f84851a996f1d3c3254b74e372036bff.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 109
![ESSI 18 -Oct-2004 An introduction to NMS-OSS Floris Grandvarlet [floris. grandvarlet@cisco. com] Session Number ESSI 18 -Oct-2004 An introduction to NMS-OSS Floris Grandvarlet [floris. grandvarlet@cisco. com] Session Number](https://present5.com/presentation/f84851a996f1d3c3254b74e372036bff/image-1.jpg) ESSI 18 -Oct-2004 An introduction to NMS-OSS Floris Grandvarlet [floris. grandvarlet@cisco. com] Session Number Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1
ESSI 18 -Oct-2004 An introduction to NMS-OSS Floris Grandvarlet [floris. grandvarlet@cisco. com] Session Number Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1
 CISCO SYSTEMS CORPORATE OVERVIEW Session Number Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2
CISCO SYSTEMS CORPORATE OVERVIEW Session Number Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2
 Video Networking and the Internet PLAY WORK LIVE Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. LEARN 3
Video Networking and the Internet PLAY WORK LIVE Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. LEARN 3
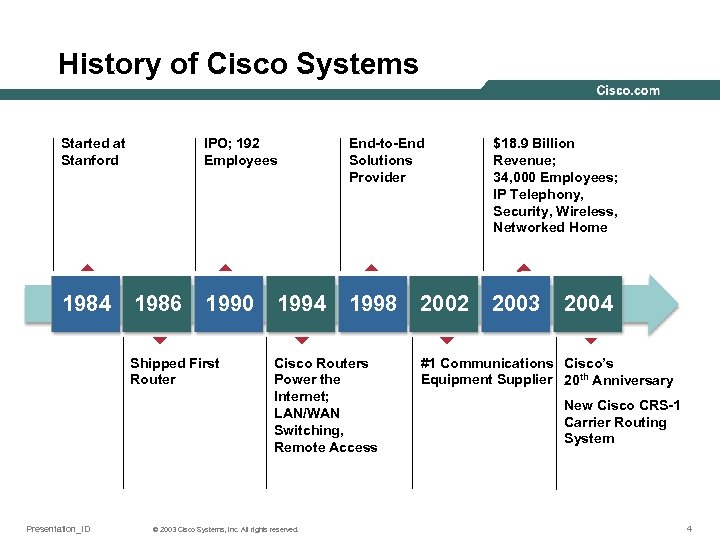 History of Cisco Systems Started at Stanford 1984 IPO; 192 Employees 1986 End-to-End Solutions Provider $18. 9 Billion Revenue; 34, 000 Employees; IP Telephony, Security, Wireless, Networked Home 1990 1998 2003 Shipped First Router Presentation_ID 1994 Cisco Routers Power the Internet; LAN/WAN Switching, Remote Access © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2002 2004 #1 Communications Cisco’s Equipment Supplier 20 th Anniversary New Cisco CRS-1 Carrier Routing System 4
History of Cisco Systems Started at Stanford 1984 IPO; 192 Employees 1986 End-to-End Solutions Provider $18. 9 Billion Revenue; 34, 000 Employees; IP Telephony, Security, Wireless, Networked Home 1990 1998 2003 Shipped First Router Presentation_ID 1994 Cisco Routers Power the Internet; LAN/WAN Switching, Remote Access © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2002 2004 #1 Communications Cisco’s Equipment Supplier 20 th Anniversary New Cisco CRS-1 Carrier Routing System 4
 Cisco—The Technology Innovator • $3. 2 billion R&D investment • Driving technology standards development for networking and the Internet • Cisco IOS® Software, the most widely deployed network system software • 12, 400 engineers working in more than 1110 labs worldwide • Acquisitions help Cisco quickly enter new markets and add staff with unique talents • More than 1100 patents have been issued to Cisco inventors R&D Presentation_ID ACQUISITIONS © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. PATENTS Cisco Public 5
Cisco—The Technology Innovator • $3. 2 billion R&D investment • Driving technology standards development for networking and the Internet • Cisco IOS® Software, the most widely deployed network system software • 12, 400 engineers working in more than 1110 labs worldwide • Acquisitions help Cisco quickly enter new markets and add staff with unique talents • More than 1100 patents have been issued to Cisco inventors R&D Presentation_ID ACQUISITIONS © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. PATENTS Cisco Public 5
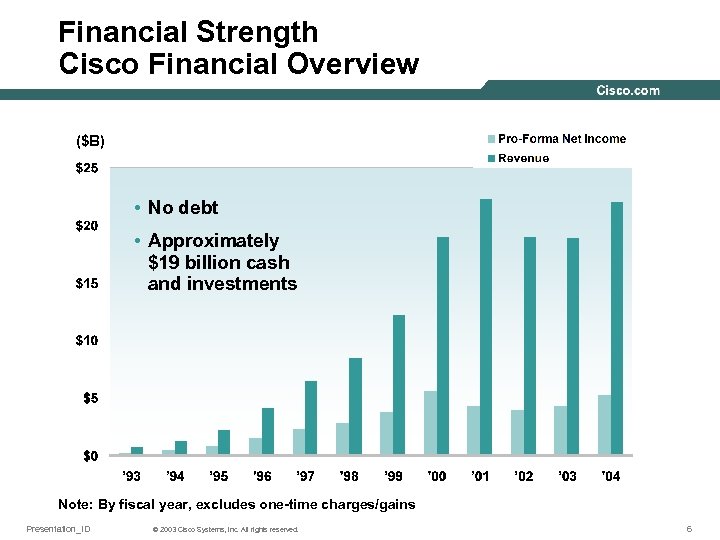 Financial Strength Cisco Financial Overview ($B) • No debt • Approximately $19 billion cash and investments Note: By fiscal year, excludes one-time charges/gains Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 6
Financial Strength Cisco Financial Overview ($B) • No debt • Approximately $19 billion cash and investments Note: By fiscal year, excludes one-time charges/gains Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 6
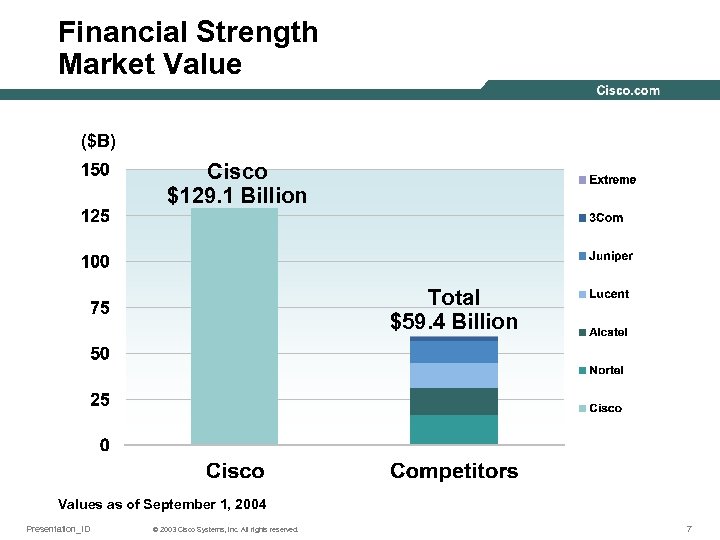 Financial Strength Market Value ($B) Cisco $129. 1 Billion Total $59. 4 Billion Values as of September 1, 2004 Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 7
Financial Strength Market Value ($B) Cisco $129. 1 Billion Total $59. 4 Billion Values as of September 1, 2004 Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 7
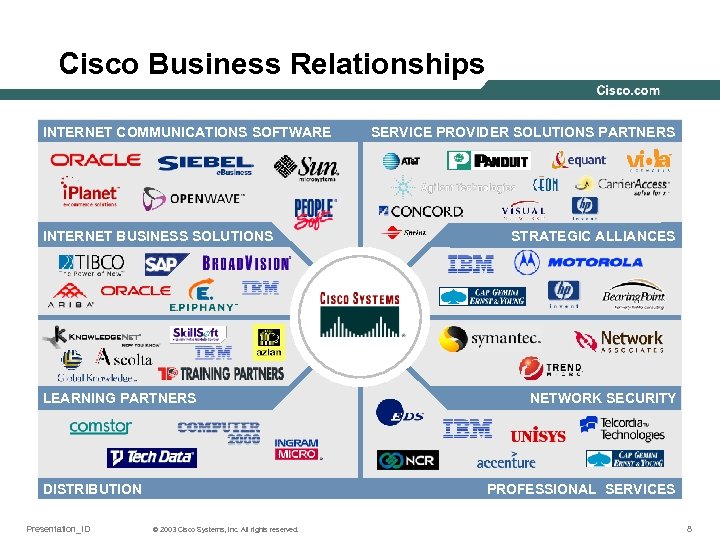 Cisco Business Relationships INTERNET COMMUNICATIONS SOFTWARE INTERNET BUSINESS SOLUTIONS LEARNING PARTNERS DISTRIBUTION Presentation_ID SERVICE PROVIDER SOLUTIONS PARTNERS STRATEGIC ALLIANCES NETWORK SECURITY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 8
Cisco Business Relationships INTERNET COMMUNICATIONS SOFTWARE INTERNET BUSINESS SOLUTIONS LEARNING PARTNERS DISTRIBUTION Presentation_ID SERVICE PROVIDER SOLUTIONS PARTNERS STRATEGIC ALLIANCES NETWORK SECURITY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 8
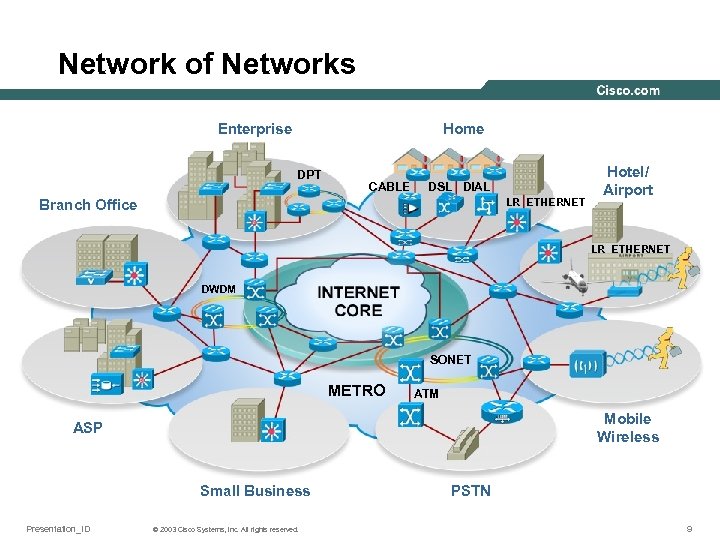 Network of Networks Enterprise Home DPT CABLE DSL DIAL LR ETHERNET Branch Office Hotel/ Airport LR ETHERNET DWDM SONET METRO ATM Mobile Wireless ASP Small Business Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. PSTN 9
Network of Networks Enterprise Home DPT CABLE DSL DIAL LR ETHERNET Branch Office Hotel/ Airport LR ETHERNET DWDM SONET METRO ATM Mobile Wireless ASP Small Business Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. PSTN 9
 Key NMS/OSS Concepts Presentation_ID © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 10
Key NMS/OSS Concepts Presentation_ID © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 10
 “ We’re all in it for the money” Frank Zappa Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 11
“ We’re all in it for the money” Frank Zappa Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 11
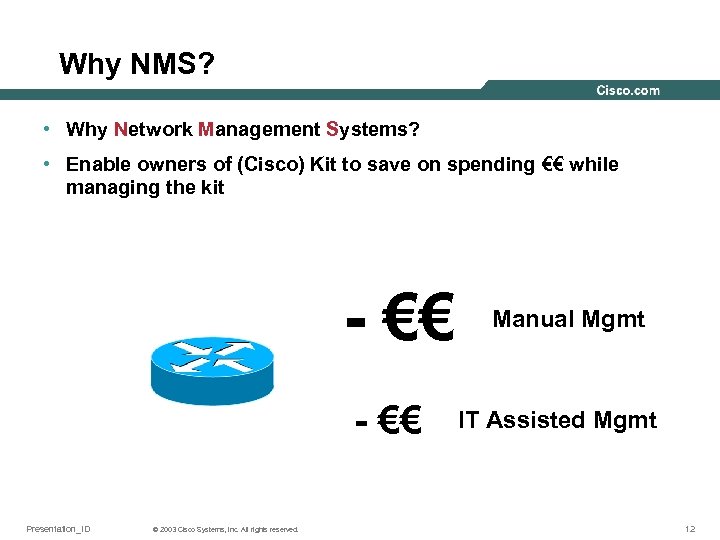 Why NMS? • Why Network Management Systems? • Enable owners of (Cisco) Kit to save on spending €€ while managing the kit - €€ Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Manual Mgmt IT Assisted Mgmt 12
Why NMS? • Why Network Management Systems? • Enable owners of (Cisco) Kit to save on spending €€ while managing the kit - €€ Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Manual Mgmt IT Assisted Mgmt 12
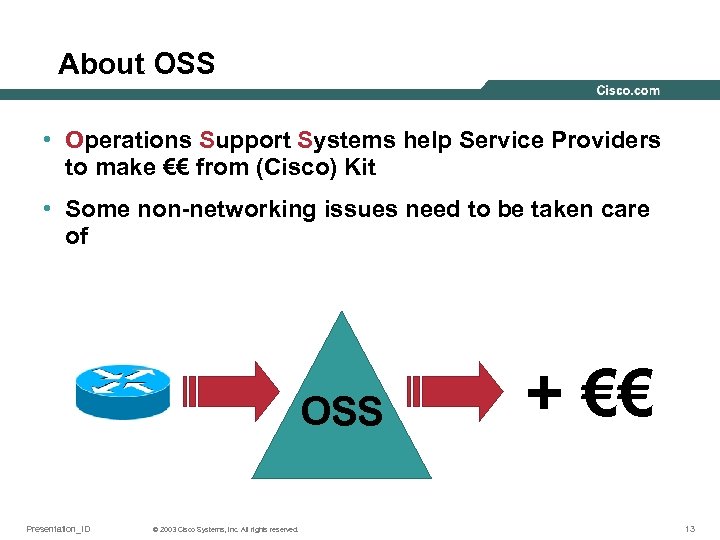 About OSS • Operations Support Systems help Service Providers to make €€ from (Cisco) Kit • Some non-networking issues need to be taken care of OSS Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. + €€ 13
About OSS • Operations Support Systems help Service Providers to make €€ from (Cisco) Kit • Some non-networking issues need to be taken care of OSS Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. + €€ 13
