a0e07c021612d37c59160256b4ddf9ee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 94
 Enterprise Resource Planning Dr. Poonam Garg Dated: 30/09/2009 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 1
Enterprise Resource Planning Dr. Poonam Garg Dated: 30/09/2009 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 1
 Course Objectives n Understand how ERP is used to integrate business processes; define and analyze a process; create a process map and improve and/or simplify the process; apply the result to an ERP implementation. n Understand how the fundamental business processes interact with SAP ERP in the functional areas of Sales and Distribution, Materials Management, Production Planning, Financial Accounting, Controlling, and Human Capital Management. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 2
Course Objectives n Understand how ERP is used to integrate business processes; define and analyze a process; create a process map and improve and/or simplify the process; apply the result to an ERP implementation. n Understand how the fundamental business processes interact with SAP ERP in the functional areas of Sales and Distribution, Materials Management, Production Planning, Financial Accounting, Controlling, and Human Capital Management. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 2
 Text Books n Text books: q ERP Demystified Alexis Leon Reference books: q Concepts in Enterprise resource planning Ellen Monk q Enterprise resource planning C. S. V. Murthy q ERP In practice Jagan Nathan Vaman Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 3
Text Books n Text books: q ERP Demystified Alexis Leon Reference books: q Concepts in Enterprise resource planning Ellen Monk q Enterprise resource planning C. S. V. Murthy q ERP In practice Jagan Nathan Vaman Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 3
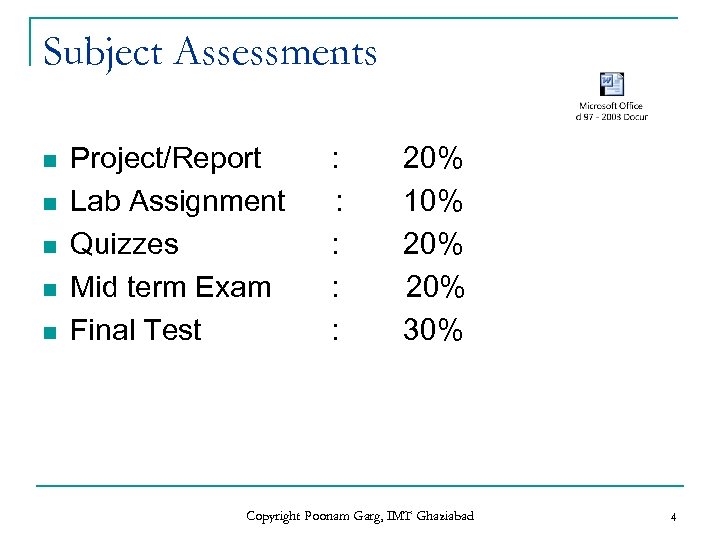 Subject Assessments n n n Project/Report Lab Assignment Quizzes Mid term Exam Final Test : : : 20% 10% 20% 30% Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 4
Subject Assessments n n n Project/Report Lab Assignment Quizzes Mid term Exam Final Test : : : 20% 10% 20% 30% Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 4
 Discussion Questions n n n n n What is ERP. How it is different from Information Systems? At what level of IS the ERP works? Why an organization should implement ERP system? Why an Organization should implement ERP if they already have functional systems? What are some of the benefits that organizations derive by implementing ERP? What do you mean by a business process? How are the business process different from business functions? Pen Incorporated IS BPR necessary for ERP implementation? Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 5
Discussion Questions n n n n n What is ERP. How it is different from Information Systems? At what level of IS the ERP works? Why an organization should implement ERP system? Why an Organization should implement ERP if they already have functional systems? What are some of the benefits that organizations derive by implementing ERP? What do you mean by a business process? How are the business process different from business functions? Pen Incorporated IS BPR necessary for ERP implementation? Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 5
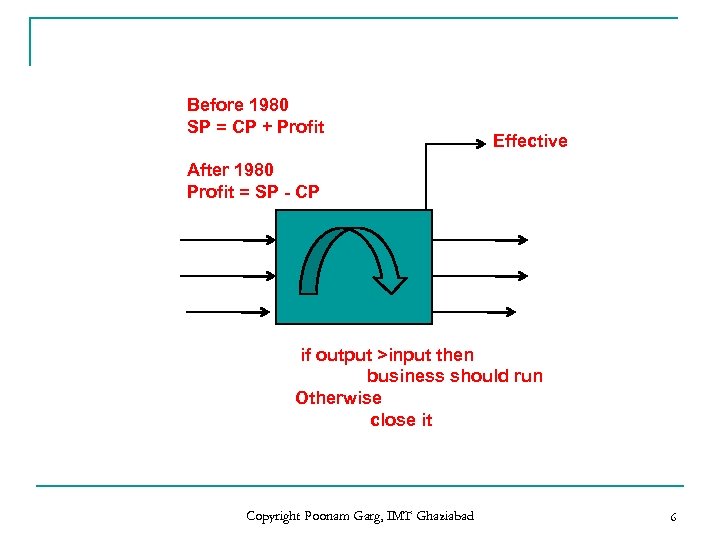 Before 1980 SP = CP + Profit Effective After 1980 Profit = SP - CP if output >input then business should run Otherwise close it Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 6
Before 1980 SP = CP + Profit Effective After 1980 Profit = SP - CP if output >input then business should run Otherwise close it Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 6
 SAP Enterprise System Pen Incorporated n n Start-up company in the promotional pen business Initially buys and re-sells different lines of promotion pens Sells to both wholesale and retail – procure and distribute Later acquires a production facility to manufacture its own product – produce and distribute
