36253a5b0ddfca98032f10bc21c95e9c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89
 Environmental Concerns
Environmental Concerns
 Air Pollution Ø Pollutants in the atmosphere l l Contribute to global warming and ozone layer depletion Largely due to the burning of fossil fuels and other toxins
Air Pollution Ø Pollutants in the atmosphere l l Contribute to global warming and ozone layer depletion Largely due to the burning of fossil fuels and other toxins
 Water Pollution Ø Contamination by foreign matter that deteriorates the quality of the water l Can limit access to clean drinking water, spread disease, kill plant and animal life which affects food chain
Water Pollution Ø Contamination by foreign matter that deteriorates the quality of the water l Can limit access to clean drinking water, spread disease, kill plant and animal life which affects food chain
 Soil / Land Pollution Ø Soils and liquid wastes, toxins in soil l l Chemicals can seep into soil, then into food and water supplies A lot of land pollution caused by toxins seeping into soil from garbage dumps / landfills
Soil / Land Pollution Ø Soils and liquid wastes, toxins in soil l l Chemicals can seep into soil, then into food and water supplies A lot of land pollution caused by toxins seeping into soil from garbage dumps / landfills
 Excessive warming of the earth’s surface by the greenhouse effect that results in a change in climate Ø The Greenhouse Effect is not the problem l This process occurs naturally due to certain gases in the atmosphere l Life on earth would not be possible without it Ø Global Warming l BUT - Global warming – increases the greenhouse gases and temperatures to dangerous levels
Excessive warming of the earth’s surface by the greenhouse effect that results in a change in climate Ø The Greenhouse Effect is not the problem l This process occurs naturally due to certain gases in the atmosphere l Life on earth would not be possible without it Ø Global Warming l BUT - Global warming – increases the greenhouse gases and temperatures to dangerous levels
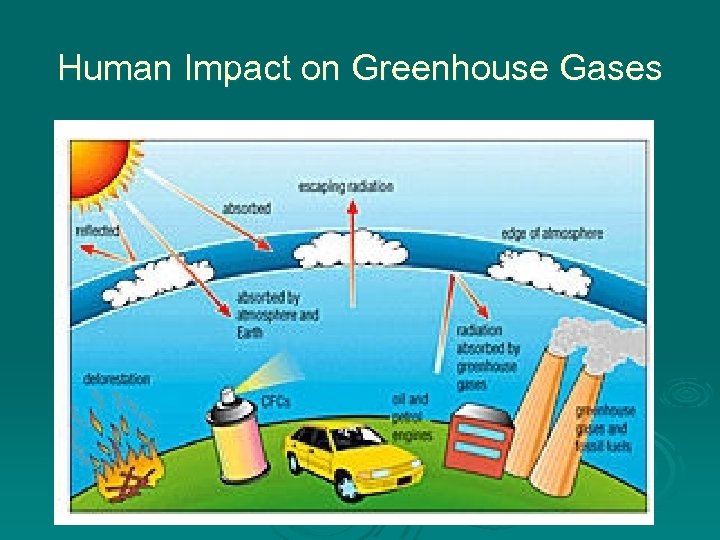 Human Impact on Greenhouse Gases
Human Impact on Greenhouse Gases
 Global Warming - Reasons Ø Carbon dioxide gases released into environment l Due to massive amounts of non-renewable fossil fuels being burned by humans, including: • Coal • Oil • Natural gas Non-renewable resources cannot be created over again and our supply of them is limited; once they run out, the resource is gone forever.
Global Warming - Reasons Ø Carbon dioxide gases released into environment l Due to massive amounts of non-renewable fossil fuels being burned by humans, including: • Coal • Oil • Natural gas Non-renewable resources cannot be created over again and our supply of them is limited; once they run out, the resource is gone forever.
 Global Warming l Some naturally occurring contributors to global warming: volcanic eruptions & meteor impacts
Global Warming l Some naturally occurring contributors to global warming: volcanic eruptions & meteor impacts
 Most Global Warming Impacts caused by Climate Change
Most Global Warming Impacts caused by Climate Change
 Climate Ø Climate is commonly defined as the weather (temperature and rainfall) averaged over a long period of time Ø The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, terrain, altitude, ice or snow cover, as well as nearby water bodies and their currents.
Climate Ø Climate is commonly defined as the weather (temperature and rainfall) averaged over a long period of time Ø The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, terrain, altitude, ice or snow cover, as well as nearby water bodies and their currents.
