54eebe84ca5c67998a17f264ad81b828.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

EPRI CIM for Market Extensions (CME) and CIM-Based Messaging to Support Markets and Reliability July 14, 2004 Terry Saxton Xtensible Solutions

This presentation was prepared by: Terry Saxton Xtensible Solutions 18125 23 rd Avenue North Plymouth, MN 55447 E-mail: tsaxton@xtensible. net

Presentation Contents p p CIM for Market Extensions (CME) How CIM-Based Message Standards Work ITC Standards Collaborative with MDA NERC Functional Model and MDI
Initiation of CIM for Market Extensions (CME) Project p p FERC requested EPRI to extend the CIM architecture to support the SMD and facilitate markets EPRI initiated CIM for Market Extensions (CME) project n n n p Made up of utility and industry organizations to support this initiative Managed by Xtensible Solutions for EPRI Focus on the Day-Ahead and Real-Time Market Processes to define extensions needed for the CIM data model to support these processes Goal of CME n Standardize information format and application interfaces to make the North American wholesale electricity market run efficiently, reduce seams issues and save substantial costs in the development of applications for each RTO p p Will allow RTOs to buy best-of-breed applications and communicate with Independent Transmission Organizations (ITOs) or other ISOs and RTOs in a standard information format Will allow marketers, Load Serving Entities (LSE), and Generator Serving Entities (GSE) to access information and bid into the RTO’s preferred format
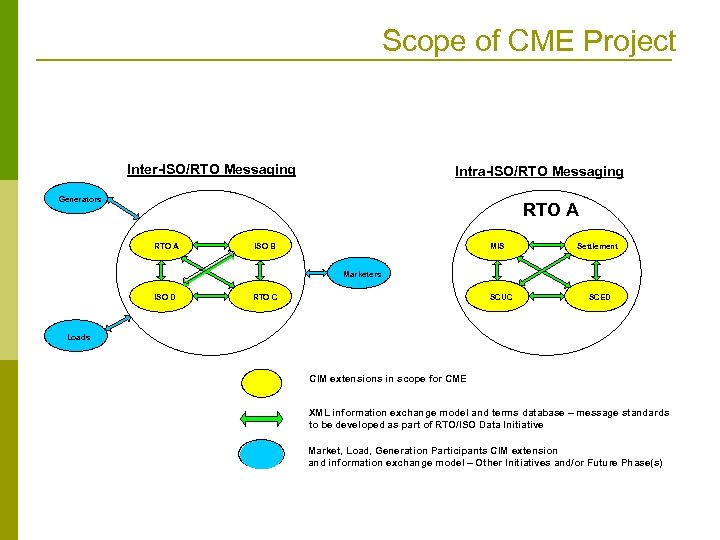
Scope of CME Project Inter-ISO/RTO Messaging Intra-ISO/RTO Messaging Generators RTO A MIS ISO B Settlement Marketers ISO D SCUC RTO C SCED Loads CIM extensions in scope for CME XML information exchange model and terms database – message standards to be developed as part of RTO/ISO Data Initiative Market, Load, Generation Participants CIM extension and information exchange model – Other Initiatives and/or Future Phase(s)
