56cee887a28caf23ba6153cc2b640c81.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 ■ Essential Question: Question –How did Jefferson’s presidency change American government, territory, & foreign policy? ■ Warm-Up Question: –How will the fact that Jefferson was a Democratic-Republican influence his policies as America’s third president?
■ Essential Question: Question –How did Jefferson’s presidency change American government, territory, & foreign policy? ■ Warm-Up Question: –How will the fact that Jefferson was a Democratic-Republican influence his policies as America’s third president?
 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. ■ George Washington John Adams Thomas Jefferson James Madison James Monroe John Q. Adams Andrew Jackson Jefferson’s defeat of Adams is often called the “Revolution of 1800”: –For the first time, a new political party took the presidency –Jefferson’s presidency marked the start of nearly 30 years of political dominance by the Democratic-Republicans
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. ■ George Washington John Adams Thomas Jefferson James Madison James Monroe John Q. Adams Andrew Jackson Jefferson’s defeat of Adams is often called the “Revolution of 1800”: –For the first time, a new political party took the presidency –Jefferson’s presidency marked the start of nearly 30 years of political dominance by the Democratic-Republicans
 Jefferson as President ■ As a Democratic-Republican, Jefferson tried to reverse Federalist policies & reduce the size & cost of the national gov’t: –He reduced the size of the army –Cut back Hamilton’s financial plan by ending all excise taxes & allowing the charter of the Bank of the U. S. to expire
Jefferson as President ■ As a Democratic-Republican, Jefferson tried to reverse Federalist policies & reduce the size & cost of the national gov’t: –He reduced the size of the army –Cut back Hamilton’s financial plan by ending all excise taxes & allowing the charter of the Bank of the U. S. to expire
 Jefferson believed that America should be an “agrarian republic” that protects liberty
Jefferson believed that America should be an “agrarian republic” that protects liberty
 “Midnight Judges” ■ Before leaving office, President Adams appointed numerous Federalist judges to federal courts –John Marshall became chief justice to the Supreme Court –Over the next 30 years, John Marshall strengthened the power of the national gov’t & the Supreme Court
“Midnight Judges” ■ Before leaving office, President Adams appointed numerous Federalist judges to federal courts –John Marshall became chief justice to the Supreme Court –Over the next 30 years, John Marshall strengthened the power of the national gov’t & the Supreme Court
 The Legacy of John Marshall In each of these cases, John Marshall helped strengthen the power of the national gov’t over the states or protected citizens from the power of their state gov’ts ■ ■ ■ Marbury v. Madison (1803) Mc. Culloch v. Maryland (1819) Dartmouth College v. Woodward (1819) Cohens v. Virginia (1821) Gibbons v. Ogden (1824) Cherokee Nation v. Georgia (1831)
