e476f79b1941a0575153aabea5f4087c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Essential Question Ch 6: What is the right price? • Section 2: How do changes in S&D affect equilibrium Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1
Essential Question Ch 6: What is the right price? • Section 2: How do changes in S&D affect equilibrium Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1
 Objectives 1. Explain why a free market naturally tends to move toward equilibrium. 2. Analyze how a market reacts to an increase or decrease in supply. 3. Analyze how a market reacts to an increase or decrease in demand. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 2
Objectives 1. Explain why a free market naturally tends to move toward equilibrium. 2. Analyze how a market reacts to an increase or decrease in supply. 3. Analyze how a market reacts to an increase or decrease in demand. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 2
 Discussion: Technology and Changing Markets • How did the invention of digital cameras affect the demand for 35 mm film cameras? – Demand for digital increase; Demand for film decrease • As digital camera technology improved, what happened to the supply of digital cameras? Why? – Supply increased to match increased demand. – Technology led to improvements and lowered costs. This increased supply – You can get a 7. 1 MP camera now for the same cost as a 3 MP camera a few years ago – Supply shifts to the right Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 3
Discussion: Technology and Changing Markets • How did the invention of digital cameras affect the demand for 35 mm film cameras? – Demand for digital increase; Demand for film decrease • As digital camera technology improved, what happened to the supply of digital cameras? Why? – Supply increased to match increased demand. – Technology led to improvements and lowered costs. This increased supply – You can get a 7. 1 MP camera now for the same cost as a 3 MP camera a few years ago – Supply shifts to the right Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 3
 Discussion: Technology and Changing Markets • What has happened to the price or quality of digital cameras over time? – Get a better camera now for the same amount of money – Price for the same camera has fallen over time Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 4
Discussion: Technology and Changing Markets • What has happened to the price or quality of digital cameras over time? – Get a better camera now for the same amount of money – Price for the same camera has fallen over time Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 4
 Discussion: Technology and Changing Markets • Kodak suffered from the invention of digital cameras. • Picasa/Shutterfly and other online picture services have boomed • What other products might have been affected by the advancement in camera technology? Digital Cameras Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 5
