21b99523d22cb4d7d380645bf2f61753.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Essential Elements in Implementing and Monitoring Quality Rt. I Procedures Rose Dymacek & Edward Daly Nebraska Department of Education University of Nebraska. Lincoln
Essential Elements in Implementing and Monitoring Quality Rt. I Procedures Rose Dymacek & Edward Daly Nebraska Department of Education University of Nebraska. Lincoln
 NDE’s View of a Quality Rt. I Process Every school must have the capacity to meet the needs of all children throughout the state. n Yet, every school district must also be able to tailor the Rt. I process to meet the needs of its unique organizational structure and priorities. n NDE is working to balance its expectations for high standards for implementation with local flexibility in how those standards are met. n
NDE’s View of a Quality Rt. I Process Every school must have the capacity to meet the needs of all children throughout the state. n Yet, every school district must also be able to tailor the Rt. I process to meet the needs of its unique organizational structure and priorities. n NDE is working to balance its expectations for high standards for implementation with local flexibility in how those standards are met. n
 Developing a Valid Rt. I Process for Students n Essential Elements of the Rt. I Process n Developmental Progression of Implementation n Strong Operational Model for Continuum of Rt. I Service Delivery
Developing a Valid Rt. I Process for Students n Essential Elements of the Rt. I Process n Developmental Progression of Implementation n Strong Operational Model for Continuum of Rt. I Service Delivery
 Essential Elements of Rt. I: Organizational Capacity n School-wide buy-in and implementation plan n Team leadership n Integration of Services n Implementation Infrastructure
Essential Elements of Rt. I: Organizational Capacity n School-wide buy-in and implementation plan n Team leadership n Integration of Services n Implementation Infrastructure
 School-wide Buy-in and Implementation Plan What it Looks Like: n All school staff is knowledgeable about Rt. I and supports implementation in the school district Forms of Evidence: n Documentation of Rt. I training n Inclusion of Rt. I in School Improvement Plan
School-wide Buy-in and Implementation Plan What it Looks Like: n All school staff is knowledgeable about Rt. I and supports implementation in the school district Forms of Evidence: n Documentation of Rt. I training n Inclusion of Rt. I in School Improvement Plan
 Team Leadership What it Looks Like: n A team that includes administrators, teachers, and support personnel provides leadership for implementing Rt. I at the district and building level Forms of Evidence: n An identifiable core team with clearly defined roles, authority, and administrative support
Team Leadership What it Looks Like: n A team that includes administrators, teachers, and support personnel provides leadership for implementing Rt. I at the district and building level Forms of Evidence: n An identifiable core team with clearly defined roles, authority, and administrative support
 Integration of Services Forms of Evidence: What it Looks Like: n Clearly defined roles at n All school staff the district/building level, collaborates to effective communication support learning for and interaction among all students across the school personnel in regular and special continuum of student education ability levels n Rt. I plan is aligned with existing initiatives including STARS, the school/district School Improvement Plan, and Improving Learning for Children with Disabilities (ILCD)
Integration of Services Forms of Evidence: What it Looks Like: n Clearly defined roles at n All school staff the district/building level, collaborates to effective communication support learning for and interaction among all students across the school personnel in regular and special continuum of student education ability levels n Rt. I plan is aligned with existing initiatives including STARS, the school/district School Improvement Plan, and Improving Learning for Children with Disabilities (ILCD)
 Implementation Infrastructure What it Looks Like: n Professional training and support, resources, and an appropriate administrative structure in place Forms of Evidence: n n n Curriculum aligned to Nebraska State Standards Ongoing professional development Assessments to determine student progress toward Nebraska State Standards and aligned to the district STARS system Assessment data utilized in making decisions about student progress Research supported interventions and teaching strategies Plan for delivering quality instruction and research based interventions as assessment
Implementation Infrastructure What it Looks Like: n Professional training and support, resources, and an appropriate administrative structure in place Forms of Evidence: n n n Curriculum aligned to Nebraska State Standards Ongoing professional development Assessments to determine student progress toward Nebraska State Standards and aligned to the district STARS system Assessment data utilized in making decisions about student progress Research supported interventions and teaching strategies Plan for delivering quality instruction and research based interventions as assessment
