15ecf3cc356166e51606b05db9955ada.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
Eshel Ben-Jacob Biochemistry & Cell Biology and CTBP, Rice University School of Physics & Astronomy, Tel Aviv University, Translating Cancer Data and Models to Clinical Practice Institute for Pure & Applied Mathematics, UCLA, Feb 10 -14, 2014

Cancer Continues to Elude Us Dormancy and Relapse Metastasis Multiple Drug Resistance Are little understood and clinically insuperable An even Greater Challenge is Posed by the Cancer–Immunity Interplay
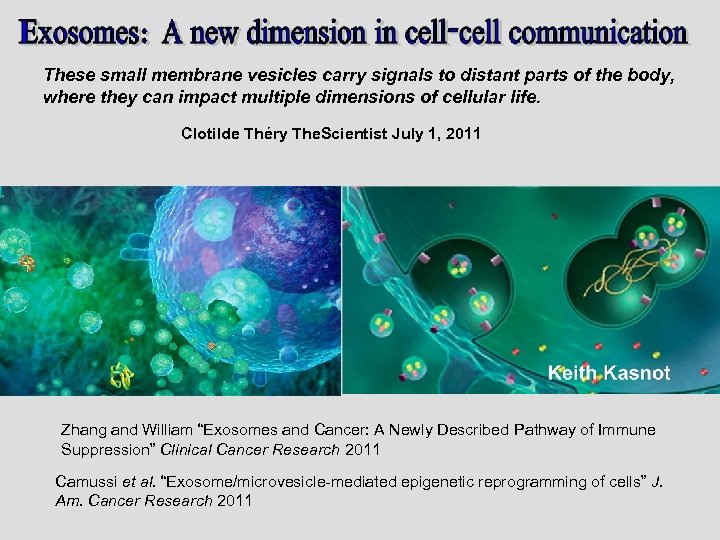
These small membrane vesicles carry signals to distant parts of the body, where they can impact multiple dimensions of cellular life. Clotilde Théry The. Scientist July 1, 2011 Zhang and William “Exosomes and Cancer: A Newly Described Pathway of Immune Suppression” Clinical Cancer Research 2011 Camussi et al. “Exosome/microvesicle-mediated epigenetic reprogramming of cells” J. Am. Cancer Research 2011
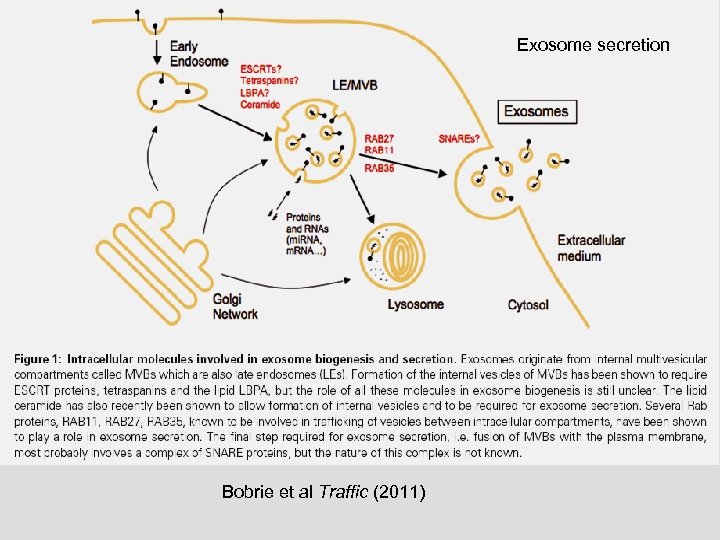
Exosome secretion Bobrie et al Traffic (2011)

