4e2387798ef4f1bb23d5844cc415e98b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 Environmental Management Systems The ISO 14001 Approach N. C. Health Physics Society Boone, NC October 19, 2001 Julie Woosley EMS Development Course for Government Agencies, Project Coordinator NC DPPEA
Environmental Management Systems The ISO 14001 Approach N. C. Health Physics Society Boone, NC October 19, 2001 Julie Woosley EMS Development Course for Government Agencies, Project Coordinator NC DPPEA
 What is an EMS? n n n Systematic way of managing an organization’s environmental affairs Based on Plan-Do-Check-Act Model (PDCA) Focused on Continual Improvement of system Addresses immediate and long-term impact of an organization’s products, services and processes on the environment. A tool to improve environmental performance
What is an EMS? n n n Systematic way of managing an organization’s environmental affairs Based on Plan-Do-Check-Act Model (PDCA) Focused on Continual Improvement of system Addresses immediate and long-term impact of an organization’s products, services and processes on the environment. A tool to improve environmental performance
 Some EMS Models n ISO 14001 n Metal Finishers National Biosolids Partnership Project XL with the United Egg Producers Agriculture EMS models (livestock, soybean) SGIA model Federal facility models (CEMP, DOE guide) Compliance-focused EMS (CFEMS) Commission for Env. Cooperation (CEC guide) n n n n
Some EMS Models n ISO 14001 n Metal Finishers National Biosolids Partnership Project XL with the United Egg Producers Agriculture EMS models (livestock, soybean) SGIA model Federal facility models (CEMP, DOE guide) Compliance-focused EMS (CFEMS) Commission for Env. Cooperation (CEC guide) n n n n
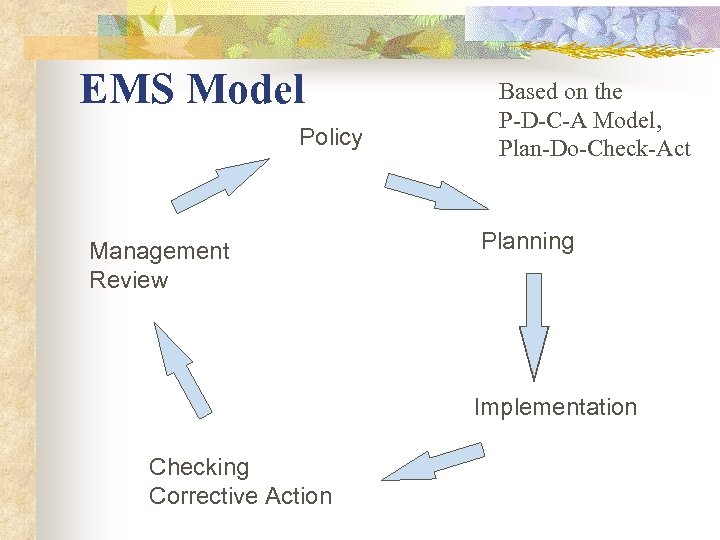 EMS Model Policy Management Review Based on the P-D-C-A Model, Plan-Do-Check-Act Planning Implementation Checking Corrective Action
EMS Model Policy Management Review Based on the P-D-C-A Model, Plan-Do-Check-Act Planning Implementation Checking Corrective Action
 Why Implement an EMS? To get your environmental ducks in a row! n n n Struggling to stay in compliance and keep track of regulations/laws Environmental management just one of many responsibilities Establish a framework to move beyond compliance Vehicle for positive change; improved employee morale, enhanced public image Employee turnover
Why Implement an EMS? To get your environmental ducks in a row! n n n Struggling to stay in compliance and keep track of regulations/laws Environmental management just one of many responsibilities Establish a framework to move beyond compliance Vehicle for positive change; improved employee morale, enhanced public image Employee turnover
 Why Implement an EMS ? More reasons: n Helps to identify the causes of environmental problems. n n Trade and competitive issues n n better to make a product right the first time cheaper to prevent a spill or other accident cost effective to prevent pollution Inconsistency in environmental regulation and enforcement Many individual parts may already be in place – just need to unify under the EMS umbrella!
Why Implement an EMS ? More reasons: n Helps to identify the causes of environmental problems. n n Trade and competitive issues n n better to make a product right the first time cheaper to prevent a spill or other accident cost effective to prevent pollution Inconsistency in environmental regulation and enforcement Many individual parts may already be in place – just need to unify under the EMS umbrella!