The Legacy of John Marshall In each of these cases, John Marshall helped strengthen the power of the national gov’t over the states or protected citizens from the power of their state gov’ts ■ ■ ■ Marbury v. Madison (1803) Mc. Culloch v. Maryland (1819) Dartmouth College v. Woodward (1819) Cohens v. Virginia (1821) Gibbons v. Ogden (1824) Cherokee Nation v. Georgia (1831)
 Marbury v. Madison ■ Jefferson invalidated as many of Adams’ midnight judges as possible –One judge, William Marbury, sued claiming that the president could not overturn an act of Congress –The case Marbury v. Madison (1803) established the principle of judicial review giving the Supreme Court the power to declare acts of Congress unconstitutional
Marbury v. Madison ■ Jefferson invalidated as many of Adams’ midnight judges as possible –One judge, William Marbury, sued claiming that the president could not overturn an act of Congress –The case Marbury v. Madison (1803) established the principle of judicial review giving the Supreme Court the power to declare acts of Congress unconstitutional
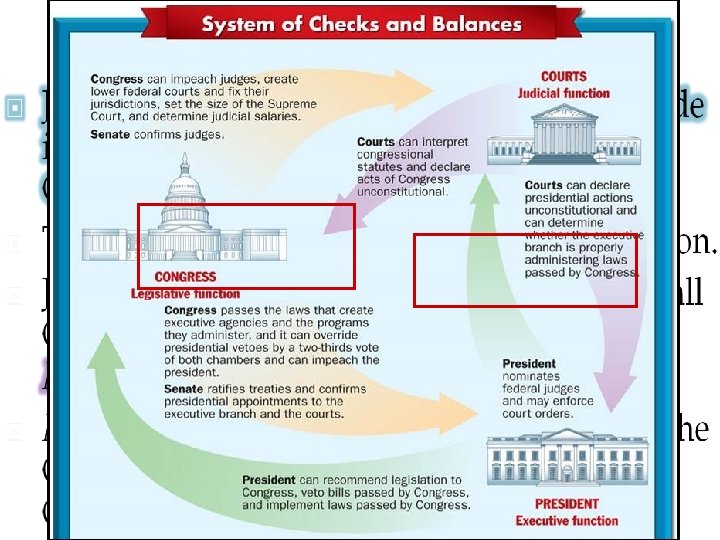 Judicial Review
Judicial Review
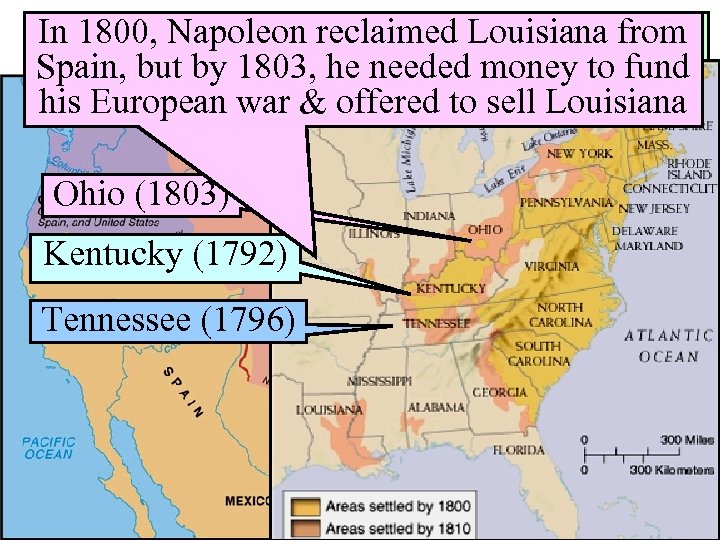 In 1800, Napoleon reclaimedin 1800 from From. The United States Louisiana by 1800 to 1810, the population grew Spain, but people, thousands flooded intofund 2 million by 1803, he needed money to the his European war & offered to sell Louisiana west, & 3 new states were added to the USA Ohio (1803) Kentucky (1792) Tennessee (1796)
In 1800, Napoleon reclaimedin 1800 from From. The United States Louisiana by 1800 to 1810, the population grew Spain, but people, thousands flooded intofund 2 million by 1803, he needed money to the his European war & offered to sell Louisiana west, & 3 new states were added to the USA Ohio (1803) Kentucky (1792) Tennessee (1796)
 As a “strict constructionist” Jefferson did The Louisiana Purchase (1803) not know if he had the Constitutional power to buy Louisiana but he did it anyway In 1803, Jefferson Lewis & authorized the Clark were sent by Jefferson to map & Louisiana Purchaseexplore this new territory; from. Their findings revealed an abundance France of natural resources for America for $15 million
As a “strict constructionist” Jefferson did The Louisiana Purchase (1803) not know if he had the Constitutional power to buy Louisiana but he did it anyway In 1803, Jefferson Lewis & authorized the Clark were sent by Jefferson to map & Louisiana Purchaseexplore this new territory; from. Their findings revealed an abundance France of natural resources for America for $15 million
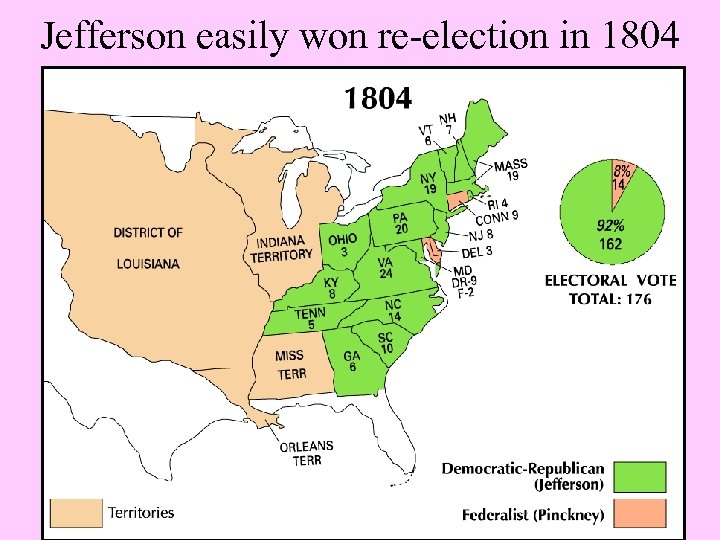 Jefferson easily won re-election in 1804
Jefferson easily won re-election in 1804
 Jefferson’s Legacy ■ Jefferson came into office trying to reduce the size & power of the national government, but: –By buying Louisiana, he expanded government power beyond that of the Constitution –He encouraged Congress to create an “embargo” (no trade) to punish England & France for violating U. S. free trade
Jefferson’s Legacy ■ Jefferson came into office trying to reduce the size & power of the national government, but: –By buying Louisiana, he expanded government power beyond that of the Constitution –He encouraged Congress to create an “embargo” (no trade) to punish England & France for violating U. S. free trade
