b85bf8517b8cd77378f83bed93b8a1e6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Era of Good Feelings Creating a Nation
Era of Good Feelings Creating a Nation
 Henry Clay’s: American System • Creation of a plan to unify the nation: • Developing transportation systems and other internal improvements • Establishing a protective tariff • Resurrecting the national bank
Henry Clay’s: American System • Creation of a plan to unify the nation: • Developing transportation systems and other internal improvements • Establishing a protective tariff • Resurrecting the national bank

 Transportation and Internal Improvements • National Road: Began in 1811 by 1838 connected Cumberland Maryland to Vandalia, Illinois • Erie Canal: took eight years, by 1825 it connected Lake Erie to the Hudson River providing a water way from Great Lakes to Atlantic Ocean • Tolls were paid to use the route, in twelve years it was paid for • Cut shipping costs, reducing selling prices
Transportation and Internal Improvements • National Road: Began in 1811 by 1838 connected Cumberland Maryland to Vandalia, Illinois • Erie Canal: took eight years, by 1825 it connected Lake Erie to the Hudson River providing a water way from Great Lakes to Atlantic Ocean • Tolls were paid to use the route, in twelve years it was paid for • Cut shipping costs, reducing selling prices
 Transportation
Transportation
 Tariffs and the National Bank • Tariff of 1816: In order to pay for these new improvements such as roads, canals, and lighthouses taxes were placed on imports. • In 1816 with much approval, the 2 nd Bank of the United States was created.
Tariffs and the National Bank • Tariff of 1816: In order to pay for these new improvements such as roads, canals, and lighthouses taxes were placed on imports. • In 1816 with much approval, the 2 nd Bank of the United States was created.
 The Rise of New York City • With these new national improvements New York rose above all other cities to become the center of economic, social, and political growth. (example: Erie Canal) • Leader in banking, finance, foreign trade, manufacturing, fashion, publishing, broadcasting, culture, and tourism • Busiest port in the country
The Rise of New York City • With these new national improvements New York rose above all other cities to become the center of economic, social, and political growth. (example: Erie Canal) • Leader in banking, finance, foreign trade, manufacturing, fashion, publishing, broadcasting, culture, and tourism • Busiest port in the country

 Nationalism • Nationalism: a social movement focusing on the nation. • National interests should be placed ahead of regional or the interests of other countries. • Mc. Culloch v. Maryland: • Maryland placed high taxes on a branch of the Bank of U. S. • Marshall denied the right of Maryland to tax the bank. • Declaring the Bank of U. S. constitutional. • Strengthens nationalism.
Nationalism • Nationalism: a social movement focusing on the nation. • National interests should be placed ahead of regional or the interests of other countries. • Mc. Culloch v. Maryland: • Maryland placed high taxes on a branch of the Bank of U. S. • Marshall denied the right of Maryland to tax the bank. • Declaring the Bank of U. S. constitutional. • Strengthens nationalism.
 The United States Expands Westward Migration • From 1800– 1810, Ohio population grows from 45, 000 to 231, 000 • Most settlers use Cumberland Gap to reach Ohio, Kentucky, Tennessee • In 1775, Daniel Boone leads clearing of Wilderness Road
The United States Expands Westward Migration • From 1800– 1810, Ohio population grows from 45, 000 to 231, 000 • Most settlers use Cumberland Gap to reach Ohio, Kentucky, Tennessee • In 1775, Daniel Boone leads clearing of Wilderness Road
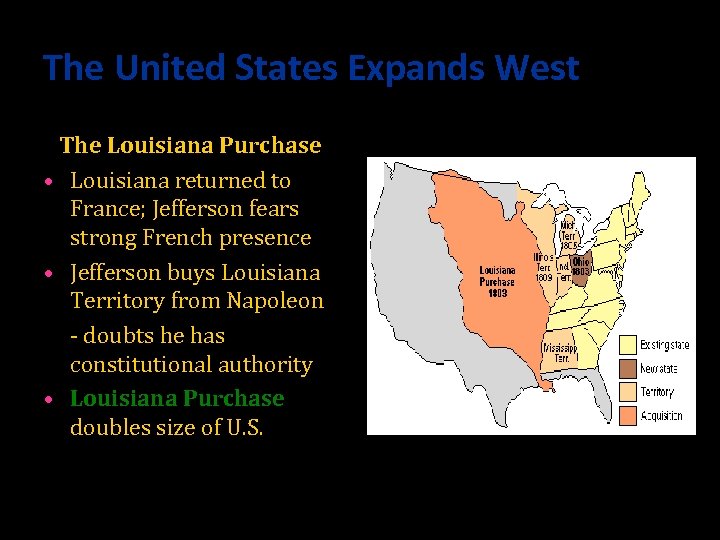 The United States Expands West The Louisiana Purchase • Louisiana returned to France; Jefferson fears strong French presence • Jefferson buys Louisiana Territory from Napoleon - doubts he has constitutional authority • Louisiana Purchase doubles size of U. S.
