9964be519245df71456b16a75077c5f3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Equity Valuation
Methods • Balance Sheet Models • Discounted Cash Flow Models • Multiplier Models
Balance Sheet Models • • Book Value Liquidation Value Replacement Cost Tobin’s q Ratio

Book Value • Book Value of Common Equity – Assets – Liabilities • Divide by Common Shares Outstanding gives Book Value per Share • Sensitive to accounting methods used • Inventory accounting • Leasing v. purchasing of long-term assets

Liquidation Value • MVassets - MVliabilities – where MV = market value • Value kept by shareholders if the firm is broken up and sold off.
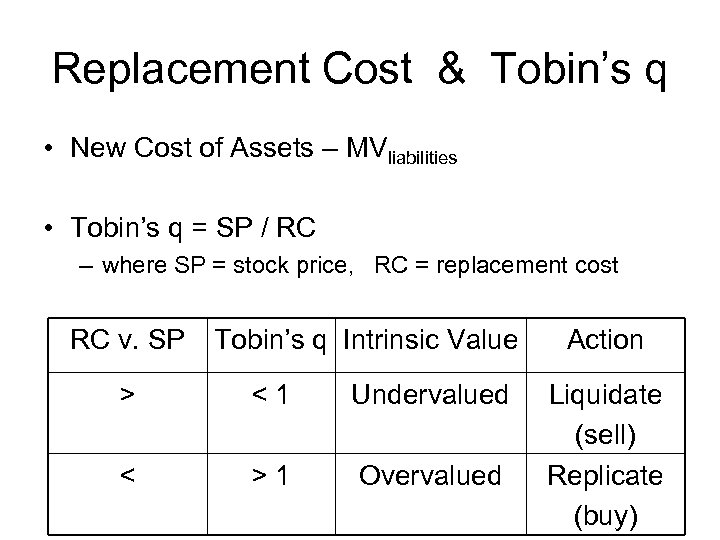
Replacement Cost & Tobin’s q • New Cost of Assets – MVliabilities • Tobin’s q = SP / RC – where SP = stock price, RC = replacement cost RC v. SP Tobin’s q Intrinsic Value > <1 Undervalued < >1 Overvalued Action Liquidate (sell) Replicate (buy)

Tobin’s q & the Market Tobin's q for the US market from 1900 to 2003. Shows when the market was overvalued or undervalued. When Tobin's q spiked upward in 1929 and 1999 the market was expensive.

Discounted Cash Flow Methods • Discounted Dividend Model • Discounted Free Cash Flow Model
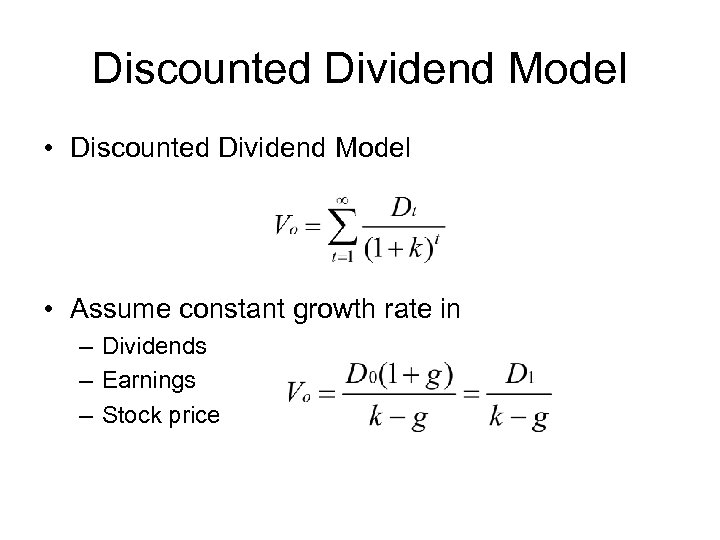
Discounted Dividend Model • Discounted Dividend Model • Assume constant growth rate in – Dividends – Earnings – Stock price

Example • Expected Net Income = $2, 000 • 1 million shares common • Half of income paid as dividends – EPS = $2 mil / 1 mil = $2. 00 per share – D = $2. 00 x 50% = $1. 00 per share • Discount Rate = 15% • Growth Rate = 5%

Example Vo SP Value Action $10 $12 ovevalued sell 10 10 fairly valued hold 10 8 undervalued buy

Discount Rate (k) • Required Rate of Return • Typically estimated from CAPM – Ki = TBill Rate + betai x Market Risk Premium

