038f1d68a403e6a7f62b13669a7cc4d8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Environmental Controls I/IG Lecture 13 Solar Geometry Shading Strategies
Environmental Controls I/IG Lecture 13 Solar Geometry Shading Strategies
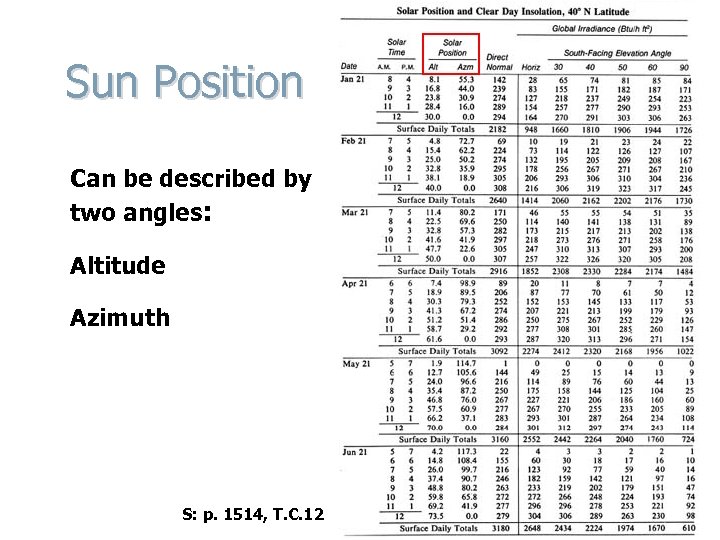 Sun Position Can be described by two angles: Altitude Azimuth S: p. 1514, T. C. 12
Sun Position Can be described by two angles: Altitude Azimuth S: p. 1514, T. C. 12
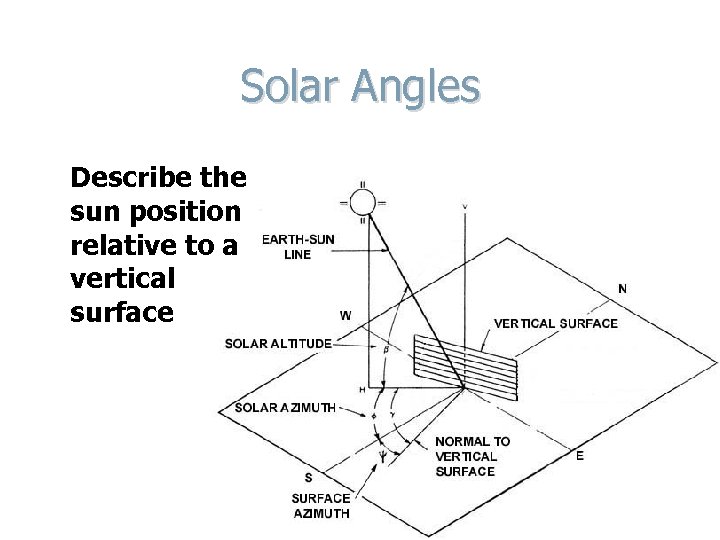 Solar Angles Describe the sun position relative to a vertical surface
Solar Angles Describe the sun position relative to a vertical surface
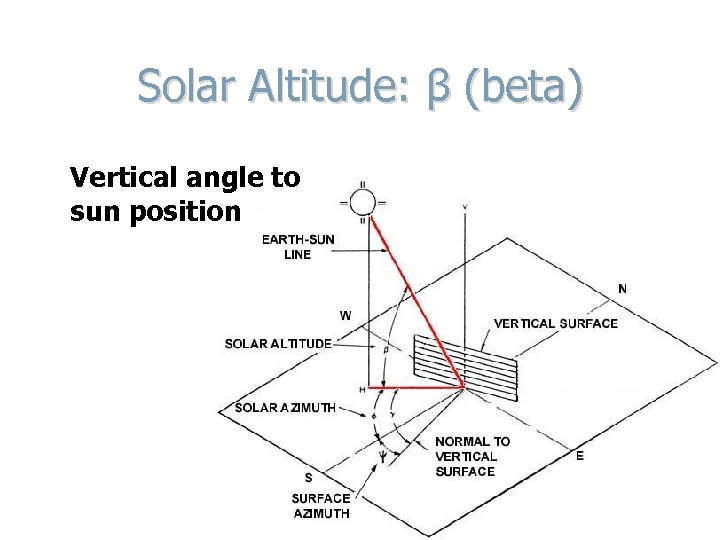 Solar Altitude: β (beta) Vertical angle to sun position
Solar Altitude: β (beta) Vertical angle to sun position
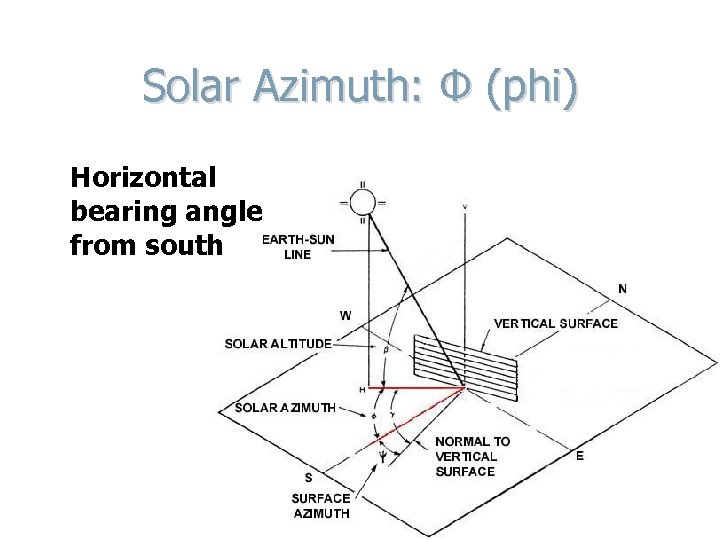 Solar Azimuth: Φ (phi) Horizontal bearing angle from south
Solar Azimuth: Φ (phi) Horizontal bearing angle from south
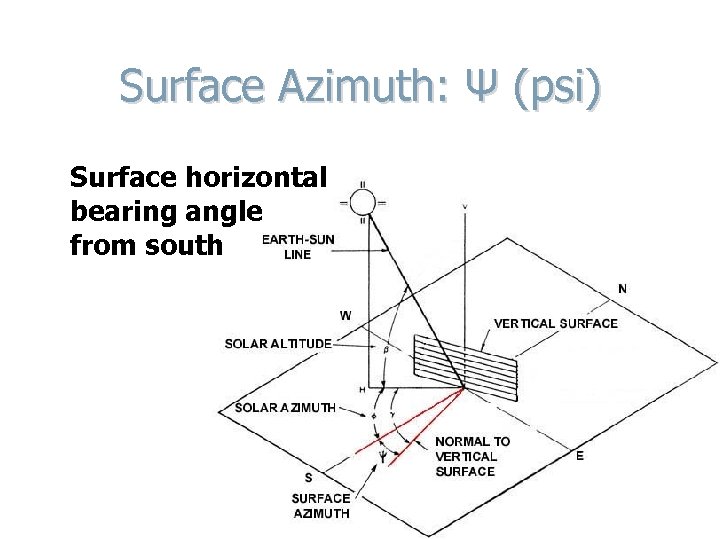 Surface Azimuth: Ψ (psi) Surface horizontal bearing angle from south