The United States Expands West The Louisiana Purchase • Louisiana returned to France; Jefferson fears strong French presence • Jefferson buys Louisiana Territory from Napoleon - doubts he has constitutional authority • Louisiana Purchase doubles size of U. S.
 The U. S. Expands West Lewis and Clark • Jefferson appoints Lewis and Clark to lead Corps of Discovery: - explore new territory, find route to Pacific - gather information about people, plants animals • Native American woman, Sacajawea, serves as interpreter, guide
The U. S. Expands West Lewis and Clark • Jefferson appoints Lewis and Clark to lead Corps of Discovery: - explore new territory, find route to Pacific - gather information about people, plants animals • Native American woman, Sacajawea, serves as interpreter, guide
 Land Ordinance of 1785 • Establishment of a system for surveying and subdividing public land outside the states • Blocks of land 36 square miles each, townships • Set aside land for public educ. and schools, with each section containing 640 acres.
Land Ordinance of 1785 • Establishment of a system for surveying and subdividing public land outside the states • Blocks of land 36 square miles each, townships • Set aside land for public educ. and schools, with each section containing 640 acres.
 Northwest Ordinance of 1787 • Specified how territories could become states • Leads to Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan and Wisconsin • Congress appointed governor, secretary, and 3 judges • When adult male pop. Reached 5, 000 send nonvoting rep. to congress • Pop. Reached 60, 000 eligible for statehood • Forbade slavery, guaranteed trial by jury, and freedom of religion • Encouraged support for education
Northwest Ordinance of 1787 • Specified how territories could become states • Leads to Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan and Wisconsin • Congress appointed governor, secretary, and 3 judges • When adult male pop. Reached 5, 000 send nonvoting rep. to congress • Pop. Reached 60, 000 eligible for statehood • Forbade slavery, guaranteed trial by jury, and freedom of religion • Encouraged support for education
 War of 1812 Second War for Independence
War of 1812 Second War for Independence
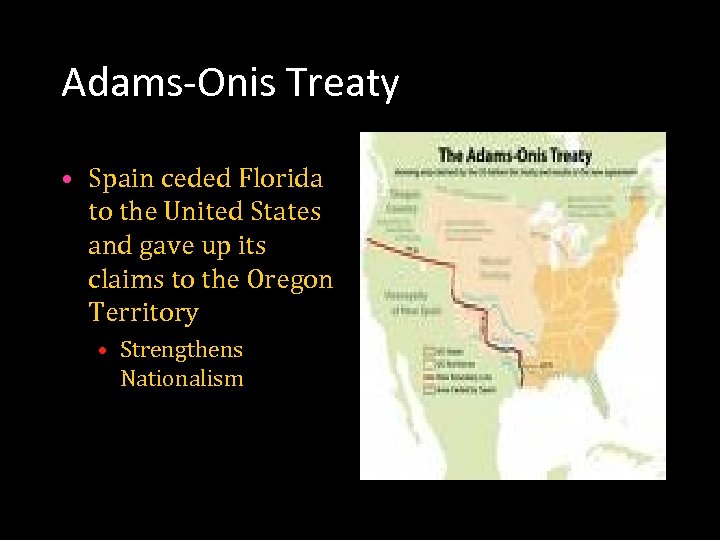 Adams-Onis Treaty • Spain ceded Florida to the United States and gave up its claims to the Oregon Territory • Strengthens Nationalism
Adams-Onis Treaty • Spain ceded Florida to the United States and gave up its claims to the Oregon Territory • Strengthens Nationalism
 Monroe Doctrine • U. S. wouldn’t interfere with European colonies already established but would not tolerate further colonization • Europe: Leave the Western Hemisphere alone. If you don’t it will be seen as a threat to Am. Safety and could be reason for war • How does this strengthen nationalism?
Monroe Doctrine • U. S. wouldn’t interfere with European colonies already established but would not tolerate further colonization • Europe: Leave the Western Hemisphere alone. If you don’t it will be seen as a threat to Am. Safety and could be reason for war • How does this strengthen nationalism?

