5a4ed7c446bcbfe4cb69f1e031afbd70.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 ESOC Navigation Support Office Ground support network for the Metop GRAS atmospheric sounding mission R. Zandbergen, A. Ballereau, M. Lorenzo, J. M. Dow, C. Marquardt, F. Wollenweber 18 April 2008 EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 1/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Ground support network for the Metop GRAS atmospheric sounding mission R. Zandbergen, A. Ballereau, M. Lorenzo, J. M. Dow, C. Marquardt, F. Wollenweber 18 April 2008 EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 1/18
 ESOC Navigation Support Office • • GNSS Receiver for Atmospheric Sounding … on board Metop • Ground • Support • Network EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 2/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office • • GNSS Receiver for Atmospheric Sounding … on board Metop • Ground • Support • Network EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 2/18
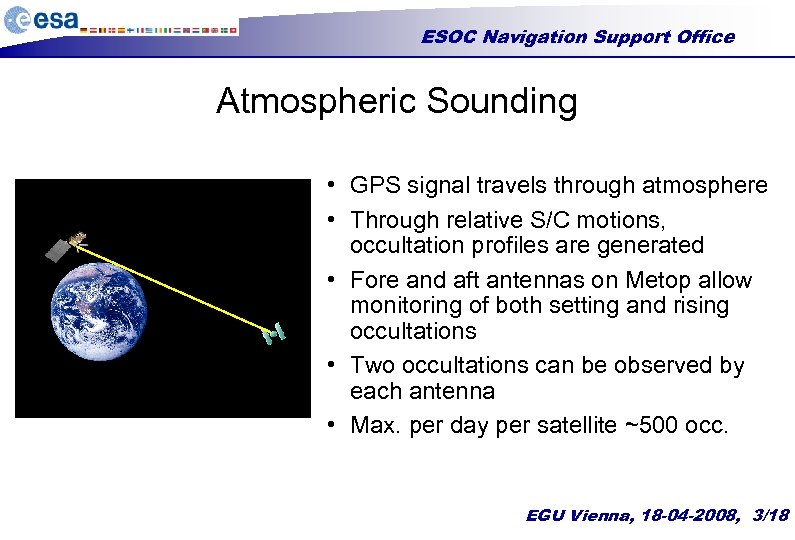 ESOC Navigation Support Office Atmospheric Sounding • GPS signal travels through atmosphere • Through relative S/C motions, occultation profiles are generated • Fore and aft antennas on Metop allow monitoring of both setting and rising occultations • Two occultations can be observed by each antenna • Max. per day per satellite ~500 occ. EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 3/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Atmospheric Sounding • GPS signal travels through atmosphere • Through relative S/C motions, occultation profiles are generated • Fore and aft antennas on Metop allow monitoring of both setting and rising occultations • Two occultations can be observed by each antenna • Max. per day per satellite ~500 occ. EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 3/18
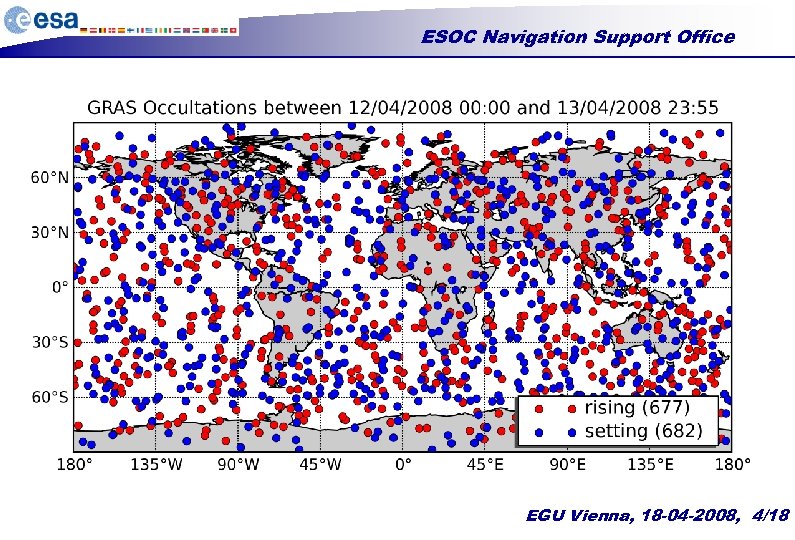 ESOC Navigation Support Office EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 4/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 4/18
 ESOC Navigation Support Office Generation of sounding profiles • • EUMETSAT will operate three Metop S/C (polar LEO) … and generate atmospheric sounding products in NRT … for delivery to European Met Offices within 3 hours The generation of profiles requires precise orbits and clock solutions for both Metop and the occulting GPS satellite • Metop POD to be performed in-house, using GRAS GPS receiver (zenith antenna) • The GPS products are considered ‘Support Data’, to be provided externally EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 5/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Generation of sounding profiles • • EUMETSAT will operate three Metop S/C (polar LEO) … and generate atmospheric sounding products in NRT … for delivery to European Met Offices within 3 hours The generation of profiles requires precise orbits and clock solutions for both Metop and the occulting GPS satellite • Metop POD to be performed in-house, using GRAS GPS receiver (zenith antenna) • The GPS products are considered ‘Support Data’, to be provided externally EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 5/18
