Entity Framework.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Entity Framework
Entity Framework
 ВВЕДЕНИЕ В EF
ВВЕДЕНИЕ В EF
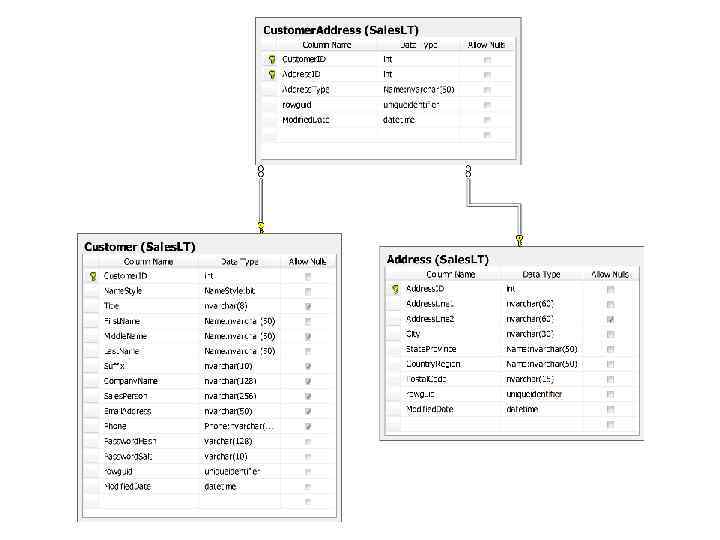 Пример базы
Пример базы
 Модель [Table("Customer", Schema = "Sales. LT")] public class Customer { public Customer() { this. Customer. Adresses = new Hash. Set
Модель [Table("Customer", Schema = "Sales. LT")] public class Customer { public Customer() { this. Customer. Adresses = new Hash. Set
 Пример использования using (var context = new Adwenture. Works. Context()) { var customers = from customer in context. Customers let cust. Address = customer. Customer. Adresses from addr in cust. Address where addr. Address. City == "Ижевск" select new { customer. First. Name, customer. Last. Name }; customers. Take(10). To. List(). For. Each(c => Console. Write. Line("{0}, {1}", c. First. Name, c. Last. Name)); var new. Address = new Address { City = "Ижевск", Address. Line 1 = "К. Маркса 246", Country. Region = "Russia", Postal. Code = "426000", State. Province = "Udmurtia" }; context. Addresses. Add(new. Address); var new. Customer = new Customer { First. Name = "Mihail", Last. Name = "Romanov", Email. Address = "mihail_romanov@epam. com", }; new. Customer. Adresses. Add(new Customer. Address { Address. Type = "Work", Address = new. Address }); context. Customers. Add(new. Customer); context. Save. Changes(); }
Пример использования using (var context = new Adwenture. Works. Context()) { var customers = from customer in context. Customers let cust. Address = customer. Customer. Adresses from addr in cust. Address where addr. Address. City == "Ижевск" select new { customer. First. Name, customer. Last. Name }; customers. Take(10). To. List(). For. Each(c => Console. Write. Line("{0}, {1}", c. First. Name, c. Last. Name)); var new. Address = new Address { City = "Ижевск", Address. Line 1 = "К. Маркса 246", Country. Region = "Russia", Postal. Code = "426000", State. Province = "Udmurtia" }; context. Addresses. Add(new. Address); var new. Customer = new Customer { First. Name = "Mihail", Last. Name = "Romanov", Email. Address = "mihail_romanov@epam. com", }; new. Customer. Adresses. Add(new Customer. Address { Address. Type = "Work", Address = new. Address }); context. Customers. Add(new. Customer); context. Save. Changes(); }
 Режимы EF • Database First • Model First • Code First
Режимы EF • Database First • Model First • Code First
