346cde5ac998d74dbe17e02be7d2dd2f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Epayment System using Java April, 11. 2001 Computer Security and Electronic Payment System Cho won chul Kim Hee Dae Lee Jung Hwan Yoon Won Jung
Epayment System using Java April, 11. 2001 Computer Security and Electronic Payment System Cho won chul Kim Hee Dae Lee Jung Hwan Yoon Won Jung
 Index 1. Introduction 2. What is E-payment system ? 3. Comparison between SSL and SET(1)(2) 4. Secure Transmission Schemes in SSL and SET Protocol(1)(2) 5. The Player and essential security Requirements in SET 6. Entities of SET protocol in Cybershopping 7. Overview of main Messages in SET 8. Smart Card (Physical layout) 2
Index 1. Introduction 2. What is E-payment system ? 3. Comparison between SSL and SET(1)(2) 4. Secure Transmission Schemes in SSL and SET Protocol(1)(2) 5. The Player and essential security Requirements in SET 6. Entities of SET protocol in Cybershopping 7. Overview of main Messages in SET 8. Smart Card (Physical layout) 2
 Index 9. Software Stack of a Java Card 10. Program Development Process 11. Cyberflex Access Cards(1)(2) 12. What should we implement in this Project 13. Java Card Security package 14. Java Layer in the Host Software Architecture 3
Index 9. Software Stack of a Java Card 10. Program Development Process 11. Cyberflex Access Cards(1)(2) 12. What should we implement in this Project 13. Java Card Security package 14. Java Layer in the Host Software Architecture 3
 1. Introduction n Describe typical electronic payment systems for EC n Compare the relationship between SSL and SET protocols n Classify and describe the types of Smart Card used for payments n Describe the characteristics of Java Card n Implement Java Smart Card applying to SET 4
1. Introduction n Describe typical electronic payment systems for EC n Compare the relationship between SSL and SET protocols n Classify and describe the types of Smart Card used for payments n Describe the characteristics of Java Card n Implement Java Smart Card applying to SET 4
 2. What is E-payment system? § § § E-payment system is the new payment methods with the emergence of electronic commerce on the Internet. Secure payment systems are critical to the success of EC. There are four essential security requirements for safe electronic payments. (Authentication, Encryption, Integrity, Non-repudiation) The key security schemes adopted for electronic payment systems are encryption. Security schemes are adopted in protocols like SSL and SET. 5
