d7f512328bc0e93a4d3590726b1f3048.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY CHP 310: Community Health Program-l Mohamed M. B. Alnoor
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY CHP 310: Community Health Program-l Mohamed M. B. Alnoor
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY • Definitions • Importance of EH • Scope of EH practice ü Traditional and Modern Hazards ü EH & ES concerns ü Water Supply Sanitation ü Waste Disposal • Major global Environmental Problems ü Population overgrowth ü Air pollution ü Ozone depletion/global warming ü Water pollution • Challenges and Obstacles
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY • Definitions • Importance of EH • Scope of EH practice ü Traditional and Modern Hazards ü EH & ES concerns ü Water Supply Sanitation ü Waste Disposal • Major global Environmental Problems ü Population overgrowth ü Air pollution ü Ozone depletion/global warming ü Water pollution • Challenges and Obstacles
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Environmental Health (EH)? Environmental health is the study and management of environmental conditions that affect health and well-being of humans
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Environmental Health (EH)? Environmental health is the study and management of environmental conditions that affect health and well-being of humans
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Pollution The introduction of harmful materials or production of harmful conditions. Contamination The introduction of undesirable materials. Polluted environment Impure, dirty, or otherwise unclean.
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Pollution The introduction of harmful materials or production of harmful conditions. Contamination The introduction of undesirable materials. Polluted environment Impure, dirty, or otherwise unclean.
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Pollutant a waste material that negatively affects air, water or soil. Three factors determine the severity of a pollutant: • chemical nature • concentration • persistence
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Pollutant a waste material that negatively affects air, water or soil. Three factors determine the severity of a pollutant: • chemical nature • concentration • persistence
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Pollutants are introduced at: • Point sources: smokestacks, accidental spills or pipes discharging into waterways. • Area sources, (non point sources): More diffuse: Urban and agricultural runoff. Mobile sources: Automobile exhaust.
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Pollutants are introduced at: • Point sources: smokestacks, accidental spills or pipes discharging into waterways. • Area sources, (non point sources): More diffuse: Urban and agricultural runoff. Mobile sources: Automobile exhaust.
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Hazards and Risks: Hazard: Is “a factor or exposure that may adversely affect health”. Risk: Is “the probability that an event will occur.
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Hazards and Risks: Hazard: Is “a factor or exposure that may adversely affect health”. Risk: Is “the probability that an event will occur.
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Environmental sanitation(ES): Control of environmental factors that form links in transmission of disease. Subsets of this category are: • solid waste management • treatment of water • treatment of wastewater • industrial-waste treatment.
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Environmental sanitation(ES): Control of environmental factors that form links in transmission of disease. Subsets of this category are: • solid waste management • treatment of water • treatment of wastewater • industrial-waste treatment.
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Importance of EH § It helps understand/control/adapt: • Pollution • Natural/technological disasters • Physical hazards • Climatic changes • Food/Nutritional deficiencies • Sanitation
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Importance of EH § It helps understand/control/adapt: • Pollution • Natural/technological disasters • Physical hazards • Climatic changes • Food/Nutritional deficiencies • Sanitation
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Importance of EH § Sanitation is cost-effective: • Interventions yield : ü 5. 6 billion productive days including: o 2. 4 billion healthy infant day o 1. 25 billion productive adult days. o 443 million school days • $1 invested • Toilet use economic return $3 - $14 30% reduction Childhood diarrhoeal deaths
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Importance of EH § Sanitation is cost-effective: • Interventions yield : ü 5. 6 billion productive days including: o 2. 4 billion healthy infant day o 1. 25 billion productive adult days. o 443 million school days • $1 invested • Toilet use economic return $3 - $14 30% reduction Childhood diarrhoeal deaths
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Importance of EH § Sanitation can be improved: Success stories • Malaysia and Thailand: universal coverage over thirty years • The Southern region of Ethiopia: elimination of open defecation. • Bangladesh: : “open-defecation-free”.
