3b30d4980517da178d989ea8a90855b2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Environmental Science Chapter 17 Solid/Hazardous Waste
Environmental Science Chapter 17 Solid/Hazardous Waste
 Key Concepts • Solid waste solutions • Reducing solid waste • Hazardous waste regulations • Hazardous waste solutions
Key Concepts • Solid waste solutions • Reducing solid waste • Hazardous waste regulations • Hazardous waste solutions
 Solid Waste • Defn: anything discarded in solid form • Sources: – Municipal garbage = 1. 5% – Industry and Agriculture = 97. 5% • Includes: mining, oil and natural gas production, agricultural activities, industrial processes Fig. 17 -2, p. 390
Solid Waste • Defn: anything discarded in solid form • Sources: – Municipal garbage = 1. 5% – Industry and Agriculture = 97. 5% • Includes: mining, oil and natural gas production, agricultural activities, industrial processes Fig. 17 -2, p. 390
 Technology Revolution • Average 50 -lb computer and 10 -in monitor requires: – ~530 lbs fossil fuel – ~50 lbs chemicals – ~3300 lbs water • Problem: technology is advancing so fast that there is the desire/need to rapidly discard old computers for better, faster new ones • Solutions: provide incentives to extend the life of computers, increase ability to upgrade computers, better recycling programs for old computers/parts
Technology Revolution • Average 50 -lb computer and 10 -in monitor requires: – ~530 lbs fossil fuel – ~50 lbs chemicals – ~3300 lbs water • Problem: technology is advancing so fast that there is the desire/need to rapidly discard old computers for better, faster new ones • Solutions: provide incentives to extend the life of computers, increase ability to upgrade computers, better recycling programs for old computers/parts
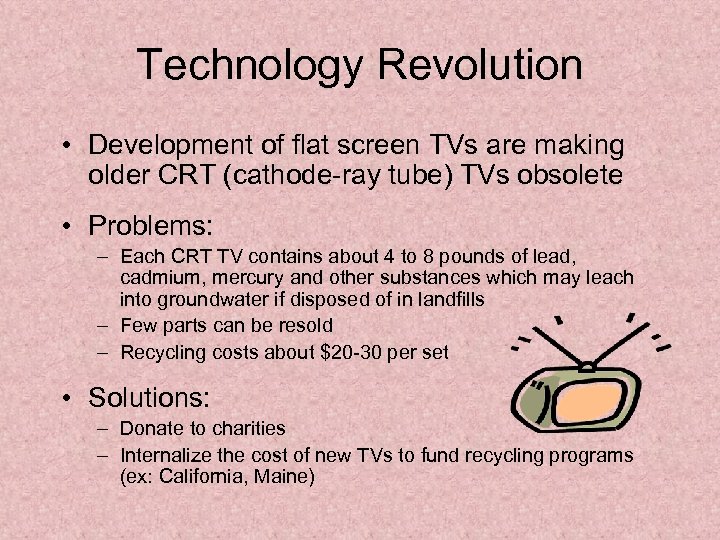 Technology Revolution • Development of flat screen TVs are making older CRT (cathode-ray tube) TVs obsolete • Problems: – Each CRT TV contains about 4 to 8 pounds of lead, cadmium, mercury and other substances which may leach into groundwater if disposed of in landfills – Few parts can be resold – Recycling costs about $20 -30 per set • Solutions: – Donate to charities – Internalize the cost of new TVs to fund recycling programs (ex: California, Maine)
Technology Revolution • Development of flat screen TVs are making older CRT (cathode-ray tube) TVs obsolete • Problems: – Each CRT TV contains about 4 to 8 pounds of lead, cadmium, mercury and other substances which may leach into groundwater if disposed of in landfills – Few parts can be resold – Recycling costs about $20 -30 per set • Solutions: – Donate to charities – Internalize the cost of new TVs to fund recycling programs (ex: California, Maine)
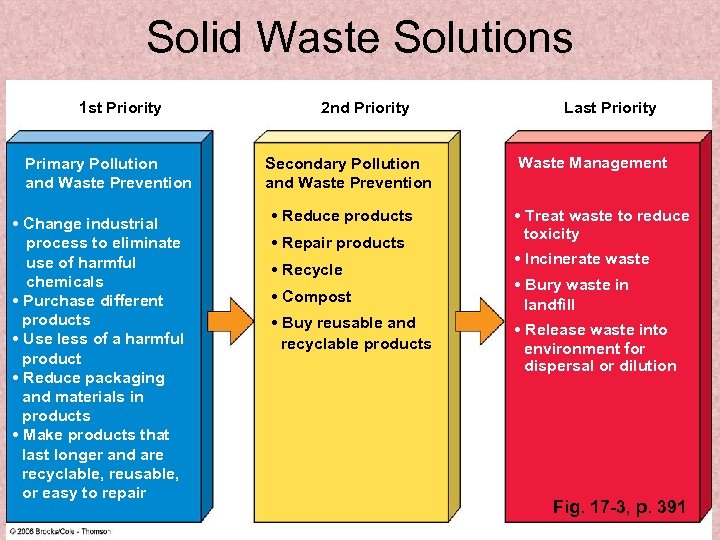 Solid Waste Solutions 1 st Priority Primary Pollution and Waste Prevention • Change industrial process to eliminate use of harmful chemicals • Purchase different products • Use less of a harmful product • Reduce packaging and materials in products • Make products that last longer and are recyclable, reusable, or easy to repair 2 nd Priority Secondary Pollution and Waste Prevention • Reduce products • Repair products • Recycle • Compost • Buy reusable and recyclable products Last Priority Waste Management • Treat waste to reduce toxicity • Incinerate waste • Bury waste in landfill • Release waste into environment for dispersal or dilution Fig. 17 -3, p. 391