2. What is E-payment system? § § § E-payment system is the new payment methods with the emergence of electronic commerce on the Internet. Secure payment systems are critical to the success of EC. There are four essential security requirements for safe electronic payments. (Authentication, Encryption, Integrity, Non-repudiation) The key security schemes adopted for electronic payment systems are encryption. Security schemes are adopted in protocols like SSL and SET. 5
 3. Comparison between SSL and SET(1) n A part of SSL (Secure Socket Layer) is available on customers’ browsers l l l it is basically an encryption mechanism for order taking, queries and other applications it does not protect against all security hazards it is mature, simple, and widely use n SET ( Secure Electronic Transaction) is a very comprehensive security protocol l it provides for privacy, authenticity, integrity, and, or Non repudiation it is used very infrequently due to its complexity and the need for a special card reader by the user it may be abandoned if it is not simplified/improved 6
3. Comparison between SSL and SET(1) n A part of SSL (Secure Socket Layer) is available on customers’ browsers l l l it is basically an encryption mechanism for order taking, queries and other applications it does not protect against all security hazards it is mature, simple, and widely use n SET ( Secure Electronic Transaction) is a very comprehensive security protocol l it provides for privacy, authenticity, integrity, and, or Non repudiation it is used very infrequently due to its complexity and the need for a special card reader by the user it may be abandoned if it is not simplified/improved 6
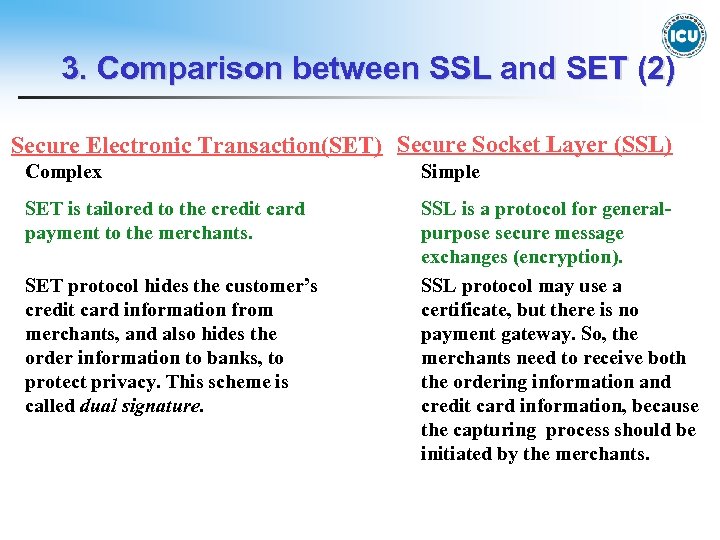 3. Comparison between SSL and SET (2) Secure Electronic Transaction(SET) Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Complex Simple SET is tailored to the credit card payment to the merchants. SSL is a protocol for generalpurpose secure message exchanges (encryption). SSL protocol may use a certificate, but there is no payment gateway. So, the merchants need to receive both the ordering information and credit card information, because the capturing process should be initiated by the merchants. SET protocol hides the customer’s credit card information from merchants, and also hides the order information to banks, to protect privacy. This scheme is called dual signature. 7