SAP Enterprise System Pen Incorporated n n Start-up company in the promotional pen business Initially buys and re-sells different lines of promotion pens Sells to both wholesale and retail – procure and distribute Later acquires a production facility to manufacture its own product – produce and distribute
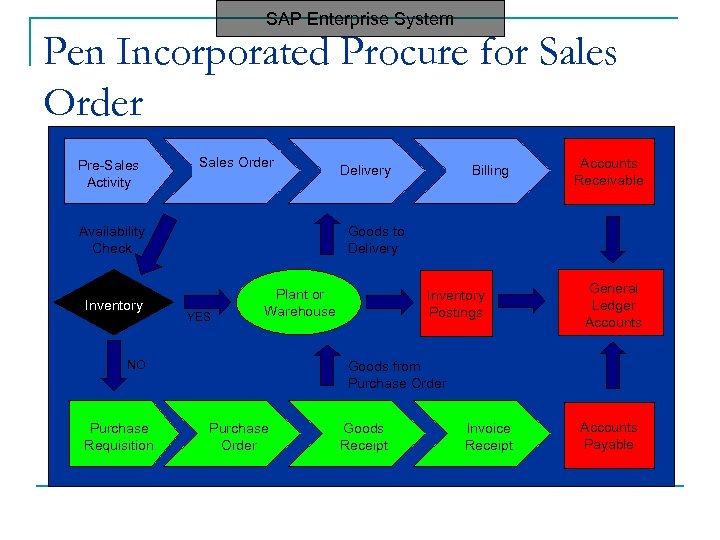 SAP Enterprise System Pen Incorporated Procure for Sales Order Pre-Sales Activity Sales Order Availability Check In Inventory Billing Accounts Receivable Goods to Delivery YES Plant or Warehouse NO Purchase Requisition Delivery Inventory Postings General Ledger Accounts Goods from Purchase Order Goods Receipt Invoice Receipt Accounts Payable
SAP Enterprise System Pen Incorporated Procure for Sales Order Pre-Sales Activity Sales Order Availability Check In Inventory Billing Accounts Receivable Goods to Delivery YES Plant or Warehouse NO Purchase Requisition Delivery Inventory Postings General Ledger Accounts Goods from Purchase Order Goods Receipt Invoice Receipt Accounts Payable
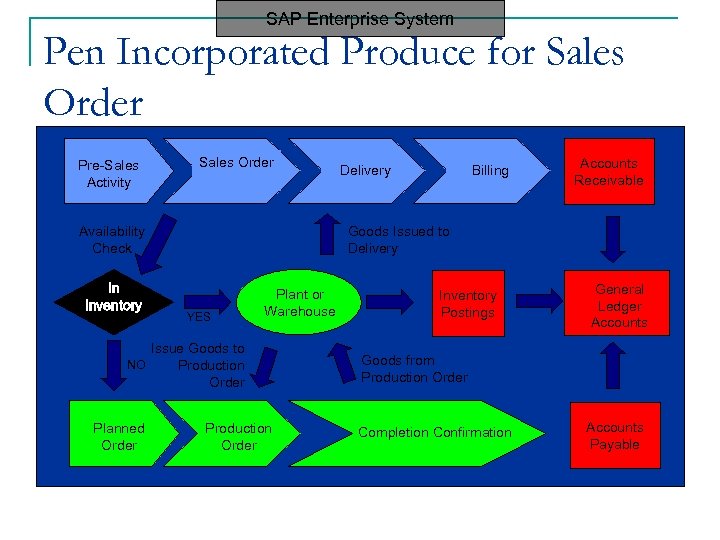 SAP Enterprise System Pen Incorporated Produce for Sales Order Pre-Sales Activity Sales Order Availability Check In Inventory Billing Accounts Receivable Goods Issued to Delivery YES Plant or Warehouse Issue Goods to NO Production Order Planned Order Delivery Production Order Inventory Postings General Ledger Accounts Goods from Production Order Completion Confirmation Accounts Payable
SAP Enterprise System Pen Incorporated Produce for Sales Order Pre-Sales Activity Sales Order Availability Check In Inventory Billing Accounts Receivable Goods Issued to Delivery YES Plant or Warehouse Issue Goods to NO Production Order Planned Order Delivery Production Order Inventory Postings General Ledger Accounts Goods from Production Order Completion Confirmation Accounts Payable
 Topics n n n What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? Evolution Of ERP Need For ERP Selection process of an ERP package Features of ERP Components / modules of ERP Comparison of ERP products Technology requirements / infrastructure Pre requisites for effective ERP implementation : Implementation phases of ERP Post implementation plan Benefits of ERP Ver. 1. 0 Slide 10
Topics n n n What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? Evolution Of ERP Need For ERP Selection process of an ERP package Features of ERP Components / modules of ERP Comparison of ERP products Technology requirements / infrastructure Pre requisites for effective ERP implementation : Implementation phases of ERP Post implementation plan Benefits of ERP Ver. 1. 0 Slide 10
 ERP Market n One of the fastest growing markets in software industry n 34. 5% of companies with revenues over $1 billion plan to purchase or upgrade n $180 billion sales in 2002 n Maybe as much as $1 trillion by 2010 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 11
ERP Market n One of the fastest growing markets in software industry n 34. 5% of companies with revenues over $1 billion plan to purchase or upgrade n $180 billion sales in 2002 n Maybe as much as $1 trillion by 2010 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 11
 ERP Systems n Major investment q n Total implementation cost – up to 2 -3% of revenues ($100 million for a $5 billion company) Variety of business justifications q q Replace legacy systems Reduce cycle times Lower operating costs Enables better management decisions n n Real-time On-line Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 12
ERP Systems n Major investment q n Total implementation cost – up to 2 -3% of revenues ($100 million for a $5 billion company) Variety of business justifications q q Replace legacy systems Reduce cycle times Lower operating costs Enables better management decisions n n Real-time On-line Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 12
