74bade299de1623424d080b4c86a2efd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 ■ Essential Question: Question –How did the U. S. mobilize civilians at home to help win World War 2 & what impact did this have on American society? ■ Warm-Up Question: Question –What other major American war is most similar in its resemblance to the U. S. entrance into WW 2?
■ Essential Question: Question –How did the U. S. mobilize civilians at home to help win World War 2 & what impact did this have on American society? ■ Warm-Up Question: Question –What other major American war is most similar in its resemblance to the U. S. entrance into WW 2?
 Mobilizing an “Arsenal of Democracy”
Mobilizing an “Arsenal of Democracy”
 The Home Front ■ WW 2 impacted all aspects of American life: –FDR hoped the U. S. would be the great “arsenal of democracy” –The boost of wartime industry ended the Great Depression –The war altered the lives of women, African-Americans, Japanese-Americans, & Mexican-Americans
The Home Front ■ WW 2 impacted all aspects of American life: –FDR hoped the U. S. would be the great “arsenal of democracy” –The boost of wartime industry ended the Great Depression –The war altered the lives of women, African-Americans, Japanese-Americans, & Mexican-Americans
 The Office ofto create The Office of War The power War to censor Mobilization the press Information new gov’t agencies. Mobilization coordinated ■ To win wars into limit& Europe & & Asia civil liberties directed press, the draft, consumer prices, personal print, meet & film demands, theproperty radio, civilian seizethe labor force U. S. & propaganda gov’t grew to its largest size ever: The Office of Strategic Services gathered –The War Powers Act espionage enemy intelligence & conductedgave the president unprecedented power The bureaucracies were formed –New. U. S. gov’t spent $250 million per day from 1941 to 1945 to direct the economy, create This is 2 x as much war bonds, propaganda, sellas all previous & gov’t spending combined prevent enemy subversion
The Office ofto create The Office of War The power War to censor Mobilization the press Information new gov’t agencies. Mobilization coordinated ■ To win wars into limit& Europe & & Asia civil liberties directed press, the draft, consumer prices, personal print, meet & film demands, theproperty radio, civilian seizethe labor force U. S. & propaganda gov’t grew to its largest size ever: The Office of Strategic Services gathered –The War Powers Act espionage enemy intelligence & conductedgave the president unprecedented power The bureaucracies were formed –New. U. S. gov’t spent $250 million per day from 1941 to 1945 to direct the economy, create This is 2 x as much war bonds, propaganda, sellas all previous & gov’t spending combined prevent enemy subversion
 Mobilization: The Demand for War Mobilization Equipment & Soldiers
Mobilization: The Demand for War Mobilization Equipment & Soldiers
 Buy, Buy a Bond: It Will Lead to VICTORY! War bonds helped raise $187 billion to support the war effort
Buy, Buy a Bond: It Will Lead to VICTORY! War bonds helped raise $187 billion to support the war effort
 War Rations
War Rations
 Victory Gardens: Grow Your Own Gardens
Victory Gardens: Grow Your Own Gardens
 Propaganda: Fighting the Enemy on the Propaganda Battlefield & on the Home Front
Propaganda: Fighting the Enemy on the Propaganda Battlefield & on the Home Front
 Fear Propaganda
Fear Propaganda
 Hollywood Pitches In Jimmy Stewart goes off to war