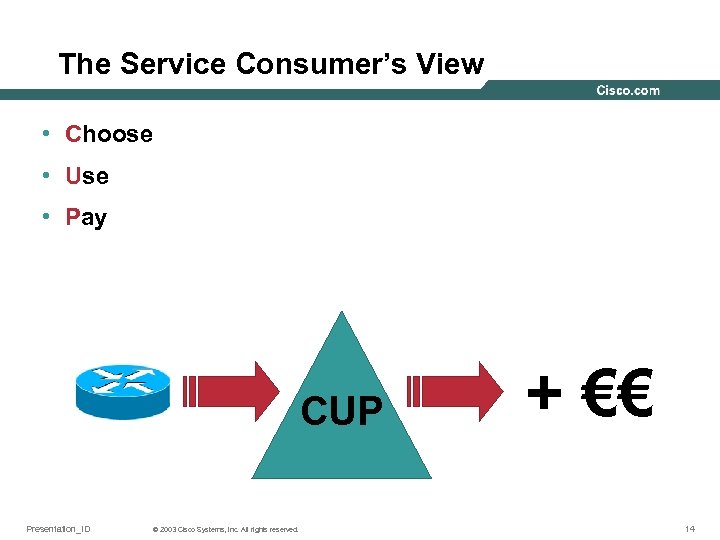 The Service Consumer’s View • Choose • Use • Pay CUP Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. + €€ 14
The Service Consumer’s View • Choose • Use • Pay CUP Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. + €€ 14
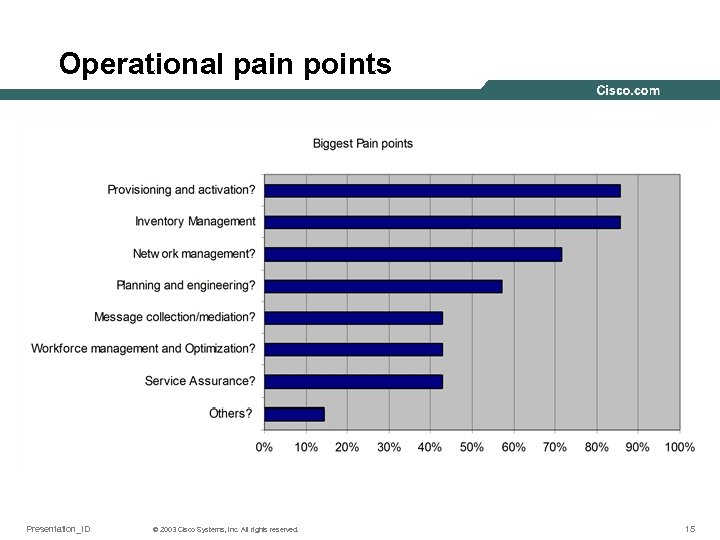 Operational pain points Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 15
Operational pain points Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 15
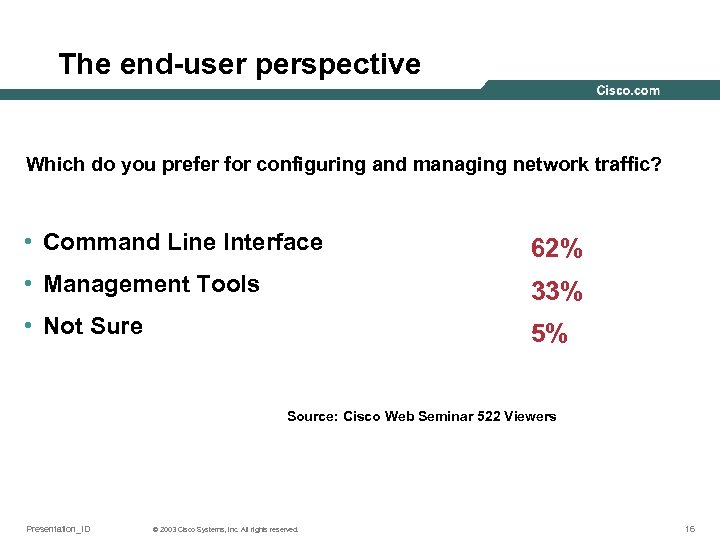 The end-user perspective Which do you prefer for configuring and managing network traffic? • Command Line Interface 62% • Management Tools 33% • Not Sure 5% Source: Cisco Web Seminar 522 Viewers Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 16
The end-user perspective Which do you prefer for configuring and managing network traffic? • Command Line Interface 62% • Management Tools 33% • Not Sure 5% Source: Cisco Web Seminar 522 Viewers Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 16
 If at first you don’t succeed …. Network Operations Failures by Cause Source: Sage Research, Inc. 75% Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 17
If at first you don’t succeed …. Network Operations Failures by Cause Source: Sage Research, Inc. 75% Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 17
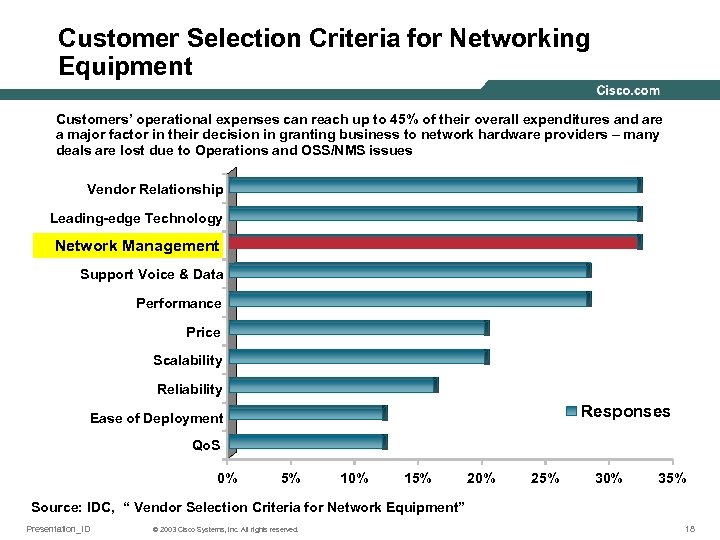 Customer Selection Criteria for Networking Equipment Customers’ operational expenses can reach up to 45% of their overall expenditures and are a major factor in their decision in granting business to network hardware providers – many deals are lost due to Operations and OSS/NMS issues Vendor Relationship Leading-edge Technology Network Management Support Voice & Data Performance Price Scalability Reliability Responses Ease of Deployment Qo. S 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% Source: IDC, “ Vendor Selection Criteria for Network Equipment” Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 18
Customer Selection Criteria for Networking Equipment Customers’ operational expenses can reach up to 45% of their overall expenditures and are a major factor in their decision in granting business to network hardware providers – many deals are lost due to Operations and OSS/NMS issues Vendor Relationship Leading-edge Technology Network Management Support Voice & Data Performance Price Scalability Reliability Responses Ease of Deployment Qo. S 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% Source: IDC, “ Vendor Selection Criteria for Network Equipment” Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 18
 Introduction Presentation_ID © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 19
Introduction Presentation_ID © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 19
 Introduction • Why are NMS/OSS Terms and Concepts Important? Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 20
Introduction • Why are NMS/OSS Terms and Concepts Important? Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 20
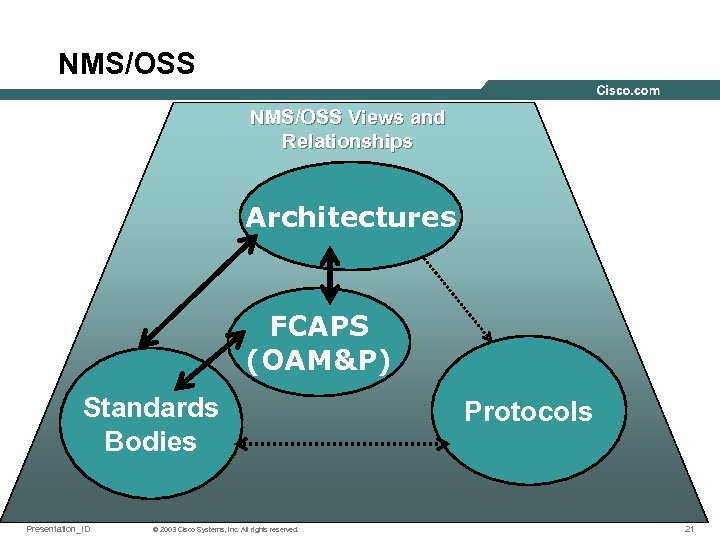 NMS/OSS Views and Relationships Architectures FCAPS (OAM&P) Standards Bodies Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Protocols 21
NMS/OSS Views and Relationships Architectures FCAPS (OAM&P) Standards Bodies Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Protocols 21
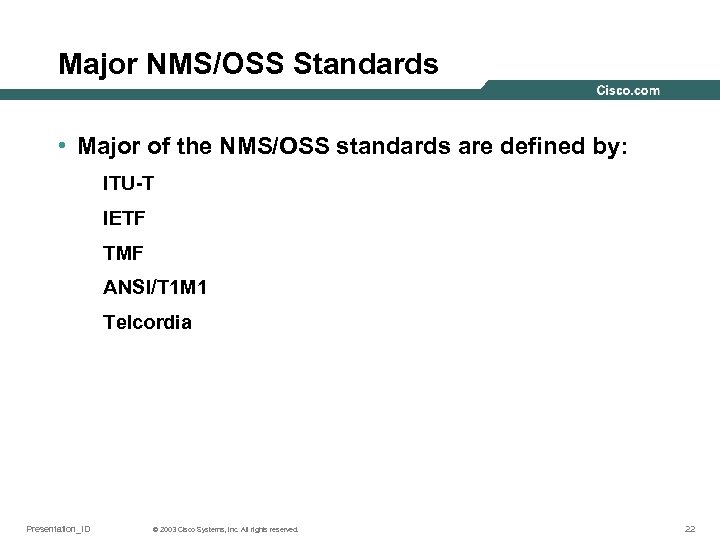 Major NMS/OSS Standards • Major of the NMS/OSS standards are defined by: ITU-T IETF TMF ANSI/T 1 M 1 Telcordia Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 22
Major NMS/OSS Standards • Major of the NMS/OSS standards are defined by: ITU-T IETF TMF ANSI/T 1 M 1 Telcordia Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 22
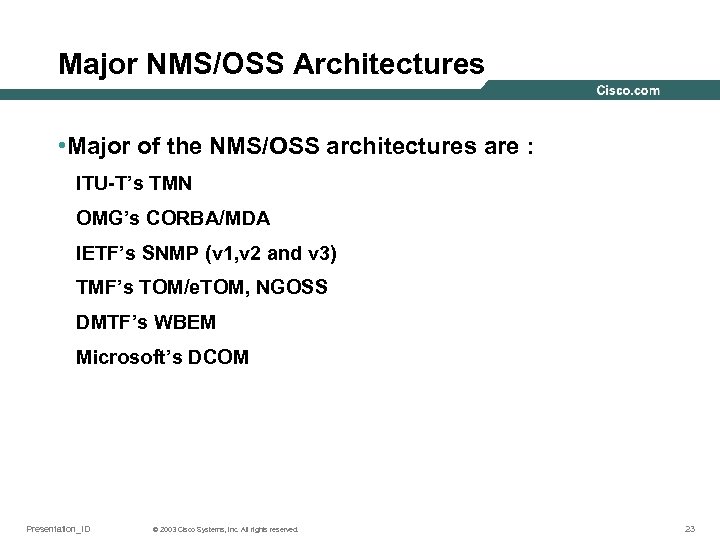 Major NMS/OSS Architectures • Major of the NMS/OSS architectures are : ITU-T’s TMN OMG’s CORBA/MDA IETF’s SNMP (v 1, v 2 and v 3) TMF’s TOM/e. TOM, NGOSS DMTF’s WBEM Microsoft’s DCOM Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 23
Major NMS/OSS Architectures • Major of the NMS/OSS architectures are : ITU-T’s TMN OMG’s CORBA/MDA IETF’s SNMP (v 1, v 2 and v 3) TMF’s TOM/e. TOM, NGOSS DMTF’s WBEM Microsoft’s DCOM Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 23
 Major NMS/OSS Protocols • NMS/OSS specifies a set of standardized protocols that create a architecture used for monitoring and management of SPs networks, services and customers. Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 24
Major NMS/OSS Protocols • NMS/OSS specifies a set of standardized protocols that create a architecture used for monitoring and management of SPs networks, services and customers. Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 24
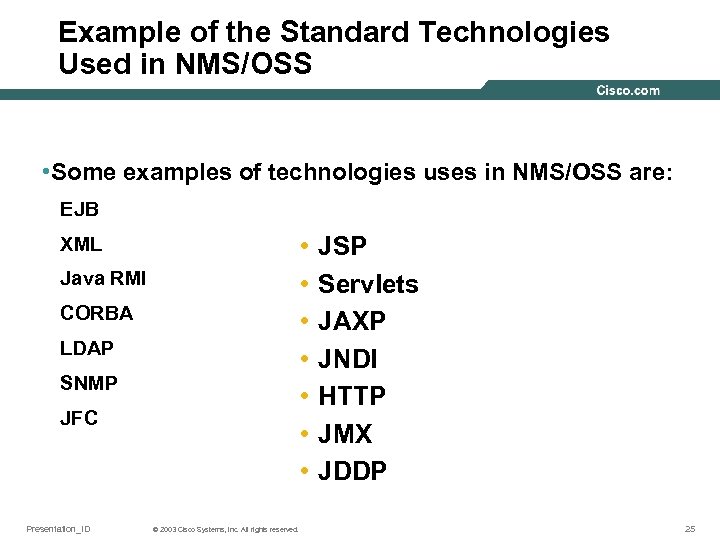 Example of the Standard Technologies Used in NMS/OSS • Some examples of technologies uses in NMS/OSS are: EJB • • XML Java RMI CORBA LDAP SNMP JFC Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. JSP Servlets JAXP JNDI HTTP JMX JDDP 25
Example of the Standard Technologies Used in NMS/OSS • Some examples of technologies uses in NMS/OSS are: EJB • • XML Java RMI CORBA LDAP SNMP JFC Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. JSP Servlets JAXP JNDI HTTP JMX JDDP 25
 ITU-T model Presentation_ID © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 26
ITU-T model Presentation_ID © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 26
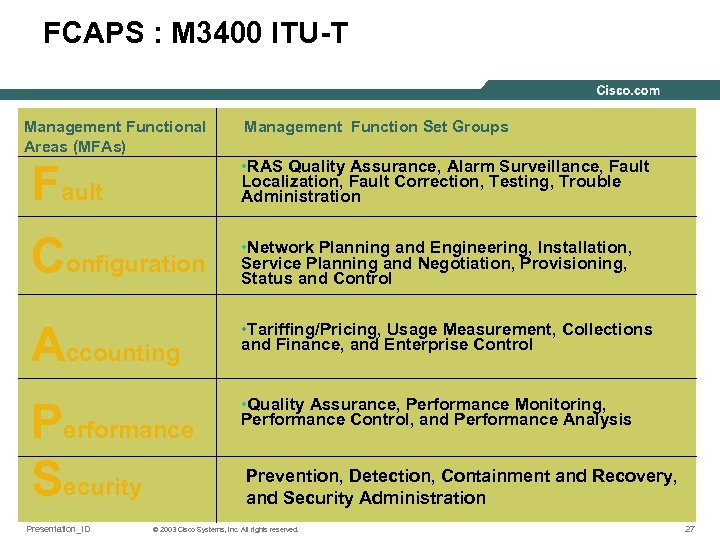 FCAPS : M 3400 ITU-T Management Functional Areas (MFAs) Management Function Set Groups Fault Configuration • RAS Quality Assurance, Alarm Surveillance, Fault Localization, Fault Correction, Testing, Trouble Administration Accounting • Tariffing/Pricing, Usage Measurement, Collections and Finance, and Enterprise Control Performance Security • Quality Assurance, Performance Monitoring, Performance Control, and Performance Analysis Presentation_ID • Network Planning and Engineering, Installation, Service Planning and Negotiation, Provisioning, Status and Control Prevention, Detection, Containment and Recovery, and Security Administration © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 27