Role of the CIM p An information model – provides common language (i. e. , semantics/data definitions) for exchange of data between various applications both within and across company boundaries n n n p Developed through efforts of EPRI, vendors and utilities through EPRI CCAPI Task Force CIM now adopted by International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as international standard for information exchange and data access NERC mandated use of CIM XML format for sharing power system models between Reliability Coordinators in North America CIM extensions n n Continues to expand to include models of distribution systems and business objects, such as assets, documents, etc. Now being extended to support Market Operations

CME Phase 1 p Define data requirements and CIM extensions needed to support the welldefined, high-priority SMD software applications n n Investigate applications and functions needed to support real-time and dayahead markets Focused on: p p p n For each application: p p Security Constrained Unit Commitment (SCUC) Security Constrained Economic Dispatch (SCED) Ex Ante LMP (based on bids) Develop data requirements Define information exchange data requirements Review CIM and identify extensions needed to support SMD Deliverable for Phase 1: n n n EPRI TR “CIM Extensions to Support Market Operations Phase 1: Day Ahead and Real Time Scheduling Applications” CIM representation of data requirements in table format with mapping to existing applications Extended CIM UML model to support the SCUC/ED/LMP data requirements p n Reuse and creation of new classes, attributes, and associations XML Schema for the Input/Output data p Presents the CIM-based XML tags proposed to support exchange of market operation data § § Tag names Definitions