Discussion: Technology and Changing Markets • Kodak suffered from the invention of digital cameras. • Picasa/Shutterfly and other online picture services have boomed • What other products might have been affected by the advancement in camera technology? Digital Cameras Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 5
 Discussion: Technology and Changing Markets • In groups of 3 -4 people, take 6 minutes to discuss the following: – Pick a pair of products you suggested in the Bell Ringer or two products from the diagram on the previous slide – Discuss in your group how the supply and demand curves for each product have changed over time • ie. Supply and demand of digital cameras increased; supply and demand of film cameras decreased – What happened to the price and why? – What related fields/products/services have been affected by the changing technology? • Select a group member to share out to the class. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 6
Discussion: Technology and Changing Markets • In groups of 3 -4 people, take 6 minutes to discuss the following: – Pick a pair of products you suggested in the Bell Ringer or two products from the diagram on the previous slide – Discuss in your group how the supply and demand curves for each product have changed over time • ie. Supply and demand of digital cameras increased; supply and demand of film cameras decreased – What happened to the price and why? – What related fields/products/services have been affected by the changing technology? • Select a group member to share out to the class. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 6
 Introduction • How do changes in supply and demand affect equilibrium? 1. Changes in supply and demand cause shifts in the curve(s) 2. Shift in a curve causes prices to go up and down, which causes disequilibrium 3. In a free market, price and quantity will tend to move toward equilibrium whenever they find themselves in disequilibrium • Chapter 6, Section 2 this is often a new equilibrium price and output Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 7
Introduction • How do changes in supply and demand affect equilibrium? 1. Changes in supply and demand cause shifts in the curve(s) 2. Shift in a curve causes prices to go up and down, which causes disequilibrium 3. In a free market, price and quantity will tend to move toward equilibrium whenever they find themselves in disequilibrium • Chapter 6, Section 2 this is often a new equilibrium price and output Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 7
 Equilibrium: a “Moving Target” • Equilibrium for most products is in constant motion. – Buyers/sellers are always adjusting the price and quantity they agree upon – Think of bargaining in a marketplace • Think of equilibrium as a “moving target” that changes as market conditions change. – As supply or demand increases or decreases, a new equilibrium is created for that product. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 8
Equilibrium: a “Moving Target” • Equilibrium for most products is in constant motion. – Buyers/sellers are always adjusting the price and quantity they agree upon – Think of bargaining in a marketplace • Think of equilibrium as a “moving target” that changes as market conditions change. – As supply or demand increases or decreases, a new equilibrium is created for that product. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 8