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Rising incidence of violent storms l North American Hurricane Season 2005
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Rising incidence of violent storms l North American Hurricane Season 2005
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Rising incidence of heat waves (Europe 2003)
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Rising incidence of heat waves (Europe 2003)
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Above average temperatures melting glaciers and sea levels are rising as a result
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Above average temperatures melting glaciers and sea levels are rising as a result
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Rising Sea Levels
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Rising Sea Levels
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Diseases are spreading more quickly and easily l l extending their ranges because of warmer temperatures Many diseases, especially those in water, reproduce more rapidly in warmer weather
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Diseases are spreading more quickly and easily l l extending their ranges because of warmer temperatures Many diseases, especially those in water, reproduce more rapidly in warmer weather
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Earlier arrival of spring in some parts of the world – impacting global agricultural patterns
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Earlier arrival of spring in some parts of the world – impacting global agricultural patterns
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø As permafrost melts, Arctic communities lose valuable shoreline
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø As permafrost melts, Arctic communities lose valuable shoreline
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Causes polar bears to starve because they cannot use the ice to hunt seals Ø Now on endangered species list
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Causes polar bears to starve because they cannot use the ice to hunt seals Ø Now on endangered species list
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Canada’s Arctic regions – sea ice shrinking l Causes sinking shorelines and death of some Arctic animals
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Canada’s Arctic regions – sea ice shrinking l Causes sinking shorelines and death of some Arctic animals
 Global Warming in Canada
Global Warming in Canada
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø In BC – increasing water temperatures have contributed to salmon spawning numbers being 1/3 of what they were in 1990 s
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø In BC – increasing water temperatures have contributed to salmon spawning numbers being 1/3 of what they were in 1990 s
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø While warmer temperatures could lengthen Canada’s short growing season – also higher risk of drought and forest fires
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø While warmer temperatures could lengthen Canada’s short growing season – also higher risk of drought and forest fires
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Warmer weather causes increasing numbers of forest fires and more droughts in Canada’s prairie areas
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Warmer weather causes increasing numbers of forest fires and more droughts in Canada’s prairie areas
 Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Canada’s oceans l l Increasing surface water temperatures, fewer nutrients are brought to the surface by the movement of colder water from deep in the ocean Nutrients support and maintain zooplankton – beginning of the food chain of sea life
