ac13a82d3b3bc7381682f8ddcdb71703.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 Enterprise Resource Planning & SAP University Alliances Version 2. 01 Sumantra Sarkar, MBA, MS, PMP, CISA Robinson College of Business 22 nd Oct, 2013 ssarkar@cis. gsu. edu
Enterprise Resource Planning & SAP University Alliances Version 2. 01 Sumantra Sarkar, MBA, MS, PMP, CISA Robinson College of Business 22 nd Oct, 2013 ssarkar@cis. gsu. edu
 background… Sumantra Sarkar 20+ years of service ; senior management positions in Global Corporations with significant experience in: • • • Program Management ERP Implementations & Software development IT Operations and Delivery - ITIL Networking IT Security and Compliance • MS in IS from Georgia State University • MBA in Operations Research • BE in Electronics & Telecommunication • Certified Project Management Professional (PMP) • Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) • ISO 20000 certified Auditor • recent research focus in Health Information technology.
background… Sumantra Sarkar 20+ years of service ; senior management positions in Global Corporations with significant experience in: • • • Program Management ERP Implementations & Software development IT Operations and Delivery - ITIL Networking IT Security and Compliance • MS in IS from Georgia State University • MBA in Operations Research • BE in Electronics & Telecommunication • Certified Project Management Professional (PMP) • Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) • ISO 20000 certified Auditor • recent research focus in Health Information technology.
 Agenda • • Business Challenges Planning MRP – MRP II – ERP - SCM Sales Order-to-Cash – Revenue Cycle Functional Modules – Generic SAP Vendor Landscape
Agenda • • Business Challenges Planning MRP – MRP II – ERP - SCM Sales Order-to-Cash – Revenue Cycle Functional Modules – Generic SAP Vendor Landscape
 Challenges – Senior Managment • Total Accounts Receivable >180 days old? • Today’s Sales Orders & Collections in North America? • Dip in Sales orders from my biggest customer? • Quantity Finished Goods do I forecast for the month’s production to achieve Sales numbers for this quarter? • Is there sufficient Raw materials in stock for production? • • How much did we Purchase this year from “X” globally? Holding cost - “Inventory Turnaround Time” for class A items? Can my Cash-On-Hand last 15 days w/out overdrafting? How much is today’s “Production Batch cost”?
Challenges – Senior Managment • Total Accounts Receivable >180 days old? • Today’s Sales Orders & Collections in North America? • Dip in Sales orders from my biggest customer? • Quantity Finished Goods do I forecast for the month’s production to achieve Sales numbers for this quarter? • Is there sufficient Raw materials in stock for production? • • How much did we Purchase this year from “X” globally? Holding cost - “Inventory Turnaround Time” for class A items? Can my Cash-On-Hand last 15 days w/out overdrafting? How much is today’s “Production Batch cost”?
 Challenges – Senior Managment • Can my Business Processes and Systems enable me with answers immediately ? • Can I see inventory and cash across all of my planning horizon? • Do I have sufficient resources?
Challenges – Senior Managment • Can my Business Processes and Systems enable me with answers immediately ? • Can I see inventory and cash across all of my planning horizon? • Do I have sufficient resources?
 What are a firm’s strategic resources? • From Classical Economics (Samuelson & Nordhaus, ’ 04) • Land • Labor • Capital • Material • Money • Machinery • Characteristics • Limited availability • Potential for depletion / consumption • Utility • Resource-based view - firms possess resources, a subset of which enables them to achieve competitive advantage, and a further subset which leads to superior long-term performance (Barney ’ 91; Grant ’ 91; Penrose ’ 59; Wernerfelt ’ 84). 6
What are a firm’s strategic resources? • From Classical Economics (Samuelson & Nordhaus, ’ 04) • Land • Labor • Capital • Material • Money • Machinery • Characteristics • Limited availability • Potential for depletion / consumption • Utility • Resource-based view - firms possess resources, a subset of which enables them to achieve competitive advantage, and a further subset which leads to superior long-term performance (Barney ’ 91; Grant ’ 91; Penrose ’ 59; Wernerfelt ’ 84). 6
 Resource Planning tool • Plan for optimized use of resources • Possible only if there transparent flow of information between all functions inside the boundaries of the organization (e. g. Production should know how much to manufacture and when? ) • Should enable the enterprise to operate as an integrated, enterprise-wide, process oriented, information-driven (not guess work), and real-time enterprise • To achieve the above…. . let’s look at the components of planning…. . what are they? 7
Resource Planning tool • Plan for optimized use of resources • Possible only if there transparent flow of information between all functions inside the boundaries of the organization (e. g. Production should know how much to manufacture and when? ) • Should enable the enterprise to operate as an integrated, enterprise-wide, process oriented, information-driven (not guess work), and real-time enterprise • To achieve the above…. . let’s look at the components of planning…. . what are they? 7
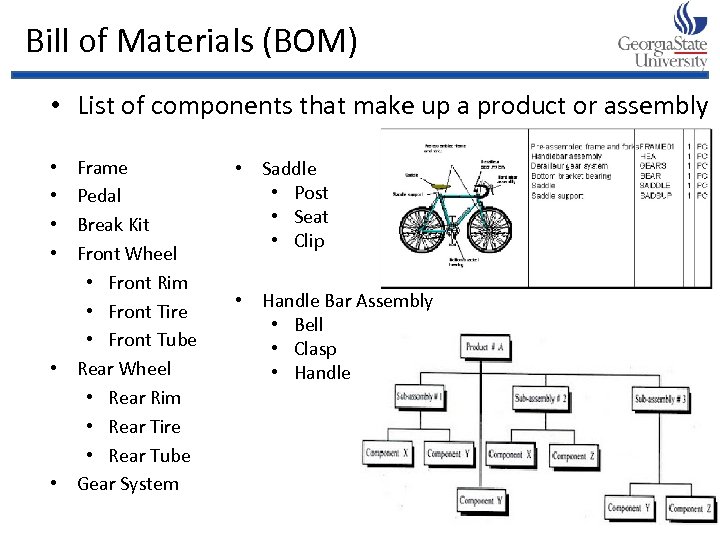 Bill of Materials (BOM) • List of components that make up a product or assembly Frame Pedal Break Kit Front Wheel • Front Rim • Front Tire • Front Tube • Rear Wheel • Rear Rim • Rear Tire • Rear Tube • Gear System • • • Saddle • Post • Seat • Clip • Handle Bar Assembly • Bell • Clasp • Handle
Bill of Materials (BOM) • List of components that make up a product or assembly Frame Pedal Break Kit Front Wheel • Front Rim • Front Tire • Front Tube • Rear Wheel • Rear Rim • Rear Tire • Rear Tube • Gear System • • • Saddle • Post • Seat • Clip • Handle Bar Assembly • Bell • Clasp • Handle
 Routings • A routing includes • the relevant operations in the order they occur • the work centers at which these operations are to be executed • descriptions of the operations to be done in the work centers • time required to complete the operation in the respective work centers
Routings • A routing includes • the relevant operations in the order they occur • the work centers at which these operations are to be executed • descriptions of the operations to be done in the work centers • time required to complete the operation in the respective work centers
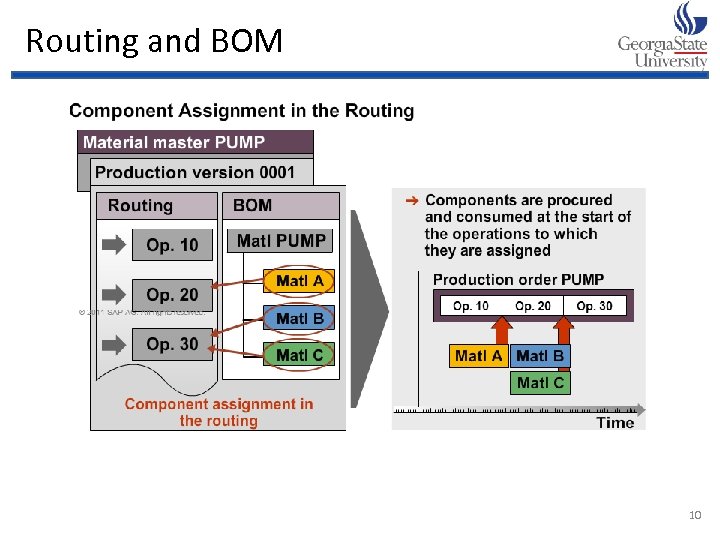 Routing and BOM 10
Routing and BOM 10
 MRP • Material Requirement Planning – (Orlicky ’ 69) • Production planning and Inventory control system used in the manufacturing process • Answers – What items are required? How many are required? When are they required? • 3 objectives • Ensure availability of • raw materials(RM) for production in time • finished goods (FG) for customers when in demand • Maintain the lowest possible RM and FG (why? ? ) • Plan purchasing, delivery & manufacturing schedules 11
