 Epidemiology of cataract Surgery in Israel: 1990 -2009 Guy Kleinmann, MD 1 Eli Rosen, MD 2 Ehud I Assia, MD 2 1. Ophthalmology Department, Kaplan Medical Center 2. Ophthalmology Department, Meir Medical Center No financial disclosure
Epidemiology of cataract Surgery in Israel: 1990 -2009 Guy Kleinmann, MD 1 Eli Rosen, MD 2 Ehud I Assia, MD 2 1. Ophthalmology Department, Kaplan Medical Center 2. Ophthalmology Department, Meir Medical Center No financial disclosure
 Purpose To present the epidemiology of cataract surgeries in Israel during the last 20 years; 1990 -2009
Purpose To present the epidemiology of cataract surgeries in Israel during the last 20 years; 1990 -2009
 Methods Ø Since 1990 questionnaires were sent to all the surgery center in Israel Ø The questionnaires evolved during those years Ø The response increased from 75% at the early years to 100% at recent years
Methods Ø Since 1990 questionnaires were sent to all the surgery center in Israel Ø The questionnaires evolved during those years Ø The response increased from 75% at the early years to 100% at recent years
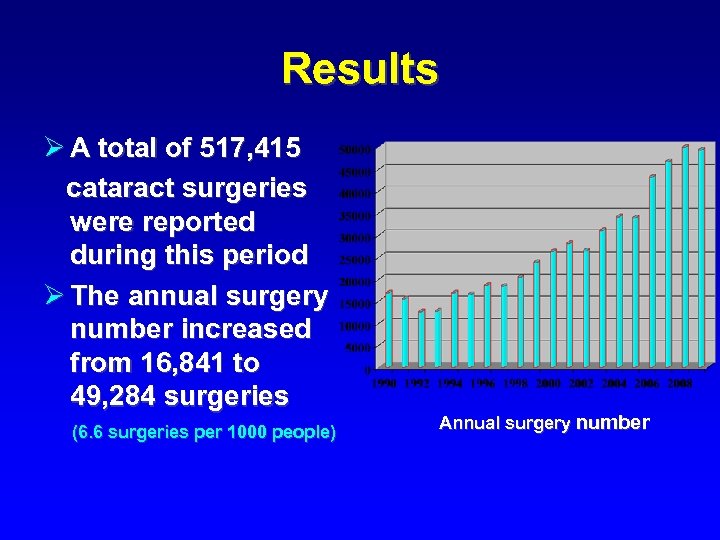 Results Ø A total of 517, 415 cataract surgeries were reported during this period Ø The annual surgery number increased from 16, 841 to 49, 284 surgeries (6. 6 surgeries per 1000 people) Annual surgery number
