38358801531a522d2a1e4e75fc4f531b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 EOQ for Production not Order (EPQ) We do not buy the product. We produce it. Total demand / year is D Demand / day or consumption rate is u Production rate is p / day
EOQ for Production not Order (EPQ) We do not buy the product. We produce it. Total demand / year is D Demand / day or consumption rate is u Production rate is p / day
 Example A toy manufacturer uses 48000 parts for one of its products. Consumption rate is uniform throughout the year. Working days are 240 / year. The firm can produce at a rate of 800 parts / day Carrying cost is $1 / part / year Setup cost for production run is $45 / setup What is the optimal production size?
Example A toy manufacturer uses 48000 parts for one of its products. Consumption rate is uniform throughout the year. Working days are 240 / year. The firm can produce at a rate of 800 parts / day Carrying cost is $1 / part / year Setup cost for production run is $45 / setup What is the optimal production size?
 Example
Example
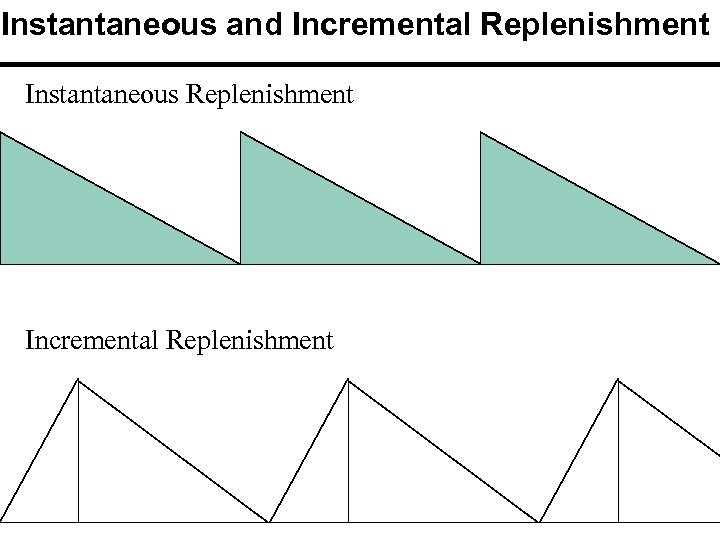 Instantaneous and Incremental Replenishment Instantaneous Replenishment Incremental Replenishment
Instantaneous and Incremental Replenishment Instantaneous Replenishment Incremental Replenishment
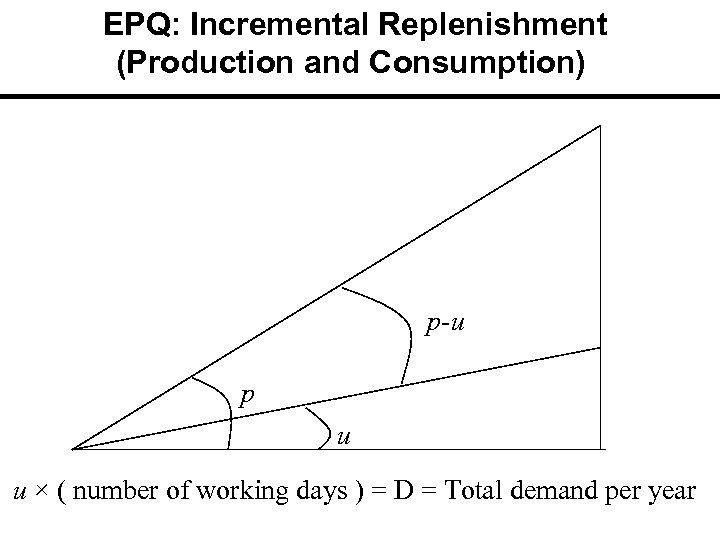 EPQ: Incremental Replenishment (Production and Consumption) p-u p u u × ( number of working days ) = D = Total demand per year