 Essential Elements of Rt. I: Implementing Rt. I in Schools n Parent Involvement n Universal Screening and Assessment n Individual Progress Monitoring n Planned Service Delivery Rules n Scientifically Supported Instruction n Intervention Delivery n SLD Verification
Essential Elements of Rt. I: Implementing Rt. I in Schools n Parent Involvement n Universal Screening and Assessment n Individual Progress Monitoring n Planned Service Delivery Rules n Scientifically Supported Instruction n Intervention Delivery n SLD Verification
 Parent Involvement What it Looks Like: n Parents are informed, knowledgeable, and involved in their children’s educational process Forms of Evidence: n Documentation that parents are included and involved in the Rt. I process n Procedures are in place for parent permission, notification, and rights to due process when appropriate
Parent Involvement What it Looks Like: n Parents are informed, knowledgeable, and involved in their children’s educational process Forms of Evidence: n Documentation that parents are included and involved in the Rt. I process n Procedures are in place for parent permission, notification, and rights to due process when appropriate
 Universal Screening and Assessment What it Looks Like: n Assessments that provide teachers with information about the progress of all students… Forms of Evidence: Assessments to determine individual student progress toward Nebraska State Standards n Systematic classroom or building screening procedures n Decisions about student progress are based on assessment data and are clearly linked to next steps n
Universal Screening and Assessment What it Looks Like: n Assessments that provide teachers with information about the progress of all students… Forms of Evidence: Assessments to determine individual student progress toward Nebraska State Standards n Systematic classroom or building screening procedures n Decisions about student progress are based on assessment data and are clearly linked to next steps n
 Individual Progress Monitoring What it Looks Like: n Assessments provide teachers with information about which students are benefiting from intervention and which need additional supports. Forms of Evidence: n n n Use of progress monitoring data “Graph-able” goals for progress A minimum of two interventions with increasing intensity A minimum of six data points to determine intervention effectiveness Evaluation based on individual goals, student progress towards state standards, and changes in student performance over time
Individual Progress Monitoring What it Looks Like: n Assessments provide teachers with information about which students are benefiting from intervention and which need additional supports. Forms of Evidence: n n n Use of progress monitoring data “Graph-able” goals for progress A minimum of two interventions with increasing intensity A minimum of six data points to determine intervention effectiveness Evaluation based on individual goals, student progress towards state standards, and changes in student performance over time
 Planned Service Delivery Decision Rules What it Looks Like: n Guidelines and procedures in place that identify sequential, coordinated delivery of interventions for students Forms of Evidence: n Decision rules for multi-tiered intervention selection, responsiveness to intervention and special education eligibility n Student performance is evaluated based on level and rate of performance as outlined by the decision rules
Planned Service Delivery Decision Rules What it Looks Like: n Guidelines and procedures in place that identify sequential, coordinated delivery of interventions for students Forms of Evidence: n Decision rules for multi-tiered intervention selection, responsiveness to intervention and special education eligibility n Student performance is evaluated based on level and rate of performance as outlined by the decision rules
 Scientifically Supported Instruction What it Looks Like: n Core instruction and interventions have been validated through scientific research Forms of Evidence: n Justification of scientifically supported, high quality instruction
Scientifically Supported Instruction What it Looks Like: n Core instruction and interventions have been validated through scientific research Forms of Evidence: n Justification of scientifically supported, high quality instruction
 Intervention Delivery What it Looks Like: n School personnel deliver high quality, scientifically supported interventions of appropriate intensity for a reasonable amount of time Forms of Evidence: n Scientifically supported interventions n A minimum of 24 sessions per intervention phase n At least two intervention phases of increasing intensity prior to SLD determination n Fidelity of implementation
Intervention Delivery What it Looks Like: n School personnel deliver high quality, scientifically supported interventions of appropriate intensity for a reasonable amount of time Forms of Evidence: n Scientifically supported interventions n A minimum of 24 sessions per intervention phase n At least two intervention phases of increasing intensity prior to SLD determination n Fidelity of implementation