Phase 1 CIM UML Extensions p New CIM Package created for Market Operations n n n p Updates to existing CIM Packages n n p Bid Resource RTO Security Constraints Clearing Results Energy Scheduling Financial Reuse of existing IEC 61970 and 61968 Packages n n 61970 – Core, Generation/Production, Measurements, others 61968 - Core 2/Top Level and Activity Record
CME Phase 2 & 3 p CME Phase 2 (Current) n Network Analysis p n n n p State Estimator, Security Analysis, Optimal Power Flow Ex-Post LMP (based on actuals, SE results) Financial Transmission Rights Facilitated Check Out (FCO) Phase 3 (Planned for 2004 if funded) n Network model maintenance p n Control Area seams-related data exchange p n Would not include user interface Data Exchange between Operations and Settlement p p n Applications include ramp data, TTC, AFC (Available Flowgate Capacity) Market participant upload bids and download of results p n Complete, incremental, and partial model transfers) Intra-RTO pending DRWG resolution Inter-RTO if use cases can be identified Market monitoring information

Presentation Contents p p CIM for Market Extensions (CME) How CIM-Based Message Standards Work ITC Standards Collaborative with MDA NERC Functional Model and MDI

CIM Provides Vocabulary CIM XML Provides Standard Messages p Webster’s Dictionary = CIM n p Sentence structure = CIM- based XML messages n p Just as you must have structured sentences to communicate orally, you must have standard messages to share data electronically Standard messages are needed to n n n p Provides standard data semantics and data types Ensure interoperability both within RTOs and between RTOs Remove seams Define that part of CIM that must be supported by an application Adapters provide CIM <-> proprietary data mappings used by applications