A Crash Course in Immunology Rethinking the Immune System Networked society of smart cells Dendritic cells (DC) play a key role in the society’s control and command Exosome-mediated immunity Rethinking Cancer Networked society of smart cells Exosome-mediated tumorigenesis Exosome-based Cancer-Immunity Cyberwar Coaching the Immune System
Reflections on the Generic Modeling Approach The Realistic Trap vs. The Reminiscence Syndrome Simplifying the complexity by the art of generic modeling Ben-Jacob Nature 2002 Generic Modeling of the Exosome-mediated Interplay Rethinking the Cancer-Immunity Interplay Therapeutic Implications
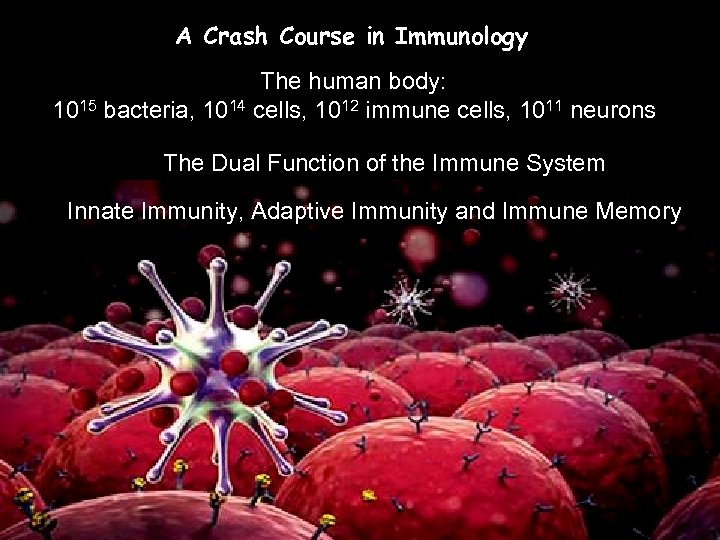
A Crash Course in Immunology The human body: 1015 bacteria, 1014 cells, 1012 immune cells, 1011 neurons The Dual Function of the Immune System Innate Immunity, Adaptive Immunity and Immune Memory
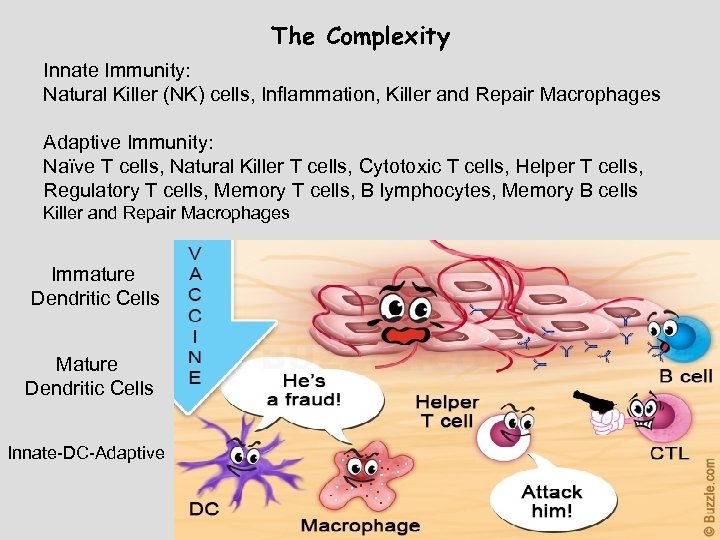
The Complexity Innate Immunity: Natural Killer (NK) cells, Inflammation, Killer and Repair Macrophages Adaptive Immunity: Naïve T cells, Natural Killer T cells, Cytotoxic T cells, Helper T cells, Regulatory T cells, Memory T cells, B lymphocytes, Memory B cells Killer and Repair Macrophages Immature Dendritic Cells Mature Dendritic Cells Helper T cells Innate-DC-Adaptive Dendritic Cell Naïve T cells