MRP • Material Requirement Planning – (Orlicky ’ 69) • Production planning and Inventory control system used in the manufacturing process • Answers – What items are required? How many are required? When are they required? • 3 objectives • Ensure availability of • raw materials(RM) for production in time • finished goods (FG) for customers when in demand • Maintain the lowest possible RM and FG (why? ? ) • Plan purchasing, delivery & manufacturing schedules 11
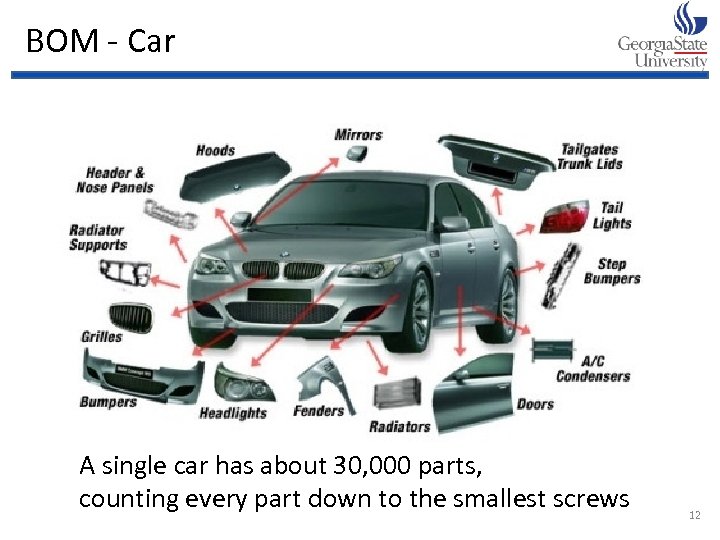 BOM - Car A single car has about 30, 000 parts, counting every part down to the smallest screws 12
BOM - Car A single car has about 30, 000 parts, counting every part down to the smallest screws 12
 MRP – MRP II - ERP 13
MRP – MRP II - ERP 13
 MRP – MRP II - ERP DEC - PDP-1 in 1960, world's first small, interactive computer. Sold at $120, 000, 14
MRP – MRP II - ERP DEC - PDP-1 in 1960, world's first small, interactive computer. Sold at $120, 000, 14
 MRP – MRP II - ERP Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC – PDP 12) 12 bit machine @ $ 27, 900 15
MRP – MRP II - ERP Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC – PDP 12) 12 bit machine @ $ 27, 900 15
 MRP – MRP II - ERP "IBM PC, " in ’ 81 - model 5150. 16
MRP – MRP II - ERP "IBM PC, " in ’ 81 - model 5150. 16
 What is ERP…then…. ? • ………framework for organizing, defining, and standardizing the business processes necessary to effectively plan and control an organization so the organization can use its internal knowledge to seek external advantage [APICS Dictionary (American Production/Inventory Control Society)– 11 th Edition] • “underlying integrated database that stores master and transactional data in a consistent way and with controlled redundancy” (Klaus, Rosemann, & Gable, 2000, p. 143). 17
What is ERP…then…. ? • ………framework for organizing, defining, and standardizing the business processes necessary to effectively plan and control an organization so the organization can use its internal knowledge to seek external advantage [APICS Dictionary (American Production/Inventory Control Society)– 11 th Edition] • “underlying integrated database that stores master and transactional data in a consistent way and with controlled redundancy” (Klaus, Rosemann, & Gable, 2000, p. 143). 17
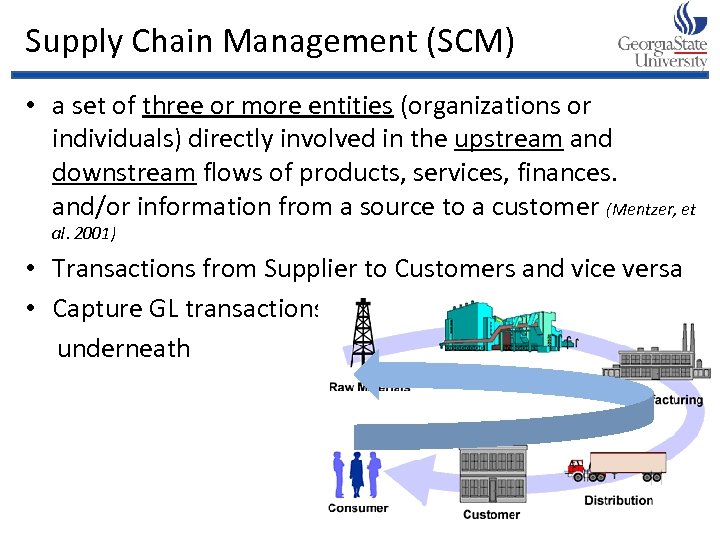 Supply Chain Management (SCM) • a set of three or more entities (organizations or individuals) directly involved in the upstream and downstream flows of products, services, finances. and/or information from a source to a customer (Mentzer, et al. 2001) • Transactions from Supplier to Customers and vice versa • Capture GL transactions underneath 18
Supply Chain Management (SCM) • a set of three or more entities (organizations or individuals) directly involved in the upstream and downstream flows of products, services, finances. and/or information from a source to a customer (Mentzer, et al. 2001) • Transactions from Supplier to Customers and vice versa • Capture GL transactions underneath 18
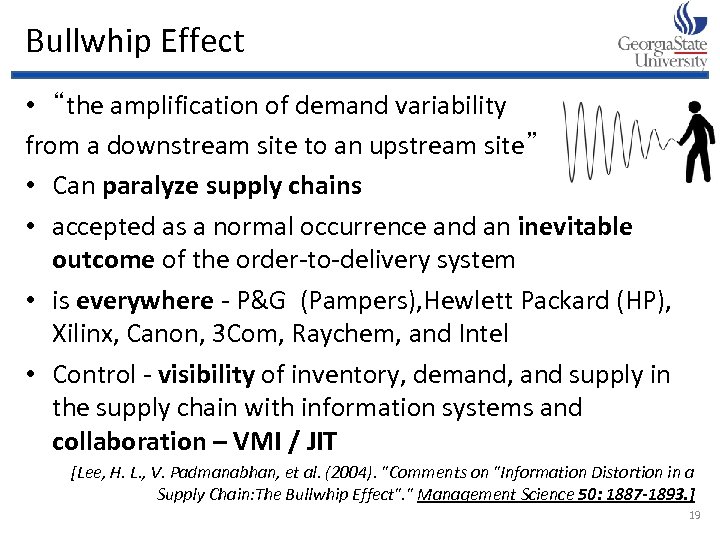 Bullwhip Effect • “the amplification of demand variability from a downstream site to an upstream site” • Can paralyze supply chains • accepted as a normal occurrence and an inevitable outcome of the order-to-delivery system • is everywhere - P&G (Pampers), Hewlett Packard (HP), Xilinx, Canon, 3 Com, Raychem, and Intel • Control - visibility of inventory, demand, and supply in the supply chain with information systems and collaboration – VMI / JIT [Lee, H. L. , V. Padmanabhan, et al. (2004). "Comments on "Information Distortion in a Supply Chain: The Bullwhip Effect". " Management Science 50: 1887 -1893. ] 19
Bullwhip Effect • “the amplification of demand variability from a downstream site to an upstream site” • Can paralyze supply chains • accepted as a normal occurrence and an inevitable outcome of the order-to-delivery system • is everywhere - P&G (Pampers), Hewlett Packard (HP), Xilinx, Canon, 3 Com, Raychem, and Intel • Control - visibility of inventory, demand, and supply in the supply chain with information systems and collaboration – VMI / JIT [Lee, H. L. , V. Padmanabhan, et al. (2004). "Comments on "Information Distortion in a Supply Chain: The Bullwhip Effect". " Management Science 50: 1887 -1893. ] 19
 So is MRP Relevant today? http: //www. orlickysmrp. com/mrp. html 20
So is MRP Relevant today? http: //www. orlickysmrp. com/mrp. html 20
 Now…let’s look at something else…. • Process view of the firm…. …… • an ability to see beyond the tasks and hierarchy and to visualize the processes in one’s organization. [Bassellier, Reich & Benbasat JMIS’ 01] • So what are the processes in an organization? ? • Only line managers are close enough to their business segments to see the most effective ways to utilize this resource. Only they possess the clout to embed IT into their strategies and to commit the necessary financial resources. Unless IT is included in line managers’ strategy and tactics, and unless line managers can effectively understand implement a process view of the world, the best IT organizations are almost powerless [Rockart, J. F. , M. J. Earl, et al. (1996). "Eight Imperatives for the New IT Organization. " Sloan Management Review 38(1): 43 -55. ] 21
Now…let’s look at something else…. • Process view of the firm…. …… • an ability to see beyond the tasks and hierarchy and to visualize the processes in one’s organization. [Bassellier, Reich & Benbasat JMIS’ 01] • So what are the processes in an organization? ? • Only line managers are close enough to their business segments to see the most effective ways to utilize this resource. Only they possess the clout to embed IT into their strategies and to commit the necessary financial resources. Unless IT is included in line managers’ strategy and tactics, and unless line managers can effectively understand implement a process view of the world, the best IT organizations are almost powerless [Rockart, J. F. , M. J. Earl, et al. (1996). "Eight Imperatives for the New IT Organization. " Sloan Management Review 38(1): 43 -55. ] 21
 SALES TO CASH OR REVENUE CYCLE 22
SALES TO CASH OR REVENUE CYCLE 22
 Functionality • • Sales Shipping and Transportation Billing Credit Management Sales Support Foreign Trade Integrates internal and external information across an entire organization - finance/accounting, manufacturing, planning, sales and service, etc.
Functionality • • Sales Shipping and Transportation Billing Credit Management Sales Support Foreign Trade Integrates internal and external information across an entire organization - finance/accounting, manufacturing, planning, sales and service, etc.
