32f16c84bc4b25f2a95452f83316d290.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 ENUM Presentation #846 Jong Lee Strategic Development Veri. Sign
ENUM Presentation #846 Jong Lee Strategic Development Veri. Sign
 A Couple of Things About ENUM It’s a Protocol – Nothing More and Nothing Less Opt-In Has to Go Carrier ENUM Matters; Public ENUM Does Not Tier 2 ENUM will Merge with SIP Location in Many Cases Technology Does Not Matter It’s Getting Too Political 2
A Couple of Things About ENUM It’s a Protocol – Nothing More and Nothing Less Opt-In Has to Go Carrier ENUM Matters; Public ENUM Does Not Tier 2 ENUM will Merge with SIP Location in Many Cases Technology Does Not Matter It’s Getting Too Political 2
 Business/Regulatory State of the “Roots” Tier 0: • • • Only one database controlled by RIPE NCC and ITU (policy only) Contains participating country codes. Delegation would be at the NPA level for the US Tier I: • • • Within North America there could be several Tier 1 databases, which would provide multiple business opportunities instead of a single monopoly. The US Tier 1 s would receive their delegation at the NPA level. Lot’s of Boring Trials Going on Now Tier II: • • 3 A Few Interesting Trials Underway Every Carrier and Cooperative will have a Root
Business/Regulatory State of the “Roots” Tier 0: • • • Only one database controlled by RIPE NCC and ITU (policy only) Contains participating country codes. Delegation would be at the NPA level for the US Tier I: • • • Within North America there could be several Tier 1 databases, which would provide multiple business opportunities instead of a single monopoly. The US Tier 1 s would receive their delegation at the NPA level. Lot’s of Boring Trials Going on Now Tier II: • • 3 A Few Interesting Trials Underway Every Carrier and Cooperative will have a Root
 Current Issues With ENUM Very few Vo. IP platforms support ENUM today Nobody has figured out how to make money from ENUM yet Nothing in ENUM you can’t do with SIP Huge political issues over data ownership • Who wants to be the root? ENUM solves only a small part of the problem • Where you are is easy – how to get to you in a secure, reliable matter is another issue 4
Current Issues With ENUM Very few Vo. IP platforms support ENUM today Nobody has figured out how to make money from ENUM yet Nothing in ENUM you can’t do with SIP Huge political issues over data ownership • Who wants to be the root? ENUM solves only a small part of the problem • Where you are is easy – how to get to you in a secure, reliable matter is another issue 4
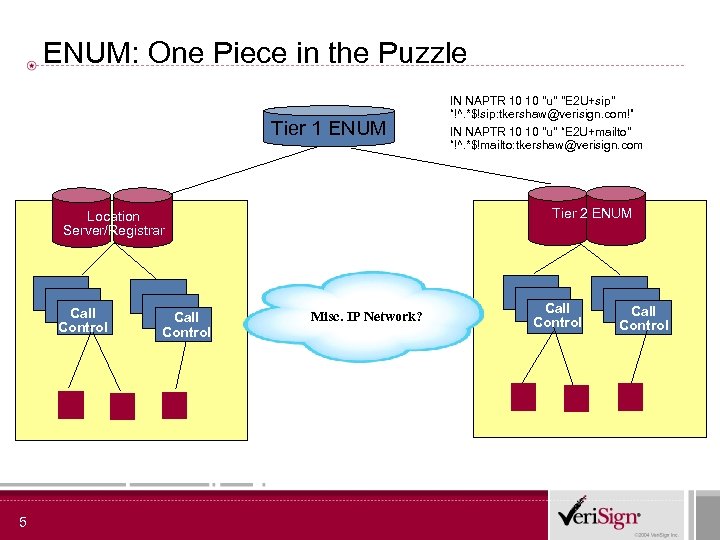 ENUM: One Piece in the Puzzle Tier 1 ENUM 5 Call Control IN NAPTR 10 10 "u" “E 2 U+mailto" “!^. *$!mailto: tkershaw@verisign. com Tier 2 ENUM Location Server/Registrar Call Control IN NAPTR 10 10 "u" "E 2 U+sip" “!^. *$!sip: tkershaw@verisign. com!” Misc. IP Network? Call Control