 Americans Napoleon’s smuggled & Jefferson had to increase the size of gov’t to enforce the embargo Empire Jefferson’s embargo was a “pain in the rear end” because it hurt Americans more than it hurt the English or French
Americans Napoleon’s smuggled & Jefferson had to increase the size of gov’t to enforce the embargo Empire Jefferson’s embargo was a “pain in the rear end” because it hurt Americans more than it hurt the English or French
 Closure Activity Marbury v Madison ■ Louisiana Purchase ■
Closure Activity Marbury v Madison ■ Louisiana Purchase ■
 ■ Essential Question: Question –How did the War of 1812 encourage American unity & nationalism? ■ Warm-Up Question: –How did Washington, Adams, & Jefferson each respond to violations of American free trade by the French & British?
■ Essential Question: Question –How did the War of 1812 encourage American unity & nationalism? ■ Warm-Up Question: –How did Washington, Adams, & Jefferson each respond to violations of American free trade by the French & British?
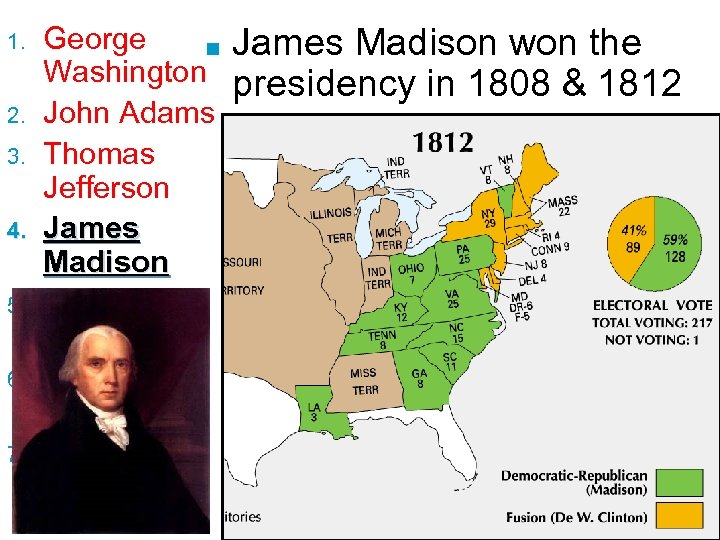 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. George ■ Washington John Adams Thomas Jefferson James Madison James Monroe John Q. Adams Andrew Jackson James Madison won the presidency in 1808 & 1812 –Madison was the architect of the Constitution, was elected to Congress, & served as Jefferson’s VP –Madison continued the dominance of the Democratic-Republican Party & tried to continue Jefferson’s policies of limited national gov’t
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. George ■ Washington John Adams Thomas Jefferson James Madison James Monroe John Q. Adams Andrew Jackson James Madison won the presidency in 1808 & 1812 –Madison was the architect of the Constitution, was elected to Congress, & served as Jefferson’s VP –Madison continued the dominance of the Democratic-Republican Party & tried to continue Jefferson’s policies of limited national gov’t
 The War of 1812 ■ Unfortunately, the war between “Free Trade & Sailors' Rights” England & France continued to was a popular battle cry cause problems for Americans: –England & France continued to violate American free trade –The British navy continued to “impress” American merchants –Many Congressmen, called “War Hawks” demanded war with Hawks Britain to defend U. S. honor
The War of 1812 ■ Unfortunately, the war between “Free Trade & Sailors' Rights” England & France continued to was a popular battle cry cause problems for Americans: –England & France continued to violate American free trade –The British navy continued to “impress” American merchants –Many Congressmen, called “War Hawks” demanded war with Hawks Britain to defend U. S. honor
 Quick Class Discussion Problem: Since 1793, Britain & France have been at war, violated free trade, & impressed merchants ■ Attempts to resolve these issues did Solution? not solve 3 possible solutions President these problems: Brainstorm –Washington’s to solve this problem Madison could use. Proclamation of Neutralitythe 1 best alternative. & select (1793) Be sure to explain your decision –Adams’ XYZ Affair (1798) –Jefferson’s failed embargo (1807) ■