 ISO 14000: A series of standards n Created by the International Organization of Standardization, a non-governmental organization (NGO) established in 1947, located in Switzerland (see handout for more info) n n ISO is not an acronym - from the Greek iso, meaning equal (as in isothermal) ISO is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies from over 100 countries; American National Standards Institute (ANSI) is US representative n They have created many standards: ISO 9000, film speeds
ISO 14000: A series of standards n Created by the International Organization of Standardization, a non-governmental organization (NGO) established in 1947, located in Switzerland (see handout for more info) n n ISO is not an acronym - from the Greek iso, meaning equal (as in isothermal) ISO is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies from over 100 countries; American National Standards Institute (ANSI) is US representative n They have created many standards: ISO 9000, film speeds
 ISO 14000 Family n A series of guidance documents and standards to help organizations address environmental issues. Ones below deal with EMS. n n n 14001: Environmental Management Systems 14004: EMS general guidelines 14010: Guidelines for Environmental Auditing 14011: Guidelines for Auditing of an EMS 14012: Auditing - Qualification criteria
ISO 14000 Family n A series of guidance documents and standards to help organizations address environmental issues. Ones below deal with EMS. n n n 14001: Environmental Management Systems 14004: EMS general guidelines 14010: Guidelines for Environmental Auditing 14011: Guidelines for Auditing of an EMS 14012: Auditing - Qualification criteria
 To Whom Do the Standards Apply? n n n Standard is Voluntary Large and Small Business & Industry Service Sectors (hospitals, hotels, etc. ) City and County Government Applicable to all types of organizations, of all sizes anywhere in the world
To Whom Do the Standards Apply? n n n Standard is Voluntary Large and Small Business & Industry Service Sectors (hospitals, hotels, etc. ) City and County Government Applicable to all types of organizations, of all sizes anywhere in the world
 Becoming ISO 14001 certified n n n ISO 14001 is the only certification standard Registration body examines EMS for conformity to the ISO 14001 standard Not a compliance audit, an EMS audit Facility awarded registration Does NOT mean that products are more environmentally friendly Does mean have a documented EMS that is fully implemented and consistently followed
Becoming ISO 14001 certified n n n ISO 14001 is the only certification standard Registration body examines EMS for conformity to the ISO 14001 standard Not a compliance audit, an EMS audit Facility awarded registration Does NOT mean that products are more environmentally friendly Does mean have a documented EMS that is fully implemented and consistently followed
 External Drivers for ISO 14001? n Suppliers encouraged to consider an EMS by: n n n n IBM Xerox (30, 000) Bristol-Myers Squibb (15, 000) Ford and GM Toyota- choice of 3 MP&M, Others? ? Approx. 271, 000 ISO 9000 certifications worldwide (est. 380 NC certifications)
External Drivers for ISO 14001? n Suppliers encouraged to consider an EMS by: n n n n IBM Xerox (30, 000) Bristol-Myers Squibb (15, 000) Ford and GM Toyota- choice of 3 MP&M, Others? ? Approx. 271, 000 ISO 9000 certifications worldwide (est. 380 NC certifications)
 World Picture n n 30, 303 ISO 14001 cert. in world as of 6/01 1, 480 ISO 14001 cert. in US as of 6/01 54 companies known certified in NC, and one municipality US is 5 th in number of certifications behind Japan (6, 648), the UK (2, 500), Germany (2, 400), and Sweden (1, 911)
World Picture n n 30, 303 ISO 14001 cert. in world as of 6/01 1, 480 ISO 14001 cert. in US as of 6/01 54 companies known certified in NC, and one municipality US is 5 th in number of certifications behind Japan (6, 648), the UK (2, 500), Germany (2, 400), and Sweden (1, 911)
 EMSs and the Federal Government n n n n Published Federal Register notice 3/12/98 EPA “Aiming for Excellence” Report Sept. 99; part of Draft EMS Action Plan http: //www. epa. gov/ems Clinton signed Executive Order 4/00 requiring federal facilities to have an EMS by 2005 EPA Performance Track June 2000 – requires an EMS Office of Water funded pilot efforts in 10 states, pilot program with governments, pilot with Biosolids Assoc. New MP&M (Metal Products and Machinery) Effluent Guidelines: final rule may include EMS-based exemptions (P 2 option) EMS and Enforcement
EMSs and the Federal Government n n n n Published Federal Register notice 3/12/98 EPA “Aiming for Excellence” Report Sept. 99; part of Draft EMS Action Plan http: //www. epa. gov/ems Clinton signed Executive Order 4/00 requiring federal facilities to have an EMS by 2005 EPA Performance Track June 2000 – requires an EMS Office of Water funded pilot efforts in 10 states, pilot program with governments, pilot with Biosolids Assoc. New MP&M (Metal Products and Machinery) Effluent Guidelines: final rule may include EMS-based exemptions (P 2 option) EMS and Enforcement
 N. C. EMS Related Activities n n n NC DENR EMS policy Aug. 1999 State Regulatory Innovation legislation Sector-based EMSs (paper industry, screenprinting, metal finishing, furniture): see http: //www. p 2 pays. org/iso/sector EMS Development Course for Government Agencies EMS Pilot Project with Pork Producers
N. C. EMS Related Activities n n n NC DENR EMS policy Aug. 1999 State Regulatory Innovation legislation Sector-based EMSs (paper industry, screenprinting, metal finishing, furniture): see http: //www. p 2 pays. org/iso/sector EMS Development Course for Government Agencies EMS Pilot Project with Pork Producers
 Multi-State Working Group n Many states (founding states are AZ, CA, IL, MA, MN, NC, OR, PA, TX, WI) n n EPA, NGO’s, National Institute of Standards & Technology, CI 2, CMA Implemented pilot projects with industry n Goal: To understand communicate the value of ISO 14000 in meeting public policy goals.