Effects / Results of Global Warming Ø Canada’s oceans l l Increasing surface water temperatures, fewer nutrients are brought to the surface by the movement of colder water from deep in the ocean Nutrients support and maintain zooplankton – beginning of the food chain of sea life
 Kyoto Protocol - 1997 Agreement among 180 industrialized nations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions Ø Canada promised to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 6% of the 1990 level by 2012 Ø Countries not meeting their reduction targets could buy credits from other countries Ø USA withdrew in 2001 Ø
Kyoto Protocol - 1997 Agreement among 180 industrialized nations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions Ø Canada promised to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 6% of the 1990 level by 2012 Ø Countries not meeting their reduction targets could buy credits from other countries Ø USA withdrew in 2001 Ø
 Arguments against Kyoto Ø Ø Ø Concerned that meeting goals will involve high costs to businesses and government and possible loss of jobs Provincial governments must regulate polluting industries despite the fact that the federal government signed the agreement without consulting the provinces Some argue not enough evidence that global warming to blame for climate change
Arguments against Kyoto Ø Ø Ø Concerned that meeting goals will involve high costs to businesses and government and possible loss of jobs Provincial governments must regulate polluting industries despite the fact that the federal government signed the agreement without consulting the provinces Some argue not enough evidence that global warming to blame for climate change

 Kyoto & Canada Ø 2006 - Canada's greenhouse gas emissions were up by 24% Ø far from the government's commitment to meet a target 6% below the 1990 levels
Kyoto & Canada Ø 2006 - Canada's greenhouse gas emissions were up by 24% Ø far from the government's commitment to meet a target 6% below the 1990 levels
 Kyoto & Canada Election of a Conservative government in 2006 brought about a reversal in Canada's climate change policy Ø 2007 – Government announced plans to introduce legislation that would regulate industrial pollutants as part of the Conservatives' proposed Clean Air Act, to take effect in January 2010. Ø said Canada will not attempt to meet Kyoto's greenhouse gas targets Ø
Kyoto & Canada Election of a Conservative government in 2006 brought about a reversal in Canada's climate change policy Ø 2007 – Government announced plans to introduce legislation that would regulate industrial pollutants as part of the Conservatives' proposed Clean Air Act, to take effect in January 2010. Ø said Canada will not attempt to meet Kyoto's greenhouse gas targets Ø
 Possible Solutions – Renewable Energy Resources Ø Sustainable sources of energy could lessen dependence on fossil fuels, such as: l Wind Turbines http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Hg 9 fi. DUroo 4
Possible Solutions – Renewable Energy Resources Ø Sustainable sources of energy could lessen dependence on fossil fuels, such as: l Wind Turbines http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Hg 9 fi. DUroo 4
 Wind Power
Wind Power
 Solutions - Solar Power Panels http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=i. G 7 FNcw 7 a 5 c&feature=related http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=0 h. Cggdt. EU-M&feature=related
Solutions - Solar Power Panels http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=i. G 7 FNcw 7 a 5 c&feature=related http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=0 h. Cggdt. EU-M&feature=related
 Solutions – Tidal Power http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=t. SBACz. RE 3 Gw&feature=related http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=q. RUl 1 m. JQHmc&feature=related http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=F 0 mzrbfz. Up. M&feature=related http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Vam. SAbwg. JKk&feature=related