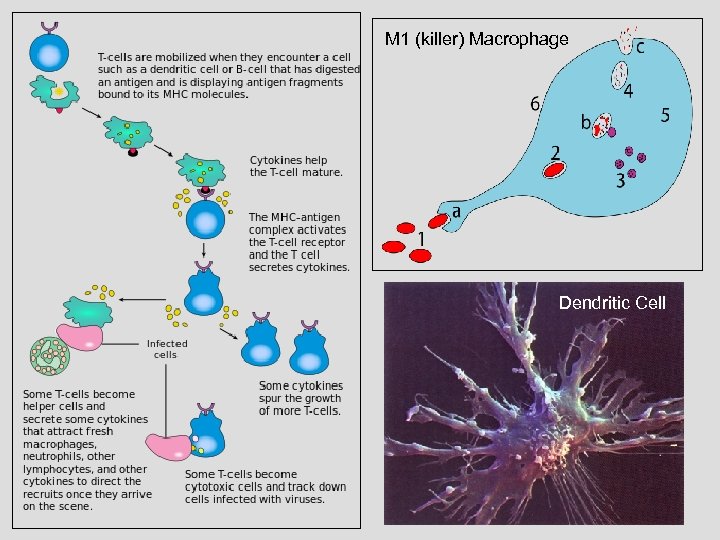
M 1 (killer) Macrophage Dendritic Cell

Networked Society of Smart Cells Immune Holography Immune development from Birth to Adulthood Madi et al. PNAS 2009, PLo. S ONE 2011, Bransbburg-Zabary et al. Phys. Bio 2013
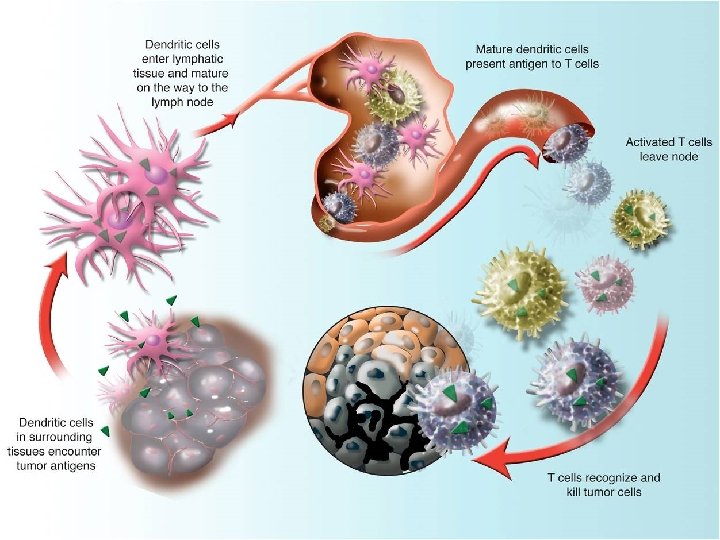
Hypothesis Dendritic Cells (DC) Play a key role in the society’s control and command Progenitors Mature DCs Bone Marrow (BM) Immature Dendritic cells DC and BM exosomes promote DC differentiation Blood circulation Tumor Stimulate the immune response Ben-Jacob m. Abs (monoclonoal antibodies) 2014
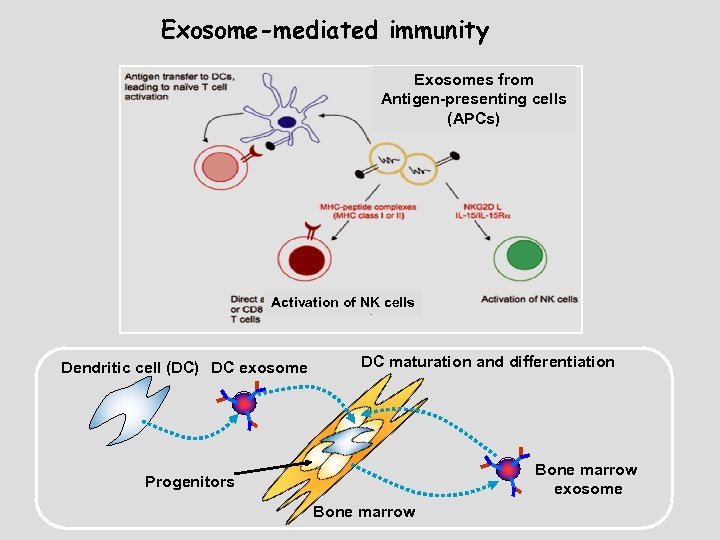
Exosome-mediated immunity Exosomes from Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) Activation of NK cells Dendritic cell (DC) DC exosome DC maturation and differentiation Bone marrow exosome Progenitors Bone marrow
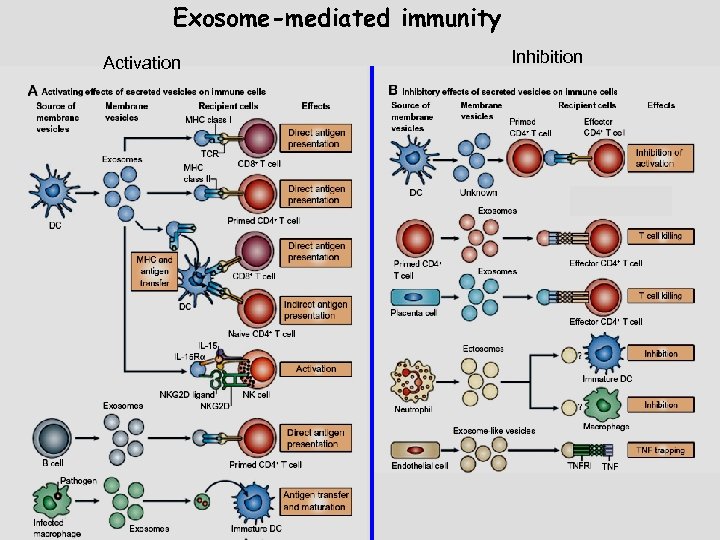
Exosome-mediated immunity Activation Inhibition

A Crash Course in Immunology Rethinking the Immune System Networked society of smart cells Dendritic cells (DC) play a key role in the society’s control and command Exosome-mediated immunity Rethinking Cancer Networked society of smart cells Exosome-mediated tumorigenesis Exosome-based Cancer-Immunity Cyberwar Coaching the Immune System