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Importance of EH § Sanitation can be improved: Success stories • Malaysia and Thailand: universal coverage over thirty years • The Southern region of Ethiopia: elimination of open defecation. • Bangladesh: : “open-defecation-free”.
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice Traditional and Modern Hazards: Traditional Hazards • Disease Vectors • Infectious agents • Housing and Shelter hazards • Drinking Water & Sanitation hazards • Indoor air Pollution • Dietary Deficiencies • Injury hazards Modern Hazards • • • Tobacco smoking Alcohol and drugs Transport hazards Environmental pollution Outdoor air pollution Chemical hazards Occupational Hazards Unbalanced Diet Stress
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice Traditional and Modern Hazards: Traditional Hazards • Disease Vectors • Infectious agents • Housing and Shelter hazards • Drinking Water & Sanitation hazards • Indoor air Pollution • Dietary Deficiencies • Injury hazards Modern Hazards • • • Tobacco smoking Alcohol and drugs Transport hazards Environmental pollution Outdoor air pollution Chemical hazards Occupational Hazards Unbalanced Diet Stress
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice Purpose of EH practice • prevention of EH hazards • promotion and protection of : ü public health ü environment Disciplines of EH: Three basic disciplines: • Environmental epidemiology : Observational studies • Toxicology : TEAM WORK Animal studies • Exposure science : Identifying and quantifying exposures.
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice Purpose of EH practice • prevention of EH hazards • promotion and protection of : ü public health ü environment Disciplines of EH: Three basic disciplines: • Environmental epidemiology : Observational studies • Toxicology : TEAM WORK Animal studies • Exposure science : Identifying and quantifying exposures.
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice EH and ES concerns : • Air, water and soil: - Quality - Pollution • Waste and toxic substances. • Climate and Disaster : - Preparedness & Management • Occupational Health & Safety • Behaviour
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice EH and ES concerns : • Air, water and soil: - Quality - Pollution • Waste and toxic substances. • Climate and Disaster : - Preparedness & Management • Occupational Health & Safety • Behaviour
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice Water Supply Sanitation: Approved type of water facilities: q Rural areas: § Point Source: (well or spring) § Communal Faucet q Urban communities : § Waterworks System
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice Water Supply Sanitation: Approved type of water facilities: q Rural areas: § Point Source: (well or spring) § Communal Faucet q Urban communities : § Waterworks System
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice Water Supply Sanitation: Water Treatment : Raw Water surface Treatment groundwater Safe drinking water § Two major processes: • Physical removal of solids COAGULATION: SEDIMENTATION : FILTRATION : • Chemical disinfection DISINFECTION : STORAGE :
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice Water Supply Sanitation: Water Treatment : Raw Water surface Treatment groundwater Safe drinking water § Two major processes: • Physical removal of solids COAGULATION: SEDIMENTATION : FILTRATION : • Chemical disinfection DISINFECTION : STORAGE :
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice Proper Excreta and Sewage Disposal: Approved types q Urban areas: § Water carriage/sewerage system/ treatment : Removing Sewage impurities (Treatment ) natural water cycle. § Separation of solids: Physical processes § Purification: Biological and Chemical processes
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice Proper Excreta and Sewage Disposal: Approved types q Urban areas: § Water carriage/sewerage system/ treatment : Removing Sewage impurities (Treatment ) natural water cycle. § Separation of solids: Physical processes § Purification: Biological and Chemical processes
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice Hospital Waste Disposal: Hospital waste: Biological Non biological • 85% are non-infectious • 10% are infectious • 5% are hazardous
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Scope of EH practice Hospital Waste Disposal: Hospital waste: Biological Non biological • 85% are non-infectious • 10% are infectious • 5% are hazardous
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS 1 - Overpopulation 2 - Air pollution: 3 - Ozone depletion and global warming: 4 - Water pollution:
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS 1 - Overpopulation 2 - Air pollution: 3 - Ozone depletion and global warming: 4 - Water pollution:
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS 1 - Overpopulation YEAR 1804 1927 1959 1974 1987 1999 2011 2050* *ESTIMATE BILLION 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 • Pollution ü ü ü Air Water Soil • Resource depletion ü ü Forests Fossil fuel • Extinction(52 species) ü ü ü Mammals Birds Amphibians
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS 1 - Overpopulation YEAR 1804 1927 1959 1974 1987 1999 2011 2050* *ESTIMATE BILLION 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 • Pollution ü ü ü Air Water Soil • Resource depletion ü ü Forests Fossil fuel • Extinction(52 species) ü ü ü Mammals Birds Amphibians
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS 2 - Air pollution: • industrialized and urbanized areas • 75% of children suffer respiratory disease • London fog (1952) killed 4000 -8000 (mostly elderly). • The six major air pollutants: ü Carbon monoxide (CO) ü Nitrogen Oxides (NO, NO 2) ü particulate matter ü sulfur dioxide (SO 2) ü Hydrocarbons ü lead.