 Sales Order Process Pre-sales Activities No financial impact (FI) Sales Order Entry Check Availability Pick Amount owed by customer is Materials Management (MM) Amount owed is and Financial Accounting (FI) Materials assigned and transferred to received and Account Receipt of Customer account receivable Receivables is reduced via automatic account Customer Payment assignment Bank XXXX Pack A/R XXXX Invoice Materials Customer Post Goods A/R XXXX Issue Sales XXXX COGS XXXX Inventory-FG XXXX *Good Sent
Sales Order Process Pre-sales Activities No financial impact (FI) Sales Order Entry Check Availability Pick Amount owed by customer is Materials Management (MM) Amount owed is and Financial Accounting (FI) Materials assigned and transferred to received and Account Receipt of Customer account receivable Receivables is reduced via automatic account Customer Payment assignment Bank XXXX Pack A/R XXXX Invoice Materials Customer Post Goods A/R XXXX Issue Sales XXXX COGS XXXX Inventory-FG XXXX *Good Sent
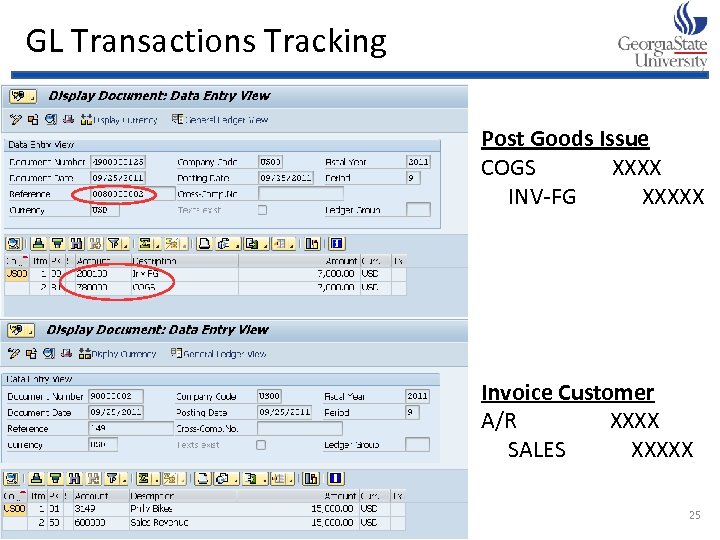 GL Transactions Tracking Post Goods Issue COGS XXXX INV-FG XXXXX Invoice Customer A/R XXXX SALES XXXXX 25
GL Transactions Tracking Post Goods Issue COGS XXXX INV-FG XXXXX Invoice Customer A/R XXXX SALES XXXXX 25
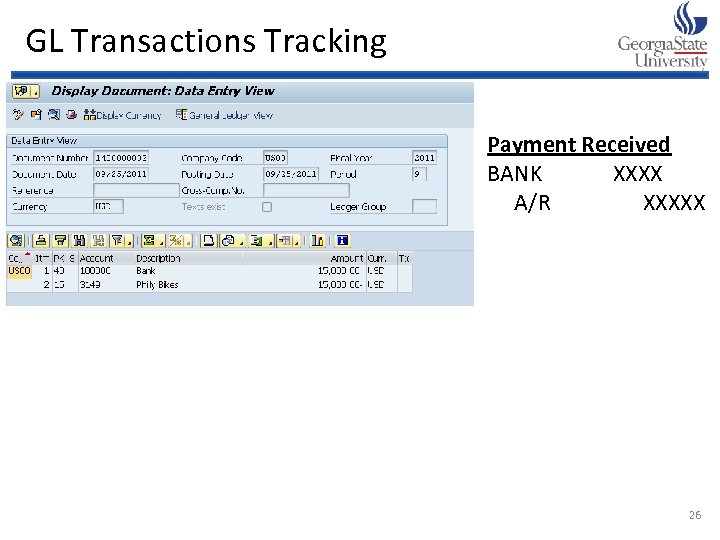 GL Transactions Tracking Payment Received BANK XXXX A/R XXXXX 26
GL Transactions Tracking Payment Received BANK XXXX A/R XXXXX 26
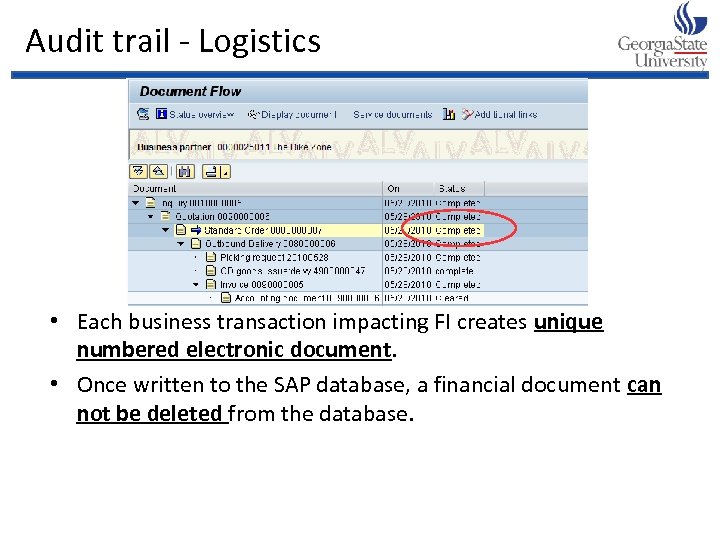 Audit trail - Logistics • Each business transaction impacting FI creates unique numbered electronic document. • Once written to the SAP database, a financial document can not be deleted from the database.
Audit trail - Logistics • Each business transaction impacting FI creates unique numbered electronic document. • Once written to the SAP database, a financial document can not be deleted from the database.
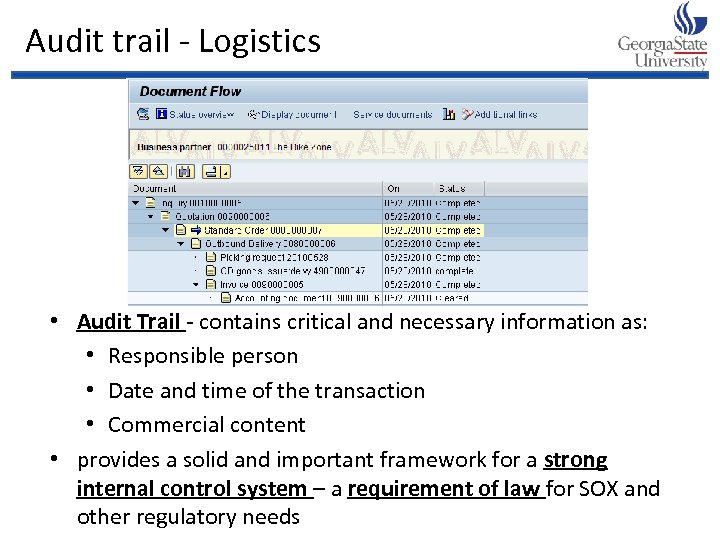 Audit trail - Logistics • Audit Trail - contains critical and necessary information as: • Responsible person • Date and time of the transaction • Commercial content • provides a solid and important framework for a strong internal control system – a requirement of law for SOX and other regulatory needs
Audit trail - Logistics • Audit Trail - contains critical and necessary information as: • Responsible person • Date and time of the transaction • Commercial content • provides a solid and important framework for a strong internal control system – a requirement of law for SOX and other regulatory needs
 Audit trail – GL Transactions Tracking S_ALR_87012291 Line item journal from Accounting General Ledger Information system Document Line item journal. 29
Audit trail – GL Transactions Tracking S_ALR_87012291 Line item journal from Accounting General Ledger Information system Document Line item journal. 29
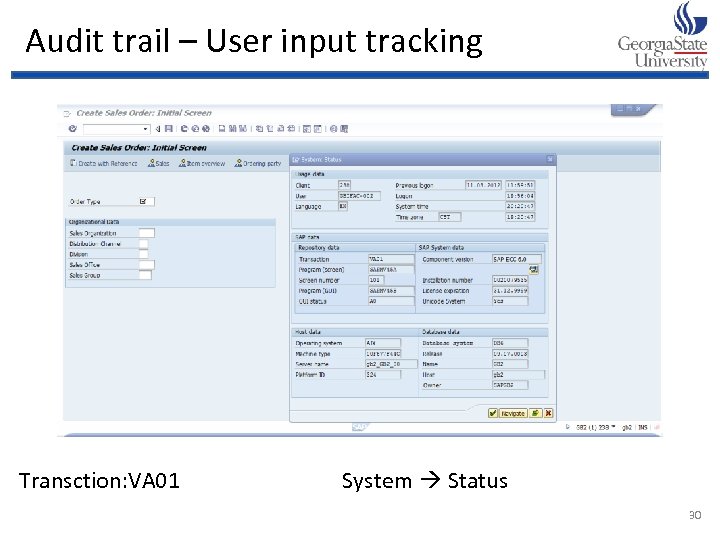 Audit trail – User input tracking Transction: VA 01 System Status 30
Audit trail – User input tracking Transction: VA 01 System Status 30
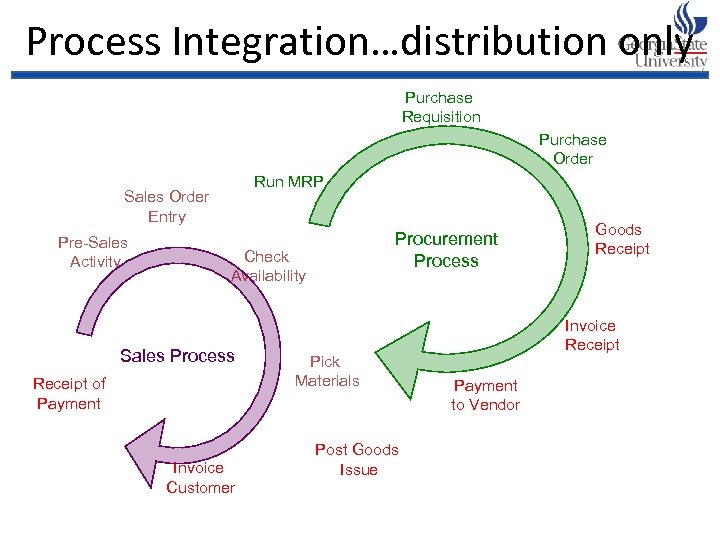 Process Integration…distribution only Purchase Requisition Purchase Order Run MRP Sales Order Entry Pre-Sales Activity Procurement Process Check Availability Sales Process Receipt of Payment Invoice Customer Pick Materials Post Goods Issue Goods Receipt Invoice Receipt Payment to Vendor
Process Integration…distribution only Purchase Requisition Purchase Order Run MRP Sales Order Entry Pre-Sales Activity Procurement Process Check Availability Sales Process Receipt of Payment Invoice Customer Pick Materials Post Goods Issue Goods Receipt Invoice Receipt Payment to Vendor