 Costs and Benefits n Implementation can take up to 2 years n Payback usually 6 -30 months n Savings based on 30% reduction in administrative and IS costs Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 13
Costs and Benefits n Implementation can take up to 2 years n Payback usually 6 -30 months n Savings based on 30% reduction in administrative and IS costs Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 13
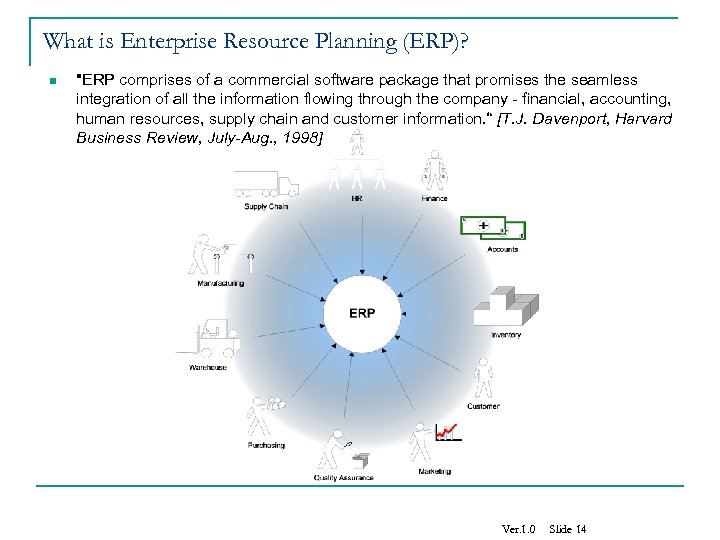 What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? n "ERP comprises of a commercial software package that promises the seamless integration of all the information flowing through the company - financial, accounting, human resources, supply chain and customer information. “ [T. J. Davenport, Harvard Business Review, July-Aug. , 1998] Ver. 1. 0 Slide 14
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? n "ERP comprises of a commercial software package that promises the seamless integration of all the information flowing through the company - financial, accounting, human resources, supply chain and customer information. “ [T. J. Davenport, Harvard Business Review, July-Aug. , 1998] Ver. 1. 0 Slide 14
 What is an ERP? n n n Enterprise-wide system integrates the business functions and processes of an organization. Integration of business functions into one seamless application Produce, share and access information in Real-time environment Helps the organization to run smoothly Usually runs on a RDBMS Replaces Countless Departmental and Workgroup Information Systems Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 15
What is an ERP? n n n Enterprise-wide system integrates the business functions and processes of an organization. Integration of business functions into one seamless application Produce, share and access information in Real-time environment Helps the organization to run smoothly Usually runs on a RDBMS Replaces Countless Departmental and Workgroup Information Systems Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 15
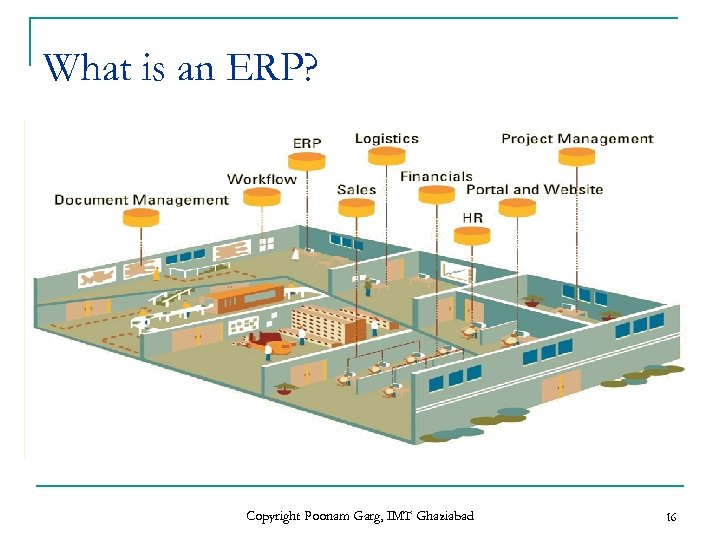 What is an ERP? Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 16
What is an ERP? Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 16
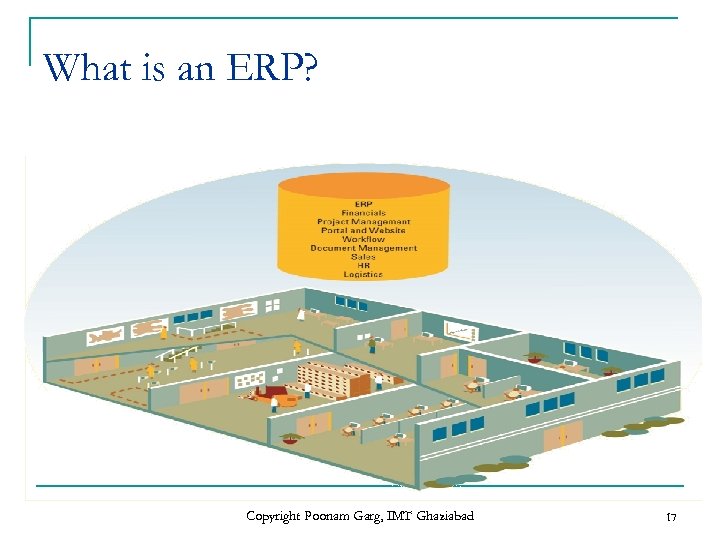 What is an ERP? Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 17
What is an ERP? Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 17
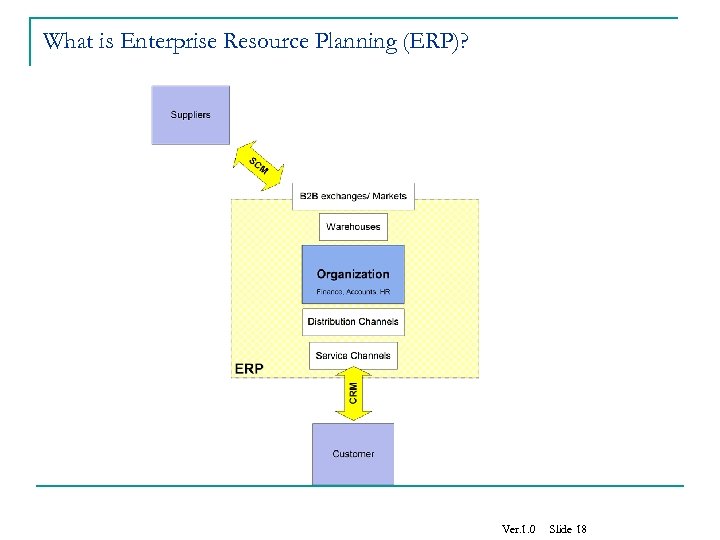 What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? Ver. 1. 0 Slide 18
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? Ver. 1. 0 Slide 18
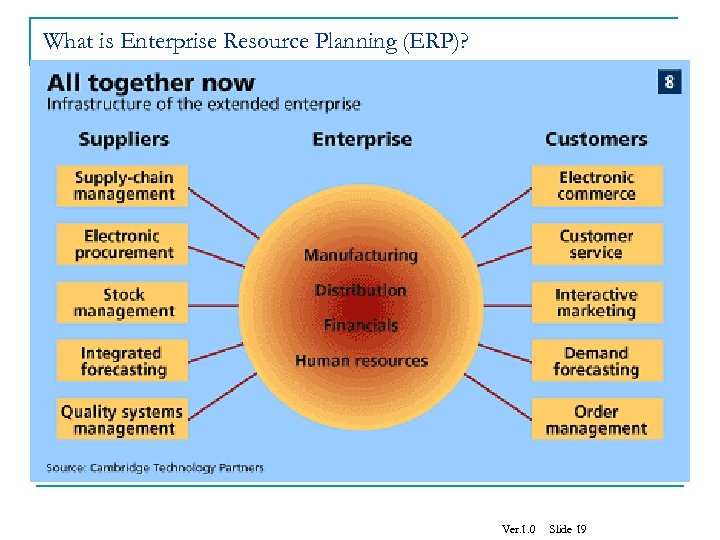 What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? Ver. 1. 0 Slide 19
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? Ver. 1. 0 Slide 19
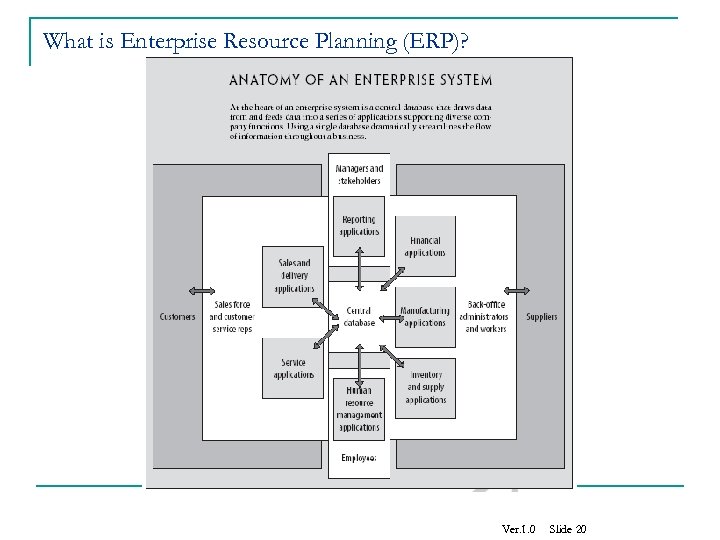 What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? Ver. 1. 0 Slide 20
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? Ver. 1. 0 Slide 20
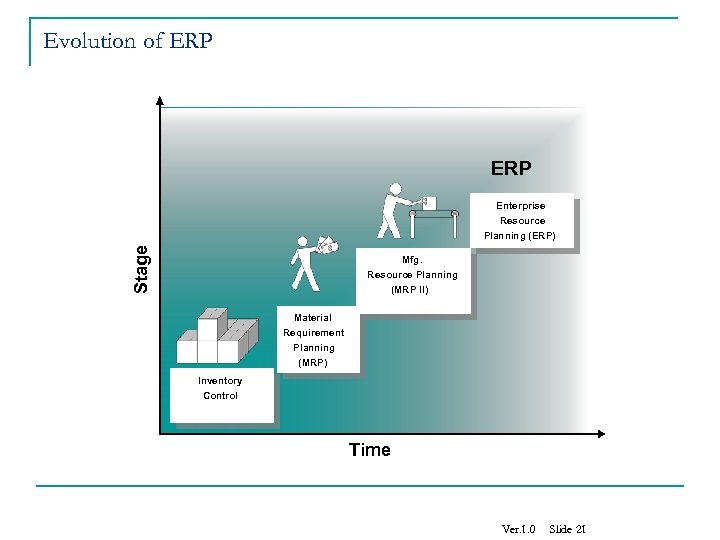 Evolution of ERP Stage Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Mfg. Resource Planning (MRP II) Material Requirement Planning (MRP) Inventory Control Time Ver. 1. 0 Slide 21
Evolution of ERP Stage Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Mfg. Resource Planning (MRP II) Material Requirement Planning (MRP) Inventory Control Time Ver. 1. 0 Slide 21
 Evolution of ERP Enterprise Resource Planning 1960’s - Systems Just for Inventory Control 1970’s - MRP – Material Requirement Planning (Inventory with material planning & procurement) 1980’s - MRP II – Manufacturing Resources Planning (Extended MRP to shop floor & distribution Mgnt. ) Mid 1990’s - ERP – Enterprise Resource Planning (Covering all the activities of an Enterprise) 2000 onwards – ERP II – Collaborative Commerce (Extending ERP to external business entities)