Quick Class Discussion Problem: Since 1793, Britain & France have been at war, violated free trade, & impressed merchants ■ Attempts to resolve these issues did Solution? not solve 3 possible solutions President these problems: Brainstorm –Washington’s to solve this problem Madison could use. Proclamation of Neutralitythe 1 best alternative. & select (1793) Be sure to explain your decision –Adams’ XYZ Affair (1798) –Jefferson’s failed embargo (1807) ■
 Patriotism surged as War Hawks claimed the War of 1812 the “Second American Revolution” Madison eventually gave in & asked Congress for a declaration of war in June 1812
Patriotism surged as War Hawks claimed the War of 1812 the “Second American Revolution” Madison eventually gave in & asked Congress for a declaration of war in June 1812
 The War of 1812 (1812— 1814) The British ■ The U. S. was attacked & burned not ready to Washington, DC… fight when the war laid siege to began …and – Had a weak Baltimore where Francis Scott Key navy & poorly wrote the “Star trained army Spangledwar went Banner” – The badly at first
The War of 1812 (1812— 1814) The British ■ The U. S. was attacked & burned not ready to Washington, DC… fight when the war laid siege to began …and – Had a weak Baltimore where Francis Scott Key navy & poorly wrote the “Star trained army Spangledwar went Banner” – The badly at first
 The War of 1812 (1812— 1814) The British ■ The U. S. was attacked & burned not ready to Washington, DC… fight when the war laid siege to began …and – Had a weak Baltimore where Francis Scott Key navy & poorly wrote the “Star trained army Spangledwar went Banner” – The badly at first
The War of 1812 (1812— 1814) The British ■ The U. S. was attacked & burned not ready to Washington, DC… fight when the war laid siege to began …and – Had a weak Baltimore where Francis Scott Key navy & poorly wrote the “Star trained army Spangledwar went Banner” – The badly at first
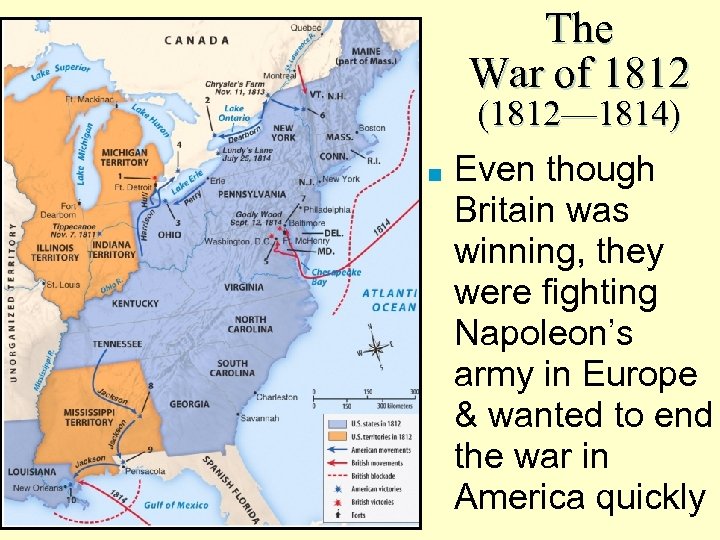 The War of 1812 (1812— 1814) ■ Even though Britain was winning, they were fighting Napoleon’s army in Europe & wanted to end the war in America quickly
The War of 1812 (1812— 1814) ■ Even though Britain was winning, they were fighting Napoleon’s army in Europe & wanted to end the war in America quickly
 The War of 1812 (1812— 1814) The Americans ■ In 1814, Britain were signed & U. S. led by Andrew Jackson the Treaty of who became a Ghent ending national hero the war The victory at ■ Before news New Orleans led arrived, the many Americans won to feel as though the Battle of they won the war New Orleans
The War of 1812 (1812— 1814) The Americans ■ In 1814, Britain were signed & U. S. led by Andrew Jackson the Treaty of who became a Ghent ending national hero the war The victory at ■ Before news New Orleans led arrived, the many Americans won to feel as though the Battle of they won the war New Orleans
 Battle of New Orleans—Johnny Horton (1959) In 1814 we took a little trip Along with Colonel Jackson down the mighty Mississip. We took a little bacon and we took a little beans And we caught the bloody British in the town of New Orleans. [Chorus: ] We fired our guns and the British kept a'comin. There wasn't nigh as many as there was a while ago. We fired once more and they began to runnin' on Down the Mississippi to the Gulf of Mexico. We looked down the river and we see'd the British come. And there must have been a hundred of'em beatin' on the drum. They stepped so high and they made the bugles ring. We stood by our cotton bales and didn't say a thing. [Chorus] Old Hickory said we could take 'em by surprise If we didn't fire our muskets 'til we looked 'em in the eye We held our fire 'til we see'd their faces well. Then we opened up with squirrel guns and really gave 'em. . . well
