d92c4f88fb5790eb89b07c6a2df75ad1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 estia centre Models of Mental Health Care for Adults with Intellectual Disabilities Nick Bouras www. estiacentre. org Models F/25. 09. 06/VA D 06
estia centre Models of Mental Health Care for Adults with Intellectual Disabilities Nick Bouras www. estiacentre. org Models F/25. 09. 06/VA D 06
 Outline ØConcepts and Definitions ØBroad International Mapping ØDelivery of Services ØEvidence based Practice
Outline ØConcepts and Definitions ØBroad International Mapping ØDelivery of Services ØEvidence based Practice
 Concepts ØMental health problems indicate the presence of psychopathology: symptoms, signs or abnormal traits ØThis approach encompass both significant behaviours and clusters of symptoms occurring as part of a mental illness ØChallenging behaviour is determined by a combination of what the person does, the setting in which they do it and how their behaviour is interpreted.
Concepts ØMental health problems indicate the presence of psychopathology: symptoms, signs or abnormal traits ØThis approach encompass both significant behaviours and clusters of symptoms occurring as part of a mental illness ØChallenging behaviour is determined by a combination of what the person does, the setting in which they do it and how their behaviour is interpreted.
 Operational Definitions ØPsychiatric Disorders in people with ID include a spectrum of problems ranging from depression, anxiety, psychosis, personality disorders and any psychiatric diagnosis as described in the international classification systems ICD-10 and DSM IV. ØSome also include serious behavioural problems/challenging behaviours requiring psychiatric intervention because of their intensity and or risks related the person with ID or others.
Operational Definitions ØPsychiatric Disorders in people with ID include a spectrum of problems ranging from depression, anxiety, psychosis, personality disorders and any psychiatric diagnosis as described in the international classification systems ICD-10 and DSM IV. ØSome also include serious behavioural problems/challenging behaviours requiring psychiatric intervention because of their intensity and or risks related the person with ID or others.