Solid Waste Solutions 1 st Priority Primary Pollution and Waste Prevention • Change industrial process to eliminate use of harmful chemicals • Purchase different products • Use less of a harmful product • Reduce packaging and materials in products • Make products that last longer and are recyclable, reusable, or easy to repair 2 nd Priority Secondary Pollution and Waste Prevention • Reduce products • Repair products • Recycle • Compost • Buy reusable and recyclable products Last Priority Waste Management • Treat waste to reduce toxicity • Incinerate waste • Bury waste in landfill • Release waste into environment for dispersal or dilution Fig. 17 -3, p. 391
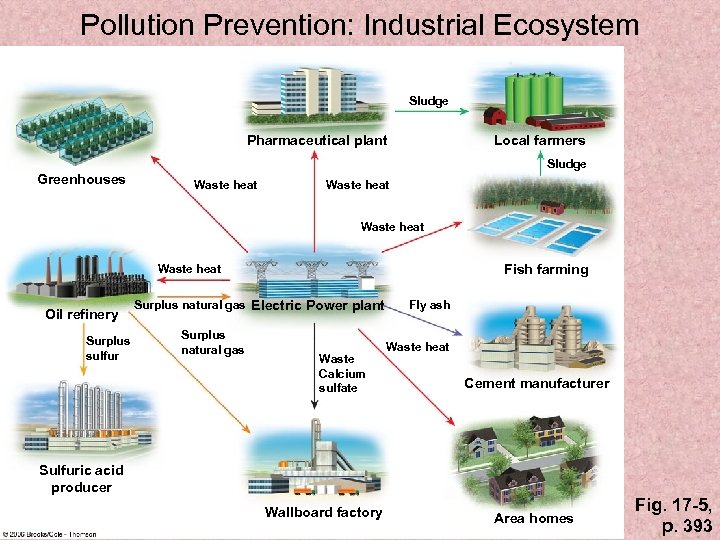 Pollution Prevention: Industrial Ecosystem Sludge Pharmaceutical plant Local farmers Sludge Greenhouses Waste heat Fish farming Waste heat Oil refinery Surplus sulfur Surplus natural gas Electric Power plant Surplus natural gas Waste Calcium sulfate Fly ash Waste heat Cement manufacturer Sulfuric acid producer Wallboard factory Area homes Fig. 17 -5, p. 393
Pollution Prevention: Industrial Ecosystem Sludge Pharmaceutical plant Local farmers Sludge Greenhouses Waste heat Fish farming Waste heat Oil refinery Surplus sulfur Surplus natural gas Electric Power plant Surplus natural gas Waste Calcium sulfate Fly ash Waste heat Cement manufacturer Sulfuric acid producer Wallboard factory Area homes Fig. 17 -5, p. 393
 Reducing Solid Waste • Sustainability six – Consume less – Redesign manufacturing processes – Produce less waste and pollution – Repair, reuse, remanufacture, compost, and recycle – Design products to last longer – Eliminate, reuse, recycle, or reduce packaging
Reducing Solid Waste • Sustainability six – Consume less – Redesign manufacturing processes – Produce less waste and pollution – Repair, reuse, remanufacture, compost, and recycle – Design products to last longer – Eliminate, reuse, recycle, or reduce packaging
 What Can You Do? Solid Waste • Follow the four R's of resource use: Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle. • Ask yourself whether you really need a particular item. • Rent, borrow, or barter goods and services when you can. • Buy things that are reusable, recyclable, or compostable, and be sure to reuse, recycle, and compost them. • Do not use throwaway paper and plastic plates, cups, and eating utensils, and other disposable items when reusable or refillable versions are available. • Use e-mail in place of conventional paper mail. • Read newspapers and magazines online. • Buy products in concentrated form whenever possible. Fig. 17 -4, p. 391