 The Pull Back to Equilibrium • When a market is in disequilibrium, there are either shortages or surpluses • The market will eventually move back toward equilibrium. – Shortages cause a firm to raise its prices. • Higher prices cause the quantity supplied to rise and the quantity demanded to fall until the two values are equal again. – Surpluses cause a firm to drop its prices. • Lower prices cause the quantity supplied to fall and the quantity demanded to rise until equilibrium is restored. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 9
The Pull Back to Equilibrium • When a market is in disequilibrium, there are either shortages or surpluses • The market will eventually move back toward equilibrium. – Shortages cause a firm to raise its prices. • Higher prices cause the quantity supplied to rise and the quantity demanded to fall until the two values are equal again. – Surpluses cause a firm to drop its prices. • Lower prices cause the quantity supplied to fall and the quantity demanded to rise until equilibrium is restored. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 9
 Changes in Supply and New Equilibrium • A shift in the supply curve will change the equilibrium price and quantity. • As supply increases, the market moves toward a new equilibrium – Price lower, Quantity higher than original equilibrium • As supply decreases, the market moves toward a new equilibrium – Price higher, Quantity lower than original equilibrium Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 10
Changes in Supply and New Equilibrium • A shift in the supply curve will change the equilibrium price and quantity. • As supply increases, the market moves toward a new equilibrium – Price lower, Quantity higher than original equilibrium • As supply decreases, the market moves toward a new equilibrium – Price higher, Quantity lower than original equilibrium Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 10
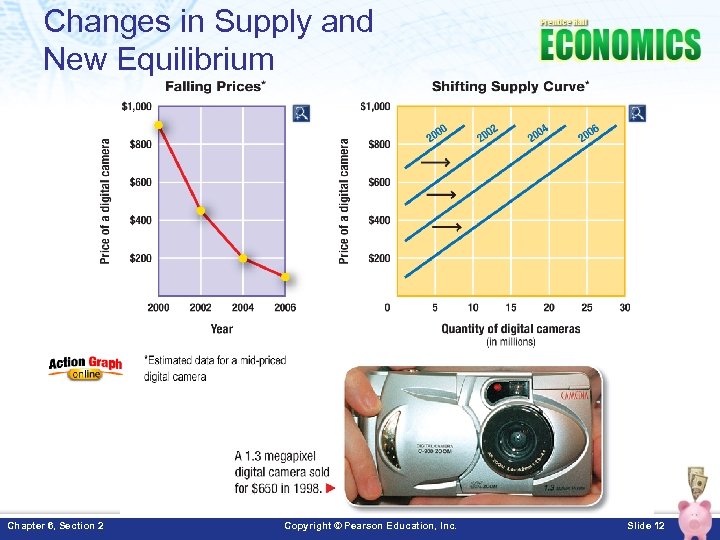
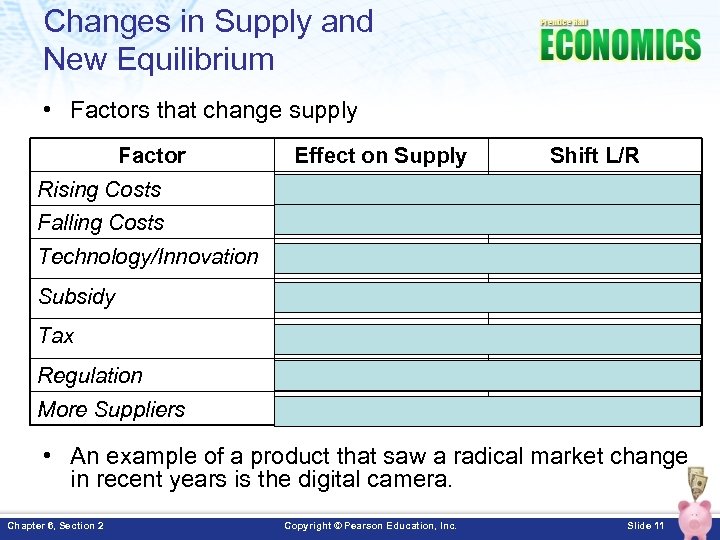 Changes in Supply and New Equilibrium • Factors that change supply Factor Effect on Supply Shift L/R Rising Costs Decrease Supply Shift Left Falling Costs Increase Supply Shift Right Technology/Innovation Increase Supply Shift Right Subsidy Increase Supply Shift Right Tax Decrease Supply Shift Left Regulation Decrease Supply Shift Left More Suppliers Increase Supply Shift Right • An example of a product that saw a radical market change in recent years is the digital camera. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 11
Changes in Supply and New Equilibrium • Factors that change supply Factor Effect on Supply Shift L/R Rising Costs Decrease Supply Shift Left Falling Costs Increase Supply Shift Right Technology/Innovation Increase Supply Shift Right Subsidy Increase Supply Shift Right Tax Decrease Supply Shift Left Regulation Decrease Supply Shift Left More Suppliers Increase Supply Shift Right • An example of a product that saw a radical market change in recent years is the digital camera. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 11