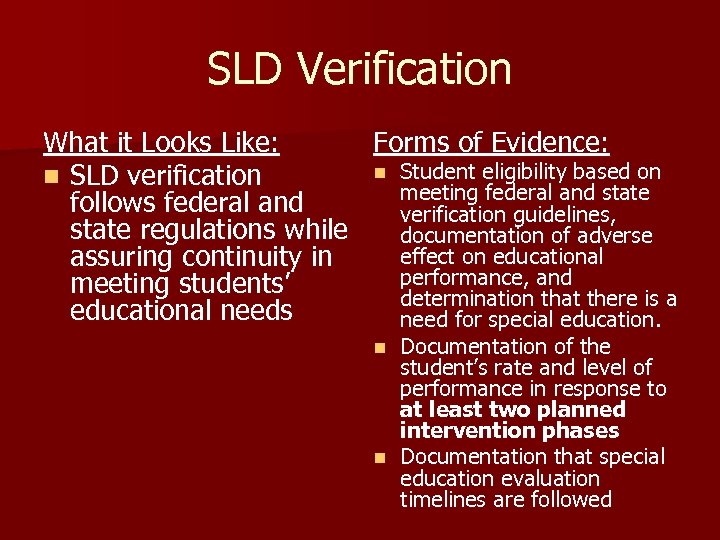 SLD Verification What it Looks Like: Forms of Evidence: n Student eligibility based on n SLD verification meeting federal and state follows federal and verification guidelines, state regulations while documentation of adverse effect on educational assuring continuity in performance, and meeting students’ determination that there is a educational needs need for special education. Documentation of the student’s rate and level of performance in response to at least two planned intervention phases n Documentation that special education evaluation timelines are followed n
SLD Verification What it Looks Like: Forms of Evidence: n Student eligibility based on n SLD verification meeting federal and state follows federal and verification guidelines, state regulations while documentation of adverse effect on educational assuring continuity in performance, and meeting students’ determination that there is a educational needs need for special education. Documentation of the student’s rate and level of performance in response to at least two planned intervention phases n Documentation that special education evaluation timelines are followed n
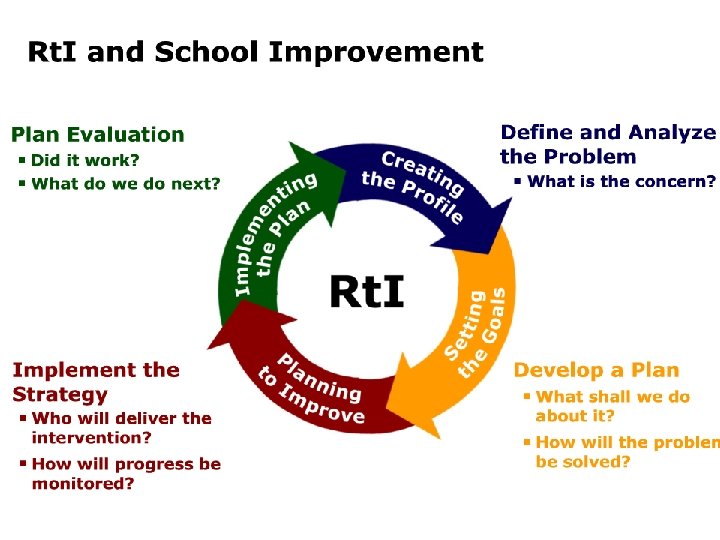
 Developmental Progression Toward Full Scale Implementation of RTI Application of Problem Solving Data to LD Eligibility Coordinated Intervention Delivery Universal Screening to Identify Students At-Risk for Academic Difficulties Problem Solving Team Engages in Data Based Problem Solving
Developmental Progression Toward Full Scale Implementation of RTI Application of Problem Solving Data to LD Eligibility Coordinated Intervention Delivery Universal Screening to Identify Students At-Risk for Academic Difficulties Problem Solving Team Engages in Data Based Problem Solving
 Integrating Rt. I With Existing Practices n School Improvement Plan n Pre-referral Intervention teams n Title I Services n Assessment n Professional Learning Communities
Integrating Rt. I With Existing Practices n School Improvement Plan n Pre-referral Intervention teams n Title I Services n Assessment n Professional Learning Communities
 Implementing Rt. I: Procedural Integrity n PROCEDURAL CHECKLIST as an operational definition of Rt. I – Accountability – Formative evaluation and program improvement
Implementing Rt. I: Procedural Integrity n PROCEDURAL CHECKLIST as an operational definition of Rt. I – Accountability – Formative evaluation and program improvement

 “The significant problems we face cannot be solved by the same level of thinking that created them. ” Albert Einstein
“The significant problems we face cannot be solved by the same level of thinking that created them. ” Albert Einstein
 Real Change in Schools n Fullan (1991) – “innovations can be adopted for symbolic political or personal reasons: to appease community pressure, to appear innovative, to gain more resources. All of these forms represent symbolic rather than real change. ” (p. 28) – “Even good ideas may represent poor investments on a large scale if the ideas have not been well developed or if the resources to support implementation are unavailable. ” (p. 28)
Real Change in Schools n Fullan (1991) – “innovations can be adopted for symbolic political or personal reasons: to appease community pressure, to appear innovative, to gain more resources. All of these forms represent symbolic rather than real change. ” (p. 28) – “Even good ideas may represent poor investments on a large scale if the ideas have not been well developed or if the resources to support implementation are unavailable. ” (p. 28)
 Conclusions n Building a Quality Rt. I Process – Essential Elements of Rt. I § “What do our children deserve? ” – Procedural Integrity § “What will they actually get? ” – Strategic and Sequential Development and Refinement § “How will you make sure you can do it well for all children and better each year? ”
Conclusions n Building a Quality Rt. I Process – Essential Elements of Rt. I § “What do our children deserve? ” – Procedural Integrity § “What will they actually get? ” – Strategic and Sequential Development and Refinement § “How will you make sure you can do it well for all children and better each year? ”
 TEAM PLANNING ACTIVITIES “Where are you at and where do you want to go with Rt. I? ” n Discuss and evaluate your school district’s organizational readiness (See the “Evaluation of Organizational Readiness…” checklist in the TA manual). – Where are you at in the process of developing Rt. I? n Goal Setting for next year: which elements will you put in place? (Developmental Progression) – Which component(s) of Rt. I will you try to implement next year? – How will you go about doing it? n Already have the infrastructure and elements? – Are you ready to develop a Procedural Checklist?
TEAM PLANNING ACTIVITIES “Where are you at and where do you want to go with Rt. I? ” n Discuss and evaluate your school district’s organizational readiness (See the “Evaluation of Organizational Readiness…” checklist in the TA manual). – Where are you at in the process of developing Rt. I? n Goal Setting for next year: which elements will you put in place? (Developmental Progression) – Which component(s) of Rt. I will you try to implement next year? – How will you go about doing it? n Already have the infrastructure and elements? – Are you ready to develop a Procedural Checklist?