3. Comparison between SSL and SET (2) Secure Electronic Transaction(SET) Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Complex Simple SET is tailored to the credit card payment to the merchants. SSL is a protocol for generalpurpose secure message exchanges (encryption). SSL protocol may use a certificate, but there is no payment gateway. So, the merchants need to receive both the ordering information and credit card information, because the capturing process should be initiated by the merchants. SET protocol hides the customer’s credit card information from merchants, and also hides the order information to banks, to protect privacy. This scheme is called dual signature. 7
 4. Secure Transmission Schemes in SSL and SET Protocol(1) Sender’s Computer 1. The message is hashed to a prefixed length of message digest. 2. The message digest is encrypted with the sender’s private signature key, and a digital signature is created. 3. The composition of message, digital signature, and Sender’s certificate is encrypted with the symmetric key which is generated at sender’s computer for every transaction. The result is an encrypted message. SET protocol uses the DES algorithm instead of RSA for encryption because DES can be executed much faster than RSA. 4. The Symmetric key itself is encrypted with the receiver’s public key which was sent to the sender in advance. The result is a digital envelope. 8
4. Secure Transmission Schemes in SSL and SET Protocol(1) Sender’s Computer 1. The message is hashed to a prefixed length of message digest. 2. The message digest is encrypted with the sender’s private signature key, and a digital signature is created. 3. The composition of message, digital signature, and Sender’s certificate is encrypted with the symmetric key which is generated at sender’s computer for every transaction. The result is an encrypted message. SET protocol uses the DES algorithm instead of RSA for encryption because DES can be executed much faster than RSA. 4. The Symmetric key itself is encrypted with the receiver’s public key which was sent to the sender in advance. The result is a digital envelope. 8
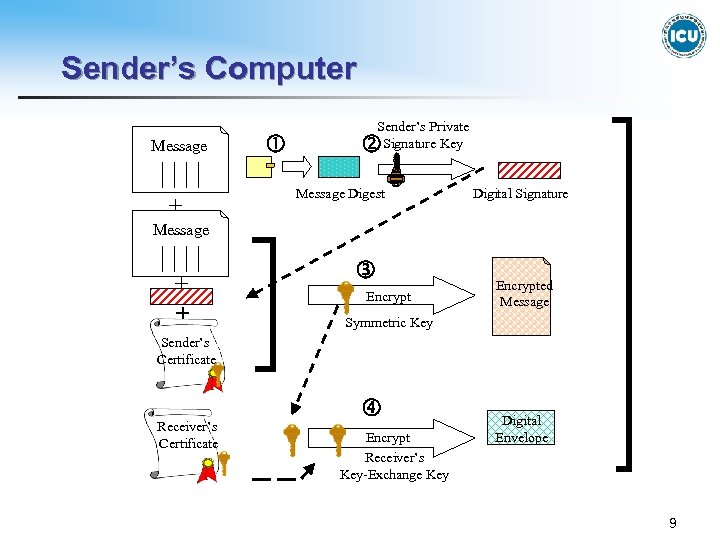 Sender’s Computer Message + Sender’s Private Signature Key Message Digest Digital Signature Message + + Encrypted Message Symmetric Key Sender’s Certificate Receiver’s Certificate Encrypt Receiver’s Key-Exchange Key Digital Envelope 9
