e3887b55b0ce98b8d075a7daaeae5acf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 ■ Essential Question: Question –What led to the Cold War between the United States & Soviet Union? ■ Warm Up Question: Question
■ Essential Question: Question –What led to the Cold War between the United States & Soviet Union? ■ Warm Up Question: Question
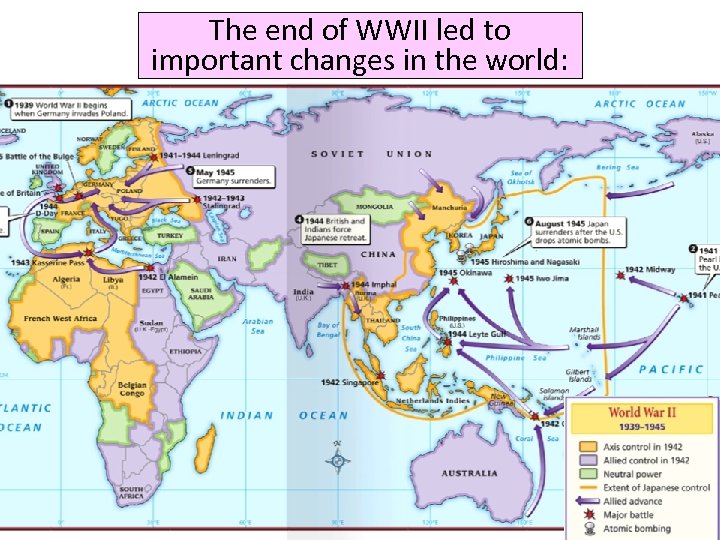 The end of WWII led to important changes in the world:
The end of WWII led to important changes in the world:
 U. N. Peacekeeping Interventions, 1945 -2009 The United Nations was created which replaced the League of Nations United Nations Headquarters is in Executive New York City Council General Assembly Member Nations
U. N. Peacekeeping Interventions, 1945 -2009 The United Nations was created which replaced the League of Nations United Nations Headquarters is in Executive New York City Council General Assembly Member Nations
 The UN created a Jewish nation called Israel which set off a series of wars with Arabs in the Middle East
The UN created a Jewish nation called Israel which set off a series of wars with Arabs in the Middle East
 The USA occupied & helped rebuild Japan
The USA occupied & helped rebuild Japan
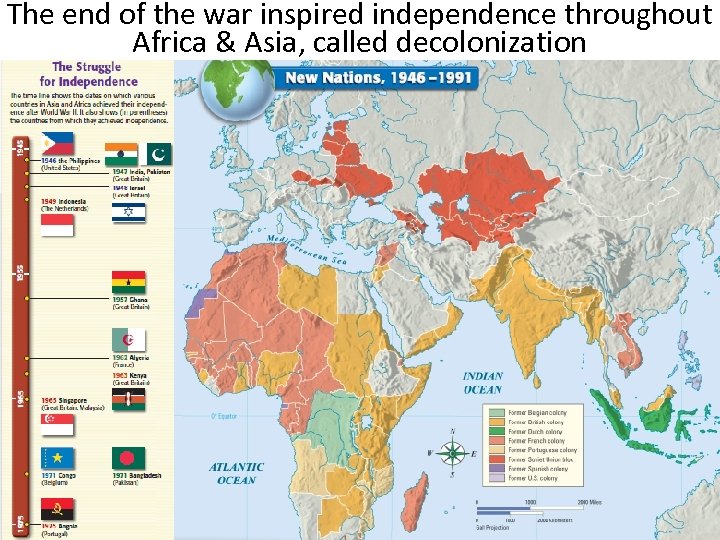 The end of the war inspired independence throughout Africa & Asia, called decolonization
The end of the war inspired independence throughout Africa & Asia, called decolonization