D 1 = $1. 00 g = 5% beta = 1. 0 Case TBill Rate MRP K V 0 1 6% 8% 14% $11. 1 1 2 8% 8% 16% $9. 09 3 8% 12% 20% $6. 67
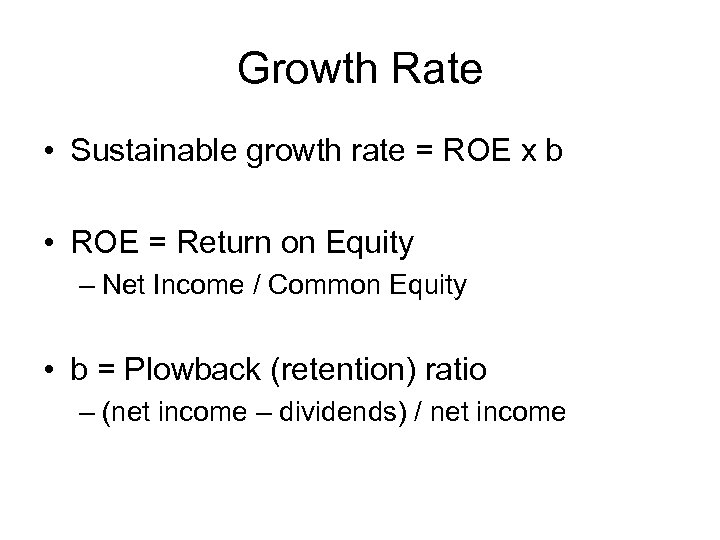
Growth Rate • Sustainable growth rate = ROE x b • ROE = Return on Equity – Net Income / Common Equity • b = Plowback (retention) ratio – (net income – dividends) / net income
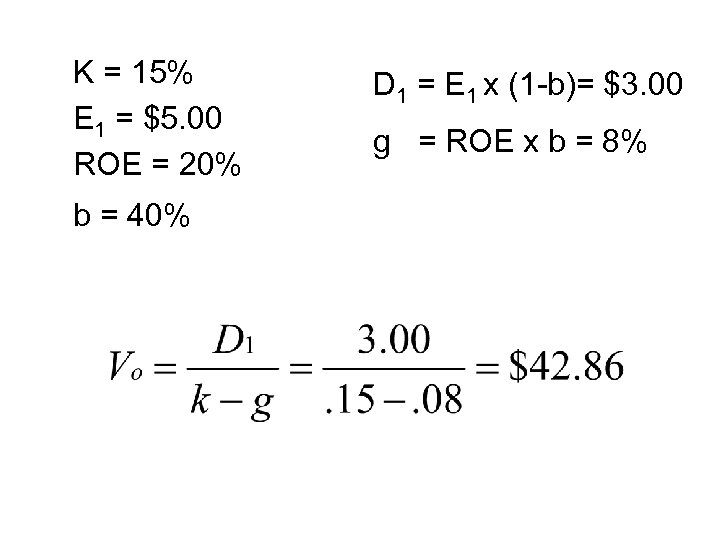
K = 15% E 1 = $5. 00 ROE = 20% b = 40% D 1 = E 1 x (1 -b)= $3. 00 g = ROE x b = 8%

Plowback & Reinvestment Rates High Rates of return on investment encourage the firm to retain earnings for reinvestment (plowback). Low Rates of return encourage the payment of dividends.

Growth Rates and Earnings E 0 NI b DE E 1 $10 10 $1 1 1. 00 0. 40 $1 0. 4 11. 0 10. 4 % DE ROE 10% 4% 10% Where: E 0 = Current Equity E 1 = Expected end-of-period equity g 10% 4%
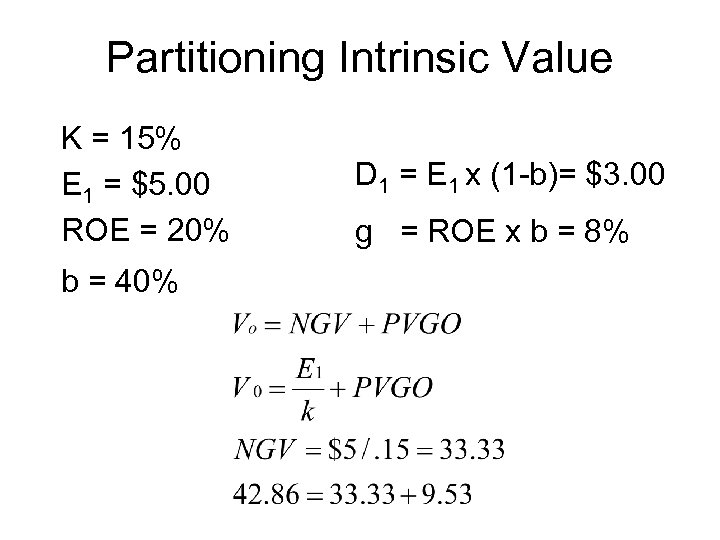
Partitioning Intrinsic Value K = 15% E 1 = $5. 00 ROE = 20% b = 40% D 1 = E 1 x (1 -b)= $3. 00 g = ROE x b = 8%

• NGV – Value of assets in place • Firm without any further future investment • PVGO – Value of future investment • Investment which will generate future cash flow – Positive if earnings reinvested at rates of return higher than what investors require on the company’s stock (ROE > k)

b D 1 g Vo Price = NGV + PVGO 10% 15% $5. 00 0% 40% 60% $5. 00 $3. 00 $2. 00 0% 4% 6% $33. 33 $27. 27 $22. 22 = = = $33. 33 + + + $0. 00 -$6. 06 -$11. 11 ROE = K= EPS = 15% $5. 00 0% 40% 60% $5. 00 $3. 00 $2. 00 0% 6% 9% $33. 33 = = = $33. 33 + + + $0. 00 ROE > K ROE = K= EPS = 20% 15% $5. 00 0% 40% 60% $5. 00 $3. 00 $2. 00 0% 8% 12% $33. 33 $42. 86 $66. 67 = = = $33. 33 + + + $0. 00 $9. 52 $33. 33 ROE < K ROE = K= EPS =

ROE = ROA x m M = 1 / (1 – DR) DR = debt ratio
9964be519245df71456b16a75077c5f3.ppt