EPQ: Incremental Replenishment (Production and Consumption) p-u p u u × ( number of working days ) = D = Total demand per year
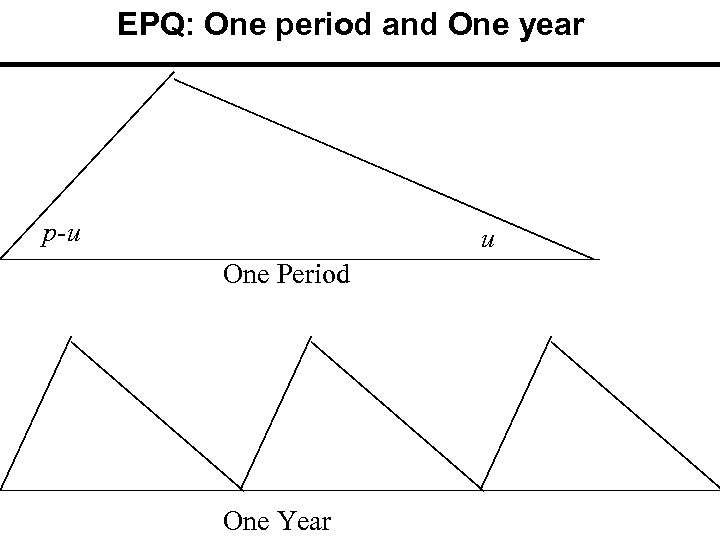 EPQ: One period and One year p-u u One Period One Year
EPQ: One period and One year p-u u One Period One Year
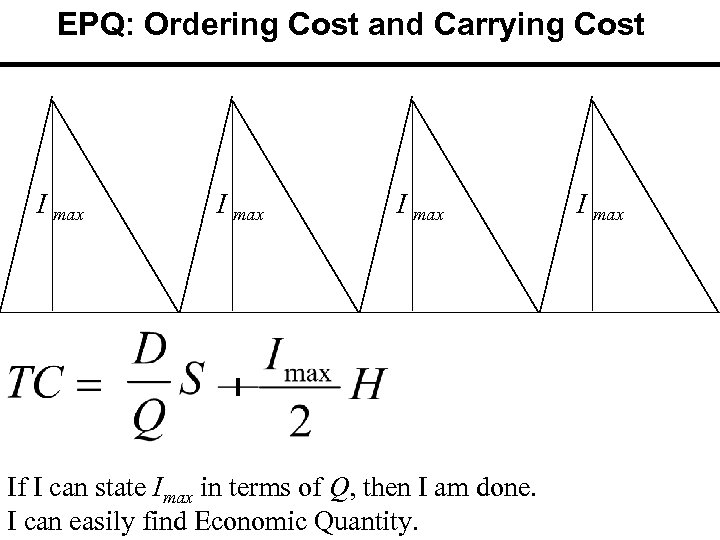 EPQ: Ordering Cost and Carrying Cost I max If I can state Imax in terms of Q, then I am done. I can easily find Economic Quantity. I max
EPQ: Ordering Cost and Carrying Cost I max If I can state Imax in terms of Q, then I am done. I can easily find Economic Quantity. I max
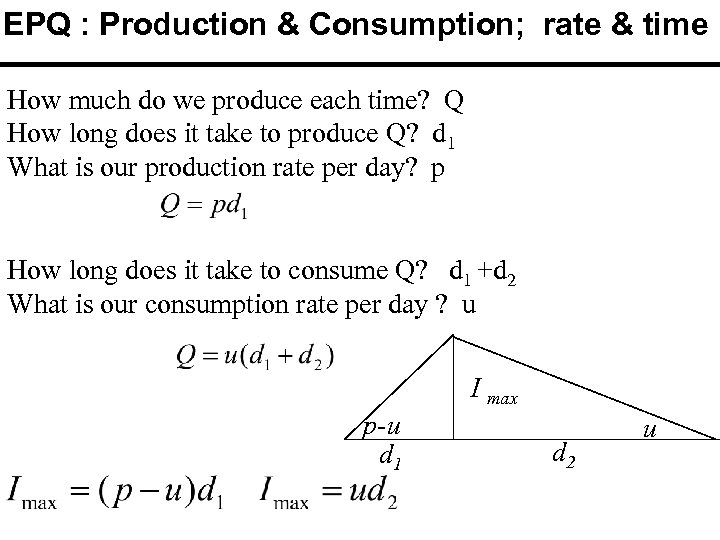 EPQ : Production & Consumption; rate & time How much do we produce each time? Q How long does it take to produce Q? d 1 What is our production rate per day? p How long does it take to consume Q? d 1 +d 2 What is our consumption rate per day ? u I max p-u d 1 d 2 u
EPQ : Production & Consumption; rate & time How much do we produce each time? Q How long does it take to produce Q? d 1 What is our production rate per day? p How long does it take to consume Q? d 1 +d 2 What is our consumption rate per day ? u I max p-u d 1 d 2 u
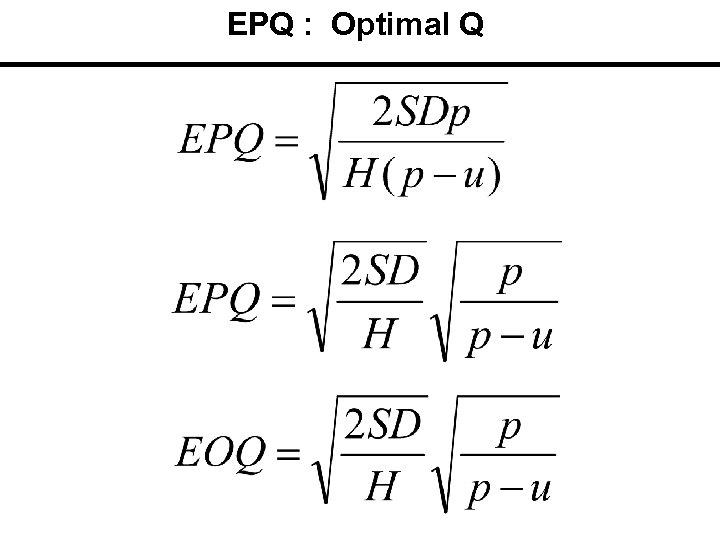 EPQ : Optimal Q
EPQ : Optimal Q
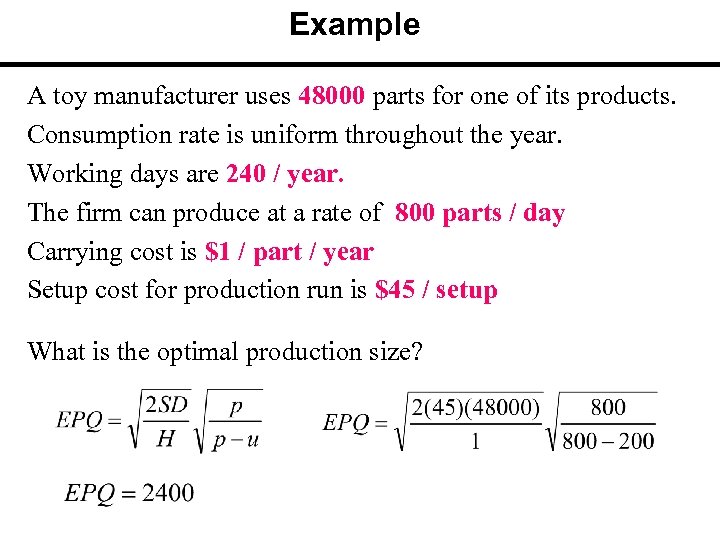 Example A toy manufacturer uses 48000 parts for one of its products. Consumption rate is uniform throughout the year. Working days are 240 / year. The firm can produce at a rate of 800 parts / day Carrying cost is $1 / part / year Setup cost for production run is $45 / setup What is the optimal production size?
