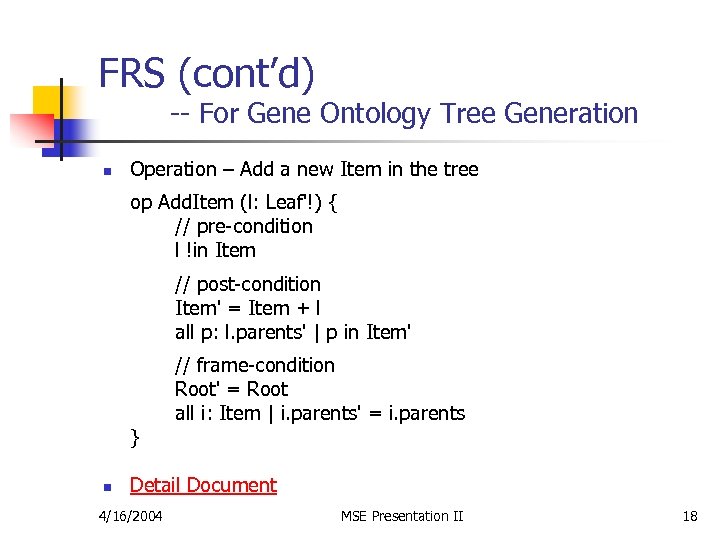
FRS (cont’d) -- For Gene Ontology Tree Generation n Operation – Add a new Item in the tree op Add. Item (l: Leaf'!) { // pre-condition l !in Item // post-condition Item' = Item + l all p: l. parents' | p in Item' } n // frame-condition Root' = Root all i: Item | i. parents' = i. parents Detail Document 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 18

Test Plan n Test Phases: n Unit testing, Integration testing, and System testing Test Items: n Connection between server and database n Each page Test Features: n Features to be tested: each function n Features not to be tested: quality of the data 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 19

Test Plan (cont’d) n n Methodology: n Functional testing (Black box) method Pass/Fail Criteria n The system will pass if the authentication works correctly and if the outputs from the queries are displayed within one minute. n Otherwise the test will fail and the code will be revised. Deliverables: n Test plan, Test case specification, and Test result Detail Document 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 20

Formal Technical Inspection n Purpose To ensure consistency in the software development life cycle and quality of the software requirements n Organization n Developer: Yinghua Dong Inspector: Acharaporn Pattaravanichanon (Ann) and Zhigang Xie Software Inspection Checklist * Completeness * Consistency * Correctness * Feasibility * Modifiablility * Traceability * Understandability * Clarity * Functionality * Reliability n Detail Document 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 21

Project Status n Finished: n n n Documentation: 1/2 of the whole project Implementation: About 1/3 Future Work: n Implementation: 2/3 workload n Documentation: User Manual, Test Report, and Evaluation n Final Presentation 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 22

References n n n Modeling Web Application Architectures with UML, Jim Conallen, http: //www 3. software. ibm. com/ibmdl/pub/software/rational/web/whitep apers/2003/webapps. pdf Software Formal Inspections, Software Assurance Technology Center (SATC), 1997, http: //satc. gsfc. nasa. gov/fi/fipage. html Software Requirements, 2 nd Edition, Karl Wiegers, Microsoft Press, 2003, http: //www. processimpact. com/process_assets/requirements_review_ch ecklist. doc n Software Engineering: A practitioner’s Approach, 5 th Edition, Roger. S. Pressman, Alloy web site, http: //sdg. lcs. mit. edu/alloy n CIS 771 lecture, Dr. Hatcliff n CIS 540, CIS 841 lecture, Dr. Gustafson n 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 23

Acknowledgments Committee: n Dr. Mitchell L. Neilsen n Dr. Gurdip Singh n Dr. Daniel Andresen 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 24

Suggestions and Comments Thank You! 4/16/2004 MSE Presentation II 25
bcb190c9d8c6341fb0bd49a0b1b35156.ppt