 Элементы ORM • Маппинг – проекция структуры классов на структуру базы – обычно требуется: • проекция классов (иерархий) на таблицы • property на поля таблиц (в т. ч. ключи) • связи между классами на связи между таблицами • Механизм запросов • Механизм обновления + отслеживание измененных объектов
Элементы ORM • Маппинг – проекция структуры классов на структуру базы – обычно требуется: • проекция классов (иерархий) на таблицы • property на поля таблиц (в т. ч. ключи) • связи между классами на связи между таблицами • Механизм запросов • Механизм обновления + отслеживание измененных объектов
 Иерархии типов и маппинг • Table per Hierarchy (TPH) • Table per Type (TPT) • Table per Concrete class (TPC)
Иерархии типов и маппинг • Table per Hierarchy (TPH) • Table per Type (TPT) • Table per Concrete class (TPC)
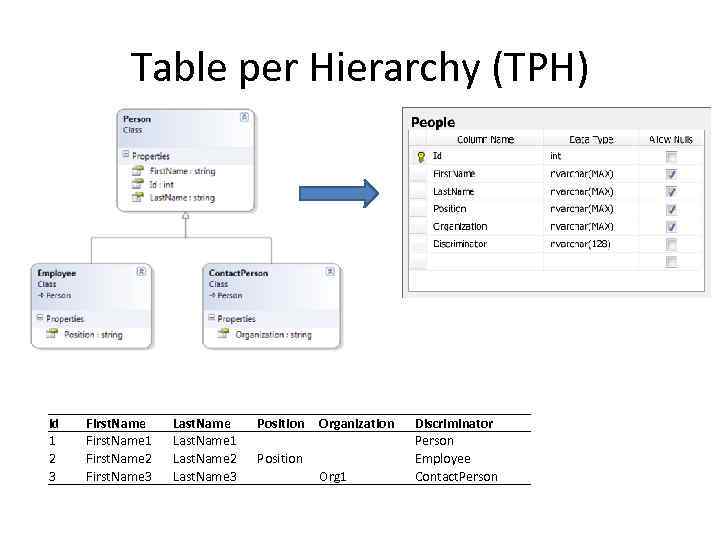 Table per Hierarchy (TPH) Id 1 2 3 First. Name 1 First. Name 2 First. Name 3 Last. Name 1 Last. Name 2 Last. Name 3 Position Organization Position Org 1 Discriminator Person Employee Contact. Person
Table per Hierarchy (TPH) Id 1 2 3 First. Name 1 First. Name 2 First. Name 3 Last. Name 1 Last. Name 2 Last. Name 3 Position Organization Position Org 1 Discriminator Person Employee Contact. Person
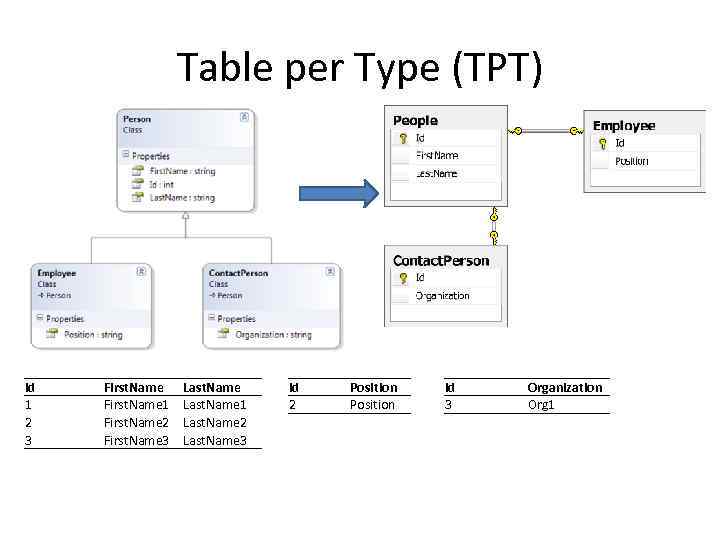 Table per Type (TPT) Id 1 2 3 First. Name 1 First. Name 2 First. Name 3 Last. Name 1 Last. Name 2 Last. Name 3 Id 2 Position Id 3 Organization Org 1
Table per Type (TPT) Id 1 2 3 First. Name 1 First. Name 2 First. Name 3 Last. Name 1 Last. Name 2 Last. Name 3 Id 2 Position Id 3 Organization Org 1
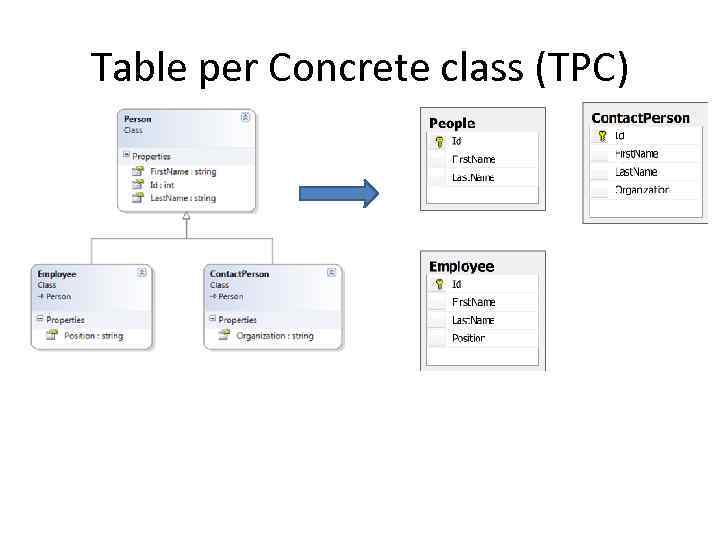 Table per Concrete class (TPC)
Table per Concrete class (TPC)
 МАППИНГ В EF
МАППИНГ В EF
 Механизмы описания маппинга в EF • Соглашения (Conventions) – например, все свойства с именем Id – первичные ключи – могут быть отключены (свои создавать пока нельзя) • Аннотации (Data Annotations) – использование атрибутов типа [Table()] • Fluent API – явное указание настроек маппинга
Механизмы описания маппинга в EF • Соглашения (Conventions) – например, все свойства с именем Id – первичные ключи – могут быть отключены (свои создавать пока нельзя) • Аннотации (Data Annotations) – использование атрибутов типа [Table()] • Fluent API – явное указание настроек маппинга
 Соглашения (Conventions) public class Adwenture. Works. Context : Db. Context { public Db. Set
Соглашения (Conventions) public class Adwenture. Works. Context : Db. Context { public Db. Set