Sender’s Computer Message + Sender’s Private Signature Key Message Digest Digital Signature Message + + Encrypted Message Symmetric Key Sender’s Certificate Receiver’s Certificate Encrypt Receiver’s Key-Exchange Key Digital Envelope 9
 4. Secure Transmission Schemes in SSL and SET Protocol (2) Receiver’s Computer 5. The encrypted message and digital envelope are transmitted to receiver’s computer via the Internet. 6. The digital envelope is decrypted with receiver’s private exchange key. 7. Using the restored symmetric key, the encrypted message can be restored to the message, digital signature, and sender’s certificate. 8. To confirm the integrity, the digital signature is decrypted by sender’s public key, obtaining the message digest. 9. The delivered message is hashed to generate message digest. 10. The message digests obtained by steps 8 and 9 respectively, are compared by the receiver to confirm whethere was any change during the transmission. This step confirms the integrity. 10
4. Secure Transmission Schemes in SSL and SET Protocol (2) Receiver’s Computer 5. The encrypted message and digital envelope are transmitted to receiver’s computer via the Internet. 6. The digital envelope is decrypted with receiver’s private exchange key. 7. Using the restored symmetric key, the encrypted message can be restored to the message, digital signature, and sender’s certificate. 8. To confirm the integrity, the digital signature is decrypted by sender’s public key, obtaining the message digest. 9. The delivered message is hashed to generate message digest. 10. The message digests obtained by steps 8 and 9 respectively, are compared by the receiver to confirm whethere was any change during the transmission. This step confirms the integrity. 10
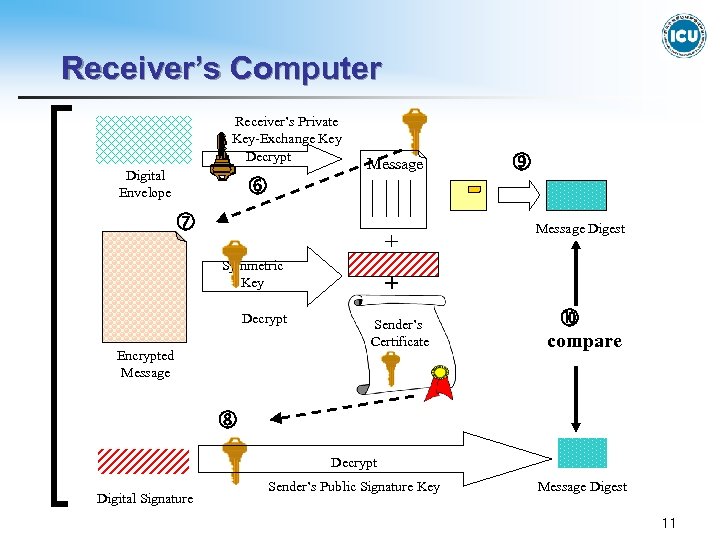 Receiver’s Computer Receiver’s Private Key-Exchange Key Decrypt Digital Envelope Message + Symmetric Key Decrypt Encrypted Message Digest + Sender’s Certificate compare Decrypt Digital Signature Sender’s Public Signature Key Message Digest 11
Receiver’s Computer Receiver’s Private Key-Exchange Key Decrypt Digital Envelope Message + Symmetric Key Decrypt Encrypted Message Digest + Sender’s Certificate compare Decrypt Digital Signature Sender’s Public Signature Key Message Digest 11
 5. The Player and essential security Requirements in SET n The player l Cardholder l Merchant (seller) l Issuer (your bank) l Acquirer (Merchant’s financial institution, acquires the sales slips) l Brand (Visa, Master Card) l Payment Gateway (e-payment infra-structure) n Essential Security Requirements in SET l Authentication l Encryption l Integrity l Non-repudiation 12