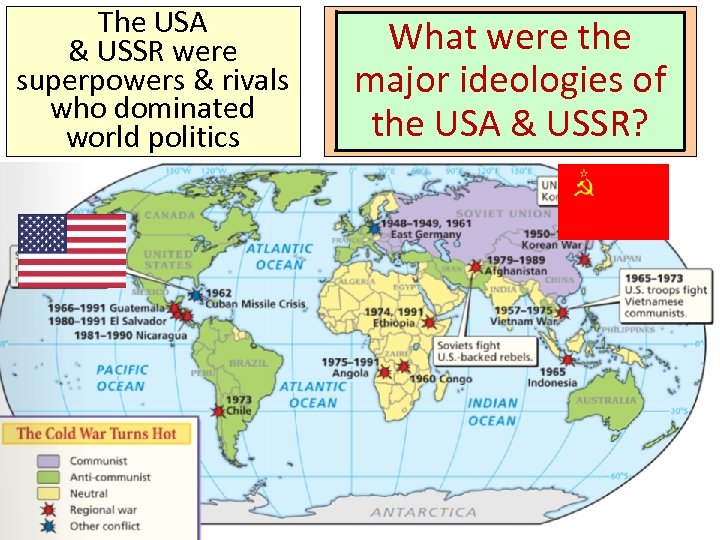 One of the most The USA importantwere & USSR changes superpowers & rivals after World War II was the beginning who dominated of the Cold War world politics From 1945 to 1991, What were the United States & Soviet Union entered of major ideologies an era of distrust & hostility the USA & USSR? known as the Cold War
One of the most The USA importantwere & USSR changes superpowers & rivals after World War II was the beginning who dominated of the Cold War world politics From 1945 to 1991, What were the United States & Soviet Union entered of major ideologies an era of distrust & hostility the USA & USSR? known as the Cold War
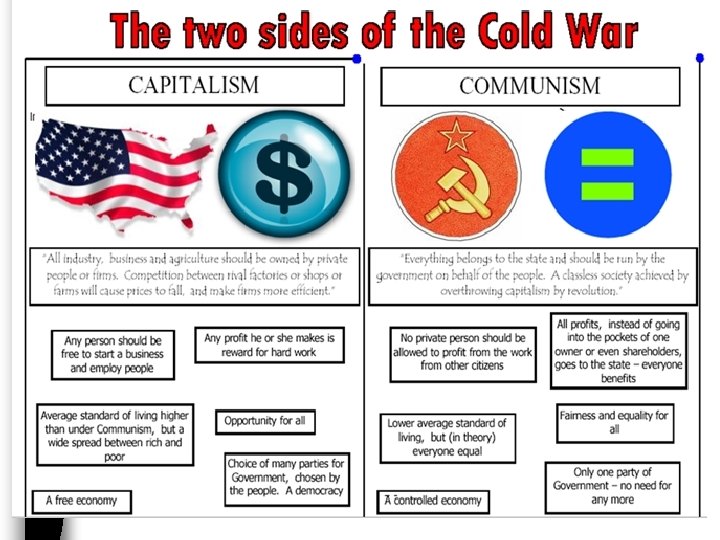
 Examining Cold War Ideologies ■ The Cold War was a conflict of ideology between the USA & Soviet Union –Step 1: Match each of the 8 cards with their appropriate definition –Step 2: Sort the cards by determining which 4 describe the USA & which 4 cards describe the USSR –Step 3: Match each of the 8 images with the correct definition
Examining Cold War Ideologies ■ The Cold War was a conflict of ideology between the USA & Soviet Union –Step 1: Match each of the 8 cards with their appropriate definition –Step 2: Sort the cards by determining which 4 describe the USA & which 4 cards describe the USSR –Step 3: Match each of the 8 images with the correct definition
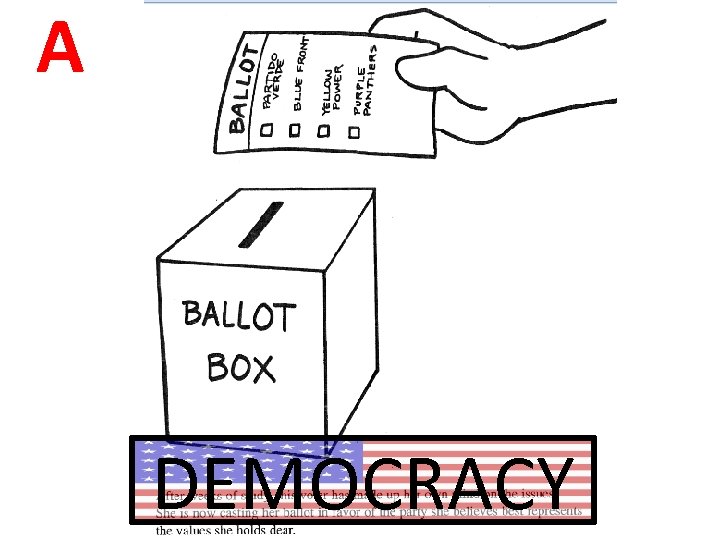 A DEMOCRACY
A DEMOCRACY
 B EQUALITY
B EQUALITY
 C CAPITALISM
C CAPITALISM
 D INDIVIDUALISM
D INDIVIDUALISM
 E COLLECTIVISM
E COLLECTIVISM
 F SOCIALISM
F SOCIALISM
 G TOTALITARIANISM
G TOTALITARIANISM
 H FREEDOM
H FREEDOM
 Table Activity: At your table, write 3 sentences comparing starting a business in the USA vs. starting a business in the Soviet Union.