 ESOC Navigation Support Office Support data for occultation processing • GPS orbits (for Metop POD and occultation processing) • GPS clock solutions – Low-rate for Metop POD – High-rate for occultation processing • EOP data (for Metop POD) • Auxiliary data (TZD, Meteo, Nav msg…) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 6/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Support data for occultation processing • GPS orbits (for Metop POD and occultation processing) • GPS clock solutions – Low-rate for Metop POD – High-rate for occultation processing • EOP data (for Metop POD) • Auxiliary data (TZD, Meteo, Nav msg…) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 6/18
 ESOC Navigation Support Office Support data for occultation processing • GPS orbits (for Metop POD and occultation processing) • GPS clock solutions – Low-rate for Metop POD – High-rate for occultation processing • EOP data (for Metop POD) • Auxiliary data (TZD, Meteo, Nav msg…) • High-rate, selected, ground receiver data why? • High-rate ground clock solutions } EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 7/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Support data for occultation processing • GPS orbits (for Metop POD and occultation processing) • GPS clock solutions – Low-rate for Metop POD – High-rate for occultation processing • EOP data (for Metop POD) • Auxiliary data (TZD, Meteo, Nav msg…) • High-rate, selected, ground receiver data why? • High-rate ground clock solutions } EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 7/18
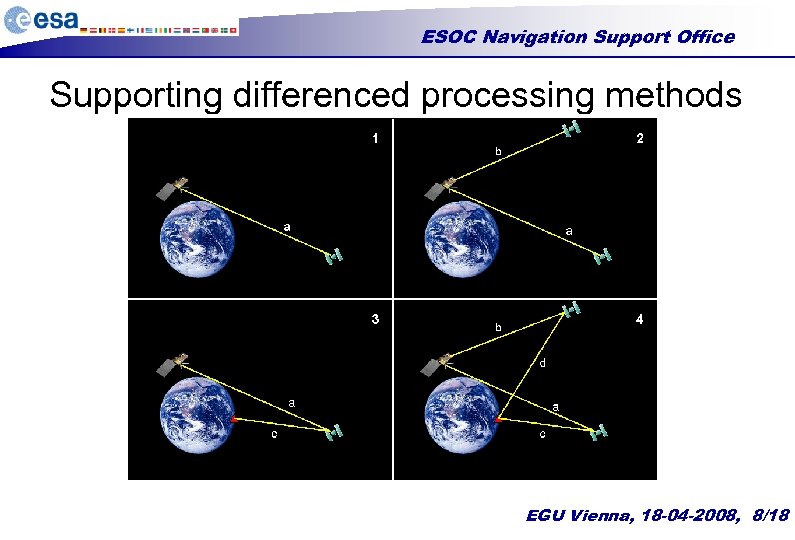 ESOC Navigation Support Office Supporting differenced processing methods EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 8/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Supporting differenced processing methods EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 8/18
 ESOC Navigation Support Office Ground (Sounding) Support Data • • Method 1: undifferenced Method 2: eliminate GRAS clock Method 3: take out the GPS clock (replace by ground clock) Method 4 not yet implemented • For method 3, accurate ground clock solutions and ground tracking data of the occulting satellite are required • EUMETSAT deliver a table of predicted occultations to ESOC and ESOC return the necessary ground data (SSD) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 9/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Ground (Sounding) Support Data • • Method 1: undifferenced Method 2: eliminate GRAS clock Method 3: take out the GPS clock (replace by ground clock) Method 4 not yet implemented • For method 3, accurate ground clock solutions and ground tracking data of the occulting satellite are required • EUMETSAT deliver a table of predicted occultations to ESOC and ESOC return the necessary ground data (SSD) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 9/18