 Соглашения (Conventions) 2 • Свойства переносятся на одноименные поля таблиц • Свойства с именем вида “ID”, “Id” или “{Имя класса}ID” являются первичным ключом – поле в базе объявлено как Identity • Поле, имеющее тип равный другой сущности или коллекции – является навигационным – поле внешнего ключа носит название {связанная сущность}Id
Соглашения (Conventions) 2 • Свойства переносятся на одноименные поля таблиц • Свойства с именем вида “ID”, “Id” или “{Имя класса}ID” являются первичным ключом – поле в базе объявлено как Identity • Поле, имеющее тип равный другой сущности или коллекции – является навигационным – поле внешнего ключа носит название {связанная сущность}Id
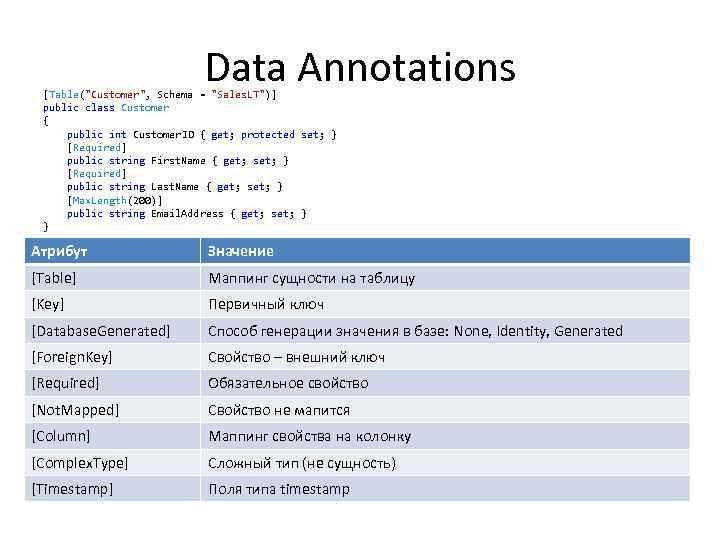 Data Annotations [Table("Customer", Schema = "Sales. LT")] public class Customer { public int Customer. ID { get; protected set; } [Required] public string First. Name { get; set; } [Required] public string Last. Name { get; set; } [Max. Length(200)] public string Email. Address { get; set; } } Атрибут Значение [Table] Маппинг сущности на таблицу [Key] Первичный ключ [Database. Generated] Способ генерации значения в базе: None, Identity, Generated [Foreign. Key] Свойство – внешний ключ [Required] Обязательное свойство [Not. Mapped] Свойство не мапится [Column] Маппинг свойства на колонку [Complex. Type] Сложный тип (не сущность) [Timestamp] Поля типа timestamp
Data Annotations [Table("Customer", Schema = "Sales. LT")] public class Customer { public int Customer. ID { get; protected set; } [Required] public string First. Name { get; set; } [Required] public string Last. Name { get; set; } [Max. Length(200)] public string Email. Address { get; set; } } Атрибут Значение [Table] Маппинг сущности на таблицу [Key] Первичный ключ [Database. Generated] Способ генерации значения в базе: None, Identity, Generated [Foreign. Key] Свойство – внешний ключ [Required] Обязательное свойство [Not. Mapped] Свойство не мапится [Column] Маппинг свойства на колонку [Complex. Type] Сложный тип (не сущность) [Timestamp] Поля типа timestamp
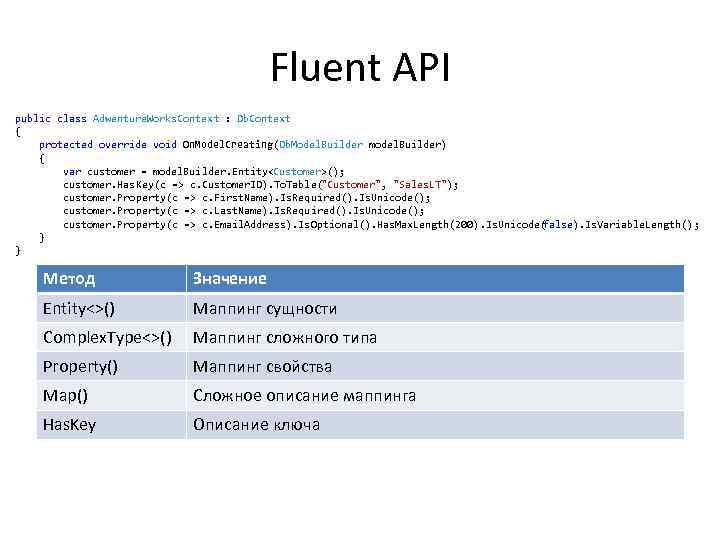 Fluent API public class Adwenture. Works. Context : Db. Context { protected override void On. Model. Creating(Db. Model. Builder model. Builder) { var customer = model. Builder. Entity
Fluent API public class Adwenture. Works. Context : Db. Context { protected override void On. Model. Creating(Db. Model. Builder model. Builder) { var customer = model. Builder. Entity
 ПОЛУЧЕНИЕ ОБЪЕКТОВ
ПОЛУЧЕНИЕ ОБЪЕКТОВ