Multi-State Working Group n Many states (founding states are AZ, CA, IL, MA, MN, NC, OR, PA, TX, WI) n n EPA, NGO’s, National Institute of Standards & Technology, CI 2, CMA Implemented pilot projects with industry n Goal: To understand communicate the value of ISO 14000 in meeting public policy goals.
 What does ISO 14001 Say?
What does ISO 14001 Say?
 17 Requirements in ISO 14001 Env. Policy 4. 2 Document control 4. 4. 5 Env. Aspects 4. 3. 1 Operational control 4. 4. 6 Legal and other req. 4. 3. 2 Emergency preparedness and response 4. 4. 7 Obj. and targets 4. 3. 3 Monitoring and measurement 4. 5. 1 Env. Mgmt. Program 4. 3. 4 Corrective/preventive action 4. 5. 2 Structure and Responsibility 4. 4. 1 Records 4. 5. 3 Training, awareness, and competence 4. 4. 2 EMS audit 4. 5. 4 Communication 4. 4. 3 Management Review 4. 6 EMS documentation 4. 4. 4
17 Requirements in ISO 14001 Env. Policy 4. 2 Document control 4. 4. 5 Env. Aspects 4. 3. 1 Operational control 4. 4. 6 Legal and other req. 4. 3. 2 Emergency preparedness and response 4. 4. 7 Obj. and targets 4. 3. 3 Monitoring and measurement 4. 5. 1 Env. Mgmt. Program 4. 3. 4 Corrective/preventive action 4. 5. 2 Structure and Responsibility 4. 4. 1 Records 4. 5. 3 Training, awareness, and competence 4. 4. 2 EMS audit 4. 5. 4 Communication 4. 4. 3 Management Review 4. 6 EMS documentation 4. 4. 4
 ISO 14001 Key Elements n n n Policy Statement Identification of Significant Environmental Impacts Development of Objectives and Targets Implementation Plan to Meet Obj. and Targets Training Management Review How you meet the elements is up to you
ISO 14001 Key Elements n n n Policy Statement Identification of Significant Environmental Impacts Development of Objectives and Targets Implementation Plan to Meet Obj. and Targets Training Management Review How you meet the elements is up to you
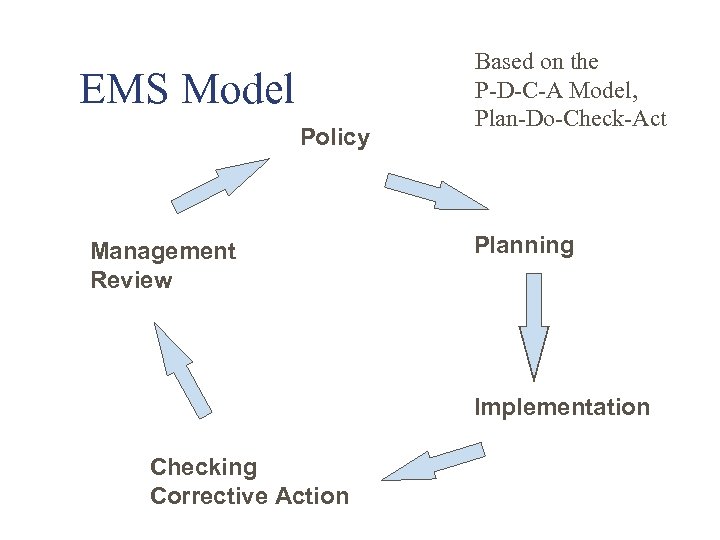 EMS Model Policy Management Review Based on the P-D-C-A Model, Plan-Do-Check-Act Planning Implementation Checking Corrective Action
EMS Model Policy Management Review Based on the P-D-C-A Model, Plan-Do-Check-Act Planning Implementation Checking Corrective Action
 ISO 14001 Policy Statement (4. 2) n n Management’s declaration of commitment to the environment. Policy Statement n 3 Main Elements (Big 3) n Commitment to Compliance n Commitment to Prevention of Pollution, and n Commitment to Continual Improvement n n Broader definition of pollution prevention Available to Interested Parties
ISO 14001 Policy Statement (4. 2) n n Management’s declaration of commitment to the environment. Policy Statement n 3 Main Elements (Big 3) n Commitment to Compliance n Commitment to Prevention of Pollution, and n Commitment to Continual Improvement n n Broader definition of pollution prevention Available to Interested Parties
 EMS Policy Statement n Must be appropriate to the nature, scale and environmental impacts of the organization’s activities, products or services n Provides a framework for setting and reviewing objectives and targets n Way of communicating environmental mission internally and externally n Broader definition of pollution prevention than EPA’s: not just source reduction, but also recycling, treatment, disposal, and material substitution
