df22952419758851d427cc920c483a17.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43

 epidemiology Occurrence 20 -80 per 100, 000 n 2 deaths per 100, 000 population due to spinal injury n male/female ratio 3/1 n
epidemiology Occurrence 20 -80 per 100, 000 n 2 deaths per 100, 000 population due to spinal injury n male/female ratio 3/1 n
 Etiology (USA) 40% n 20% n 15% n - motor vehicle accidents falls industrial sports and recreation
Etiology (USA) 40% n 20% n 15% n - motor vehicle accidents falls industrial sports and recreation
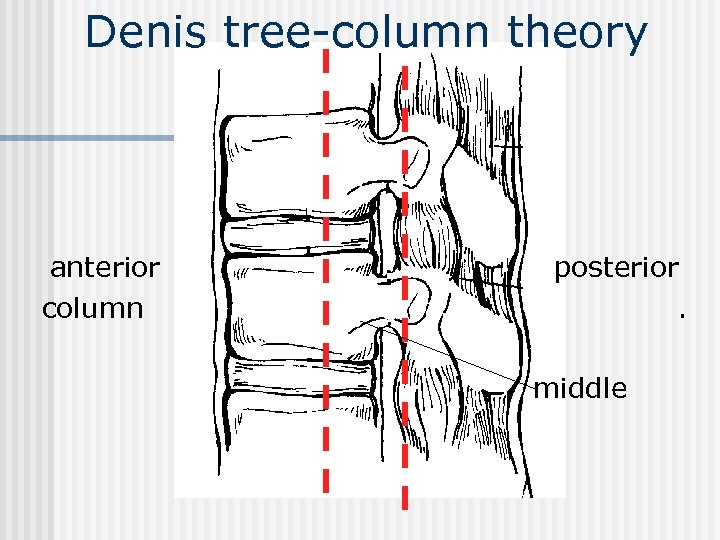 Denis tree-column theory anterior column posterior. middle
Denis tree-column theory anterior column posterior. middle
 Mechanisms of spine injury Flexion n Flexion-rotation n Extention n Compression n
Mechanisms of spine injury Flexion n Flexion-rotation n Extention n Compression n
 Mechanisms of injury n n n Compression Flexion-Rotation.
Mechanisms of injury n n n Compression Flexion-Rotation.
 n n n Shear. Flexion-Distraction. Extension
n n n Shear. Flexion-Distraction. Extension
 Classification of injury to the spine Depending on integrity of the skin 1. 2. Closed open, depending on integrity of dural sac a) b) missile nonmissile Clinical forms of injury to the spine 2. contusion 2. Injury to the ligaments and capsules 3. Rupture of intervertebral disk 4. Facet dislocation 5. Complete bilateral facet dislocationn (locked facets) 6. Fracture of vertebra corpus (compressive, burst) 7. Fractures of posterior elements of vertebras (joint, transverse, spinous processes and arch) 8. Fracture-dislocation (unilateral and bilateral) 9. Multiple fractures of vertebra elements Violation of support function 1. 3. 1. 2. Stable Instable
Classification of injury to the spine Depending on integrity of the skin 1. 2. Closed open, depending on integrity of dural sac a) b) missile nonmissile Clinical forms of injury to the spine 2. contusion 2. Injury to the ligaments and capsules 3. Rupture of intervertebral disk 4. Facet dislocation 5. Complete bilateral facet dislocationn (locked facets) 6. Fracture of vertebra corpus (compressive, burst) 7. Fractures of posterior elements of vertebras (joint, transverse, spinous processes and arch) 8. Fracture-dislocation (unilateral and bilateral) 9. Multiple fractures of vertebra elements Violation of support function 1. 3. 1. 2. Stable Instable
 Types of injury to the cervical spine n n n Occipital condyle fractures Atlanto-occipital dislocation Fractures of the atlas n n n Jefferson fracture Fracture of posterior arch Axis fractures n n n Fractures of the odontoid process (I-III types) Lateral mass fractures Traumatic spondylolisthesis (hangman's fracture)
Types of injury to the cervical spine n n n Occipital condyle fractures Atlanto-occipital dislocation Fractures of the atlas n n n Jefferson fracture Fracture of posterior arch Axis fractures n n n Fractures of the odontoid process (I-III types) Lateral mass fractures Traumatic spondylolisthesis (hangman's fracture)