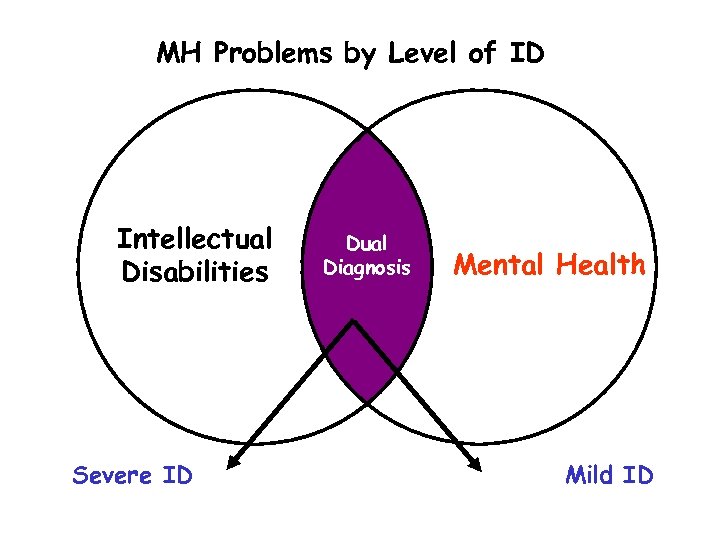 MH Problems by Level of ID Intellectual Disabilities Severe ID Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Mild ID
MH Problems by Level of ID Intellectual Disabilities Severe ID Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Mild ID
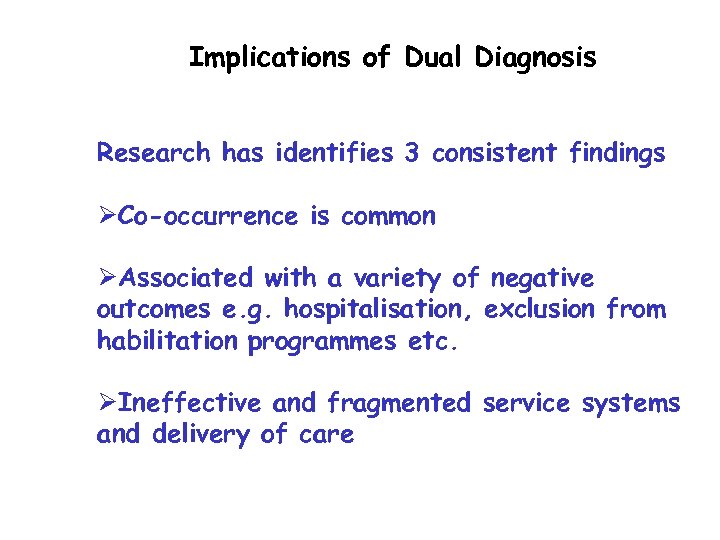 Implications of Dual Diagnosis Research has identifies 3 consistent findings ØCo-occurrence is common ØAssociated with a variety of negative outcomes e. g. hospitalisation, exclusion from habilitation programmes etc. ØIneffective and fragmented service systems and delivery of care
Implications of Dual Diagnosis Research has identifies 3 consistent findings ØCo-occurrence is common ØAssociated with a variety of negative outcomes e. g. hospitalisation, exclusion from habilitation programmes etc. ØIneffective and fragmented service systems and delivery of care
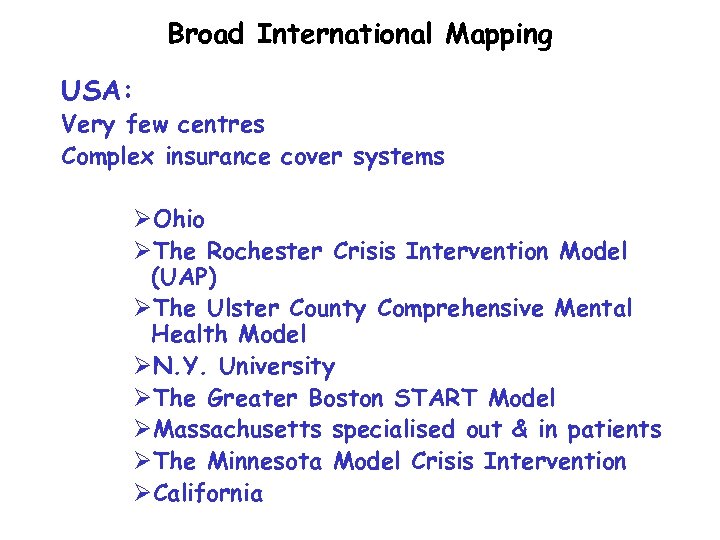 Broad International Mapping USA: Very few centres Complex insurance cover systems ØOhio ØThe Rochester Crisis Intervention Model (UAP) ØThe Ulster County Comprehensive Mental Health Model ØN. Y. University ØThe Greater Boston START Model ØMassachusetts specialised out & in patients ØThe Minnesota Model Crisis Intervention ØCalifornia
Broad International Mapping USA: Very few centres Complex insurance cover systems ØOhio ØThe Rochester Crisis Intervention Model (UAP) ØThe Ulster County Comprehensive Mental Health Model ØN. Y. University ØThe Greater Boston START Model ØMassachusetts specialised out & in patients ØThe Minnesota Model Crisis Intervention ØCalifornia
 Canada: Rapid de-institutionalisation Small centres individually led Lack of trained psychiatrists Moving towards specialist MH services Ø The Toronto MATCH Project Ø Vancouver Ø Montreal
Canada: Rapid de-institutionalisation Small centres individually led Lack of trained psychiatrists Moving towards specialist MH services Ø The Toronto MATCH Project Ø Vancouver Ø Montreal