EMS Policy Statement n Must be appropriate to the nature, scale and environmental impacts of the organization’s activities, products or services n Provides a framework for setting and reviewing objectives and targets n Way of communicating environmental mission internally and externally n Broader definition of pollution prevention than EPA’s: not just source reduction, but also recycling, treatment, disposal, and material substitution
 HOW TWO N. C. COMPANIES COMMUNICATED THEIR POLICY STATEMENT TO EMPLOYEES
HOW TWO N. C. COMPANIES COMMUNICATED THEIR POLICY STATEMENT TO EMPLOYEES
 Aspects and Impacts (4. 3. 1) n n n An organization evaluates and addresses its own significant aspects, including nonregulated aspects May be positive or negative Think from the fenceline: n n Aspect: Cause or Input: Element of an organization’s activities, products, or services which can interact with the environment Impact: Effect or Output: Any change to the environment, whether adverse or beneficial, resulting from an organization’s activities, products, or services
Aspects and Impacts (4. 3. 1) n n n An organization evaluates and addresses its own significant aspects, including nonregulated aspects May be positive or negative Think from the fenceline: n n Aspect: Cause or Input: Element of an organization’s activities, products, or services which can interact with the environment Impact: Effect or Output: Any change to the environment, whether adverse or beneficial, resulting from an organization’s activities, products, or services
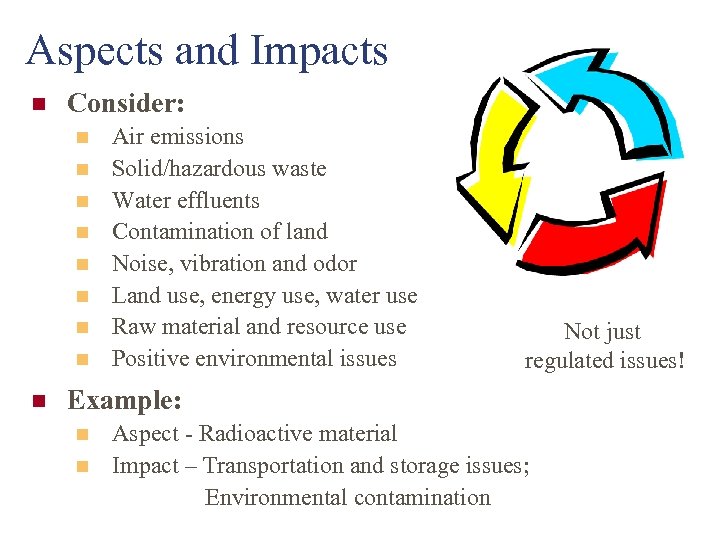 Aspects and Impacts n Consider: n n n n n Air emissions Solid/hazardous waste Water effluents Contamination of land Noise, vibration and odor Land use, energy use, water use Raw material and resource use Positive environmental issues Not just regulated issues! Example: n n Aspect - Radioactive material Impact – Transportation and storage issues; Environmental contamination
Aspects and Impacts n Consider: n n n n n Air emissions Solid/hazardous waste Water effluents Contamination of land Noise, vibration and odor Land use, energy use, water use Raw material and resource use Positive environmental issues Not just regulated issues! Example: n n Aspect - Radioactive material Impact – Transportation and storage issues; Environmental contamination
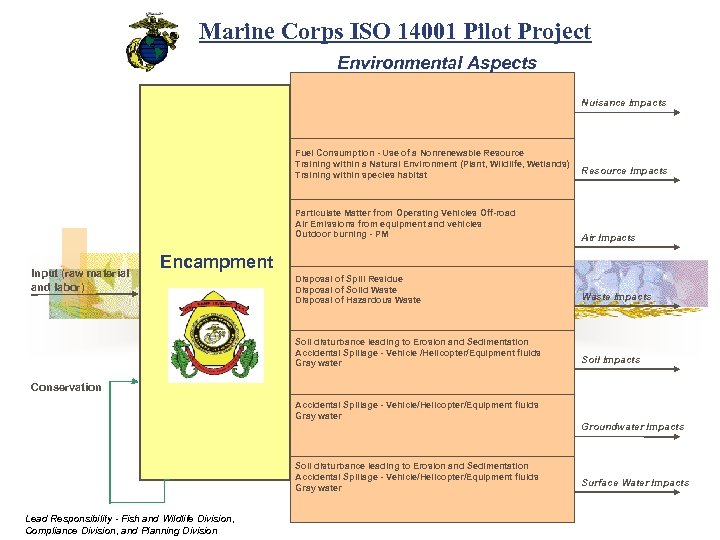 Marine Corps ISO 14001 Pilot Project Environmental Aspects Nuisance Impacts Fuel Consumption - Use of a Nonrenewable Resource Training within a Natural Environment (Plant, Wildlife, Wetlands) Training within species habitat Particulate Matter from Operating Vehicles Off-road Air Emissions from equipment and vehicles Outdoor burning - PM Air Impacts Disposal of Spill Residue Disposal of Solid Waste Disposal of Hazardous Waste Impacts Soil disturbance leading to Erosion and Sedimentation Accidental Spillage - Vehicle /Helicopter/Equipment fluids Gray water Input (raw material and labor) Resource Impacts Soil Impacts Encampment Conservation Accidental Spillage - Vehicle/Helicopter/Equipment fluids Gray water Groundwater Impacts Soil disturbance leading to Erosion and Sedimentation Accidental Spillage - Vehicle/Helicopter/Equipment fluids Gray water Lead Responsibility - Fish and Wildlife Division, Compliance Division, and Planning Division Surface Water Impacts