FCAPS : M 3400 ITU-T Management Functional Areas (MFAs) Management Function Set Groups Fault Configuration • RAS Quality Assurance, Alarm Surveillance, Fault Localization, Fault Correction, Testing, Trouble Administration Accounting • Tariffing/Pricing, Usage Measurement, Collections and Finance, and Enterprise Control Performance Security • Quality Assurance, Performance Monitoring, Performance Control, and Performance Analysis Presentation_ID • Network Planning and Engineering, Installation, Service Planning and Negotiation, Provisioning, Status and Control Prevention, Detection, Containment and Recovery, and Security Administration © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 27
 TMN Model Presentation_ID © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 28
TMN Model Presentation_ID © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 28
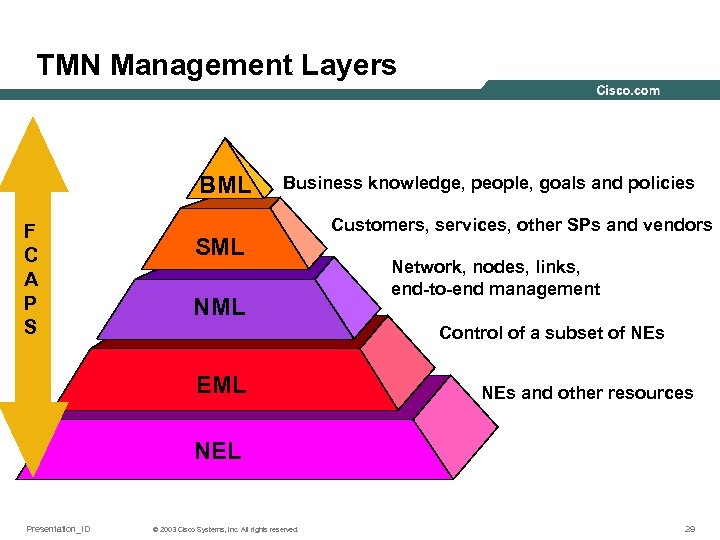 TMN Management Layers BML F C A P S Business knowledge, people, goals and policies SML NML Customers, services, other SPs and vendors Network, nodes, links, end-to-end management Control of a subset of NEs EML NEs and other resources NEL Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 29
TMN Management Layers BML F C A P S Business knowledge, people, goals and policies SML NML Customers, services, other SPs and vendors Network, nodes, links, end-to-end management Control of a subset of NEs EML NEs and other resources NEL Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 29
 TMF model Presentation_ID © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 30
TMF model Presentation_ID © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 30
 Enhanced TOM (e. TOM) • e. Tom: Is a business process framework based on TOM. Provides enterprise processes required for an SP. Is the key component of the NGOSS business view. Enables SPs for the development of process automation solutions for their organizations. Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 31
Enhanced TOM (e. TOM) • e. Tom: Is a business process framework based on TOM. Provides enterprise processes required for an SP. Is the key component of the NGOSS business view. Enables SPs for the development of process automation solutions for their organizations. Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 31
 What does e. TOM Do? • Service Providers are pushing for a common e. TOM industry framework that: Broadens TOM to a total enterprise model Reflects the increased complexity in service provider business relationships Evolves processes to support convergence of information and communications services and technologies Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 32
What does e. TOM Do? • Service Providers are pushing for a common e. TOM industry framework that: Broadens TOM to a total enterprise model Reflects the increased complexity in service provider business relationships Evolves processes to support convergence of information and communications services and technologies Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 32
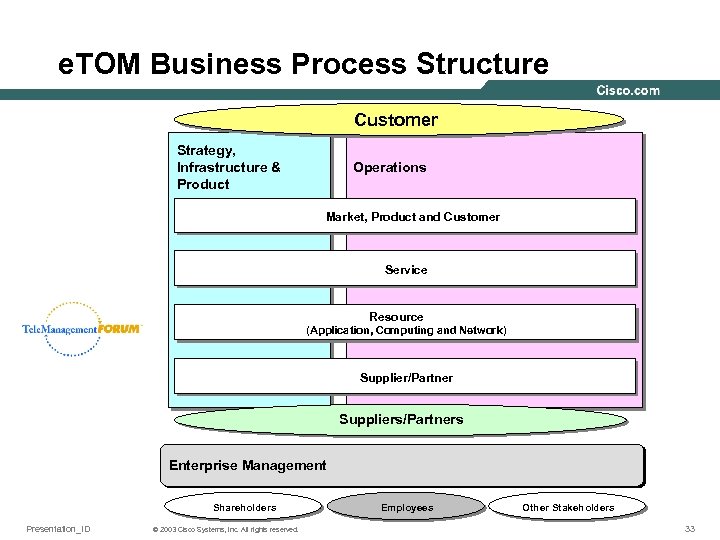 e. TOM Business Process Structure Customer Strategy, Infrastructure & Product Operations Market, Product and Customer Service Resource (Application, Computing and Network) Supplier/Partner Suppliers/Partners Enterprise Management Shareholders Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Employees Other Stakeholders 33
e. TOM Business Process Structure Customer Strategy, Infrastructure & Product Operations Market, Product and Customer Service Resource (Application, Computing and Network) Supplier/Partner Suppliers/Partners Enterprise Management Shareholders Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Employees Other Stakeholders 33
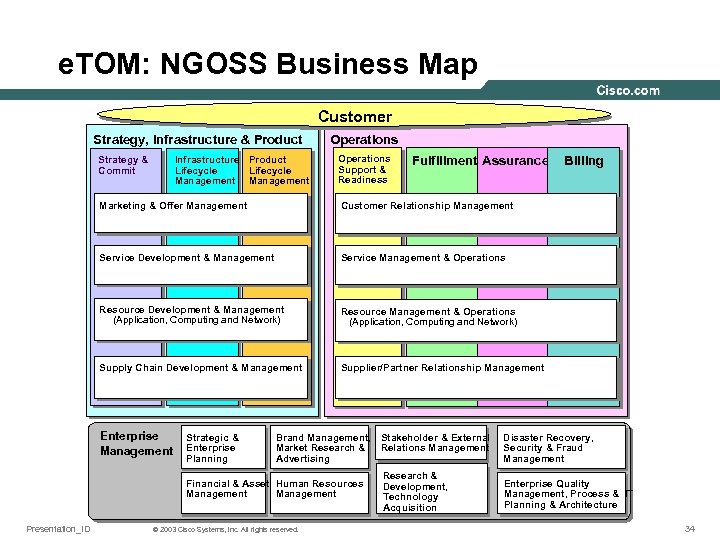 e. TOM: NGOSS Business Map Customer Strategy, Infrastructure & Product Strategy & Commit Infrastructure Product Lifecycle Management Operations Support & Readiness Fulfillment Assurance Marketing & Offer Management Customer Relationship Management Service Development & Management Service Management & Operations Resource Development & Management (Application, Computing and Network) Resource Management & Operations (Application, Computing and Network) Supply Chain Development & Management Supplier/Partner Relationship Management Enterprise Management Strategic & Enterprise Planning Brand Management, Stakeholder & External Market Research & Relations Management Advertising Financial & Asset Human Resources Management Presentation_ID Billing © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Research & Development, Technology Acquisition Disaster Recovery, Security & Fraud Management Enterprise Quality Management, Process & IT Planning & Architecture 34
e. TOM: NGOSS Business Map Customer Strategy, Infrastructure & Product Strategy & Commit Infrastructure Product Lifecycle Management Operations Support & Readiness Fulfillment Assurance Marketing & Offer Management Customer Relationship Management Service Development & Management Service Management & Operations Resource Development & Management (Application, Computing and Network) Resource Management & Operations (Application, Computing and Network) Supply Chain Development & Management Supplier/Partner Relationship Management Enterprise Management Strategic & Enterprise Planning Brand Management, Stakeholder & External Market Research & Relations Management Advertising Financial & Asset Human Resources Management Presentation_ID Billing © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Research & Development, Technology Acquisition Disaster Recovery, Security & Fraud Management Enterprise Quality Management, Process & IT Planning & Architecture 34
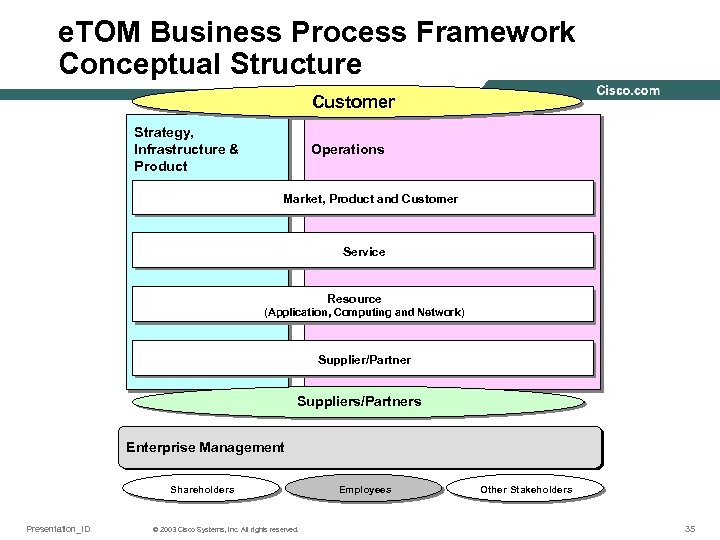 e. TOM Business Process Framework Conceptual Structure Customer Strategy, Infrastructure & Product Operations Market, Product and Customer Service Resource (Application, Computing and Network) Supplier/Partner Suppliers/Partners Enterprise Management Shareholders Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Employees Other Stakeholders 35
e. TOM Business Process Framework Conceptual Structure Customer Strategy, Infrastructure & Product Operations Market, Product and Customer Service Resource (Application, Computing and Network) Supplier/Partner Suppliers/Partners Enterprise Management Shareholders Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Employees Other Stakeholders 35