Results Ø A total of 517, 415 cataract surgeries were reported during this period Ø The annual surgery number increased from 16, 841 to 49, 284 surgeries (6. 6 surgeries per 1000 people) Annual surgery number
 Results – cont. A shift from the university affiliated Hospitals to the ambulatory surgery centers: 1999 – 66% of the surgeries were done in the university hospitals 2009 – 51. 5% of the surgeries were done in the university hospitals
Results – cont. A shift from the university affiliated Hospitals to the ambulatory surgery centers: 1999 – 66% of the surgeries were done in the university hospitals 2009 – 51. 5% of the surgeries were done in the university hospitals
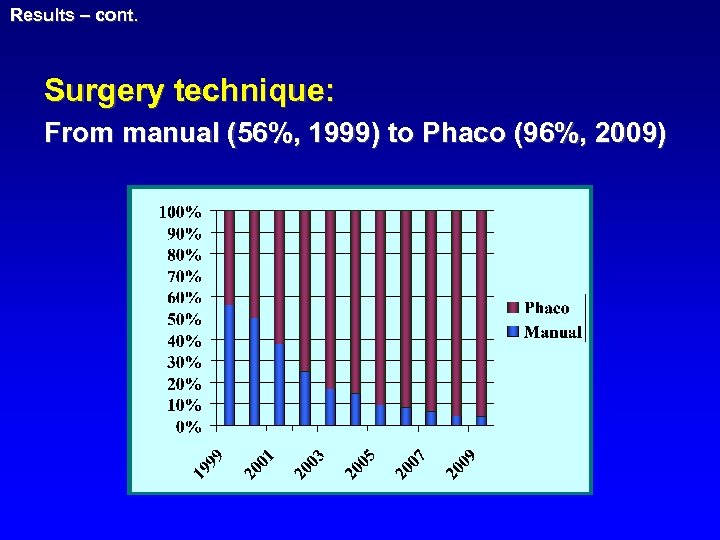 Results – cont. Surgery technique: From manual (56%, 1999) to Phaco (96%, 2009)
Results – cont. Surgery technique: From manual (56%, 1999) to Phaco (96%, 2009)
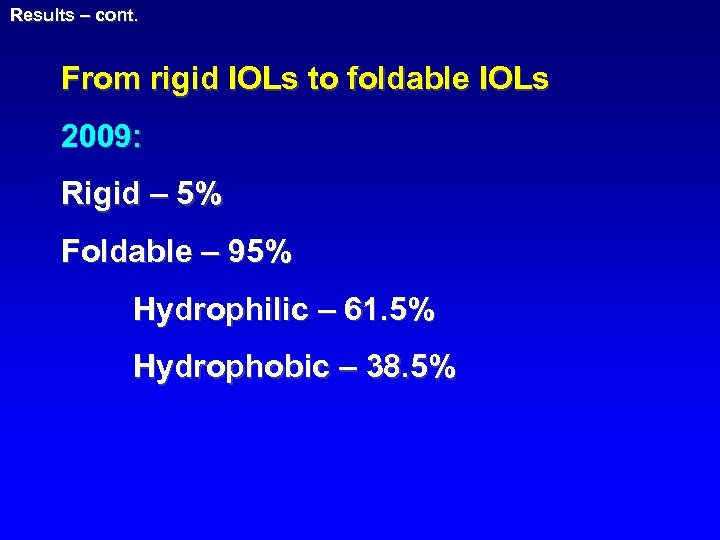 Results – cont. From rigid IOLs to foldable IOLs 2009: Rigid – 5% Foldable – 95% Hydrophilic – 61. 5% Hydrophobic – 38. 5%
Results – cont. From rigid IOLs to foldable IOLs 2009: Rigid – 5% Foldable – 95% Hydrophilic – 61. 5% Hydrophobic – 38. 5%
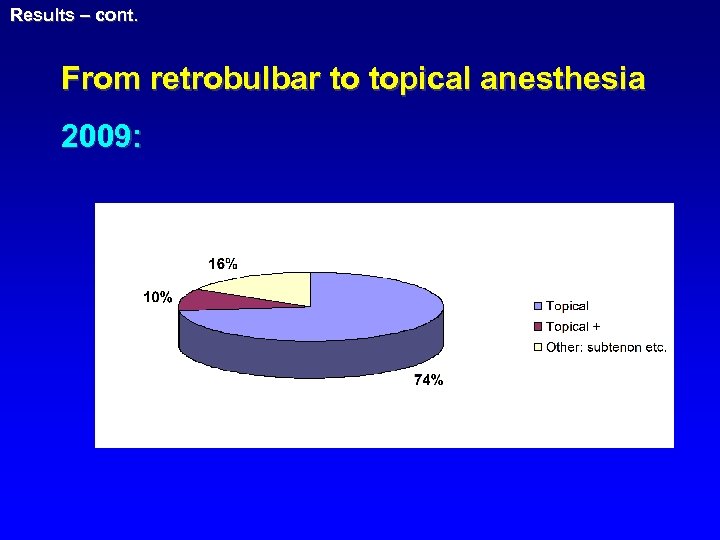 Results – cont. From retrobulbar to topical anesthesia 2009:
Results – cont. From retrobulbar to topical anesthesia 2009:
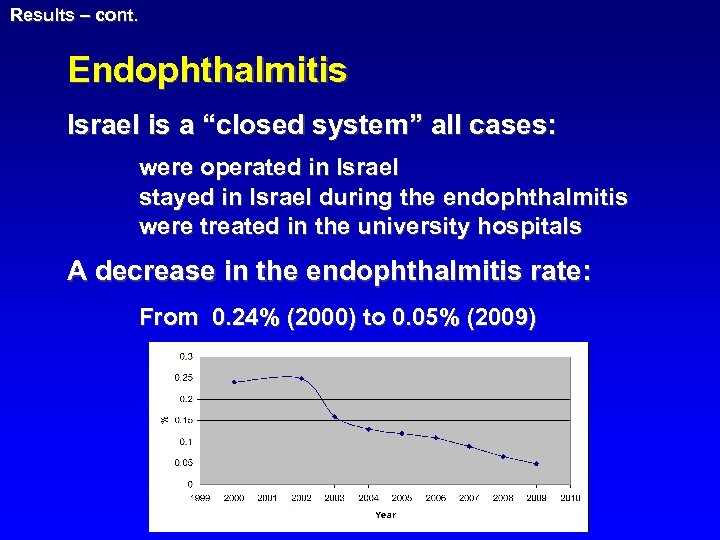 Results – cont. Endophthalmitis Israel is a “closed system” all cases: were operated in Israel stayed in Israel during the endophthalmitis were treated in the university hospitals A decrease in the endophthalmitis rate: From 0. 24% (2000) to 0. 05% (2009)
Results – cont. Endophthalmitis Israel is a “closed system” all cases: were operated in Israel stayed in Israel during the endophthalmitis were treated in the university hospitals A decrease in the endophthalmitis rate: From 0. 24% (2000) to 0. 05% (2009)
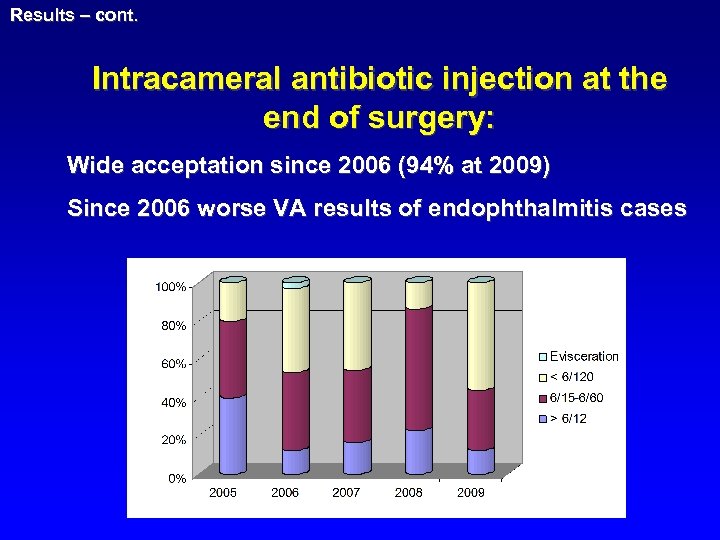 Results – cont. Intracameral antibiotic injection at the end of surgery: Wide acceptation since 2006 (94% at 2009) Since 2006 worse VA results of endophthalmitis cases
Results – cont. Intracameral antibiotic injection at the end of surgery: Wide acceptation since 2006 (94% at 2009) Since 2006 worse VA results of endophthalmitis cases
 Conclusion During the last 20 years we found: Ø Continuous increase in cataract surgeries annual number Ø Progression in cataract surgery technique Ø Decrease in the severe complication rate (i. e. endophthalmitis)
Conclusion During the last 20 years we found: Ø Continuous increase in cataract surgeries annual number Ø Progression in cataract surgery technique Ø Decrease in the severe complication rate (i. e. endophthalmitis)