 Запросы var customer. Id 1 = context. Customers. Find(1); var customers = from customer in context. Customers let cust. Address = customer. Customer. Adresses from addr in cust. Address where addr. Address. City == "Ижевск" select new { customer. First. Name, customer. Last. Name }; var customers 1 = context. Set
Запросы var customer. Id 1 = context. Customers. Find(1); var customers = from customer in context. Customers let cust. Address = customer. Customer. Adresses from addr in cust. Address where addr. Address. City == "Ижевск" select new { customer. First. Name, customer. Last. Name }; var customers 1 = context. Set
 Загрузка связанных сущностей • По умолчанию загружаются только сами сущности, но не связанные! • Стратегии загрузки в EF – Ленивая – Жадная – Явная (по требованию)
Загрузка связанных сущностей • По умолчанию загружаются только сами сущности, но не связанные! • Стратегии загрузки в EF – Ленивая – Жадная – Явная (по требованию)
 Ленивая загрузка (Lazily Loading) var customer. Id 1 = context. Customers. Find(1); var adresses = customer. Id 1. Customer. Adresses; • Требования – класс должен быть объявлен как • public • не sealed и не abstract • с публичным или защищенным конструктором – навигационное свойство должно быть • virtual • иметь public getter
Ленивая загрузка (Lazily Loading) var customer. Id 1 = context. Customers. Find(1); var adresses = customer. Id 1. Customer. Adresses; • Требования – класс должен быть объявлен как • public • не sealed и не abstract • с публичным или защищенным конструктором – навигационное свойство должно быть • virtual • иметь public getter
 Жадная загрузка (Eagerly Loading) var customers 1 = context. Customers. Include(c => c. Customer. Adresses); var customers 2 = context. Customers. Include(c => c. Customer. Adresses. Select(ca => ca. Address)); var customers 3 = context. Customers. Include("Customer. Adresses"); • Внутри Include нельзя использовать фильтрацию!!!
Жадная загрузка (Eagerly Loading) var customers 1 = context. Customers. Include(c => c. Customer. Adresses); var customers 2 = context. Customers. Include(c => c. Customer. Adresses. Select(ca => ca. Address)); var customers 3 = context. Customers. Include("Customer. Adresses"); • Внутри Include нельзя использовать фильтрацию!!!
 Явная загрузка (Explicitly Loading) var customer. Id 1 = context. Customers. Find(1); context. Entry(customer. Id 1). Collection(c => c. Customer. Adresses). Load(); context. Entry(customer. Id 1). Collection(c => c. Customer. Adresses). Query(). Where(ca => ca. Address. City == "Ижевск"). Load(); var cust. Address = context. Set