Table Activity: At your table, write 3 sentences comparing starting a business in the USA vs. starting a business in the Soviet Union.
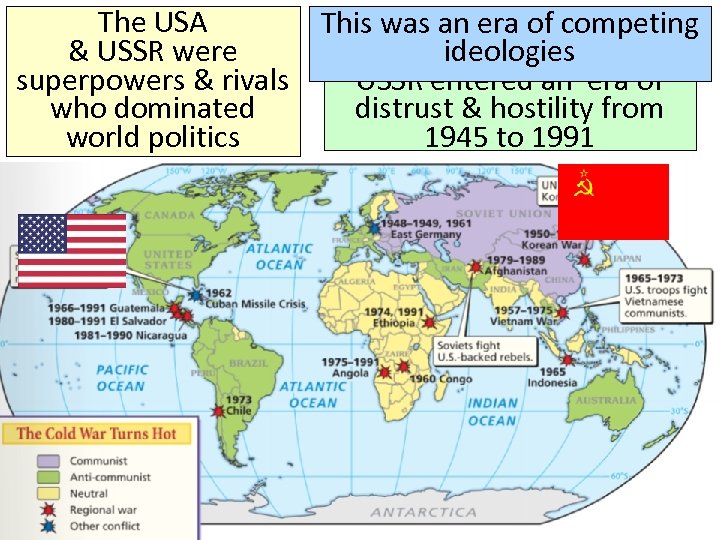 One of the most The USA This. During the Cold War, was an era of competing importantwere & USSR changes the USA & ideologies superpowers & rivals after World War II USSR entered an era of was the beginning who dominated distrust & hostility from of the Cold War world politics 1945 to 1991
One of the most The USA This. During the Cold War, was an era of competing importantwere & USSR changes the USA & ideologies superpowers & rivals after World War II USSR entered an era of was the beginning who dominated distrust & hostility from of the Cold War world politics 1945 to 1991
 What Caused the Cold War? Distrust began when the USA sent troops to fight the “Red Army” during the Russian Civil War
What Caused the Cold War? Distrust began when the USA sent troops to fight the “Red Army” during the Russian Civil War
 WWII increased tensions between the USA and USSR
WWII increased tensions between the USA and USSR
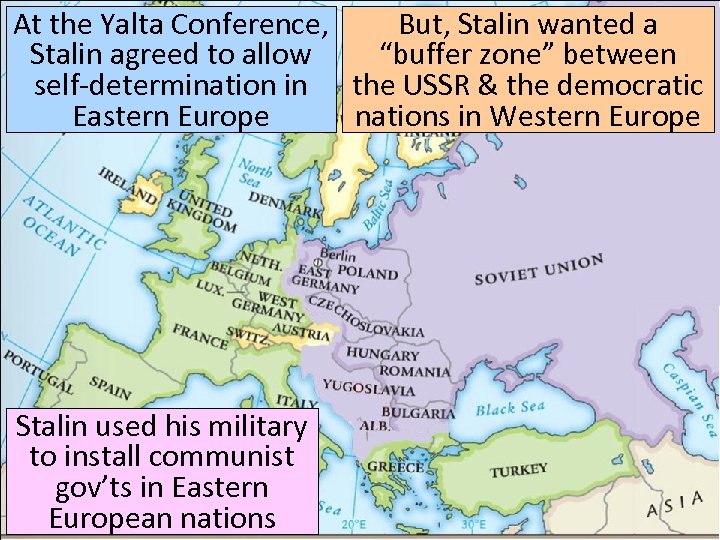 At the Yalta Conference, But, Stalin wanted a Stalin agreed to allow “buffer zone” between self-determination in the USSR & the democratic Eastern Europe nations in Western Europe Stalin used his military to install communist gov’ts in Eastern European nations