 Australia: Ø Melbourne Ø Ø GP – Child Psychiatry led The Victorian Dual Disability Service MMH led: specialist consultative-advisory service Ø Queensland: Specialist MH - GP led Ø Sidney: Child Psychiatry
Australia: Ø Melbourne Ø Ø GP – Child Psychiatry led The Victorian Dual Disability Service MMH led: specialist consultative-advisory service Ø Queensland: Specialist MH - GP led Ø Sidney: Child Psychiatry
 Asia: Institutional care Hong Kong: Specialist MH service linked to MMH
Asia: Institutional care Hong Kong: Specialist MH service linked to MMH
 Europe: ØMEROPY study Holt et al 2001 ØInstitutional care ØDe-institutionalisation programmes ØDutch Regional Advisory and Consultative Service ØEmerging services in some European countries without clear trends yet
Europe: ØMEROPY study Holt et al 2001 ØInstitutional care ØDe-institutionalisation programmes ØDutch Regional Advisory and Consultative Service ØEmerging services in some European countries without clear trends yet
 MEROPE EUROPEAN PROJECT: • Implications of current policy not fully considered for PWID & MH • Policy separates ID & MH • Lack of clear policy guidance • Lack of specialist training • Lack of good quality data at clinical & epidemiological level
MEROPE EUROPEAN PROJECT: • Implications of current policy not fully considered for PWID & MH • Policy separates ID & MH • Lack of clear policy guidance • Lack of specialist training • Lack of good quality data at clinical & epidemiological level
 SERVICE SYSTEMS ISSUES Ø Mainstream Vs. specialist mental health services Ø Admissions for assessment & treatment Ø Support services for people with DD
SERVICE SYSTEMS ISSUES Ø Mainstream Vs. specialist mental health services Ø Admissions for assessment & treatment Ø Support services for people with DD
 CURRENT STATE OF AFFAIRS ØIndecision ØAmbiguity ØConfusion ØDemands have increased ØAdditional clinical services and resources are not forthcoming ØSeveral thousand people with ID and psychiatric disorders have been placed in dispersed facilities out of the place of origin
CURRENT STATE OF AFFAIRS ØIndecision ØAmbiguity ØConfusion ØDemands have increased ØAdditional clinical services and resources are not forthcoming ØSeveral thousand people with ID and psychiatric disorders have been placed in dispersed facilities out of the place of origin