Example A toy manufacturer uses 48000 parts for one of its products. Consumption rate is uniform throughout the year. Working days are 240 / year. The firm can produce at a rate of 800 parts / day Carrying cost is $1 / part / year Setup cost for production run is $45 / setup What is the optimal production size?
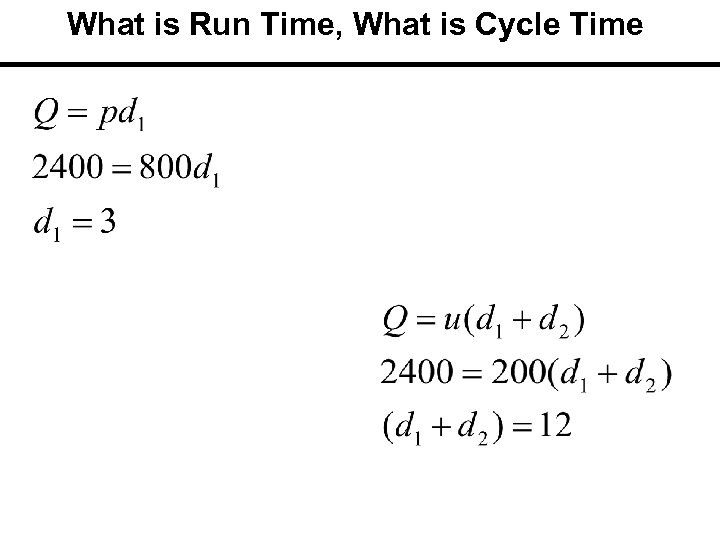 What is Run Time, What is Cycle Time
What is Run Time, What is Cycle Time
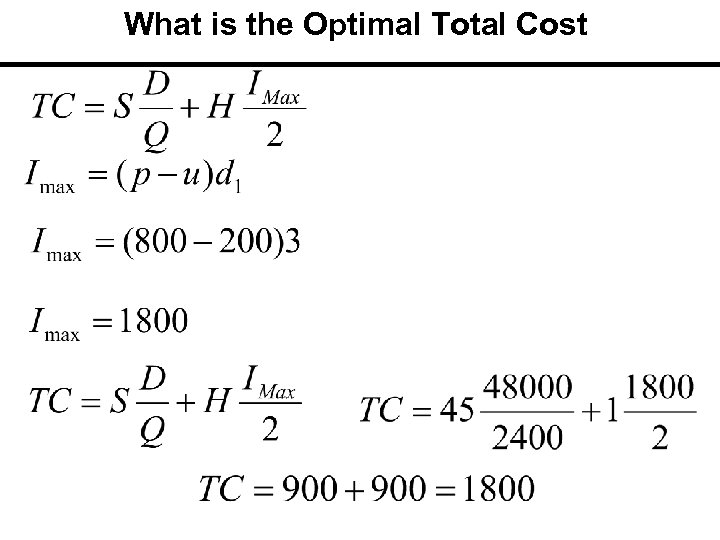 What is the Optimal Total Cost
What is the Optimal Total Cost
 ROP If setup time takes 2 days, at which level of inventory we should start setup? 2(200) = 400
ROP If setup time takes 2 days, at which level of inventory we should start setup? 2(200) = 400
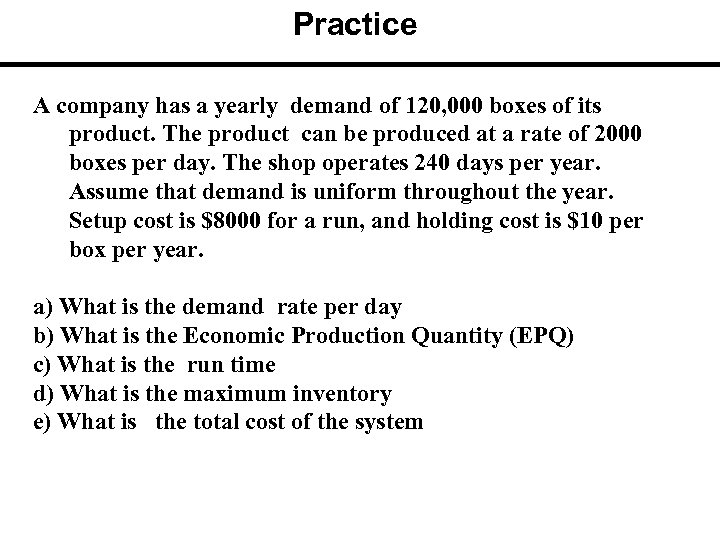 Practice A company has a yearly demand of 120, 000 boxes of its product. The product can be produced at a rate of 2000 boxes per day. The shop operates 240 days per year. Assume that demand is uniform throughout the year. Setup cost is $8000 for a run, and holding cost is $10 per box per year. a) What is the demand rate per day b) What is the Economic Production Quantity (EPQ) c) What is the run time d) What is the maximum inventory e) What is the total cost of the system