Marine Corps ISO 14001 Pilot Project Environmental Aspects Nuisance Impacts Fuel Consumption - Use of a Nonrenewable Resource Training within a Natural Environment (Plant, Wildlife, Wetlands) Training within species habitat Particulate Matter from Operating Vehicles Off-road Air Emissions from equipment and vehicles Outdoor burning - PM Air Impacts Disposal of Spill Residue Disposal of Solid Waste Disposal of Hazardous Waste Impacts Soil disturbance leading to Erosion and Sedimentation Accidental Spillage - Vehicle /Helicopter/Equipment fluids Gray water Input (raw material and labor) Resource Impacts Soil Impacts Encampment Conservation Accidental Spillage - Vehicle/Helicopter/Equipment fluids Gray water Groundwater Impacts Soil disturbance leading to Erosion and Sedimentation Accidental Spillage - Vehicle/Helicopter/Equipment fluids Gray water Lead Responsibility - Fish and Wildlife Division, Compliance Division, and Planning Division Surface Water Impacts

 Ranking/Significance Scoring Consider: n Environmental Concerns n n Business Concerns: n n n Regulatory/legal exposure; health/env. risks; conservation Effect on the public image; community concerns Cost savings; cost recovery period; equipment/facility Other issues: n n n Scale, duration, and zone of impact Probability of occurrence - frequent, likely, possible, rarely, unlikely Severity of impact - catastrophic, severe, moderate, minor
Ranking/Significance Scoring Consider: n Environmental Concerns n n Business Concerns: n n n Regulatory/legal exposure; health/env. risks; conservation Effect on the public image; community concerns Cost savings; cost recovery period; equipment/facility Other issues: n n n Scale, duration, and zone of impact Probability of occurrence - frequent, likely, possible, rarely, unlikely Severity of impact - catastrophic, severe, moderate, minor
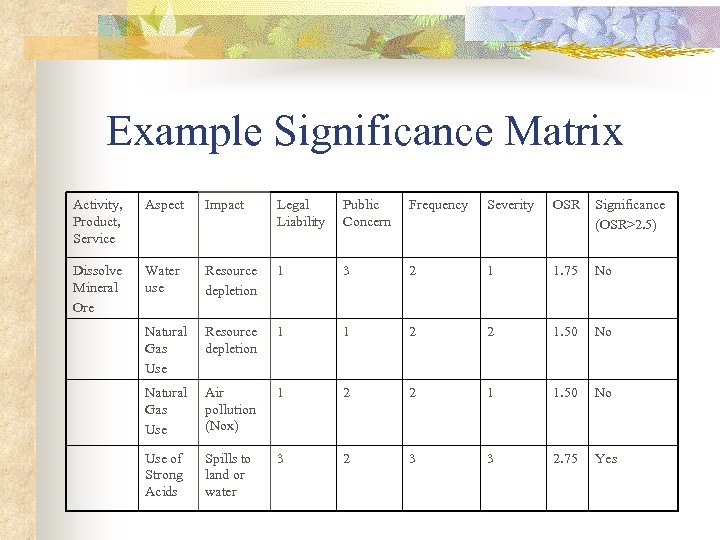 Example Significance Matrix Activity, Product, Service Aspect Impact Legal Liability Public Concern Frequency Severity OSR Significance (OSR>2. 5) Dissolve Mineral Ore Water use Resource depletion 1 3 2 1 1. 75 No Natural Gas Use Resource depletion 1 1 2 2 1. 50 No Natural Gas Use Air pollution (Nox) 1 2 2 1 1. 50 No Use of Strong Acids Spills to land or water 3 2 3 3 2. 75 Yes
Example Significance Matrix Activity, Product, Service Aspect Impact Legal Liability Public Concern Frequency Severity OSR Significance (OSR>2. 5) Dissolve Mineral Ore Water use Resource depletion 1 3 2 1 1. 75 No Natural Gas Use Resource depletion 1 1 2 2 1. 50 No Natural Gas Use Air pollution (Nox) 1 2 2 1 1. 50 No Use of Strong Acids Spills to land or water 3 2 3 3 2. 75 Yes
 Marine Corps ISO 14001 Pilot Project Scoring Guide for Ranking Significance Environmental Planning Division
Marine Corps ISO 14001 Pilot Project Scoring Guide for Ranking Significance Environmental Planning Division