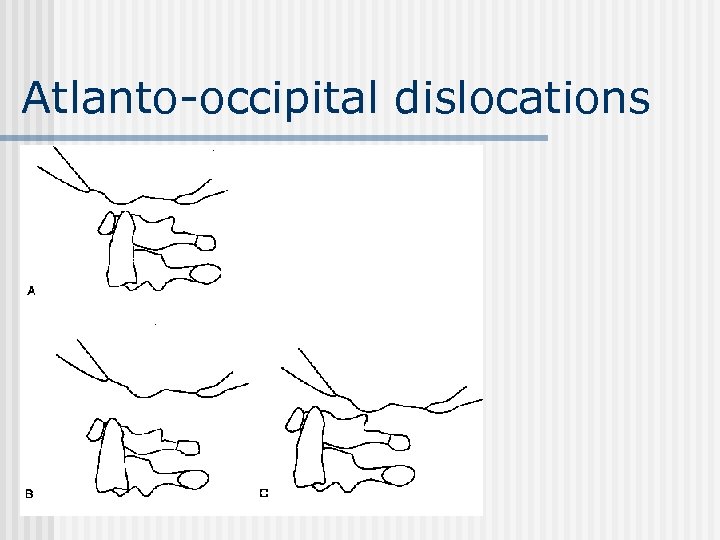 Atlanto-occipital dislocations
Atlanto-occipital dislocations
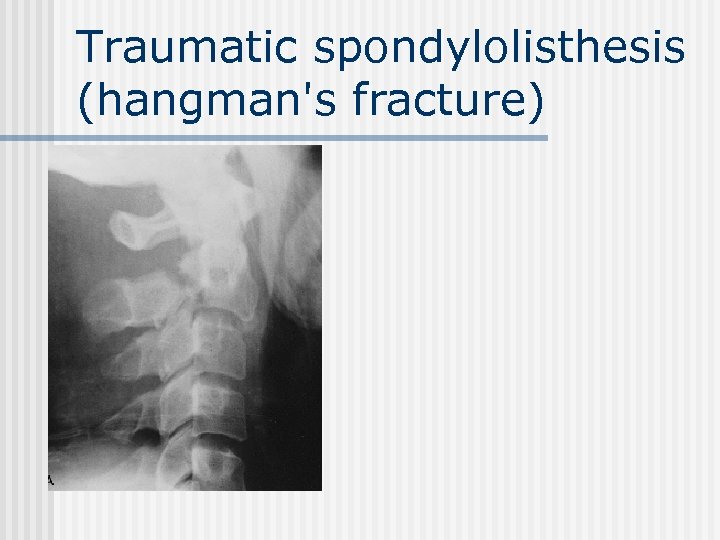 Traumatic spondylolisthesis (hangman's fracture)
Traumatic spondylolisthesis (hangman's fracture)
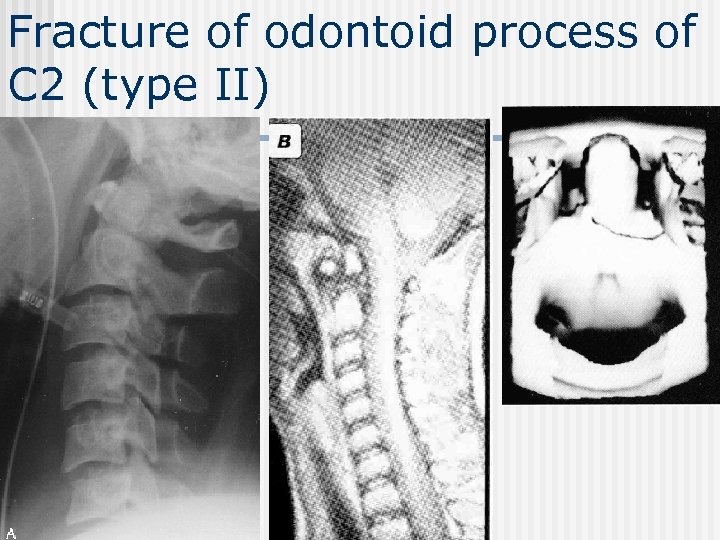 Fracture of odontoid process of C 2 (type II)
Fracture of odontoid process of C 2 (type II)
 Types of injury to the cervical spine n Fractures and dislocations of C 3 -C 7 n n n n n Compression fractures Burst fractures Teardrop fractures Unilateral facet dislocation Bilateral facet dislocation (locked facets) hyperextension dislocation hyperextension fracture-dislocation laminar fractures Fracture of spinous process
Types of injury to the cervical spine n Fractures and dislocations of C 3 -C 7 n n n n n Compression fractures Burst fractures Teardrop fractures Unilateral facet dislocation Bilateral facet dislocation (locked facets) hyperextension dislocation hyperextension fracture-dislocation laminar fractures Fracture of spinous process
 Compressive fracture of С 5
Compressive fracture of С 5
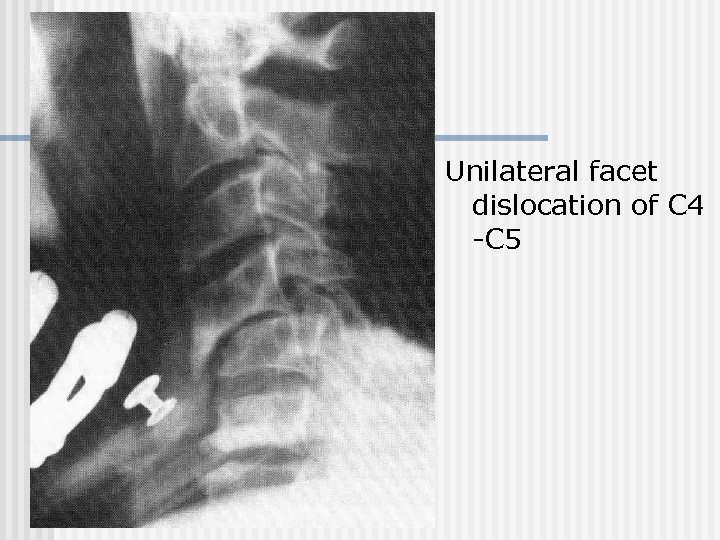 Unilateral facet dislocation of C 4 -C 5
Unilateral facet dislocation of C 4 -C 5
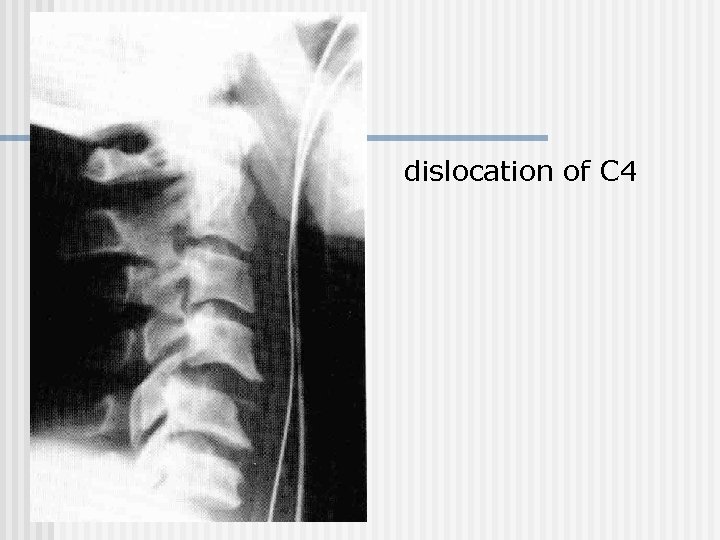 dislocation of С 4
dislocation of С 4
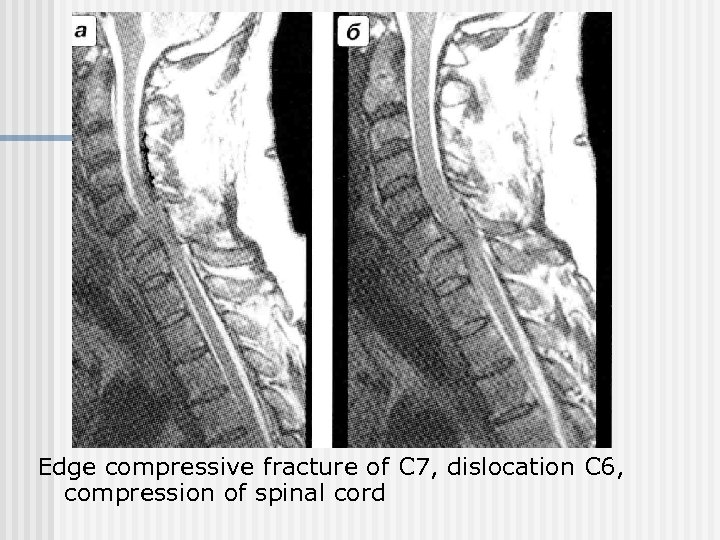 Edge compressive fracture of С 7, dislocation С 6, compression of spinal cord