 Patterns of services ØDiverse ØMix in expertise, staffing levels and funding options ØPredictions of service use and need vary according local circumstances and population profile
Patterns of services ØDiverse ØMix in expertise, staffing levels and funding options ØPredictions of service use and need vary according local circumstances and population profile
 DELIVERY OF CARE ISSUES FOR PWID & MH PROBLEMS Ø Provided within ID services Ø Delivered from mainstream mental health services Ø Specialist MH services either within ID or mainstream MH services
DELIVERY OF CARE ISSUES FOR PWID & MH PROBLEMS Ø Provided within ID services Ø Delivered from mainstream mental health services Ø Specialist MH services either within ID or mainstream MH services
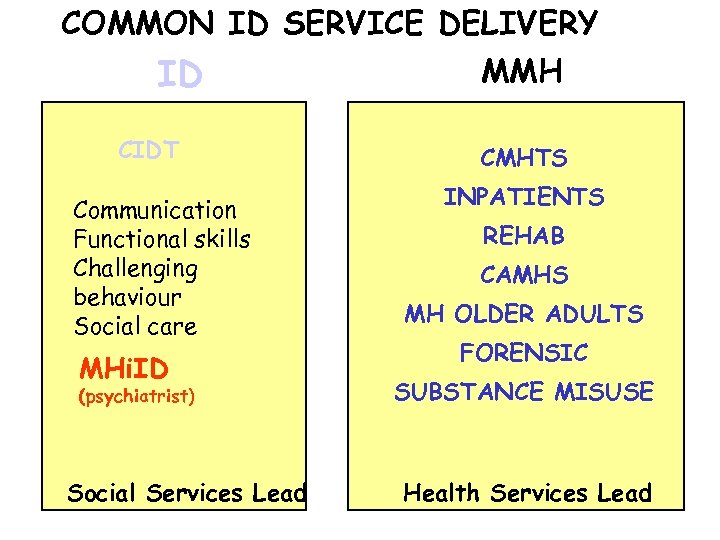 COMMON ID SERVICE DELIVERY ID CIDT Communication Functional skills Challenging behaviour Social care MHi. ID (psychiatrist) Social Services Lead MMH CMHTS INPATIENTS REHAB CAMHS MH OLDER ADULTS FORENSIC SUBSTANCE MISUSE Health Services Lead
COMMON ID SERVICE DELIVERY ID CIDT Communication Functional skills Challenging behaviour Social care MHi. ID (psychiatrist) Social Services Lead MMH CMHTS INPATIENTS REHAB CAMHS MH OLDER ADULTS FORENSIC SUBSTANCE MISUSE Health Services Lead
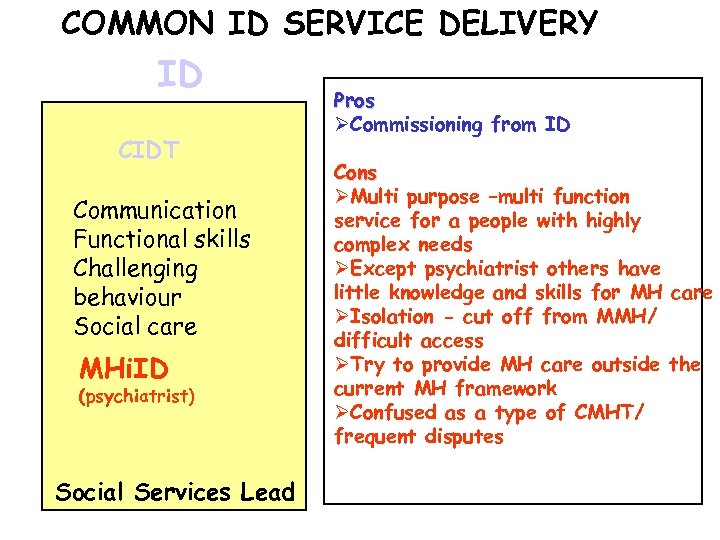 COMMON ID SERVICE DELIVERY ID CIDT Communication Functional skills Challenging behaviour Social care MHi. ID (psychiatrist) Social Services Lead Pros ØCommissioning from ID Cons ØMulti purpose –multi function service for a people with highly complex needs ØExcept psychiatrist others have little knowledge and skills for MH care ØIsolation - cut off from MMH/ difficult access ØTry to provide MH care outside the current MH framework ØConfused as a type of CMHT/ frequent disputes