5. The Player and essential security Requirements in SET n The player l Cardholder l Merchant (seller) l Issuer (your bank) l Acquirer (Merchant’s financial institution, acquires the sales slips) l Brand (Visa, Master Card) l Payment Gateway (e-payment infra-structure) n Essential Security Requirements in SET l Authentication l Encryption l Integrity l Non-repudiation 12
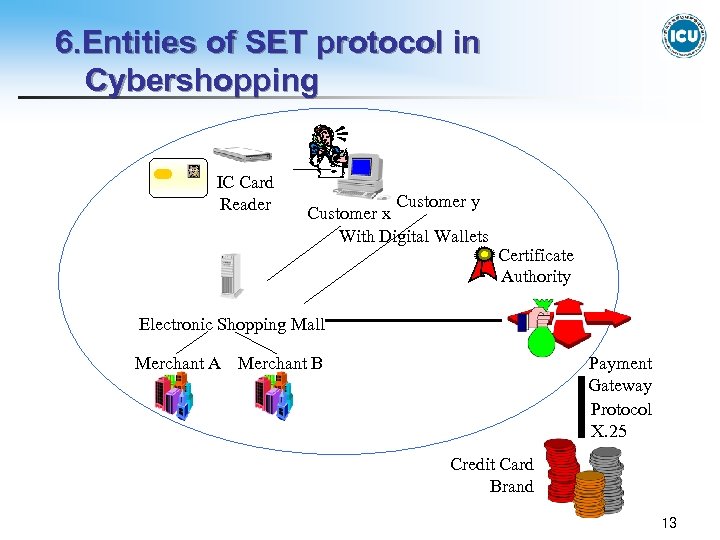 6. Entities of SET protocol in Cybershopping IC Card Reader Customer y Customer x With Digital Wallets Certificate Authority Electronic Shopping Mall Payment Gateway Protocol X. 25 Merchant A Merchant B Credit Card Brand 13
6. Entities of SET protocol in Cybershopping IC Card Reader Customer y Customer x With Digital Wallets Certificate Authority Electronic Shopping Mall Payment Gateway Protocol X. 25 Merchant A Merchant B Credit Card Brand 13
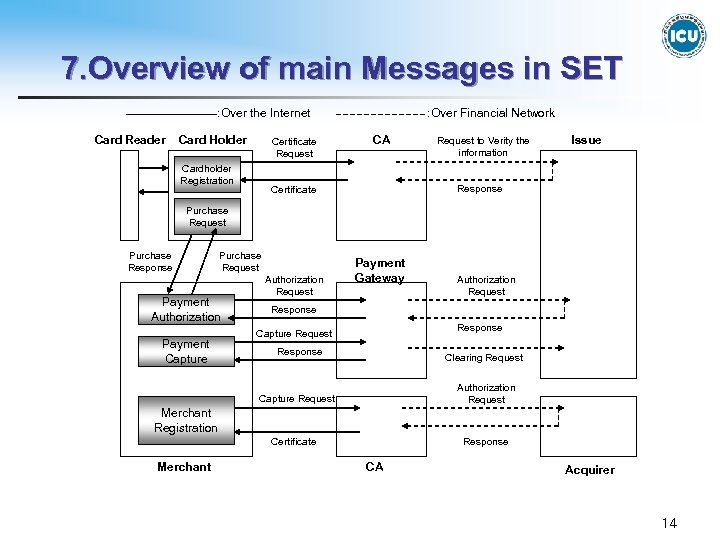 7. Overview of main Messages in SET : Over the Internet Card Reader Card Holder Certificate Request Cardholder Registration : Over Financial Network CA Request to Verity the information Issue Response Certificate Purchase Request Purchase Response Purchase Request Payment Authorization Payment Capture Authorization Request Payment Gateway Authorization Request Response Capture Request Response Clearing Request Authorization Request Capture Request Merchant Registration Certificate Merchant Response CA Acquirer 14
7. Overview of main Messages in SET : Over the Internet Card Reader Card Holder Certificate Request Cardholder Registration : Over Financial Network CA Request to Verity the information Issue Response Certificate Purchase Request Purchase Response Purchase Request Payment Authorization Payment Capture Authorization Request Payment Gateway Authorization Request Response Capture Request Response Clearing Request Authorization Request Capture Request Merchant Registration Certificate Merchant Response CA Acquirer 14
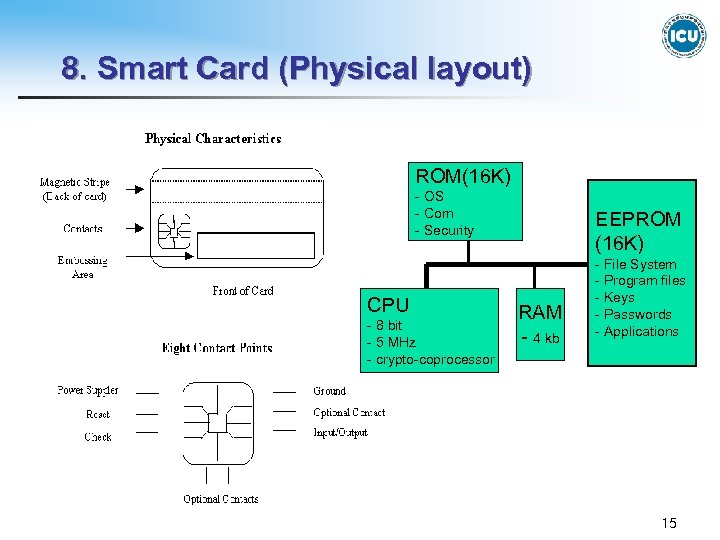 8. Smart Card (Physical layout) ROM(16 K) - OS - Com - Security CPU - 8 bit - 5 MHz - crypto-coprocessor EEPROM (16 K) RAM - 4 kb - File System - Program files - Keys - Passwords - Applications 15
8. Smart Card (Physical layout) ROM(16 K) - OS - Com - Security CPU - 8 bit - 5 MHz - crypto-coprocessor EEPROM (16 K) RAM - 4 kb - File System - Program files - Keys - Passwords - Applications 15