ENUM: One Piece in the Puzzle Tier 1 ENUM 5 Call Control IN NAPTR 10 10 "u" “E 2 U+mailto" “!^. *$!mailto: tkershaw@verisign. com Tier 2 ENUM Location Server/Registrar Call Control IN NAPTR 10 10 "u" "E 2 U+sip" “!^. *$!sip: tkershaw@verisign. com!” Misc. IP Network? Call Control
 ENUM: Missing Pieces I Know the Destination Domain of the Called Party I Can Now Query the Destination to Find the IP Address But: What Qo. S Rules are Associated with the Destination What Protocol/Variations are Available at the Destination What Network Path to Take What Security Policies/Keys Are Needed ENUM provides the information, but assumes the network will be able to figure it out. Reality: It Won’t (at least not yet) 6
ENUM: Missing Pieces I Know the Destination Domain of the Called Party I Can Now Query the Destination to Find the IP Address But: What Qo. S Rules are Associated with the Destination What Protocol/Variations are Available at the Destination What Network Path to Take What Security Policies/Keys Are Needed ENUM provides the information, but assumes the network will be able to figure it out. Reality: It Won’t (at least not yet) 6
 ENUM Issues to Be Resolved Critical Mass (the Network Problem) Application developers Public or private directories Update rate One or many - providers, databases, … Regulatory and policy issues New identifiers Coverage PSTN Service Logic 7
ENUM Issues to Be Resolved Critical Mass (the Network Problem) Application developers Public or private directories Update rate One or many - providers, databases, … Regulatory and policy issues New identifiers Coverage PSTN Service Logic 7
 Conclusions ENUM is starting to happen in trials Public trials have yet to generate anything interesting Private Tier 2 trials are getting interesting (like car wrecks are interesting) Interop, Qo. S and Security are barriers Need more Free Market input Opt-Out of Opt-In 8
Conclusions ENUM is starting to happen in trials Public trials have yet to generate anything interesting Private Tier 2 trials are getting interesting (like car wrecks are interesting) Interop, Qo. S and Security are barriers Need more Free Market input Opt-Out of Opt-In 8
 Clearing and Peering: New Models for Carrier and Enterprise Interconnect
Clearing and Peering: New Models for Carrier and Enterprise Interconnect
 Conclusions (Answer Before Question) Clearing Is Over Peering is the New Model Old Model: Exchanging Traffic New Model: Peered Route Resolution Issues: Data Ownership Security Network Engineering Interoperability 10
Conclusions (Answer Before Question) Clearing Is Over Peering is the New Model Old Model: Exchanging Traffic New Model: Peered Route Resolution Issues: Data Ownership Security Network Engineering Interoperability 10
 Radical Statement 1: If a Call Starts on an IP Device and Ends on an IP Device, it should use the IP network end to end