What Can You Do? Solid Waste • Follow the four R's of resource use: Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle. • Ask yourself whether you really need a particular item. • Rent, borrow, or barter goods and services when you can. • Buy things that are reusable, recyclable, or compostable, and be sure to reuse, recycle, and compost them. • Do not use throwaway paper and plastic plates, cups, and eating utensils, and other disposable items when reusable or refillable versions are available. • Use e-mail in place of conventional paper mail. • Read newspapers and magazines online. • Buy products in concentrated form whenever possible. Fig. 17 -4, p. 391
 Hazardous Waste • Main sources of hazardous wastes are mining and electric power plants • Legal definition: – Any solid or liquid that: • Contains one or more of the 39 toxic compounds above established levels; • Catches fire easily; • Is reactive or unstable; or • Is capable of eroding metal containers • Yet, this does not include such items as radioactive wastes, mining wastes or wastes from small businesses
Hazardous Waste • Main sources of hazardous wastes are mining and electric power plants • Legal definition: – Any solid or liquid that: • Contains one or more of the 39 toxic compounds above established levels; • Catches fire easily; • Is reactive or unstable; or • Is capable of eroding metal containers • Yet, this does not include such items as radioactive wastes, mining wastes or wastes from small businesses
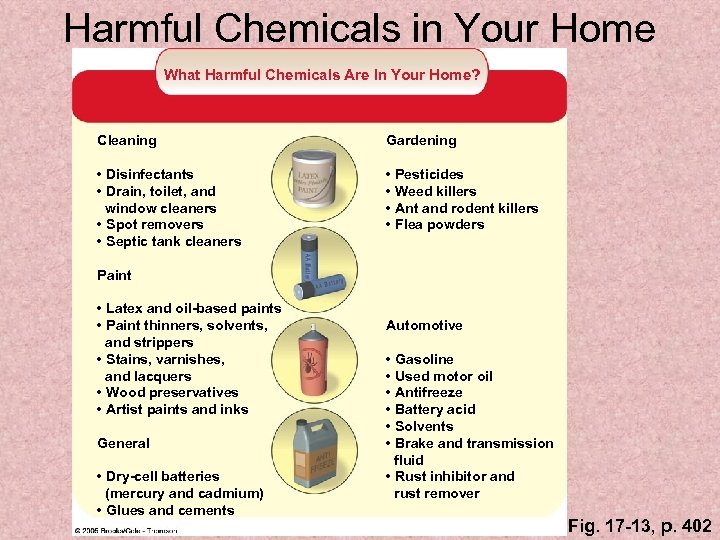 Harmful Chemicals in Your Home What Harmful Chemicals Are In Your Home? Cleaning Gardening • Disinfectants • Drain, toilet, and window cleaners • Spot removers • Septic tank cleaners • Pesticides • Weed killers • Ant and rodent killers • Flea powders Paint • Latex and oil-based paints • Paint thinners, solvents, and strippers • Stains, varnishes, and lacquers • Wood preservatives • Artist paints and inks General • Dry-cell batteries (mercury and cadmium) • Glues and cements Automotive • Gasoline • Used motor oil • Antifreeze • Battery acid • Solvents • Brake and transmission fluid • Rust inhibitor and rust remover Fig. 17 -13, p. 402
Harmful Chemicals in Your Home What Harmful Chemicals Are In Your Home? Cleaning Gardening • Disinfectants • Drain, toilet, and window cleaners • Spot removers • Septic tank cleaners • Pesticides • Weed killers • Ant and rodent killers • Flea powders Paint • Latex and oil-based paints • Paint thinners, solvents, and strippers • Stains, varnishes, and lacquers • Wood preservatives • Artist paints and inks General • Dry-cell batteries (mercury and cadmium) • Glues and cements Automotive • Gasoline • Used motor oil • Antifreeze • Battery acid • Solvents • Brake and transmission fluid • Rust inhibitor and rust remover Fig. 17 -13, p. 402
 Hazardous Waste Regulation • Resource Conservation and Recovery Act of 1976 – EPA identified and set standards for management of hazardous waste – Companies that store, treat or dispose of more than 220 pounds of hazardous wastes per month must be permitted – Companies must record all information about wastes from where it was produced to where it was disposed • Superfund Act of 1980 – Identifies old hazardous waste dump sites or leaking underground tanks – Cleans up those sites and affected groundwater – Attempts to locate responsible parties to pay for the clean-up For a list of sites by county in Florida: www. epa. gov/superfund/sites/npl/fl. htm