Battle of New Orleans—Johnny Horton (1959) In 1814 we took a little trip Along with Colonel Jackson down the mighty Mississip. We took a little bacon and we took a little beans And we caught the bloody British in the town of New Orleans. [Chorus: ] We fired our guns and the British kept a'comin. There wasn't nigh as many as there was a while ago. We fired once more and they began to runnin' on Down the Mississippi to the Gulf of Mexico. We looked down the river and we see'd the British come. And there must have been a hundred of'em beatin' on the drum. They stepped so high and they made the bugles ring. We stood by our cotton bales and didn't say a thing. [Chorus] Old Hickory said we could take 'em by surprise If we didn't fire our muskets 'til we looked 'em in the eye We held our fire 'til we see'd their faces well. Then we opened up with squirrel guns and really gave 'em. . . well
 Treaty of Ghent ended the war, but it did not address trade rights or other causes of the war ■ Effects of the War of 1812: –Americans were united in a sense of nationalism, believing that they had beaten the British –America entered an “Era of Good Feelings” with a popular president & booming national economy ■
Treaty of Ghent ended the war, but it did not address trade rights or other causes of the war ■ Effects of the War of 1812: –Americans were united in a sense of nationalism, believing that they had beaten the British –America entered an “Era of Good Feelings” with a popular president & booming national economy ■
 Closure Activity ■ War of 1812?
Closure Activity ■ War of 1812?
 ■ Essential Question: Question –How did American nationalism increase under James Monroe? ■ Warm-Up Question: –What caused the War of 1812? –What changed as a result of the War of 1812 & Treaty of Ghent?
■ Essential Question: Question –How did American nationalism increase under James Monroe? ■ Warm-Up Question: –What caused the War of 1812? –What changed as a result of the War of 1812 & Treaty of Ghent?
 James Monroe
James Monroe
 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. George ■ Washington John Adams Thomas Jefferson James Madison James ■ Monroe John Q. Adams Andrew Jackson James Monroe was elected president in 1816 & 1820 with a clear set of goals: –To promote national unity –To promote America’s power in the world Monroe was a Democratic. Republican, but by 1816 the Federalists were so weak that the Republicans could do almost anything
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. George ■ Washington John Adams Thomas Jefferson James Madison James ■ Monroe John Q. Adams Andrew Jackson James Monroe was elected president in 1816 & 1820 with a clear set of goals: –To promote national unity –To promote America’s power in the world Monroe was a Democratic. Republican, but by 1816 the Federalists were so weak that the Republicans could do almost anything