Radical Statement 1: If a Call Starts on an IP Device and Ends on an IP Device, it should use the IP network end to end
 Radical Statement 2: If a Call Starts or Stops on the PSTN, Use the PSTN
Radical Statement 2: If a Call Starts or Stops on the PSTN, Use the PSTN
 Fact: We Are Not Following Rule #1 or Rule #2 Today
Fact: We Are Not Following Rule #1 or Rule #2 Today
 Clearing and Peering: A History Vo. IP “Peering” Has Been Going on For Many Years More Clearing than Peering Arbitrage to Arbitrage Focus Replacing IXC/International Trunks with IP Long Haul Trunking Savings Bypass/Arbitrate This market is pretty much done New Models for Peering are Endpoint Focused Rather than Trunk Focused 14
Clearing and Peering: A History Vo. IP “Peering” Has Been Going on For Many Years More Clearing than Peering Arbitrage to Arbitrage Focus Replacing IXC/International Trunks with IP Long Haul Trunking Savings Bypass/Arbitrate This market is pretty much done New Models for Peering are Endpoint Focused Rather than Trunk Focused 14
 There Is No Vo. IP Today Current model for Vo. IP carrier is local only Offnet calls connect via PSTN, even if destination is IP Many operators in more than one market use PSTN even for on-net traffic between platforms Small Operators face standard interconnect agreements for terminating offnet traffic Why Vo. IP Peering is Good Reduce costs of PSTN interconnect for IP-IP Calls Reduce operational burden of maintaining interconnects, MGs and SS 7 links Enable new services like video, collaboration and presence Regional Operators Encounter Specific Challenges Economies of scale, Turnkey Solutions Enable cooperative application development and delivery – History of ILEC market shows this is critical to success 15
There Is No Vo. IP Today Current model for Vo. IP carrier is local only Offnet calls connect via PSTN, even if destination is IP Many operators in more than one market use PSTN even for on-net traffic between platforms Small Operators face standard interconnect agreements for terminating offnet traffic Why Vo. IP Peering is Good Reduce costs of PSTN interconnect for IP-IP Calls Reduce operational burden of maintaining interconnects, MGs and SS 7 links Enable new services like video, collaboration and presence Regional Operators Encounter Specific Challenges Economies of scale, Turnkey Solutions Enable cooperative application development and delivery – History of ILEC market shows this is critical to success 15
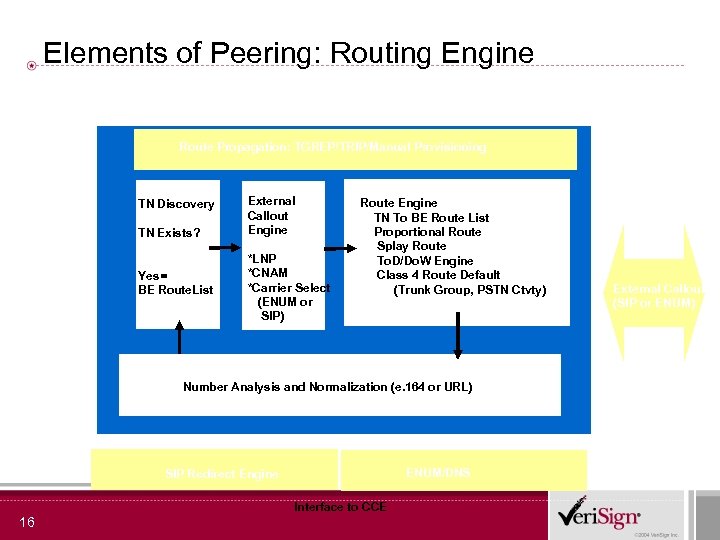 Elements of Peering: Routing Engine Route Propagation: TGREP/TRIP/Manual Provisioning TN Discovery TN Exists? Yes= BE Route. List External Callout Engine *LNP *CNAM *Carrier Select (ENUM or SIP) Route Engine TN To BE Route List Proportional Route Splay Route To. D/Do. W Engine Class 4 Route Default (Trunk Group, PSTN Ctvty) Number Analysis and Normalization (e. 164 or URL) ENUM/DNS SIP Redirect Engine Interface to CCE 16 External Callouts (SIP or ENUM)
Elements of Peering: Routing Engine Route Propagation: TGREP/TRIP/Manual Provisioning TN Discovery TN Exists? Yes= BE Route. List External Callout Engine *LNP *CNAM *Carrier Select (ENUM or SIP) Route Engine TN To BE Route List Proportional Route Splay Route To. D/Do. W Engine Class 4 Route Default (Trunk Group, PSTN Ctvty) Number Analysis and Normalization (e. 164 or URL) ENUM/DNS SIP Redirect Engine Interface to CCE 16 External Callouts (SIP or ENUM)
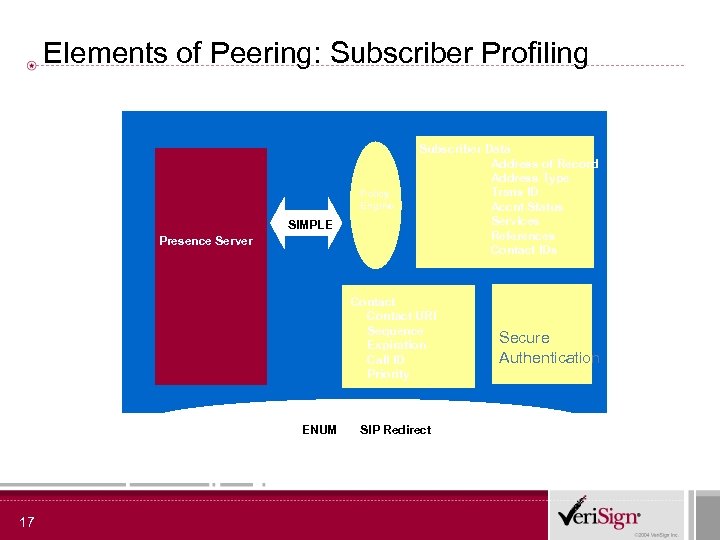 Elements of Peering: Subscriber Profiling Policy Engine SIMPLE Presence Server Subscriber Data Address of Record Address Type Trans ID Accnt Status Services References Contact IDs Contact URI Sequence Expiration Call ID Priority ENUM 17 SIP Redirect Secure Authentication
Elements of Peering: Subscriber Profiling Policy Engine SIMPLE Presence Server Subscriber Data Address of Record Address Type Trans ID Accnt Status Services References Contact IDs Contact URI Sequence Expiration Call ID Priority ENUM 17 SIP Redirect Secure Authentication
 Role of ENUM Provides protocol and architecture to discover if a given phone call is IP -IP Returns carrier domain of destination number Allows end-to-end Vo. IP interconnection However: ENUM is not widely deployed on SS, BE or SIP Proxy infrastructure ENUM does not solve the entire problem – directory of destinations is just one piece in secure peering ENUM has become very political 18
Role of ENUM Provides protocol and architecture to discover if a given phone call is IP -IP Returns carrier domain of destination number Allows end-to-end Vo. IP interconnection However: ENUM is not widely deployed on SS, BE or SIP Proxy infrastructure ENUM does not solve the entire problem – directory of destinations is just one piece in secure peering ENUM has become very political 18
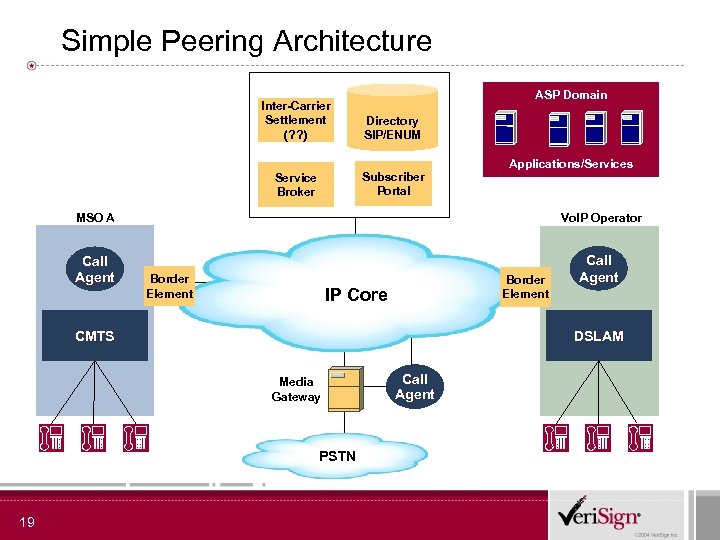 Simple Peering Architecture ASP Domain Inter-Carrier Settlement (? ? ) Directory SIP/ENUM Service Broker Subscriber Portal Applications/Services MSO A Vo. IP Operator Call Agent Border Element IP Core CMTS DSLAM Media Gateway PSTN 19 Call Agent
Simple Peering Architecture ASP Domain Inter-Carrier Settlement (? ? ) Directory SIP/ENUM Service Broker Subscriber Portal Applications/Services MSO A Vo. IP Operator Call Agent Border Element IP Core CMTS DSLAM Media Gateway PSTN 19 Call Agent
 Peering Architectural Components Core Vo. IP directory provides ENUM and/or SIP resolution of queries • • Returns domain/IP of the partner that owns the subscriber Admin portal allows operators to monitor and access their own data in real time Management of Network Border • • • Border and Firewall management NAT Transversal and Pinhole Management Firewall Integrity and Intrusion Detection Billing and Settlement between Vo. IP Carriers • • • Open questions on settlement: Will there be Compensation? What is the Service Model (per registration, per transaction, per termination) Even with “bill and keep” settlement, call record exchange will be necessary for traffic engineering purposes Application Sharing 20
Peering Architectural Components Core Vo. IP directory provides ENUM and/or SIP resolution of queries • • Returns domain/IP of the partner that owns the subscriber Admin portal allows operators to monitor and access their own data in real time Management of Network Border • • • Border and Firewall management NAT Transversal and Pinhole Management Firewall Integrity and Intrusion Detection Billing and Settlement between Vo. IP Carriers • • • Open questions on settlement: Will there be Compensation? What is the Service Model (per registration, per transaction, per termination) Even with “bill and keep” settlement, call record exchange will be necessary for traffic engineering purposes Application Sharing 20
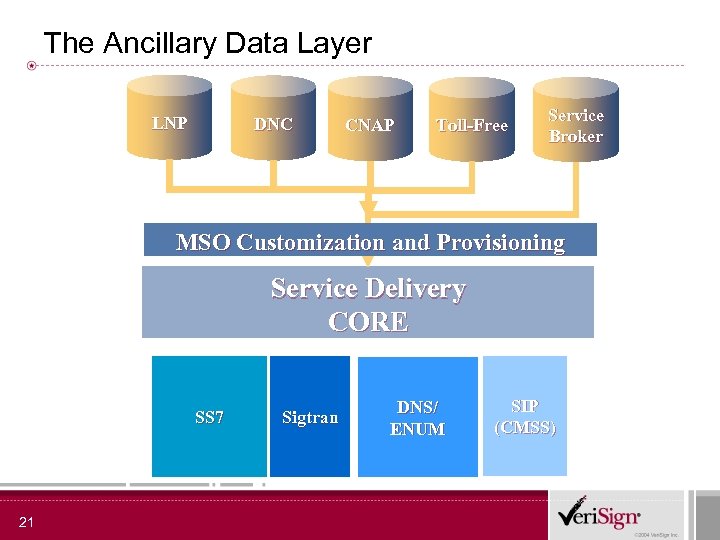 The Ancillary Data Layer LNP DNC CNAP Toll-Free Service Broker MSO Customization and Provisioning Service Delivery CORE SS 7 21 Sigtran DNS/ ENUM SIP (CMSS)
The Ancillary Data Layer LNP DNC CNAP Toll-Free Service Broker MSO Customization and Provisioning Service Delivery CORE SS 7 21 Sigtran DNS/ ENUM SIP (CMSS)
 Peering Architecture: Operator to Enterprise In addition to Inter-Carrier peering, Carriers will want to interconnect to other Vo. IP islands Enterprises Public Sector In addition to directory and security, interoperability must be addressed Enterprises are largely H. 323 based today; slow migration to SIP Other carriers are running different variations of SIP Example: Privacy. ID Protocol normalization will be necessary at the edge of the network to protect the application delivery function Quality of Service: Is All Routing Created Equal? 22
Peering Architecture: Operator to Enterprise In addition to Inter-Carrier peering, Carriers will want to interconnect to other Vo. IP islands Enterprises Public Sector In addition to directory and security, interoperability must be addressed Enterprises are largely H. 323 based today; slow migration to SIP Other carriers are running different variations of SIP Example: Privacy. ID Protocol normalization will be necessary at the edge of the network to protect the application delivery function Quality of Service: Is All Routing Created Equal? 22
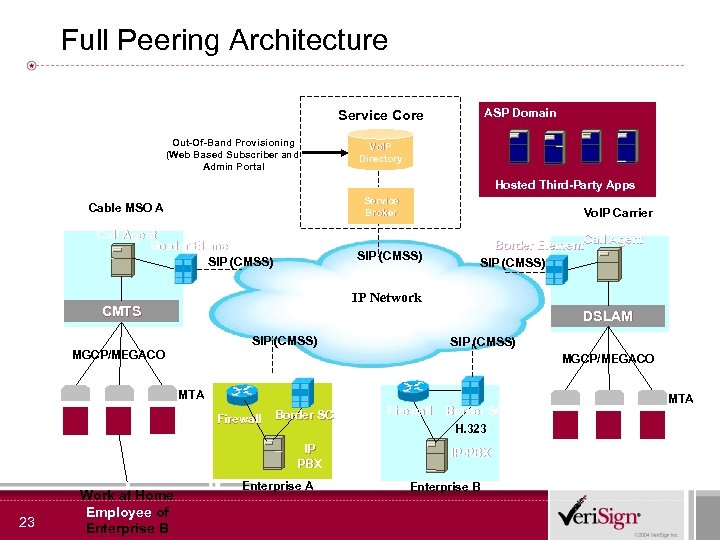 Full Peering Architecture ASP Domain Service Core Out-Of-Band Provisioning (Web Based Subscriber and Admin Portal Vo. IP Directory Hosted Third-Party Apps Service Broker Cable MSO A Call Agent Border Element SIP (CMSS) Vo. IP Carrier SIP (CMSS) Border Element. Call Agent SIP (CMSS) IP Network CMTS DSLAM SIP (CMSS) MGCP/MEGACO MTA Firewall Border SC 23 Border SC H. 323 IP PBX Work at Home Employee of Enterprise B Firewall Enterprise A IP-PBX Enterprise B MTA
Full Peering Architecture ASP Domain Service Core Out-Of-Band Provisioning (Web Based Subscriber and Admin Portal Vo. IP Directory Hosted Third-Party Apps Service Broker Cable MSO A Call Agent Border Element SIP (CMSS) Vo. IP Carrier SIP (CMSS) Border Element. Call Agent SIP (CMSS) IP Network CMTS DSLAM SIP (CMSS) MGCP/MEGACO MTA Firewall Border SC 23 Border SC H. 323 IP PBX Work at Home Employee of Enterprise B Firewall Enterprise A IP-PBX Enterprise B MTA
 Advantages of Full Peering Model Reduces cost of calls between operators by eliminating need to hand off to IXC/PSTN Creates end-to-end Vo. IP network to enable shared value-added services Provides highly predictable network cost model Maintains complete perimeter security Maintains a SIP core network while enabling carriers to connect to every other Vo. IP operator in the world Allows operators to Address Key Subscriber Demographics Teleworkers 16 -25 Demographic 24
Advantages of Full Peering Model Reduces cost of calls between operators by eliminating need to hand off to IXC/PSTN Creates end-to-end Vo. IP network to enable shared value-added services Provides highly predictable network cost model Maintains complete perimeter security Maintains a SIP core network while enabling carriers to connect to every other Vo. IP operator in the world Allows operators to Address Key Subscriber Demographics Teleworkers 16 -25 Demographic 24
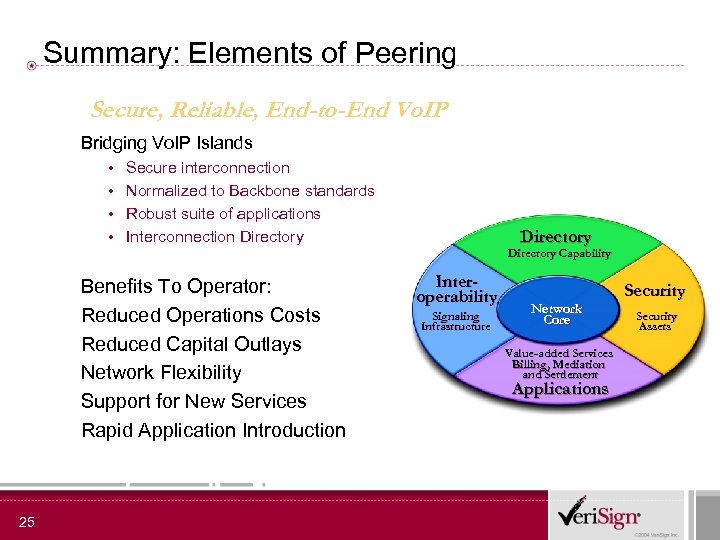 Summary: Elements of Peering Secure, Reliable, End-to-End Vo. IP Bridging Vo. IP Islands • • Secure interconnection Normalized to Backbone standards Robust suite of applications Interconnection Directory Dir e c t o r y Directory Capability Benefits To Operator: Reduced Operations Costs Reduced Capital Outlays Network Flexibility Support for New Services Rapid Application Introduction 25 I nt e r o p e r ab i l i t y Signaling Infrastructure Network Core Value-added Services Billing, Mediation and Settlement A p p l i c at i o n s Se c ur it y Security Assets
Summary: Elements of Peering Secure, Reliable, End-to-End Vo. IP Bridging Vo. IP Islands • • Secure interconnection Normalized to Backbone standards Robust suite of applications Interconnection Directory Dir e c t o r y Directory Capability Benefits To Operator: Reduced Operations Costs Reduced Capital Outlays Network Flexibility Support for New Services Rapid Application Introduction 25 I nt e r o p e r ab i l i t y Signaling Infrastructure Network Core Value-added Services Billing, Mediation and Settlement A p p l i c at i o n s Se c ur it y Security Assets
 Thank You! jlee@verisign. com 703 -948 -3359
Thank You! jlee@verisign. com 703 -948 -3359