Edge compressive fracture of С 7, dislocation С 6, compression of spinal cord
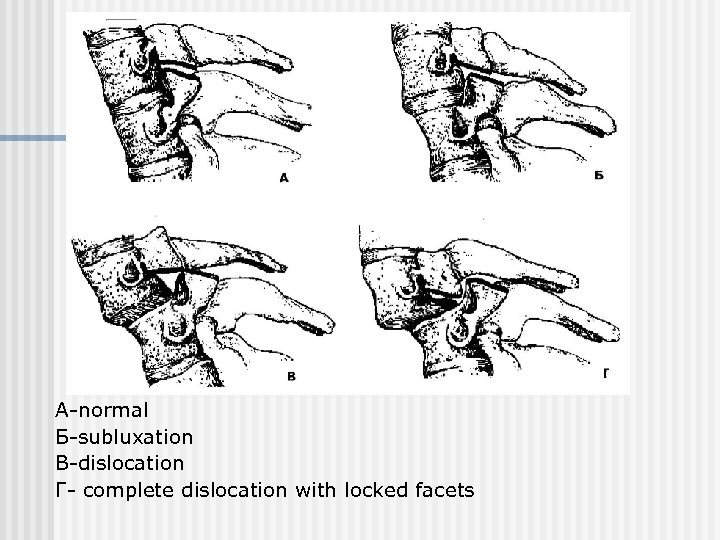 А-normal Б-subluxation В-dislocation Г- complete dislocation with locked facets
А-normal Б-subluxation В-dislocation Г- complete dislocation with locked facets
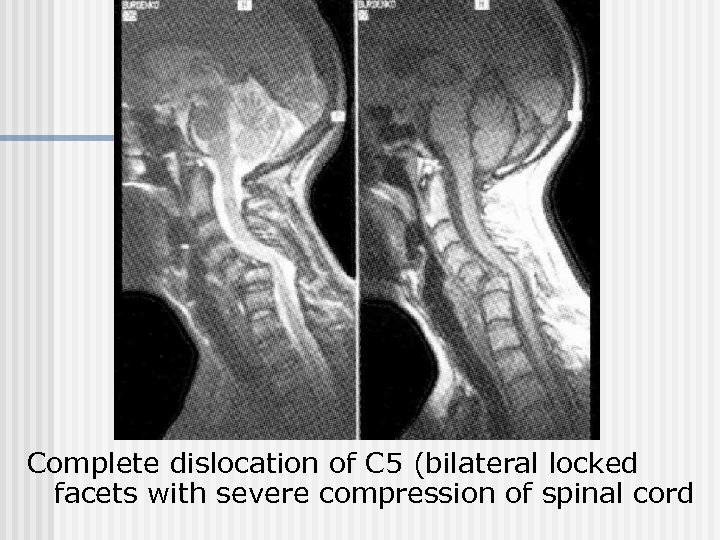 Complete dislocation of C 5 (bilateral locked facets with severe compression of spinal cord
Complete dislocation of C 5 (bilateral locked facets with severe compression of spinal cord
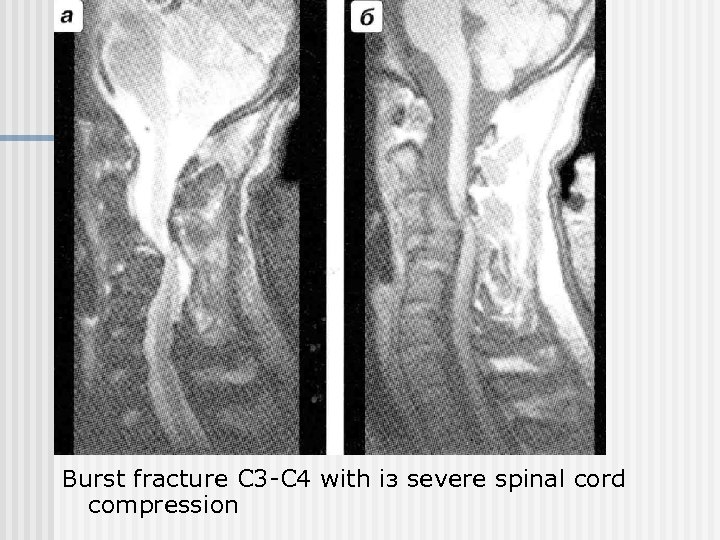 Burst fracture С 3 -С 4 with із severe spinal cord compression
Burst fracture С 3 -С 4 with із severe spinal cord compression
 Typical injuries to the thoracolumbalis and lumbalis spine Wedge compression fractures n Burst fractures n Seat belt–type injuries n Fracture-dislocations n
Typical injuries to the thoracolumbalis and lumbalis spine Wedge compression fractures n Burst fractures n Seat belt–type injuries n Fracture-dislocations n
 Wedge compression fracture
Wedge compression fracture
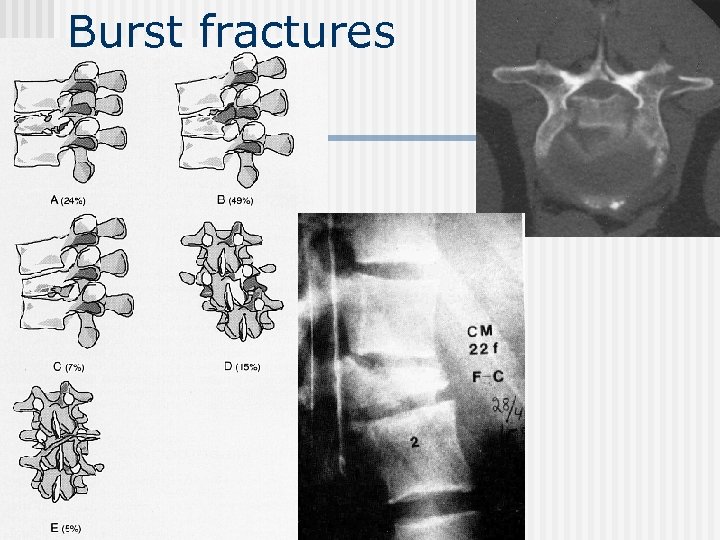 Burst fractures
Burst fractures
 Seat belt–type injuries
Seat belt–type injuries
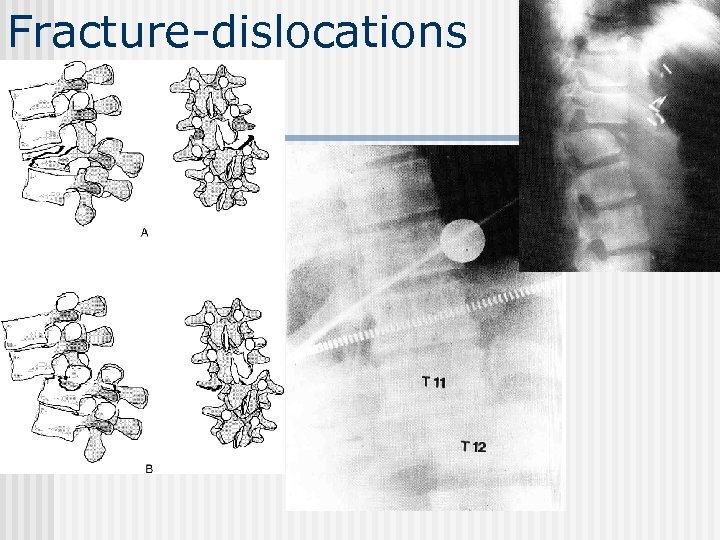 Fracture-dislocations
Fracture-dislocations