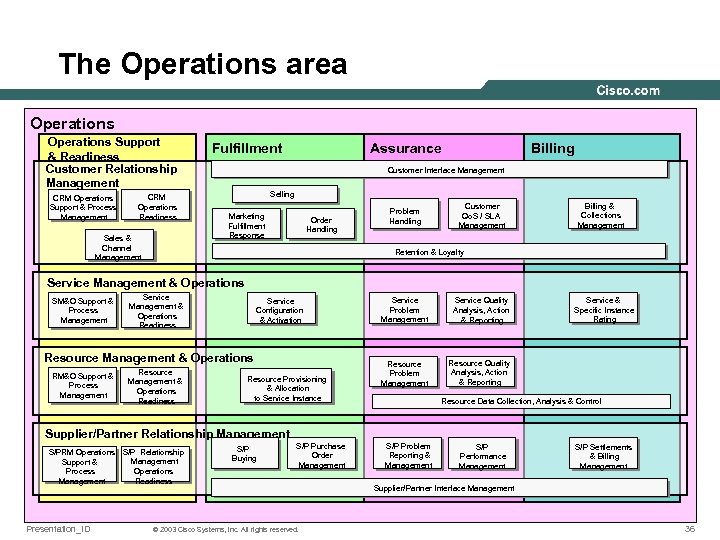 The Operations area Operations Support & Readiness Customer Relationship Management CRM Operations Support & Process Management CRM Operations Readiness Sales & Channel Management Fulfillment Assurance Billing Customer Interface Management Selling Marketing Fulfillment Response Order Handling Problem Handling Customer Qo. S / SLA Management Billing & Collections Management Retention & Loyalty Service Management & Operations SM&O Support & Process Management Service Management & Operations Readiness Service Configuration & Activation Resource Management & Operations RM&O Support & Process Management Resource Management & Operations Readiness Resource Provisioning & Allocation to Service Instance Service Problem Management Service Quality Analysis, Action & Reporting Resource Problem Management Service & Specific Instance Rating Resource Quality Analysis, Action & Reporting Resource Data Collection, Analysis & Control Supplier/Partner Relationship Management S/PRM Operations S/P Relationship Management Support & Operations Process Readiness Management Presentation_ID S/P Buying S/P Purchase Order Management © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. S/P Problem Reporting & Management S/P Performance Management S/P Settlements & Billing Management Supplier/Partner Interface Management 36
The Operations area Operations Support & Readiness Customer Relationship Management CRM Operations Support & Process Management CRM Operations Readiness Sales & Channel Management Fulfillment Assurance Billing Customer Interface Management Selling Marketing Fulfillment Response Order Handling Problem Handling Customer Qo. S / SLA Management Billing & Collections Management Retention & Loyalty Service Management & Operations SM&O Support & Process Management Service Management & Operations Readiness Service Configuration & Activation Resource Management & Operations RM&O Support & Process Management Resource Management & Operations Readiness Resource Provisioning & Allocation to Service Instance Service Problem Management Service Quality Analysis, Action & Reporting Resource Problem Management Service & Specific Instance Rating Resource Quality Analysis, Action & Reporting Resource Data Collection, Analysis & Control Supplier/Partner Relationship Management S/PRM Operations S/P Relationship Management Support & Operations Process Readiness Management Presentation_ID S/P Buying S/P Purchase Order Management © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. S/P Problem Reporting & Management S/P Performance Management S/P Settlements & Billing Management Supplier/Partner Interface Management 36
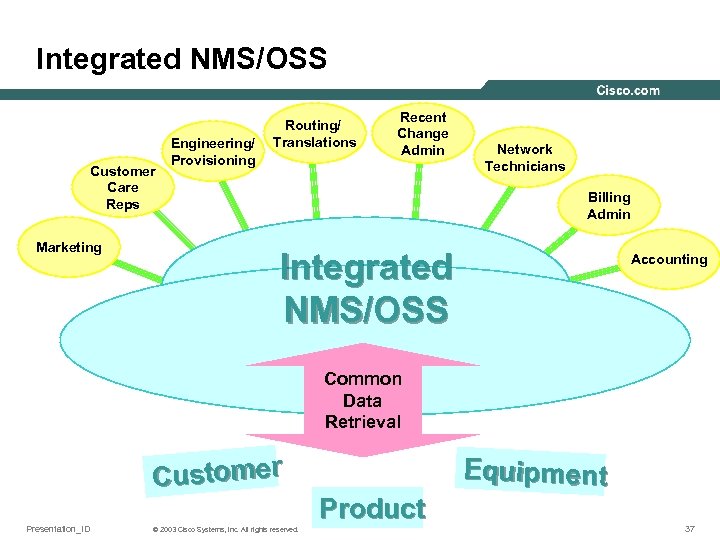 Integrated NMS/OSS Customer Care Reps Marketing Engineering/ Provisioning Routing/ Translations Recent Change Admin Network Technicians Billing Admin Integrated NMS/OSS Accounting Common Data Retrieval Customer Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Equipment Product 37
Integrated NMS/OSS Customer Care Reps Marketing Engineering/ Provisioning Routing/ Translations Recent Change Admin Network Technicians Billing Admin Integrated NMS/OSS Accounting Common Data Retrieval Customer Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Equipment Product 37
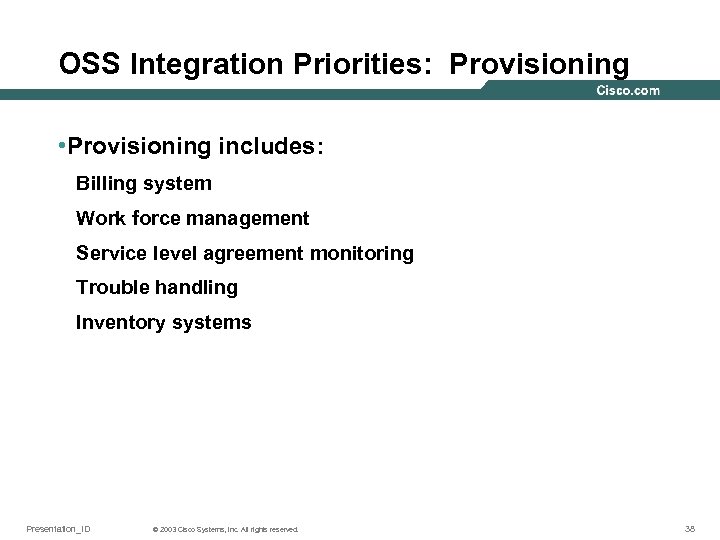 OSS Integration Priorities: Provisioning • Provisioning includes: Billing system Work force management Service level agreement monitoring Trouble handling Inventory systems Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 38
OSS Integration Priorities: Provisioning • Provisioning includes: Billing system Work force management Service level agreement monitoring Trouble handling Inventory systems Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 38
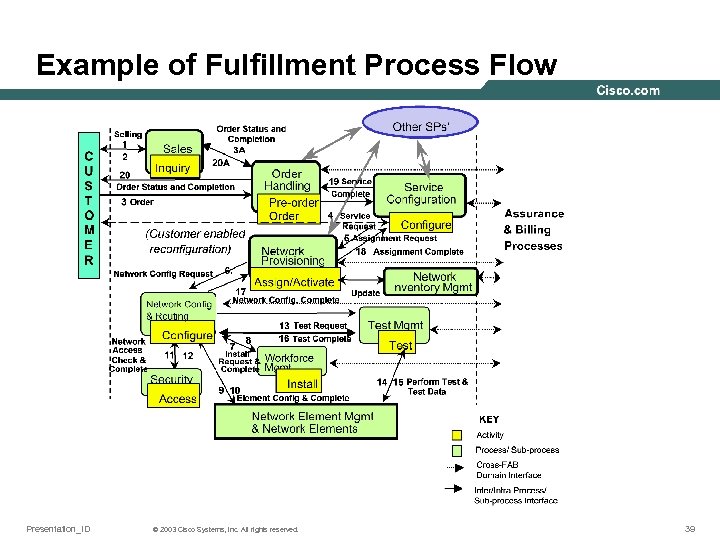 Example of Fulfillment Process Flow Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 39
Example of Fulfillment Process Flow Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 39
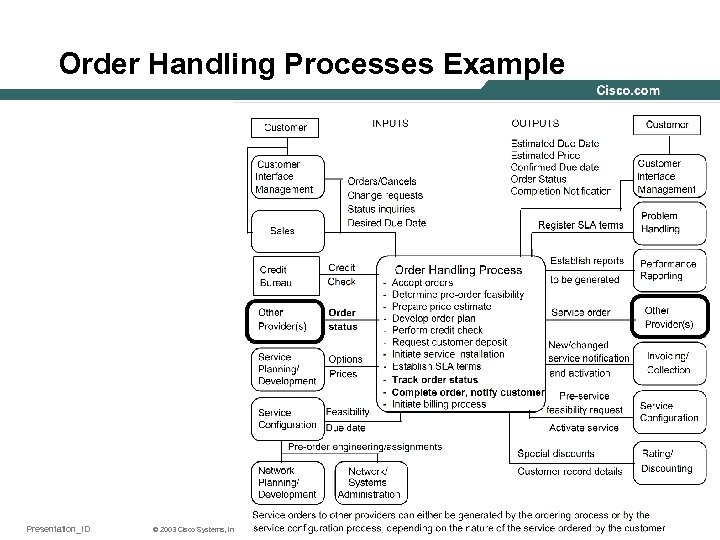 Order Handling Processes Example Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 40
Order Handling Processes Example Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 40
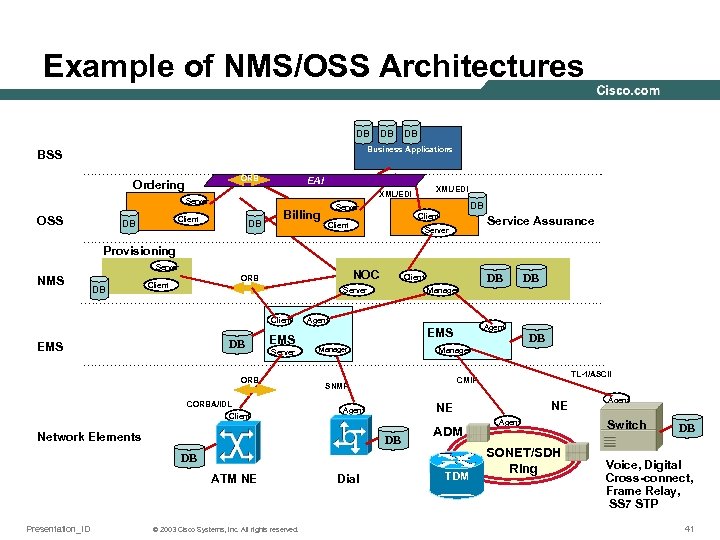 Example of NMS/OSS Architectures DB DB DB Business Applications BSS ORB Ordering EAI OSS Client DB XML/EDI Server DB Billing Server DB Client Service Assurance Server Provisioning Server NMS DB NOC ORB Client Server Client DB EMS Server ORB CORBA/IDL Client DB Client Agent EMS Manager ADM DB Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. NE NE Agent Dial TL-1/ASCII CMIP DB ATM NE DB Manager SNMP Network Elements DB Manager TDM Agent SONET/SDH Ring Agent Switch DB Voice, Digital Cross-connect, Frame Relay, SS 7 STP 41
Example of NMS/OSS Architectures DB DB DB Business Applications BSS ORB Ordering EAI OSS Client DB XML/EDI Server DB Billing Server DB Client Service Assurance Server Provisioning Server NMS DB NOC ORB Client Server Client DB EMS Server ORB CORBA/IDL Client DB Client Agent EMS Manager ADM DB Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. NE NE Agent Dial TL-1/ASCII CMIP DB ATM NE DB Manager SNMP Network Elements DB Manager TDM Agent SONET/SDH Ring Agent Switch DB Voice, Digital Cross-connect, Frame Relay, SS 7 STP 41
 Video Network is everywhere Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 42
Video Network is everywhere Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 42
 Example Fault Managment Session Number Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 43
Example Fault Managment Session Number Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 43
 Why do we need fault management ? • To monitor the network and know what’s going on ? • To identify the root cause of network faults ? • To measure downtime (uptime) ? • To meet SLA’s ? • Because everybody else does it ? • Because I’ve been told it’s important ? Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 44
Why do we need fault management ? • To monitor the network and know what’s going on ? • To identify the root cause of network faults ? • To measure downtime (uptime) ? • To meet SLA’s ? • Because everybody else does it ? • Because I’ve been told it’s important ? Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 44
