cc9d7124e28cc686dce1f27a6439b720.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Environmental Science Do Now 1 -9 -18 Take your Do Now sheet out and re-write the following paragraph to show sustainable practices. • • I woke up early this morning with morning breath. I turned on the cold water to wet my toothbrush and left the faucet running while I brushed my teeth. After I brushed my teeth, I took a 50 minute hot shower, dried off and put on my clothes. I went downstairs and turned every light on as I walked into the kitchen and made myself a cup of coffee. After I made my coffee, I opened the refrigerator door and just stood there for 1 -2 minutes trying to think about what I should carry for lunch.
Environmental Science Do Now 1 -9 -18 Take your Do Now sheet out and re-write the following paragraph to show sustainable practices. • • I woke up early this morning with morning breath. I turned on the cold water to wet my toothbrush and left the faucet running while I brushed my teeth. After I brushed my teeth, I took a 50 minute hot shower, dried off and put on my clothes. I went downstairs and turned every light on as I walked into the kitchen and made myself a cup of coffee. After I made my coffee, I opened the refrigerator door and just stood there for 1 -2 minutes trying to think about what I should carry for lunch.
 Environmental Science Do Now 1 -9 -18 Take your Do Now sheet out and re-write the following paragraph to show sustainable practices. • • I woke up early this morning with morning breath. I turned on the cold water to wet my toothbrush and immediately turned off the water while I brushed my teeth. After I brushed my teeth, I took a 5 minute lukewarm shower, dried off and put on my clothes. I went downstairs turned on the kitchen light and made myself a cup of coffee. After I made my coffee, I thought about what I wanted out of the refrigerator for lunch, then, opened the refrigerator door.
Environmental Science Do Now 1 -9 -18 Take your Do Now sheet out and re-write the following paragraph to show sustainable practices. • • I woke up early this morning with morning breath. I turned on the cold water to wet my toothbrush and immediately turned off the water while I brushed my teeth. After I brushed my teeth, I took a 5 minute lukewarm shower, dried off and put on my clothes. I went downstairs turned on the kitchen light and made myself a cup of coffee. After I made my coffee, I thought about what I wanted out of the refrigerator for lunch, then, opened the refrigerator door.
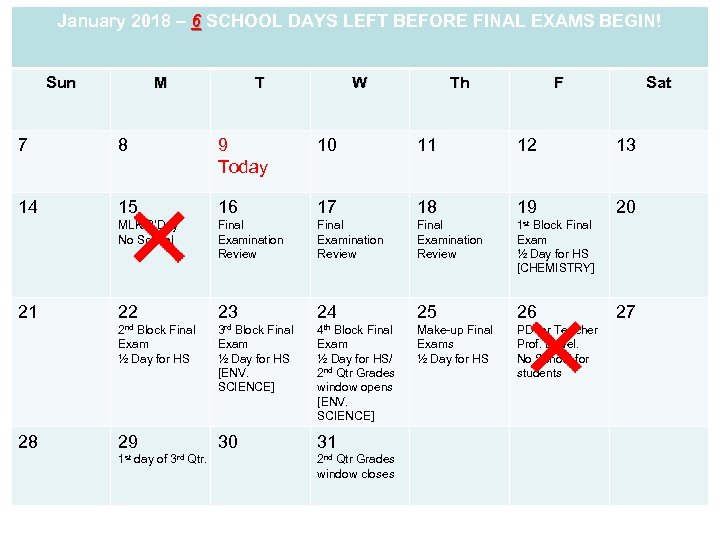 January 2018 – 6 SCHOOL DAYS LEFT BEFORE FINAL EXAMS BEGIN! Sun M T W Th F Sat 7 8 9 Today 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 MLK B’Day No School Final Examination Review 22 23 24 25 26 3 rd Block Final 4 th Block Final Exam ½ Day for HS 28 Final Examination Review 2 nd Block Final 21 Final Examination Review 1 st Block Final Exam ½ Day for HS [ENV. SCIENCE] Exam ½ Day for HS/ 2 nd Qtr Grades window opens [ENV. SCIENCE] Make-up Final Exams ½ Day for HS PD for Teacher Prof. Devel. No School for students 29 30 31 1 st day of 3 rd Qtr. 2 nd Qtr Grades window closes Exam ½ Day for HS [CHEMISTRY] 27