 Classification of the injury to the spinal cord n Complete syndrome – n n central cord syndrome – n n n total loss of motor and lateral column sensory function (pain and temperature), dorsal column function (i. e. , proprioception, touch, and position sense) is spared conus medullaris syndrome n n weakness of the upper extremities greater than the lower extremities anterior cord syndrome n n total loss of motor and sensory function below injury level combination of spinal cord and nerve root involvement Cauda equine syndrome Brown-Sequard syndrome
Classification of the injury to the spinal cord n Complete syndrome – n n central cord syndrome – n n n total loss of motor and lateral column sensory function (pain and temperature), dorsal column function (i. e. , proprioception, touch, and position sense) is spared conus medullaris syndrome n n weakness of the upper extremities greater than the lower extremities anterior cord syndrome n n total loss of motor and sensory function below injury level combination of spinal cord and nerve root involvement Cauda equine syndrome Brown-Sequard syndrome
 Scheme of blood supply of spinal cord and typical ischemical changes 1 -vertebral arteria 2 -5 -radicularmedular arteries 6 -spinal cord А – loose type of blood supply Б, В, Г – variants of magistral types of bood supply
Scheme of blood supply of spinal cord and typical ischemical changes 1 -vertebral arteria 2 -5 -radicularmedular arteries 6 -spinal cord А – loose type of blood supply Б, В, Г – variants of magistral types of bood supply
 Classification of spinal cord injury n Frankel (A) complete, n (B) sensory only, n (C) motor useless, n (D) motor useful, n (E) recovery. n