![Fault Management • [ISO Definition] Handling errors, faults and alarms in a timely and Fault Management • [ISO Definition] Handling errors, faults and alarms in a timely and](https://present5.com/presentation/f84851a996f1d3c3254b74e372036bff/image-45.jpg) Fault Management • [ISO Definition] Handling errors, faults and alarms in a timely and controlled manner. Error: Deviation of system from normal operations Fault: Physical or algorithmic cause of a malfunction Alarm: Notification of a specific event, may or may not represent an error • A fault is an unplanned failure of software, hardware, or wetware • Not every outage is due to a fault • Not every fault results in an outage Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 45
Fault Management • [ISO Definition] Handling errors, faults and alarms in a timely and controlled manner. Error: Deviation of system from normal operations Fault: Physical or algorithmic cause of a malfunction Alarm: Notification of a specific event, may or may not represent an error • A fault is an unplanned failure of software, hardware, or wetware • Not every outage is due to a fault • Not every fault results in an outage Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 45
 “What tools do I need if I get 30 traps per sec sustained on my network? ” “A pen to write my resignation. ” Source : One 2 One NOC Manager Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 46
“What tools do I need if I get 30 traps per sec sustained on my network? ” “A pen to write my resignation. ” Source : One 2 One NOC Manager Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 46
 Sources • Routers, switches, wires, fiber, PDUs, DNS servers, HVACs, power companies, squirrels, flooding, soft drinks, clumsy people, nuclear accelerators, bulldozers, users, network managers, … Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 47
Sources • Routers, switches, wires, fiber, PDUs, DNS servers, HVACs, power companies, squirrels, flooding, soft drinks, clumsy people, nuclear accelerators, bulldozers, users, network managers, … Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 47
 Fault Management Needs • Keep me out of trouble! – Let me know when I’m having a problem or about to have a problem • Support my growing Cisco network as one ‘system’ – Routed and switched environment – IP telephony – call managers, phones, etc. – Network connectivity analysis • Don’t make me add more staff – Out-of-the-box with no rules to write – Support new devices in a timely manner • Fit into my present mode of operations (PMO) – DFM, ITEM, CIC, HP OV, Tivoli, Micromuse, SMARTS, etc. Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 48
Fault Management Needs • Keep me out of trouble! – Let me know when I’m having a problem or about to have a problem • Support my growing Cisco network as one ‘system’ – Routed and switched environment – IP telephony – call managers, phones, etc. – Network connectivity analysis • Don’t make me add more staff – Out-of-the-box with no rules to write – Support new devices in a timely manner • Fit into my present mode of operations (PMO) – DFM, ITEM, CIC, HP OV, Tivoli, Micromuse, SMARTS, etc. Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 48
 Device Fault Management IP fabric Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco. Works Device Fault Manager 49
Device Fault Management IP fabric Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco. Works Device Fault Manager 49
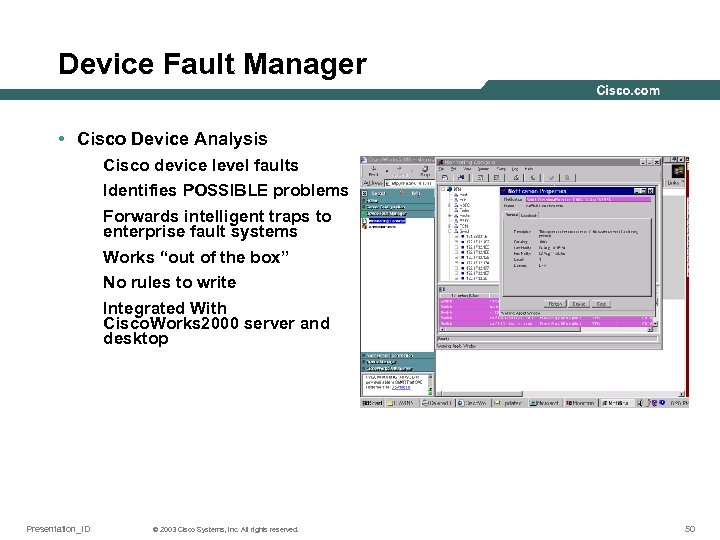 Device Fault Manager • Cisco Device Analysis Cisco device level faults Identifies POSSIBLE problems Forwards intelligent traps to enterprise fault systems Works “out of the box” No rules to write Integrated With Cisco. Works 2000 server and desktop Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 50
Device Fault Manager • Cisco Device Analysis Cisco device level faults Identifies POSSIBLE problems Forwards intelligent traps to enterprise fault systems Works “out of the box” No rules to write Integrated With Cisco. Works 2000 server and desktop Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 50
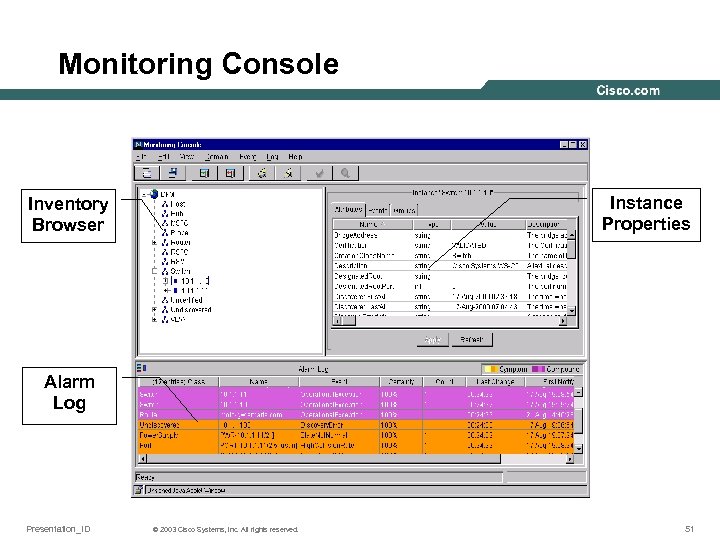 Monitoring Console Instance Properties Inventory Browser Alarm Log Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 51
Monitoring Console Instance Properties Inventory Browser Alarm Log Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 51
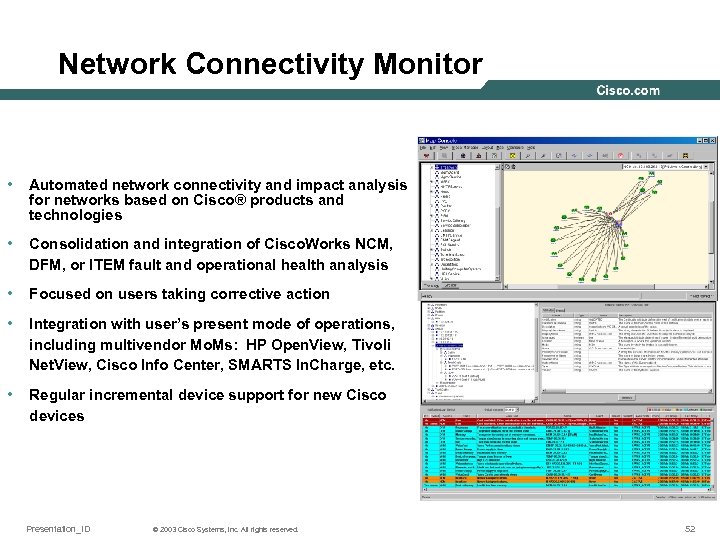 Network Connectivity Monitor • Automated network connectivity and impact analysis for networks based on Cisco® products and technologies • Consolidation and integration of Cisco. Works NCM, DFM, or ITEM fault and operational health analysis • Focused on users taking corrective action • Integration with user’s present mode of operations, including multivendor Mo. Ms: HP Open. View, Tivoli Net. View, Cisco Info Center, SMARTS In. Charge, etc. • Regular incremental device support for new Cisco devices Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 52
Network Connectivity Monitor • Automated network connectivity and impact analysis for networks based on Cisco® products and technologies • Consolidation and integration of Cisco. Works NCM, DFM, or ITEM fault and operational health analysis • Focused on users taking corrective action • Integration with user’s present mode of operations, including multivendor Mo. Ms: HP Open. View, Tivoli Net. View, Cisco Info Center, SMARTS In. Charge, etc. • Regular incremental device support for new Cisco devices Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 52
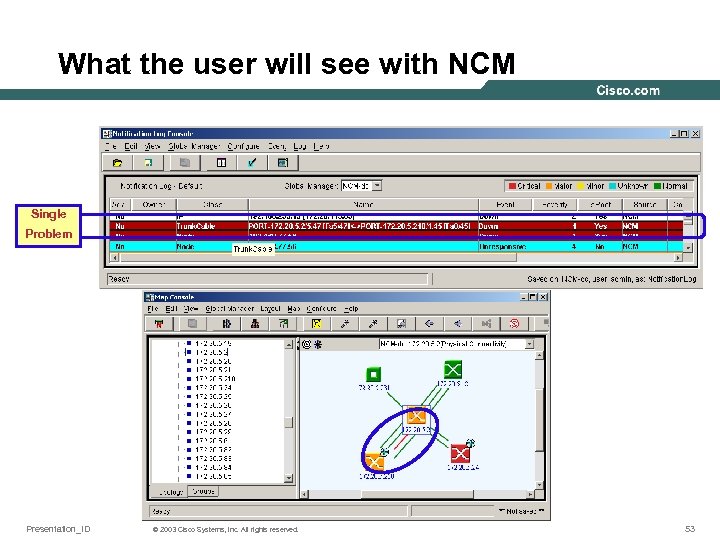 What the user will see with NCM Single Problem Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 53
What the user will see with NCM Single Problem Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 53
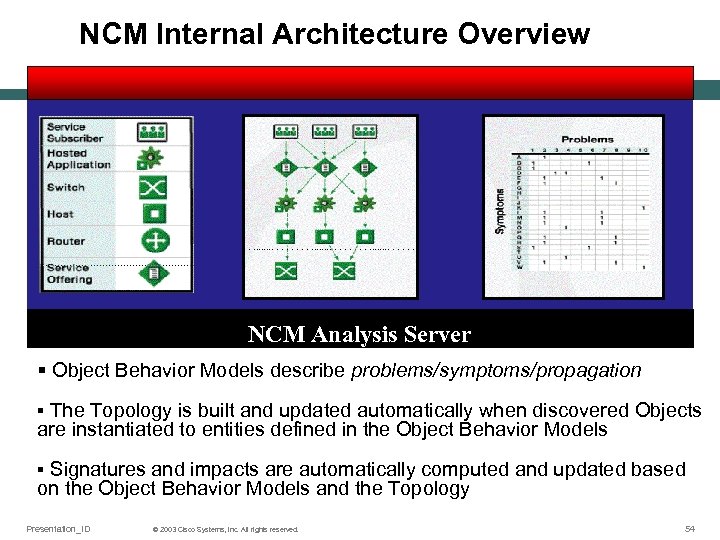 NCM Internal Architecture Overview Topology NCM Analysis Server § Object Behavior Models describe problems/symptoms/propagation The Topology is built and updated automatically when discovered Objects are instantiated to entities defined in the Object Behavior Models § Signatures and impacts are automatically computed and updated based on the Object Behavior Models and the Topology § Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 54
NCM Internal Architecture Overview Topology NCM Analysis Server § Object Behavior Models describe problems/symptoms/propagation The Topology is built and updated automatically when discovered Objects are instantiated to entities defined in the Object Behavior Models § Signatures and impacts are automatically computed and updated based on the Object Behavior Models and the Topology § Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 54
 Authentic Problem Signatures Symptoms Problems Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 55