Solutions – Tidal Power http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=t. SBACz. RE 3 Gw&feature=related http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=q. RUl 1 m. JQHmc&feature=related http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=F 0 mzrbfz. Up. M&feature=related http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Vam. SAbwg. JKk&feature=related
 Solutions – Ground Source Energy http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=k. Uvd. Nr. OD 4 PY http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=l. D 82 e 5 RYf. W 8&feature=related
Solutions – Ground Source Energy http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=k. Uvd. Nr. OD 4 PY http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=l. D 82 e 5 RYf. W 8&feature=related
 Solutions – Biofuels Ø Ethanol – some made from Corn
Solutions – Biofuels Ø Ethanol – some made from Corn
 Ethanol – Concerns o Ethanol – while reduces levels of carbon monoxide and other toxic air pollutants, corn-based ethanol production is energy intensive, and in some instances uses nearly as much energy to produce (including the energy needed for farming and making fertilizers) than it supplies, although new technologies are improving the efficiency of production. http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=j 9 QQc. P_Y 1 II http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=8 R 012 X 3 t. U 6 Y&feature=related
Ethanol – Concerns o Ethanol – while reduces levels of carbon monoxide and other toxic air pollutants, corn-based ethanol production is energy intensive, and in some instances uses nearly as much energy to produce (including the energy needed for farming and making fertilizers) than it supplies, although new technologies are improving the efficiency of production. http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=j 9 QQc. P_Y 1 II http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=8 R 012 X 3 t. U 6 Y&feature=related
 Biofuels – instead of gasoline http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=WRB 5 VQMb 5 RI
Biofuels – instead of gasoline http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=WRB 5 VQMb 5 RI
 Geothermal Energy Ø Heat from the ground harvested
Geothermal Energy Ø Heat from the ground harvested
 Alternatives to Reduce Fossil Fuel Use Ø Hydrogen or methanol fuelled power cells for automobiles
Alternatives to Reduce Fossil Fuel Use Ø Hydrogen or methanol fuelled power cells for automobiles
 Alternatives to Reduce Fossil Fuel Use Ø Reduce, re-use, recycle
Alternatives to Reduce Fossil Fuel Use Ø Reduce, re-use, recycle
 Alternatives to Reduce Fossil Fuel Use Ø Carpool, use public transportation, ride bicycle or walk
Alternatives to Reduce Fossil Fuel Use Ø Carpool, use public transportation, ride bicycle or walk

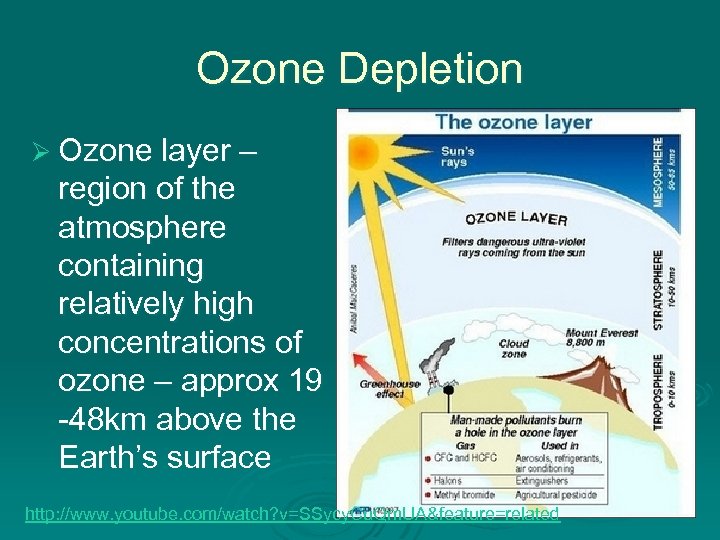 Ozone Depletion Ø Ozone layer – region of the atmosphere containing relatively high concentrations of ozone – approx 19 -48 km above the Earth’s surface http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=SSycy. Cu. Qm. UA&feature=related
Ozone Depletion Ø Ozone layer – region of the atmosphere containing relatively high concentrations of ozone – approx 19 -48 km above the Earth’s surface http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=SSycy. Cu. Qm. UA&feature=related
 Ozone Depletion Ø Ozone is formed by the action of solar ultraviolet light on oxygen Ø It’s the only gas able to block out the ultraviolet rays from the sun http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=e 9 fqpnki. Ui 0&feature=related
Ozone Depletion Ø Ozone is formed by the action of solar ultraviolet light on oxygen Ø It’s the only gas able to block out the ultraviolet rays from the sun http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=e 9 fqpnki. Ui 0&feature=related