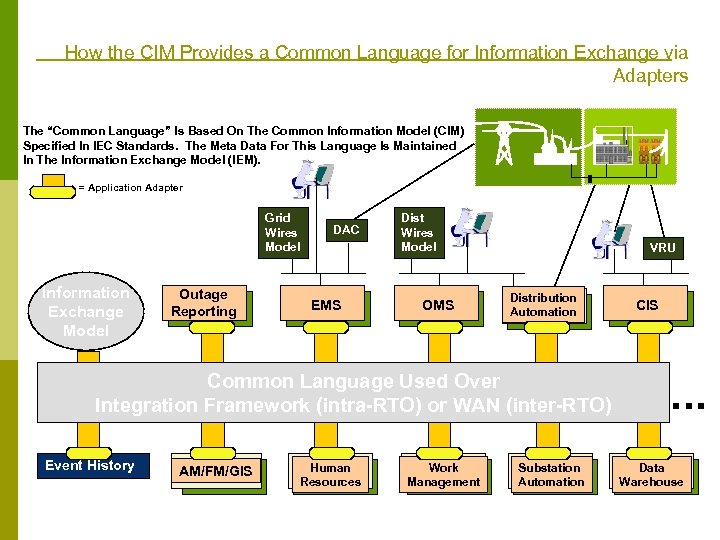
How the CIM Provides a Common Language for Information Exchange via Adapters The “Common Language” Is Based On The Common Information Model (CIM) Specified In IEC Standards. The Meta Data For This Language Is Maintained In The Information Exchange Model (IEM). = Application Adapter Grid Wires Model Information Exchange Model Outage Reporting DAC EMS Dist Wires Model OMS VRU Distribution Automation Common Language Used Over Integration Framework (intra-RTO) or WAN (inter-RTO) Event History AM/FM/GIS Human Resources Work Management Substation Automation CIS . . . Data Warehouse
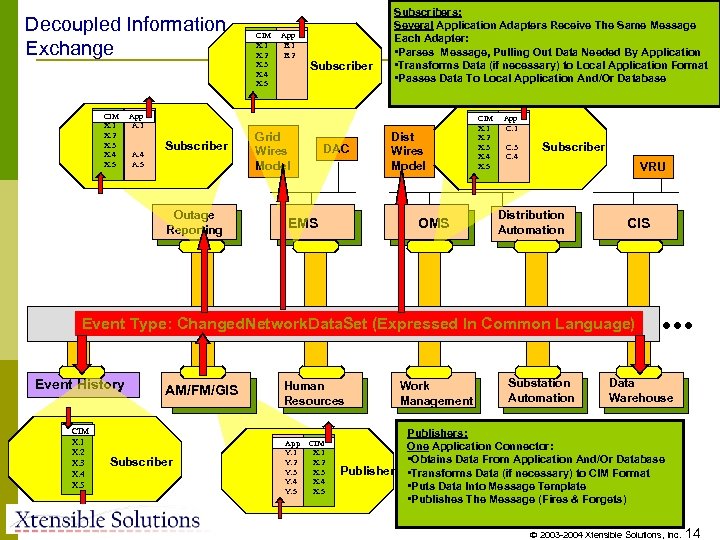
Decoupled Information Exchange CIM X. 1 X. 2 X. 3 X. 4 X. 5 App B. 1 B. 2 Subscribers: Several Application Adapters Receive The Same Message Each Adapter: • Parses Message, Pulling Out Data Needed By Application • Transforms Data (if necessary) to Local Application Format • Passes Data To Local Application And/Or Database App A. 1 A. 4 A. 5 Subscriber Outage Reporting Grid Wires Model DAC Dist Wires Model EMS OMS CIM X. 1 X. 2 X. 3 X. 4 X. 5 App C. 1 C. 3 C. 4 Subscriber VRU Distribution Automation CIS Event Type: Changed. Network. Data. Set (Expressed In Common Language) Event History CIM X. 1 X. 2 X. 3 X. 4 X. 5 AM/FM/GIS Subscriber Human Resources App Y. 1 Y. 2 Y. 3 Y. 4 Y. 5 CIM X. 1 X. 2 X. 3 X. 4 X. 5 Publisher Work Management Substation Automation . . . Data Warehouse Publishers: One Application Connector: • Obtains Data From Application And/Or Database • Transforms Data (if necessary) to CIM Format • Puts Data Into Message Template • Publishes The Message (Fires & Forgets) 2003 -2004 Xtensible Solutions, Inc. 14