Authentic Problem Signatures Symptoms Problems Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 55
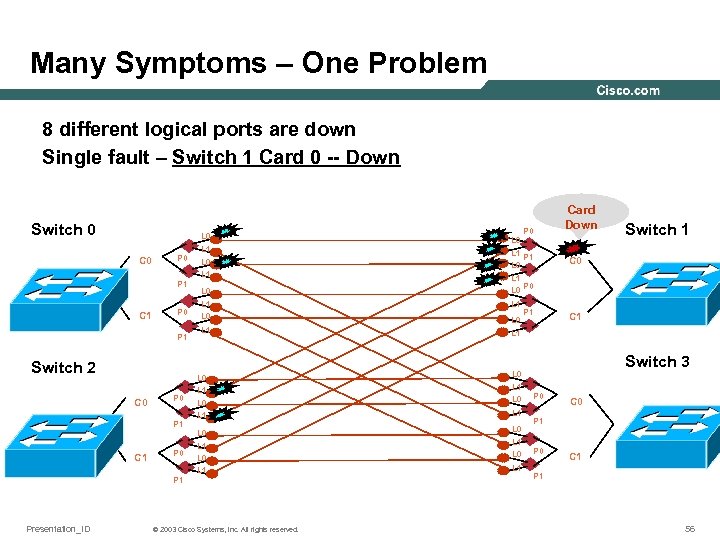 Many Symptoms – One Problem 8 different logical ports are down Single fault – Switch 1 Card 0 -- Down Switch 0 L 0 C 0 P 1 C 1 P 0 P 1 Switch 2 L 1 L 0 L 0 L 1 L 1 L 0 L 1 P 0 P 1 C 1 P 0 P 1 Switch 1 C 0 L 1 L 0 C 0 Presentation_ID L 1 L 0 Card Down L 1 L 0 L 0 L 1 L 1 P 1 C 1 Switch 3 L 0 L 1 P 0 L 1 © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. L 0 L 1 P 0 C 0 P 1 P 0 C 1 P 1 56
Many Symptoms – One Problem 8 different logical ports are down Single fault – Switch 1 Card 0 -- Down Switch 0 L 0 C 0 P 1 C 1 P 0 P 1 Switch 2 L 1 L 0 L 0 L 1 L 1 L 0 L 1 P 0 P 1 C 1 P 0 P 1 Switch 1 C 0 L 1 L 0 C 0 Presentation_ID L 1 L 0 Card Down L 1 L 0 L 0 L 1 L 1 P 1 C 1 Switch 3 L 0 L 1 P 0 L 1 © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. L 0 L 1 P 0 C 0 P 1 P 0 C 1 P 1 56
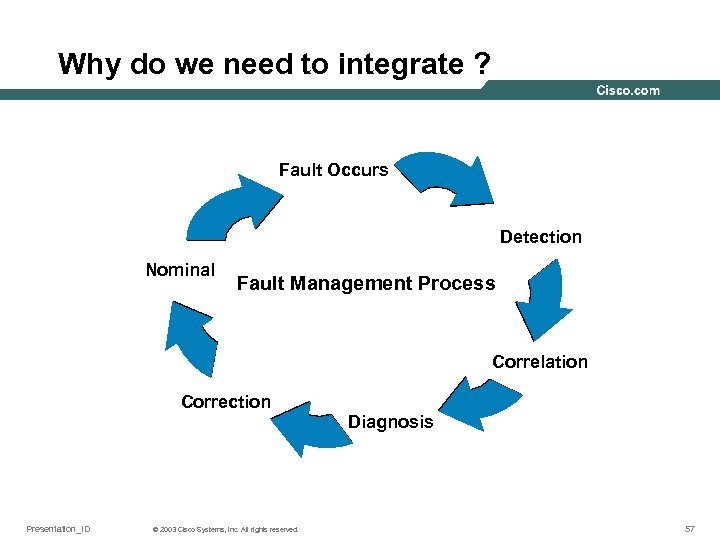 Why do we need to integrate ? Fault Occurs Detection Nominal Fault Management Process Correlation Correction Diagnosis Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 57
Why do we need to integrate ? Fault Occurs Detection Nominal Fault Management Process Correlation Correction Diagnosis Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 57
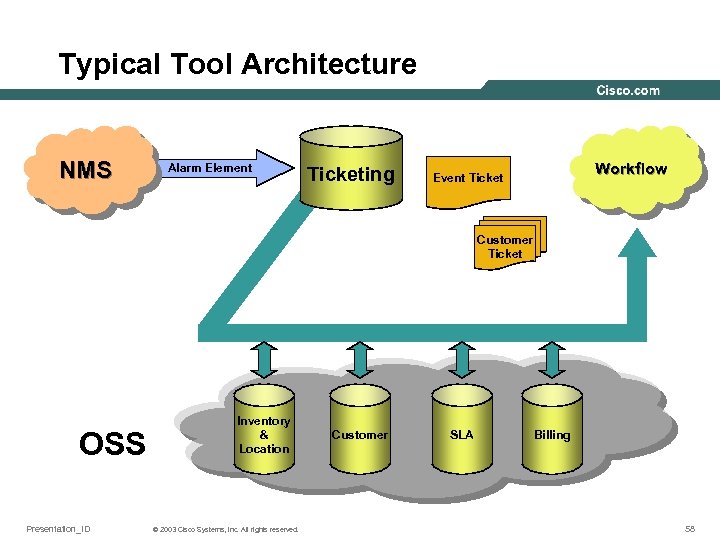 Typical Tool Architecture NMS Alarm Element Ticketing Workflow Event Ticket Customer Ticket OSS Presentation_ID Inventory & Location © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Customer SLA Billing 58
Typical Tool Architecture NMS Alarm Element Ticketing Workflow Event Ticket Customer Ticket OSS Presentation_ID Inventory & Location © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Customer SLA Billing 58
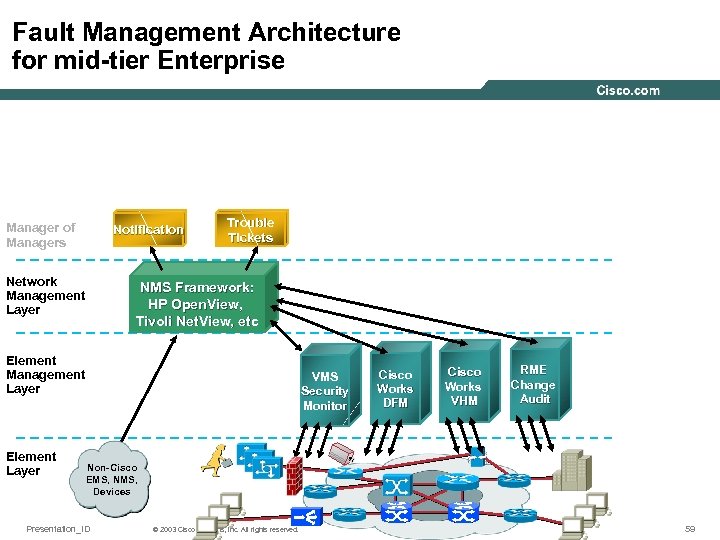 Fault Management Architecture for mid-tier Enterprise Manager of Managers Notification Network Management Layer Trouble Tickets NMS Framework: HP Open. View, Tivoli Net. View, etc Element Management Layer Element Layer CIC, CA Unicenter, etc. VMS Security Monitor Cisco Works DFM Cisco Works VHM RME Change Audit Non-Cisco EMS, NMS, Devices Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 59
Fault Management Architecture for mid-tier Enterprise Manager of Managers Notification Network Management Layer Trouble Tickets NMS Framework: HP Open. View, Tivoli Net. View, etc Element Management Layer Element Layer CIC, CA Unicenter, etc. VMS Security Monitor Cisco Works DFM Cisco Works VHM RME Change Audit Non-Cisco EMS, NMS, Devices Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 59
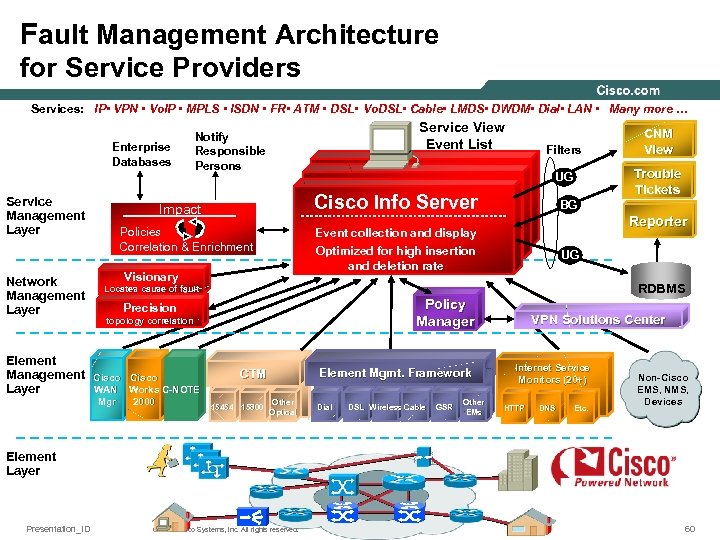 Fault Management Architecture for Service Providers Services: IP • VPN • Vo. IP • MPLS • ISDN • FR • ATM • DSL • Vo. DSL • Cable • LMDS • DWDM • Dial • LAN • Many more … Enterprise Databases Service Management Layer Network Management Layer Element Management Layer Service View Event List Notify Responsible Persons Filters Trouble Tickets UG Cisco Info Server Impact Policies Correlation & Enrichment BG Reporter Event collection and display Optimized for high insertion and deletion rate Visionary UG RDBMS Locates cause of fault Policy Manager Precision topology correlation Cisco WAN Works C-NOTE Mgr 2000 CNM View Element Mgmt. Framework CTM 15454 15800 Other Optical Dial DSL Wireless Cable GSR Other EMs VPN Solutions Center Internet Service Monitors (20+) HTTP DNS Etc. Non-Cisco EMS, NMS, Devices Element Layer Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 60
Fault Management Architecture for Service Providers Services: IP • VPN • Vo. IP • MPLS • ISDN • FR • ATM • DSL • Vo. DSL • Cable • LMDS • DWDM • Dial • LAN • Many more … Enterprise Databases Service Management Layer Network Management Layer Element Management Layer Service View Event List Notify Responsible Persons Filters Trouble Tickets UG Cisco Info Server Impact Policies Correlation & Enrichment BG Reporter Event collection and display Optimized for high insertion and deletion rate Visionary UG RDBMS Locates cause of fault Policy Manager Precision topology correlation Cisco WAN Works C-NOTE Mgr 2000 CNM View Element Mgmt. Framework CTM 15454 15800 Other Optical Dial DSL Wireless Cable GSR Other EMs VPN Solutions Center Internet Service Monitors (20+) HTTP DNS Etc. Non-Cisco EMS, NMS, Devices Element Layer Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 60
 Case study Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 61
Case study Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 61
 Background • > 2500 devices Cisco-only • Limited staff • ”Custom” devices • Needed to improve their fault management • Did not want to have to maintain lots of rules and/or add people Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 62
Background • > 2500 devices Cisco-only • Limited staff • ”Custom” devices • Needed to improve their fault management • Did not want to have to maintain lots of rules and/or add people Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 62
 Solution Products • Cisco. Works DFM Device-level monitoring • Cisco. Works NCM • Cisco Info Center • Concord e. Health Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 63
Solution Products • Cisco. Works DFM Device-level monitoring • Cisco. Works NCM • Cisco Info Center • Concord e. Health Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 63
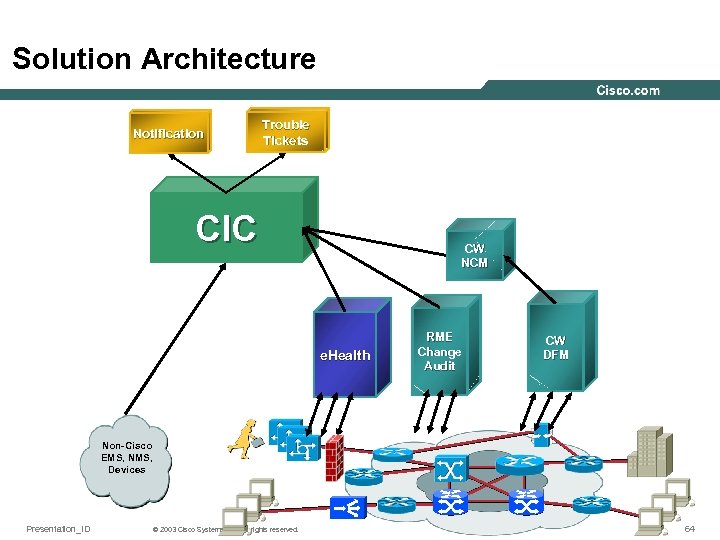 Solution Architecture Notification Trouble Tickets CIC, CA Unicenter, etc. CIC CW NCM e. Health RME Change Audit CW DFM Non-Cisco EMS, NMS, Devices Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 64
Solution Architecture Notification Trouble Tickets CIC, CA Unicenter, etc. CIC CW NCM e. Health RME Change Audit CW DFM Non-Cisco EMS, NMS, Devices Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 64
 Self Provisioning Flow Session Number Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 65
Self Provisioning Flow Session Number Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 65
 Promiscuous Registration Mode • Only the modem is registered • CPEs receive service based on the modem they are behind (prov vs. unprov) • Modem can be restricted to a provisioning group (otherwise goes back to unprov) • Can be system wide or per Cable Modem basis Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 66