January 2018 – 6 SCHOOL DAYS LEFT BEFORE FINAL EXAMS BEGIN! Sun M T W Th F Sat 7 8 9 Today 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 MLK B’Day No School Final Examination Review 22 23 24 25 26 3 rd Block Final 4 th Block Final Exam ½ Day for HS 28 Final Examination Review 2 nd Block Final 21 Final Examination Review 1 st Block Final Exam ½ Day for HS [ENV. SCIENCE] Exam ½ Day for HS/ 2 nd Qtr Grades window opens [ENV. SCIENCE] Make-up Final Exams ½ Day for HS PD for Teacher Prof. Devel. No School for students 29 30 31 1 st day of 3 rd Qtr. 2 nd Qtr Grades window closes Exam ½ Day for HS [CHEMISTRY] 27
 Final Examination Schedule for 9 th - 11 th Grade: • (9: 00 AM-12: 30 PM) January 19 th - First Block [Chemistry] January 22 nd - Second Block January 23 rd - Third Block [Environmental Science] January 24 th -Fourth Block [Environmental Science]
Final Examination Schedule for 9 th - 11 th Grade: • (9: 00 AM-12: 30 PM) January 19 th - First Block [Chemistry] January 22 nd - Second Block January 23 rd - Third Block [Environmental Science] January 24 th -Fourth Block [Environmental Science]
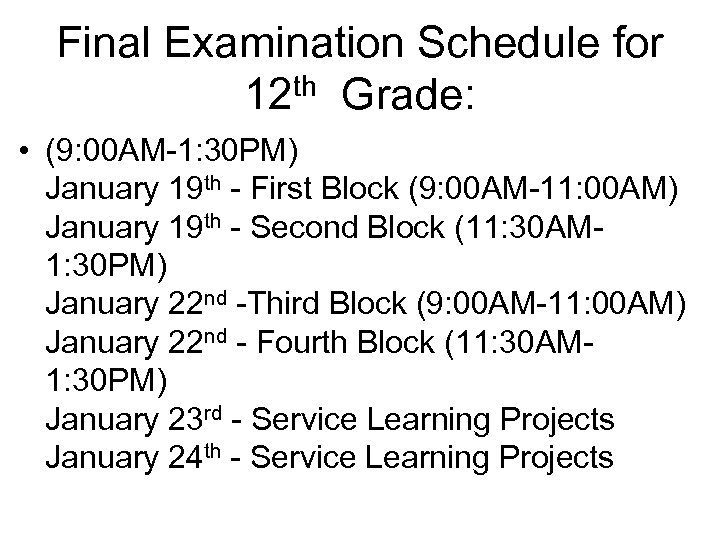 Final Examination Schedule for 12 th Grade: • (9: 00 AM-1: 30 PM) January 19 th - First Block (9: 00 AM-11: 00 AM) January 19 th - Second Block (11: 30 AM 1: 30 PM) January 22 nd -Third Block (9: 00 AM-11: 00 AM) January 22 nd - Fourth Block (11: 30 AM 1: 30 PM) January 23 rd - Service Learning Projects January 24 th - Service Learning Projects
Final Examination Schedule for 12 th Grade: • (9: 00 AM-1: 30 PM) January 19 th - First Block (9: 00 AM-11: 00 AM) January 19 th - Second Block (11: 30 AM 1: 30 PM) January 22 nd -Third Block (9: 00 AM-11: 00 AM) January 22 nd - Fourth Block (11: 30 AM 1: 30 PM) January 23 rd - Service Learning Projects January 24 th - Service Learning Projects
![100 points – close read annotations [classwork] 500 points – TDQs answered [classwork] 660 100 points – close read annotations [classwork] 500 points – TDQs answered [classwork] 660](https://present5.com/presentation/cc9d7124e28cc686dce1f27a6439b720/image-6.jpg) 100 points – close read annotations [classwork] 500 points – TDQs answered [classwork] 660 points – 22 slides of notes [participation] 240 points – concept check questions [classwork] TOTAL POINTS AVAILABLE TODAY: 1500 POINTS
100 points – close read annotations [classwork] 500 points – TDQs answered [classwork] 660 points – 22 slides of notes [participation] 240 points – concept check questions [classwork] TOTAL POINTS AVAILABLE TODAY: 1500 POINTS
![Sustainable Development [Worth 660 points] Unit VI: Sustainable Future January 3, 2018 Happy New Sustainable Development [Worth 660 points] Unit VI: Sustainable Future January 3, 2018 Happy New](https://present5.com/presentation/cc9d7124e28cc686dce1f27a6439b720/image-7.jpg) Sustainable Development [Worth 660 points] Unit VI: Sustainable Future January 3, 2018 Happy New Year! COPY ALL NOTES ON THE NEXT 22 SLIDES!