Surface Azimuth: Ψ (psi) Surface horizontal bearing angle from south
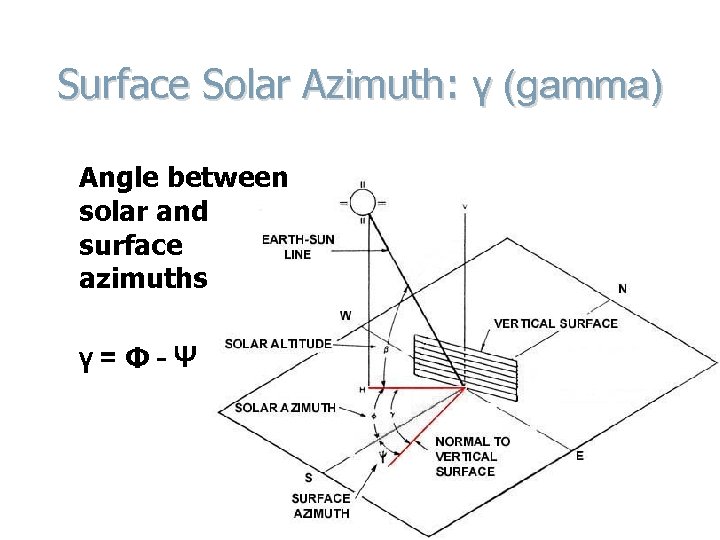 Surface Solar Azimuth: γ (gamma) Angle between solar and surface azimuths γ=Φ-Ψ
Surface Solar Azimuth: γ (gamma) Angle between solar and surface azimuths γ=Φ-Ψ
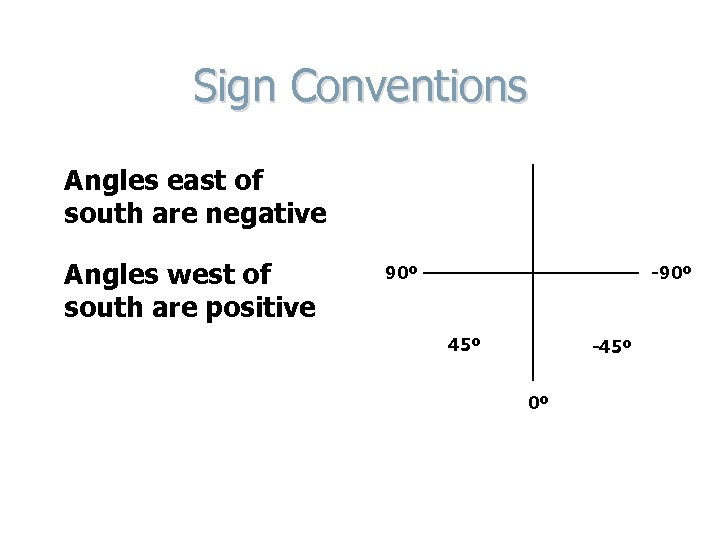 Sign Conventions Angles east of south are negative Angles west of south are positive 90º -90º 45º + -45º 0º S
Sign Conventions Angles east of south are negative Angles west of south are positive 90º -90º 45º + -45º 0º S
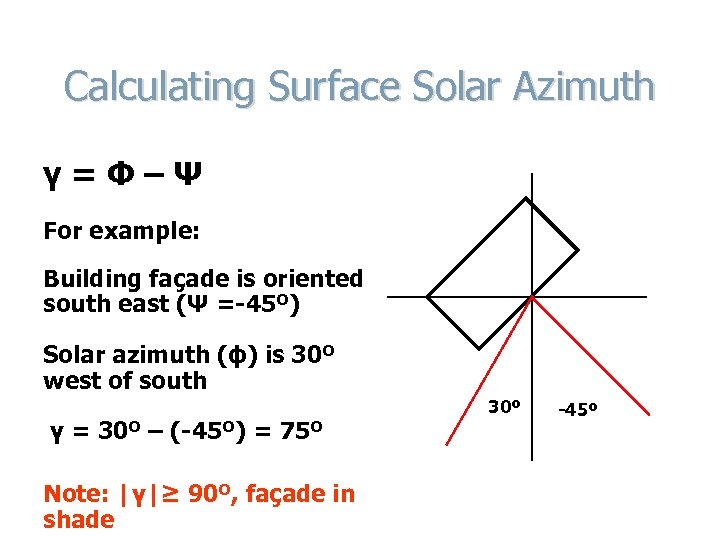 Calculating Surface Solar Azimuth γ=Φ–Ψ For example: Building façade is oriented south east (Ψ =-45º) Solar azimuth (ϕ) is 30º west of south γ = 30º – (-45º) = 75º Note: |γ|≥ 90º, façade in shade 30º -45º
Calculating Surface Solar Azimuth γ=Φ–Ψ For example: Building façade is oriented south east (Ψ =-45º) Solar azimuth (ϕ) is 30º west of south γ = 30º – (-45º) = 75º Note: |γ|≥ 90º, façade in shade 30º -45º