Classification of spinal cord injury n Frankel (A) complete, n (B) sensory only, n (C) motor useless, n (D) motor useful, n (E) recovery. n

 Prehospital care 1. ABC n n n 2. A (airway), cleaning, airway tube if indicated B (breathing) – supplemental oxygen of mask C (circulation) – maintaining normal blood pressure – fluids Immobilization backboard rigid cervical collar,
Prehospital care 1. ABC n n n 2. A (airway), cleaning, airway tube if indicated B (breathing) – supplemental oxygen of mask C (circulation) – maintaining normal blood pressure – fluids Immobilization backboard rigid cervical collar,
 Emergency room management n ABCDE n Cont ABC protocol • Supplemental oxygen for all • Fluids and pressors for maintaining normal blood pressure n n n D - (disability) - assessment of neurological status E – (exposure) - removal of all clothes for throughout examination methylprednisolone - iv bolus of 30 mg per kg followed 5. 4 mg per kg per hour continuous infusion during the next 23 hours.
Emergency room management n ABCDE n Cont ABC protocol • Supplemental oxygen for all • Fluids and pressors for maintaining normal blood pressure n n n D - (disability) - assessment of neurological status E – (exposure) - removal of all clothes for throughout examination methylprednisolone - iv bolus of 30 mg per kg followed 5. 4 mg per kg per hour continuous infusion during the next 23 hours.