COMMON ID SERVICE DELIVERY ID CIDT Communication Functional skills Challenging behaviour Social care MHi. ID (psychiatrist) Social Services Lead Pros ØCommissioning from ID Cons ØMulti purpose –multi function service for a people with highly complex needs ØExcept psychiatrist others have little knowledge and skills for MH care ØIsolation - cut off from MMH/ difficult access ØTry to provide MH care outside the current MH framework ØConfused as a type of CMHT/ frequent disputes
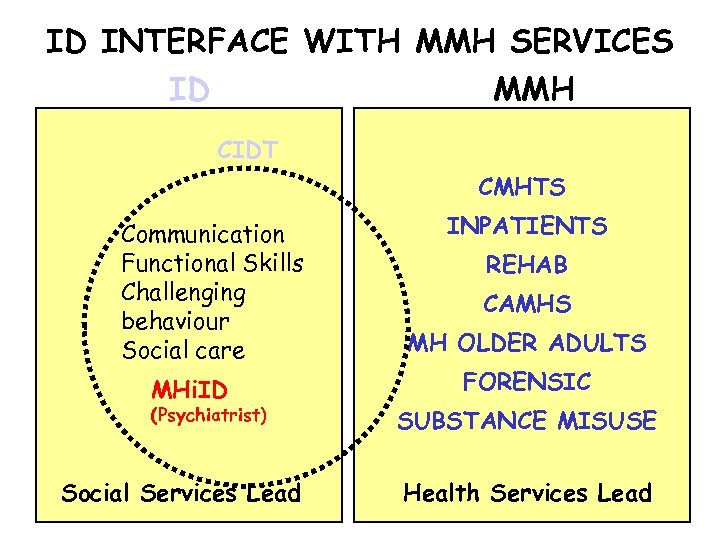 ID INTERFACE WITH MMH SERVICES ID MMH CIDT CMHTS Communication Functional Skills Challenging behaviour Social care MHi. ID (Psychiatrist) Social Services Lead INPATIENTS REHAB CAMHS MH OLDER ADULTS FORENSIC SUBSTANCE MISUSE Health Services Lead
ID INTERFACE WITH MMH SERVICES ID MMH CIDT CMHTS Communication Functional Skills Challenging behaviour Social care MHi. ID (Psychiatrist) Social Services Lead INPATIENTS REHAB CAMHS MH OLDER ADULTS FORENSIC SUBSTANCE MISUSE Health Services Lead
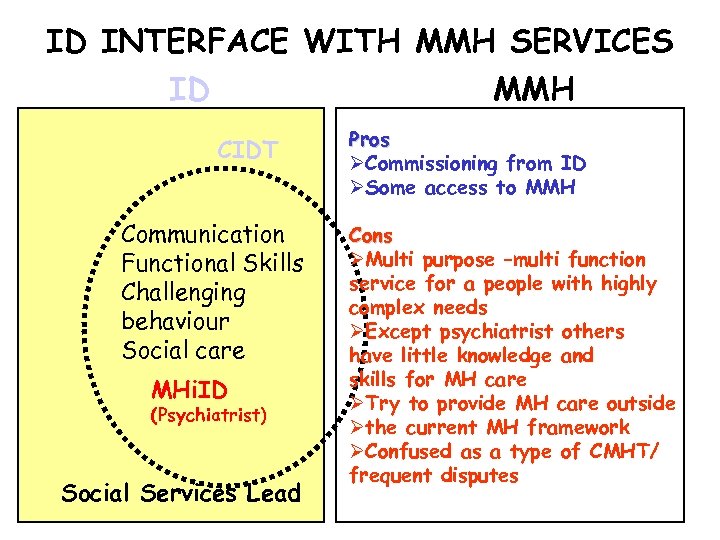 ID INTERFACE WITH MMH SERVICES ID MMH CIDT Communication Functional Skills Challenging behaviour Social care MHi. ID (Psychiatrist) Social Services Lead Pros ØCommissioning from ID ØSome access to MMH Cons ØMulti purpose –multi function service for a people with highly complex needs ØExcept psychiatrist others have little knowledge and skills for MH care ØTry to provide MH care outside Øthe current MH framework ØConfused as a type of CMHT/ frequent disputes
ID INTERFACE WITH MMH SERVICES ID MMH CIDT Communication Functional Skills Challenging behaviour Social care MHi. ID (Psychiatrist) Social Services Lead Pros ØCommissioning from ID ØSome access to MMH Cons ØMulti purpose –multi function service for a people with highly complex needs ØExcept psychiatrist others have little knowledge and skills for MH care ØTry to provide MH care outside Øthe current MH framework ØConfused as a type of CMHT/ frequent disputes
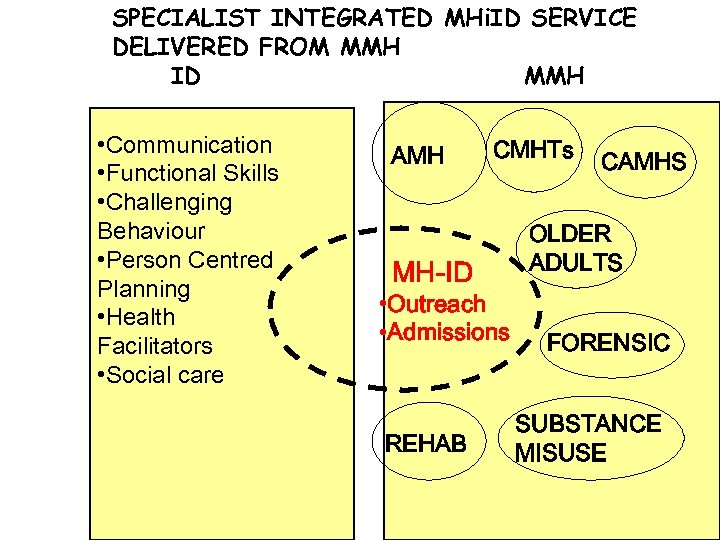 SPECIALIST INTEGRATED MHi. ID SERVICE DELIVERED FROM MMH ID MMH • Communication • Functional Skills • Challenging Behaviour • Person Centred Planning • Health Facilitators • Social care AMH MH-ID CMHTs • Outreach • Admissions REHAB CAMHS OLDER ADULTS FORENSIC SUBSTANCE MISUSE