At the Yalta Conference, But, Stalin wanted a Stalin agreed to allow “buffer zone” between self-determination in the USSR & the democratic Eastern Europe nations in Western Europe Stalin used his military to install communist gov’ts in Eastern European nations
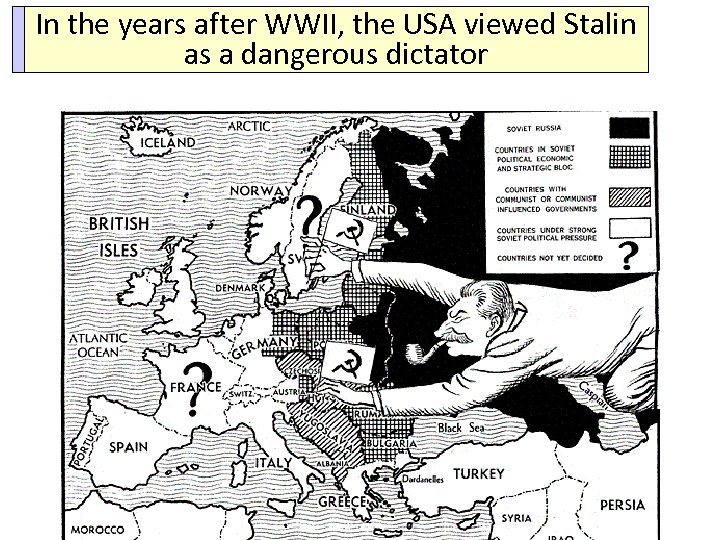 In the years after WWII, the USA viewed Stalin As a result, Eastern European nations turned communist & became Soviet satellites as a dangerous dictator
In the years after WWII, the USA viewed Stalin As a result, Eastern European nations turned communist & became Soviet satellites as a dangerous dictator
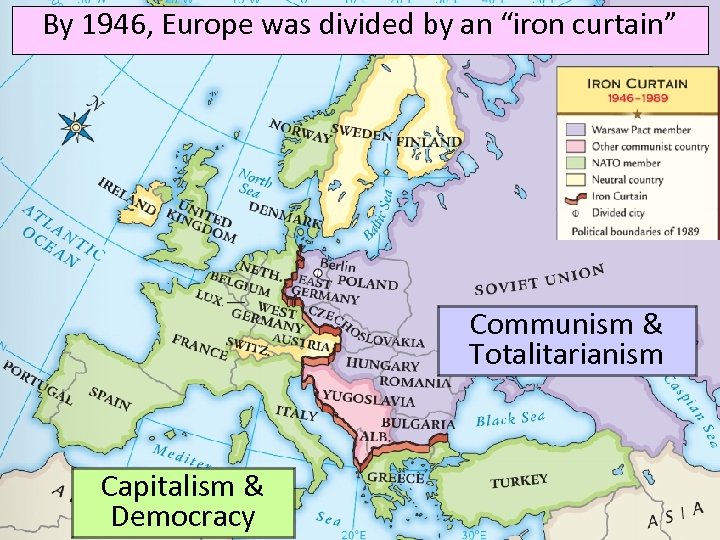 By 1946, Europe was divided by an “iron curtain” Communism & Totalitarianism Capitalism & Democracy
By 1946, Europe was divided by an “iron curtain” Communism & Totalitarianism Capitalism & Democracy
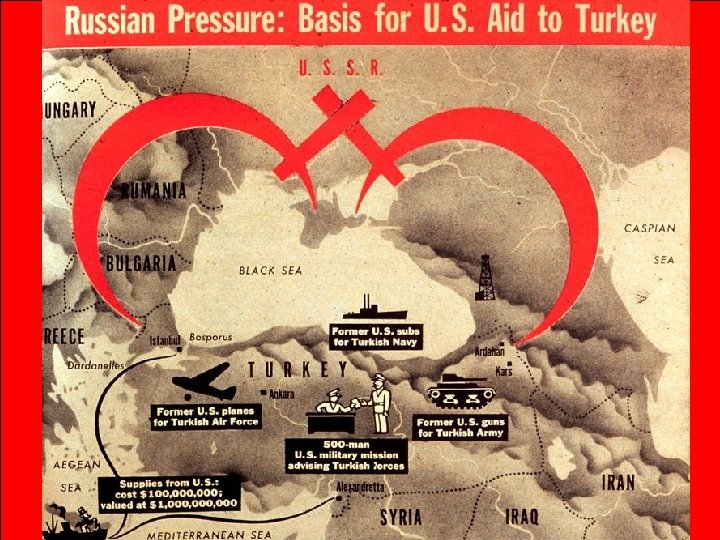
 The U. S. created a foreign policy called containment When the USSR began to pressure Greece & Turkey to turn communist, the U. S. created the Truman Doctrine T=
The U. S. created a foreign policy called containment When the USSR began to pressure Greece & Turkey to turn communist, the U. S. created the Truman Doctrine T=
