 ENTRY-SEQUENCED DATA SET Pavel Yarkov , 2013 © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 1
ENTRY-SEQUENCED DATA SET Pavel Yarkov , 2013 © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 1
 ESDS structure Records are held in an ESDS in the order in which they were first loaded into the data set. Each record is identified by its relative byte address (RBA). Cluster consists of data component only. © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 2
ESDS structure Records are held in an ESDS in the order in which they were first loaded into the data set. Each record is identified by its relative byte address (RBA). Cluster consists of data component only. © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 2
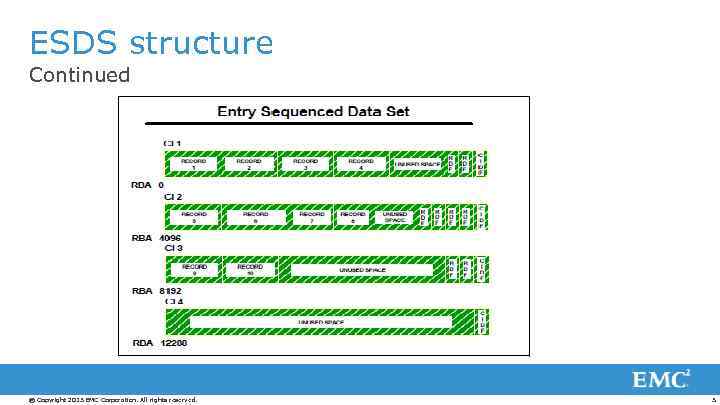 ESDS structure Continued © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 3
ESDS structure Continued © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 3
 ESDS structure Control information consists of RDF (Record Descriptor Field) and CIDF (Control Interval Descriptor Field). CIDF(last 4 bytes in Control Interval) – information about free space. RDF - In case of fixed size records each CI contains two RDF's and each RDF is 3 bytes in length. In case of the variable size records, there is a separate RDF for each record in the CI. © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 4
ESDS structure Control information consists of RDF (Record Descriptor Field) and CIDF (Control Interval Descriptor Field). CIDF(last 4 bytes in Control Interval) – information about free space. RDF - In case of fixed size records each CI contains two RDF's and each RDF is 3 bytes in length. In case of the variable size records, there is a separate RDF for each record in the CI. © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 4
 RBA & XRBA A standard RBA is an unsigned 32 -bit number. Extended format, extended addressing ESDS data set is a different kind of ESDS that supports 64 bit extended relative byte addresses (XRBAs). © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 5
RBA & XRBA A standard RBA is an unsigned 32 -bit number. Extended format, extended addressing ESDS data set is a different kind of ESDS that supports 64 bit extended relative byte addresses (XRBAs). © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 5
 ESDS A record can be accessed sequentially or directly by its RBA: Sequential processing — VSAM automatically retrieves records in stored sequence. Sequential processing can be started from the beginning or somewhere in the middle of a data set. Direct processing — When a record is loaded or added, VSAM indicates its RBA. To retrieve records directly, you must supply the RBA for the record as a search argument. © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 6
ESDS A record can be accessed sequentially or directly by its RBA: Sequential processing — VSAM automatically retrieves records in stored sequence. Sequential processing can be started from the beginning or somewhere in the middle of a data set. Direct processing — When a record is loaded or added, VSAM indicates its RBA. To retrieve records directly, you must supply the RBA for the record as a search argument. © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 6
 Creating ESDS //DEFCLU 5 JOB. . . //STEP 1 EXEC PGM=IDCAMS //SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=A //SYSIN DD * DEFINE CLUSTER – (NAME(EXAMPLE. ESDS 2) – RECORDSIZE(2500 3000) – SPANNED – VOLUMES(VSER 03) – CYLINDERS(2 1) – NONINDEXED – CATALOG(RSTUCAT 2) /* © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 7
Creating ESDS //DEFCLU 5 JOB. . . //STEP 1 EXEC PGM=IDCAMS //SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=A //SYSIN DD * DEFINE CLUSTER – (NAME(EXAMPLE. ESDS 2) – RECORDSIZE(2500 3000) – SPANNED – VOLUMES(VSER 03) – CYLINDERS(2 1) – NONINDEXED – CATALOG(RSTUCAT 2) /* © Copyright 2013 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 7