Hazardous Waste Regulation • Resource Conservation and Recovery Act of 1976 – EPA identified and set standards for management of hazardous waste – Companies that store, treat or dispose of more than 220 pounds of hazardous wastes per month must be permitted – Companies must record all information about wastes from where it was produced to where it was disposed • Superfund Act of 1980 – Identifies old hazardous waste dump sites or leaking underground tanks – Cleans up those sites and affected groundwater – Attempts to locate responsible parties to pay for the clean-up For a list of sites by county in Florida: www. epa. gov/superfund/sites/npl/fl. htm
 Hazardous Waste Solutions • Bioremediation • Phytoremediation • Incineration • Deep-well disposal • Surface impoundments • Secure landfills • Aboveground buildings • Prevention is better than disposal or cleanup
Hazardous Waste Solutions • Bioremediation • Phytoremediation • Incineration • Deep-well disposal • Surface impoundments • Secure landfills • Aboveground buildings • Prevention is better than disposal or cleanup
 What Can You Do? Hazardous Waste • Use pesticides in the smallest amount possible. • Use less harmful substances instead of commercial chemicals for most household cleaners. For example, use liquid ammonia to clean appliances and windows; vinegar to polish metals, clean surfaces, and remove stains and mildew; baking soda to clean household utensils, deodorize, and remove stains; borax to remove stains and mildew. • Do not dispose of pesticides, paints, solvents, oil, antifreeze, or other products containing hazardous chemicals by flushing them down the toilet, pouring them down the drain, burying them, throwing them into the garbage, or dumping them down storm drains. Fig. 17 -20, p. 406
What Can You Do? Hazardous Waste • Use pesticides in the smallest amount possible. • Use less harmful substances instead of commercial chemicals for most household cleaners. For example, use liquid ammonia to clean appliances and windows; vinegar to polish metals, clean surfaces, and remove stains and mildew; baking soda to clean household utensils, deodorize, and remove stains; borax to remove stains and mildew. • Do not dispose of pesticides, paints, solvents, oil, antifreeze, or other products containing hazardous chemicals by flushing them down the toilet, pouring them down the drain, burying them, throwing them into the garbage, or dumping them down storm drains. Fig. 17 -20, p. 406
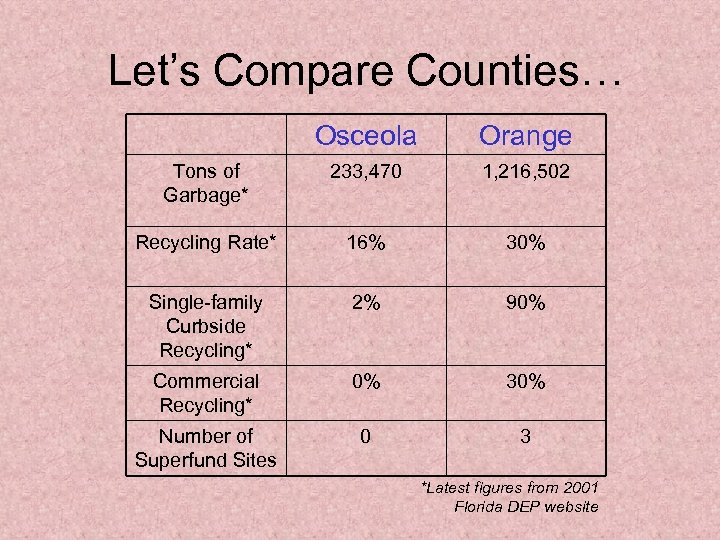 Let’s Compare Counties… Osceola Orange Tons of Garbage* 233, 470 1, 216, 502 Recycling Rate* 16% 30% Single-family Curbside Recycling* 2% 90% Commercial Recycling* 0% 30% Number of Superfund Sites 0 3 *Latest figures from 2001 Florida DEP website
Let’s Compare Counties… Osceola Orange Tons of Garbage* 233, 470 1, 216, 502 Recycling Rate* 16% 30% Single-family Curbside Recycling* 2% 90% Commercial Recycling* 0% 30% Number of Superfund Sites 0 3 *Latest figures from 2001 Florida DEP website
 Any Questions?
Any Questions?