Practice A company has a yearly demand of 120, 000 boxes of its product. The product can be produced at a rate of 2000 boxes per day. The shop operates 240 days per year. Assume that demand is uniform throughout the year. Setup cost is $8000 for a run, and holding cost is $10 per box per year. a) What is the demand rate per day b) What is the Economic Production Quantity (EPQ) c) What is the run time d) What is the maximum inventory e) What is the total cost of the system
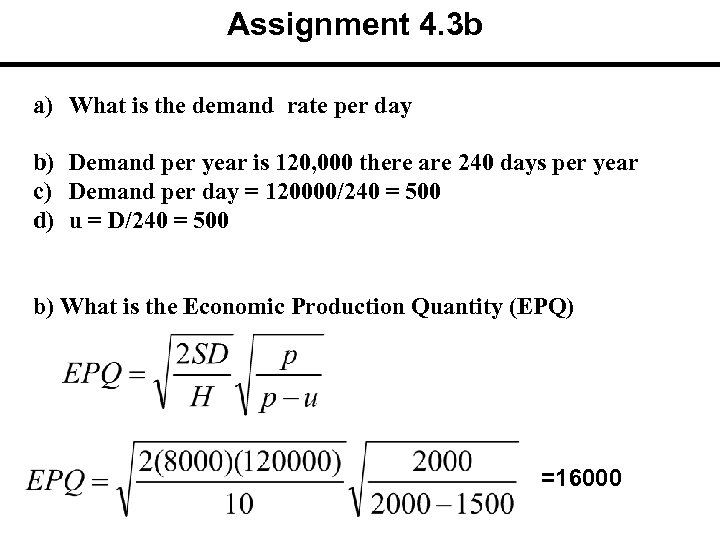 Assignment 4. 3 b a) What is the demand rate per day b) Demand per year is 120, 000 there are 240 days per year c) Demand per day = 120000/240 = 500 d) u = D/240 = 500 b) What is the Economic Production Quantity (EPQ) =16000
Assignment 4. 3 b a) What is the demand rate per day b) Demand per year is 120, 000 there are 240 days per year c) Demand per day = 120000/240 = 500 d) u = D/240 = 500 b) What is the Economic Production Quantity (EPQ) =16000
 Assignment 4. 3 b c) What is the run time We produce 16000 units Our production rate is 2000 per day It takes 16000/2000 = 8 days d 1 = EPQ/p = 8 days d) What is the maximum inventory We produce for 8 days. Each day we produce 2000 units and we consume 500 units of it. Therefore we add to our inventory at rate of 1500 per day for 8 days. That is Imax = 8(1500) = 12000 Imax = pd 1 = 8(1500) = 12000
Assignment 4. 3 b c) What is the run time We produce 16000 units Our production rate is 2000 per day It takes 16000/2000 = 8 days d 1 = EPQ/p = 8 days d) What is the maximum inventory We produce for 8 days. Each day we produce 2000 units and we consume 500 units of it. Therefore we add to our inventory at rate of 1500 per day for 8 days. That is Imax = 8(1500) = 12000 Imax = pd 1 = 8(1500) = 12000