SPECIALIST INTEGRATED MHi. ID SERVICE DELIVERED FROM MMH ID MMH • Communication • Functional Skills • Challenging Behaviour • Person Centred Planning • Health Facilitators • Social care AMH MH-ID CMHTs • Outreach • Admissions REHAB CAMHS OLDER ADULTS FORENSIC SUBSTANCE MISUSE
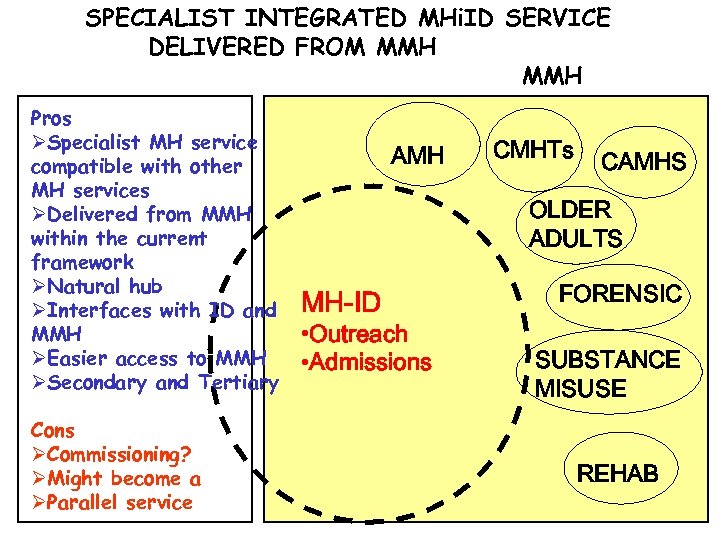 SPECIALIST INTEGRATED MHi. ID SERVICE DELIVERED FROM MMH Pros ØSpecialist MH service compatible with other MH services ØDelivered from MMH within the current framework ØNatural hub ØInterfaces with ID and MMH ØEasier access to MMH ØSecondary and Tertiary Cons ØCommissioning? ØMight become a ØParallel service AMH CMHTs CAMHS OLDER ADULTS MH-ID • Outreach • Admissions FORENSIC SUBSTANCE MISUSE REHAB
SPECIALIST INTEGRATED MHi. ID SERVICE DELIVERED FROM MMH Pros ØSpecialist MH service compatible with other MH services ØDelivered from MMH within the current framework ØNatural hub ØInterfaces with ID and MMH ØEasier access to MMH ØSecondary and Tertiary Cons ØCommissioning? ØMight become a ØParallel service AMH CMHTs CAMHS OLDER ADULTS MH-ID • Outreach • Admissions FORENSIC SUBSTANCE MISUSE REHAB
 WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE BASED PRACTICE ? Ø“Age of Enlightenment” ØInconclusive ØRetrospective reports ØUncontrolled studies ØSmall numbers of participants ØFew examples of systematic descriptive studies ØService users’ and carers’ views ØEmerging in the last years
WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE BASED PRACTICE ? Ø“Age of Enlightenment” ØInconclusive ØRetrospective reports ØUncontrolled studies ØSmall numbers of participants ØFew examples of systematic descriptive studies ØService users’ and carers’ views ØEmerging in the last years
 RANDOMISED CONTROLLED TRIALS ID ØA Dutch study showed reduction in hospitalisation from a service provided by a Community ID Service (Van Minnen et al. 1997) ØIntensive case management has shown to improved adaptive functioning in people with ID and mental disorders (Coalhole et al. 1993) ØUK 700 study found that people with borderline ID spent less time in hospital if they received intensive community care (Tyrer et al. 1999)