 The Era of Good Feelings ■ After the War of 1812, America experienced an “Era of Good Feelings” from 1815 to 1825: –Monroe & the Republicans in Congress used this time to promote American nationalism –Nationalism—the interests of Nationalism the USA should be placed ahead of regional interests
The Era of Good Feelings ■ After the War of 1812, America experienced an “Era of Good Feelings” from 1815 to 1825: –Monroe & the Republicans in Congress used this time to promote American nationalism –Nationalism—the interests of Nationalism the USA should be placed ahead of regional interests
 American Nationalism ■ Monroe & the Republicans in Congress promoted nationalism & American unity in 3 ways: –Gov’t: Increasing the power of the national gov’t over the states
American Nationalism ■ Monroe & the Republicans in Congress promoted nationalism & American unity in 3 ways: –Gov’t: Increasing the power of the national gov’t over the states
 American Nationalism ■ John Marshall (1801 -1835) used the Supreme Court to strengthen the power of the national gov’t:
American Nationalism ■ John Marshall (1801 -1835) used the Supreme Court to strengthen the power of the national gov’t:
 American Nationalism ■ Monroe & the Republicans in Congress promoted nationalism & American unity in 3 ways: –Gov’t: Increasing the power of the national gov’t over the states –Economy: Encourage industry & build better transportation to link the South, North, & West
American Nationalism ■ Monroe & the Republicans in Congress promoted nationalism & American unity in 3 ways: –Gov’t: Increasing the power of the national gov’t over the states –Economy: Encourage industry & build better transportation to link the South, North, & West
 The American System ■ In 1816, Congressman Henry Clay proposed the American System to unify the economies of the North, South, & West –Created a 2 nd Bank of the U. S. –Created a tariff to promote U. S. industry & limit the importation of British manufactured goods –A nat’l system of roads & canals
The American System ■ In 1816, Congressman Henry Clay proposed the American System to unify the economies of the North, South, & West –Created a 2 nd Bank of the U. S. –Created a tariff to promote U. S. industry & limit the importation of British manufactured goods –A nat’l system of roads & canals
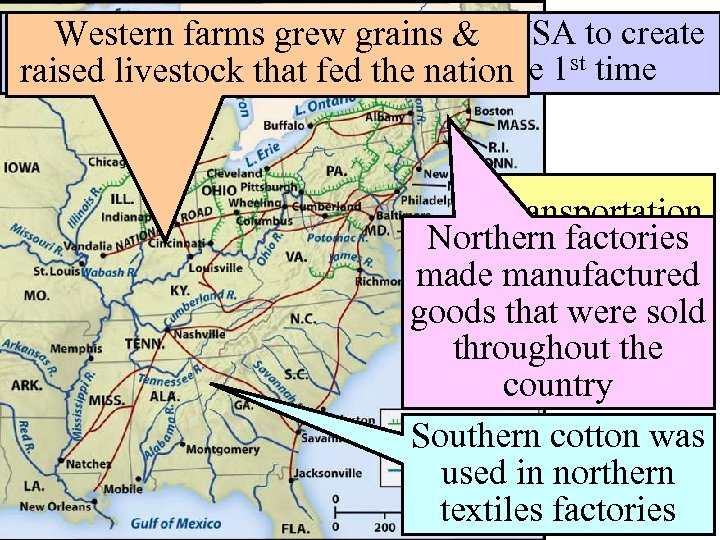 The American System allowed & USA to create Western farms grew grains the a national market fed the nation raised livestock that economy for the 1 st time Transportation Northern factories by 1840: made. Rivers, Roads, manufactured goods that were & Canals, sold throughout the Railroads country Southern cotton was used in northern textiles factories
The American System allowed & USA to create Western farms grew grains the a national market fed the nation raised livestock that economy for the 1 st time Transportation Northern factories by 1840: made. Rivers, Roads, manufactured goods that were & Canals, sold throughout the Railroads country Southern cotton was used in northern textiles factories
 Kentucky Congressman Henry Clay ■ What aspects of this portrait reveal parts of Henry Clay’s “American System”?
Kentucky Congressman Henry Clay ■ What aspects of this portrait reveal parts of Henry Clay’s “American System”?