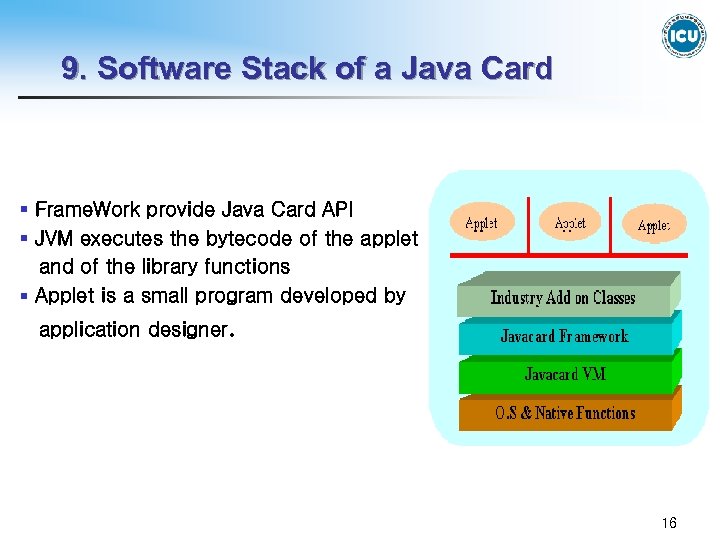 9. Software Stack of a Java Card § Frame. Work provide Java Card API § JVM executes the bytecode of the applet and of the library functions § Applet is a small program developed by application designer. 16
9. Software Stack of a Java Card § Frame. Work provide Java Card API § JVM executes the bytecode of the applet and of the library functions § Applet is a small program developed by application designer. 16
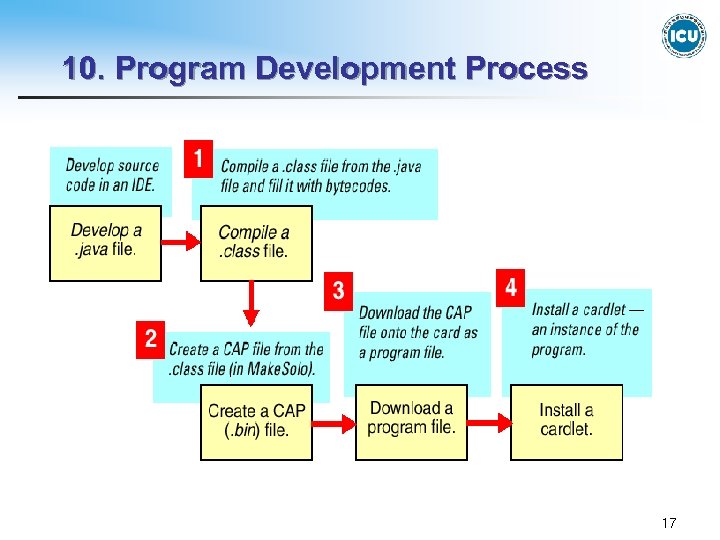 10. Program Development Process 17
10. Program Development Process 17
 11. Cyberflex(TM) Access Cards(1) n Manufacture : Schlumberger n General Characteristics : - Communication protocol : ISO T=0 - Data transmission baud rate : 9600 bit/sec by default, up to 55, 800 bit/sec - Nonvolatile memory : 16 KB of EEPROM (13. 5 KB available for cardlet, keys, and certificate ) - APDU buffer : 255 + 5 bytes - Access control structure : As many as 8 identities per directory/program - Fast native file system 18
11. Cyberflex(TM) Access Cards(1) n Manufacture : Schlumberger n General Characteristics : - Communication protocol : ISO T=0 - Data transmission baud rate : 9600 bit/sec by default, up to 55, 800 bit/sec - Nonvolatile memory : 16 KB of EEPROM (13. 5 KB available for cardlet, keys, and certificate ) - APDU buffer : 255 + 5 bytes - Access control structure : As many as 8 identities per directory/program - Fast native file system 18
 Cyberflex(TM) Access Cards(2) n Cryptographic Features - Host system generation of DES keys and RSA keys(512, 768, 1024 bits) - Enciphering and deciphering data with DES or 3 DES keys in CBC mode - External Authentication with DES or 3 DES keys - Internal Authentication with DES or 3 DES keys in EBC mode, or with RSA digital signatures - SHA-1 and MAC hashing(carried out by Java APIs, not by APDUs) 19
Cyberflex(TM) Access Cards(2) n Cryptographic Features - Host system generation of DES keys and RSA keys(512, 768, 1024 bits) - Enciphering and deciphering data with DES or 3 DES keys in CBC mode - External Authentication with DES or 3 DES keys - Internal Authentication with DES or 3 DES keys in EBC mode, or with RSA digital signatures - SHA-1 and MAC hashing(carried out by Java APIs, not by APDUs) 19