Learning from bacteria about cancer Cancer as a Networked Society of Smart Cells Ben-Jacob, Coffey, Levine Opinion in Trends in Microbiology (2012)
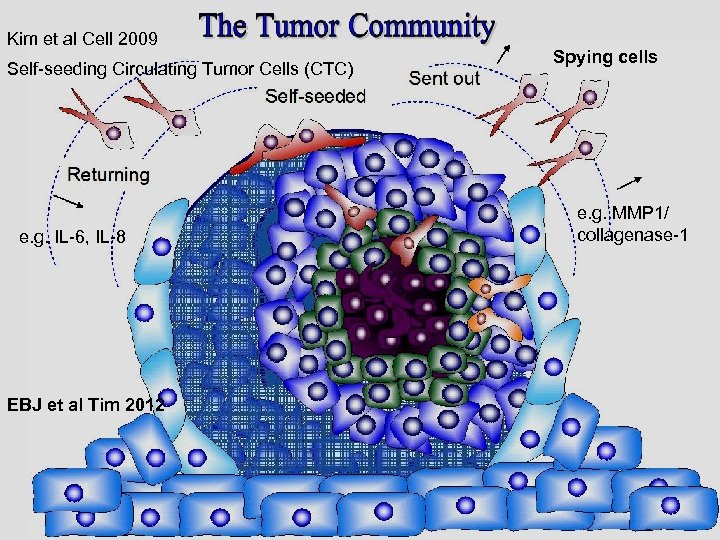
Kim et al Cell 2009 Self-seeding Circulating Tumor Cells (CTC) e. g. IL-6, IL-8 EBJ et al Tim 2012 Spying cells e. g. MMP 1/ collagenase-1
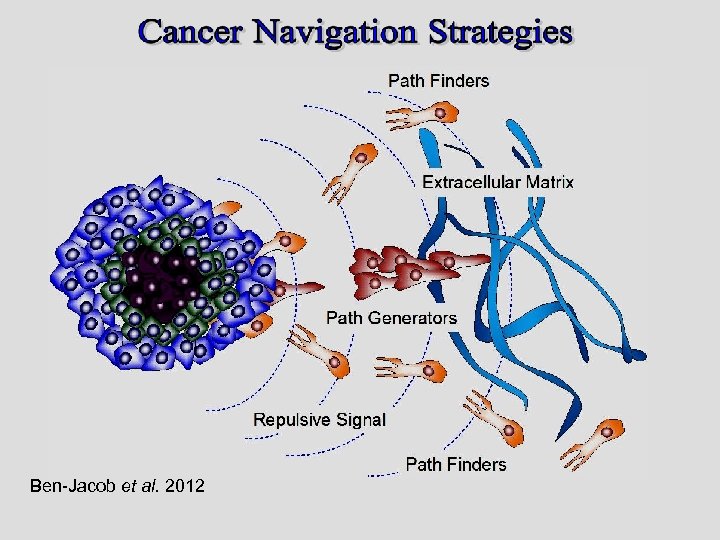
Path generating Path finding Ben-Jacob et al. 2012
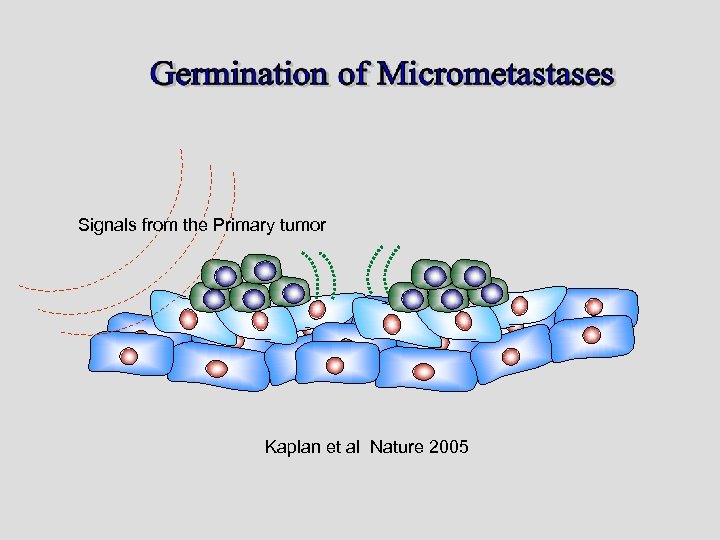
Signals from the Primary tumor Kaplan et al Nature 2005
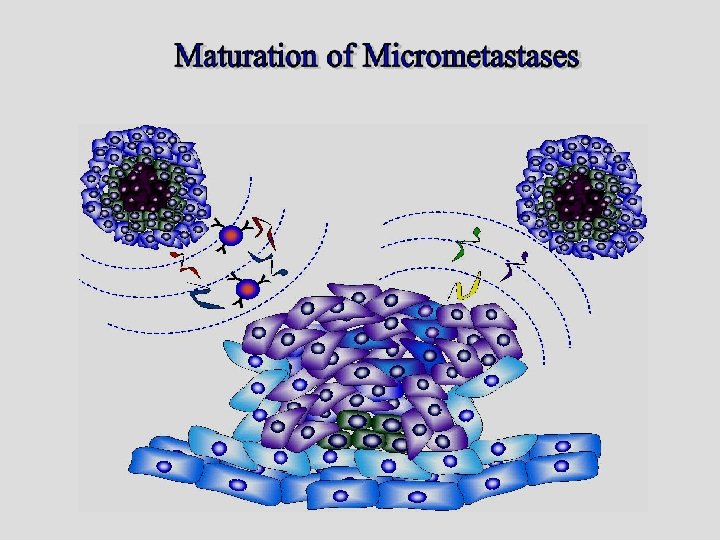
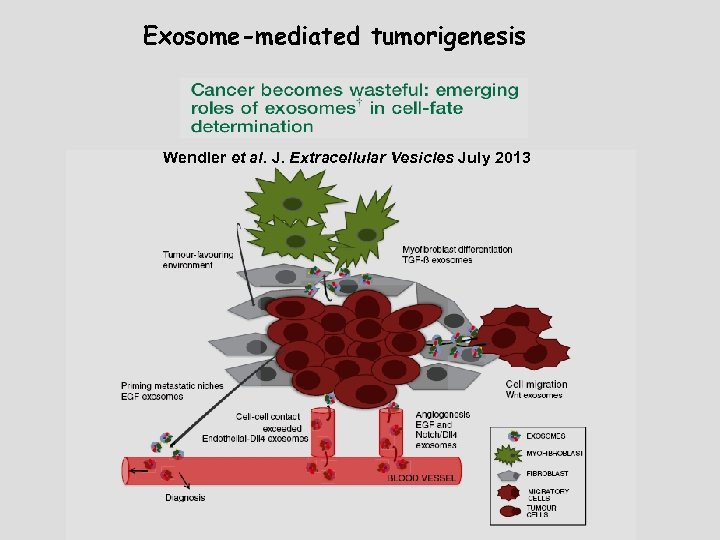
Exosome-mediated tumorigenesis Wendler et al. J. Extracellular Vesicles July 2013
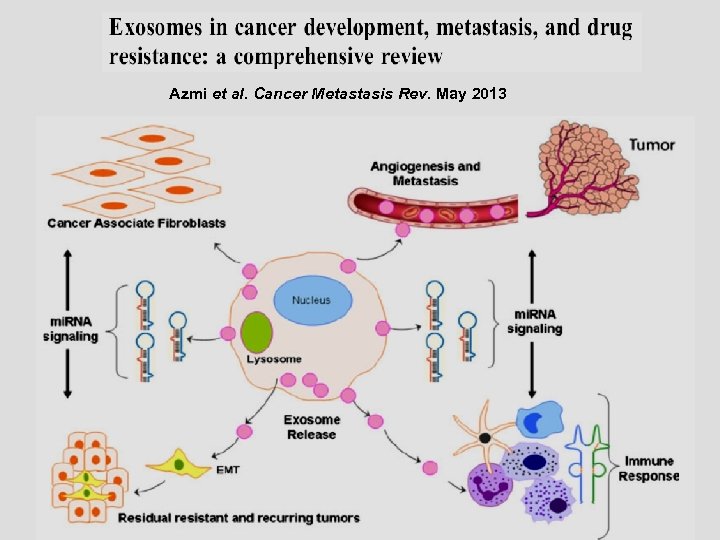
Azmi et al. Cancer Metastasis Rev. May 2013

Cancer Continues to Elude Us Tumor Can Evade and Deceive the Immune System Example: Tumor-Associated-Macrophages (TAMs) Bone marrow-derived leukocytes are solicited and directed by cancer to adopt unique phenotypes that can facilitate Tumor growth and survival. Rethinking the Cancer-Immunity Interplay A battle between two networked societies of smart cells