Evolution of ERP Enterprise Resource Planning 1960’s - Systems Just for Inventory Control 1970’s - MRP – Material Requirement Planning (Inventory with material planning & procurement) 1980’s - MRP II – Manufacturing Resources Planning (Extended MRP to shop floor & distribution Mgnt. ) Mid 1990’s - ERP – Enterprise Resource Planning (Covering all the activities of an Enterprise) 2000 onwards – ERP II – Collaborative Commerce (Extending ERP to external business entities)
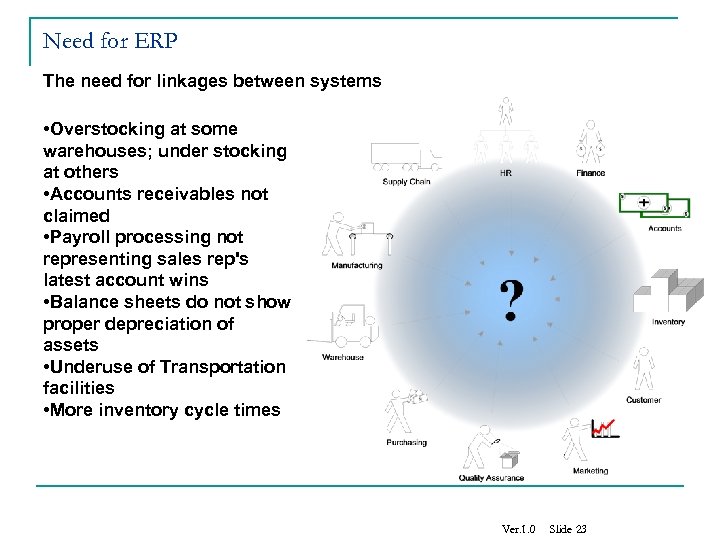 Need for ERP The need for linkages between systems • Overstocking at some warehouses; under stocking at others • Accounts receivables not claimed • Payroll processing not representing sales rep's latest account wins • Balance sheets do not show proper depreciation of assets • Underuse of Transportation facilities • More inventory cycle times Ver. 1. 0 Slide 23
Need for ERP The need for linkages between systems • Overstocking at some warehouses; under stocking at others • Accounts receivables not claimed • Payroll processing not representing sales rep's latest account wins • Balance sheets do not show proper depreciation of assets • Underuse of Transportation facilities • More inventory cycle times Ver. 1. 0 Slide 23
 Objectives of ERP Implementation a) Business drivers: v v v b) To streamline business processes. To get an integrated view of data. To ensure better monitoring of KPI’s. Technology driver: v To achieve a single technology platform. 24
Objectives of ERP Implementation a) Business drivers: v v v b) To streamline business processes. To get an integrated view of data. To ensure better monitoring of KPI’s. Technology driver: v To achieve a single technology platform. 24
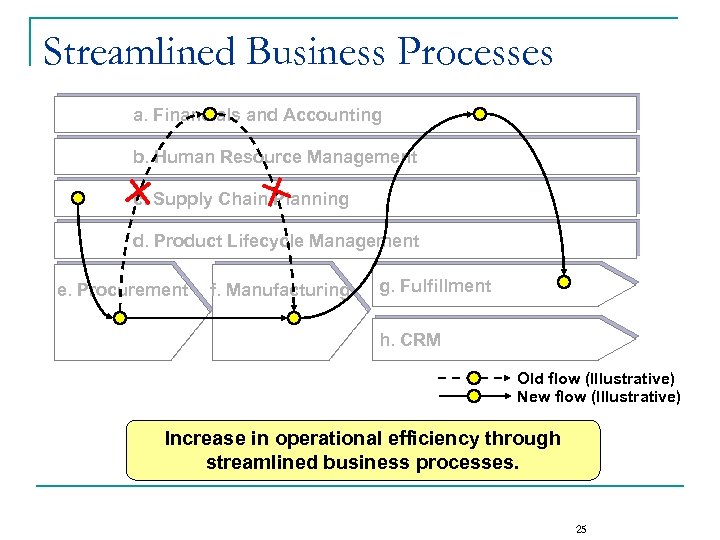 Streamlined Business Processes a. Financials and Accounting b. Human Resource Management c. Supply Chain Planning d. Product Lifecycle Management e. Procurement f. Manufacturing g. Fulfillment h. CRM Old flow (Illustrative) New flow (Illustrative) Increase in operational efficiency through streamlined business processes. 25
Streamlined Business Processes a. Financials and Accounting b. Human Resource Management c. Supply Chain Planning d. Product Lifecycle Management e. Procurement f. Manufacturing g. Fulfillment h. CRM Old flow (Illustrative) New flow (Illustrative) Increase in operational efficiency through streamlined business processes. 25
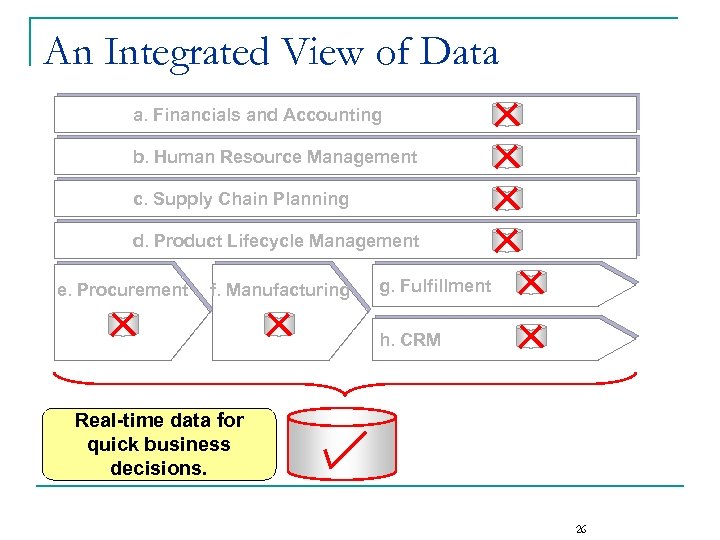 An Integrated View of Data a. Financials and Accounting b. Human Resource Management c. Supply Chain Planning d. Product Lifecycle Management e. Procurement f. Manufacturing g. Fulfillment h. CRM Real-time data for quick business decisions. 26
An Integrated View of Data a. Financials and Accounting b. Human Resource Management c. Supply Chain Planning d. Product Lifecycle Management e. Procurement f. Manufacturing g. Fulfillment h. CRM Real-time data for quick business decisions. 26
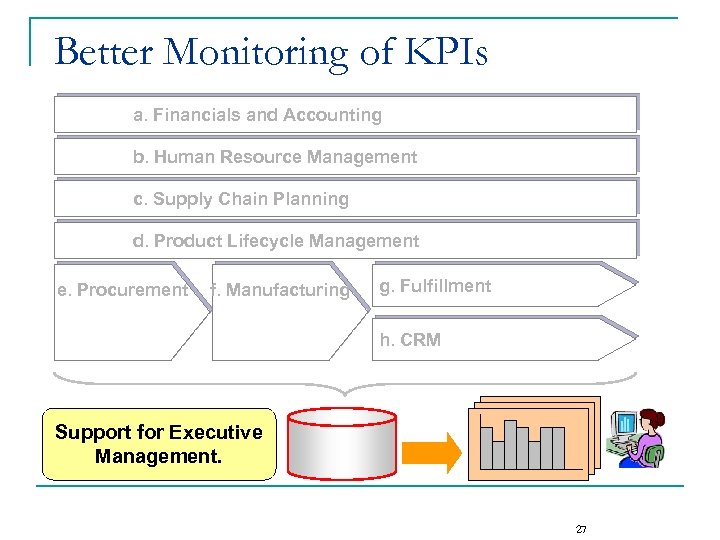 Better Monitoring of KPIs a. Financials and Accounting b. Human Resource Management c. Supply Chain Planning d. Product Lifecycle Management e. Procurement f. Manufacturing g. Fulfillment h. CRM Support for Executive Management. 27
Better Monitoring of KPIs a. Financials and Accounting b. Human Resource Management c. Supply Chain Planning d. Product Lifecycle Management e. Procurement f. Manufacturing g. Fulfillment h. CRM Support for Executive Management. 27
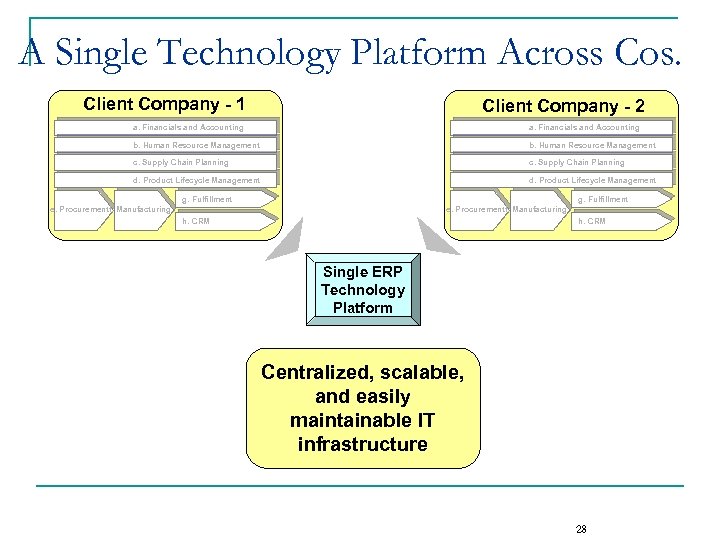 A Single Technology Platform Across Cos. Client Company - 1 Client Company - 2 a. Financials and Accounting b. Human Resource Management c. Supply Chain Planning d. Product Lifecycle Management g. Fulfillment e. Procurementf. Manufacturing h. CRM Single ERP Technology Platform Centralized, scalable, and easily maintainable IT infrastructure 28