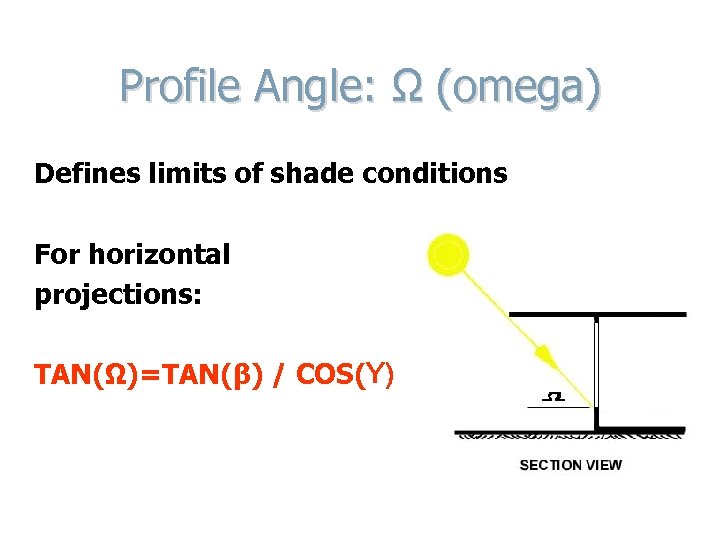 Profile Angle: Ω (omega) Defines limits of shade conditions For horizontal projections: TAN(Ω)=TAN(β) / COS(Y)
Profile Angle: Ω (omega) Defines limits of shade conditions For horizontal projections: TAN(Ω)=TAN(β) / COS(Y)
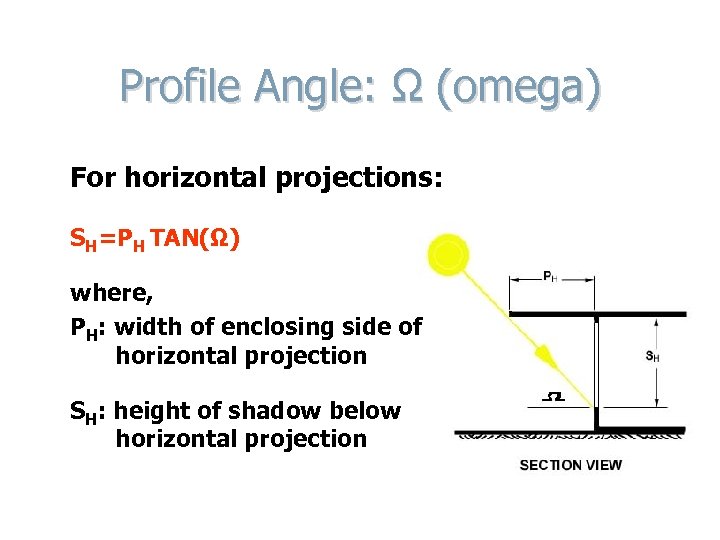 Profile Angle: Ω (omega) For horizontal projections: SH=PH TAN(Ω) where, PH: width of enclosing side of horizontal projection SH: height of shadow below horizontal projection
Profile Angle: Ω (omega) For horizontal projections: SH=PH TAN(Ω) where, PH: width of enclosing side of horizontal projection SH: height of shadow below horizontal projection
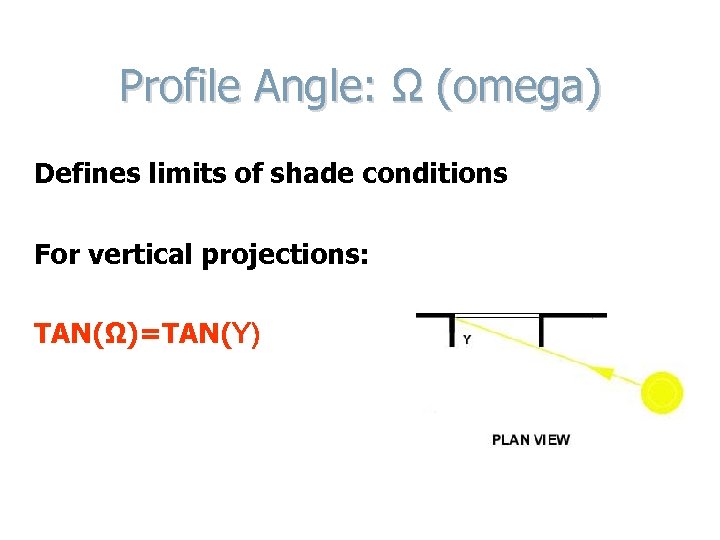 Profile Angle: Ω (omega) Defines limits of shade conditions For vertical projections: TAN(Ω)=TAN(Y)
Profile Angle: Ω (omega) Defines limits of shade conditions For vertical projections: TAN(Ω)=TAN(Y)