RANDOMISED CONTROLLED TRIALS ID ØA Dutch study showed reduction in hospitalisation from a service provided by a Community ID Service (Van Minnen et al. 1997) ØIntensive case management has shown to improved adaptive functioning in people with ID and mental disorders (Coalhole et al. 1993) ØUK 700 study found that people with borderline ID spent less time in hospital if they received intensive community care (Tyrer et al. 1999)
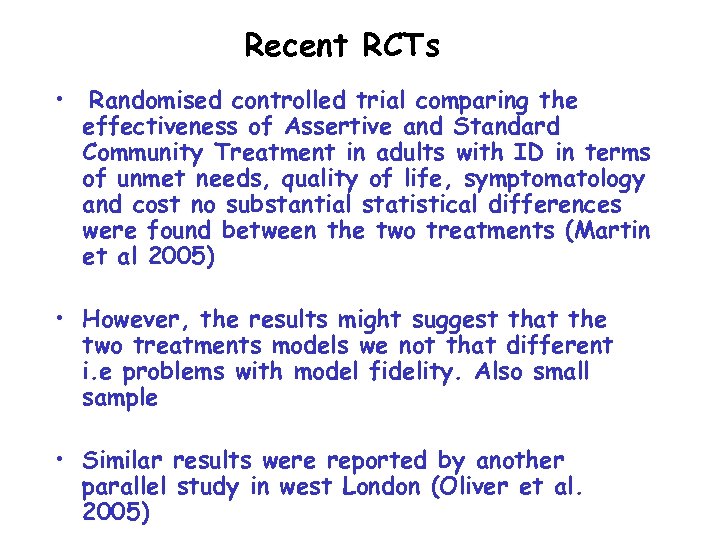 Recent RCTs • Randomised controlled trial comparing the effectiveness of Assertive and Standard Community Treatment in adults with ID in terms of unmet needs, quality of life, symptomatology and cost no substantial statistical differences were found between the two treatments (Martin et al 2005) • However, the results might suggest that the two treatments models we not that different i. e problems with model fidelity. Also small sample • Similar results were reported by another parallel study in west London (Oliver et al. 2005)
Recent RCTs • Randomised controlled trial comparing the effectiveness of Assertive and Standard Community Treatment in adults with ID in terms of unmet needs, quality of life, symptomatology and cost no substantial statistical differences were found between the two treatments (Martin et al 2005) • However, the results might suggest that the two treatments models we not that different i. e problems with model fidelity. Also small sample • Similar results were reported by another parallel study in west London (Oliver et al. 2005)
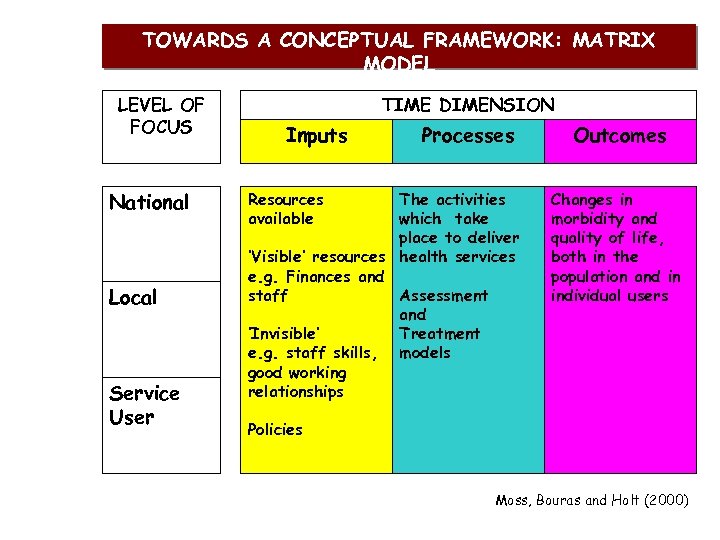 TOWARDS A CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK: MATRIX MODEL LEVEL OF FOCUS National Local Service User TIME DIMENSION Inputs Resources available Processes The activities which take place to deliver ‘Visible’ resources health services e. g. Finances and staff Assessment and ‘Invisible’ Treatment e. g. staff skills, models good working relationships Outcomes Changes in morbidity and quality of life, both in the population and in individual users Policies Moss, Bouras and Holt (2000)