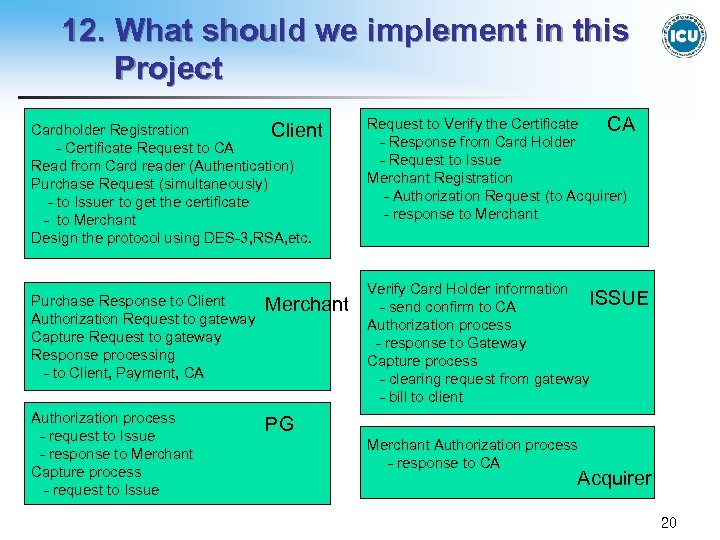 12. What should we implement in this Project Cardholder Registration Client - Certificate Request to CA Read from Card reader (Authentication) Purchase Request (simultaneously) - to Issuer to get the certificate - to Merchant Design the protocol using DES-3, RSA, etc. Purchase Response to Client Authorization Request to gateway Capture Request to gateway Response processing - to Client, Payment, CA Merchant Authorization process - request to Issue - response to Merchant Capture process - request to Issue Request to Verify the Certificate CA - Response from Card Holder - Request to Issue Merchant Registration - Authorization Request (to Acquirer) - response to Merchant Verify Card Holder information ISSUE - send confirm to CA Authorization process - response to Gateway Capture process - clearing request from gateway - bill to client PG Merchant Authorization process - response to CA Acquirer 20
12. What should we implement in this Project Cardholder Registration Client - Certificate Request to CA Read from Card reader (Authentication) Purchase Request (simultaneously) - to Issuer to get the certificate - to Merchant Design the protocol using DES-3, RSA, etc. Purchase Response to Client Authorization Request to gateway Capture Request to gateway Response processing - to Client, Payment, CA Merchant Authorization process - request to Issue - response to Merchant Capture process - request to Issue Request to Verify the Certificate CA - Response from Card Holder - Request to Issue Merchant Registration - Authorization Request (to Acquirer) - response to Merchant Verify Card Holder information ISSUE - send confirm to CA Authorization process - response to Gateway Capture process - clearing request from gateway - bill to client PG Merchant Authorization process - response to CA Acquirer 20
 13. Java Card Security package needed in this project n Key n DSAKey n Secret. Key n DSAPrivate. Key n DESKey n DSAPublic. Key n Private. Key n Key. Builder n Public. Key n Message. Digest n RSAPrivate. Key n Signature n RSAPrivate. Crt. Key n Random. Data n RSAPublic. Key n Cryto. Exception 21
13. Java Card Security package needed in this project n Key n DSAKey n Secret. Key n DSAPrivate. Key n DESKey n DSAPublic. Key n Private. Key n Key. Builder n Public. Key n Message. Digest n RSAPrivate. Key n Signature n RSAPrivate. Crt. Key n Random. Data n RSAPublic. Key n Cryto. Exception 21
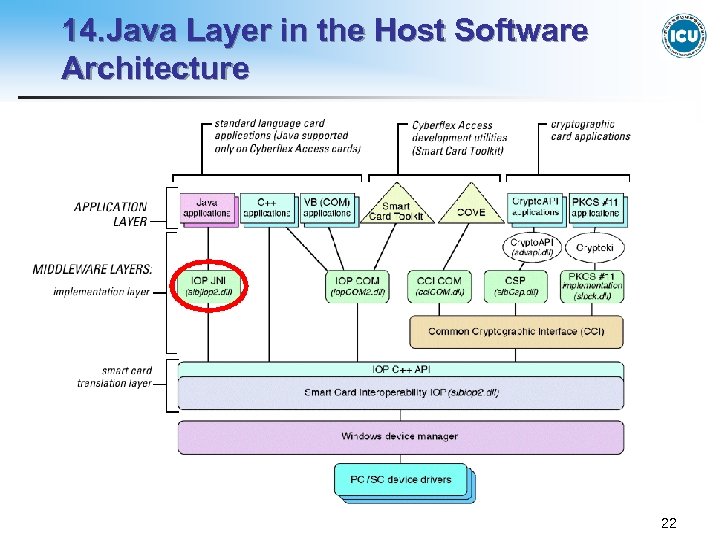 14. Java Layer in the Host Software Architecture 22
14. Java Layer in the Host Software Architecture 22