 Ozone - Damage Ø Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) l l Have done 80% of the damage to the Ozone Layer (creating “holes”) Widely used in coolants for refrigerators and air conditioners, solvents, and aerosol cans
Ozone - Damage Ø Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) l l Have done 80% of the damage to the Ozone Layer (creating “holes”) Widely used in coolants for refrigerators and air conditioners, solvents, and aerosol cans
 Results of Ozone Depletion
Results of Ozone Depletion
 Results of Ozone Depletion Ø Higher incidences of skin cancer
Results of Ozone Depletion Ø Higher incidences of skin cancer
 Results of Ozone Depletion Ø Reduction of microscopic marine life like phytoplankton which will impact the food chain
Results of Ozone Depletion Ø Reduction of microscopic marine life like phytoplankton which will impact the food chain
 Results of Ozone Depletion Ø Mutations of genetic structure of plants and animals
Results of Ozone Depletion Ø Mutations of genetic structure of plants and animals
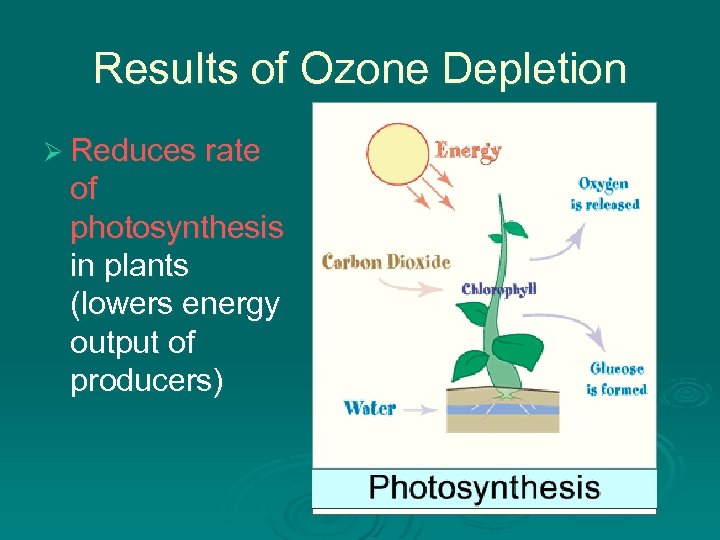 Results of Ozone Depletion Ø Reduces rate of photosynthesis in plants (lowers energy output of producers)
Results of Ozone Depletion Ø Reduces rate of photosynthesis in plants (lowers energy output of producers)
 Possible Responses to Ozone Depletion Ø Montreal Protocol – 1987 l Agreement between all industrial nations to cut use of CFCs in an effort to eliminate these chemicals by 2000 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Dn 3 Kv. Z_Xyqs&feature=related
Possible Responses to Ozone Depletion Ø Montreal Protocol – 1987 l Agreement between all industrial nations to cut use of CFCs in an effort to eliminate these chemicals by 2000 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Dn 3 Kv. Z_Xyqs&feature=related
 Possible Responses to Ozone Depletion Ø Avoid using plastic foam packaging and goods that use CFCs (some aerosol cans)
Possible Responses to Ozone Depletion Ø Avoid using plastic foam packaging and goods that use CFCs (some aerosol cans)
 Possible Responses to Ozone Depletion Ø Dispose of old refrigerators, freezers, and air conditioners safely
Possible Responses to Ozone Depletion Ø Dispose of old refrigerators, freezers, and air conditioners safely
 Fresh Water Supplies Ø 70% of Earth’s Surface – covered by water Ø However- most not readily accessible for human use
Fresh Water Supplies Ø 70% of Earth’s Surface – covered by water Ø However- most not readily accessible for human use
 Fresh Water Ø Water stored in: l l l Soil Aquifers (Ground water) Lakes Rivers streams
Fresh Water Ø Water stored in: l l l Soil Aquifers (Ground water) Lakes Rivers streams
 Fresh Water Ø Only 3% fresh water – 78% of which is stored in ice caps and glaciers Ø Canada has 18% of all surface fresh water on Earth Ø Large portion of this in Great Lakes
Fresh Water Ø Only 3% fresh water – 78% of which is stored in ice caps and glaciers Ø Canada has 18% of all surface fresh water on Earth Ø Large portion of this in Great Lakes
 Fresh Water Issues in Developing World Ø Ø Ø Ø Mismanagement / Overuse Limited access Lack of proper sanitation systems Lack of water treatment facilities Drought Privatization (water is owned by a private company and is expensive to buy) Cost (poorest of poor cannot afford)
Fresh Water Issues in Developing World Ø Ø Ø Ø Mismanagement / Overuse Limited access Lack of proper sanitation systems Lack of water treatment facilities Drought Privatization (water is owned by a private company and is expensive to buy) Cost (poorest of poor cannot afford)
 Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Contamination l l l Oil tanker accidents Natural causes Dumping of waste
Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Contamination l l l Oil tanker accidents Natural causes Dumping of waste
 Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Contamination l Agricultural • Chemicals used in herbicides / pesticides • Can seep into nearby streams and ground water
Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Contamination l Agricultural • Chemicals used in herbicides / pesticides • Can seep into nearby streams and ground water
 Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Contamination l Industrial • By-products of production in oil refineries, pulp mills, nuclear reactors, and chemical factories
Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Contamination l Industrial • By-products of production in oil refineries, pulp mills, nuclear reactors, and chemical factories
 Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Contamination l Municipal • Raw sewage, detergents, and solvents
Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Contamination l Municipal • Raw sewage, detergents, and solvents
 Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Misuse l l 67% of accessible surface water is used by agriculture When farmers till land – lose moisture – so land is irrigated – watered by artificial means
Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Misuse l l 67% of accessible surface water is used by agriculture When farmers till land – lose moisture – so land is irrigated – watered by artificial means
 Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Misuse l l 19% fresh water used for industry 9% for municipal / residential services
Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Misuse l l 19% fresh water used for industry 9% for municipal / residential services
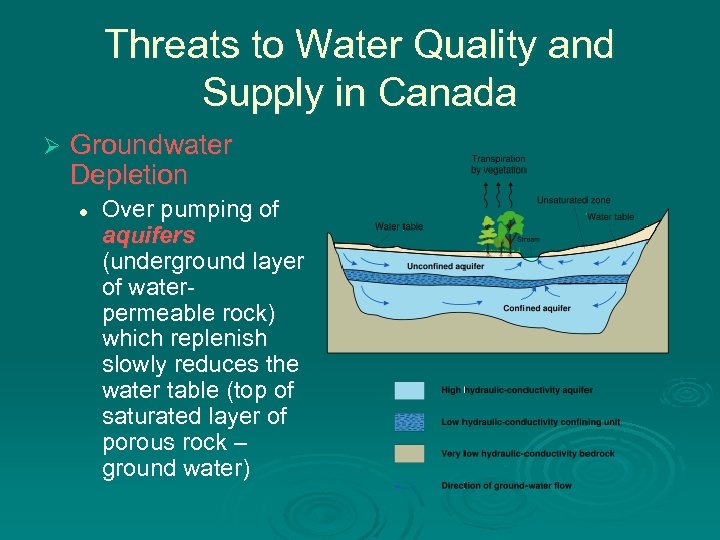 Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Groundwater Depletion l Over pumping of aquifers (underground layer of waterpermeable rock) which replenish slowly reduces the water table (top of saturated layer of porous rock – ground water)
Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Groundwater Depletion l Over pumping of aquifers (underground layer of waterpermeable rock) which replenish slowly reduces the water table (top of saturated layer of porous rock – ground water)
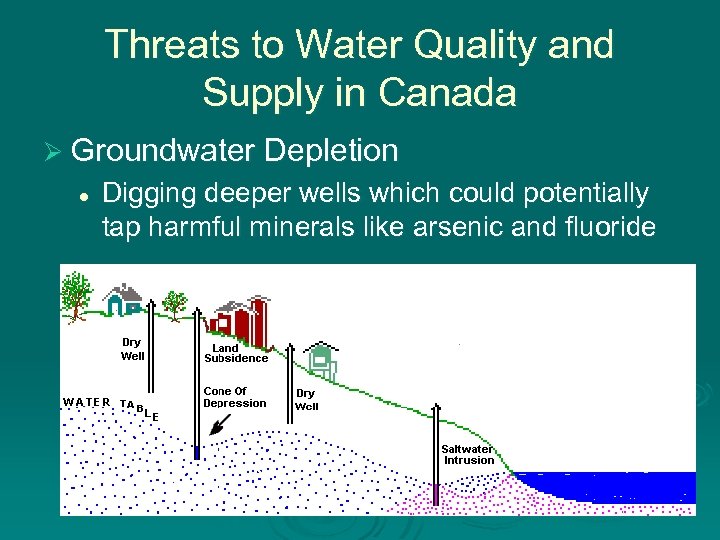 Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Groundwater Depletion l Digging deeper wells which could potentially tap harmful minerals like arsenic and fluoride
Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Groundwater Depletion l Digging deeper wells which could potentially tap harmful minerals like arsenic and fluoride
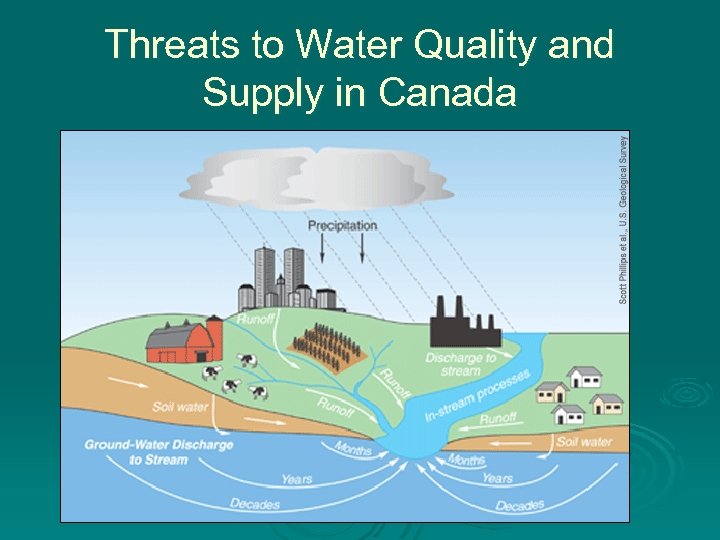 Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada
Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada
 Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Water Exports l l The transfer water over long distances Example: California would like to buy BC water; however, this could influence water table levels in BC
Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Water Exports l l The transfer water over long distances Example: California would like to buy BC water; however, this could influence water table levels in BC
 Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Increasing Populations l Main threat to world’s freshwater supply’s shortages threaten world agricultural production as the amount to irrigated land has more than doubled in the 2 nd half of the 20 th. C
Threats to Water Quality and Supply in Canada Ø Increasing Populations l Main threat to world’s freshwater supply’s shortages threaten world agricultural production as the amount to irrigated land has more than doubled in the 2 nd half of the 20 th. C
 Possible Solutions to Water Supply Threats Ø Treatment technologies (Water Treatment Plants)
Possible Solutions to Water Supply Threats Ø Treatment technologies (Water Treatment Plants)
 Possible Solutions to Water Supply Threats Ø Desalination of sea water (remove salt)
Possible Solutions to Water Supply Threats Ø Desalination of sea water (remove salt)
 Possible Solutions to Water Supply Threats Ø Reclaimed or recycled water technologies Ø Rainwater harvesting