Promiscuous Registration Mode • Only the modem is registered • CPEs receive service based on the modem they are behind (prov vs. unprov) • Modem can be restricted to a provisioning group (otherwise goes back to unprov) • Can be system wide or per Cable Modem basis Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 66
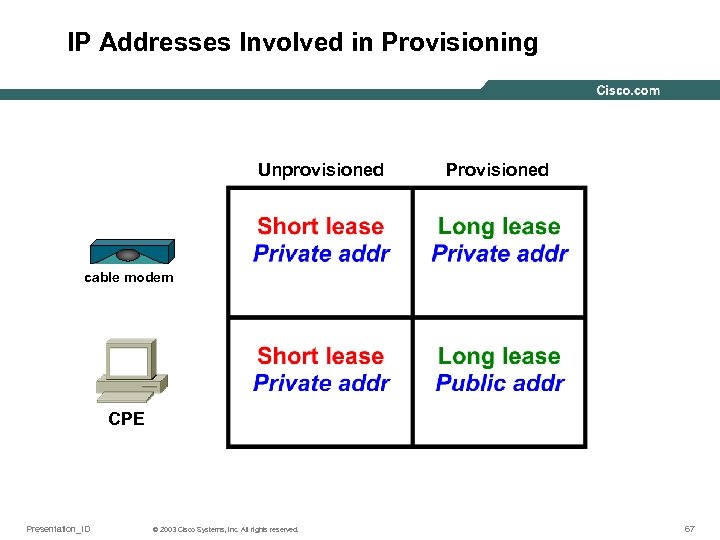 IP Addresses Involved in Provisioning Unprovisioned Provisioned cable modem CPE Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 67
IP Addresses Involved in Provisioning Unprovisioned Provisioned cable modem CPE Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 67
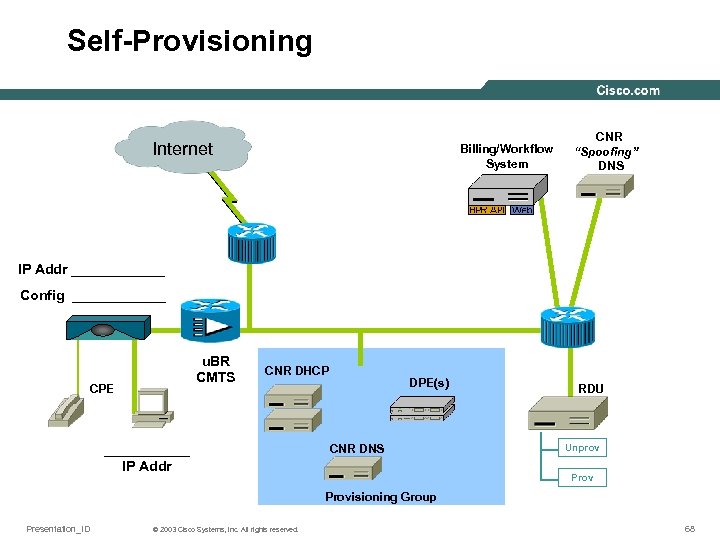 Self-Provisioning Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP ______ IP Addr DPE(s) CNR DNS RDU Unprov Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 68
Self-Provisioning Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP ______ IP Addr DPE(s) CNR DNS RDU Unprov Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 68
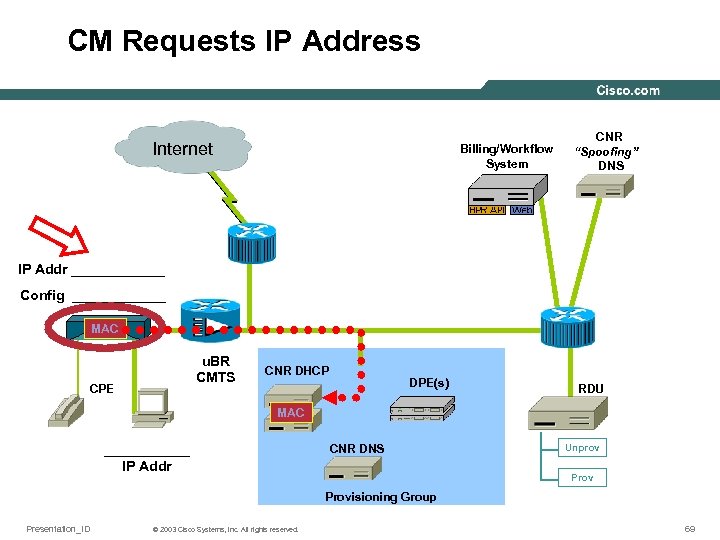 CM Requests IP Address Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ MAC u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 69
CM Requests IP Address Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ MAC u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 69
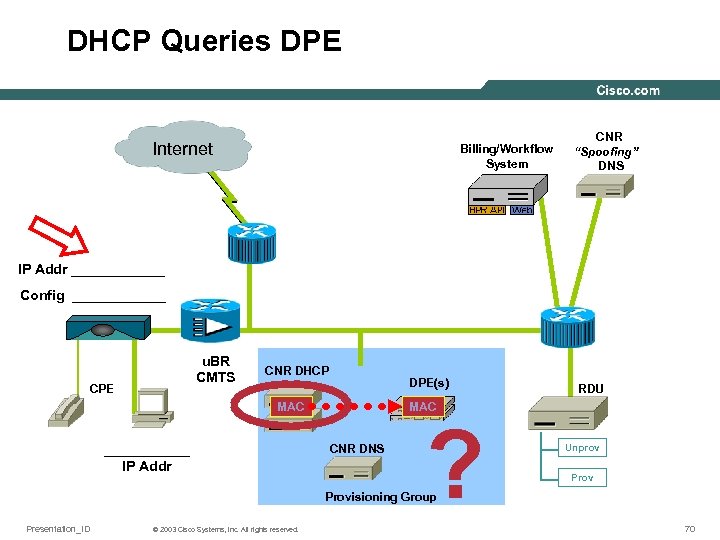 DHCP Queries DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU CNR DNS ? Unprov Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 70
DHCP Queries DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU CNR DNS ? Unprov Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 70
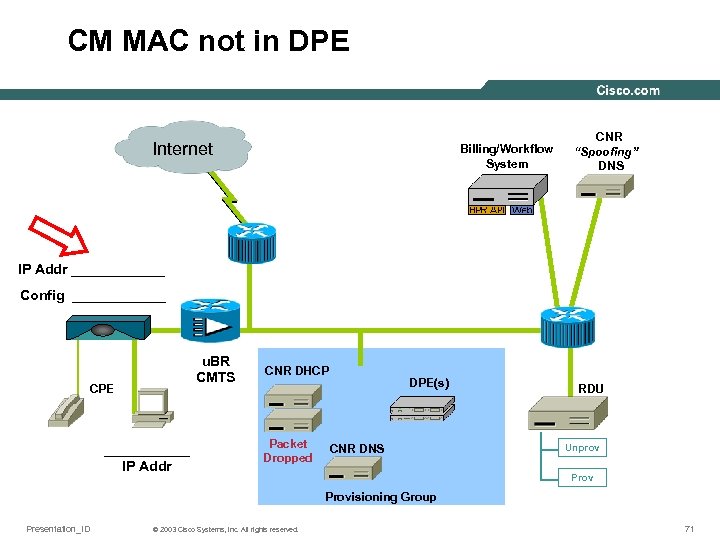 CM MAC not in DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE ______ IP Addr CNR DHCP Packet Dropped DPE(s) CNR DNS RDU Unprov Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 71
CM MAC not in DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE ______ IP Addr CNR DHCP Packet Dropped DPE(s) CNR DNS RDU Unprov Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 71
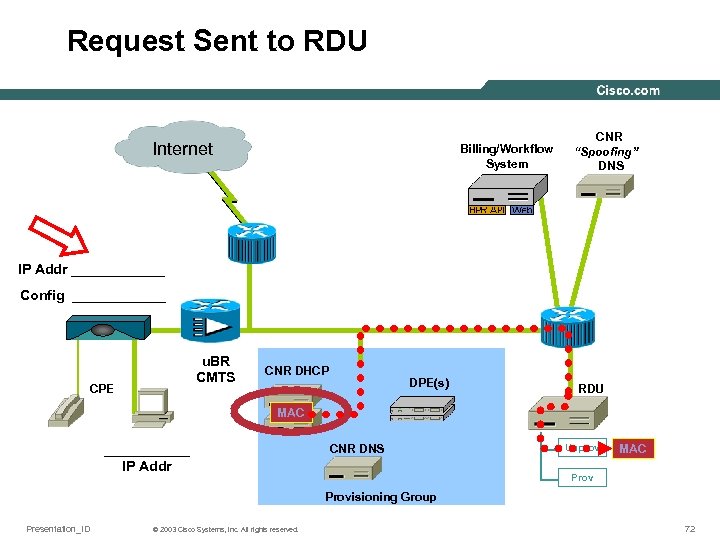 Request Sent to RDU Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 72
Request Sent to RDU Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 72
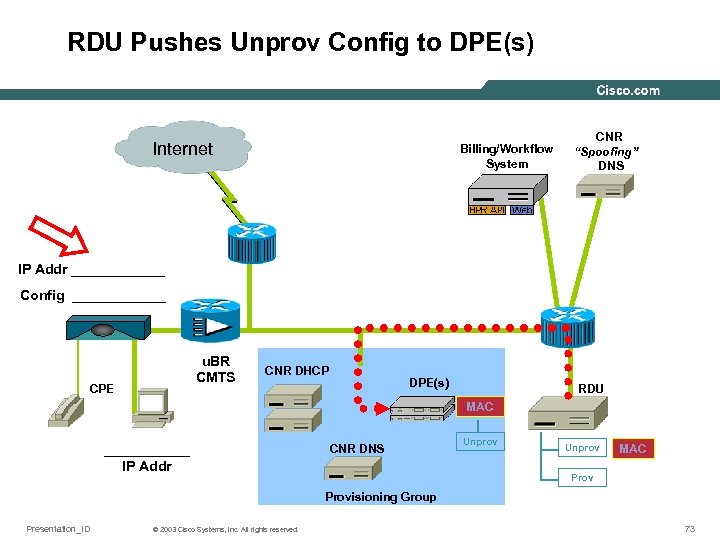 RDU Pushes Unprov Config to DPE(s) Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 73
RDU Pushes Unprov Config to DPE(s) Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 73
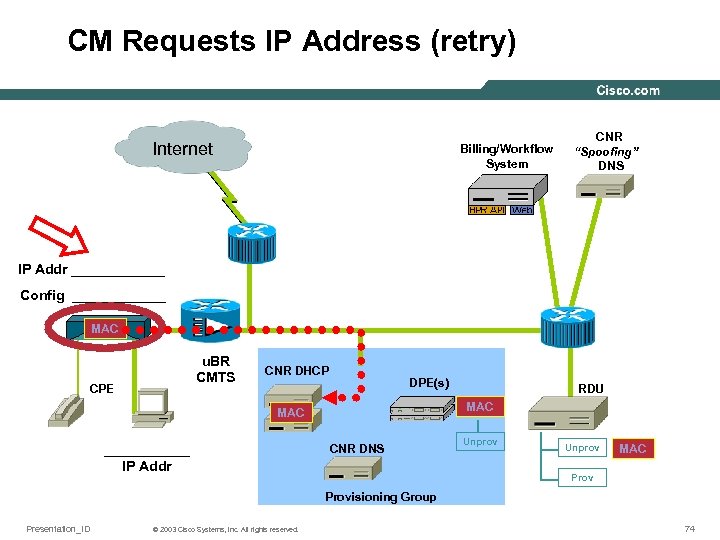 CM Requests IP Address (retry) Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ MAC u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 74
CM Requests IP Address (retry) Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ MAC u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 74
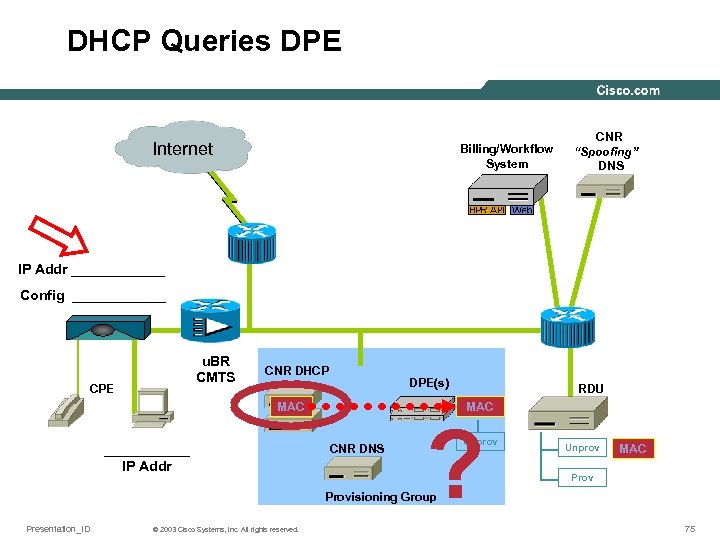 DHCP Queries DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS ? Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 75
DHCP Queries DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS ? Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 75
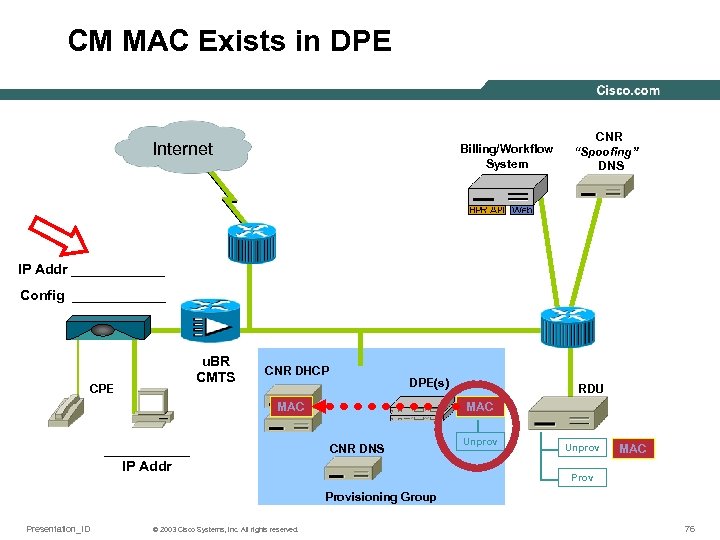 CM MAC Exists in DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 76
CM MAC Exists in DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 76
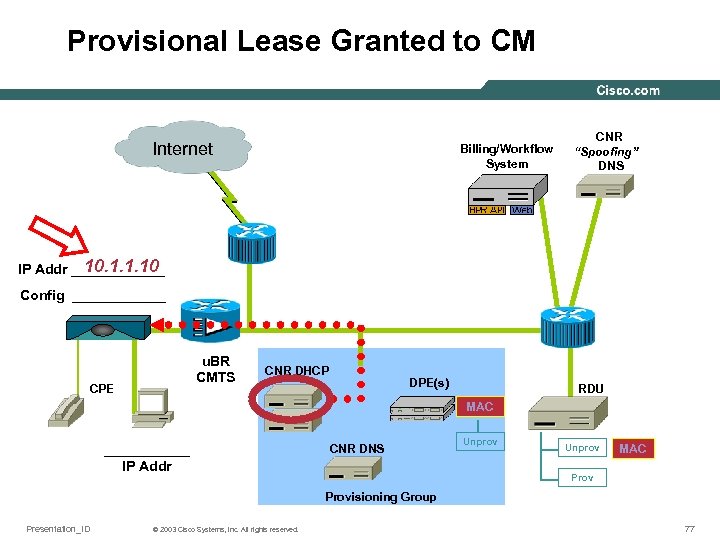 Provisional Lease Granted to CM Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 77
Provisional Lease Granted to CM Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 77
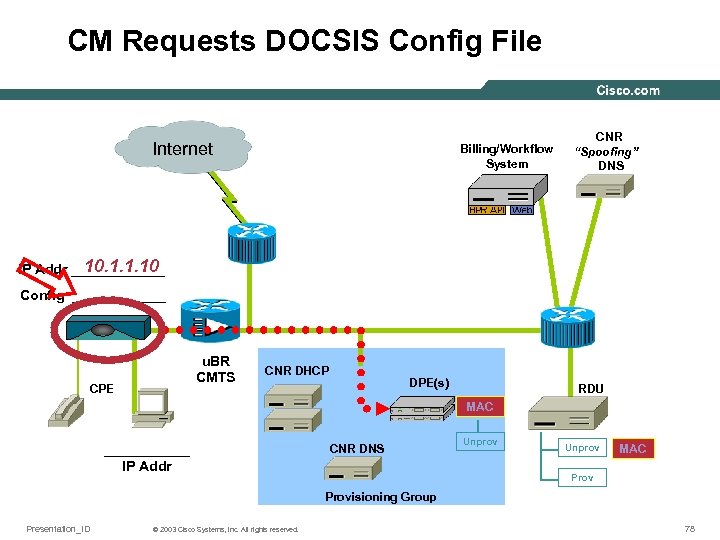 CM Requests DOCSIS Config File Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 78
CM Requests DOCSIS Config File Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 78
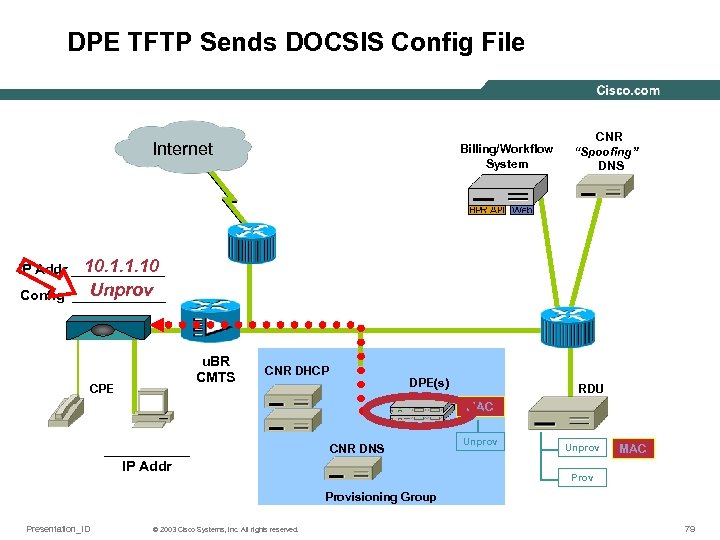 DPE TFTP Sends DOCSIS Config File Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 79
DPE TFTP Sends DOCSIS Config File Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 79
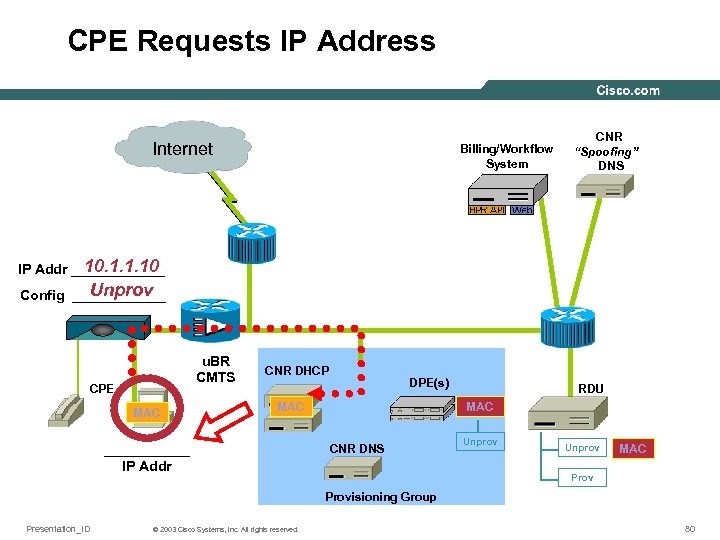 CPE Requests IP Address Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE MAC CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 80
CPE Requests IP Address Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE MAC CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 80
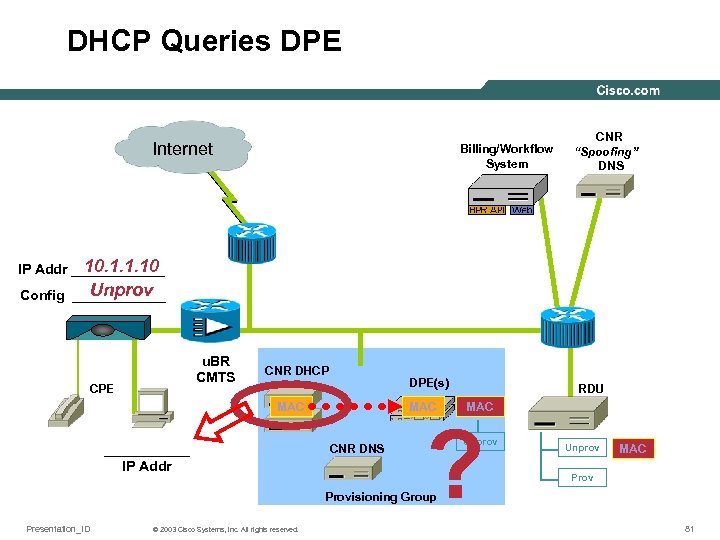 DHCP Queries DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS RDU MAC ? Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 81
DHCP Queries DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS RDU MAC ? Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 81
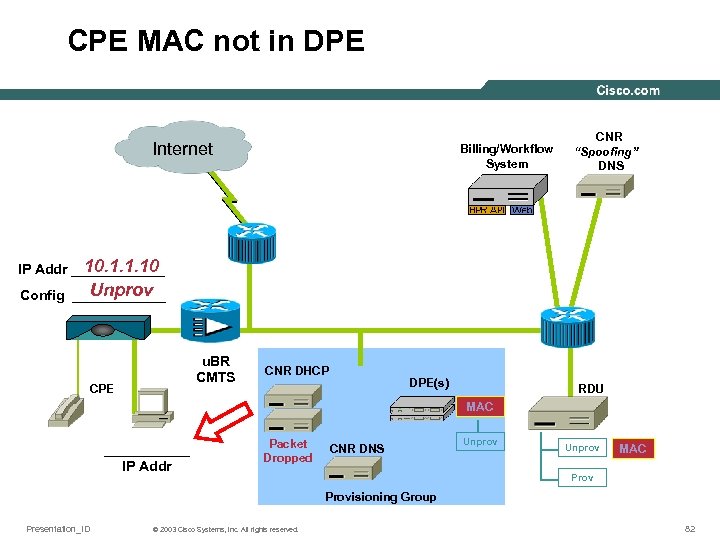 CPE MAC not in DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr Packet Dropped CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 82
CPE MAC not in DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr Packet Dropped CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 82
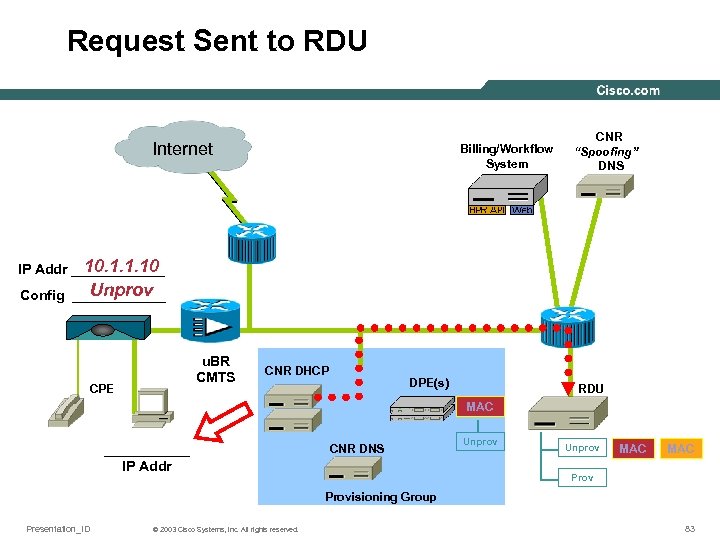 Request Sent to RDU Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 83
Request Sent to RDU Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 83
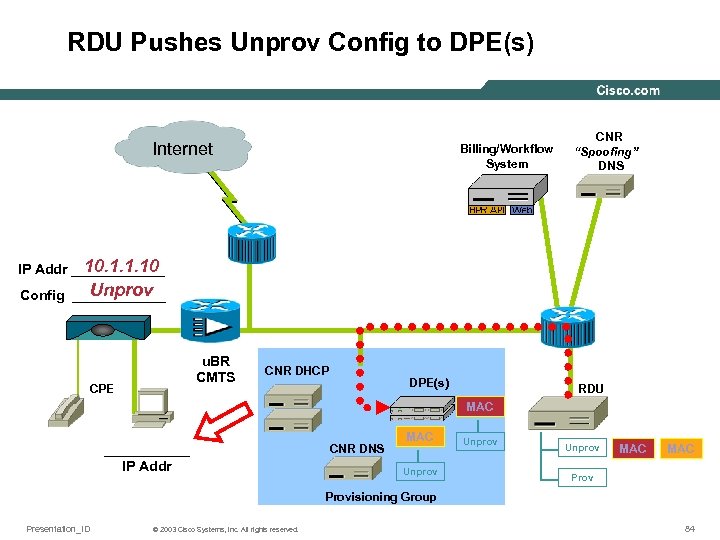 RDU Pushes Unprov Config to DPE(s) Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 84
RDU Pushes Unprov Config to DPE(s) Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 84
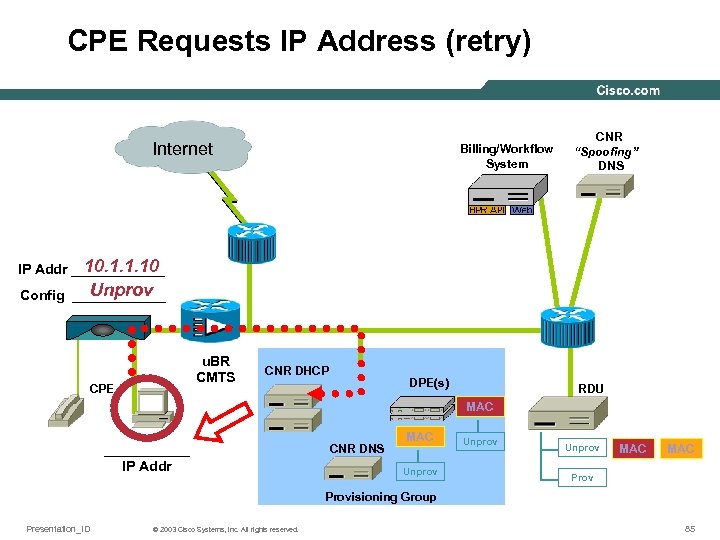 CPE Requests IP Address (retry) Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 85
CPE Requests IP Address (retry) Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 85
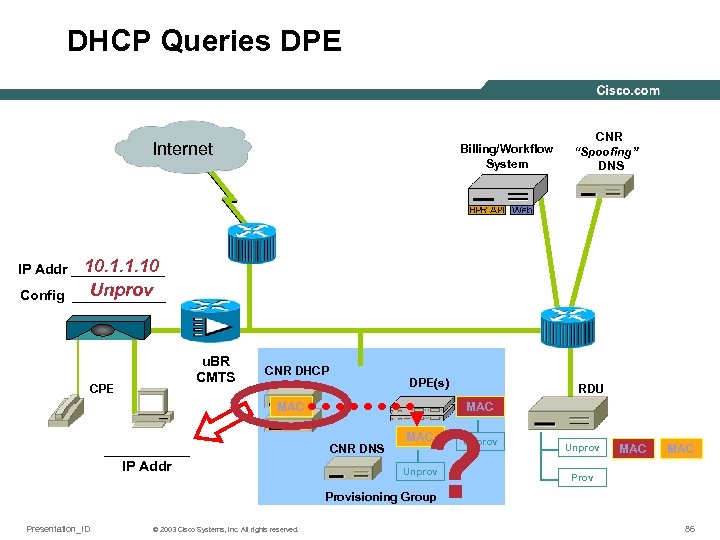 DHCP Queries DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS ? MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 86
DHCP Queries DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS ? MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 86
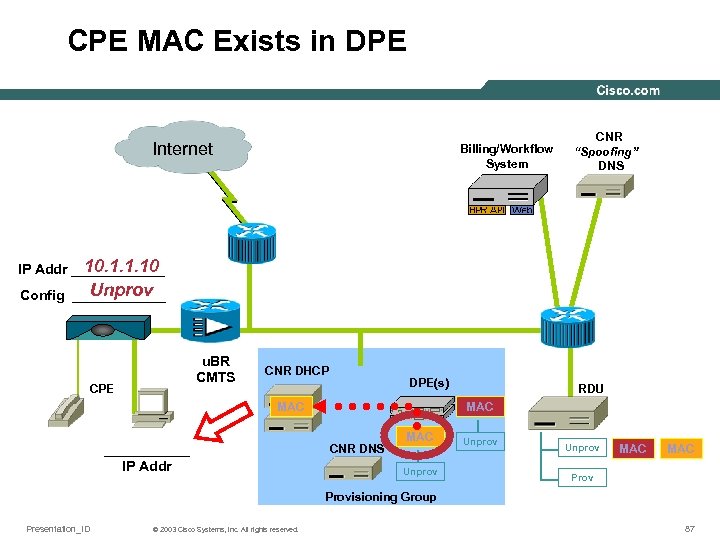 CPE MAC Exists in DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 87
CPE MAC Exists in DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 87
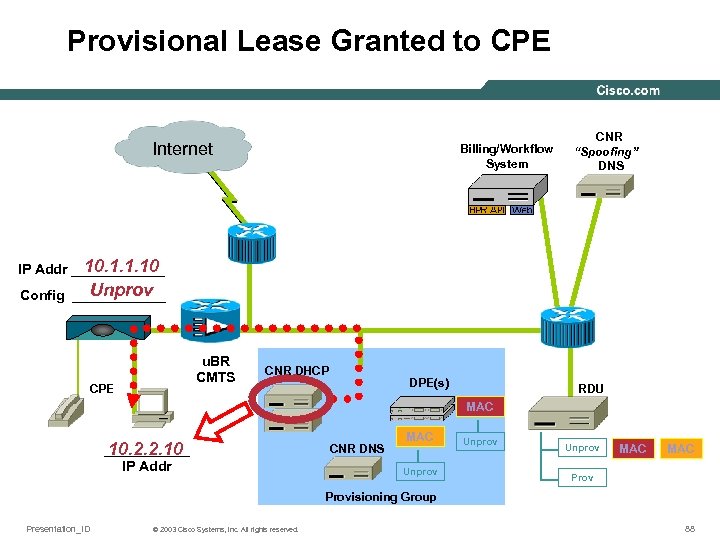 Provisional Lease Granted to CPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ 10. 2. 2. 10 IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 88
Provisional Lease Granted to CPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ 10. 2. 2. 10 IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 88