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS 2 - Air pollution: • industrialized and urbanized areas • 75% of children suffer respiratory disease • London fog (1952) killed 4000 -8000 (mostly elderly). • The six major air pollutants: ü Carbon monoxide (CO) ü Nitrogen Oxides (NO, NO 2) ü particulate matter ü sulfur dioxide (SO 2) ü Hydrocarbons ü lead.
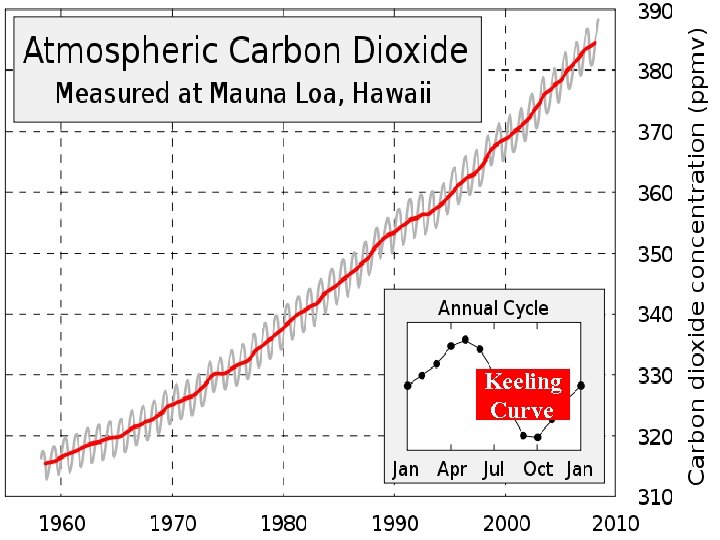 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS 3 - Ozone depletion and global warming: plant/ animal ultraviolet rays (skin cancer, cataracts, etc) § Refrigerants : chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), • 1930: introduced(Freon) • 1976: 750 million lb. /year Keeling • 1980 s: $28 billions/year Curve § CO 2 from fossil fuel
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS 3 - Ozone depletion and global warming: plant/ animal ultraviolet rays (skin cancer, cataracts, etc) § Refrigerants : chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), • 1930: introduced(Freon) • 1976: 750 million lb. /year Keeling • 1980 s: $28 billions/year Curve § CO 2 from fossil fuel
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS 3 - Ozone depletion and global warming: several thousand x the CFCs greenhouse potential CO 2 CFCs cooling of the stratosphere accelerates ozone depletion What can we do? • Reduce home energy usage • Buy cars that are fuel-smart • Transportation alternatives : mass transit, , bicycling • Plant trees • Educate others
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS 3 - Ozone depletion and global warming: several thousand x the CFCs greenhouse potential CO 2 CFCs cooling of the stratosphere accelerates ozone depletion What can we do? • Reduce home energy usage • Buy cars that are fuel-smart • Transportation alternatives : mass transit, , bicycling • Plant trees • Educate others
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS 4 - Water pollution: § Causes of water pollution • Population growth. • Outputs (Industrial, agricultural and urban) § Control of water pollution: • Domestic sewage • wastewater ü Industrial ü Agricultural • stormwater ü Construction site ü Urban runoff
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS 4 - Water pollution: § Causes of water pollution • Population growth. • Outputs (Industrial, agricultural and urban) § Control of water pollution: • Domestic sewage • wastewater ü Industrial ü Agricultural • stormwater ü Construction site ü Urban runoff
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS Pollution control : most favoured option least favoured option PREVENT REDUCE REUSE RECYCLE MITIGATE COMPOST DISPOSE