Явная загрузка (Explicitly Loading) var customer. Id 1 = context. Customers. Find(1); context. Entry(customer. Id 1). Collection(c => c. Customer. Adresses). Load(); context. Entry(customer. Id 1). Collection(c => c. Customer. Adresses). Query(). Where(ca => ca. Address. City == "Ижевск"). Load(); var cust. Address = context. Set
 Прямое выполнение SQL-команд var customers = context. Customers. Sql. Query("select * from Sales. LT. Customer where Customer. Id = @Id", new Sql. Parameter("Id", 1)). To. List(); context. Database. Execute. Sql. Command( "update Sales. LT. Customer set Phone = '+79096545' where Customer. Id = 1"); • Можно вызывать хранимые процедуры
Прямое выполнение SQL-команд var customers = context. Customers. Sql. Query("select * from Sales. LT. Customer where Customer. Id = @Id", new Sql. Parameter("Id", 1)). To. List(); context. Database. Execute. Sql. Command( "update Sales. LT. Customer set Phone = '+79096545' where Customer. Id = 1"); • Можно вызывать хранимые процедуры
 ИЗМЕНЕНИЕ ОБЪЕКТОВ
ИЗМЕНЕНИЕ ОБЪЕКТОВ
 Операции изменения using (var context = new Adwenture. Works. Context()) { var new. Address = new Address { City = "Ижевск", Address. Line 1 = "К. Маркса 246", Country. Region = "Russia", Postal. Code = "426000", State. Province = "Udmurtia" }; context. Addresses. Add(new. Address); var customer = context. Customers. Find(1); customer. First. Name = "Alister"; customer. Last. Name = "Aben"; customer. Customer. Adresses. Clear(); customer. Customer. Adresses. Add( new Customer. Address { Address = new. Address, Address. Type = "Work" }); context. Addresses. Remove(context. Addresses. Find(1)); context. Save. Changes(); }
Операции изменения using (var context = new Adwenture. Works. Context()) { var new. Address = new Address { City = "Ижевск", Address. Line 1 = "К. Маркса 246", Country. Region = "Russia", Postal. Code = "426000", State. Province = "Udmurtia" }; context. Addresses. Add(new. Address); var customer = context. Customers. Find(1); customer. First. Name = "Alister"; customer. Last. Name = "Aben"; customer. Customer. Adresses. Clear(); customer. Customer. Adresses. Add( new Customer. Address { Address = new. Address, Address. Type = "Work" }); context. Addresses. Remove(context. Addresses. Find(1)); context. Save. Changes(); }