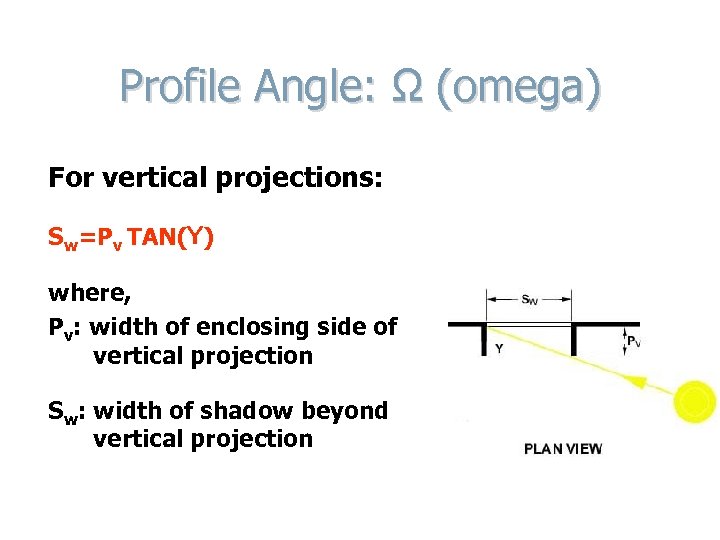 Profile Angle: Ω (omega) For vertical projections: Sw=Pv TAN(Y) where, Pv: width of enclosing side of vertical projection Sw: width of shadow beyond vertical projection
Profile Angle: Ω (omega) For vertical projections: Sw=Pv TAN(Y) where, Pv: width of enclosing side of vertical projection Sw: width of shadow beyond vertical projection
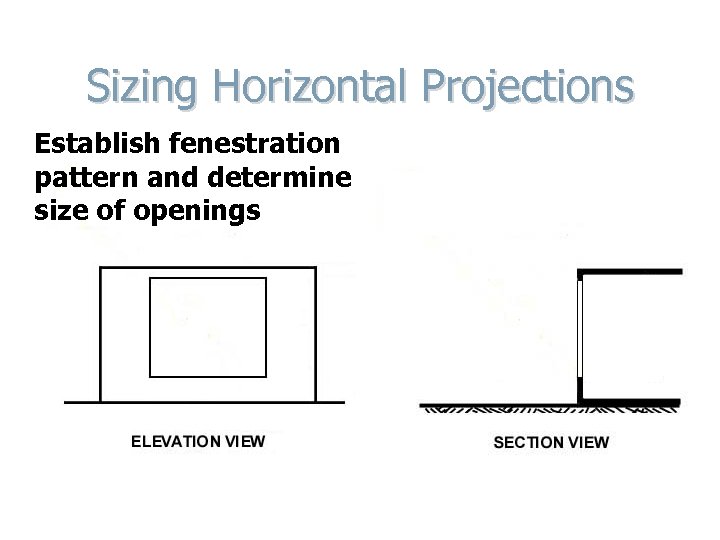 Sizing Horizontal Projections Establish fenestration pattern and determine size of openings
Sizing Horizontal Projections Establish fenestration pattern and determine size of openings
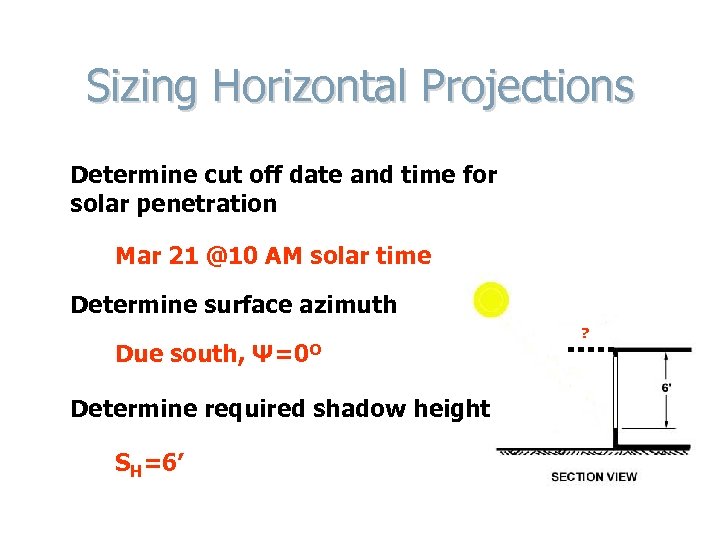 Sizing Horizontal Projections Determine cut off date and time for solar penetration Mar 21 @10 AM solar time Determine surface azimuth Due south, Ψ=0º Determine required shadow height SH=6’ ?
Sizing Horizontal Projections Determine cut off date and time for solar penetration Mar 21 @10 AM solar time Determine surface azimuth Due south, Ψ=0º Determine required shadow height SH=6’ ?