 Treatment of cervical spine injury n n Cervical traction Reduction of dislocation n Immobilization with orthoses n n Manual reduction Traction Collars Cervicothoracic, thoracolumbar braces Halo-orthosis Surgical decompression and stabilization
Treatment of cervical spine injury n n Cervical traction Reduction of dislocation n Immobilization with orthoses n n Manual reduction Traction Collars Cervicothoracic, thoracolumbar braces Halo-orthosis Surgical decompression and stabilization
 Typical indications for surgery n n Almost all thoraco-lumbar injuries with neurological deficit thoraco-lumbar injuries without neurological deficit in cases of progressive deformation (kifosis) Cervical burst fractures and fracturesdislocation Other cervical injuries after ineffectiveness of conservative treatment (cervical traction, manual reposition, halo-orthoses)
Typical indications for surgery n n Almost all thoraco-lumbar injuries with neurological deficit thoraco-lumbar injuries without neurological deficit in cases of progressive deformation (kifosis) Cervical burst fractures and fracturesdislocation Other cervical injuries after ineffectiveness of conservative treatment (cervical traction, manual reposition, halo-orthoses)
 Accompanying problems and complication Dysfunction of bladder and bowel n Urinary infection n Decubitus (trophic ulcers) n Spasticity (late) n Progressive deformation of the spine n
Accompanying problems and complication Dysfunction of bladder and bowel n Urinary infection n Decubitus (trophic ulcers) n Spasticity (late) n Progressive deformation of the spine n