A Single Technology Platform Across Cos. Client Company - 1 Client Company - 2 a. Financials and Accounting b. Human Resource Management c. Supply Chain Planning d. Product Lifecycle Management g. Fulfillment e. Procurementf. Manufacturing h. CRM Single ERP Technology Platform Centralized, scalable, and easily maintainable IT infrastructure 28
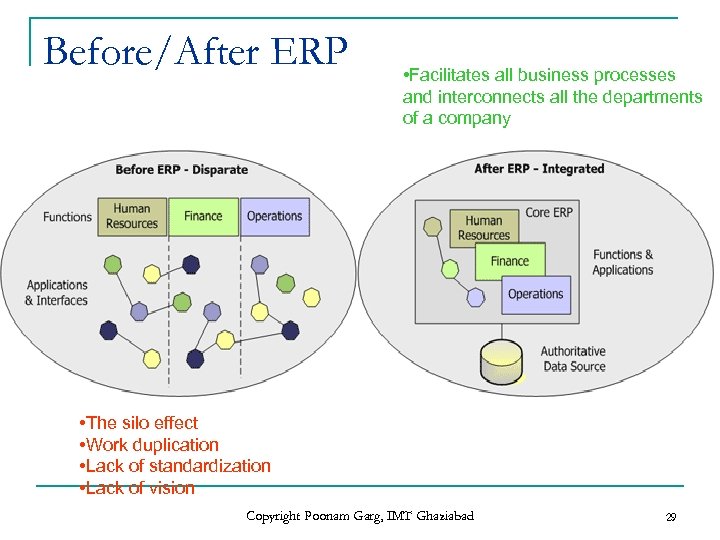 Before/After ERP • Facilitates all business processes and interconnects all the departments of a company • The silo effect • Work duplication • Lack of standardization • Lack of vision Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 29
Before/After ERP • Facilitates all business processes and interconnects all the departments of a company • The silo effect • Work duplication • Lack of standardization • Lack of vision Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 29
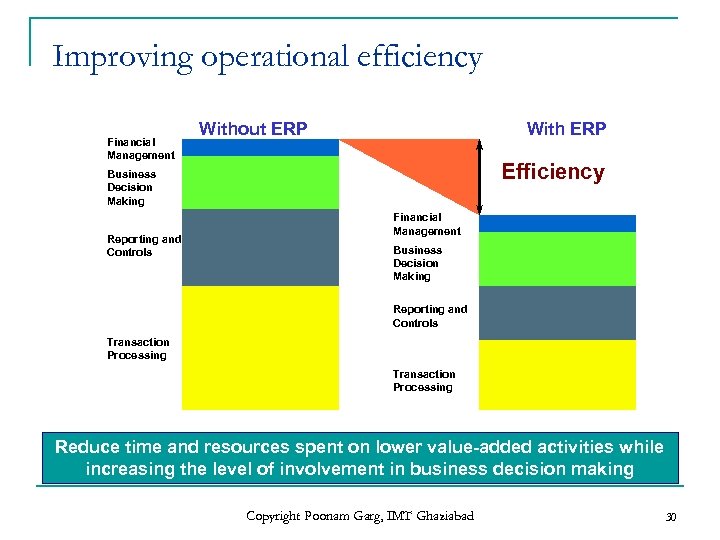 Improving operational efficiency Financial Management Without ERP With ERP Efficiency Business Decision Making Reporting and Controls Financial Management Business Decision Making Reporting and Controls Transaction Processing Reduce time and resources spent on lower value-added activities while increasing the level of involvement in business decision making Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 30
Improving operational efficiency Financial Management Without ERP With ERP Efficiency Business Decision Making Reporting and Controls Financial Management Business Decision Making Reporting and Controls Transaction Processing Reduce time and resources spent on lower value-added activities while increasing the level of involvement in business decision making Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 30
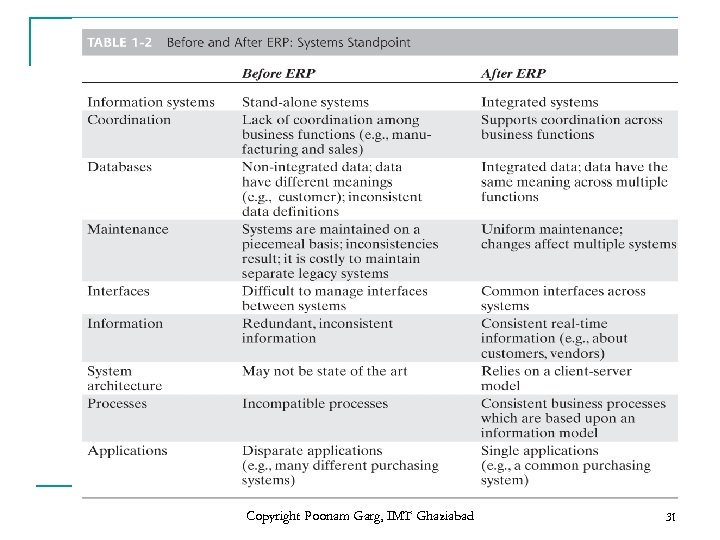 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 31
Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 31
 ERP - Benefits n n n Eliminates the duplication and redundancy in data Faster and cheaper Delivers quality information to produce a quality enterprise Satisfying Partners/Customers Reducing required manpower Increases the return on investment made on IT implementations ERP Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 32
ERP - Benefits n n n Eliminates the duplication and redundancy in data Faster and cheaper Delivers quality information to produce a quality enterprise Satisfying Partners/Customers Reducing required manpower Increases the return on investment made on IT implementations ERP Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 32
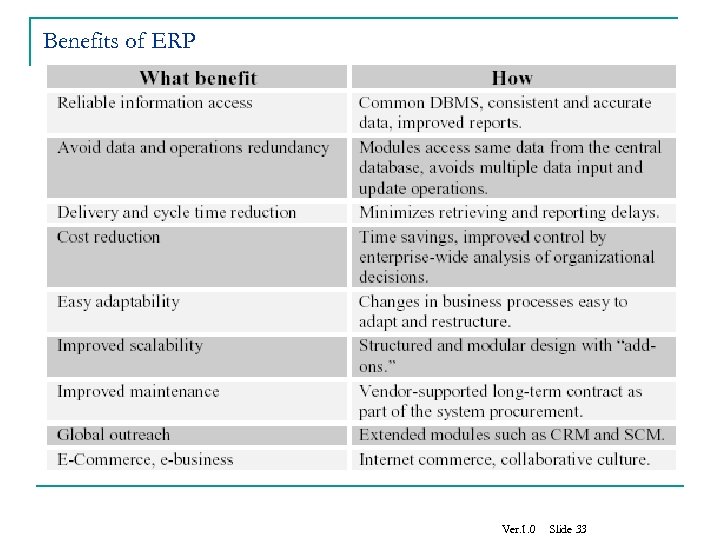 Benefits of ERP Ver. 1. 0 Slide 33
Benefits of ERP Ver. 1. 0 Slide 33
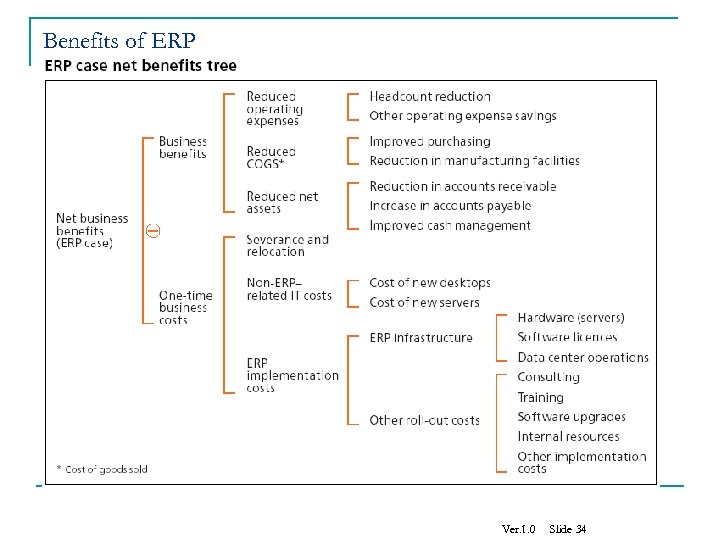 Benefits of ERP Ver. 1. 0 Slide 34
Benefits of ERP Ver. 1. 0 Slide 34
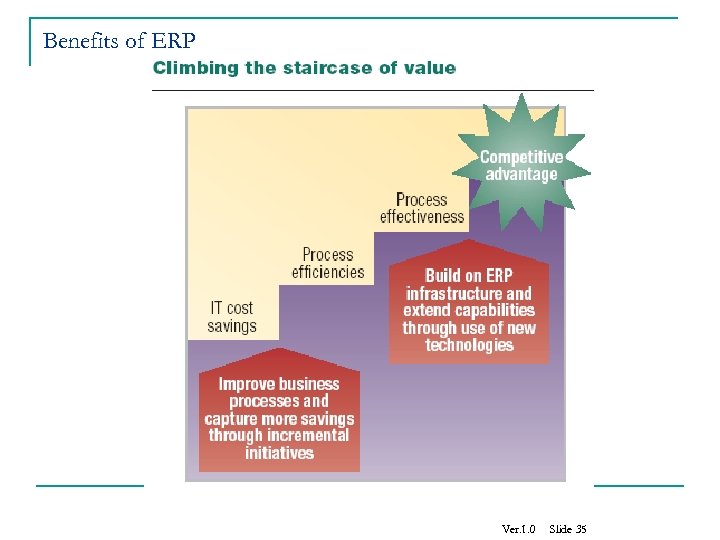 Benefits of ERP Ver. 1. 0 Slide 35
Benefits of ERP Ver. 1. 0 Slide 35
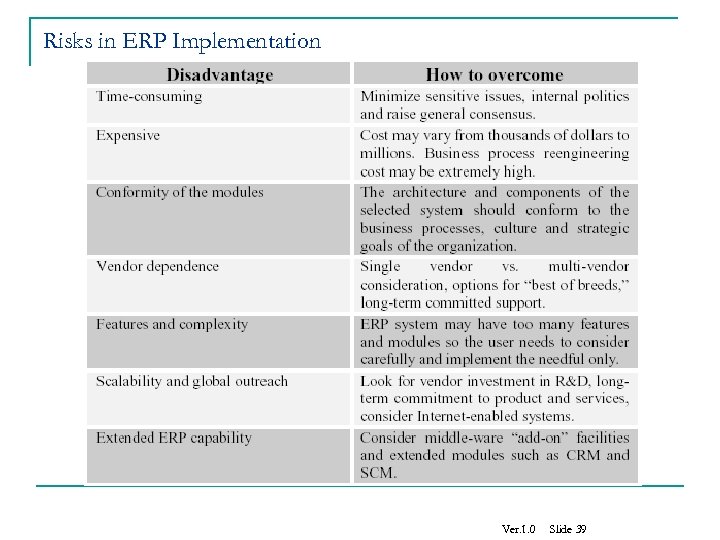
 Disadvantages of ERP n n ERP implementation is very difficult. There is a change in the way business is done. From a business function approach to a process approach. ERP systems are very expensive to implement. Can take years and cost 10’s of millions of dollars. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 36
Disadvantages of ERP n n ERP implementation is very difficult. There is a change in the way business is done. From a business function approach to a process approach. ERP systems are very expensive to implement. Can take years and cost 10’s of millions of dollars. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 36
 Disadvantages of ERP It takes time to realize the benefits of an ERP system. n Forces people to change and change = resistance: n q q q Share information that was once closely guarded (i. e. , “their information”). Make decisions they were never required to make. Do things they were never required to do before Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 37