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY MAJOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS Pollution control : most favoured option least favoured option PREVENT REDUCE REUSE RECYCLE MITIGATE COMPOST DISPOSE
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY CHALLENGES and OBSTACLES to IMPROVED SANITATION § Demographic Issues (more people) • Growth in number • Increase in Consumption § Consumption Patterns: More wastes § Growth of cities (More large cities and slums)
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY CHALLENGES and OBSTACLES to IMPROVED SANITATION § Demographic Issues (more people) • Growth in number • Increase in Consumption § Consumption Patterns: More wastes § Growth of cities (More large cities and slums)
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY CHALLENGES and OBSTACLES to IMPROVED SANITATION § Macro Economic Policies • More use and degradation of resources § Poverty: > 1 billion live below poverty line( $ 1. 25/day) § Behavioural and perception barriers: – low environmental concern – benefits of improved sanitation not widely understood
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY CHALLENGES and OBSTACLES to IMPROVED SANITATION § Macro Economic Policies • More use and degradation of resources § Poverty: > 1 billion live below poverty line( $ 1. 25/day) § Behavioural and perception barriers: – low environmental concern – benefits of improved sanitation not widely understood
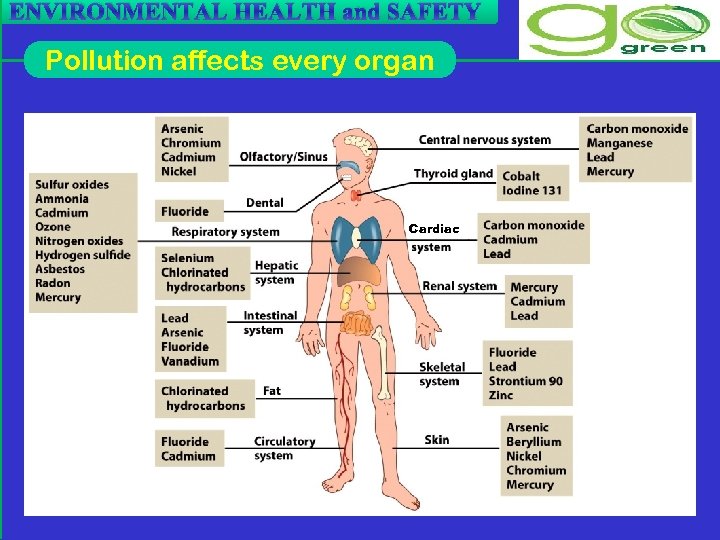 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Pollution affects every organ Cardiac
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY Pollution affects every organ Cardiac
 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY The basic requirements for healthy environment q Clean Air q Safe and Sufficient Water q Adequate and Safe Food q Safe and Peaceful Settlements q Stable Global Environment
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH and SAFETY The basic requirements for healthy environment q Clean Air q Safe and Sufficient Water q Adequate and Safe Food q Safe and Peaceful Settlements q Stable Global Environment
 Summary Environmental health is the broadest scope of health problem definition Environmental health studies the impact of the environment on populations It is a population based science that can be scaled to study individuals within populations Problem definition and potential resolution is possible through the implementation of a systematic approach
Summary Environmental health is the broadest scope of health problem definition Environmental health studies the impact of the environment on populations It is a population based science that can be scaled to study individuals within populations Problem definition and potential resolution is possible through the implementation of a systematic approach