Hollywood Pitches In Jimmy Stewart goes off to war
 The Wartime Economy U. S. made 2 x more goods than ■ Germany & decisive factor for Allied The most 5 x more than Japan victory was America’s ability to outproduce both Germany & Japan –Heavy industry was converted to war & was directed by the War Production Board (WPB) – 15 million U. S. soldiers fought but 60 million workers & farmers supplied them with supplies
The Wartime Economy U. S. made 2 x more goods than ■ Germany & decisive factor for Allied The most 5 x more than Japan victory was America’s ability to outproduce both Germany & Japan –Heavy industry was converted to war & was directed by the War Production Board (WPB) – 15 million U. S. soldiers fought but 60 million workers & farmers supplied them with supplies
 Ford made. Willow Run Factory hour Ford’s one B-24 bomber every
Ford made. Willow Run Factory hour Ford’s one B-24 bomber every
 Henry Kaiser’s West Coast Shipyards The Allies won the Battle of the Atlantic, in part, because the USA produced ships faster than German u-boats could sink them Kaiser standardized battleship building & reduced the time it took to make a battleship from 355 days to 14 days
Henry Kaiser’s West Coast Shipyards The Allies won the Battle of the Atlantic, in part, because the USA produced ships faster than German u-boats could sink them Kaiser standardized battleship building & reduced the time it took to make a battleship from 355 days to 14 days
 ■ Essential Question: Question –How did the U. S. mobilize civilians at home to help win World War 2 & what impact did this have on American society? ■ Reading Quiz Ch 25 B (904 -922)
■ Essential Question: Question –How did the U. S. mobilize civilians at home to help win World War 2 & what impact did this have on American society? ■ Reading Quiz Ch 25 B (904 -922)
 WW 2 Changed American Society FDR Video #2
WW 2 Changed American Society FDR Video #2
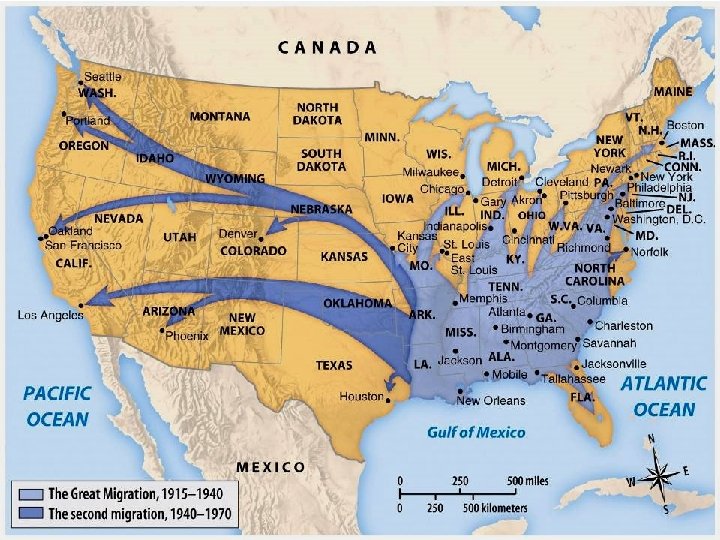
 Regional Changes ■ The war effort transformed the Western & Southern U. S. : –California became the major 9 million defense workers moved to new center for industry South & West factories & shipyards in to support the war effort in the Pacific – 60 of the 100 new military based were built in the South –Southern textile factories & industrial jobs helped end sharecropping & tenant farming
Regional Changes ■ The war effort transformed the Western & Southern U. S. : –California became the major 9 million defense workers moved to new center for industry South & West factories & shipyards in to support the war effort in the Pacific – 60 of the 100 new military based were built in the South –Southern textile factories & industrial jobs helped end sharecropping & tenant farming
 Women ■ The war presented new economic opportunities for women: –Dramatic rise in employment (14 million to the life I have had. “To hell with 19 million by 1945) This war is too [serious], and it –Most too [important] to win it. ”were new female workers is married, many middle-aged –Entered “exclusively male” fields –Temporarily redefined “woman’s sphere” from “just at home”
Women ■ The war presented new economic opportunities for women: –Dramatic rise in employment (14 million to the life I have had. “To hell with 19 million by 1945) This war is too [serious], and it –Most too [important] to win it. ”were new female workers is married, many middle-aged –Entered “exclusively male” fields –Temporarily redefined “woman’s sphere” from “just at home”
 “Rosie, the Riveter”
“Rosie, the Riveter”