Disadvantages of ERP It takes time to realize the benefits of an ERP system. n Forces people to change and change = resistance: n q q q Share information that was once closely guarded (i. e. , “their information”). Make decisions they were never required to make. Do things they were never required to do before Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 37
 Disadvantages of ERP n n n ERP systems are strategic solutions. In essence some companies are betting their future on a successful ERP implementation. If the implementation fails, the consequences to the company can be terrible. Companies have gone out of business as a result of a failed ERP implementation effort. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 38
Disadvantages of ERP n n n ERP systems are strategic solutions. In essence some companies are betting their future on a successful ERP implementation. If the implementation fails, the consequences to the company can be terrible. Companies have gone out of business as a result of a failed ERP implementation effort. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 38
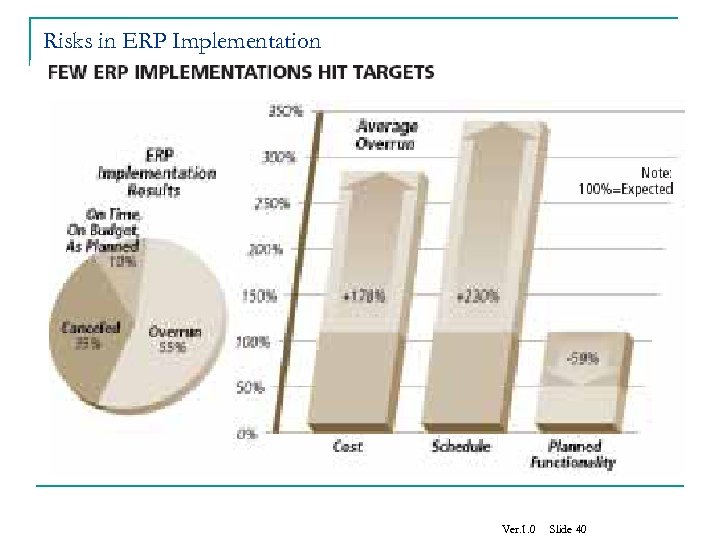
 Risks in ERP Implementation Ver. 1. 0 Slide 39
Risks in ERP Implementation Ver. 1. 0 Slide 39
 Risks in ERP Implementation Ver. 1. 0 Slide 40
Risks in ERP Implementation Ver. 1. 0 Slide 40
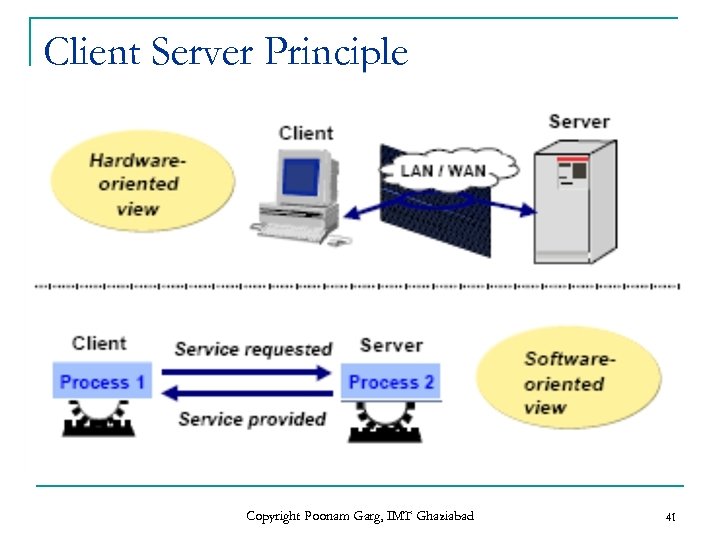 Client Server Principle Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 41
Client Server Principle Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 41
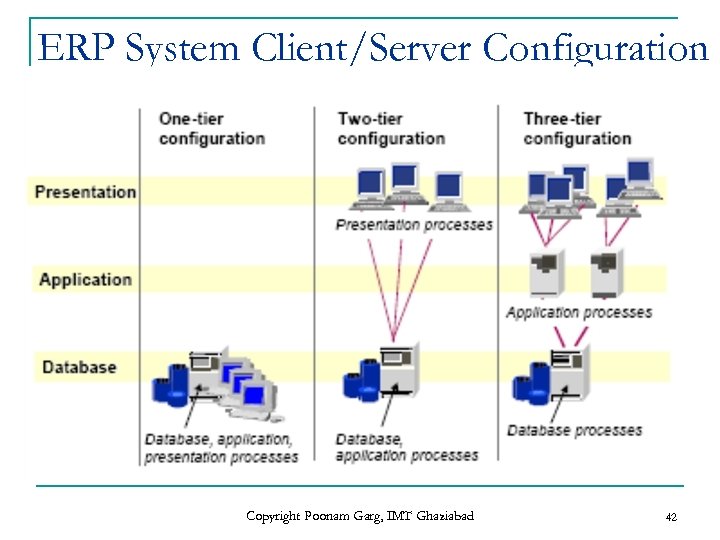 ERP System Client/Server Configuration Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 42
ERP System Client/Server Configuration Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 42
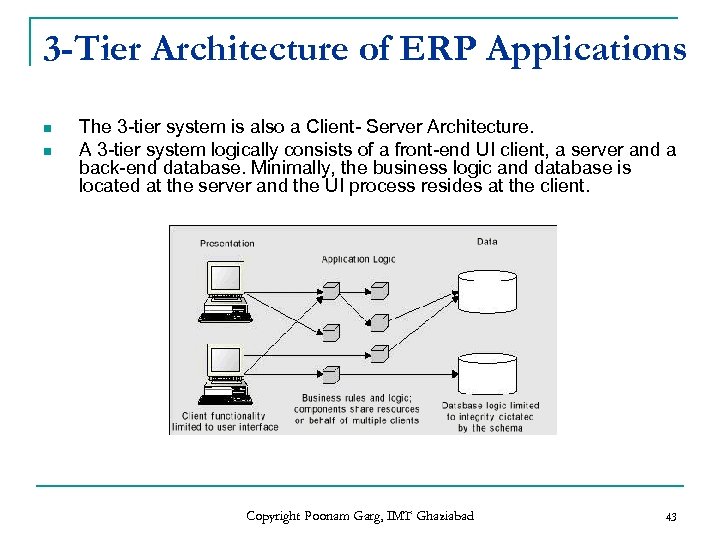 3 -Tier Architecture of ERP Applications n n The 3 -tier system is also a Client- Server Architecture. A 3 -tier system logically consists of a front-end UI client, a server and a back-end database. Minimally, the business logic and database is located at the server and the UI process resides at the client. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 43
3 -Tier Architecture of ERP Applications n n The 3 -tier system is also a Client- Server Architecture. A 3 -tier system logically consists of a front-end UI client, a server and a back-end database. Minimally, the business logic and database is located at the server and the UI process resides at the client. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 43
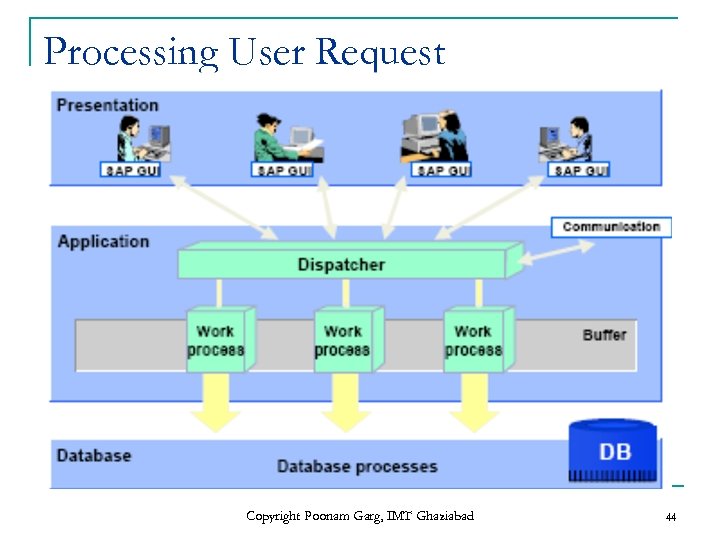 Processing User Request Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 44
Processing User Request Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 44
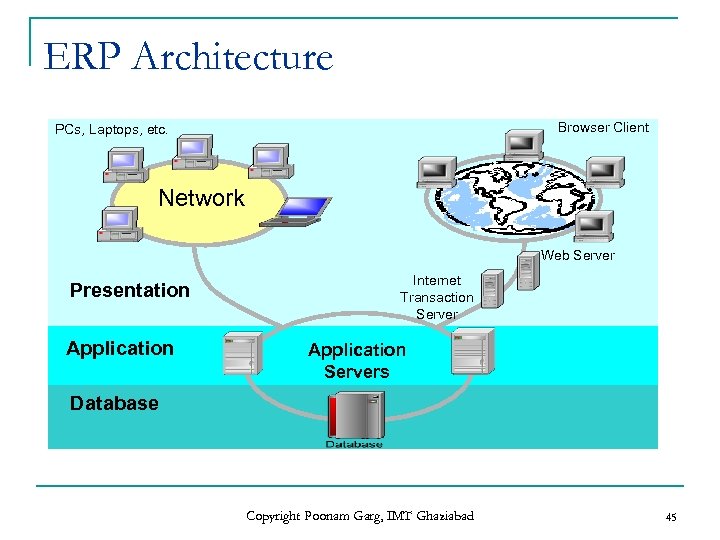 ERP Architecture Browser Client PCs, Laptops, etc. Network Web Server Presentation Application Internet Transaction Server Application Servers Database Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 45
ERP Architecture Browser Client PCs, Laptops, etc. Network Web Server Presentation Application Internet Transaction Server Application Servers Database Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 45
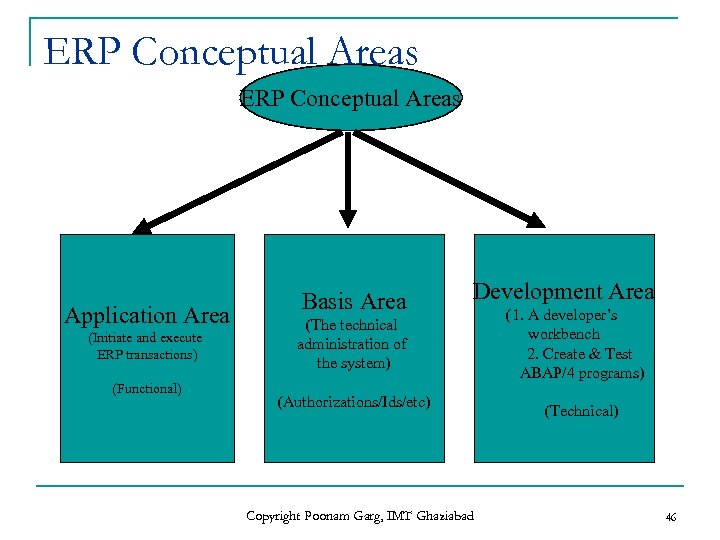 ERP Conceptual Areas Application Area (Initiate and execute ERP transactions) (Functional) Basis Area Development Area (The technical administration of the system) (Authorizations/Ids/etc) Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad (1. A developer’s workbench 2. Create & Test ABAP/4 programs) (Technical) 46
ERP Conceptual Areas Application Area (Initiate and execute ERP transactions) (Functional) Basis Area Development Area (The technical administration of the system) (Authorizations/Ids/etc) Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad (1. A developer’s workbench 2. Create & Test ABAP/4 programs) (Technical) 46
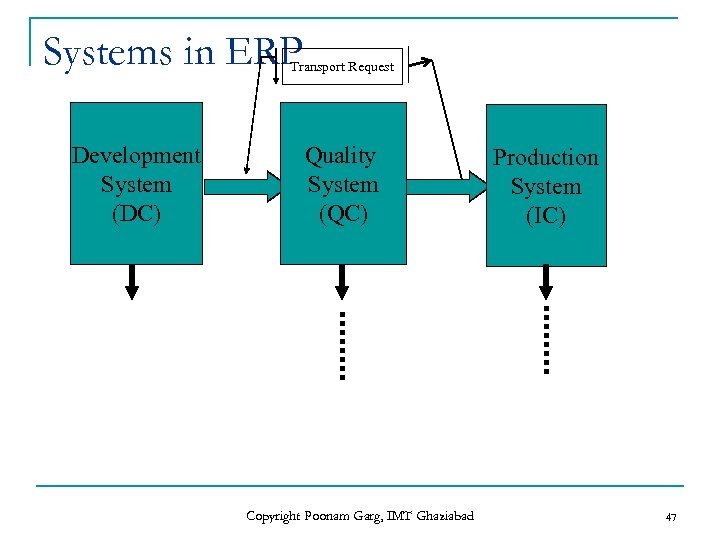 Systems in ERP Transport Request Development System (DC) Quality System (QC) Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad Production System (IC) 47