TOWARDS A CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK: MATRIX MODEL LEVEL OF FOCUS National Local Service User TIME DIMENSION Inputs Resources available Processes The activities which take place to deliver ‘Visible’ resources health services e. g. Finances and staff Assessment and ‘Invisible’ Treatment e. g. staff skills, models good working relationships Outcomes Changes in morbidity and quality of life, both in the population and in individual users Policies Moss, Bouras and Holt (2000)
 Matrix Model MHi. ID
Matrix Model MHi. ID
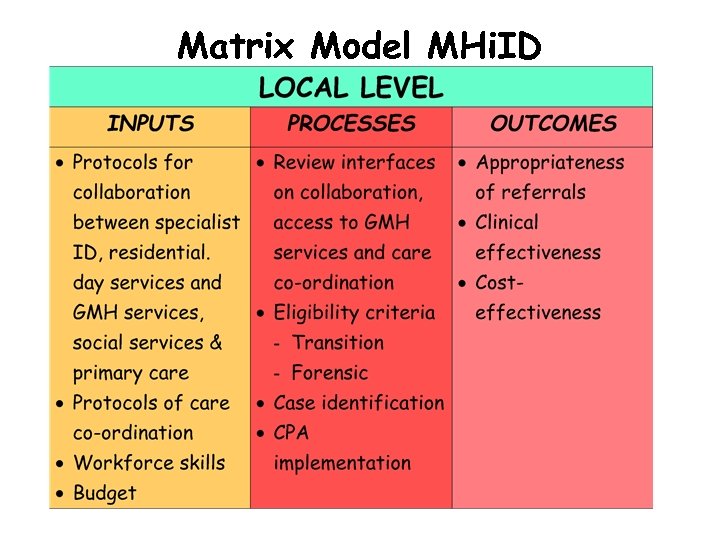 Matrix Model MHi. ID
Matrix Model MHi. ID
 Matrix Model MHi. LD
Matrix Model MHi. LD
 The Right to Quality MH Care Every person with ID should have: ØAccess to expert assessment leading to: ØAccurate and comprehensive diagnosis ØIndividualised treatment plan: ØDelivered at the right time and place and in the right amount ØAppropriate support for housing, day time activities, case management etc.
The Right to Quality MH Care Every person with ID should have: ØAccess to expert assessment leading to: ØAccurate and comprehensive diagnosis ØIndividualised treatment plan: ØDelivered at the right time and place and in the right amount ØAppropriate support for housing, day time activities, case management etc.
 Coordinated and Comprehensive MH Care A MH service system for People with ID should provide: ØFull access to assessment, treatment and support services ØCoordinated, comprehensive and culturally competent delivery of service ØContinuity of care ØTherapeutic intervention supported by evidence based practices ØPharmacological treatment based on efficacy ØSupport services for housing, employment when ever possible and leisure activities ØAssist in improving independence and quality of life
Coordinated and Comprehensive MH Care A MH service system for People with ID should provide: ØFull access to assessment, treatment and support services ØCoordinated, comprehensive and culturally competent delivery of service ØContinuity of care ØTherapeutic intervention supported by evidence based practices ØPharmacological treatment based on efficacy ØSupport services for housing, employment when ever possible and leisure activities ØAssist in improving independence and quality of life