 Sizing Horizontal Projections Establish profile (Ω) angles for the solstices at solar noon using surface solar azimuth (Y = Φ –Ψ). At solar noon (Φ=0º) and for L=40º, Ψ=0º: 12/21 β=90 -23. 5 -L=26. 5º TAN(Ωw)=TAN(β)/COS(Y) Ωw=26. 5º 6/21β=90+23. 5 -L=73. 5º TAN(Ωs)=TAN(β)/COS(Y) Ωs=73. 5º
Sizing Horizontal Projections Establish profile (Ω) angles for the solstices at solar noon using surface solar azimuth (Y = Φ –Ψ). At solar noon (Φ=0º) and for L=40º, Ψ=0º: 12/21 β=90 -23. 5 -L=26. 5º TAN(Ωw)=TAN(β)/COS(Y) Ωw=26. 5º 6/21β=90+23. 5 -L=73. 5º TAN(Ωs)=TAN(β)/COS(Y) Ωs=73. 5º
 Sizing Horizontal Projections Establish profile (Ω) angles for cut off date and time using surface solar azimuth (Y = Φ –Ψ). At 10 AM solar time and for L=40º, Ψ=0º:
Sizing Horizontal Projections Establish profile (Ω) angles for cut off date and time using surface solar azimuth (Y = Φ –Ψ). At 10 AM solar time and for L=40º, Ψ=0º:
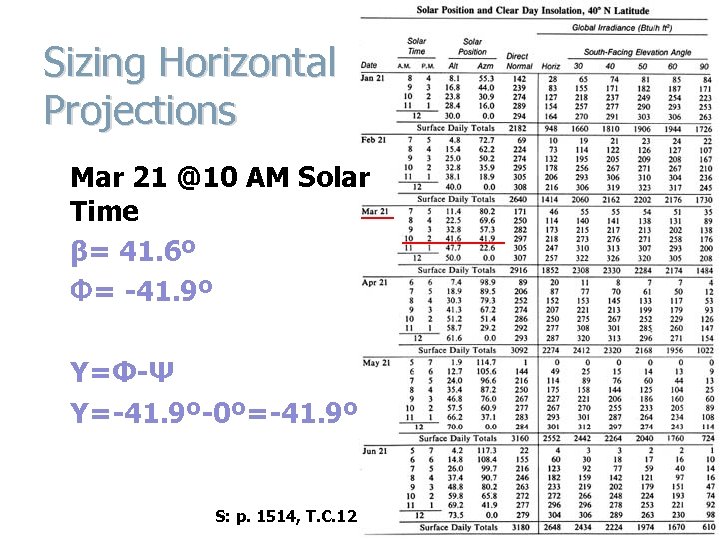 Sizing Horizontal Projections Mar 21 @10 AM Solar Time β= 41. 6º Φ= -41. 9º Y=Φ-Ψ Y=-41. 9º-0º=-41. 9º S: p. 1514, T. C. 12
Sizing Horizontal Projections Mar 21 @10 AM Solar Time β= 41. 6º Φ= -41. 9º Y=Φ-Ψ Y=-41. 9º-0º=-41. 9º S: p. 1514, T. C. 12
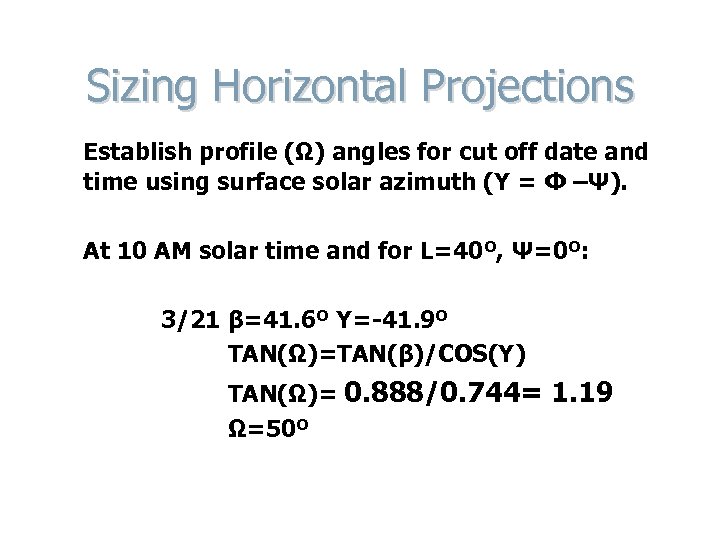 Sizing Horizontal Projections Establish profile (Ω) angles for cut off date and time using surface solar azimuth (Y = Φ –Ψ). At 10 AM solar time and for L=40º, Ψ=0º: 3/21 β=41. 6º Y=-41. 9º TAN(Ω)=TAN(β)/COS(Y) TAN(Ω)= 0. 888/0. 744= 1. 19 Ω=50º
Sizing Horizontal Projections Establish profile (Ω) angles for cut off date and time using surface solar azimuth (Y = Φ –Ψ). At 10 AM solar time and for L=40º, Ψ=0º: 3/21 β=41. 6º Y=-41. 9º TAN(Ω)=TAN(β)/COS(Y) TAN(Ω)= 0. 888/0. 744= 1. 19 Ω=50º