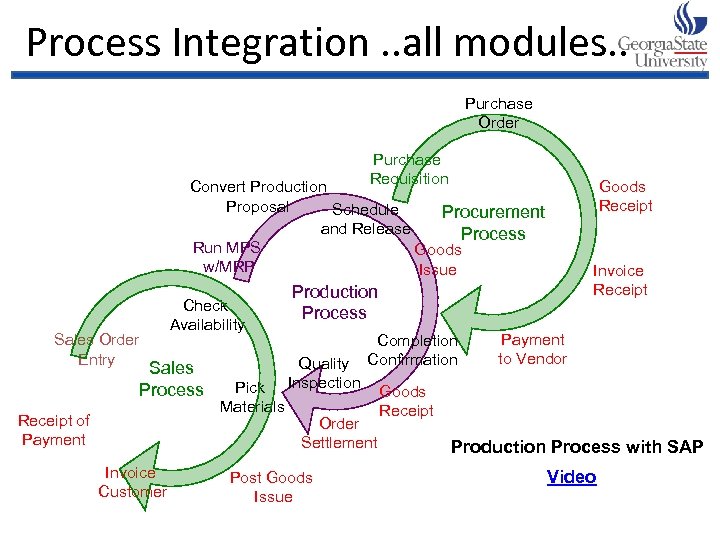 Process Integration. . all modules. . Purchase Order Purchase Requisition Goods Receipt Convert Production Proposal Schedule Procurement and Release Process Run MPS Goods w/MRP Issue Sales Order Entry Check Availability Sales Process Receipt of Payment Invoice Customer Pick Materials Invoice Receipt Production Process Quality Inspection Completion Confirmation Order Settlement Post Goods Issue Payment to Vendor Goods Receipt Production Process with SAP Video
Process Integration. . all modules. . Purchase Order Purchase Requisition Goods Receipt Convert Production Proposal Schedule Procurement and Release Process Run MPS Goods w/MRP Issue Sales Order Entry Check Availability Sales Process Receipt of Payment Invoice Customer Pick Materials Invoice Receipt Production Process Quality Inspection Completion Confirmation Order Settlement Post Goods Issue Payment to Vendor Goods Receipt Production Process with SAP Video
 So what did we cover……. . ü • Resource Planning……. ü • Process Flow……… ü • Financial Integration……
So what did we cover……. . ü • Resource Planning……. ü • Process Flow……… ü • Financial Integration……
 Challenges – Senior Managment • ü • ü • ü ü How much Accounts Receivable is more than 180 days? Today’s Sales Orders & Collections in North America? Dip in Sales orders from my biggest customer? How much Finished Goods do I forecast production for this month to achieve Sales numbers for this quarter? Is there sufficient Raw materials in stock for production? How much did we Purchase this year from “X” globally? Holding cost - “Inventory Turnaround Time” for class A items? Can my Cash-On-Hand last me for 15 days w/out overdraft? How much is today’s “Production Batch cost”?
Challenges – Senior Managment • ü • ü • ü ü How much Accounts Receivable is more than 180 days? Today’s Sales Orders & Collections in North America? Dip in Sales orders from my biggest customer? How much Finished Goods do I forecast production for this month to achieve Sales numbers for this quarter? Is there sufficient Raw materials in stock for production? How much did we Purchase this year from “X” globally? Holding cost - “Inventory Turnaround Time” for class A items? Can my Cash-On-Hand last me for 15 days w/out overdraft? How much is today’s “Production Batch cost”?
 Questions? Thank you Sumantra Sarkar ssarkar@cis. gsu. edu
Questions? Thank you Sumantra Sarkar ssarkar@cis. gsu. edu
 SAP 36
SAP 36
 Introduction to SAP ERP
Introduction to SAP ERP
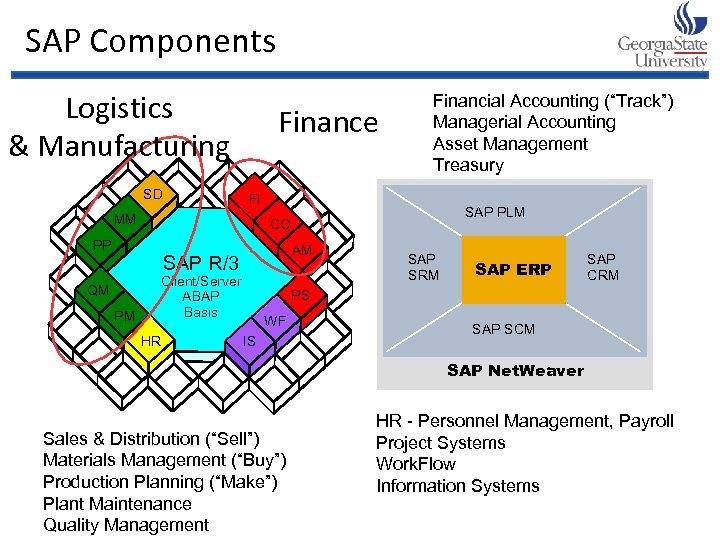 SAP Components Logistics & Manufacturing SD Finance FI MM AM SAP R/3 PM SAP PLM CO PP QM Financial Accounting (“Track”) Managerial Accounting Asset Management Treasury Client/Server ABAP Basis HR SAP SRM SAP ERP SAP CRM PS WF IS SAP SCM SAP Net. Weaver Sales & Distribution (“Sell”) Materials Management (“Buy”) Production Planning (“Make”) Plant Maintenance Quality Management HR - Personnel Management, Payroll Project Systems Work. Flow Information Systems
SAP Components Logistics & Manufacturing SD Finance FI MM AM SAP R/3 PM SAP PLM CO PP QM Financial Accounting (“Track”) Managerial Accounting Asset Management Treasury Client/Server ABAP Basis HR SAP SRM SAP ERP SAP CRM PS WF IS SAP SCM SAP Net. Weaver Sales & Distribution (“Sell”) Materials Management (“Buy”) Production Planning (“Make”) Plant Maintenance Quality Management HR - Personnel Management, Payroll Project Systems Work. Flow Information Systems
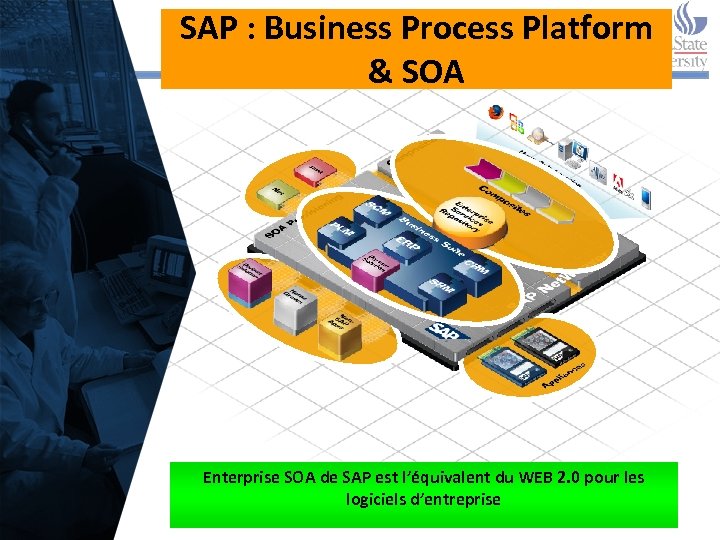 SAP : Business Process Platform & SOA Enterprise SOA de SAP est l’équivalent du WEB 2. 0 pour les logiciels d’entreprise
SAP : Business Process Platform & SOA Enterprise SOA de SAP est l’équivalent du WEB 2. 0 pour les logiciels d’entreprise