Possible Solutions to Water Supply Threats Ø Reclaimed or recycled water technologies Ø Rainwater harvesting
 Possible Solutions to Water Supply Threats Ø Conservation Ø Low energy sprinkler systems and washing machines Ø Low flush toilets and other small-scale supply systems Ø Water Management technology
Possible Solutions to Water Supply Threats Ø Conservation Ø Low energy sprinkler systems and washing machines Ø Low flush toilets and other small-scale supply systems Ø Water Management technology

 Possible Solutions to Water Supply Threats Ø Farmers change watering schedules to coincide with seasonal rains Ø Shallow wells or use new technology / techniques in well drilling so farmers are able to tap groundwater in aquifers Ø Drip irrigation which directs water to plant roots – less evaporation
Possible Solutions to Water Supply Threats Ø Farmers change watering schedules to coincide with seasonal rains Ø Shallow wells or use new technology / techniques in well drilling so farmers are able to tap groundwater in aquifers Ø Drip irrigation which directs water to plant roots – less evaporation
 Possible Solutions to Water Supply Threats Ø Micro-dams rather than large-scale projects that cause major harm to the environment Ø Stronger government regulations Ø Taxes or user rates could be introduced to encourage conservation Ø Set watering patterns within municipalities
Possible Solutions to Water Supply Threats Ø Micro-dams rather than large-scale projects that cause major harm to the environment Ø Stronger government regulations Ø Taxes or user rates could be introduced to encourage conservation Ø Set watering patterns within municipalities
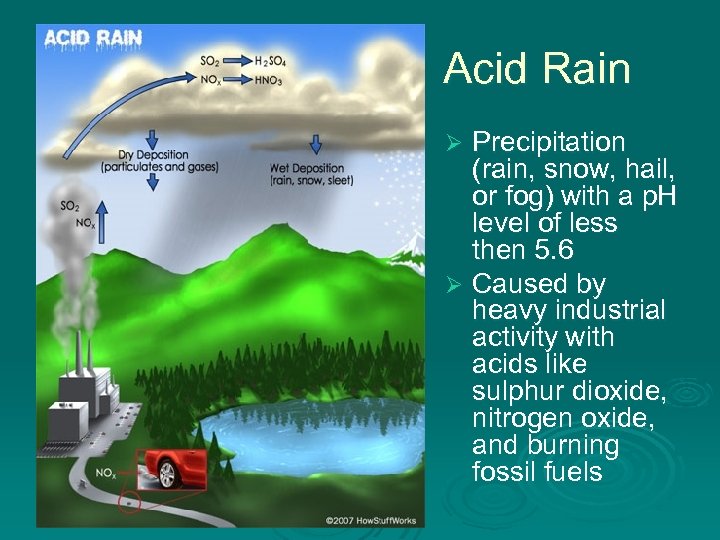 Acid Rain Precipitation (rain, snow, hail, or fog) with a p. H level of less then 5. 6 Ø Caused by heavy industrial activity with acids like sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, and burning fossil fuels Ø
Acid Rain Precipitation (rain, snow, hail, or fog) with a p. H level of less then 5. 6 Ø Caused by heavy industrial activity with acids like sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, and burning fossil fuels Ø
 Acid Rain Can poison plant life and wildlife of an area Ø Cause genetic mutations Ø Decrease growth rates of trees Ø Corrode steel Ø Affect lung capacity in humans Ø Especially predominant in Great Lakes area Ø
Acid Rain Can poison plant life and wildlife of an area Ø Cause genetic mutations Ø Decrease growth rates of trees Ø Corrode steel Ø Affect lung capacity in humans Ø Especially predominant in Great Lakes area Ø
 Acid Rain - Response Ø Canada- United States Air Quality Agreement signed by Canada and the US in Ottawa - 1991 Ø addresses transboundary air pollution leading to acid rain
Acid Rain - Response Ø Canada- United States Air Quality Agreement signed by Canada and the US in Ottawa - 1991 Ø addresses transboundary air pollution leading to acid rain
 Deforestation
Deforestation
 Deforestation The permanent loss of old growth forests Ø Has a drastic effect on the forests of the world Ø Important to the recycling of carbon dioxide, and the release of oxygen into the atmosphere Ø Leads to more global warming Ø Survival of some species threatened Ø
Deforestation The permanent loss of old growth forests Ø Has a drastic effect on the forests of the world Ø Important to the recycling of carbon dioxide, and the release of oxygen into the atmosphere Ø Leads to more global warming Ø Survival of some species threatened Ø
 Deforestation Ø Brazilian Rainforest l l Develop rainforest through farming, cattle ranching, mining, and lumbering Often no reforestation occurs and removal of forests lead to dry wastelands http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Gqk_sre 54 WA&feature=related
Deforestation Ø Brazilian Rainforest l l Develop rainforest through farming, cattle ranching, mining, and lumbering Often no reforestation occurs and removal of forests lead to dry wastelands http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Gqk_sre 54 WA&feature=related