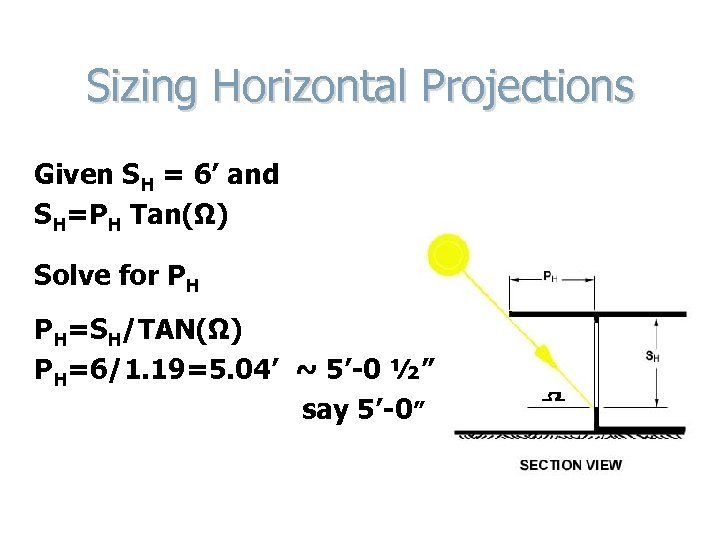 Sizing Horizontal Projections Given SH = 6’ and SH=PH Tan(Ω) Solve for PH PH=SH/TAN(Ω) PH=6/1. 19=5. 04’ ~ 5’-0 ½” say 5’-0 ”
Sizing Horizontal Projections Given SH = 6’ and SH=PH Tan(Ω) Solve for PH PH=SH/TAN(Ω) PH=6/1. 19=5. 04’ ~ 5’-0 ½” say 5’-0 ”
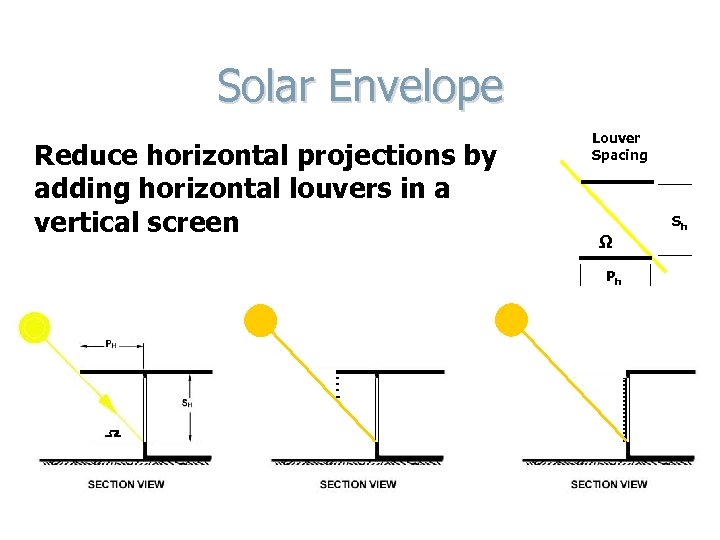 Solar Envelope Reduce horizontal projections by adding horizontal louvers in a vertical screen Louver Spacing Ω Ph Sh
Solar Envelope Reduce horizontal projections by adding horizontal louvers in a vertical screen Louver Spacing Ω Ph Sh
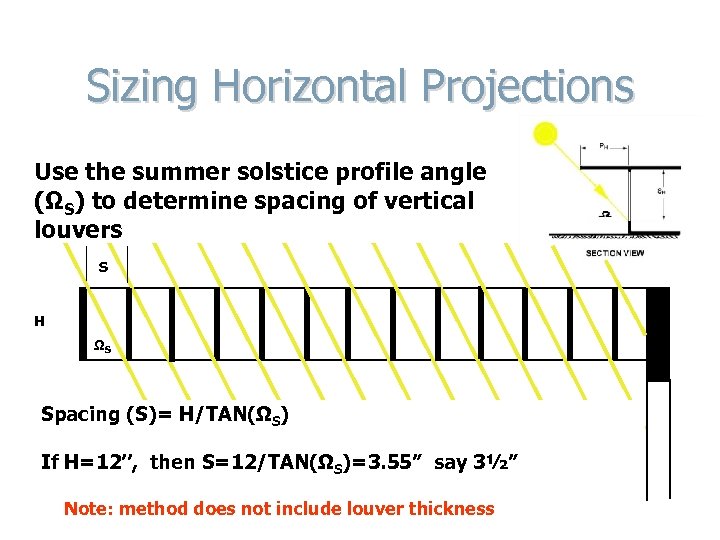 Sizing Horizontal Projections Use the summer solstice profile angle (ΩS) to determine spacing of vertical louvers S H ΩS Spacing (S)= H/TAN(ΩS) If H=12’’, then S=12/TAN(ΩS)=3. 55” say 3½” Note: method does not include louver thickness
Sizing Horizontal Projections Use the summer solstice profile angle (ΩS) to determine spacing of vertical louvers S H ΩS Spacing (S)= H/TAN(ΩS) If H=12’’, then S=12/TAN(ΩS)=3. 55” say 3½” Note: method does not include louver thickness
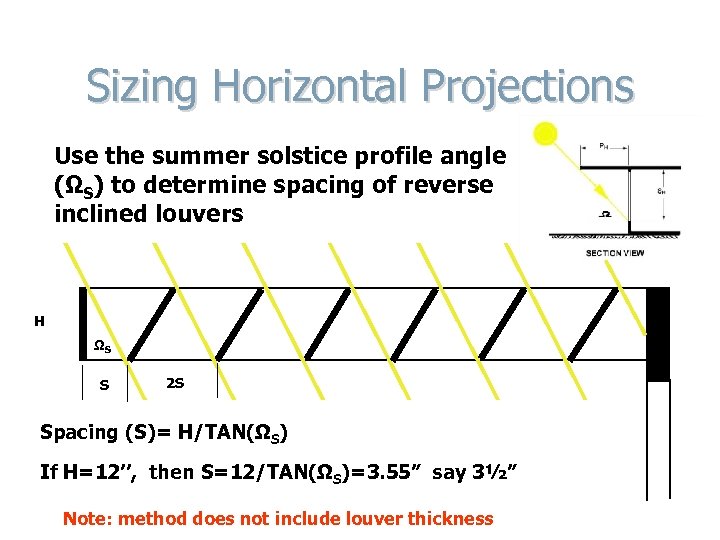 Sizing Horizontal Projections Use the summer solstice profile angle (ΩS) to determine spacing of reverse inclined louvers H ΩS S 2 S Spacing (S)= H/TAN(ΩS) If H=12’’, then S=12/TAN(ΩS)=3. 55” say 3½” Note: method does not include louver thickness
Sizing Horizontal Projections Use the summer solstice profile angle (ΩS) to determine spacing of reverse inclined louvers H ΩS S 2 S Spacing (S)= H/TAN(ΩS) If H=12’’, then S=12/TAN(ΩS)=3. 55” say 3½” Note: method does not include louver thickness