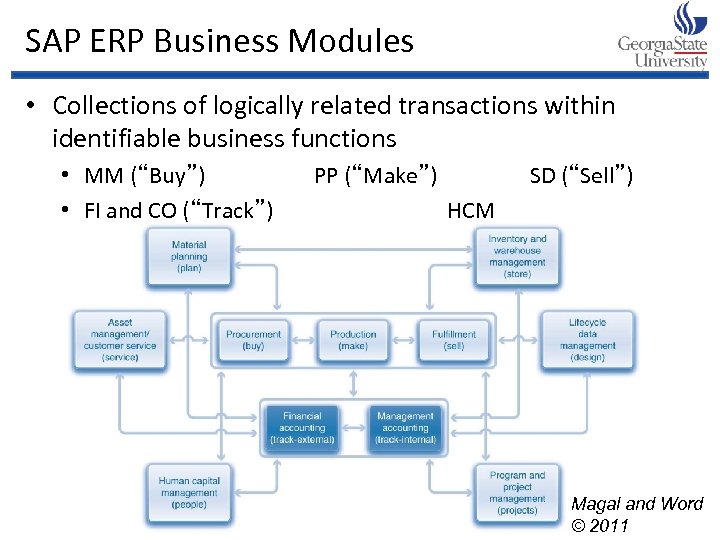 SAP ERP Business Modules • Collections of logically related transactions within identifiable business functions • MM (“Buy”) PP (“Make”) SD (“Sell”) • FI and CO (“Track”) HCM Magal and Word © 2011
SAP ERP Business Modules • Collections of logically related transactions within identifiable business functions • MM (“Buy”) PP (“Make”) SD (“Sell”) • FI and CO (“Track”) HCM Magal and Word © 2011
 SAP ERP Core Applications • Logistics • Accounting & Finance • Sales & Distribution • Materials Management • Production Planning • Plant Maintenance • Quality Management • • Financial Accounting Managerial Accounting Asset Management Treasury • Human Resources • Personnel Management • Benefits • Payroll
SAP ERP Core Applications • Logistics • Accounting & Finance • Sales & Distribution • Materials Management • Production Planning • Plant Maintenance • Quality Management • • Financial Accounting Managerial Accounting Asset Management Treasury • Human Resources • Personnel Management • Benefits • Payroll
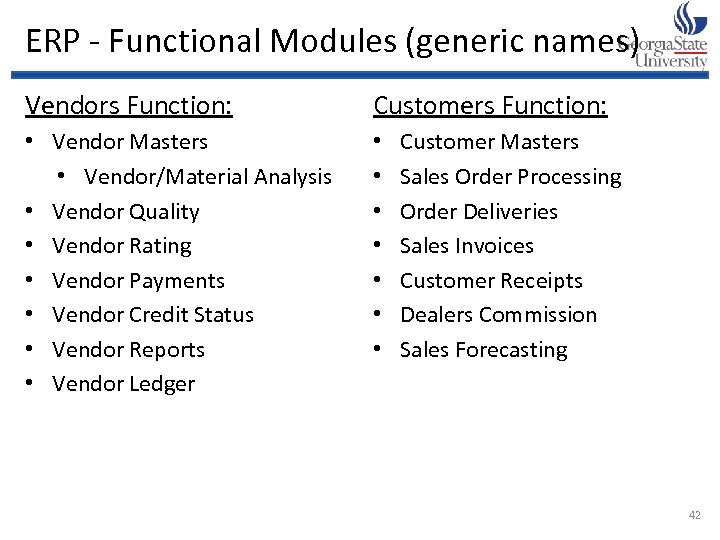 ERP - Functional Modules (generic names) Vendors Function: Customers Function: • Vendor Masters • Vendor/Material Analysis • Vendor Quality • Vendor Rating • Vendor Payments • Vendor Credit Status • Vendor Reports • Vendor Ledger • • Customer Masters Sales Order Processing Order Deliveries Sales Invoices Customer Receipts Dealers Commission Sales Forecasting 42
ERP - Functional Modules (generic names) Vendors Function: Customers Function: • Vendor Masters • Vendor/Material Analysis • Vendor Quality • Vendor Rating • Vendor Payments • Vendor Credit Status • Vendor Reports • Vendor Ledger • • Customer Masters Sales Order Processing Order Deliveries Sales Invoices Customer Receipts Dealers Commission Sales Forecasting 42
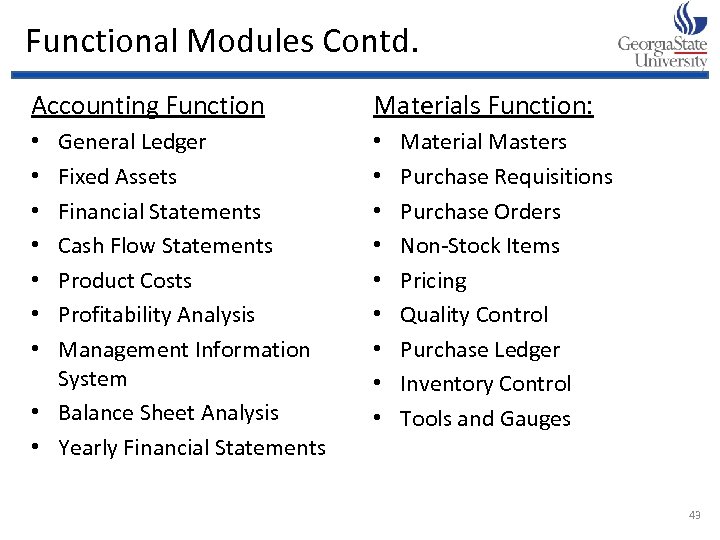 Functional Modules Contd. Accounting Function Materials Function: General Ledger Fixed Assets Financial Statements Cash Flow Statements Product Costs Profitability Analysis Management Information System • Balance Sheet Analysis • Yearly Financial Statements • • • • Material Masters Purchase Requisitions Purchase Orders Non-Stock Items Pricing Quality Control Purchase Ledger Inventory Control Tools and Gauges 43
Functional Modules Contd. Accounting Function Materials Function: General Ledger Fixed Assets Financial Statements Cash Flow Statements Product Costs Profitability Analysis Management Information System • Balance Sheet Analysis • Yearly Financial Statements • • • • Material Masters Purchase Requisitions Purchase Orders Non-Stock Items Pricing Quality Control Purchase Ledger Inventory Control Tools and Gauges 43
 SAP Main Menu
SAP Main Menu
 SAP ERP Reference Models • use Reference models - provide predefined, adaptable content that you can tailor according to the requirements of your company. • enables you to access and reuse existing process knowledge, and to realize projects faster.
SAP ERP Reference Models • use Reference models - provide predefined, adaptable content that you can tailor according to the requirements of your company. • enables you to access and reuse existing process knowledge, and to realize projects faster.
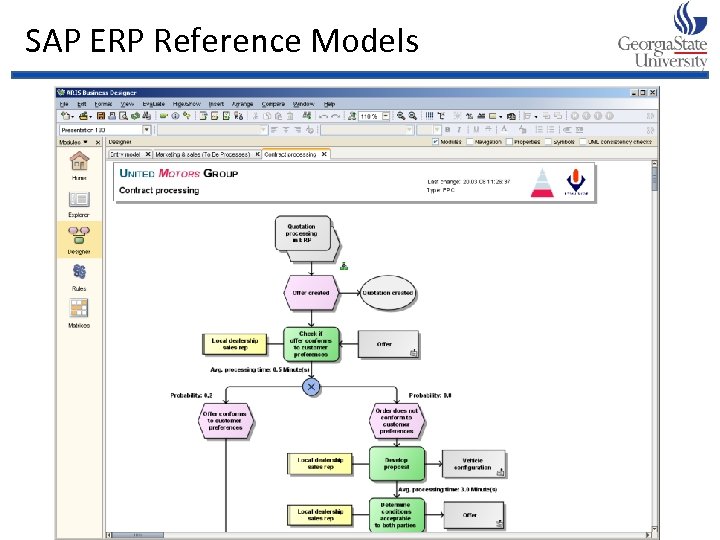 SAP ERP Reference Models
SAP ERP Reference Models
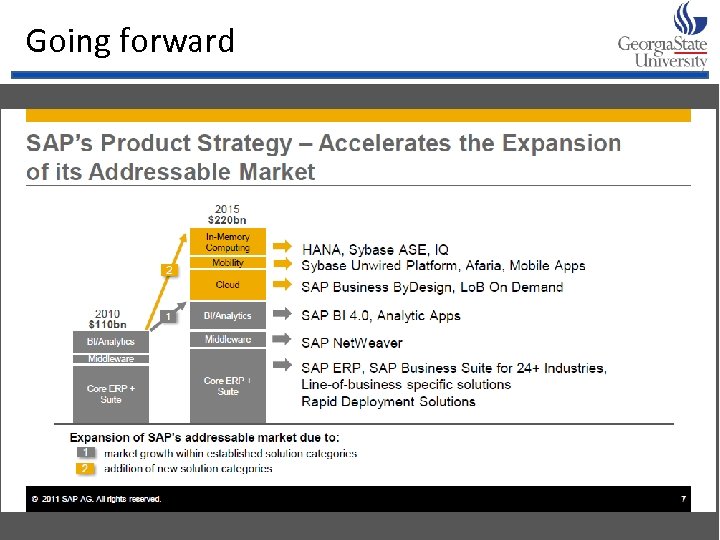 Going forward
Going forward
 SAP 48
SAP 48
 What is SAP? “Systeme, Anwendungen und Produkte in der Datenverarbeitung” (English: “Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing”) • SAP AG • Founded in Walldorf, Germany in 1972 • World’s Largest Business Software Company • World’s Third-largest Independent Software Provider • World-wide usage • Designed to satisfy the information needs for all business sizes (small local to large all international) • Multi-lingual • Multi-currency • Multi-balance (parallel G/L Accounting)