 ESOC Navigation Support Office Support data key requirements • The most fundamental requirements were studied in 2001: – Timeliness: 60 min. for orbits and clocks – Clock accuracy: 1 ns at 2 -sigma for each satellite – Clocks to be interpolated at 50 Hz – GPS satellite velocity accuracy requirement! – Guaranteed high availability (99% & limited interruptions) – Can be operated for 15 years, 2 satellites in parallel – Extensible to other missions with similar requirements EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 10/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Support data key requirements • The most fundamental requirements were studied in 2001: – Timeliness: 60 min. for orbits and clocks – Clock accuracy: 1 ns at 2 -sigma for each satellite – Clocks to be interpolated at 50 Hz – GPS satellite velocity accuracy requirement! – Guaranteed high availability (99% & limited interruptions) – Can be operated for 15 years, 2 satellites in parallel – Extensible to other missions with similar requirements EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 10/18
 ESOC Navigation Support Office High-level design • A dedicated and fully redundant network of approximately 20 sites (i. e. in total 40) – Resulted in contracts with existing network operators: GFZ, NRCan and Fugro Seastar • • A processing centre in ESOC GPS orbits computed every 3 hours, delivering predictions Clocks computed every 15 minutes, not predicted To support the 50 Hz GRAS data rate, compute and deliver 1 Hz GPS clocks (not interpolated) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 11/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office High-level design • A dedicated and fully redundant network of approximately 20 sites (i. e. in total 40) – Resulted in contracts with existing network operators: GFZ, NRCan and Fugro Seastar • • A processing centre in ESOC GPS orbits computed every 3 hours, delivering predictions Clocks computed every 15 minutes, not predicted To support the 50 Hz GRAS data rate, compute and deliver 1 Hz GPS clocks (not interpolated) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 11/18
 ESOC Navigation Support Office The GSN Network (prime sites) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 12/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office The GSN Network (prime sites) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 12/18
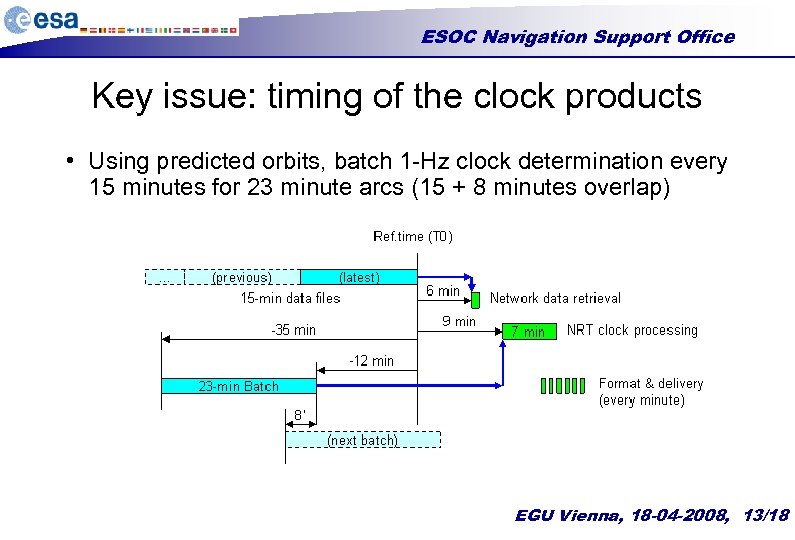 ESOC Navigation Support Office Key issue: timing of the clock products • Using predicted orbits, batch 1 -Hz clock determination every 15 minutes for 23 minute arcs (15 + 8 minutes overlap) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 13/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Key issue: timing of the clock products • Using predicted orbits, batch 1 -Hz clock determination every 15 minutes for 23 minute arcs (15 + 8 minutes overlap) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 13/18
 ESOC Navigation Support Office Current status • Successful validation of GRAS GSN in February 2006 • Launch of the first satellite (Metop-2) October 2006 • Activation of GRAS GSN operations one month prior to launch • First year of operations completed September 2007 • Accuracy and availability requirements met by a good margin (first year availability 99. 71%) • Support to COSMIC mission has started EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 14/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Current status • Successful validation of GRAS GSN in February 2006 • Launch of the first satellite (Metop-2) October 2006 • Activation of GRAS GSN operations one month prior to launch • First year of operations completed September 2007 • Accuracy and availability requirements met by a good margin (first year availability 99. 71%) • Support to COSMIC mission has started EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 14/18