 Changes in Supply and New Equilibrium Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 12
Changes in Supply and New Equilibrium Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 12
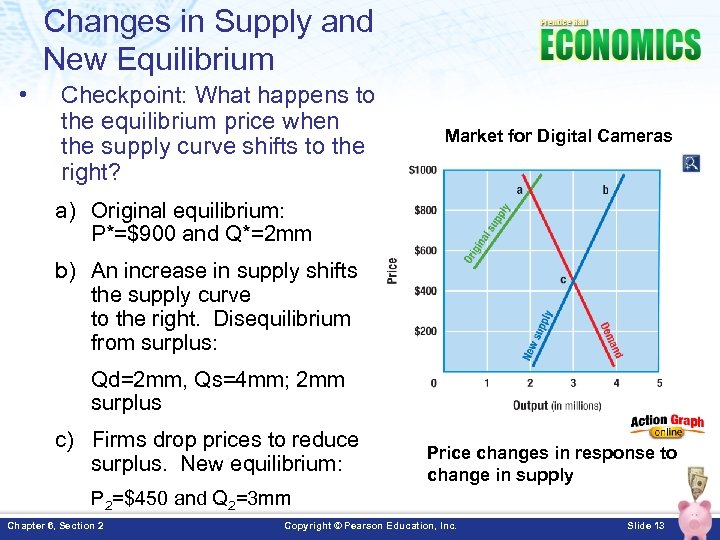 Changes in Supply and New Equilibrium • Checkpoint: What happens to the equilibrium price when the supply curve shifts to the right? Market for Digital Cameras a) Original equilibrium: P*=$900 and Q*=2 mm b) An increase in supply shifts the supply curve to the right. Disequilibrium from surplus: Qd=2 mm, Qs=4 mm; 2 mm surplus c) Firms drop prices to reduce surplus. New equilibrium: Price changes in response to change in supply P 2=$450 and Q 2=3 mm Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 13
Changes in Supply and New Equilibrium • Checkpoint: What happens to the equilibrium price when the supply curve shifts to the right? Market for Digital Cameras a) Original equilibrium: P*=$900 and Q*=2 mm b) An increase in supply shifts the supply curve to the right. Disequilibrium from surplus: Qd=2 mm, Qs=4 mm; 2 mm surplus c) Firms drop prices to reduce surplus. New equilibrium: Price changes in response to change in supply P 2=$450 and Q 2=3 mm Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 13
 Changes in Demand New Equilibrium • A shift in the demand curve will change the equilibrium price and quantity. • As demand increases, the market moves toward a new equilibrium – Price higher, Quantity higher than original equilibrium • As demand decreases, the market moves toward a new equilibrium – Price lower, Quantity lower than original equilibrium Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 14
Changes in Demand New Equilibrium • A shift in the demand curve will change the equilibrium price and quantity. • As demand increases, the market moves toward a new equilibrium – Price higher, Quantity higher than original equilibrium • As demand decreases, the market moves toward a new equilibrium – Price lower, Quantity lower than original equilibrium Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 14
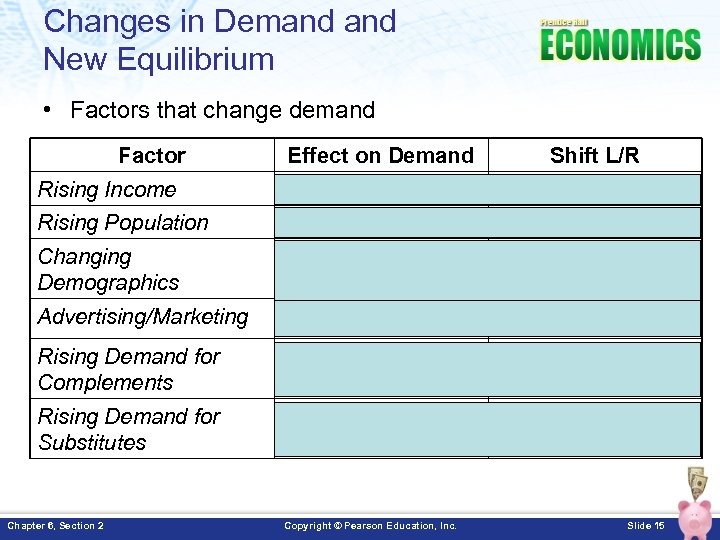 Changes in Demand New Equilibrium • Factors that change demand Factor Effect on Demand Shift L/R Rising Income Increase Demand Shift Right Rising Population Increase Demand Shift Right Changing Demographics Depends Advertising/Marketing Increase Demand Shift Right Rising Demand for Complements Increase Demand Shift Right Rising Demand for Substitutes Decrease Demand Shift Left Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 15
Changes in Demand New Equilibrium • Factors that change demand Factor Effect on Demand Shift L/R Rising Income Increase Demand Shift Right Rising Population Increase Demand Shift Right Changing Demographics Depends Advertising/Marketing Increase Demand Shift Right Rising Demand for Complements Increase Demand Shift Right Rising Demand for Substitutes Decrease Demand Shift Left Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 15