What is SAP? “Systeme, Anwendungen und Produkte in der Datenverarbeitung” (English: “Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing”) • SAP AG • Founded in Walldorf, Germany in 1972 • World’s Largest Business Software Company • World’s Third-largest Independent Software Provider • World-wide usage • Designed to satisfy the information needs for all business sizes (small local to large all international) • Multi-lingual • Multi-currency • Multi-balance (parallel G/L Accounting)
 SAP 50
SAP 50
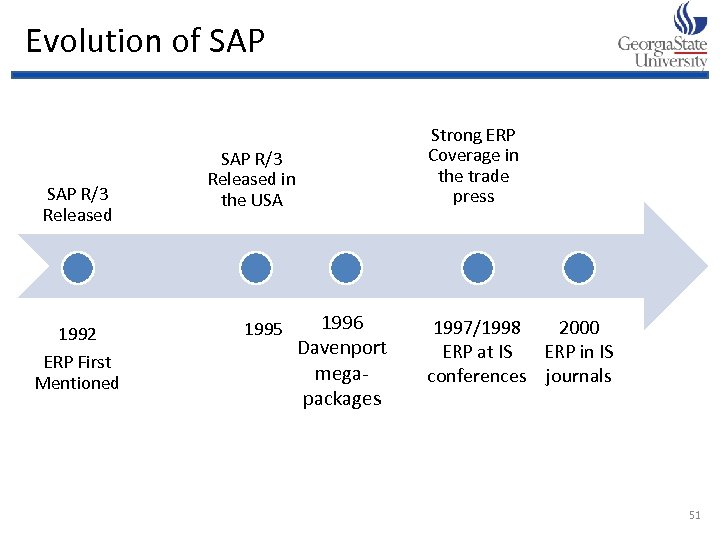 Evolution of SAP R/3 Released 1992 ERP First Mentioned SAP R/3 Released in the USA 1995 1996 Davenport megapackages Strong ERP Coverage in the trade press 1997/1998 2000 ERP at IS ERP in IS conferences journals 51
Evolution of SAP R/3 Released 1992 ERP First Mentioned SAP R/3 Released in the USA 1995 1996 Davenport megapackages Strong ERP Coverage in the trade press 1997/1998 2000 ERP at IS ERP in IS conferences journals 51
 SAP Enterprise Resource Planning (SAP ERP) • Enables a company to support and optimize its business processes • Ties together disparate business functions (integrated business solution) such as • • Finance (Financial Accounting, Managerial Accounting, Treasury, …) Logistics (Sales, Procurement, Production, Fulfillment, …) Human Resources … • Helps the organization run smoothly • Real-time environment • Scalable and flexible
SAP Enterprise Resource Planning (SAP ERP) • Enables a company to support and optimize its business processes • Ties together disparate business functions (integrated business solution) such as • • Finance (Financial Accounting, Managerial Accounting, Treasury, …) Logistics (Sales, Procurement, Production, Fulfillment, …) Human Resources … • Helps the organization run smoothly • Real-time environment • Scalable and flexible
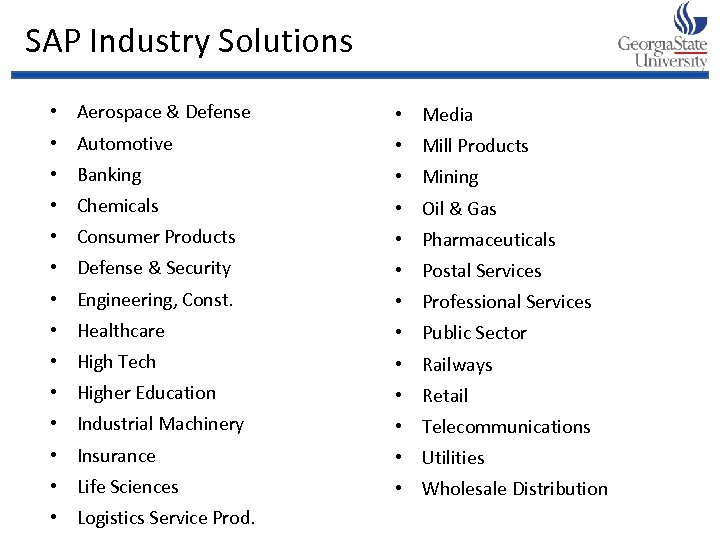 SAP Industry Solutions • Aerospace & Defense • Media • Automotive • Mill Products • Banking • Mining • Chemicals • Oil & Gas • Consumer Products • Pharmaceuticals • Defense & Security • Postal Services • Engineering, Const. • Professional Services • Healthcare • Public Sector • High Tech • Railways • Higher Education • Retail • Industrial Machinery • Telecommunications • Insurance • Utilities • Life Sciences • Wholesale Distribution • Logistics Service Prod.
SAP Industry Solutions • Aerospace & Defense • Media • Automotive • Mill Products • Banking • Mining • Chemicals • Oil & Gas • Consumer Products • Pharmaceuticals • Defense & Security • Postal Services • Engineering, Const. • Professional Services • Healthcare • Public Sector • High Tech • Railways • Higher Education • Retail • Industrial Machinery • Telecommunications • Insurance • Utilities • Life Sciences • Wholesale Distribution • Logistics Service Prod.
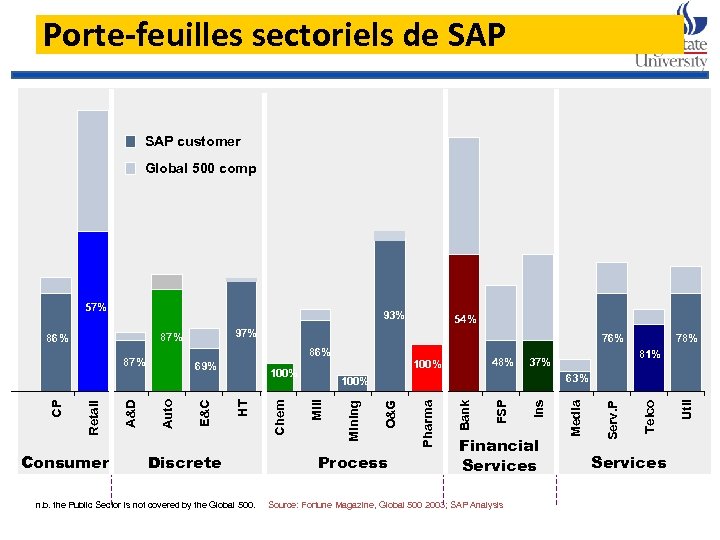 Porte-feuilles sectoriels de SAP customer Global 500 comp 93% Discrete 48% 100% Process n. b. the Public Sector is not covered by the Global 500. Source: Fortune Magazine, Global 500 2003; SAP Analysis Telco Serv. P Ins FSP Bank Pharma Financial Services Media 63% O&G Mining 78% 81% 37% 100% Mill Chem 100% HT E&C 69% Auto A&D Retail Consumer 76% 87% CP 97% 86% 54% Services Util 57%
Porte-feuilles sectoriels de SAP customer Global 500 comp 93% Discrete 48% 100% Process n. b. the Public Sector is not covered by the Global 500. Source: Fortune Magazine, Global 500 2003; SAP Analysis Telco Serv. P Ins FSP Bank Pharma Financial Services Media 63% O&G Mining 78% 81% 37% 100% Mill Chem 100% HT E&C 69% Auto A&D Retail Consumer 76% 87% CP 97% 86% 54% Services Util 57%