 Legal and Other Environmental Requirements (4. 3. 2) n Setting legal framework for the EMS n have a procedure to identify and access the legal requirements: state, federal, local n have a documented system for keeping up-to-date communicate to the right people n n Industry-specific requirements n n n CMA Responsible Care Int’l. Chamber of Commerce (ICC) Charter Other voluntary requirements n n EPA Climate. Wise, Waste. Wise, 33/50 Program Green Seal
Legal and Other Environmental Requirements (4. 3. 2) n Setting legal framework for the EMS n have a procedure to identify and access the legal requirements: state, federal, local n have a documented system for keeping up-to-date communicate to the right people n n Industry-specific requirements n n n CMA Responsible Care Int’l. Chamber of Commerce (ICC) Charter Other voluntary requirements n n EPA Climate. Wise, Waste. Wise, 33/50 Program Green Seal
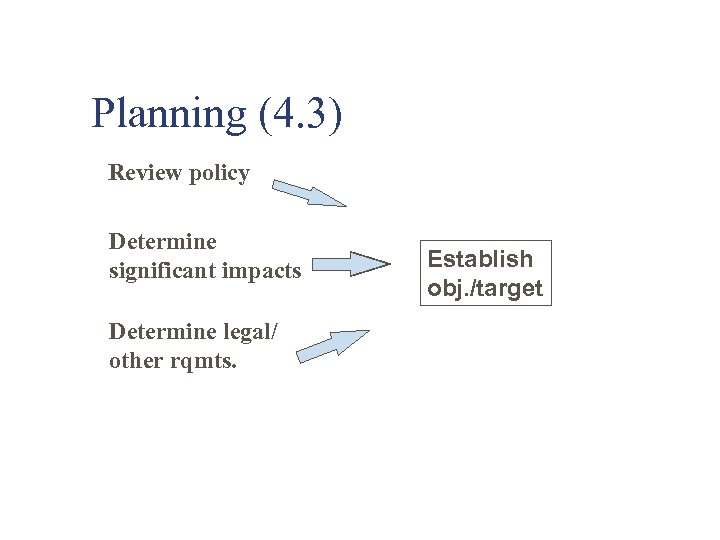 Planning (4. 3) Review policy Determine significant impacts Determine legal/ other rqmts. Establish obj. /target
Planning (4. 3) Review policy Determine significant impacts Determine legal/ other rqmts. Establish obj. /target
 Objectives &Targets (4. 3. 3) n The organization shall establish and maintain documented environmental objectives and targets. n Can include commitment to: n n reduce waste reduce or eliminate release of pollutant design product to minimize environmental impact in production, use, and disposal. Be realistic. Keep objectives simple, flexible, and measurable.
Objectives &Targets (4. 3. 3) n The organization shall establish and maintain documented environmental objectives and targets. n Can include commitment to: n n reduce waste reduce or eliminate release of pollutant design product to minimize environmental impact in production, use, and disposal. Be realistic. Keep objectives simple, flexible, and measurable.
 OBJECTIVES & TARGETS n n Reduce generation of hazardous waste Improve indoor air quality by reducing solvent odors Prevent spills Reduce electrical use n n Reduce spent solvent by 80% by 01/2002 Reduce emissions by 90% by 05/2002 Max. of 2 /yr. by 2003 Reduce electricity use by 10% by 08/2002
OBJECTIVES & TARGETS n n Reduce generation of hazardous waste Improve indoor air quality by reducing solvent odors Prevent spills Reduce electrical use n n Reduce spent solvent by 80% by 01/2002 Reduce emissions by 90% by 05/2002 Max. of 2 /yr. by 2003 Reduce electricity use by 10% by 08/2002
 Planning Review policy Determine significant impacts Determine legal/ other rqmts. Establish obj. /target Develop Env. Mgmt. program
Planning Review policy Determine significant impacts Determine legal/ other rqmts. Establish obj. /target Develop Env. Mgmt. program
 Env. Mgmt. Program n n n Plan: Switch to aqueous cleaning process Action- Substitute water based cleaning process for vapor degreasing process Responsibilities - Process Engineering Schedule Bench top trials 2 months (date) Full scale pilot 3 months (date) Implementation period - 1 month (date) Resources needed - 1 FTE for 4 months - Est. Budget $12, 000
Env. Mgmt. Program n n n Plan: Switch to aqueous cleaning process Action- Substitute water based cleaning process for vapor degreasing process Responsibilities - Process Engineering Schedule Bench top trials 2 months (date) Full scale pilot 3 months (date) Implementation period - 1 month (date) Resources needed - 1 FTE for 4 months - Est. Budget $12, 000
