Equity valuation.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 17

Equity valuation Basic concepts
Discounted dividend model FCF Valuation Price Multiples Residual Income

One/two period DDM

Multi-period DDM
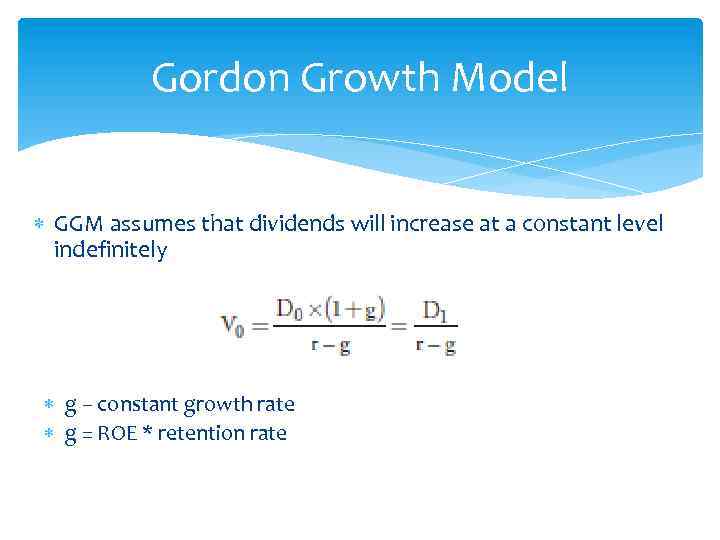
Gordon Growth Model GGM assumes that dividends will increase at a constant level indefinitely g – constant growth rate g = ROE * retention rate
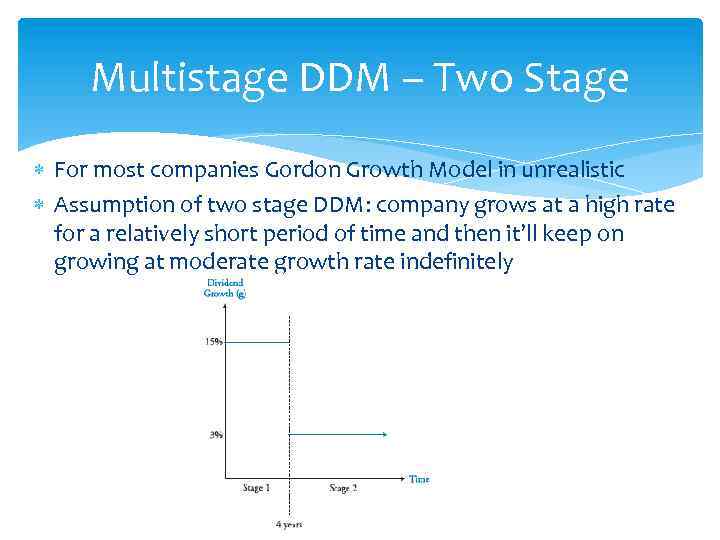
Multistage DDM – Two Stage For most companies Gordon Growth Model in unrealistic Assumption of two stage DDM: company grows at a high rate for a relatively short period of time and then it’ll keep on growing at moderate growth rate indefinitely
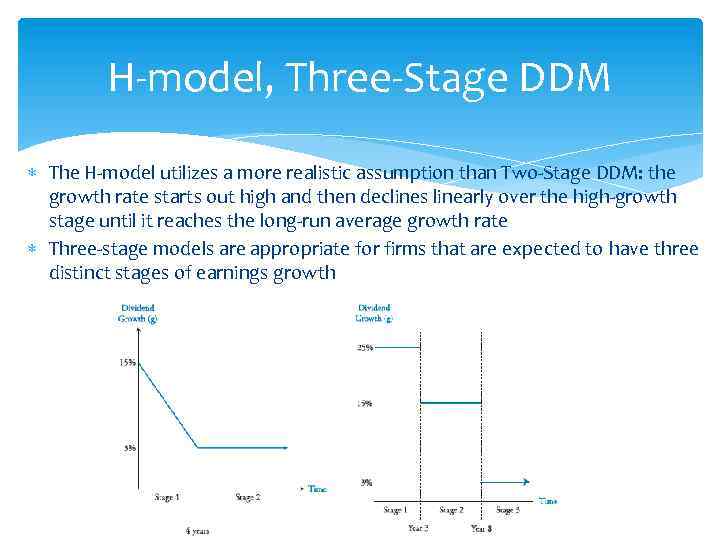
H-model, Three-Stage DDM The H-model utilizes a more realistic assumption than Two-Stage DDM: the growth rate starts out high and then declines linearly over the high-growth stage until it reaches the long-run average growth rate Three-stage models are appropriate for firms that are expected to have three distinct stages of earnings growth
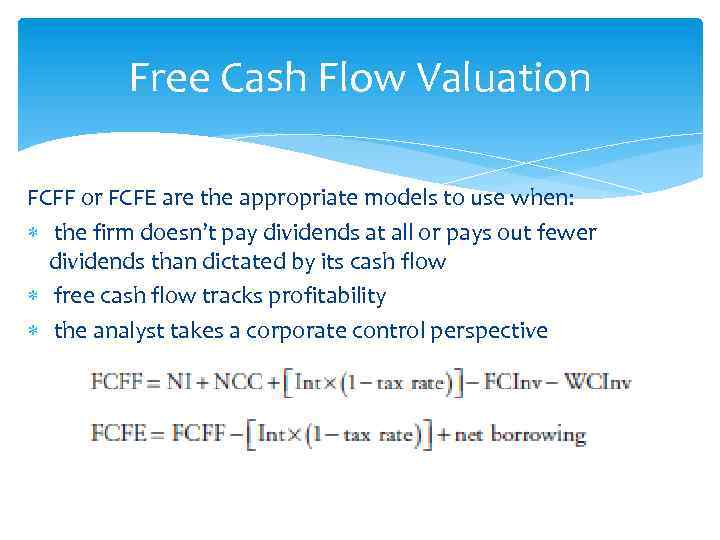
Free Cash Flow Valuation FCFF or FCFE are the appropriate models to use when: the firm doesn’t pay dividends at all or pays out fewer dividends than dictated by its cash flow free cash flow tracks profitability the analyst takes a corporate control perspective
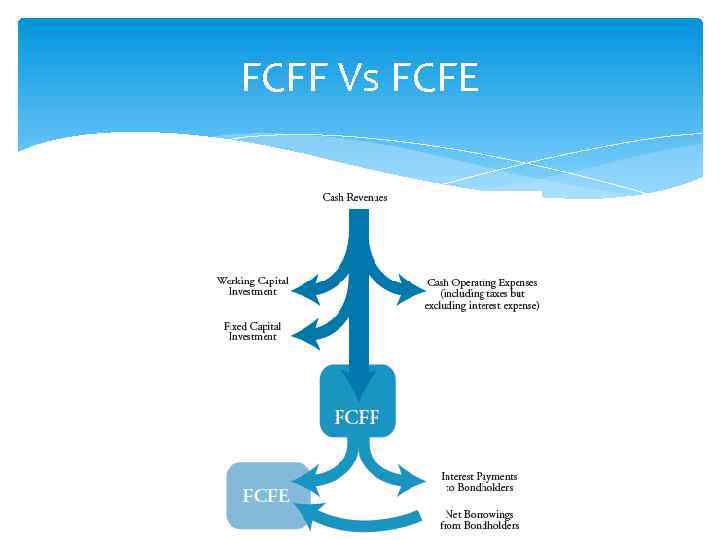
FCFF Vs FCFE