Sustainable Development [Worth 660 points] Unit VI: Sustainable Future January 3, 2018 Happy New Year! COPY ALL NOTES ON THE NEXT 22 SLIDES!
 Setting the stage to sustainable development • Principle of population – Population when unchecked increased in a geometric ratio and subsistence for man in an arithmetical ratio – Limits to growth – Warnings of immediate collapse • Sooner or later unchecked consumption/use of resources will get us [humans] in trouble
Setting the stage to sustainable development • Principle of population – Population when unchecked increased in a geometric ratio and subsistence for man in an arithmetical ratio – Limits to growth – Warnings of immediate collapse • Sooner or later unchecked consumption/use of resources will get us [humans] in trouble
 Setting the stage to sustainable development • Increased population pressures act as an incentive to the development of new technology and food production
Setting the stage to sustainable development • Increased population pressures act as an incentive to the development of new technology and food production
 Long run vs short run • In the long run, we are limited without changes in technology • In the short run, we rely on human ingenuity to keep us going
Long run vs short run • In the long run, we are limited without changes in technology • In the short run, we rely on human ingenuity to keep us going
 Sustainability • Selected to bridge development and environment • Originally used in – Fisheries “maximum sustainable yield” – Forestry “maximum sustainable cut” – Hydrology “maximum sustainable pumping rate”
Sustainability • Selected to bridge development and environment • Originally used in – Fisheries “maximum sustainable yield” – Forestry “maximum sustainable cut” – Hydrology “maximum sustainable pumping rate”
 Renewable Resources Population growth • Based on Logistic or density dependent growth • Upper limit to the ultimate size [carrying capacity] • Determined by carrying capacity – What defines CC? – The carrying capacity is the number of people, other living organisms, or crops that a region can support without environmental degradation.
Renewable Resources Population growth • Based on Logistic or density dependent growth • Upper limit to the ultimate size [carrying capacity] • Determined by carrying capacity – What defines CC? – The carrying capacity is the number of people, other living organisms, or crops that a region can support without environmental degradation.
![Maximum Sustainable Yield [MSY] MSY the largest yield/catch that can be taken from a Maximum Sustainable Yield [MSY] MSY the largest yield/catch that can be taken from a](https://present5.com/presentation/cc9d7124e28cc686dce1f27a6439b720/image-13.jpg) Maximum Sustainable Yield [MSY] MSY the largest yield/catch that can be taken from a species' stock over an indefinite period. The MSY will be exactly equal to half the carrying capacity of a species.
Maximum Sustainable Yield [MSY] MSY the largest yield/catch that can be taken from a species' stock over an indefinite period. The MSY will be exactly equal to half the carrying capacity of a species.
 Sustainability? • What is a sustainable fishery? • How would you define it?
Sustainability? • What is a sustainable fishery? • How would you define it?
![Five ways to achieve sustainability 1. Leave everything in pristine [original] state, or return Five ways to achieve sustainability 1. Leave everything in pristine [original] state, or return](https://present5.com/presentation/cc9d7124e28cc686dce1f27a6439b720/image-15.jpg) Five ways to achieve sustainability 1. Leave everything in pristine [original] state, or return it to pristine state 2. Develop in a way that doesn’t overwhelm carrying capacity of the system 3. Let sustainability will take care of itself 4. Arrive at efficient solutions 5. Leave for future generations the options or the capacity to be as well off as we are
Five ways to achieve sustainability 1. Leave everything in pristine [original] state, or return it to pristine state 2. Develop in a way that doesn’t overwhelm carrying capacity of the system 3. Let sustainability will take care of itself 4. Arrive at efficient solutions 5. Leave for future generations the options or the capacity to be as well off as we are
 Sustainable Development “Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs" Brundtland Commission “Our common future” 1987
Sustainable Development “Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs" Brundtland Commission “Our common future” 1987
 Dissecting the definition of sustainable development • “meeting the needs” – each person has the resources they need • “the present” – today • “compromise” – sacrifice • “ability of future generations” - ability of our children • “meet their own needs” – children’s need are met
Dissecting the definition of sustainable development • “meeting the needs” – each person has the resources they need • “the present” – today • “compromise” – sacrifice • “ability of future generations” - ability of our children • “meet their own needs” – children’s need are met
 Views for Sustainable Development “The core idea of sustainability implies that our economic system should be managed so we can live off the dividends of our resources”.