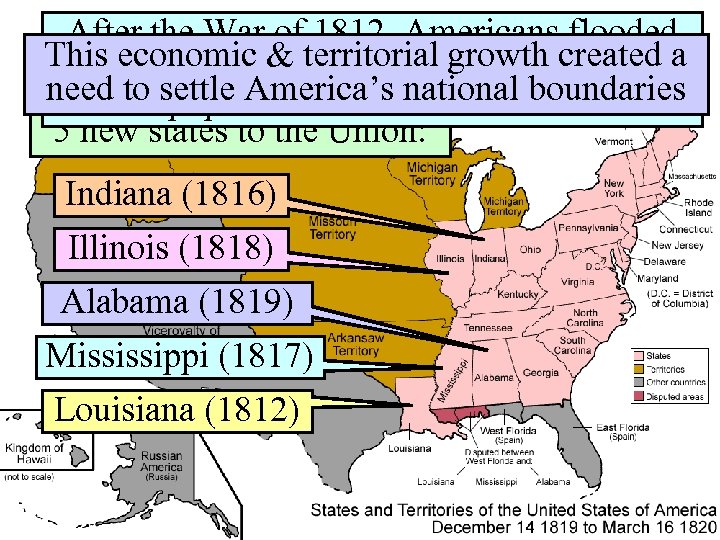 Settlement ofof 1812, Americans flooded After the War the Trans-Mississippi Thisinto the West; territorial over 1/3 created a economic & By 1840 growth of the need to settle America’s national boundaries Congress quickly admitted the West population lived in 5 new states to the Union: Indiana (1816) Illinois (1818) Alabama (1819) Mississippi (1817) Louisiana (1812)
Settlement ofof 1812, Americans flooded After the War the Trans-Mississippi Thisinto the West; territorial over 1/3 created a economic & By 1840 growth of the need to settle America’s national boundaries Congress quickly admitted the West population lived in 5 new states to the Union: Indiana (1816) Illinois (1818) Alabama (1819) Mississippi (1817) Louisiana (1812)
 American Nationalism ■ Monroe & the Republicans in Congress promoted nationalism & American unity in 3 ways: –Gov’t: Increasing the power of the national gov’t over the states –Economy: Encourage industry & build better transportation to link the South, North, & West –Foreign Policy: Expanding U. S. borders & increasing America’s role in world affairs
American Nationalism ■ Monroe & the Republicans in Congress promoted nationalism & American unity in 3 ways: –Gov’t: Increasing the power of the national gov’t over the states –Economy: Encourage industry & build better transportation to link the South, North, & West –Foreign Policy: Expanding U. S. borders & increasing America’s role in world affairs
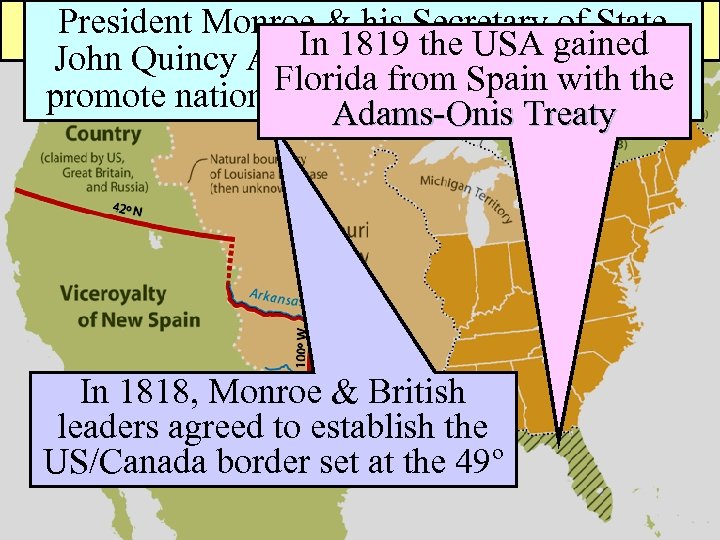 President Monroe &Nationalism of State his American 1819 Secretary gained In usedthe USApolicy to John Quincy Adams foreign Florida from Spain with the promote nationalism & territorial. Treaty expansion Adams-Onis In 1818, Monroe & British leaders agreed to establish the US/Canada border set at the 49º
President Monroe &Nationalism of State his American 1819 Secretary gained In usedthe USApolicy to John Quincy Adams foreign Florida from Spain with the promote nationalism & territorial. Treaty expansion Adams-Onis In 1818, Monroe & British leaders agreed to establish the US/Canada border set at the 49º
 Nationalist Foreign Policy ■ When Latin American nations gained independence, the U. S. supported the new republics: –Monroe did not want Europeans re-colonizing in Latin America –Monroe Doctrine (1823) warned European nations that the USA would protect the Western Hemisphere & that the U. S. would not interfere in Europe
Nationalist Foreign Policy ■ When Latin American nations gained independence, the U. S. supported the new republics: –Monroe did not want Europeans re-colonizing in Latin America –Monroe Doctrine (1823) warned European nations that the USA would protect the Western Hemisphere & that the U. S. would not interfere in Europe