Systems in ERP Transport Request Development System (DC) Quality System (QC) Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad Production System (IC) 47
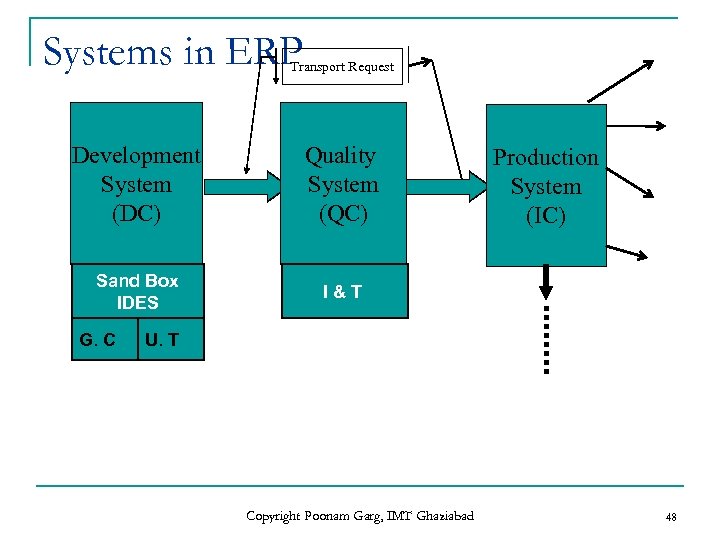 Systems in ERP Transport Request Development System (DC) Quality System (QC) Sand Box IDES I&T G. C Production System (IC) U. T Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 48
Systems in ERP Transport Request Development System (DC) Quality System (QC) Sand Box IDES I&T G. C Production System (IC) U. T Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 48
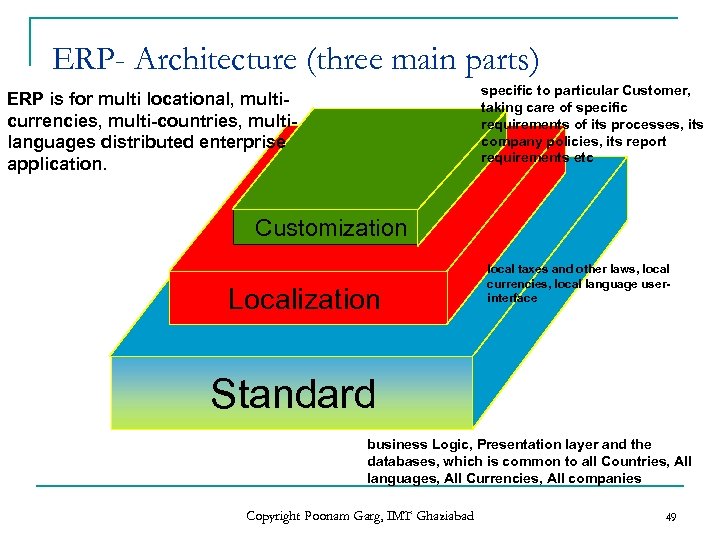 ERP- Architecture (three main parts) specific to particular Customer, taking care of specific requirements of its processes, its company policies, its report requirements etc ERP is for multi locational, multicurrencies, multi-countries, multilanguages distributed enterprise application. Customization Localization local taxes and other laws, local currencies, local language userinterface Standard business Logic, Presentation layer and the databases, which is common to all Countries, All languages, All Currencies, All companies Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 49
ERP- Architecture (three main parts) specific to particular Customer, taking care of specific requirements of its processes, its company policies, its report requirements etc ERP is for multi locational, multicurrencies, multi-countries, multilanguages distributed enterprise application. Customization Localization local taxes and other laws, local currencies, local language userinterface Standard business Logic, Presentation layer and the databases, which is common to all Countries, All languages, All Currencies, All companies Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 49
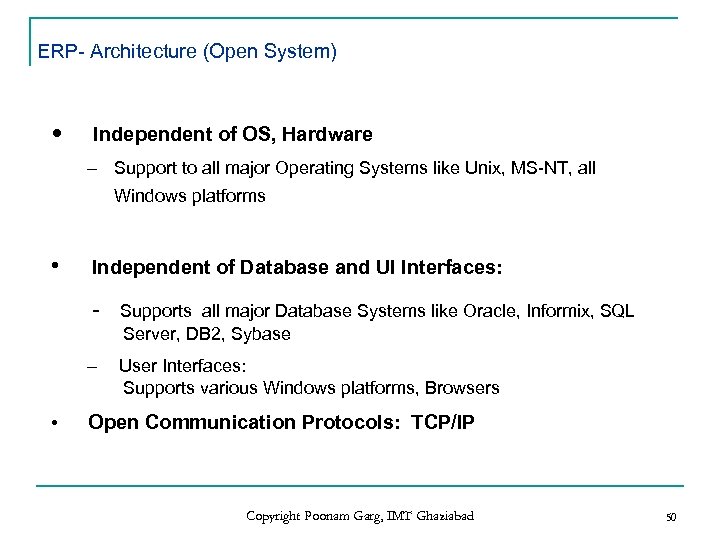 ERP- Architecture (Open System) • Independent of OS, Hardware – Support to all major Operating Systems like Unix, MS-NT, all Windows platforms • Independent of Database and UI Interfaces: – • Supports all major Database Systems like Oracle, Informix, SQL Server, DB 2, Sybase User Interfaces: Supports various Windows platforms, Browsers Open Communication Protocols: TCP/IP Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 50
ERP- Architecture (Open System) • Independent of OS, Hardware – Support to all major Operating Systems like Unix, MS-NT, all Windows platforms • Independent of Database and UI Interfaces: – • Supports all major Database Systems like Oracle, Informix, SQL Server, DB 2, Sybase User Interfaces: Supports various Windows platforms, Browsers Open Communication Protocols: TCP/IP Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 50
 Typical REQUIREMENTS with ERP Architecture n Performance: Good performance for processing and opening pages/ giving outputs. However it depends on UI design, S/W modularity, Inter-process communications etc n Distributed System - Different data/ Modules/ Transactions to be used at different locations - Disparate Operating Systems n Security - Data/ Processes for only authorized persons - Sensitive Business data security from outsiders Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 51
Typical REQUIREMENTS with ERP Architecture n Performance: Good performance for processing and opening pages/ giving outputs. However it depends on UI design, S/W modularity, Inter-process communications etc n Distributed System - Different data/ Modules/ Transactions to be used at different locations - Disparate Operating Systems n Security - Data/ Processes for only authorized persons - Sensitive Business data security from outsiders Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 51
 Typical REQUIREMENTS with ERP Architecture n Scalability: @ Larger volume of Data / larger no. of users @ Load balancing / Server Farm @ Multi-language Support n Flexibility @ Ease of Change/ Update/ Replace @ Integration to new Technologies (Bar Code/ RFID) n Maintainability @ Ease of decoding, debugging @ Normally supported by different vendors Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 52