 Implementation (4. 4) n n n n Structure/responsibility (4. 4. 1) Training, awareness, & competence (4. 4. 2) Communication (internal/external) (4. 4. 3) Env. Mgmt. System Documentation (4. 4. 4) Document control (4. 4. 5) Operational control (4. 4. 6) Emergency preparedness and response (4. 4. 7) Sections overlap: For example, 4. 4. 2 and 4. 4. 6 require that employees have info. on EMS as well as knowledge of environmental impacts from operations and activities
Implementation (4. 4) n n n n Structure/responsibility (4. 4. 1) Training, awareness, & competence (4. 4. 2) Communication (internal/external) (4. 4. 3) Env. Mgmt. System Documentation (4. 4. 4) Document control (4. 4. 5) Operational control (4. 4. 6) Emergency preparedness and response (4. 4. 7) Sections overlap: For example, 4. 4. 2 and 4. 4. 6 require that employees have info. on EMS as well as knowledge of environmental impacts from operations and activities
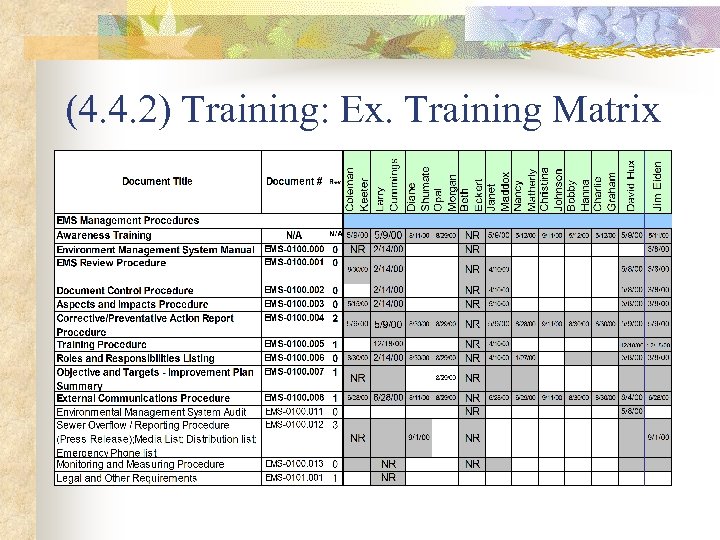 (4. 4. 2) Training: Ex. Training Matrix
(4. 4. 2) Training: Ex. Training Matrix
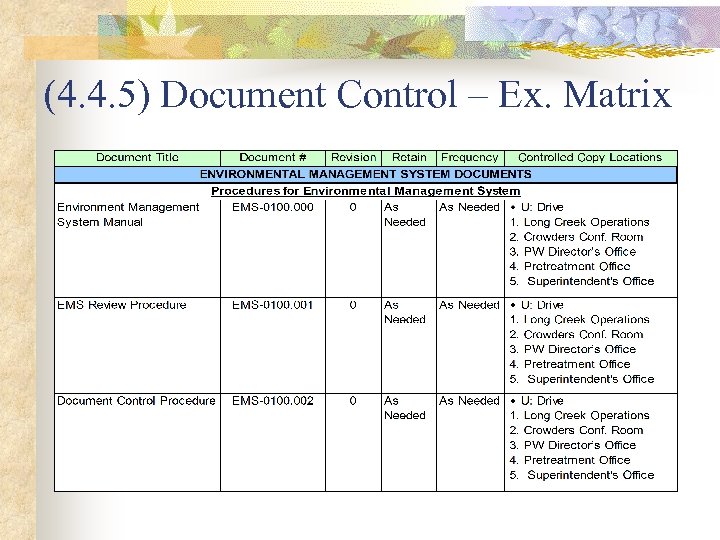 (4. 4. 5) Document Control – Ex. Matrix
(4. 4. 5) Document Control – Ex. Matrix
 Checking/Corrective Action (4. 5) Monitoring and Measuring (4. 5. 1) Records (4. 5. 3) EMS Auditing (4. 5. 4) Non-conformance and Corrective/Preventive Action (4. 5. 2)
Checking/Corrective Action (4. 5) Monitoring and Measuring (4. 5. 1) Records (4. 5. 3) EMS Auditing (4. 5. 4) Non-conformance and Corrective/Preventive Action (4. 5. 2)
 (4. 5. 1) Monitoring and Measuring n n The organization shall establish and maintain documented procedures to monitor and measure. . . the key characteristics of its operations that can have a significant impact on the environment. Track how well the system is working Measure the key characteristics of those activities that can have significant impacts Analyze the root causes of problems
(4. 5. 1) Monitoring and Measuring n n The organization shall establish and maintain documented procedures to monitor and measure. . . the key characteristics of its operations that can have a significant impact on the environment. Track how well the system is working Measure the key characteristics of those activities that can have significant impacts Analyze the root causes of problems
 (4. 5. 2) Non Conformance and Corrective and Preventive Action n Develop procedure for investigating, correcting, and preventing system deficiencies Set up process for assigning responsibilities for and tracking completion of corrective action Set up process to revise EMS procedures based on corrective actions
(4. 5. 2) Non Conformance and Corrective and Preventive Action n Develop procedure for investigating, correcting, and preventing system deficiencies Set up process for assigning responsibilities for and tracking completion of corrective action Set up process to revise EMS procedures based on corrective actions
 (4. 5. 3) Records n n The organization shall establish and maintain procedures for the identification, maintenance and disposition of environmental records Include - training records, audits, management reviews