 Industrial Revolution • Transformation during the 1700’s and early 1800’s from making goods in small shops or homes by hand to making them in factories with machines. • Changed the world from a rural, agricultural society to an urban and industrial one.
Industrial Revolution • Transformation during the 1700’s and early 1800’s from making goods in small shops or homes by hand to making them in factories with machines. • Changed the world from a rural, agricultural society to an urban and industrial one.

 Early Inventions: Eli Whitney • Cotton Gin: Separated seeds from cotton • Before it took a person a full day to remove seeds from 1 lb. of cotton • Made cotton profitable, increasing demand for slaves • Enabled a person to process 50 lbs. /day
Early Inventions: Eli Whitney • Cotton Gin: Separated seeds from cotton • Before it took a person a full day to remove seeds from 1 lb. of cotton • Made cotton profitable, increasing demand for slaves • Enabled a person to process 50 lbs. /day
 Early Inventions: Eli Whitney • Interchangeable parts: • Whitney received a contract for 10, 000 muskets in 1798 and used interchangeable parts to manufacture firearms in his factory • One of the first uses of mass production methods • Influence Henry Ford, Samuel Colt and others
Early Inventions: Eli Whitney • Interchangeable parts: • Whitney received a contract for 10, 000 muskets in 1798 and used interchangeable parts to manufacture firearms in his factory • One of the first uses of mass production methods • Influence Henry Ford, Samuel Colt and others
 Westward Expansion • Manifest Destiny: Belief that the United States Destiny was to extend to the Pacific Ocean
Westward Expansion • Manifest Destiny: Belief that the United States Destiny was to extend to the Pacific Ocean
 Native Americans and Manifest Destiny • Treaty of Ft. Laramie: provided various Native American nations control of the Central Plains. • In turn Native Americans promised not to attack settlers and to allow construction of government forts and roads. Government would make payments to them. • Movement of settlers increase, decreasing the number of buffalo and elk. U. S. violated terms of treaty
Native Americans and Manifest Destiny • Treaty of Ft. Laramie: provided various Native American nations control of the Central Plains. • In turn Native Americans promised not to attack settlers and to allow construction of government forts and roads. Government would make payments to them. • Movement of settlers increase, decreasing the number of buffalo and elk. U. S. violated terms of treaty
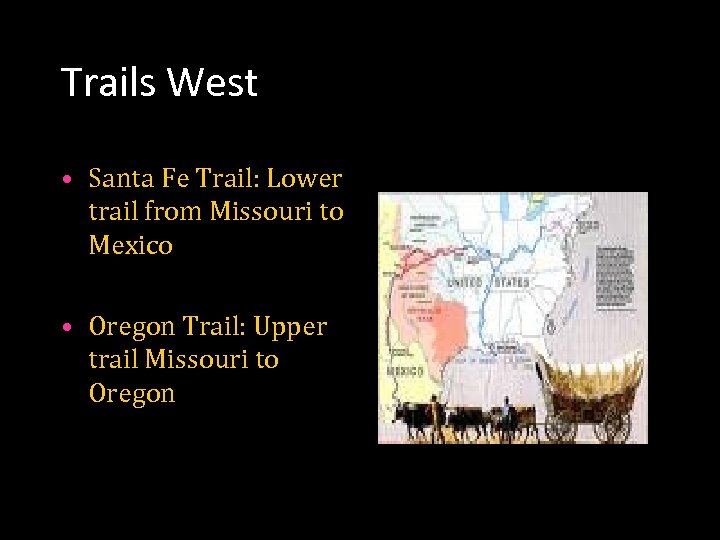 Trails West • Santa Fe Trail: Lower trail from Missouri to Mexico • Oregon Trail: Upper trail Missouri to Oregon
Trails West • Santa Fe Trail: Lower trail from Missouri to Mexico • Oregon Trail: Upper trail Missouri to Oregon
 Prison Reform • Dorothea Dix: known as prison reformer • Dix discovered that jails often house mentally ill people. • Began to emphasize rehabilitation and treatment
Prison Reform • Dorothea Dix: known as prison reformer • Dix discovered that jails often house mentally ill people. • Began to emphasize rehabilitation and treatment
 School Reform • Before mid 1800’s no uniform education policy existed • Mass. And Vermont were the only states before Civil War that passed compulsory school laws. • All children were in one classroom • By 1830’s demand for tax supported public schools • By 1833 42 percent of elem. School aged children were attending public school
School Reform • Before mid 1800’s no uniform education policy existed • Mass. And Vermont were the only states before Civil War that passed compulsory school laws. • All children were in one classroom • By 1830’s demand for tax supported public schools • By 1833 42 percent of elem. School aged children were attending public school

 Slavery Reform • Abolitionism: call to outlaw slavery • Frederick Douglas: Born into slavery: knowledge is the pathway from slavery to freedom, pushed for abolitionism • What was slavery like?