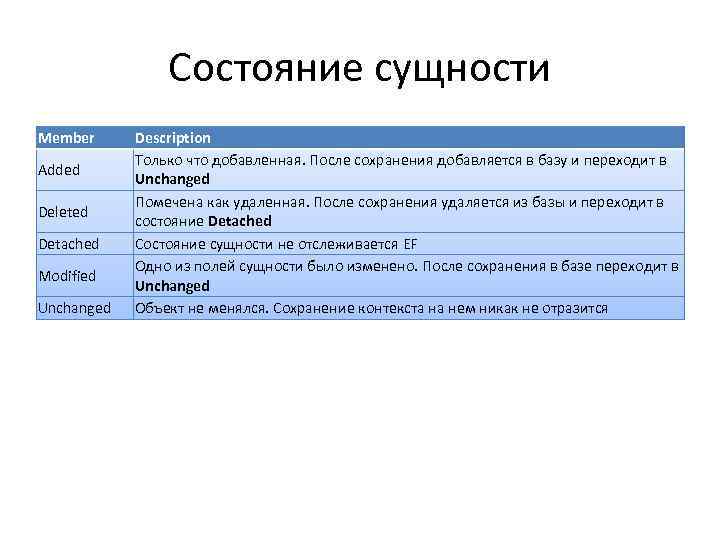 Состояние сущности Member Added Deleted Detached Modified Unchanged Description Только что добавленная. После сохранения добавляется в базу и переходит в Unchanged Помечена как удаленная. После сохранения удаляется из базы и переходит в состояние Detached Состояние сущности не отслеживается EF Одно из полей сущности было изменено. После сохранения в базе переходит в Unchanged Объект не менялся. Сохранение контекста на нем никак не отразится
Состояние сущности Member Added Deleted Detached Modified Unchanged Description Только что добавленная. После сохранения добавляется в базу и переходит в Unchanged Помечена как удаленная. После сохранения удаляется из базы и переходит в состояние Detached Состояние сущности не отслеживается EF Одно из полей сущности было изменено. После сохранения в базе переходит в Unchanged Объект не менялся. Сохранение контекста на нем никак не отразится
 Change Tracking API • 2 API: – Object. Context API (класс System. Data. Objects. Object. State. Manager) – Db. Context API (класс System. Data. Entity. Infrastructure. Db. Change. Tracker) • обертка над Object. Context • менее функционален • Внутреннее представление сущности: – System. Data. Objects. Object. State. Entry – System. Data. Entity. Infrastructure. Db. Entity. Entry
Change Tracking API • 2 API: – Object. Context API (класс System. Data. Objects. Object. State. Manager) – Db. Context API (класс System. Data. Entity. Infrastructure. Db. Change. Tracker) • обертка над Object. Context • менее функционален • Внутреннее представление сущности: – System. Data. Objects. Object. State. Entry – System. Data. Entity. Infrastructure. Db. Entity. Entry
 Отслеживание изменений (для Db. Context API) • Snapshot Mechanism – метод Detect. Changes – вызывается в методах • Add, Attach, Find, Local, Remove в Db. Set • Get. Validation. Errors, Entry, Save. Changes в Db. Context • Entries в Db. Change. Tracker – исходные значения через Original. Values в Db. Entity. Entry – для улучшения производительности рекомендуется отключать при массовых изменениях try { context. Configuration. Auto. Detect. Changes. Enabled = false; foreach (var c in new. Customers) { context. Customers. Add(c); } } finally { context. Configuration. Auto. Detect. Changes. Enabled = true; }
Отслеживание изменений (для Db. Context API) • Snapshot Mechanism – метод Detect. Changes – вызывается в методах • Add, Attach, Find, Local, Remove в Db. Set • Get. Validation. Errors, Entry, Save. Changes в Db. Context • Entries в Db. Change. Tracker – исходные значения через Original. Values в Db. Entity. Entry – для улучшения производительности рекомендуется отключать при массовых изменениях try { context. Configuration. Auto. Detect. Changes. Enabled = false; foreach (var c in new. Customers) { context. Customers. Add(c); } } finally { context. Configuration. Auto. Detect. Changes. Enabled = true; }