Presentation Contents p p CIM for Market Extensions (CME) How CIM-Based Message Standards Work ITC Standards Collaborative with MDA NERC Functional Model and MDI

ISO/RTO Standards Collaborative p Objective n p Bring together organizations interested in developing IT standards for North American ISO/RTOs business processes Goals n n n For first deliverable, select a single application/process to produce short-term results Review and update the CIM/CME model in the context of selected process Validate a practical & repeatable process to develop standardsbased messages and interfaces for ISO/RTO processes p Discussed two message development processes § MDA (Model Driven Architecture) from OMG § Best for stateless messages § MDI (Model Driven Integration) from IEC § Best for stateful, transactional business processes § Both methods are standards-based and are repeatable § Selected the MDA methodology for the SCUC standards
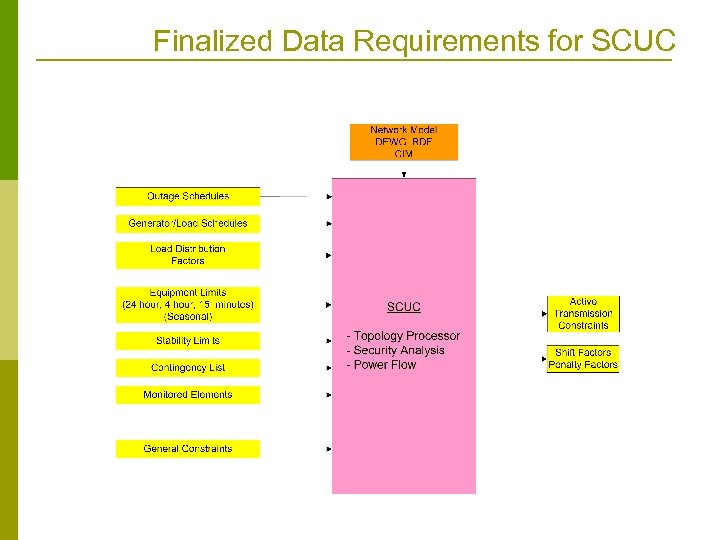
Finalized Data Requirements for SCUC
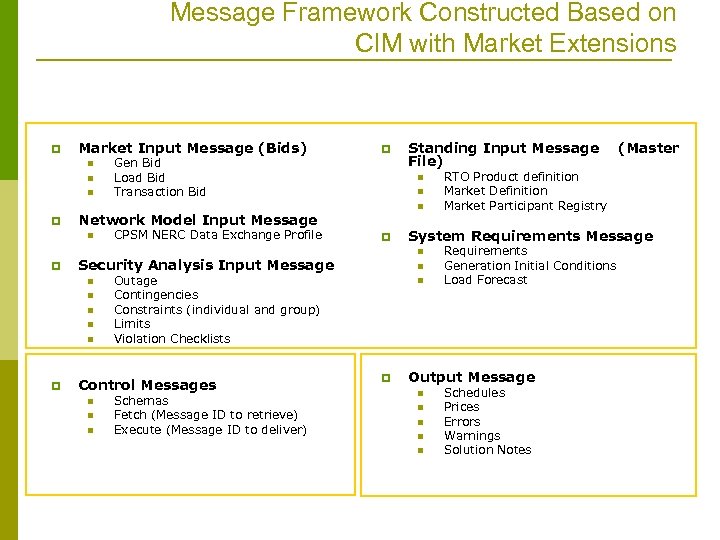
Message Framework Constructed Based on CIM with Market Extensions p Market Input Message (Bids) n n n p n n Control Messages n n Outage Contingencies Constraints (individual and group) Limits Violation Checklists Schemas Fetch (Message ID to retrieve) Execute (Message ID to deliver) n p (Master RTO Product definition Market Definition Market Participant Registry System Requirements Message n Security Analysis Input Message n p CPSM NERC Data Exchange Profile Standing Input Message File) n Network Model Input Message n p p Gen Bid Load Bid Transaction Bid Requirements Generation Initial Conditions Load Forecast Output Message n n n Schedules Prices Errors Warnings Solution Notes
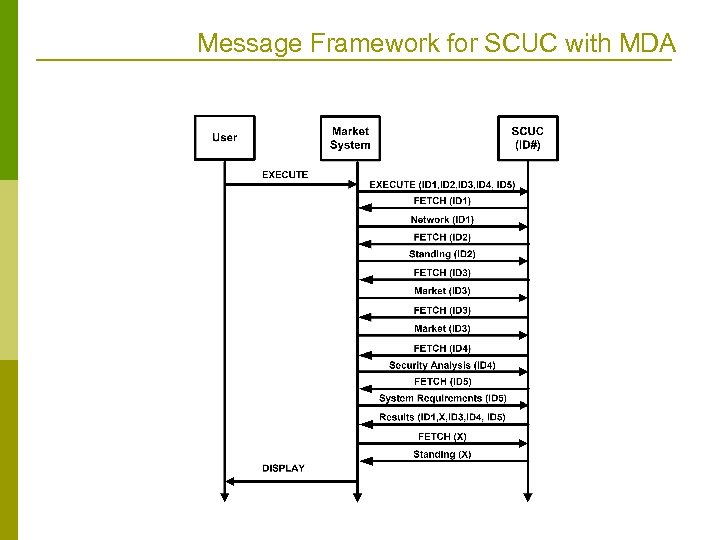
Message Framework for SCUC with MDA