Slavery Reform • Abolitionism: call to outlaw slavery • Frederick Douglas: Born into slavery: knowledge is the pathway from slavery to freedom, pushed for abolitionism • What was slavery like?
 Women and Reform • Sarah and Angelina Grimke: daughters of a SC slaveholder • Women abolitionist: • Mary C. Vaughn: temperance movement • The effort to prohibit the drinking of alcohol
Women and Reform • Sarah and Angelina Grimke: daughters of a SC slaveholder • Women abolitionist: • Mary C. Vaughn: temperance movement • The effort to prohibit the drinking of alcohol
 Women and Reform • Elizabeth Cady Stanton: • Women’s Rights Movement • Seneca Falls Convention • Creation of Declaration of Women’s Rights − Suffrage/right to vote
Women and Reform • Elizabeth Cady Stanton: • Women’s Rights Movement • Seneca Falls Convention • Creation of Declaration of Women’s Rights − Suffrage/right to vote
 The Age of Jackson • The Election of 1824 • Jackson wins the popular vote but lacked the electoral college votes • John Quincy Adams names Henry Clay as Secretary of State: “corrupt bargaining”
The Age of Jackson • The Election of 1824 • Jackson wins the popular vote but lacked the electoral college votes • John Quincy Adams names Henry Clay as Secretary of State: “corrupt bargaining”
 Age of Jackson • Jackson wins the Election of 1828 • Spoils system gives government jobs to supporters
Age of Jackson • Jackson wins the Election of 1828 • Spoils system gives government jobs to supporters
 Jacksonian Democracy • Believed in Western Expansion • Universal Suffrage- all white men should be able to vote not just property owners • “Common Man” • Laissez-Faire- Hands Off • Strict interpretation of the Constitution
Jacksonian Democracy • Believed in Western Expansion • Universal Suffrage- all white men should be able to vote not just property owners • “Common Man” • Laissez-Faire- Hands Off • Strict interpretation of the Constitution
 Age of Jackson • The Indian Removal Act forces Native Americans off their lands • Supreme Court rules Georgia cannot give orders to Cherokee • Worcester v. Georgia
Age of Jackson • The Indian Removal Act forces Native Americans off their lands • Supreme Court rules Georgia cannot give orders to Cherokee • Worcester v. Georgia
 States’ Rights: South Faces Economic Problems • Rise in tariff (tariff of 1828) • Tariff of Abominations: • lowers sale of British goods and Southern cotton • South forced to buy expensive Northern goods
States’ Rights: South Faces Economic Problems • Rise in tariff (tariff of 1828) • Tariff of Abominations: • lowers sale of British goods and Southern cotton • South forced to buy expensive Northern goods
 The Nullification Crisis • Calhoun’s idea of nullification: states say if law is constitutional • South Carolina declares Tariff of 1828 null; threatens secession (leave the union) • Compromise bill lowers tariff
The Nullification Crisis • Calhoun’s idea of nullification: states say if law is constitutional • South Carolina declares Tariff of 1828 null; threatens secession (leave the union) • Compromise bill lowers tariff
 Jackson’s Bank War • Federal funds removed from Bank of the U. S. ; put in PET state banks • Jackson’s policies angered many including some in his own political party (Republicans). They formed the Whig party • Whig’s promoted the ideas of Henry Clay’s American System.
Jackson’s Bank War • Federal funds removed from Bank of the U. S. ; put in PET state banks • Jackson’s policies angered many including some in his own political party (Republicans). They formed the Whig party • Whig’s promoted the ideas of Henry Clay’s American System.
 Election of 1836 • Democrat Martin Van Buren wins election with Jackson’s support
Election of 1836 • Democrat Martin Van Buren wins election with Jackson’s support
 The Panic of 1837 • Many pet banks print money in excess of gold and silver deposits • Banks close, credit system collapses, 1/3 of population jobless
The Panic of 1837 • Many pet banks print money in excess of gold and silver deposits • Banks close, credit system collapses, 1/3 of population jobless
 Trail of Tears • U. S. soldiers force Cherokee to march west along Trail of Tears • on the 800 mile trip many Cherokee died en route. Burying more that ¼ of their people.
Trail of Tears • U. S. soldiers force Cherokee to march west along Trail of Tears • on the 800 mile trip many Cherokee died en route. Burying more that ¼ of their people.