 Sectionalism ■ The Era of Good Feelings was a time of nationalism, but there were problems between North & South –Sectionalism—when regional Sectionalism interests are placed above national interests –Northerners & Southerners disagreed over slavery, national taxes, & the role of national gov’t –These disagreements dominated politics from 1820 to 1860
Sectionalism ■ The Era of Good Feelings was a time of nationalism, but there were problems between North & South –Sectionalism—when regional Sectionalism interests are placed above national interests –Northerners & Southerners disagreed over slavery, national taxes, & the role of national gov’t –These disagreements dominated politics from 1820 to 1860
 Missouri Compromise Because of the 3/5 Compromise, When Missouri applied to become athe South had sectionalism emerged U. S. state, more members in the House of Representatives –Missouri wanted to become a President state, like the South slave Monroe was from Virginia, so the South controlled the presidency too –Northerners did not want to see Southern slave states increase their power in the national gov’t –If Missouri entered as a slave state, the South would have 2 more Senators than the North ■
Missouri Compromise Because of the 3/5 Compromise, When Missouri applied to become athe South had sectionalism emerged U. S. state, more members in the House of Representatives –Missouri wanted to become a President state, like the South slave Monroe was from Virginia, so the South controlled the presidency too –Northerners did not want to see Southern slave states increase their power in the national gov’t –If Missouri entered as a slave state, the South would have 2 more Senators than the North ■
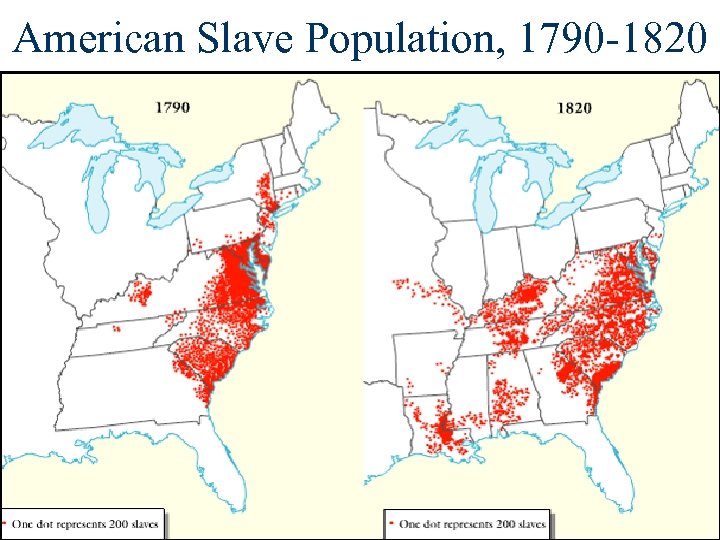 American Slave Population, 1790 -1820
American Slave Population, 1790 -1820
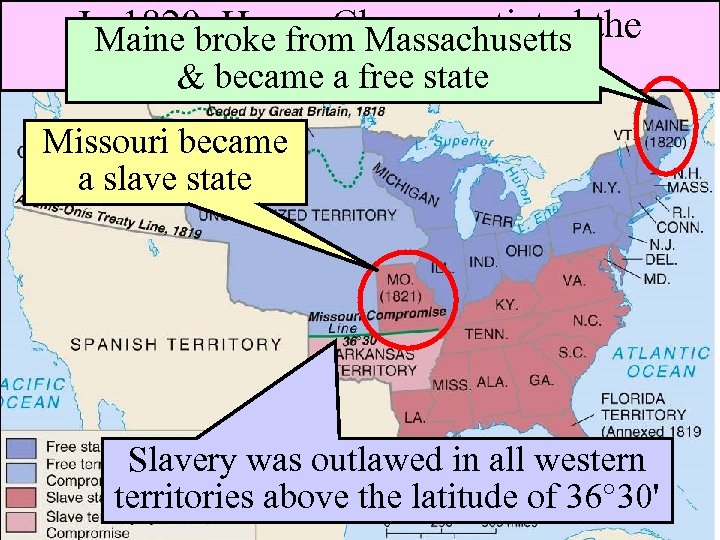 In 1820, Henry Clay negotiated the Maine broke from Massachusetts Missouri a free state & became Compromise Missouri became a slave state Slavery was outlawed in all western territories above the latitude of 36° 30'
In 1820, Henry Clay negotiated the Maine broke from Massachusetts Missouri a free state & became Compromise Missouri became a slave state Slavery was outlawed in all western territories above the latitude of 36° 30'
 Closure Activity ■ Examine this political cartoon: –What do you see? –What can you deduce about how the Monroe Doctrine might be used by the U. S. in the future?
Closure Activity ■ Examine this political cartoon: –What do you see? –What can you deduce about how the Monroe Doctrine might be used by the U. S. in the future?