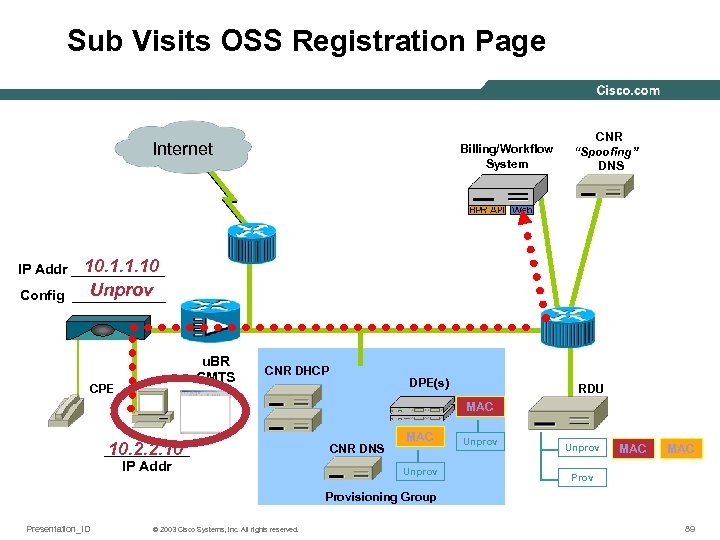 Sub Visits OSS Registration Page Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ 10. 2. 2. 10 IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 89
Sub Visits OSS Registration Page Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ 10. 2. 2. 10 IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 89
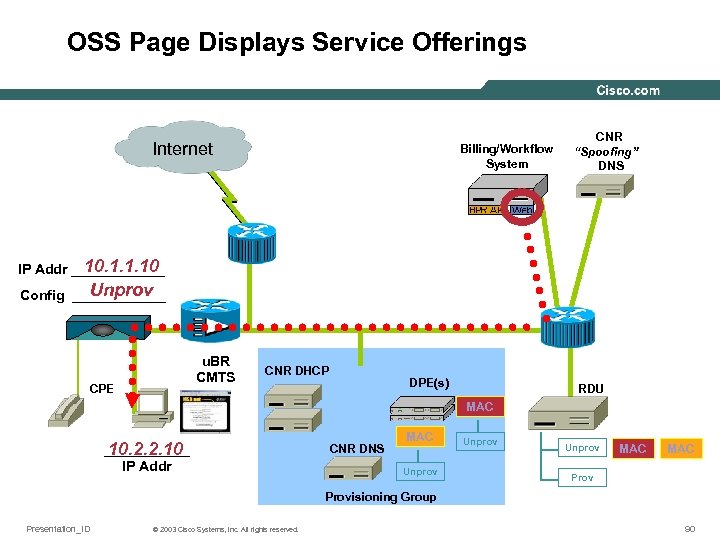 OSS Page Displays Service Offerings Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ 10. 2. 2. 10 IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 90
OSS Page Displays Service Offerings Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ 10. 2. 2. 10 IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 90
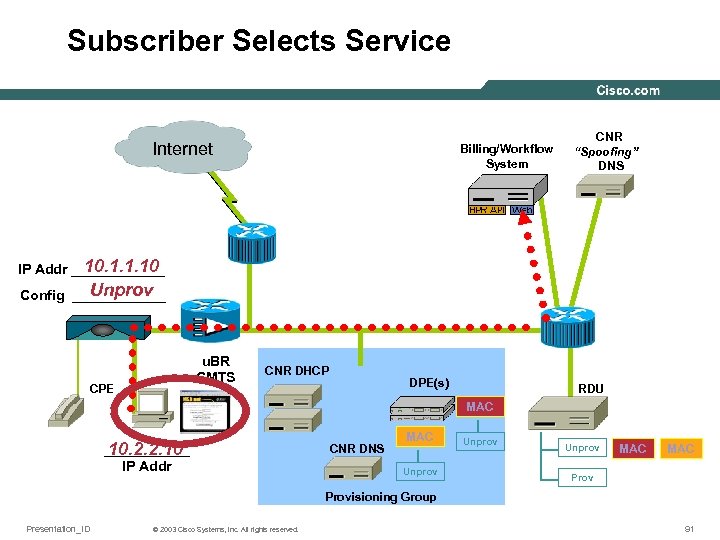 Subscriber Selects Service Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ 10. 2. 2. 10 IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 91
Subscriber Selects Service Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ 10. 2. 2. 10 IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 91
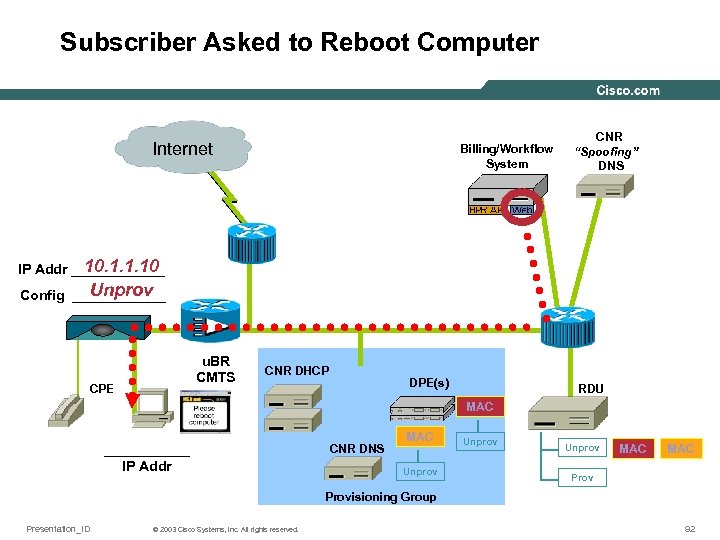 Subscriber Asked to Reboot Computer Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ 10. 2. 2. 10 IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 92
Subscriber Asked to Reboot Computer Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ 10. 2. 2. 10 IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 92
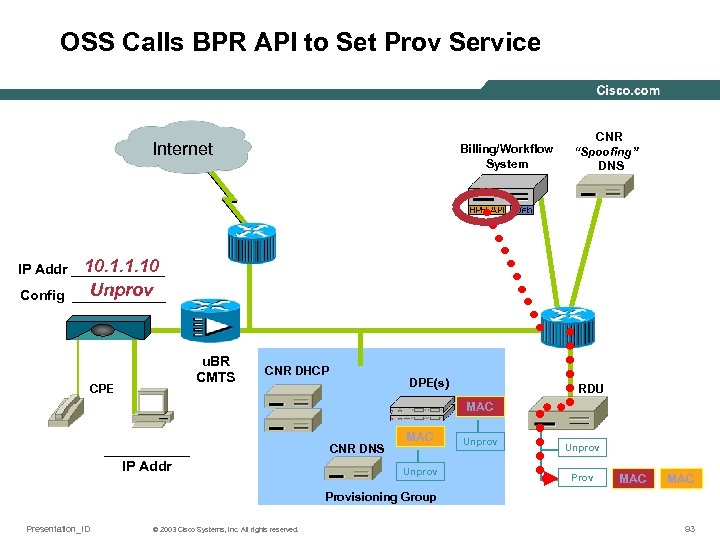 OSS Calls BPR API to Set Prov Service Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 93
OSS Calls BPR API to Set Prov Service Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Unprov MAC MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 93
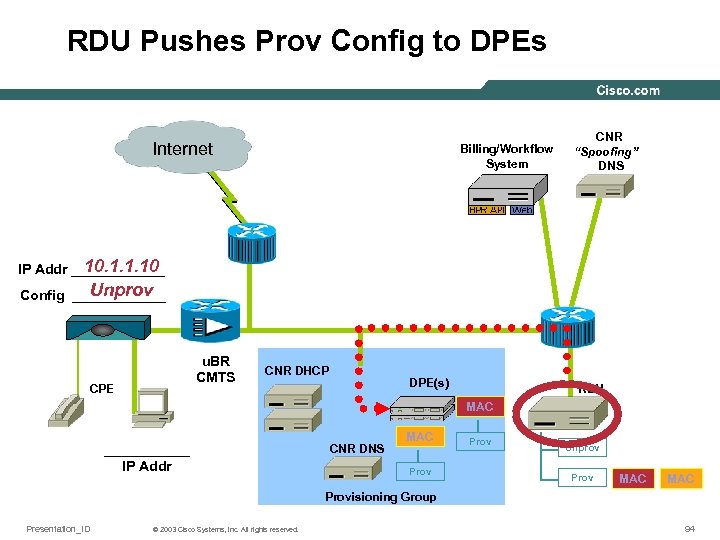 RDU Pushes Prov Config to DPEs Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Default Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 94
RDU Pushes Prov Config to DPEs Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Default Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 94
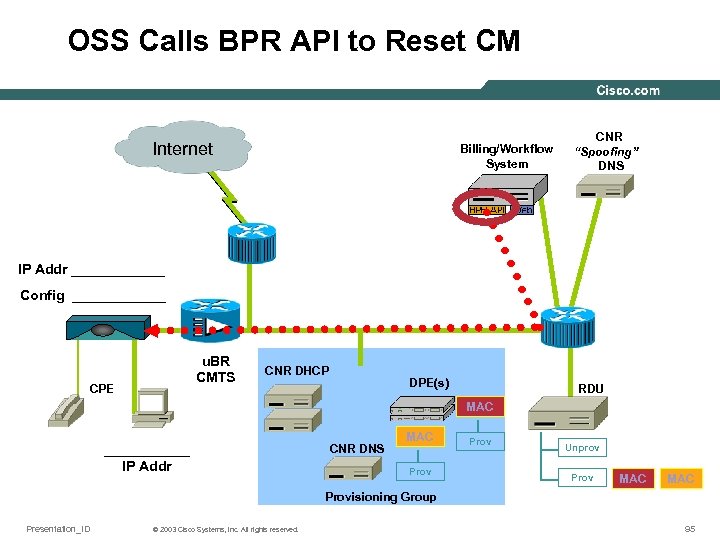 OSS Calls BPR API to Reset CM Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 95
OSS Calls BPR API to Reset CM Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 1. 1. 10 IP Addr ______ Unprov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 95
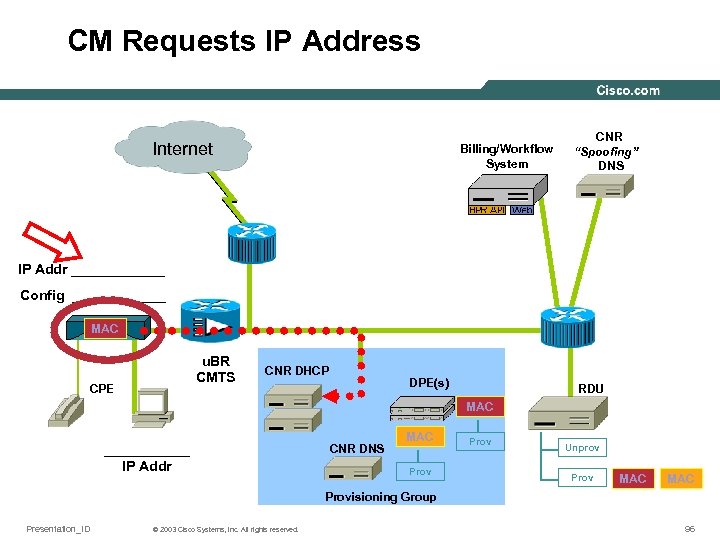 CM Requests IP Address Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ MAC u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 96
CM Requests IP Address Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ MAC u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 96
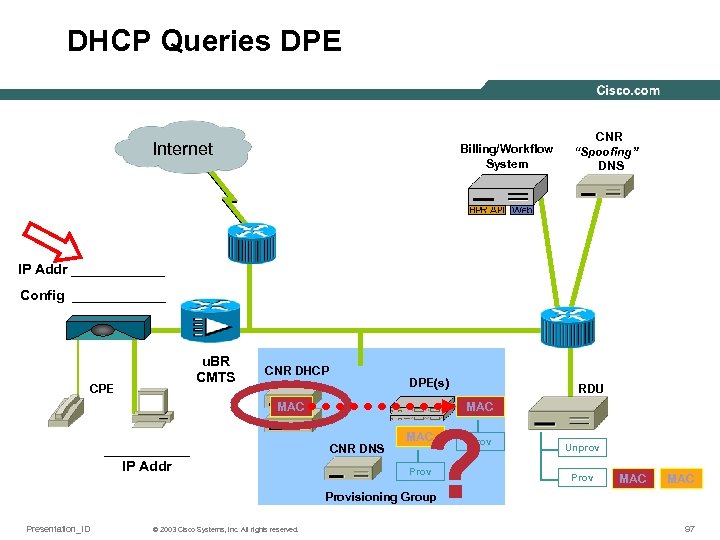 DHCP Queries DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS ? MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 97
DHCP Queries DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS ? MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 97
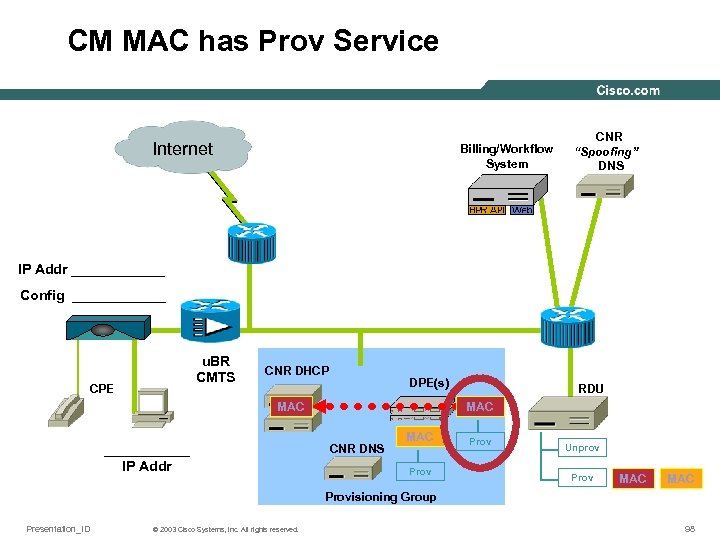 CM MAC has Prov Service Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 98
CM MAC has Prov Service Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 98
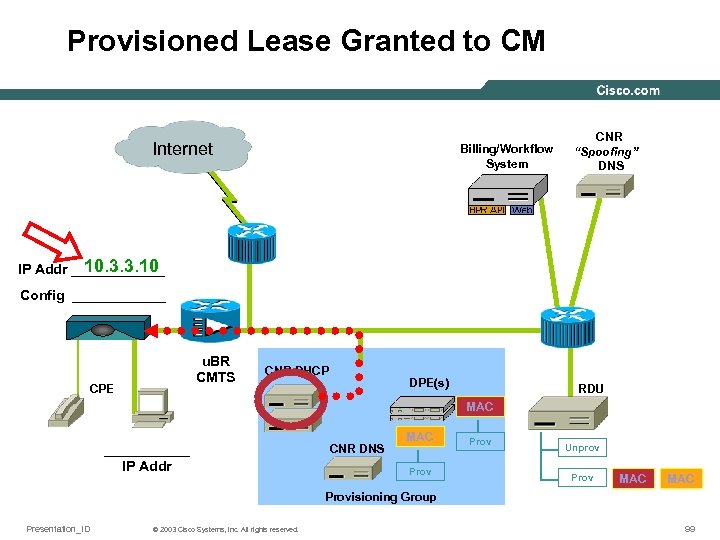 Provisioned Lease Granted to CM Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 99
Provisioned Lease Granted to CM Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 99
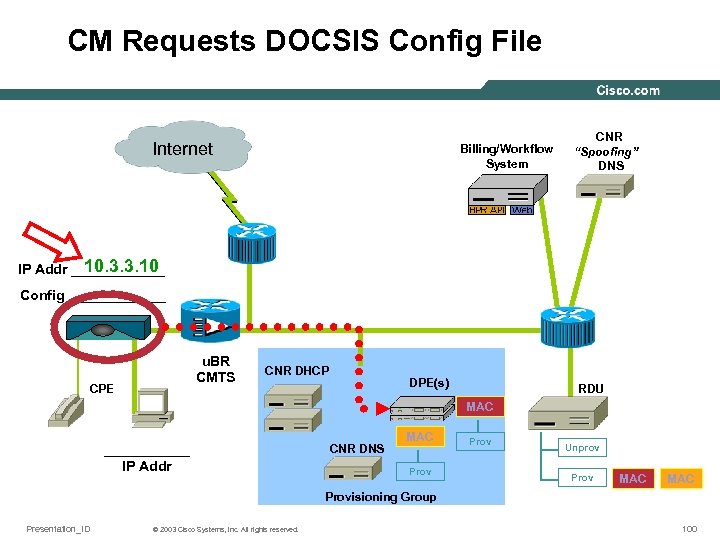 CM Requests DOCSIS Config File Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 100
CM Requests DOCSIS Config File Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 100
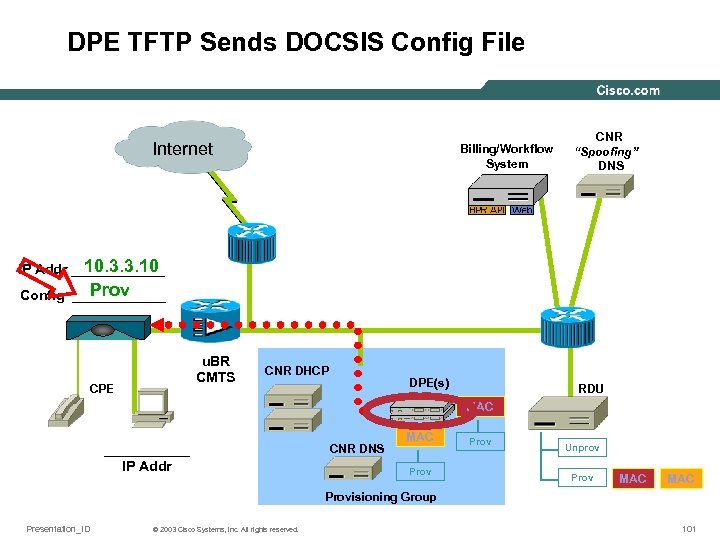 DPE TFTP Sends DOCSIS Config File Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Prov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 101
DPE TFTP Sends DOCSIS Config File Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Prov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 101
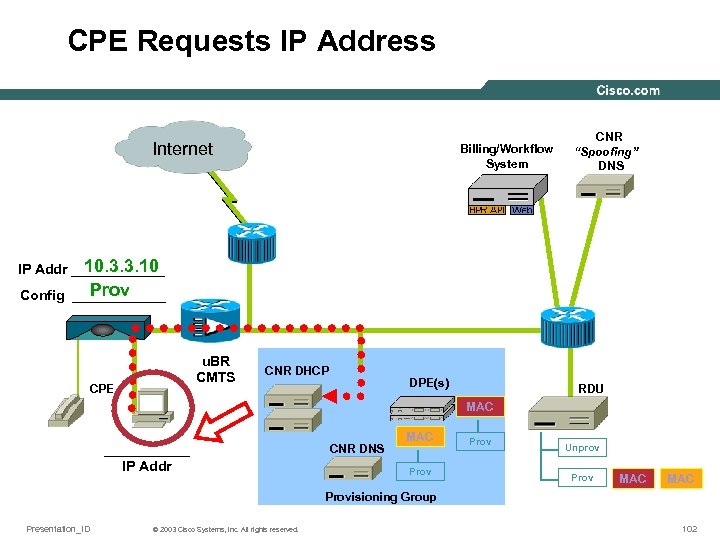 CPE Requests IP Address Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Prov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 102
CPE Requests IP Address Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Prov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 102
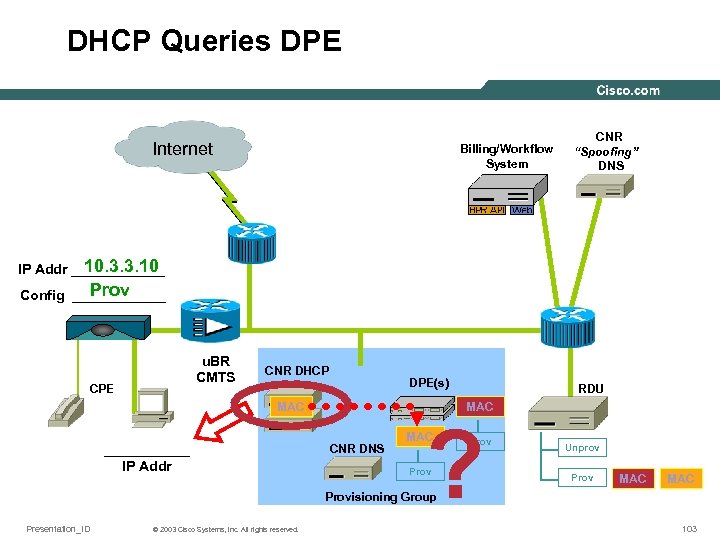 DHCP Queries DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Prov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS ? MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 103
DHCP Queries DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Prov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS ? MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 103
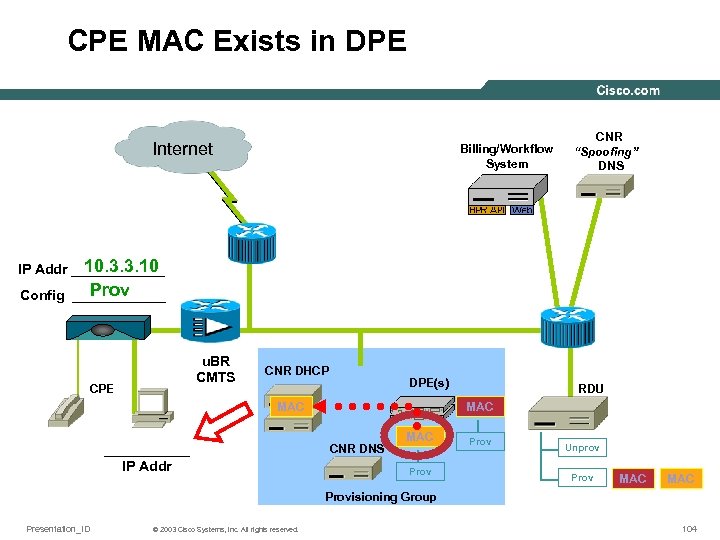 CPE MAC Exists in DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Prov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 104
CPE MAC Exists in DPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Prov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) MAC ______ IP Addr RDU MAC CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 104
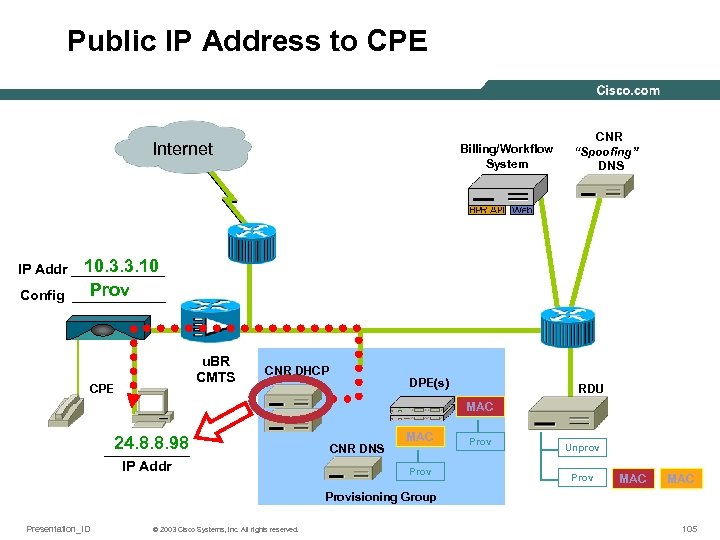 Public IP Address to CPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Prov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC 24. 8. 8. 98 ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 105
Public IP Address to CPE Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Prov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC 24. 8. 8. 98 ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 105
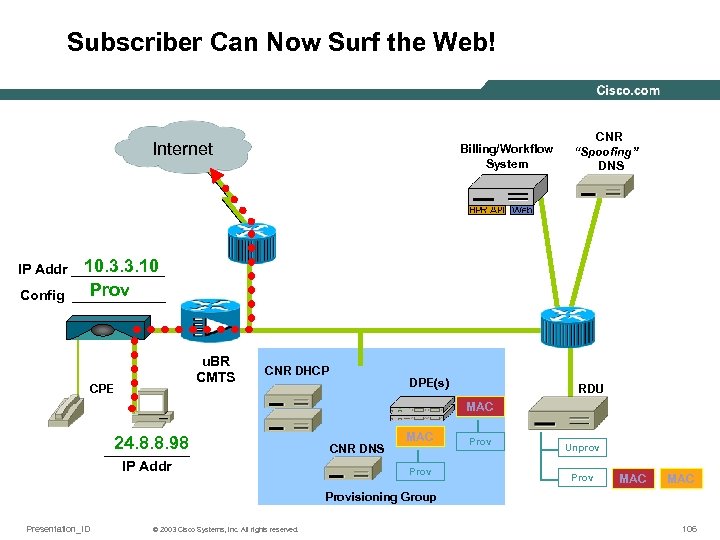 Subscriber Can Now Surf the Web! Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Prov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC 24. 8. 8. 98 ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 106
Subscriber Can Now Surf the Web! Internet Billing/Workflow System CNR “Spoofing” DNS 10. 3. 3. 10 IP Addr ______ Prov Config ______ u. BR CMTS CPE CNR DHCP DPE(s) RDU MAC 24. 8. 8. 98 ______ IP Addr CNR DNS MAC Prov Unprov Prov MAC Provisioning Group Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 106
 Fast. Web Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 107
Fast. Web Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 107
 Q&A Session Number Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 108
Q&A Session Number Presentation_ID © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 108
 Presentation_ID © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 109
Presentation_ID © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 109