 ESOC Navigation Support Office Achieving the accuracy requirements • Requirements verification by comparing to IGS finals • Accuracy requirements are met almost continually • Accuracy requirements from EUMETSAT equivalent to 95 percentile • In IGS terms (‘typical RMS’), orbit prediction accuracy based on the relatively small network is around 10 cm. • Clock accuracy is corresponding to this (around 0. 3 ns, removing only a single common clock bias) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 15/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Achieving the accuracy requirements • Requirements verification by comparing to IGS finals • Accuracy requirements are met almost continually • Accuracy requirements from EUMETSAT equivalent to 95 percentile • In IGS terms (‘typical RMS’), orbit prediction accuracy based on the relatively small network is around 10 cm. • Clock accuracy is corresponding to this (around 0. 3 ns, removing only a single common clock bias) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 15/18
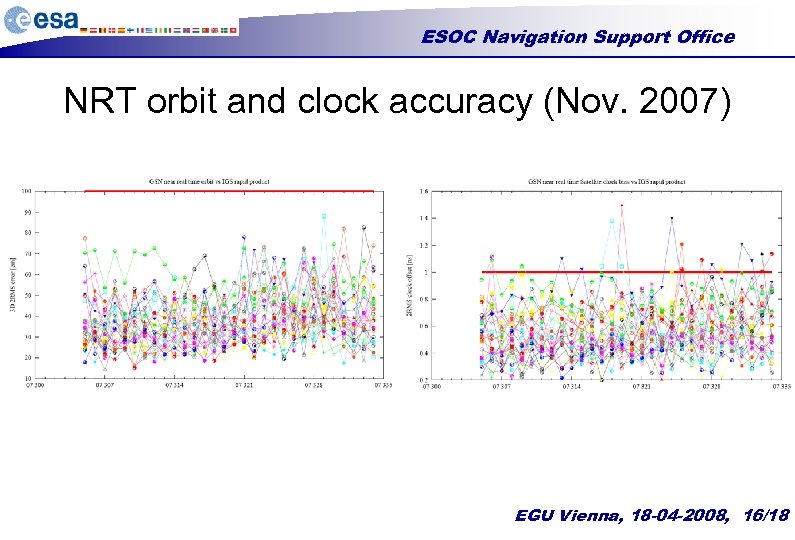 ESOC Navigation Support Office NRT orbit and clock accuracy (Nov. 2007) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 16/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office NRT orbit and clock accuracy (Nov. 2007) EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 16/18
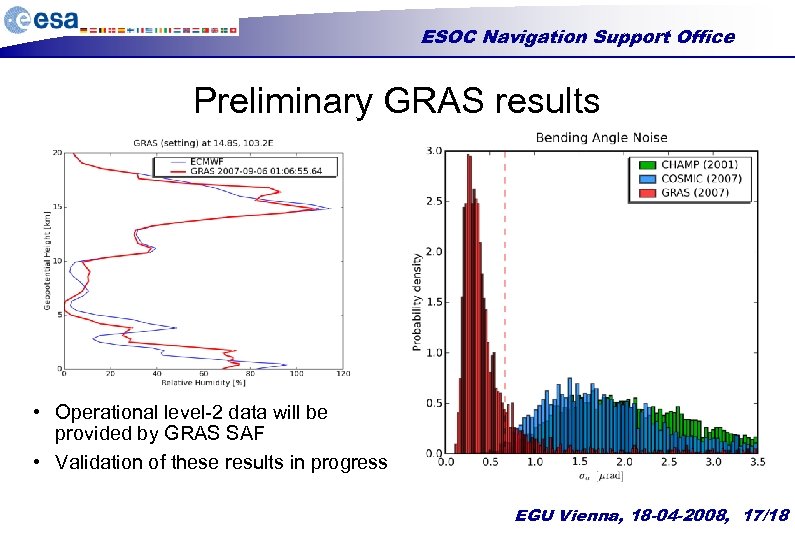 ESOC Navigation Support Office Preliminary GRAS results • Operational level-2 data will be provided by GRAS SAF • Validation of these results in progress EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 17/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Preliminary GRAS results • Operational level-2 data will be provided by GRAS SAF • Validation of these results in progress EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 17/18
 ESOC Navigation Support Office Acknowledgments are due to: • Station network providers: • Météo France Tahiti For the excellent quality of their support and data products • The EUMETSAT team: F. Wollenweber, C. Marquardt, Y. Andres • The ESOC team: ESA: A. Ballereau, R. Zandbergen, J. M. Dow GMV SA: M. Lorenzo, P. Alfaro, J. Tegedor, I. Romero, F. Lopes Pereira, C. Garcia, J. Fernandez EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 18/18
ESOC Navigation Support Office Acknowledgments are due to: • Station network providers: • Météo France Tahiti For the excellent quality of their support and data products • The EUMETSAT team: F. Wollenweber, C. Marquardt, Y. Andres • The ESOC team: ESA: A. Ballereau, R. Zandbergen, J. M. Dow GMV SA: M. Lorenzo, P. Alfaro, J. Tegedor, I. Romero, F. Lopes Pereira, C. Garcia, J. Fernandez EGU Vienna, 18 -04 -2008, 18/18