(4. 5. 3) Records n n The organization shall establish and maintain procedures for the identification, maintenance and disposition of environmental records Include - training records, audits, management reviews
 (4. 5. 4) EMS Auditing Develop internal EMS audit program n Are all EMS requirements met? (Are we meeting the standard? ) n Is the system working? (Are we doing what we said we would? ) Determine audit frequency and procedures; train auditors; keep records of audits, findings, and follow up actions
(4. 5. 4) EMS Auditing Develop internal EMS audit program n Are all EMS requirements met? (Are we meeting the standard? ) n Is the system working? (Are we doing what we said we would? ) Determine audit frequency and procedures; train auditors; keep records of audits, findings, and follow up actions
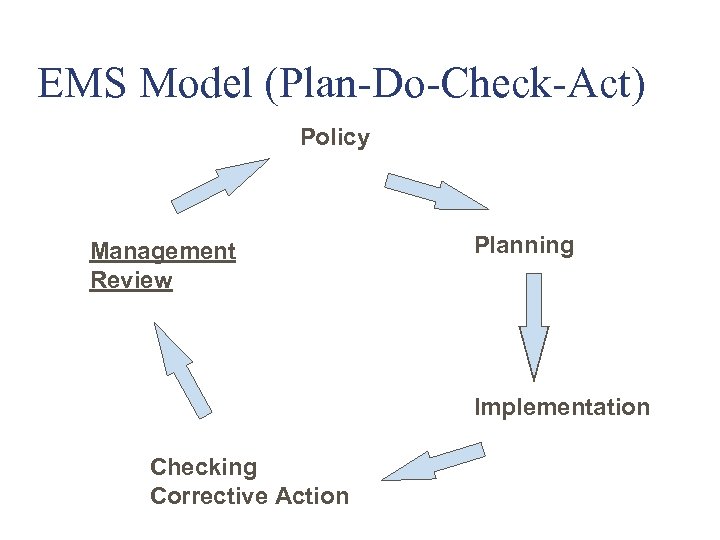 EMS Model (Plan-Do-Check-Act) Policy Management Review Planning Implementation Checking Corrective Action
EMS Model (Plan-Do-Check-Act) Policy Management Review Planning Implementation Checking Corrective Action
 (4. 6) Management Review n n Reviews EMS to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy and effectiveness Reviews process to ensure necessary information is collected for evaluation Review must be documented Consider changes to: n n n policy objectives other EMS elements
(4. 6) Management Review n n Reviews EMS to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy and effectiveness Reviews process to ensure necessary information is collected for evaluation Review must be documented Consider changes to: n n n policy objectives other EMS elements
 Thoughts on Going for ISO 14001 n n n n n Attend an overview class (need a champion, know what’s coming) Start with gap analysis or “road map” 6 -18 months to design and fully implement Work in teams or task groups Staff resources Incorporate Health and Safety? Level of Involvement of Suppliers/Contractors Training (internal/lead auditor, overview) Using an accredited trainer/registrar
Thoughts on Going for ISO 14001 n n n n n Attend an overview class (need a champion, know what’s coming) Start with gap analysis or “road map” 6 -18 months to design and fully implement Work in teams or task groups Staff resources Incorporate Health and Safety? Level of Involvement of Suppliers/Contractors Training (internal/lead auditor, overview) Using an accredited trainer/registrar
 For More Information n n DPPEA offers free on-site EMS assistance and training DPPEA EMS web site: http: //www. p 2 pays. org/iso/ Julie Woosley EMS Gov. Project Coor. 919 -715 -6527 or 800 -763 -0136 Julie. Woosley@ncmail. net Beth Graves, EMS Project Coor. (919) 715 -6506 Beth. Graves@ncmail. net Barb Satler, EMS and Pork Producer Coor. (919) 715 -6519, barb. satler@ncmail. net
For More Information n n DPPEA offers free on-site EMS assistance and training DPPEA EMS web site: http: //www. p 2 pays. org/iso/ Julie Woosley EMS Gov. Project Coor. 919 -715 -6527 or 800 -763 -0136 Julie. Woosley@ncmail. net Beth Graves, EMS Project Coor. (919) 715 -6506 Beth. Graves@ncmail. net Barb Satler, EMS and Pork Producer Coor. (919) 715 -6519, barb. satler@ncmail. net