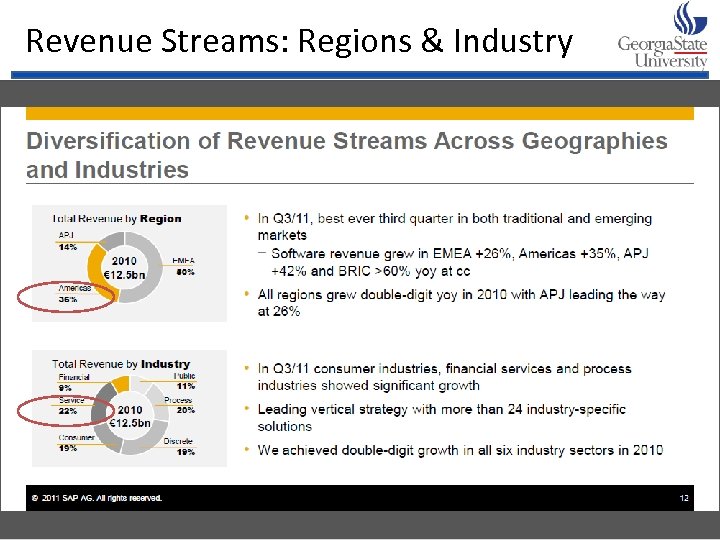 Revenue Streams: Regions & Industry
Revenue Streams: Regions & Industry
 VENDOR LANDSCAPE 56
VENDOR LANDSCAPE 56
 ERP Market - Revenues 57
ERP Market - Revenues 57
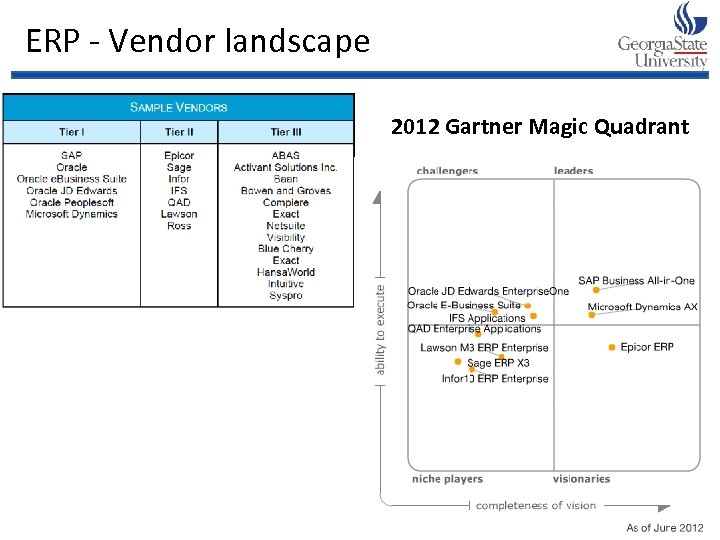 ERP - Vendor landscape 2012 Gartner Magic Quadrant 58
ERP - Vendor landscape 2012 Gartner Magic Quadrant 58
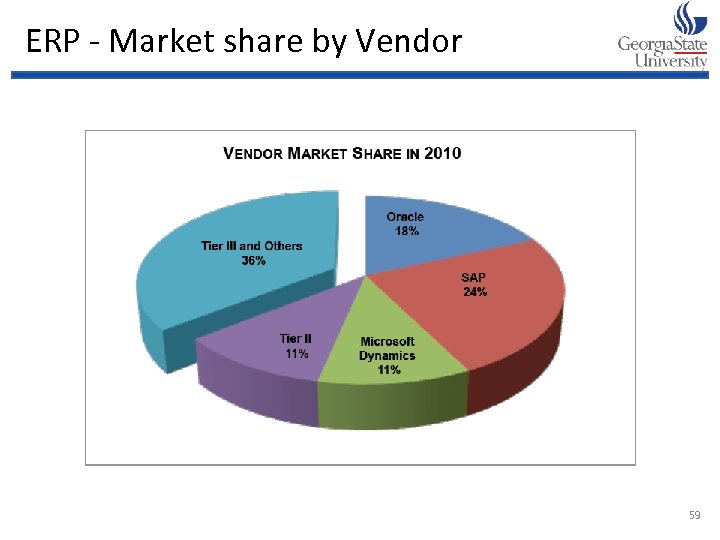 ERP - Market share by Vendor 59
ERP - Market share by Vendor 59
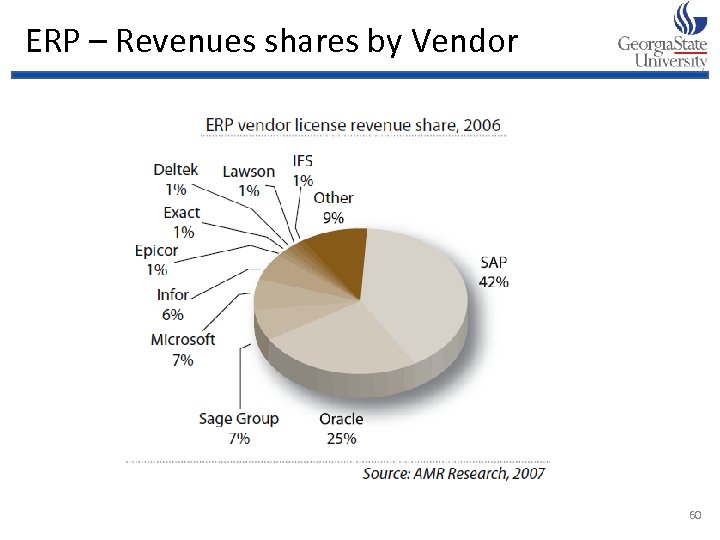 ERP – Revenues shares by Vendor 60
ERP – Revenues shares by Vendor 60
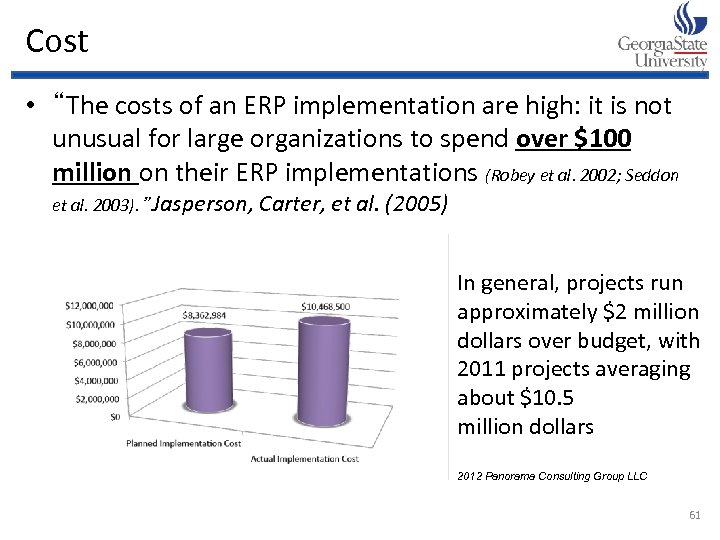 Cost • “The costs of an ERP implementation are high: it is not unusual for large organizations to spend over $100 million on their ERP implementations (Robey et al. 2002; Seddon et al. 2003). ” Jasperson, Carter, et al. (2005) In general, projects run approximately $2 million dollars over budget, with 2011 projects averaging about $10. 5 million dollars 2012 Panorama Consulting Group LLC 61
Cost • “The costs of an ERP implementation are high: it is not unusual for large organizations to spend over $100 million on their ERP implementations (Robey et al. 2002; Seddon et al. 2003). ” Jasperson, Carter, et al. (2005) In general, projects run approximately $2 million dollars over budget, with 2011 projects averaging about $10. 5 million dollars 2012 Panorama Consulting Group LLC 61
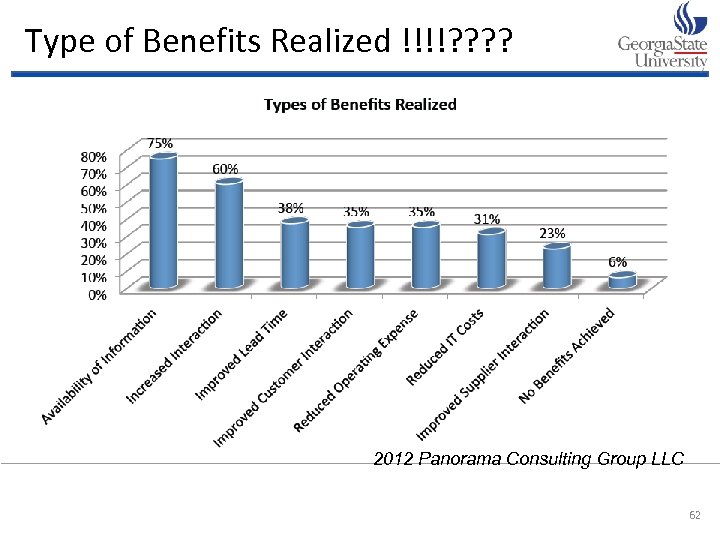 Type of Benefits Realized !!!!? ? 2010 Panorama Consulting Group LLC 2012 Panorama Consulting Group LLC 62
Type of Benefits Realized !!!!? ? 2010 Panorama Consulting Group LLC 2012 Panorama Consulting Group LLC 62
 ERP – who is using it? 63
ERP – who is using it? 63
 ERP Failures (2010) http: //www. cio. com/article/647564/Biggest_ERP_Failures_of_2010 • • New York's City. Time 'disaster' - City. Time, an effort by New York City to modernize its payroll system, is more of an ERP "project failure of the decade" - originally budgeted at around US$60 million, but has since ballooned to a colossal $700 million-plus BSky. B (BSY) gets £ 318 million settlement from Hewlett-Packard/EDS (HPQ) - A court found that HP's EDS division had lied about how long it would take to finish the project, which was started in 2000 and originally budgeted at £ 48 million. BSky. B fired EDS in 2002 and completed the job itself, but costs ultimately quintupled. Marin County's "rip and replace" - Marin County sued system integrator Deloitte Consulting in connection with the system earlier this year, saying Deloitte used the project as "a trial-and-error training ground" SAP settles with Waste Management - One of the ugliest ERP project legal battles in memory came to an end in May, when SAP reached a settlement with trash hauler Waste Management originally sued SAP for fraud in March 2008 over an allegedly failed implementation of its ERP software. The company claimed it suffered significant damages, including more than US$100 million it spent on the project, as well as more than $350 million for benefits it would have gained if the software had worked as intended. 64
