a1072a3150e61e0617a292ef08cf72c4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Entrepreneurship & Small Business Entrepreneurship The process of creating and managing a business to achieve desired objectives is our working definition for entrepreneurship. 6 -1

Entrepreneurship & Small Business Entrepreneurship & Entrepreneurs Ability to see emerging trends & create company that satisfies those consumer needs. (Dell Computers) Create new markets (Amazon. com) Improve or re-package existing products (Starbucks) 6 -2

Entrepreneurship & Small Business What is a Small Business? “Smallness” is relative. Defined, small business is any independently owned and operated business, not dominant in its competitive area, employing less than 500 people. 6 -3
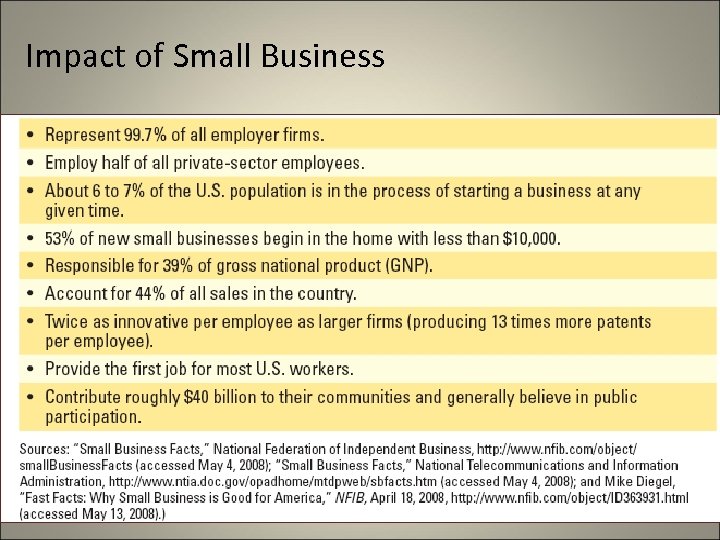
Impact of Small Business 6 -4

Impact of Small Business 60 -80% of all new jobs, annually, created by small business in the last 10 years. 6 -5

Small Business & Innovation 55% of all innovations • Airplane • Audio tap recorder • Double-knit fabric • Fiber-optic examining equipment • Heart valve • Optical scanner • Personal computer • Soft contact lenses • Zipper 6 -6

Small Business Industries that Attract Small Business Retailing and wholesaling, services, manufacturing and high technology are especially attractive to entrepreneurs. 6 -7

Retailing & Wholesaling Selling directly to the consumer • • Music stores Sporting-goods shops Dry cleaners Boutiques Drugstores Restaurants Hardware stores 6 -8 14

Small Business Services • 66% of the economy • Employs 70% of workforce 6 -9

Small Business Manufacturing Small business advantage over large firms – product customization Artwork, clothing, jewelry, clothing, furniture 6 -10

Small Business High Technology Businesses that depend heavily on advanced scientific and engineering knowledge. • 39% of high-tech jobs are in small business 6 -11

Advantages of Small Business Ownership • Independence • Costs • Flexibility • Focus • Reputation 6 -12

Disadvantages of Small-Business Ownership • High Stress Level • High Failure Rate • 90% of all new businesses fail within the first 5 years • Undercapitalization • Lack of funds to operate a business normally 6 -13

Disadvantages of Small-Business Ownership • Managerial Inexperience or Incompetence • Inability to Cope with Growth 6 -14

Starting the Small Business • • • Start with a concept or general idea Devise a strategy to guide planning & development Make Decisions • • • Form of ownership Financial resources needed Acquire existing business Start a new business Buy a franchise 6 -15

The Business Plan – a precise statement of the rationale for the business and a step-by-step explanation of how it will achieve its goals. Acts as a guide and reference document. • Explanation of the business • Analysis of competition • Income/Expense estimates 6 -16
Forms of Business Ownership • Sole Proprietorship • Partnership • Corporation 6 -17

Financial Resources • Provide your own personal capital (money) • Obtain capital (Financing options) 6 -18

Starting a Small Business Do I start from scratch? Do I buy an existing business? Do I buy a franchise? 6 -19

Starting a Small Business Franchising A license to sell another’s products or to use another’s name in business, or both 6 -20

Starting a Small Business Franchising Franchiser – the company that sells a franchise (e. g. Dunkin’ Donuts, Mc. Donald’s, Subway, Re/Max) Franchisee – the purchaser of a franchise 6 -21
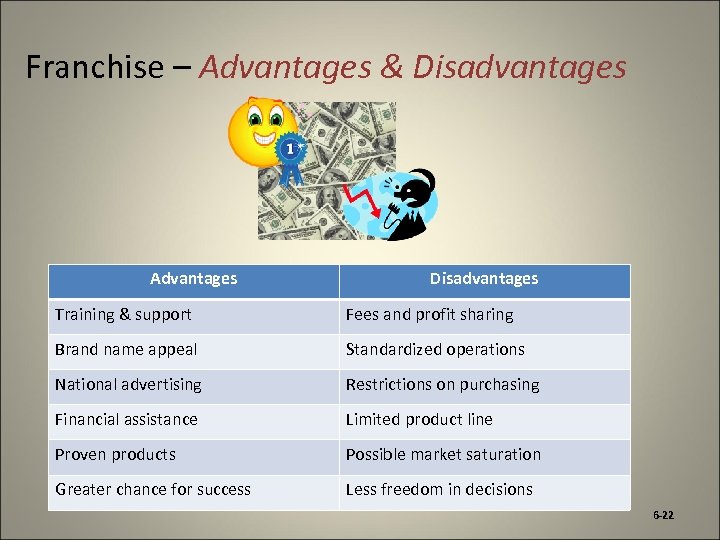
Franchise – Advantages & Disadvantages Advantages Disadvantages Training & support Fees and profit sharing Brand name appeal Standardized operations National advertising Restrictions on purchasing Financial assistance Limited product line Proven products Possible market saturation Greater chance for success Less freedom in decisions 6 -22
a1072a3150e61e0617a292ef08cf72c4.ppt