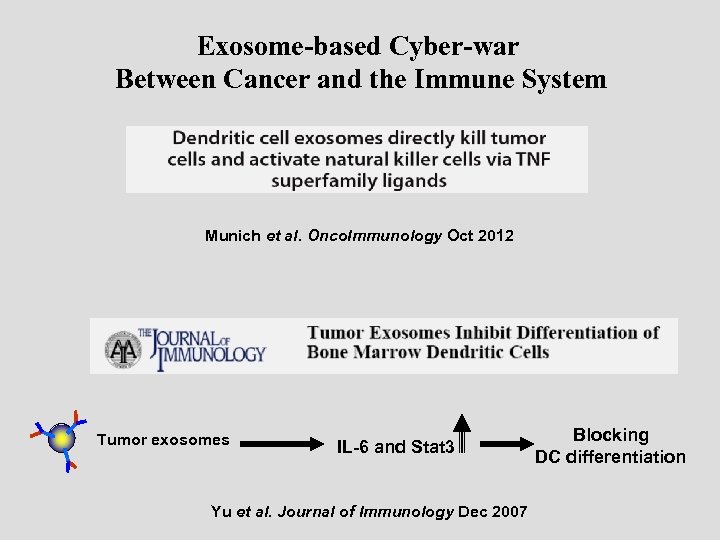
Exosome-based Cyber-war Between Cancer and the Immune System Munich et al. Onco. Immunology Oct 2012 Tumor exosomes IL-6 and Stat 3 Yu et al. Journal of Immunology Dec 2007 Blocking DC differentiation

Fed. Exosomes: Engineering Therapeutic Exosomes that Truly Deliver Towards Dialysis of Tumor Exosomes Using Bacteria to Coach Dendritic Cells Exosome-based Cancer Vaccination?
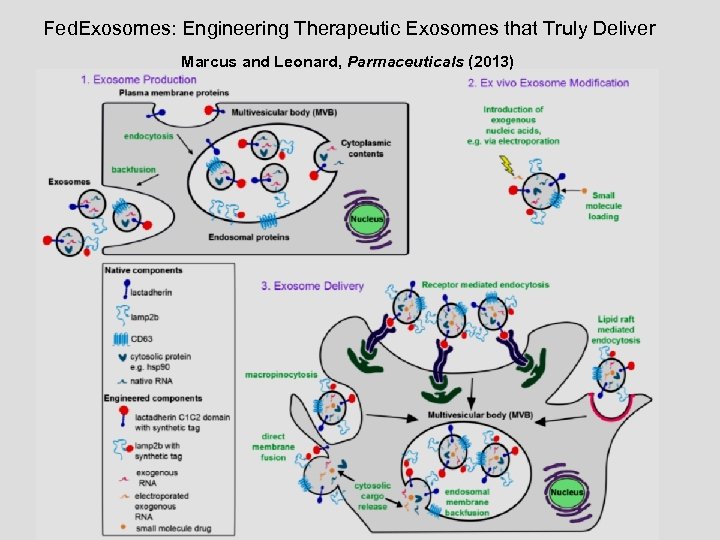
Fed. Exosomes: Engineering Therapeutic Exosomes that Truly Deliver Marcus and Leonard, Parmaceuticals (2013)
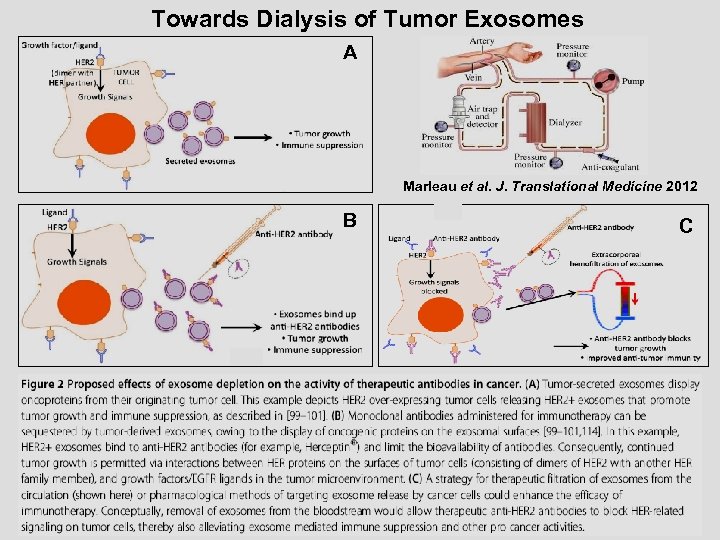
Towards Dialysis of Tumor Exosomes A Marleau et al. J. Translational Medicine 2012 B C

Using Bacteria to Coach Dendritic Cells Ben-Jacob et al Trends in Microbiology 2012 Next: Engineering Exosome-secreting Bacteria
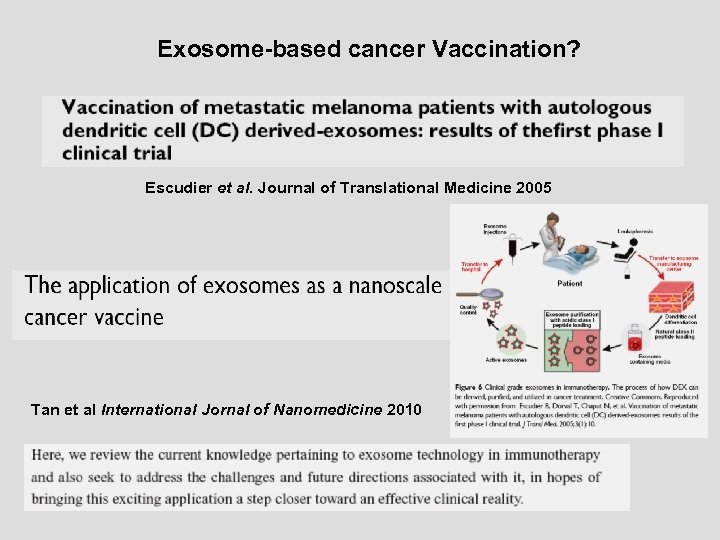
Exosome-based cancer Vaccination? Escudier et al. Journal of Translational Medicine 2005 Tan et al International Jornal of Nanomedicine 2010
Reflections on the Generic Modeling Approach The Realistic Trap vs. The Reminiscence Syndrome Simplifying the complexity by the art of generic modeling Ben-Jacob Nature 2002 Generic Modeling of the Exosome-mediated Interplay Rethinking the Cancer-Immunity Interplay Therapeutic Implications