 European nations had difficulty recovering after WWII which led to fears of communism in Europe The U. S. created the Marshall Plan M= By 1952, Western Europe recovered & Communism never took root
European nations had difficulty recovering after WWII which led to fears of communism in Europe The U. S. created the Marshall Plan M= By 1952, Western Europe recovered & Communism never took root
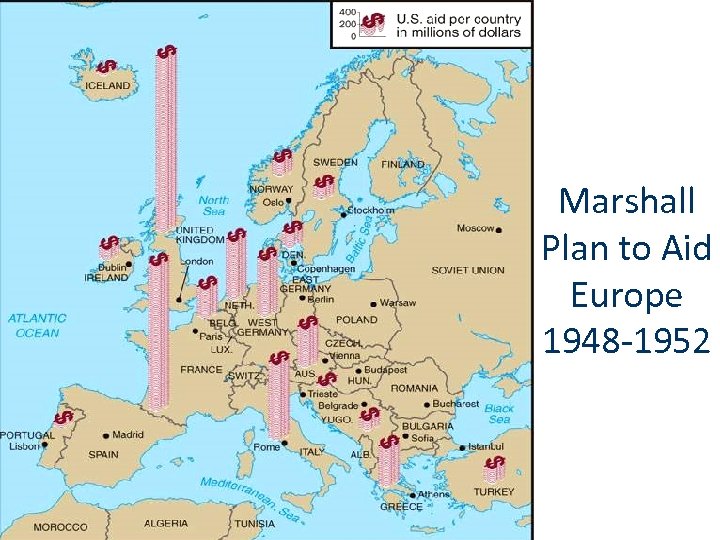 Marshall Plan to Aid Europe 1948 -1952
Marshall Plan to Aid Europe 1948 -1952
 In 1948, the USSR used military force to turn Czechoslovakia to communism In 1949, the USA formed the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO): a military alliance among democratic countries in Europe & North America
In 1948, the USSR used military force to turn Czechoslovakia to communism In 1949, the USA formed the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO): a military alliance among democratic countries in Europe & North America
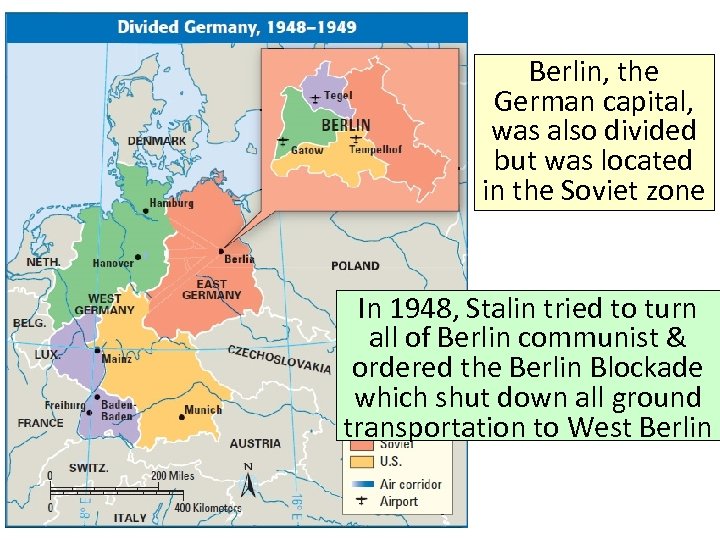 Berlin, the German capital, was also divided but was located in the Soviet zone In 1948, Stalin tried to turn all of Berlin communist & ordered the Berlin Blockade which shut down all ground transportation to West Berlin