Typical REQUIREMENTS with ERP Architecture n Scalability: @ Larger volume of Data / larger no. of users @ Load balancing / Server Farm @ Multi-language Support n Flexibility @ Ease of Change/ Update/ Replace @ Integration to new Technologies (Bar Code/ RFID) n Maintainability @ Ease of decoding, debugging @ Normally supported by different vendors Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 52
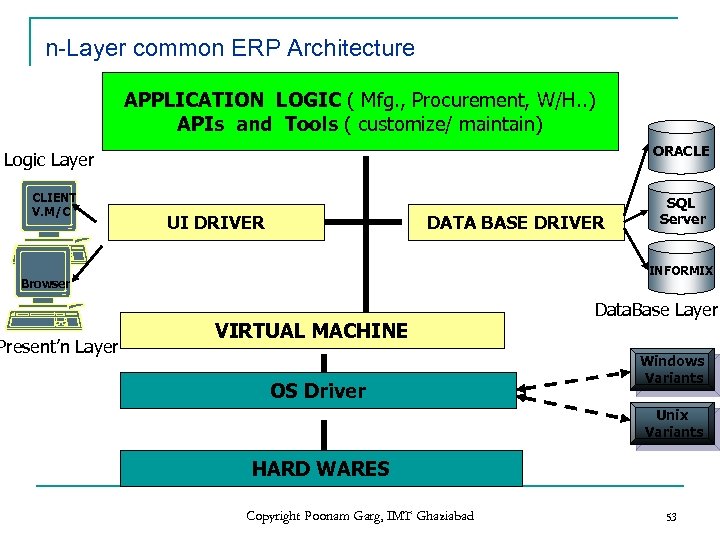 n-Layer common ERP Architecture APPLICATION LOGIC ( Mfg. , Procurement, W/H. . ) APIs and Tools ( customize/ maintain) ORACLE Logic Layer CLIENT V. M/C UI DRIVER DATA BASE DRIVER INFORMIX Browser Present’n Layer SQL Server VIRTUAL MACHINE OS Driver Data. Base Layer Windows Variants Unix Variants HARD WARES Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 53
n-Layer common ERP Architecture APPLICATION LOGIC ( Mfg. , Procurement, W/H. . ) APIs and Tools ( customize/ maintain) ORACLE Logic Layer CLIENT V. M/C UI DRIVER DATA BASE DRIVER INFORMIX Browser Present’n Layer SQL Server VIRTUAL MACHINE OS Driver Data. Base Layer Windows Variants Unix Variants HARD WARES Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 53
 1. OS Driver: Operating System Driver, is a program , which identifies from which OS the connection is made in the network (whether Unix, Windows like MS-NT and accordingly manages the interactions (input/ output etc) 2. Database Drivers: This is a program, which identifies from which database (Oracle 8 i/ 9 i or DB 2 or MS-SQL etc) the data is coming and accordingly manages the interactions including inputs/ outputs 3. UI Driver: User Interface Driver is a program which identifies from which User Interface (Client program on the Client machine, or browser etc) the interactions are taking place and accordingly manages the interactions including inputs/ outputs 4. Application Logic layer: This layer has the main business logic (depicting the functionalities of procurement, manufacturing, sales and delivery etc). This layer also has the Tools and APIs, which are to be used to make any modification, customization, maintenance of the application. 5. Virtual machine: this set of middleware program layer manages the package configuration, data dictionary, other layers of program, program workflow, transaction completion etc of the various processes. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 54
1. OS Driver: Operating System Driver, is a program , which identifies from which OS the connection is made in the network (whether Unix, Windows like MS-NT and accordingly manages the interactions (input/ output etc) 2. Database Drivers: This is a program, which identifies from which database (Oracle 8 i/ 9 i or DB 2 or MS-SQL etc) the data is coming and accordingly manages the interactions including inputs/ outputs 3. UI Driver: User Interface Driver is a program which identifies from which User Interface (Client program on the Client machine, or browser etc) the interactions are taking place and accordingly manages the interactions including inputs/ outputs 4. Application Logic layer: This layer has the main business logic (depicting the functionalities of procurement, manufacturing, sales and delivery etc). This layer also has the Tools and APIs, which are to be used to make any modification, customization, maintenance of the application. 5. Virtual machine: this set of middleware program layer manages the package configuration, data dictionary, other layers of program, program workflow, transaction completion etc of the various processes. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 54
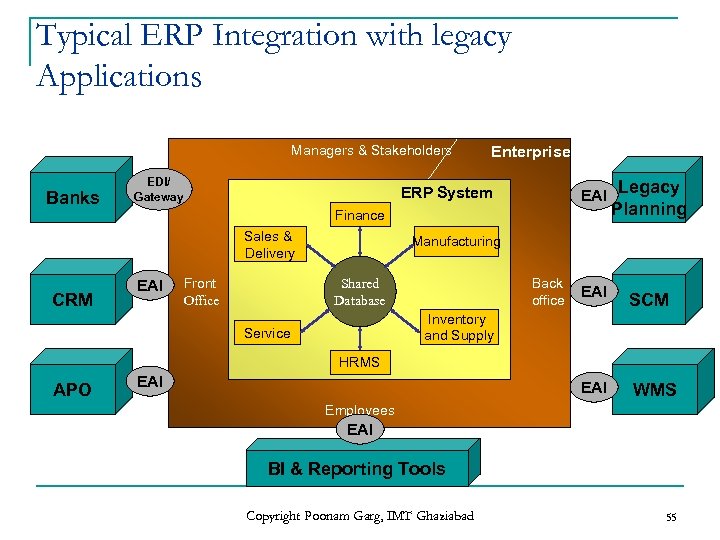 Typical ERP Integration with legacy Applications Managers & Stakeholders Banks EDI/ Gateway EAI Legacy ERP System Planning Finance Sales & