c1cb729b469355946d8852fc02404bce.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Entrez Neuron: an OWL/RDFa–based Web Application for Information Exploration and Integration in Neuroscience Matthias Samwald, Ernest Lim, Peter Masiar, Luis Marenco, Huajun Chen, Thomas Morse, Gordon Shepherd, Perry Miller and Kei Cheung Yale Center for Medical informatics, Yale University Medical University of Vienna, Austria School of Computer Science, Zhejiang University

Outline • Sense. Lab Overview • Entrez Neuron Project – Semantic Data Conversion – Semantic Data Browsing/Querying • Future Development • Online demo
Yale Sense. Lab Overview Sense. Lab’s development was funded by the Human Brain Project to disseminate information related to neuronal membrane properties with special emphasis on the olfactory system. • A major information resource for international neuroscience research. • Have garnered several million hits and unique visits over the years.
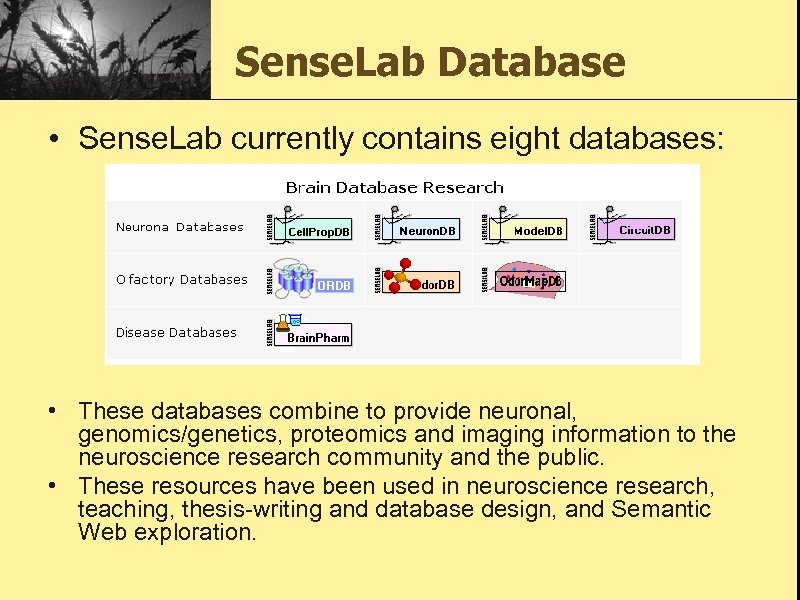
Sense. Lab Database • Sense. Lab currently contains eight databases: • These databases combine to provide neuronal, genomics/genetics, proteomics and imaging information to the neuroscience research community and the public. • These resources have been used in neuroscience research, teaching, thesis-writing and database design, and Semantic Web exploration.
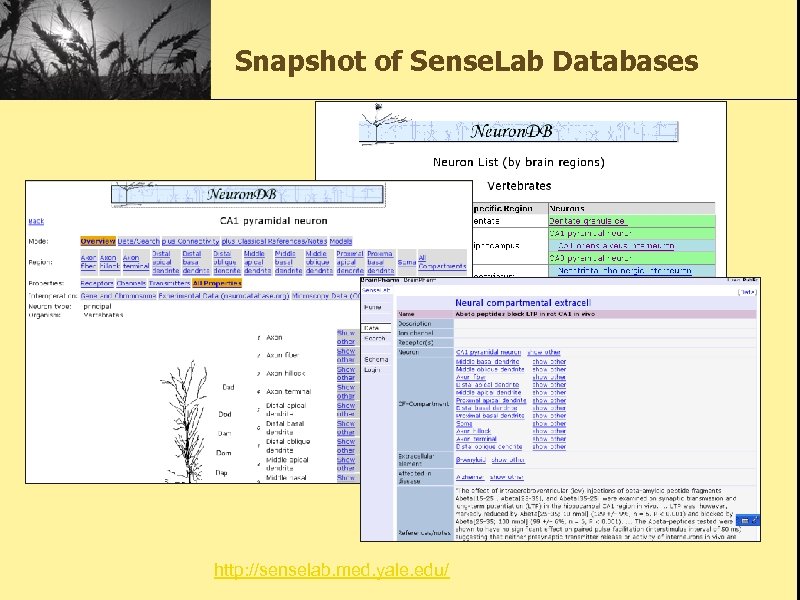
Snapshot of Sense. Lab Databases http: //senselab. med. yale. edu/

Entrez Neuron Project A neuron-centric interface that allows for keyword-based queries against a coherent repository of OWL ontologies about neuronal structure, physiology, mathematical models and microscopy.
Technical Approach • Careful modeling of neuroscience domain knowledge in consideration of reusing many well-defined general purpose biomedical ontologies. • Convert legacy Senselab data to desired RDF/OWL model. • Map out to external biomedical resources. • Provide integrated ontological browse, search services over the knowledge base. • Use RDFa to publish the knowledge as HTML.

Ontology modeling • Basic ontology: an ontology containing basic class hierarchies and relations was manually created, based on the structure of existing Sense. Lab databases. • The ontologies were built upon established foundational ontologies in order to maximize the interoperability with other existing and forthcoming biomedical Semantic Web resources. These ontologies were: – the Relation Ontology [RO] from the Open Biomedical Ontologies repository [OBO], which defines basic relations such as 'part of', 'participant of' or 'contained in'. – the Basic Formal Ontology [BFO], which defines basic classes such as 'process', 'object', 'quality' or 'function'.

Data conversion • Based on this manually created basic ontology, the data from the Sense. Lab databases were then automatically converted to OWL using programs written in Java and Python. • The automated export scripts extends the manually created basic ontology through the creation of subclasses, OWL property restrictions and individuals.

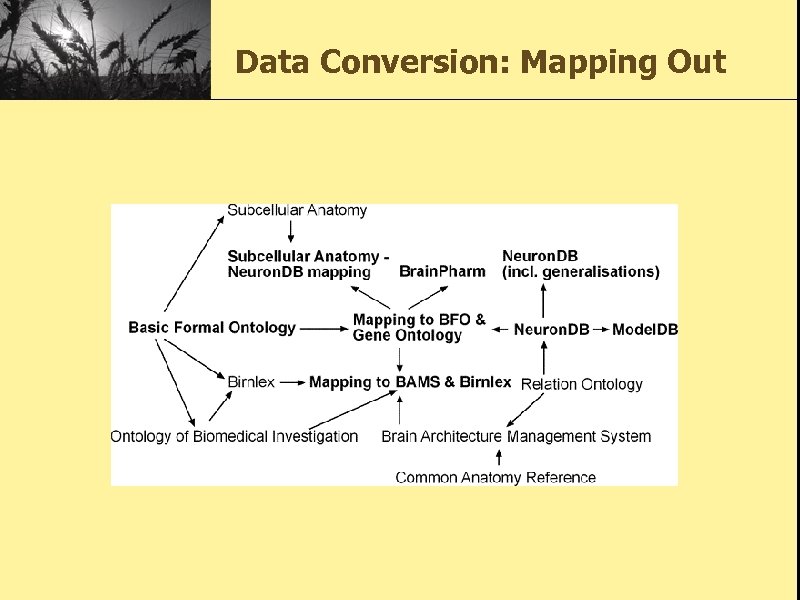
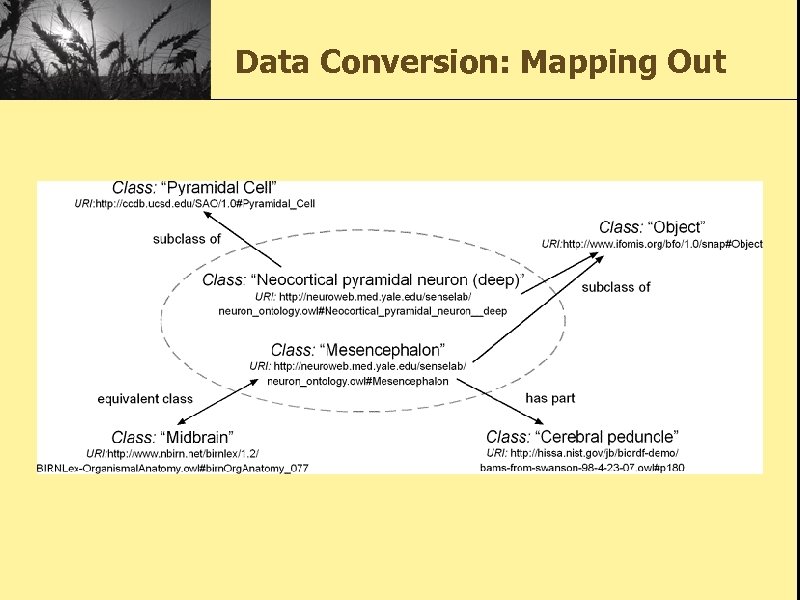
Data Conversion: Mapping Out • Mappings were made to the following ontologies: – the BAMS ontology which was derived from the Brain Architecture Management System [BAMS] – the Subcellular Anatomy Ontology (SAO) created by the Cell Centered Database project. [SAO] – the Birn. Lex ontology developed by members of the Biomedical Informatics Research Network [BIRNLEX] – the Common Anatomy Reference Ontology (CARO) [CARO] – the Gene Ontology [GO] – the Ontology of Biomedical Investigation (OBI) [OBI]
Data Conversion: Mapping Out
Data Conversion: Mapping Out
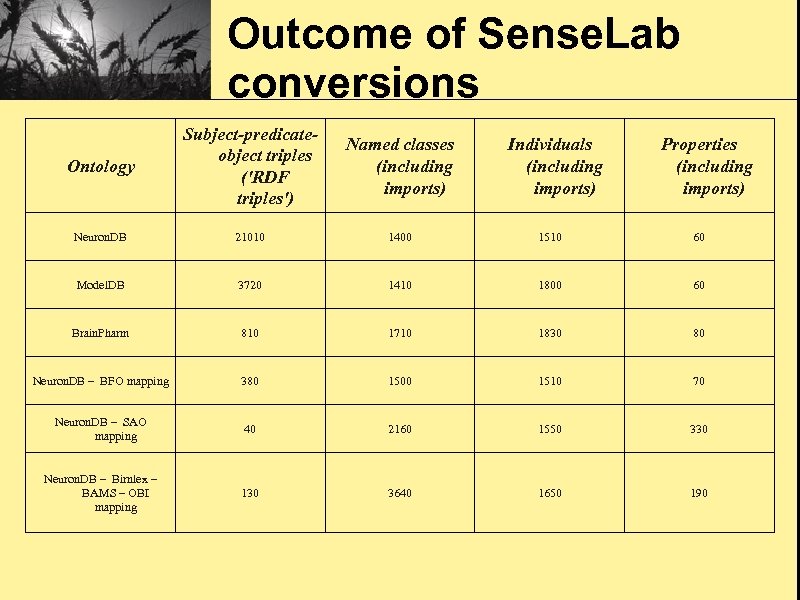
Outcome of Sense. Lab conversions Ontology Subject-predicateobject triples ('RDF triples') Named classes (including imports) Neuron. DB 21010 1400 1510 60 Model. DB 3720 1410 1800 60 Brain. Pharm 810 1710 1830 80 Neuron. DB – BFO mapping 380 1500 1510 70 Neuron. DB – SAO mapping 40 2160 1550 330 Neuron. DB – Birnlex – BAMS – OBI mapping 130 3640 1650 190 Individuals (including imports) Properties (including imports)
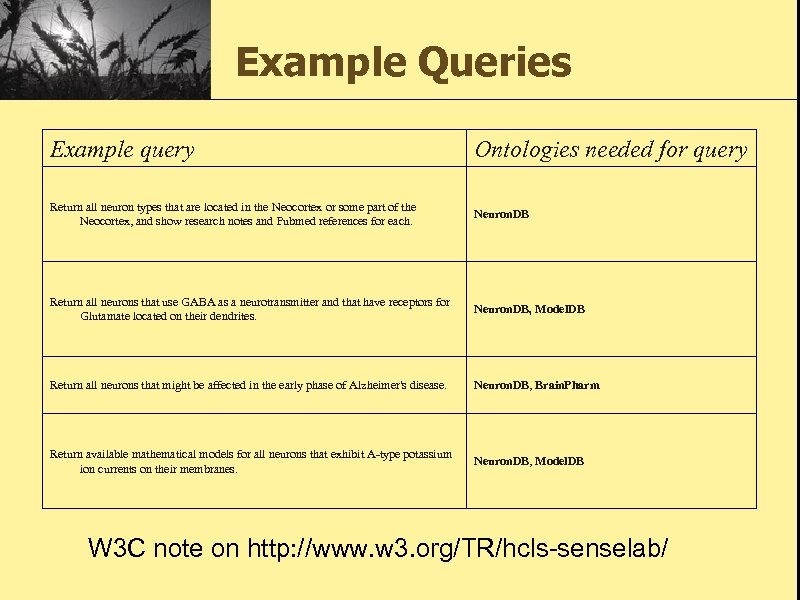
Example Queries Example query Ontologies needed for query Return all neuron types that are located in the Neocortex or some part of the Neocortex, and show research notes and Pubmed references for each. Neuron. DB Return all neurons that use GABA as a neurotransmitter and that have receptors for Glutamate located on their dendrites. Neuron. DB, Model. DB Return all neurons that might be affected in the early phase of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. DB, Brain. Pharm Return available mathematical models for all neurons that exhibit A-type potassium ion currents on their membranes. Neuron. DB, Model. DB W 3 C note on http: //www. w 3. org/TR/hcls-senselab/
But how can end-users profit? Lack of user-friendly interfaces Spectrum of Semantic Web user interfaces with two extremes: • Very flexible, but very generic and therefore not user friendly • Very specific and user-friendly, but only geared towards a small set of ontological entities Practical user interfaces probably need to be positioned somewhere in the middle
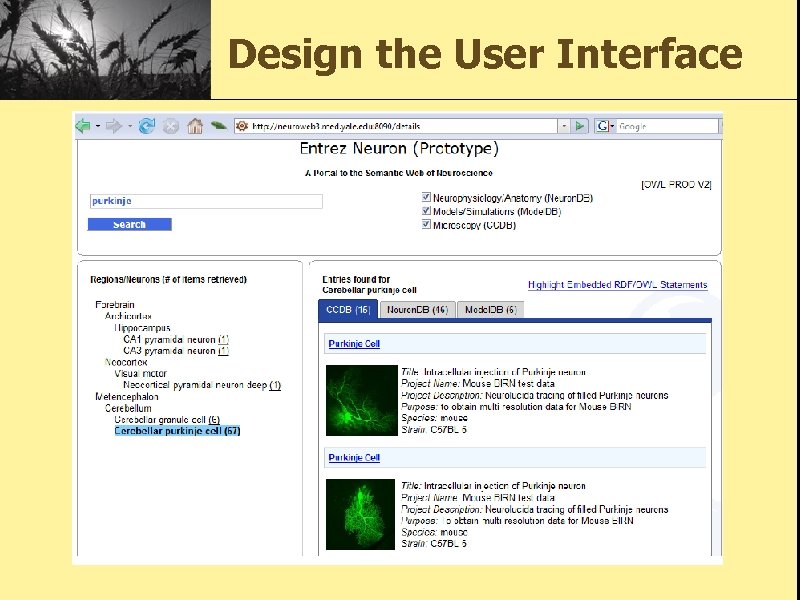
Design the User Interface

Key Features • Facet Search enabled by ontology description. • Use RDFa to encode the semantic information to HTML
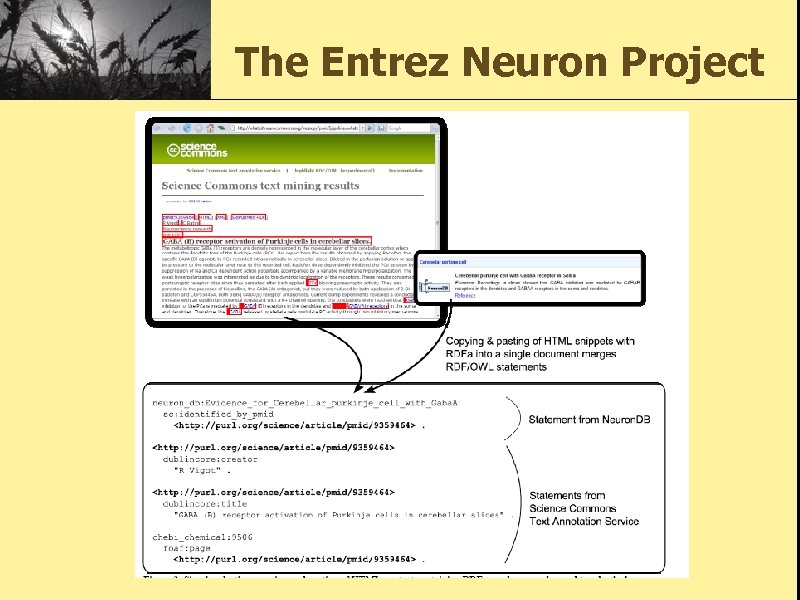
The Entrez Neuron Project
Future developments • Adding more RDF/OWL data – PDSP Ki database (ligand-receptor interactions) – SWAN ontology (Alzheimer's disease hypotheses) – Further OBO ontologies • Querying and Reasoning – Switch to using SPARQL (instead of Oracle RDF query language) – Explore and expand reasoning capabilities

Future developments • User interface – Add more features to the existing user interface – 3 D Visualization • Community development – Establish Entrez Neuron as an open community platform

Acknowledgement • Cell Centered Database: Maryann Martone, Willy Wong • Science Commons: Alan Ruttenberg • Oracle: Melliyal Annamalai, Alan Wu

Thanks for your Attention
c1cb729b469355946d8852fc02404bce.ppt