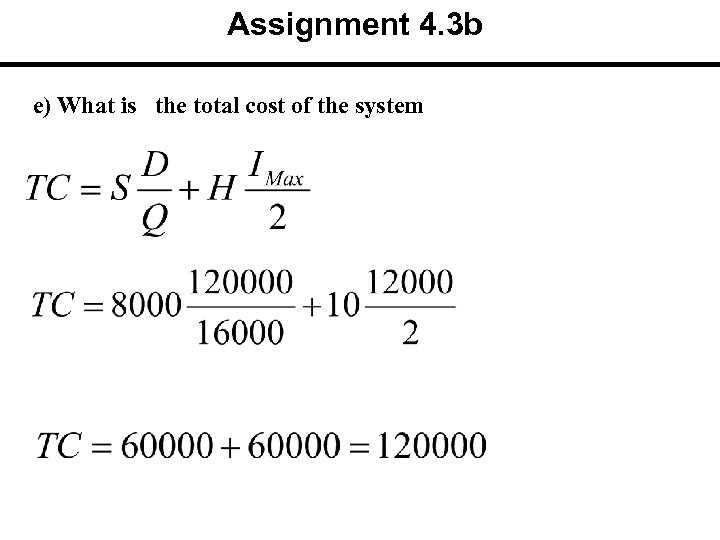 Assignment 4. 3 b e) What is the total cost of the system
Assignment 4. 3 b e) What is the total cost of the system
 Assignment 12. c Problem : The Dine Corporation is both a producer and a user of brass couplings. The firm operates 220 days a year and uses the couplings at a steady rate of 50 per day. u = 50. Couplings can be produced at rate of 200 per day. p=200. Annual storage cost is $1 per coupling, H=1, and machine setup cost is $35 per run, S=35. Since there are 220 days per year and u is equal to 50, yearly demand is 50(220), D= 11000. a) b) c) d) e) Determine the economic run size. Approximately how many runs per year will there be? Compute the maximum inventory level. Determine the cycle time, run time and pure consumption time. Compute the total cost.
Assignment 12. c Problem : The Dine Corporation is both a producer and a user of brass couplings. The firm operates 220 days a year and uses the couplings at a steady rate of 50 per day. u = 50. Couplings can be produced at rate of 200 per day. p=200. Annual storage cost is $1 per coupling, H=1, and machine setup cost is $35 per run, S=35. Since there are 220 days per year and u is equal to 50, yearly demand is 50(220), D= 11000. a) b) c) d) e) Determine the economic run size. Approximately how many runs per year will there be? Compute the maximum inventory level. Determine the cycle time, run time and pure consumption time. Compute the total cost.


