11bdadd81e5c9491cc5e127a143fe41b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Establishing Efficient Marketplaces - lessons learned APEx Annual Conference Cartagena, October 15 , 2003 Presentation by: Kjell Asserlind kjell. asserlind@om. com 1

OM The world’s leading provider of transaction technology to financial and energy markets. Partner of choice and leading provider of exchange technology to over 25 international exchanges and clearing houses. OM operates marketplaces, develops new marketplaces and makes existing marketplaces more efficient. 2

OM Customer examples System Solutions 3 System Operation Exchange Ownership

What is deregulation into a competitive environment all about? l … to achieve the highest possible efficiency in electricity supply through market mechanisms instead of natural monopoly and regulation… 4
Important market mechanisms l Voluntary - Choices for the market participants – OTC markets – Brokers – Exchanges l Trust – Clear and sufficient market rules – How is the price calculated? 5
Evolution of Power markets l l l OTC, Bilateral contracts Development of short-term or spot- market for physical balancing Market acquires transparency as prices are quoted Spot prices accepted as benchmarks Separation of supply and pricing Resulting volatility generates needs to manage price risk => Forwards & Futures markets 6

Future/forward market l Liquid traded forward markets are essential to healthy power markets in order to provide: l hedging and trading opportunities l the correct long-term investment signals to generators and suppliers l 7 Definition of liquid market: A Market allowing the buying or selling of large quantities of an asset at any time and at low transactions costs
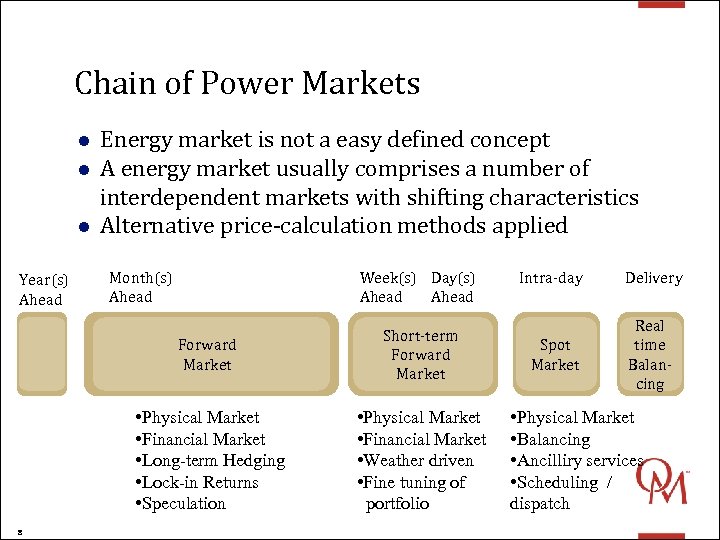
Chain of Power Markets l l l Year(s) Ahead Energy market is not a easy defined concept A energy market usually comprises a number of interdependent markets with shifting characteristics Alternative price-calculation methods applied Month(s) Ahead Week(s) Day(s) Ahead Forward Market • Physical Market • Financial Market • Long-term Hedging • Lock-in Returns • Speculation 8 Short-term Forward Market • Physical Market • Financial Market • Weather driven • Fine tuning of portfolio Intra-day Delivery Spot Market Real time Balancing • Physical Market • Balancing • Ancilliry services • Scheduling / dispatch
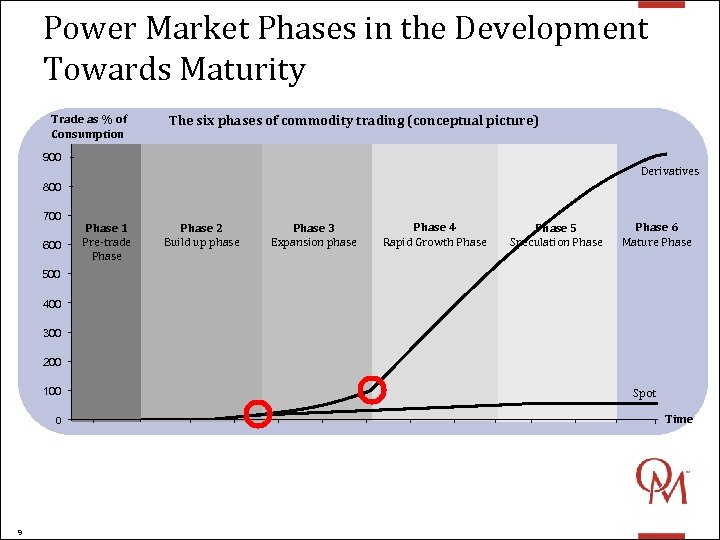
Power Market Phases in the Development Towards Maturity Trade as % of Consumption The six phases of commodity trading (conceptual picture) 900 Derivatives 800 700 600 Phase 1 Pre-trade Phase 2 Build up phase Phase 3 Expansion phase Phase 4 Rapid Growth Phase 5 Speculation Phase 6 Mature Phase 500 400 300 200 100 0 9 Spot Time
The issue of liquidity l Prerequisites – Market design that is easy to understand for ALL market participants – Transparent market information – Attract speculators/ traders – Strong credit rating and clearing facilities l Obstacles – Insufficient or inadequate liberalisation / rules – Market design – Market power 10

Establishing Efficient Marketplaces - lessons learned l Clear vision by all stakeholders of the benefits of electricity market deregulation l l l 11 Supportive and vigilant regulator is most critical Voluntary - Choices for the market participants Clear and well defined price discovery mechanism to gain confidence among traders for price reference Minimize impact of grid and operational constraints on energy price reference to gain confidence among traders outside traditional energy sector Complete chain of markets. -Sole focus on short-term spot markets for physical delivery leads to high market volatility

“Establishment of a power exchange may not be a necessity in a particular power market. However, a power exchange greatly facilitates trade, timely dissemination of pricesensitive information, and greater market competition and liquidity. ” 12

A world leader in transaction technology 13
11bdadd81e5c9491cc5e127a143fe41b.ppt