 Отслеживание изменений (для Db. Context API) • Change-tracking proxy objects – для каждого загружаемого объекта в реальности создается Proxy-объект – требования к объектам: • класс должен быть объявлен как – public – не sealed и не abstract – с публичным или защищенным конструктором • каждое свойство должно – быть public и virtual – иметь getter и setter (оба публичные) – вместо new следует использовать System. Data. Entity. Db. Set. Create метод
Отслеживание изменений (для Db. Context API) • Change-tracking proxy objects – для каждого загружаемого объекта в реальности создается Proxy-объект – требования к объектам: • класс должен быть объявлен как – public – не sealed и не abstract – с публичным или защищенным конструктором • каждое свойство должно – быть public и virtual – иметь getter и setter (оба публичные) – вместо new следует использовать System. Data. Entity. Db. Set. Create метод
 НАСТРОЙКИ
НАСТРОЙКИ
 Настройки в app. config • Строки подключения – по умолчанию имя строки подключения = имя класса контекста
Настройки в app. config • Строки подключения – по умолчанию имя строки подключения = имя класса контекста
 ПРОЧИЕ ВОЗМОЖНОСТИ
ПРОЧИЕ ВОЗМОЖНОСТИ
 Инициализация базы • Несколько стратегий – Create. Database. If. Not. Exists – Drop. Create. Database. Always – Drop. Create. Database. If. Model. Changes – Migrate. Database. To. Latest. Version • Могут переопределяться Database. Set. Initializer(new Create. Database. If. Not. Exists
Инициализация базы • Несколько стратегий – Create. Database. If. Not. Exists – Drop. Create. Database. Always – Drop. Create. Database. If. Model. Changes – Migrate. Database. To. Latest. Version • Могут переопределяться Database. Set. Initializer(new Create. Database. If. Not. Exists
 Миграция базы • Code First Migrations public class Migration : Db. Migration { public override void Up() { this. Add. Column("Customer", "Address. Line 2", c => c. String()); } public override void Down() { this. Drop. Column("Customer", "Address. Line 2"); } }
Миграция базы • Code First Migrations public class Migration : Db. Migration { public override void Up() { this. Add. Column("Customer", "Address. Line 2", c => c. String()); } public override void Down() { this. Drop. Column("Customer", "Address. Line 2"); } }