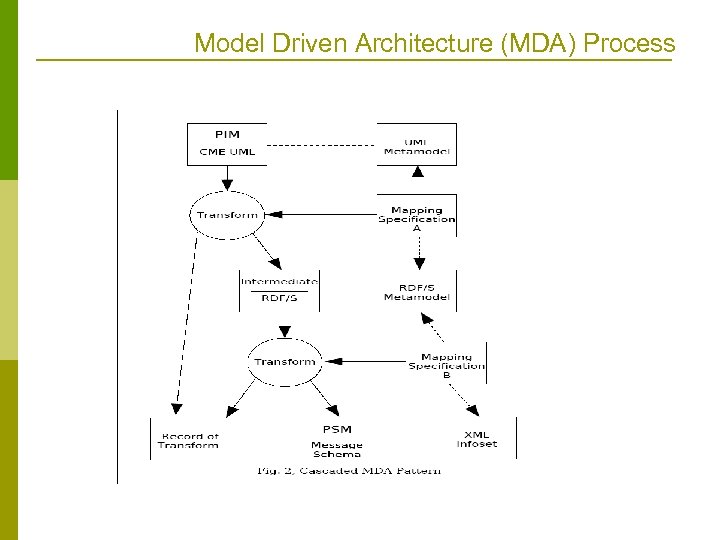
Model Driven Architecture (MDA) Process
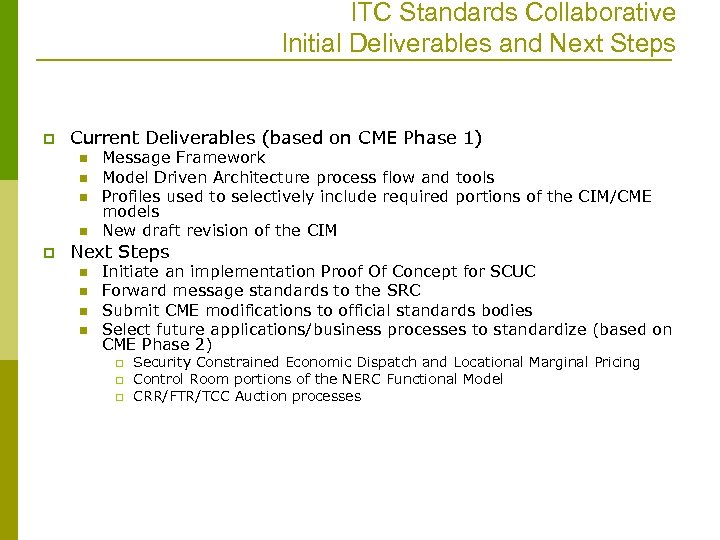
ITC Standards Collaborative Initial Deliverables and Next Steps p Current Deliverables (based on CME Phase 1) n n p Message Framework Model Driven Architecture process flow and tools Profiles used to selectively include required portions of the CIM/CME models New draft revision of the CIM Next Steps n n Initiate an implementation Proof Of Concept for SCUC Forward message standards to the SRC Submit CME modifications to official standards bodies Select future applications/business processes to standardize (based on CME Phase 2) p p p Security Constrained Economic Dispatch and Locational Marginal Pricing Control Room portions of the NERC Functional Model CRR/FTR/TCC Auction processes

Presentation Contents p p CIM for Market Extensions (CME) How CIM-Based Message Standards Work ITC Standards Collaborative with MDA NERC Functional Model and MDI

Message Definition Process with MDI Based on NERC Functional Model p Current ITC Standards Collaborative methodology for SCUC is based on MDA n n p Input/Output data requirements for legacy software applications plus process knowledge Start with existing applications, extend CIM in UML, then work in XML to define messages MDI starts with business processes to derive information exchange requirements and message standards based on the NERC Functional Model and the CIM n n Stay in UML until last step, starting with NERC Functional Model use cases Each RTO/ISO can map their business processes onto this model
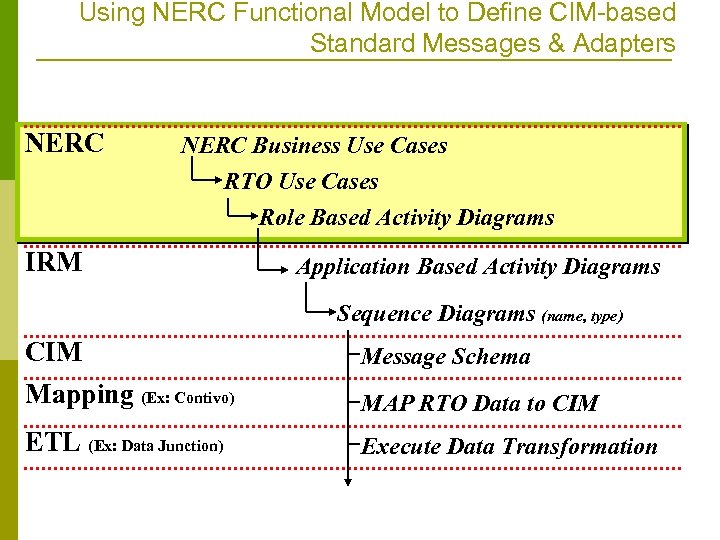
Using NERC Functional Model to Define CIM-based Standard Messages & Adapters NERC Business Use Cases RTO Use Cases Role Based Activity Diagrams IRM Application Based Activity Diagrams Sequence Diagrams (name, type) CIM Mapping (Ex: Contivo) Message Schema ETL (Ex: Data Junction) Execute Data Transformation MAP RTO Data to CIM