ERP Failures (2010) http: //www. cio. com/article/647564/Biggest_ERP_Failures_of_2010 • • New York's City. Time 'disaster' - City. Time, an effort by New York City to modernize its payroll system, is more of an ERP "project failure of the decade" - originally budgeted at around US$60 million, but has since ballooned to a colossal $700 million-plus BSky. B (BSY) gets £ 318 million settlement from Hewlett-Packard/EDS (HPQ) - A court found that HP's EDS division had lied about how long it would take to finish the project, which was started in 2000 and originally budgeted at £ 48 million. BSky. B fired EDS in 2002 and completed the job itself, but costs ultimately quintupled. Marin County's "rip and replace" - Marin County sued system integrator Deloitte Consulting in connection with the system earlier this year, saying Deloitte used the project as "a trial-and-error training ground" SAP settles with Waste Management - One of the ugliest ERP project legal battles in memory came to an end in May, when SAP reached a settlement with trash hauler Waste Management originally sued SAP for fraud in March 2008 over an allegedly failed implementation of its ERP software. The company claimed it suffered significant damages, including more than US$100 million it spent on the project, as well as more than $350 million for benefits it would have gained if the software had worked as intended. 64
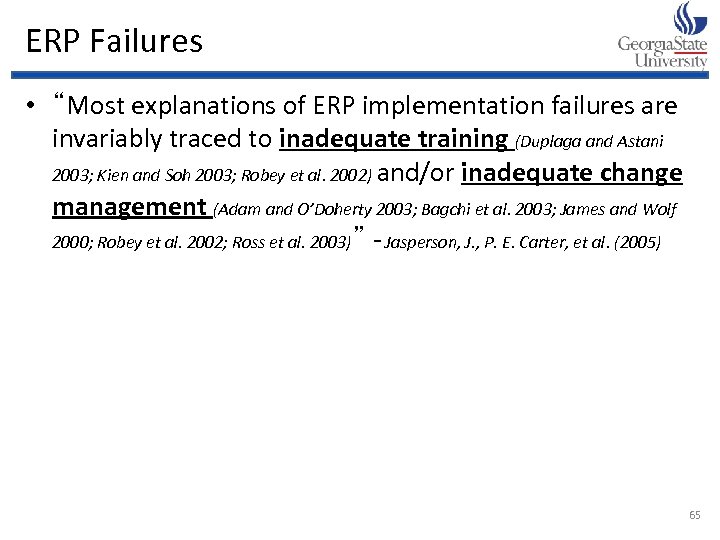 ERP Failures • “Most explanations of ERP implementation failures are invariably traced to inadequate training (Duplaga and Astani 2003; Kien and Soh 2003; Robey et al. 2002) and/or inadequate change management (Adam and O’Doherty 2003; Bagchi et al. 2003; James and Wolf 2000; Robey et al. 2002; Ross et al. 2003)” - Jasperson, J. , P. E. Carter, et al. (2005) 65
ERP Failures • “Most explanations of ERP implementation failures are invariably traced to inadequate training (Duplaga and Astani 2003; Kien and Soh 2003; Robey et al. 2002) and/or inadequate change management (Adam and O’Doherty 2003; Bagchi et al. 2003; James and Wolf 2000; Robey et al. 2002; Ross et al. 2003)” - Jasperson, J. , P. E. Carter, et al. (2005) 65
 Hershey Foods Corporation (1999) • One of the largest known project failures linked to an ERP system • SAP was implemented in a short amount of time • The big bang approach was elected as a cutover strategy • Hershey lost large amounts of revenue during a high season (Halloween) because they could not fulfill orders in time, even though the inventory was available. • Software was not the issue • The processes were mapped in a poor manner • A Project failure than an ERP failure 66
Hershey Foods Corporation (1999) • One of the largest known project failures linked to an ERP system • SAP was implemented in a short amount of time • The big bang approach was elected as a cutover strategy • Hershey lost large amounts of revenue during a high season (Halloween) because they could not fulfill orders in time, even though the inventory was available. • Software was not the issue • The processes were mapped in a poor manner • A Project failure than an ERP failure 66
 Questions? Thank you Sumantra Sarkar ssarkar@cis. gsu. edu
Questions? Thank you Sumantra Sarkar ssarkar@cis. gsu. edu
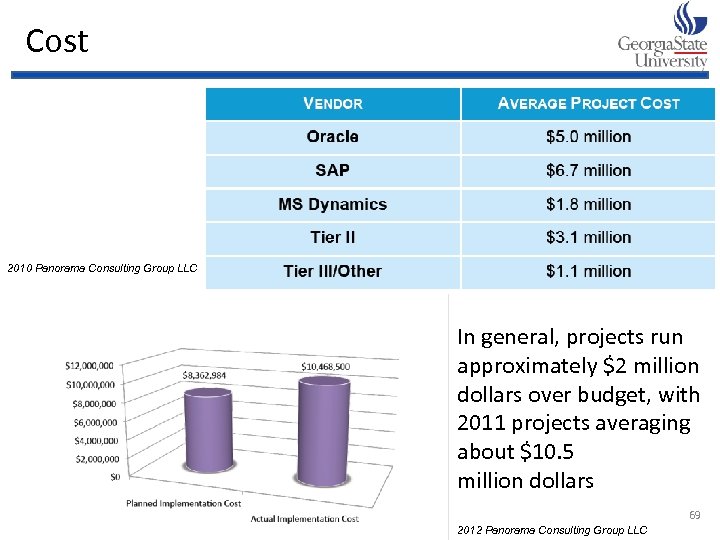 Cost 2010 Panorama Consulting Group LLC In general, projects run approximately $2 million dollars over budget, with 2011 projects averaging about $10. 5 million dollars 69 2012 Panorama Consulting Group LLC
Cost 2010 Panorama Consulting Group LLC In general, projects run approximately $2 million dollars over budget, with 2011 projects averaging about $10. 5 million dollars 69 2012 Panorama Consulting Group LLC
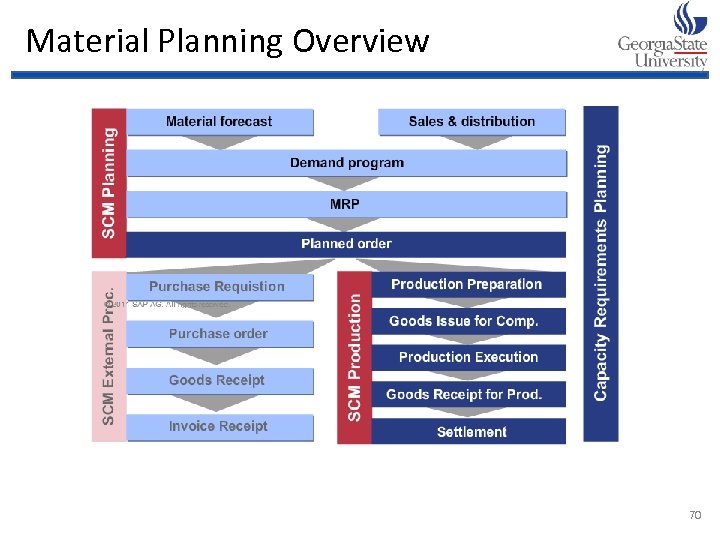 Material Planning Overview 70
Material Planning Overview 70
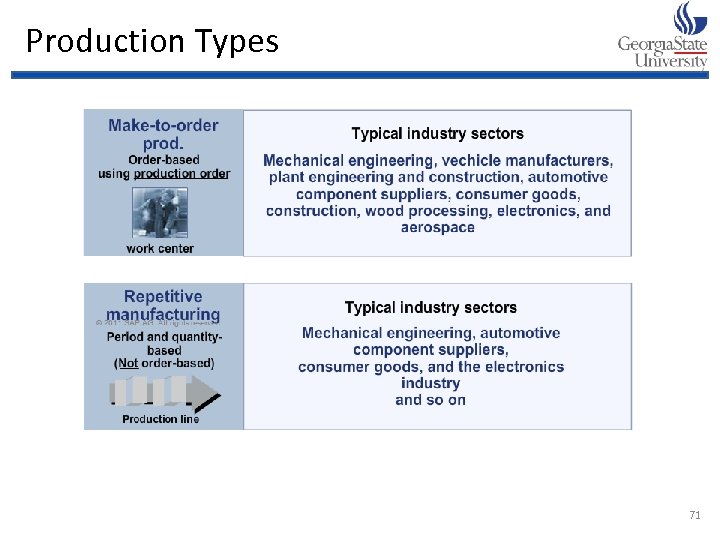 Production Types 71
Production Types 71
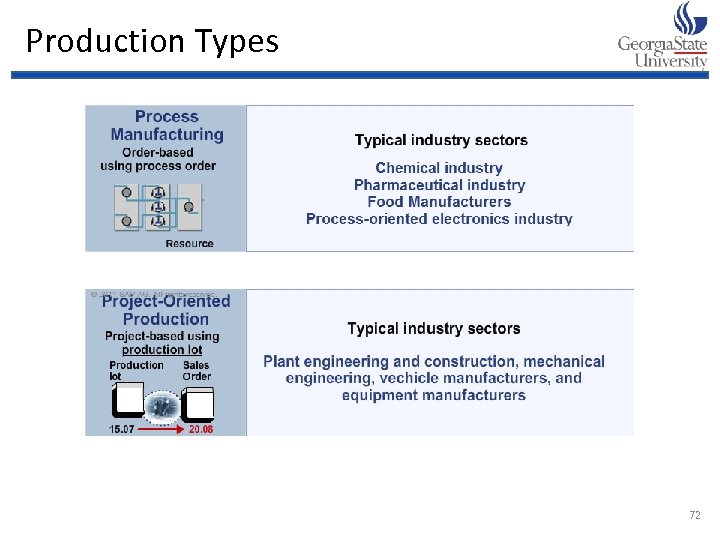 Production Types 72
Production Types 72
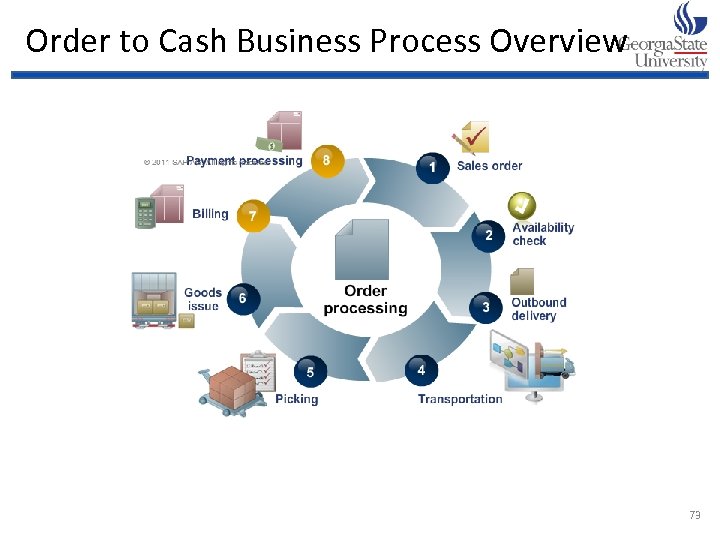 Order to Cash Business Process Overview 73
Order to Cash Business Process Overview 73