Support at Rice Mingyang Lu, Rice Univ. Jose’ Onuchic, Rice Univ. Bin Huang, Rice Univ. Sam Hanash, MD Anderson Eshel Ben-Jacob, Rice And Tel Aviv Univ. Support at Tel Aviv: The Tauber Family Funds and the Maguey-Glass Chair
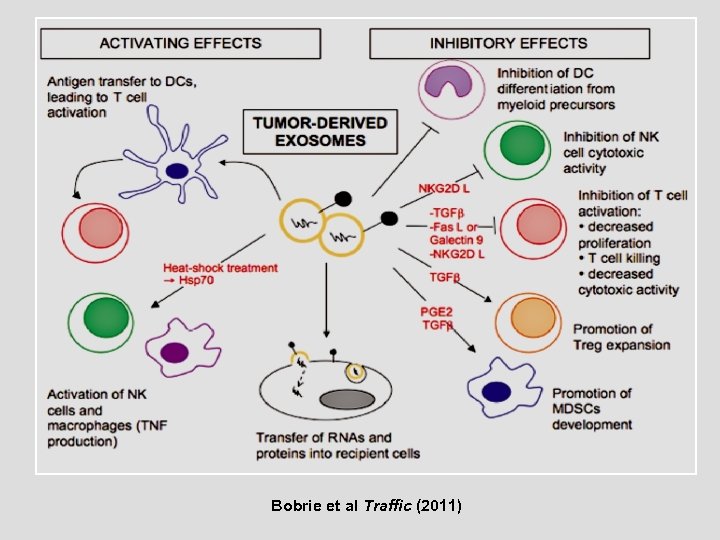
Bobrie et al Traffic (2011)
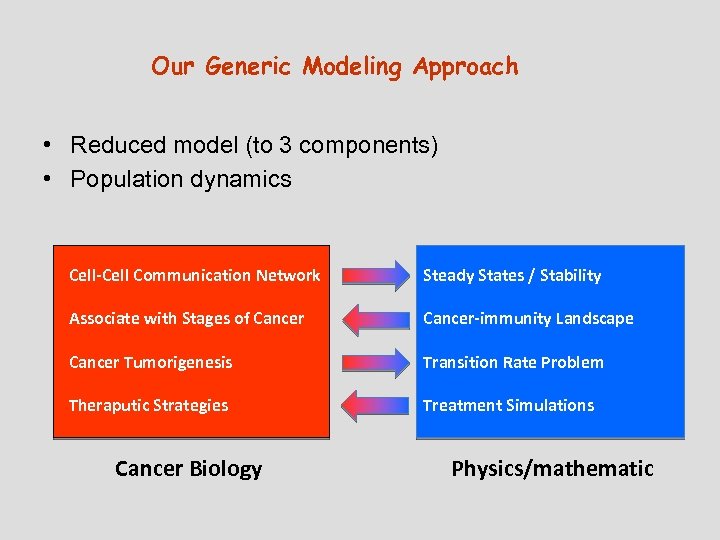
Our Generic Modeling Approach • Reduced model (to 3 components) • Population dynamics Cell-Cell Communication Network Steady States / Stability Associate with Stages of Cancer-immunity Landscape Cancer Tumorigenesis Transition Rate Problem Theraputic Strategies Treatment Simulations Cancer Biology Physics/mathematic
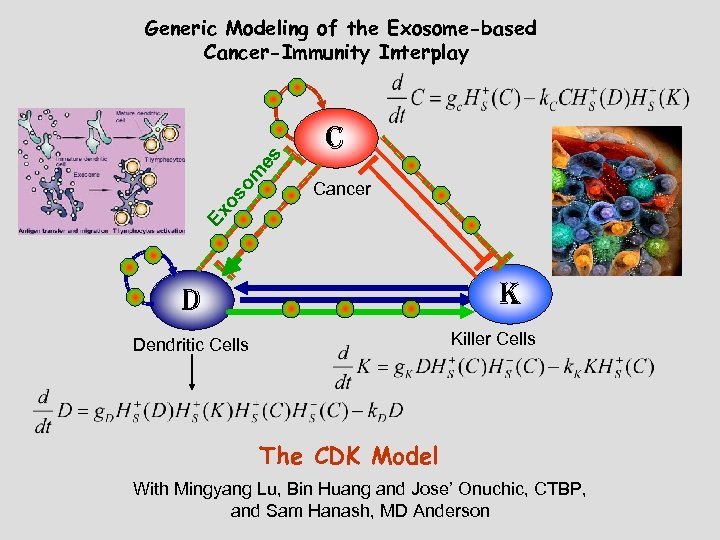
C Cancer Ex os om es Generic Modeling of the Exosome-based Cancer-Immunity Interplay K D Killer Cells Dendritic Cells The CDK Model With Mingyang Lu, Bin Huang and Jose’ Onuchic, CTBP, and Sam Hanash, MD Anderson
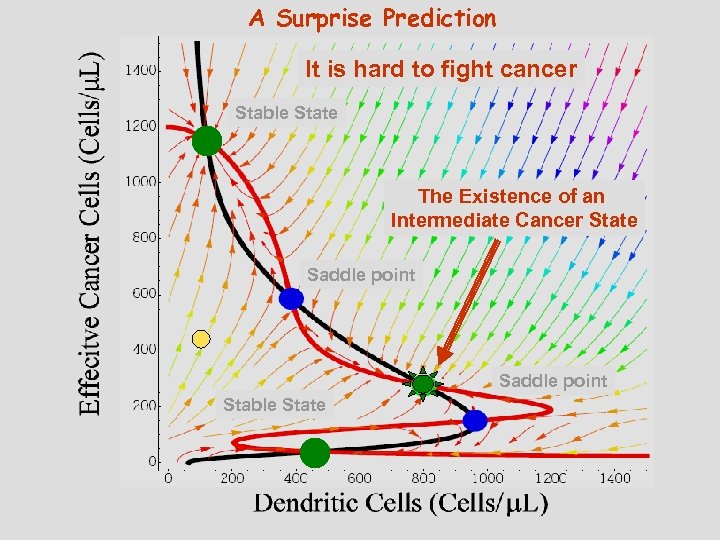
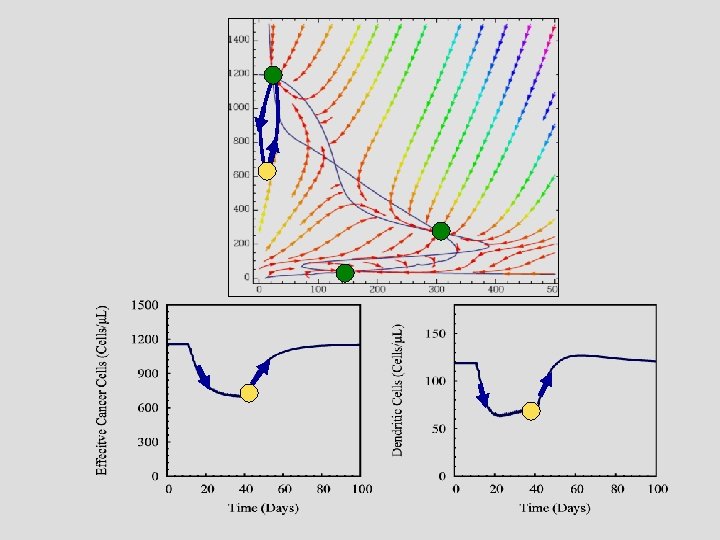
A Surprise Prediction It is hard to fight cancer Stable State The Existence of an Intermediate Cancer State Saddle point Stable State