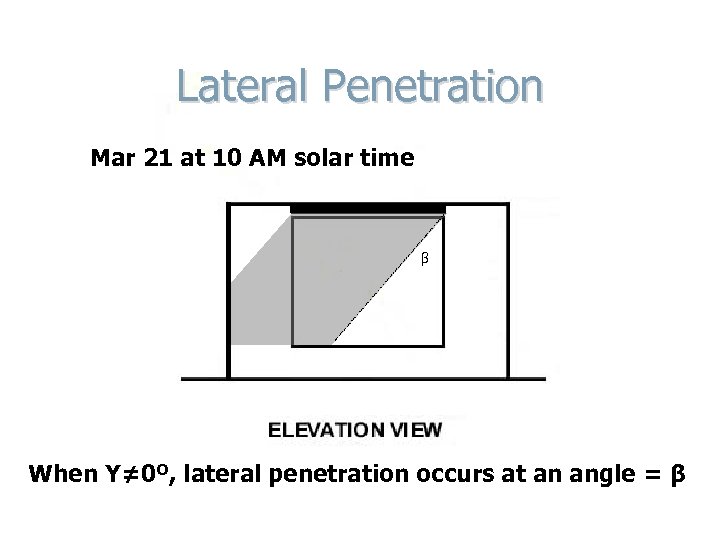 Lateral Penetration Mar 21 at 10 AM solar time β When Y≠ 0º, lateral penetration occurs at an angle = β
Lateral Penetration Mar 21 at 10 AM solar time β When Y≠ 0º, lateral penetration occurs at an angle = β
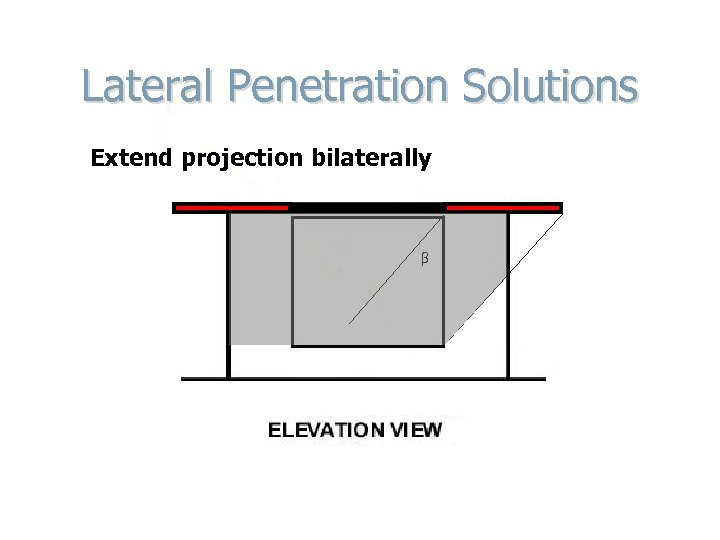 Lateral Penetration Solutions Extend projection bilaterally β
Lateral Penetration Solutions Extend projection bilaterally β
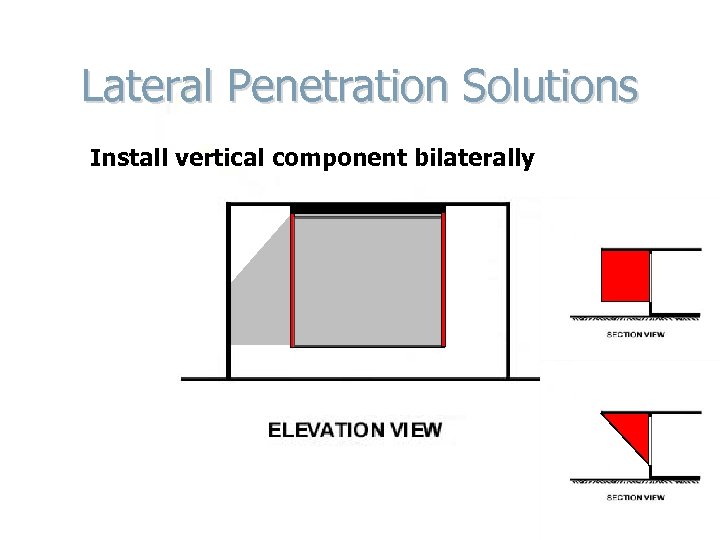 Lateral Penetration Solutions Install vertical component bilaterally
Lateral Penetration Solutions Install vertical component bilaterally
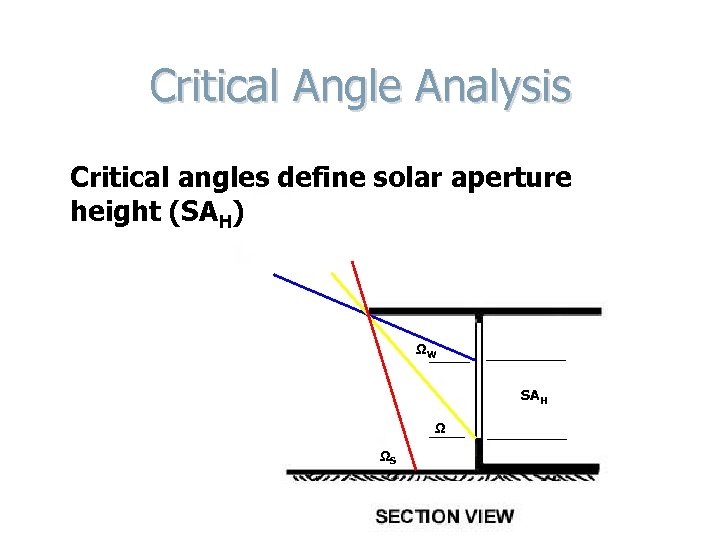 Critical Angle Analysis Critical angles define solar aperture height (SAH) ΩW SAH Ω ΩS
Critical Angle Analysis Critical angles define solar aperture height (SAH) ΩW SAH Ω ΩS
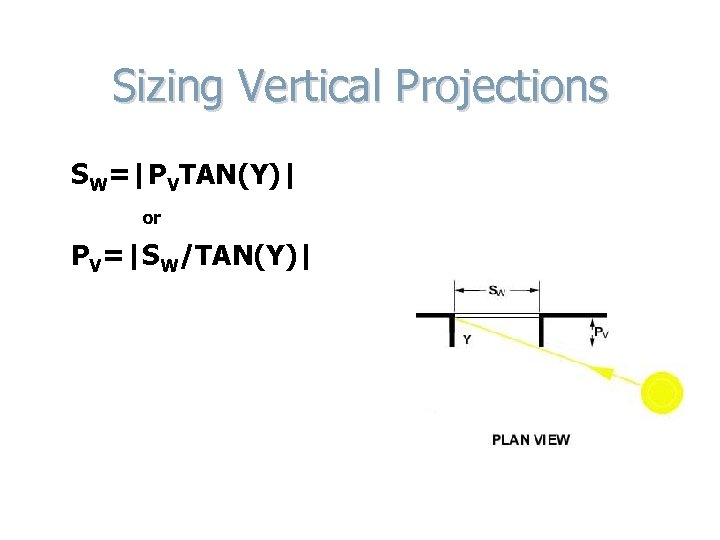 Sizing Vertical Projections SW=|PVTAN(Y)| or PV=|SW/TAN(Y)|
Sizing Vertical Projections SW=|PVTAN(Y)| or PV=|SW/TAN(Y)|
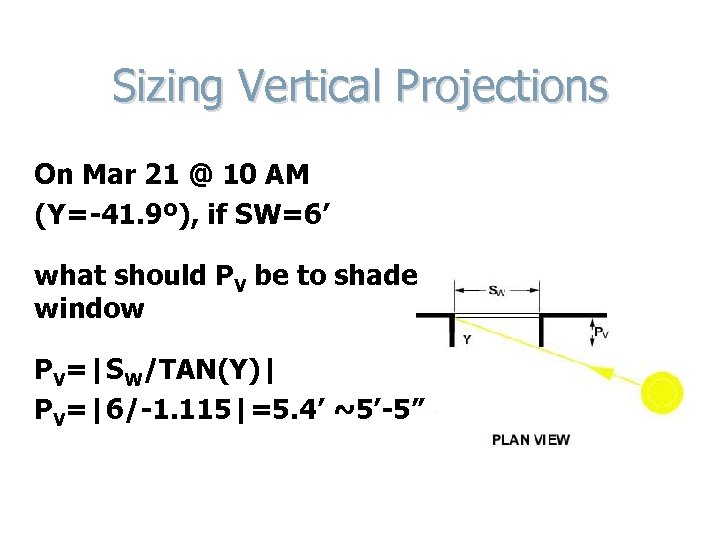 Sizing Vertical Projections On Mar 21 @ 10 AM (Y=-41. 9º), if SW=6’ what should PV be to shade window PV=|SW/TAN(Y)| PV=|6/-1. 115|=5. 4’ ~5’-5”
Sizing Vertical Projections On Mar 21 @ 10 AM (Y=-41. 9º), if SW=6’ what should PV be to shade window PV=|SW/TAN(Y)| PV=|6/-1. 115|=5. 4’ ~5’-5”
 Shading Strategies
Shading Strategies
 Shading Devices – Overview South Façade: Horizontal overhang or Brise-soleil San Cristobal Stables The Capital (Chandigarh)
Shading Devices – Overview South Façade: Horizontal overhang or Brise-soleil San Cristobal Stables The Capital (Chandigarh)