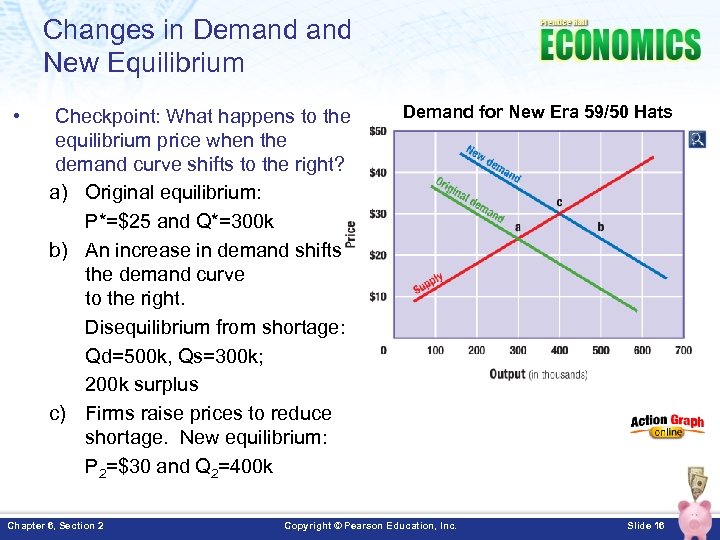 Changes in Demand New Equilibrium • Checkpoint: What happens to the equilibrium price when the demand curve shifts to the right? a) Original equilibrium: P*=$25 and Q*=300 k b) An increase in demand shifts the demand curve to the right. Disequilibrium from shortage: Qd=500 k, Qs=300 k; 200 k surplus c) Firms raise prices to reduce shortage. New equilibrium: P 2=$30 and Q 2=400 k Chapter 6, Section 2 Demand for New Era 59/50 Hats Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 16
Changes in Demand New Equilibrium • Checkpoint: What happens to the equilibrium price when the demand curve shifts to the right? a) Original equilibrium: P*=$25 and Q*=300 k b) An increase in demand shifts the demand curve to the right. Disequilibrium from shortage: Qd=500 k, Qs=300 k; 200 k surplus c) Firms raise prices to reduce shortage. New equilibrium: P 2=$30 and Q 2=400 k Chapter 6, Section 2 Demand for New Era 59/50 Hats Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 16
 Fads and Shortages • Fads often lead to an increase in demand for a particular good. • As a result of fads, shortages appear to customers in different forms: – Empty shelves at the stores – Long lines to buy a product in short supply – Rising search costs, such as driving to multiple stores to find a product. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 17
Fads and Shortages • Fads often lead to an increase in demand for a particular good. • As a result of fads, shortages appear to customers in different forms: – Empty shelves at the stores – Long lines to buy a product in short supply – Rising search costs, such as driving to multiple stores to find a product. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 17
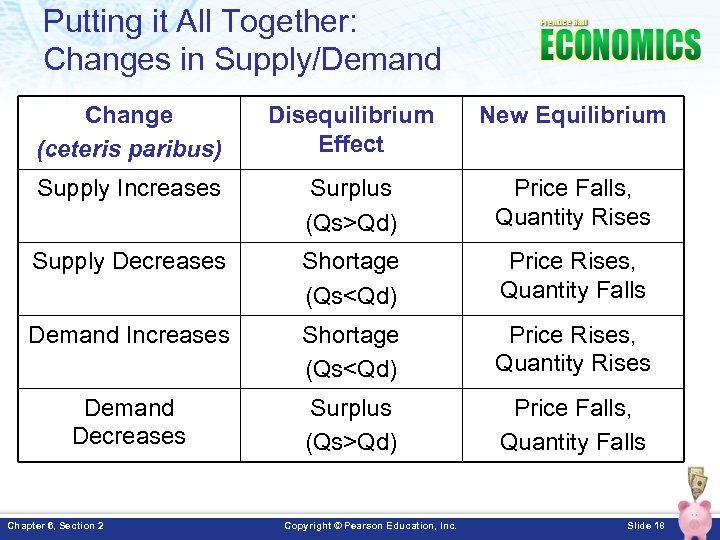 Putting it All Together: Changes in Supply/Demand Change (ceteris paribus) Disequilibrium Effect New Equilibrium Supply Increases Surplus (Qs>Qd) Price Falls, Quantity Rises Supply Decreases Shortage (Qs
Putting it All Together: Changes in Supply/Demand Change (ceteris paribus) Disequilibrium Effect New Equilibrium Supply Increases Surplus (Qs>Qd) Price Falls, Quantity Rises Supply Decreases Shortage (Qs
 Key Terms • inventory: the quantity of goods that a firm has on hand (this gets bigger when there is a surplus and smaller when there is a shortage) • fad: a product that is popular for a short period of time • search costs: the financial and opportunity costs that consumers pay when searching for a good or service (increased from a shortage). Internet has decreased search costs. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 19
Key Terms • inventory: the quantity of goods that a firm has on hand (this gets bigger when there is a surplus and smaller when there is a shortage) • fad: a product that is popular for a short period of time • search costs: the financial and opportunity costs that consumers pay when searching for a good or service (increased from a shortage). Internet has decreased search costs. Chapter 6, Section 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 19