 Diagnostic procedures Plain X-ray examination (min 2 views) n Functional X-ray examination n CT n Myelography and postmyelography CT n MRI n CSF dynamic tests n
Diagnostic procedures Plain X-ray examination (min 2 views) n Functional X-ray examination n CT n Myelography and postmyelography CT n MRI n CSF dynamic tests n
 Reposition of cervical spine dislocations А- traction Б- bending to the “healthy” side В- rotation to the opposite side
Reposition of cervical spine dislocations А- traction Б- bending to the “healthy” side В- rotation to the opposite side
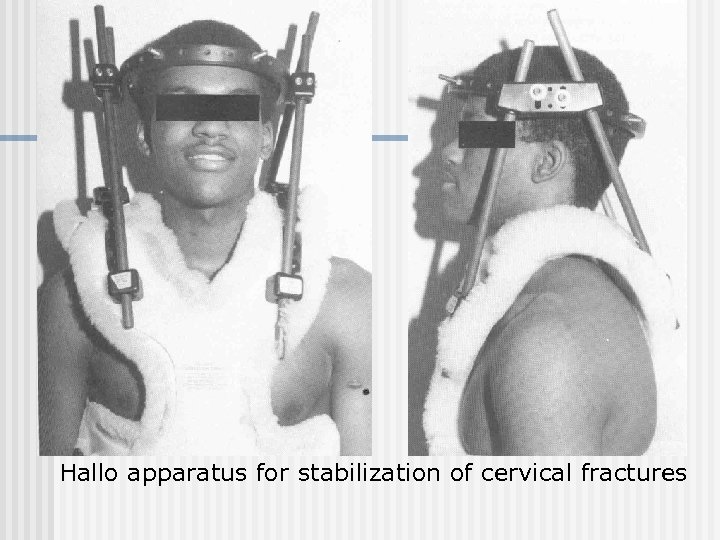 Hallo apparatus for stabilization of cervical fractures
Hallo apparatus for stabilization of cervical fractures
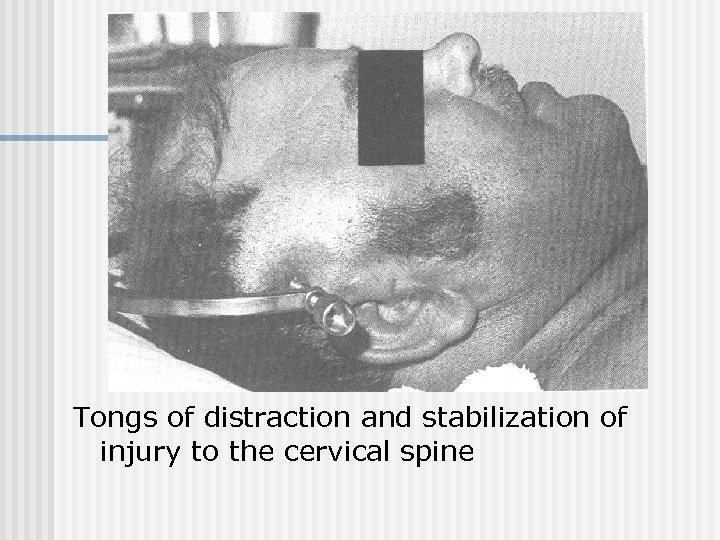 Tongs of distraction and stabilization of injury to the cervical spine
Tongs of distraction and stabilization of injury to the cervical spine
 Surgical stabilization n Corporodesis C 3 -C 5, anterior approach
Surgical stabilization n Corporodesis C 3 -C 5, anterior approach
 Surgical stabilization n Transpedicular fixation
Surgical stabilization n Transpedicular fixation
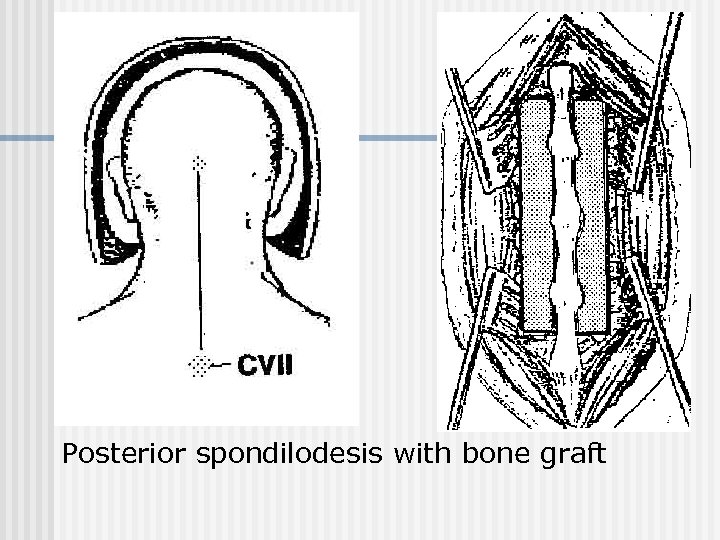 Posterior spondilodesis with bone graft
Posterior spondilodesis with bone graft
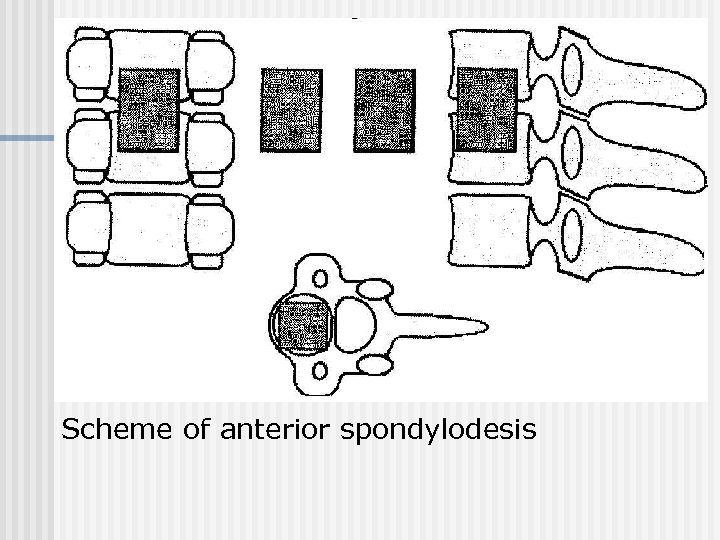 Scheme of anterior spondylodesis
Scheme of anterior spondylodesis
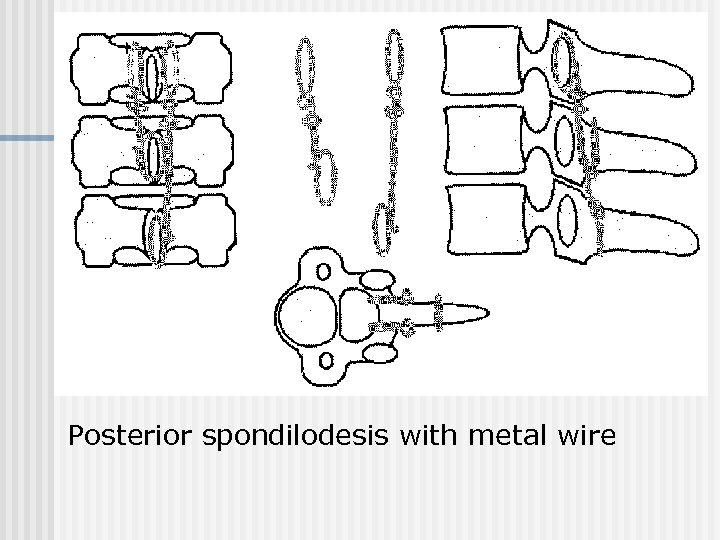 Posterior spondilodesis with metal wire
Posterior spondilodesis with metal wire