Views for Sustainable Development “The core idea of sustainability implies that our economic system should be managed so we can live off the dividends of our resources”.
 Views for Sustainable Development • Sustainable development permits continued improvements in the quality of life with a lower use of resource use, but leaving adequate natural resources behind.
Views for Sustainable Development • Sustainable development permits continued improvements in the quality of life with a lower use of resource use, but leaving adequate natural resources behind.
 Three Approaches of Sustainable Development • Economic: Maximize income while maintaining a constant or increasing stock of capital • Ecological: Maintaining resilience and robustness of biological and physical systems • Socio-cultural: Maintaining the stability of social and cultural systems
Three Approaches of Sustainable Development • Economic: Maximize income while maintaining a constant or increasing stock of capital • Ecological: Maintaining resilience and robustness of biological and physical systems • Socio-cultural: Maintaining the stability of social and cultural systems
 Economic dimension Capital: produces a stream of goods and services into the future
Economic dimension Capital: produces a stream of goods and services into the future
 Ecological approach to Sustainable Development • Sustainable development is about maintenance of essential ecological processes and life support systems, the preservation of genetic diversity and the sustainable utilization of species and ecosystems.
Ecological approach to Sustainable Development • Sustainable development is about maintenance of essential ecological processes and life support systems, the preservation of genetic diversity and the sustainable utilization of species and ecosystems.
 Social Approach to SD • Sustainable development is directly concerned with increasing the standard of living of the poor and indirectly concerned with total economic growth.
Social Approach to SD • Sustainable development is directly concerned with increasing the standard of living of the poor and indirectly concerned with total economic growth.
 Economic dimension • An economically sustainable system must be able to produce goods and services on a continuing basis
Economic dimension • An economically sustainable system must be able to produce goods and services on a continuing basis
 Environmental dimension • A stable resource base, do not overwhelm the waste production ability of the environment, the regenerative services of the environment, or deplete nonrenewables.
Environmental dimension • A stable resource base, do not overwhelm the waste production ability of the environment, the regenerative services of the environment, or deplete nonrenewables.
 Social Dimension • Achieve fair distribution of resources, sufficient delivery of social services.
Social Dimension • Achieve fair distribution of resources, sufficient delivery of social services.
 The principle • Protect the environment and while fulfilling economic and social objectives.
The principle • Protect the environment and while fulfilling economic and social objectives.
 The three core drivers of unsustainability • Consumption – Use of resources beyond the reasonable limits set by nature • Production – Gross inefficiencies in production. • Distribution – Inequitable distribution e. g. distribution of global income between rich and poor
The three core drivers of unsustainability • Consumption – Use of resources beyond the reasonable limits set by nature • Production – Gross inefficiencies in production. • Distribution – Inequitable distribution e. g. distribution of global income between rich and poor
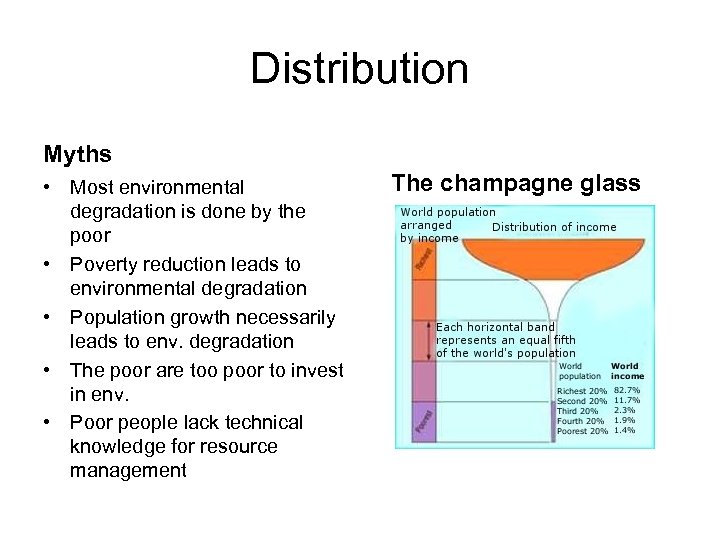 Distribution Myths • Most environmental degradation is done by the poor • Poverty reduction leads to environmental degradation • Population growth necessarily leads to env. degradation • The poor are too poor to invest in env. • Poor people lack technical knowledge for resource management The champagne glass
Distribution Myths • Most environmental degradation is done by the poor • Poverty reduction leads to environmental degradation • Population growth necessarily leads to env. degradation • The poor are too poor to invest in env. • Poor people lack technical knowledge for resource management The champagne glass