The effect of immune recognition The meaning of steady-state solutions in light of tumorigenesis The Singular Effect of Exosomes The Effect of Time Delay Therapeutic implications Reassuring retrospect agreement The risk of over treatment The need for two stage therapy
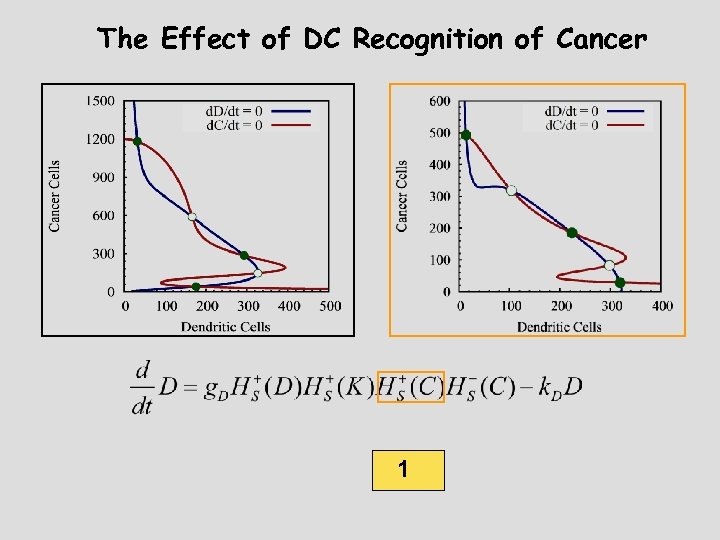
The Effect of DC Recognition of Cancer 1
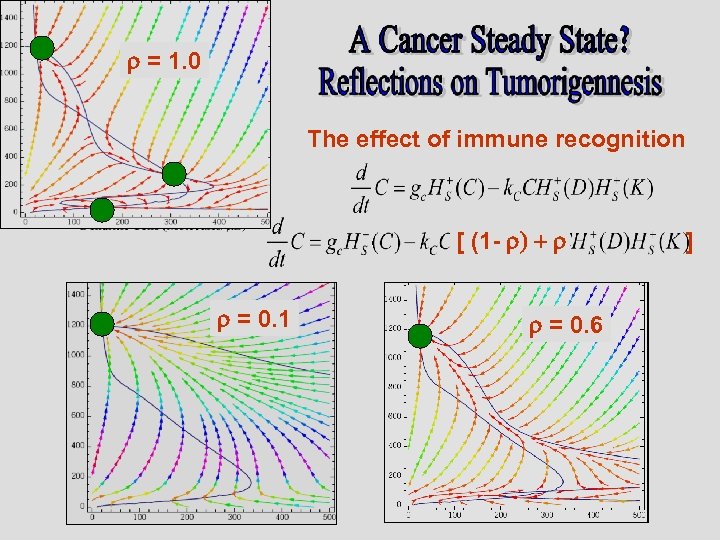
r = 1. 0 The effect of immune recognition [ (1 - r) + r r = 0. 1 r = 0. 6 ]
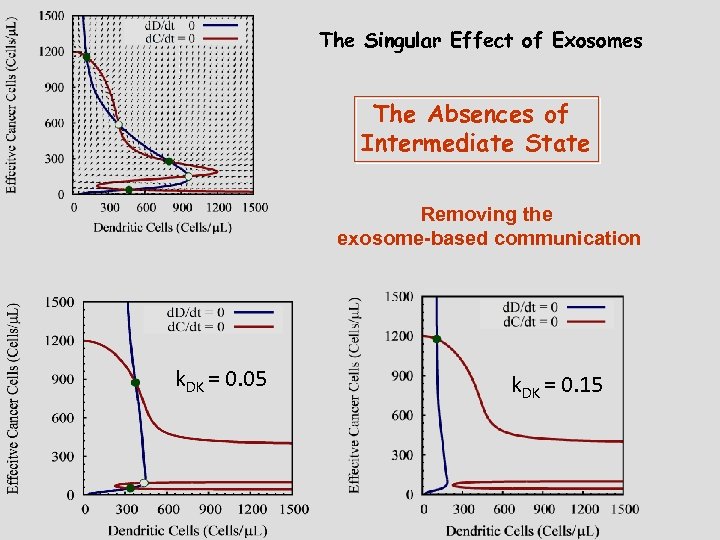
The Singular Effect of Exosomes The Absences of Intermediate State Removing the exosome-based communication k. DK = 0. 05 k. DK = 0. 15
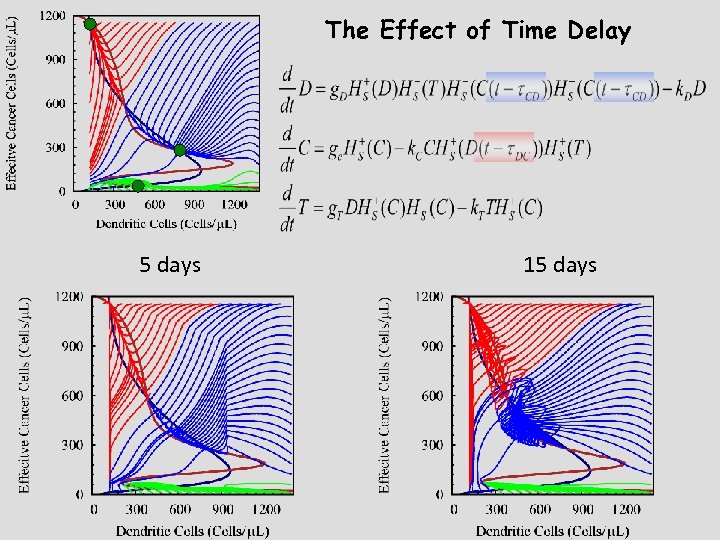
The Effect of Time Delay 5 days 15 days
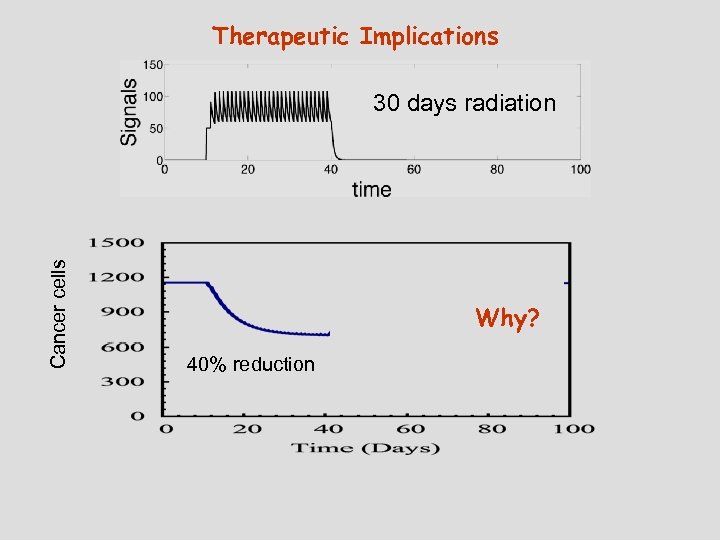
Therapeutic Implications Cancer cells 30 days radiation Why? 40% reduction
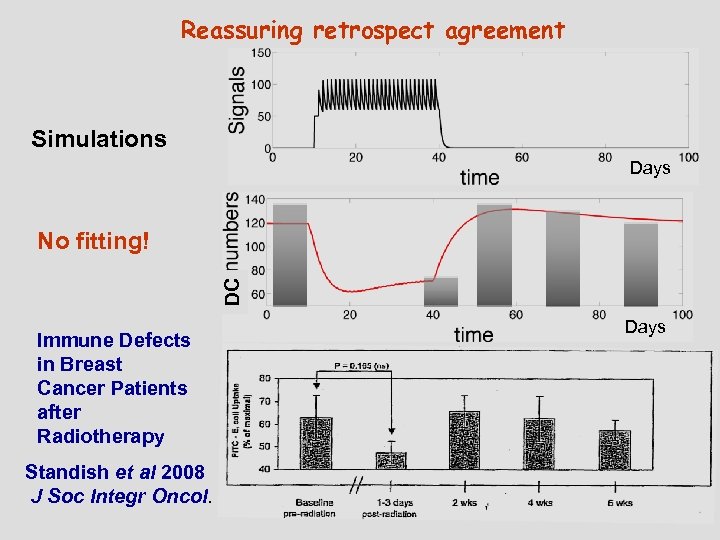
Reassuring retrospect agreement Simulations Days DC No fitting! Immune Defects in Breast Cancer Patients after Radiotherapy Standish et al 2008 J Soc Integr Oncol. Days

Therapeutic Implications – The Need for Two Stage therapy Stage I Therapy: H 2 IT Inducing High to Intermediate Cancer State Transitions Stage II Therapy: I 2 LT Inducing Intermediate to Low Cancer State Transitions
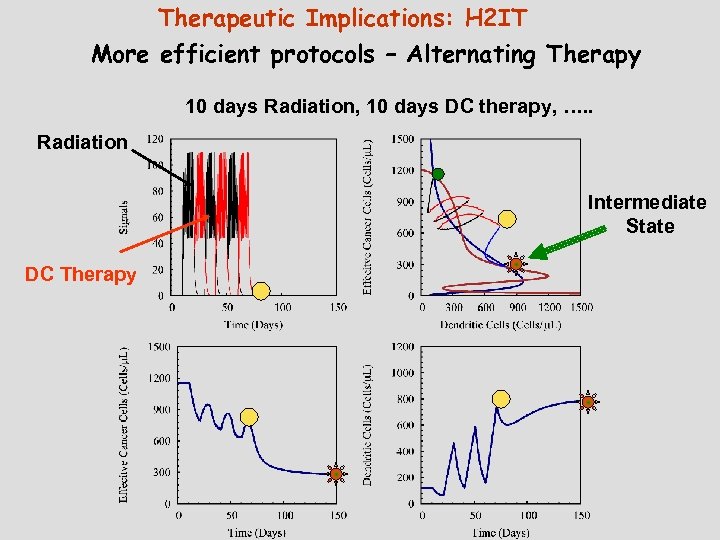
Therapeutic Implications: H 2 IT More efficient protocols – Alternating Therapy 10 days Radiation, 10 days DC therapy, …. . Radiation Intermediate State DC Therapy
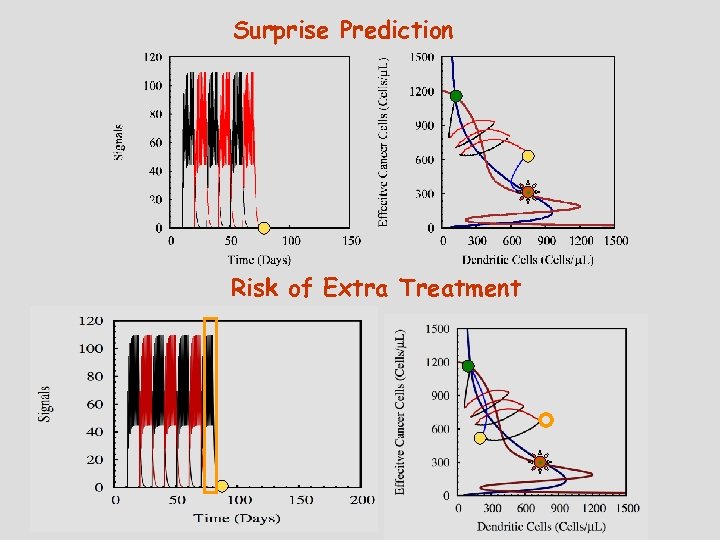
Surprise Prediction Risk of Extra Treatment
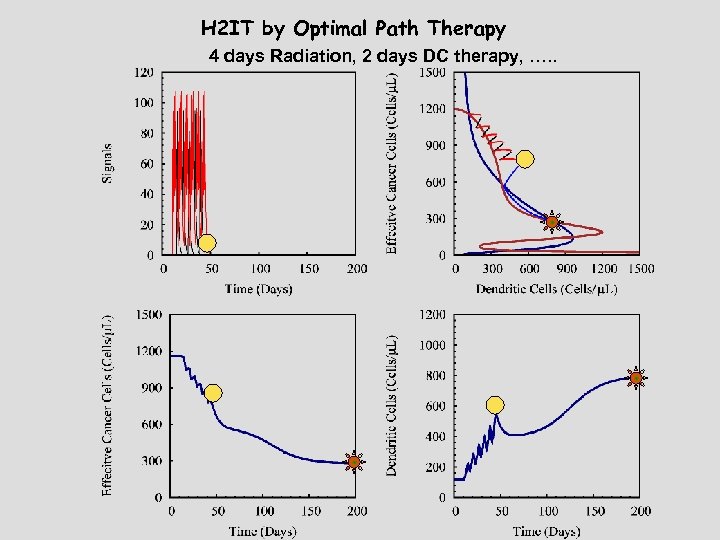
H 2 IT by Optimal Path Therapy 4 days Radiation, 2 days DC therapy, …. .
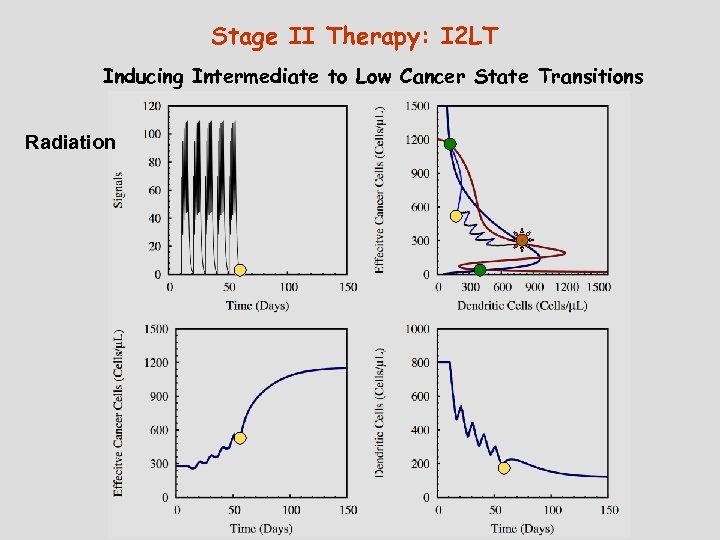
Stage II Therapy: I 2 LT Inducing Intermediate to Low Cancer State Transitions Radiation
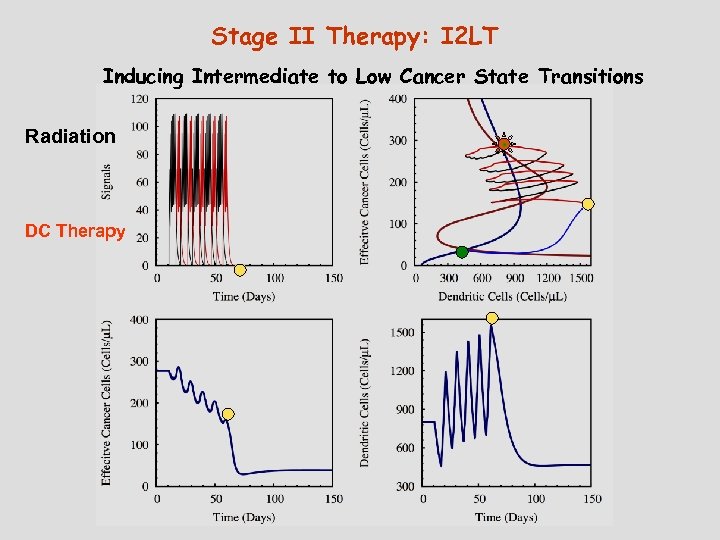
Stage II Therapy: I 2 LT Inducing Intermediate to Low Cancer State Transitions Radiation DC Therapy
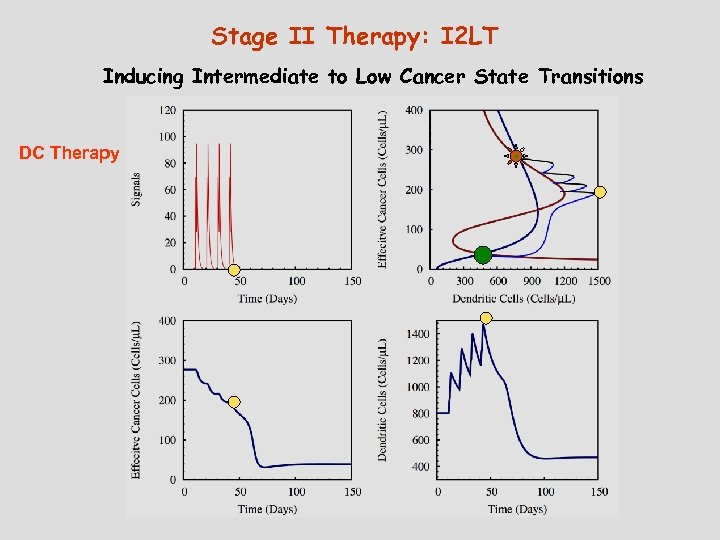
Stage II Therapy: I 2 LT Inducing Intermediate to Low Cancer State Transitions DC Therapy

New Hope Rethinking the Interplay Between Cancer and the Immune System Understanding the Role of Exosomes The Existence of Intermediate State Optimal Path Based Alternating Therapy Two stage Therapy The End
15ecf3cc356166e51606b05db9955ada.ppt