 Deforestation Affects Ø Ø Nearby bodies of water because soil no longer covered by forest, it becomes stripped away by rain or snow Washed-out soil raises riverbeds, which leads to flooding, clogs reservoirs, and shortens life of dams Also contributes to formation of new islands, which depletes coastal fisheries Many insect, animal, and plant species have become extinct or endangered due to deforestation
Deforestation Affects Ø Ø Nearby bodies of water because soil no longer covered by forest, it becomes stripped away by rain or snow Washed-out soil raises riverbeds, which leads to flooding, clogs reservoirs, and shortens life of dams Also contributes to formation of new islands, which depletes coastal fisheries Many insect, animal, and plant species have become extinct or endangered due to deforestation
 Canada’s Forests Ø Canada has: l l l ¼ of the world’s temperate deciduous coastal forest 1/3 of world’s boreal coniferous forest Virtually all of the world’s old growth pine
Canada’s Forests Ø Canada has: l l l ¼ of the world’s temperate deciduous coastal forest 1/3 of world’s boreal coniferous forest Virtually all of the world’s old growth pine
 Decline of Canada’s Forests due to Forest fires Ø Industrial development Ø Logging Ø In BC: Pine Beetle Epidemic Ø • Largely due to global warming • Winters not cold enough to kill them
Decline of Canada’s Forests due to Forest fires Ø Industrial development Ø Logging Ø In BC: Pine Beetle Epidemic Ø • Largely due to global warming • Winters not cold enough to kill them
 Desertification
Desertification
 Desertification Ø Expansion of deserts due to mismanagement of the land in agriculture l l Using too much irrigation and artificial fertilizers to grow food out of season can make soils too salty to continue to grow crops Farmland can become a wasteland or desert on which very little can grow or survive
Desertification Ø Expansion of deserts due to mismanagement of the land in agriculture l l Using too much irrigation and artificial fertilizers to grow food out of season can make soils too salty to continue to grow crops Farmland can become a wasteland or desert on which very little can grow or survive
 Desertification process whereby the productivity of droughtprone land decreases because of a variety of factors including: Ø overgrazing (poor rangeland management), Ø poor irrigation (waterlogging and salinization), Ø deforestation, Ø Over-cultivation, Ø drought, Ø soil erosion, Ø chemical action Ø and other practices. Ø http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=z. LBYfyp 24 Xc&feature=related
Desertification process whereby the productivity of droughtprone land decreases because of a variety of factors including: Ø overgrazing (poor rangeland management), Ø poor irrigation (waterlogging and salinization), Ø deforestation, Ø Over-cultivation, Ø drought, Ø soil erosion, Ø chemical action Ø and other practices. Ø http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=z. LBYfyp 24 Xc&feature=related
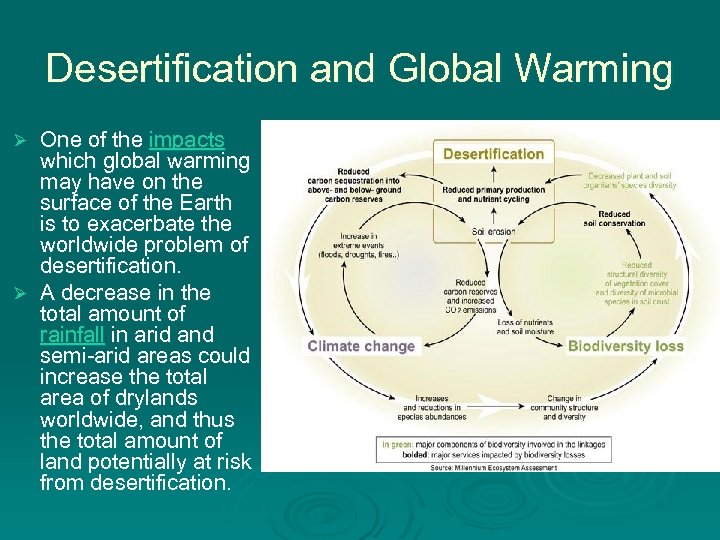 Desertification and Global Warming One of the impacts which global warming may have on the surface of the Earth is to exacerbate the worldwide problem of desertification. Ø A decrease in the total amount of rainfall in arid and semi-arid areas could increase the total area of drylands worldwide, and thus the total amount of land potentially at risk from desertification. Ø
Desertification and Global Warming One of the impacts which global warming may have on the surface of the Earth is to exacerbate the worldwide problem of desertification. Ø A decrease in the total amount of rainfall in arid and semi-arid areas could increase the total area of drylands worldwide, and thus the total amount of land potentially at risk from desertification. Ø
 Think About it…
Think About it…