 International Organizations, Meetings & Agreements… Related to Sustainable Development Related to Climate & Atmosphere • The World Conservation Union (IUCN), 1948 • UN Conference on Human Environment, 1972 • UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED or Earth Summit) Rio de Janeiro, 1992 • World Summit on Sustainable Development, Johannesburg, 2002 • Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 1988 • Framework Convention on Climate Change, Rio de Janeiro, 1992 • Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, 1987 • Kyoto Protocol on Climate Change, 1997
International Organizations, Meetings & Agreements… Related to Sustainable Development Related to Climate & Atmosphere • The World Conservation Union (IUCN), 1948 • UN Conference on Human Environment, 1972 • UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED or Earth Summit) Rio de Janeiro, 1992 • World Summit on Sustainable Development, Johannesburg, 2002 • Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 1988 • Framework Convention on Climate Change, Rio de Janeiro, 1992 • Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, 1987 • Kyoto Protocol on Climate Change, 1997
 UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED or Earth Summit) Rio de Janeiro, 1992 • The Earth Summit was a sign of new levels of international environmental awareness and cooperation. • Worldwide representatives drew up many agreements, such as, Agenda 21 which addressed a range of environmental problems while allowing continued economic development.
UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED or Earth Summit) Rio de Janeiro, 1992 • The Earth Summit was a sign of new levels of international environmental awareness and cooperation. • Worldwide representatives drew up many agreements, such as, Agenda 21 which addressed a range of environmental problems while allowing continued economic development.
 Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, 1987 • This treaty successfully reduced the amount of ozone-destroying chemicals [CFCs] in the atmosphere. • However, signing the treaty was not mandatory, so some countries did not agree to sign.
Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, 1987 • This treaty successfully reduced the amount of ozone-destroying chemicals [CFCs] in the atmosphere. • However, signing the treaty was not mandatory, so some countries did not agree to sign.
 Kyoto Protocol on Climate Change, 1997 • Was an agreement to reduce worldwide emissions of greenhouse gases and promote pollution-free development
Kyoto Protocol on Climate Change, 1997 • Was an agreement to reduce worldwide emissions of greenhouse gases and promote pollution-free development
![Concept Check Questions [240 points] • • • 1) How does population relate to Concept Check Questions [240 points] • • • 1) How does population relate to](https://present5.com/presentation/cc9d7124e28cc686dce1f27a6439b720/image-34.jpg) Concept Check Questions [240 points] • • • 1) How does population relate to sustainable development? 2) Define the term “sustainable”. 3) What is carrying capacity? 4) What is maximum sustainable yield? Name an industry that uses this term. 5) What are five ways to become sustainable? 6) Explain the meaning of sustainable development “Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs“. • 7) What is a goal of sustainable development? • 8) Name and explain the 3 main approaches to sustainable development. • 9) Name and explain the 3 major driving forces behind our unsustainable lifestyle. • 10) What are three ecological goals of sustainable development? • 11) Explain the importance of each international agreement related to climate change or sustainable development. – A) Earth Summit of 1992 – B) Montreal Protocol of 1987 – C) Kyoto Protocol of 1997
Concept Check Questions [240 points] • • • 1) How does population relate to sustainable development? 2) Define the term “sustainable”. 3) What is carrying capacity? 4) What is maximum sustainable yield? Name an industry that uses this term. 5) What are five ways to become sustainable? 6) Explain the meaning of sustainable development “Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs“. • 7) What is a goal of sustainable development? • 8) Name and explain the 3 main approaches to sustainable development. • 9) Name and explain the 3 major driving forces behind our unsustainable lifestyle. • 10) What are three ecological goals of sustainable development? • 11) Explain the importance of each international agreement related to climate change or sustainable development. – A) Earth Summit of 1992 – B) Montreal Protocol of 1987 – C) Kyoto Protocol of 1997