Berlin, the German capital, was also divided but was located in the Soviet zone In 1948, Stalin tried to turn all of Berlin communist & ordered the Berlin Blockade which shut down all ground transportation to West Berlin
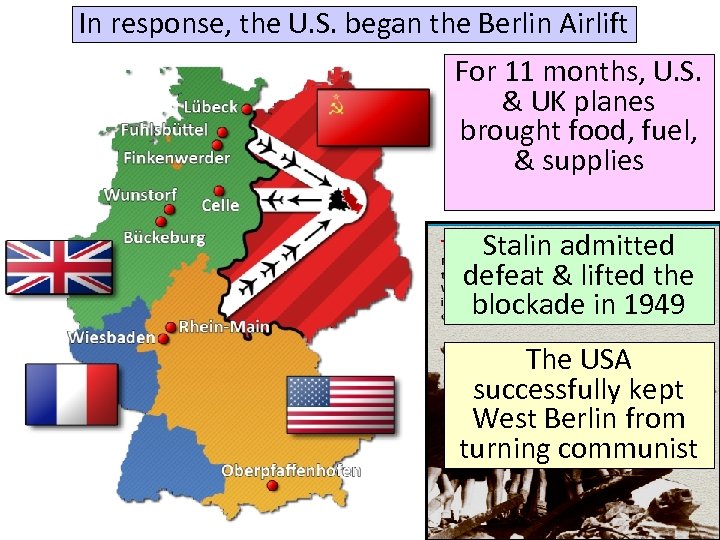 In response, the U. S. began the Berlin Airlift For 11 months, U. S. & UK planes brought food, fuel, & supplies Stalin admitted defeat & lifted the blockade in 1949 The USA successfully kept West Berlin from turning communist
In response, the U. S. began the Berlin Airlift For 11 months, U. S. & UK planes brought food, fuel, & supplies Stalin admitted defeat & lifted the blockade in 1949 The USA successfully kept West Berlin from turning communist
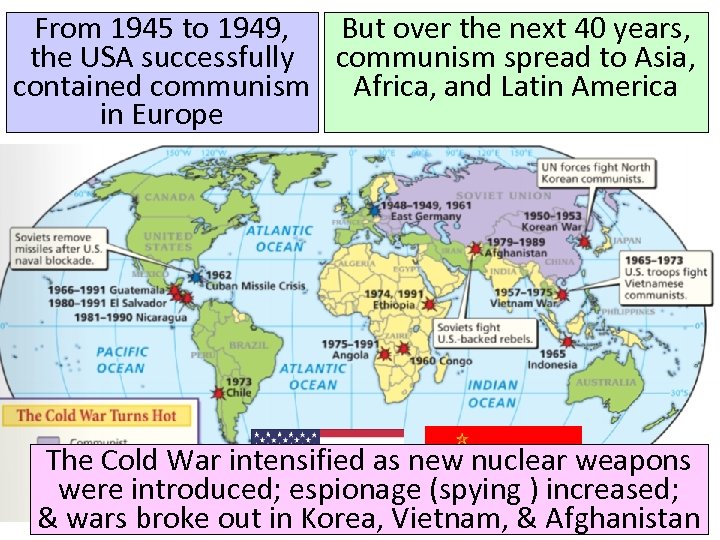 From 1945 to 1949, But over the next 40 years, the USA successfully communism spread to Asia, contained communism Africa, and Latin America in Europe The Cold War intensified as new nuclear weapons were introduced; espionage (spying ) increased; & wars broke out in Korea, Vietnam, & Afghanistan
From 1945 to 1949, But over the next 40 years, the USA successfully communism spread to Asia, contained communism Africa, and Latin America in Europe The Cold War intensified as new nuclear weapons were introduced; espionage (spying ) increased; & wars broke out in Korea, Vietnam, & Afghanistan