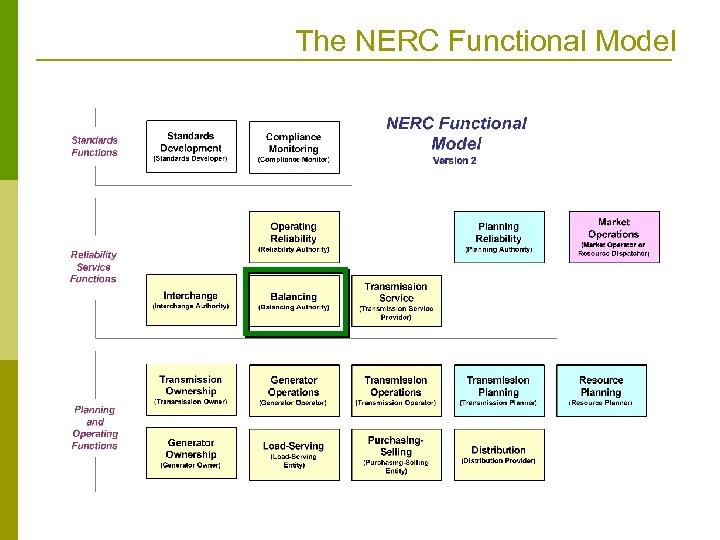
The NERC Functional Model
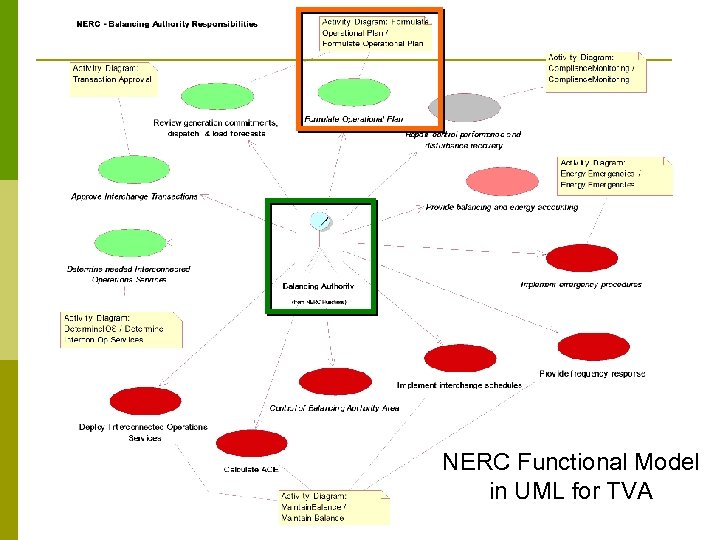
NERC Functional Model in UML for TVA
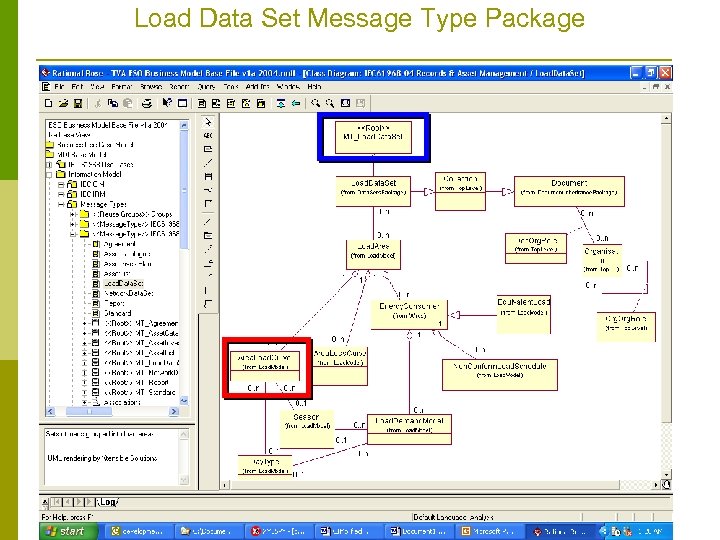
Load Data Set Message Type Package
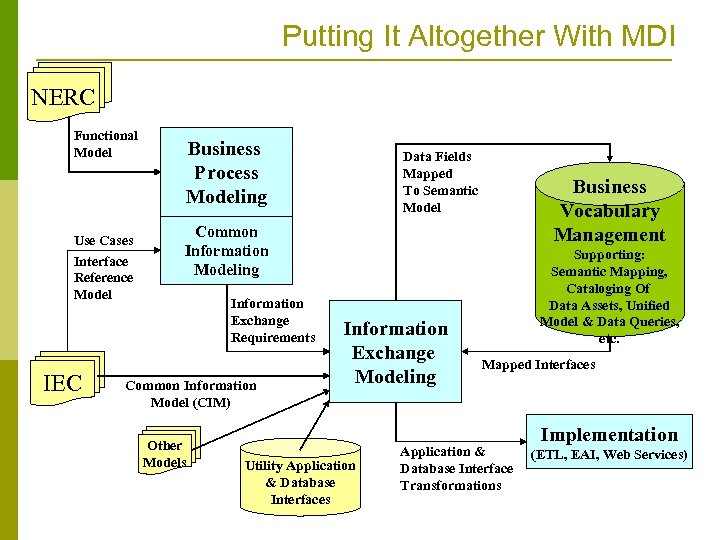
Putting It Altogether With MDI NERC Functional Model Use Cases Interface Reference Model IEC Business Process Modeling Data Fields Mapped To Semantic Model Business Vocabulary Management Common Information Modeling Information Exchange Requirements Common Information Model (CIM) Other Models Information Exchange Modeling Utility Application & Database Interfaces Supporting: Semantic Mapping, Cataloging Of Data Assets, Unified Model & Data Queries, etc. Mapped Interfaces Application & Database Interface Transformations Implementation (ETL, EAI, Web Services)
NERC Functional Model & MDI Conclusions p p Improved ability to integrate business processes across commercialoff-the-shelf (COTS) applications n while lowering dependence on individual vendors Can articulate how business objectives are implemented n p Reusable approach for growth and change n n p Provides end-to-end requirements traceability back to functional model Methodology Business process models Common information models Information exchange models Faster integration of application systems and information: n Improving ability to react to business changes p p while providing the right information to where it is needed Run time support with Business Vocabulary Management, Message Standards Repository, and Adapters n One repository of all source, target, and CIM-based messages to ensure consistency and leverage existing message definitions
54eebe84ca5c67998a17f264ad81b828.ppt