 Shading Devices –Overview East/West Façade: Vertical fins angled to the north and/or Brise-soleil Keio University Graduate School Research Center Monastery of Ste Marie de La Tourette
Shading Devices –Overview East/West Façade: Vertical fins angled to the north and/or Brise-soleil Keio University Graduate School Research Center Monastery of Ste Marie de La Tourette
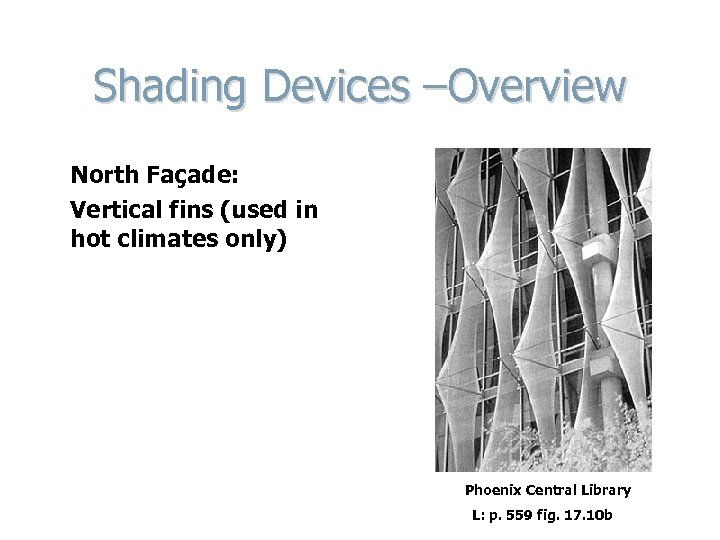 Shading Devices –Overview North Façade: Vertical fins (used in hot climates only) Phoenix Central Library L: p. 559 fig. 17. 10 b
Shading Devices –Overview North Façade: Vertical fins (used in hot climates only) Phoenix Central Library L: p. 559 fig. 17. 10 b
 Shading Devices – Tectonics n Vertical Louvers or Screens John Deere Headquarters, Moline IL Jewett Art Center, Wellesley, MA
Shading Devices – Tectonics n Vertical Louvers or Screens John Deere Headquarters, Moline IL Jewett Art Center, Wellesley, MA
 Shading Devices – Tectonics n Horizontal Solid and louvered planes, projections or recesses Paimio Sanatorium, Finland Getty Center Los Angeles, CA
Shading Devices – Tectonics n Horizontal Solid and louvered planes, projections or recesses Paimio Sanatorium, Finland Getty Center Los Angeles, CA
 Shading Devices –Tectonics n Sculptural Form Thickness Projections Screens Reynolds Aluminum Building, Detroit, MI Unity Temple, Oak Park, IL Beach House, Lido Shores, FL Obayashi Tokyo Design Center
Shading Devices –Tectonics n Sculptural Form Thickness Projections Screens Reynolds Aluminum Building, Detroit, MI Unity Temple, Oak Park, IL Beach House, Lido Shores, FL Obayashi Tokyo Design Center