FCFF VS FCFE techniques The same basic principle of discounted cash flows !!! § firm value = FCFF discounted at the WACC § equity value = FCFE discounted at the required return on equity § equity value = firm value – market value of debt

FCF Vs DDM Analysts often prefer to use free cash flow rather than dividendbased valuation for the following reasons: § Many firms pay no, or low, cash dividends § Dividends are paid at the discretion of the board of directors. It may, consequently, be poorly aligned with the firm’s long-run profitability § If a company is viewed as an acquisition target, free cash flow is a more appropriate measure because the new owners will have discretion over its distribution (control perspective) § Free cash flows may be more related to long-run profitability of the firm as compared to dividends

Residual Income Valuation accounting profit cash flows economic profit

Economic Value Added (EVA) Look similar ? ? ?

Residual Income Valuation Residual income (RI), or economic profit, is the net income of a firm less a charge that measures stockholders’ opportunity cost of capital Residual income explicitly deducts all capital costs RI t = residual income in year t E t = expected EPS for year t r = required return on equity B t – 1 = book value of equity in year t – 1
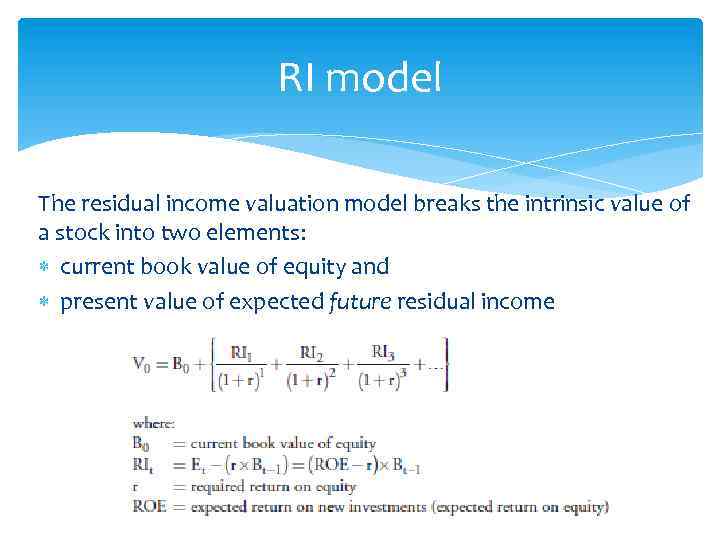
RI model The residual income valuation model breaks the intrinsic value of a stock into two elements: current book value of equity and present value of expected future residual income

What model to use ? Dividends are appropriate when: § The company has a history of dividend payments § The dividend policy is clear and related to the earnings of the firm § The asset is being valued from the position of a minority shareholder Free cash flow is appropriate when: § The company does not have a dividend payment history or has a dividend payment history that is not related to earnings § The free cash flow corresponds with the firm’s profitability § The asset is being valued from the position of a controlling shareholder Residual income is most appropriate for firms that: § Do not have dividend payment histories § Have negative free cash flow for the foreseeable future § Have transparent financial reporting and high-quality earnings

Thanks for your attention
Equity valuation.pptx