 S. . t. . r. . e. . t. . c. . h That Food!
S. . t. . r. . e. . t. . c. . h That Food!
 Women Accepted for Volunteer Join the Women’s Army Air Emergency Service (WAVES) Corps Pilots Army Corps (WACs)
Women Accepted for Volunteer Join the Women’s Army Air Emergency Service (WAVES) Corps Pilots Army Corps (WACs)
 Families …and high of war & divorce rates ■ The uncertainties economic affluence of the 1940 s led to a dramatic rise in marriage ■ The influx of women into the workforce led to a new demand for daycare centers & to an increase in child delinquency ■ Public health improved as more families had access to doctors, dentists, & prescription drugs
Families …and high of war & divorce rates ■ The uncertainties economic affluence of the 1940 s led to a dramatic rise in marriage ■ The influx of women into the workforce led to a new demand for daycare centers & to an increase in child delinquency ■ Public health improved as more families had access to doctors, dentists, & prescription drugs
 African-Americans Banned discrimination in ■ 1 million blacks served in U. S. defense industries & gov’t military but few saw combat ■ Discrimination in the workforce led A. Philip Randolph to pressure FDR to create a Fair Employment Practices Committee ■ Continued black migration into the North & West made race relations a national issue
African-Americans Banned discrimination in ■ 1 million blacks served in U. S. defense industries & gov’t military but few saw combat ■ Discrimination in the workforce led A. Philip Randolph to pressure FDR to create a Fair Employment Practices Committee ■ Continued black migration into the North & West made race relations a national issue
 Segregated units…again Tuskegee Airmen
Segregated units…again Tuskegee Airmen
 Double V: Victory at Home & Abroad A. Philip Randolph threatened a “March on Washington” to protest war time discrimination Other groups, like the Congress of Racial Equality (CORE), staged sit-ins in restaurants in major cities to protest discrimination
Double V: Victory at Home & Abroad A. Philip Randolph threatened a “March on Washington” to protest war time discrimination Other groups, like the Congress of Racial Equality (CORE), staged sit-ins in restaurants in major cities to protest discrimination
 Mexican-Americans ■ Mexican-Americans: –Served in quasi-segregated military units, often in the most hazardous branches –Mexican-American workers found jobs in SW agriculture & west coast industry –Faced discrimination, especially during the Zoot Suit Riots
Mexican-Americans ■ Mexican-Americans: –Served in quasi-segregated military units, often in the most hazardous branches –Mexican-American workers found jobs in SW agriculture & west coast industry –Faced discrimination, especially during the Zoot Suit Riots
 “Zoot Suit” Riot in Los Angeles
“Zoot Suit” Riot in Los Angeles
 Japanese-Americans ■ Due to Pearl Harbor, many in the U. S. feared Japanese-Americans were helping prepare for a Japanese who were not American Japanese invasion in the West citizens living in the U. S. ■ Civil liberties were restricted: –Issei had their assets frozen –Used racial stereotypes (“Japs”) –In 1942, FDR ordered 112, 000 Japanese-Americans moved to internment camps
Japanese-Americans ■ Due to Pearl Harbor, many in the U. S. feared Japanese-Americans were helping prepare for a Japanese who were not American Japanese invasion in the West citizens living in the U. S. ■ Civil liberties were restricted: –Issei had their assets frozen –Used racial stereotypes (“Japs”) –In 1942, FDR ordered 112, 000 Japanese-Americans moved to internment camps
 Families were given one week nd The all Japanese-American 442 to Division close their businesses & homes fought in Europe & received over 1, 000 citations for bravery Japanese. American Internment Camps
Families were given one week nd The all Japanese-American 442 to Division close their businesses & homes fought in Europe & received over 1, 000 citations for bravery Japanese. American Internment Camps
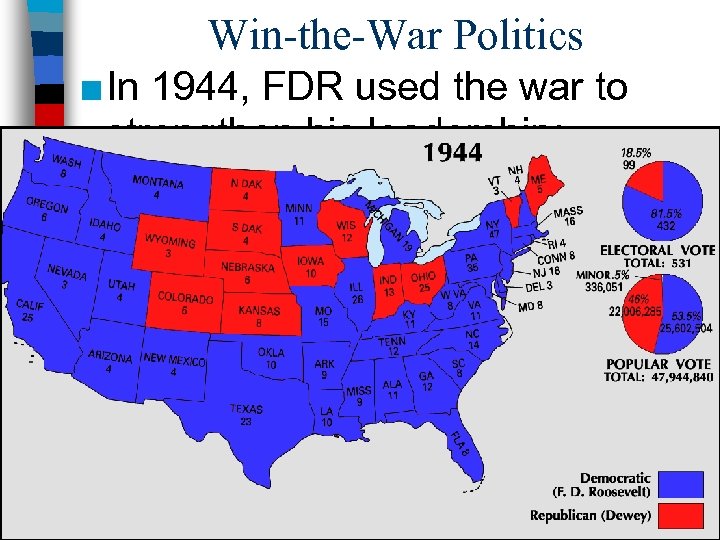 Win-the-War Politics ■ In 1944, FDR used the war to strengthen his leadership: –“Mr. New Deal” had shifted to “Mr. Win the War” –Opponent Thomas Dewey made communism & FDR’s health the focus of the election –FDR switched VPs from liberal Henry Wallace to moderate Harry Truman to gain appeal
Win-the-War Politics ■ In 1944, FDR used the war to strengthen his leadership: –“Mr. New Deal” had shifted to “Mr. Win the War” –Opponent Thomas Dewey made communism & FDR’s health the focus of the election –FDR switched VPs from liberal Henry Wallace to moderate Harry Truman to gain appeal


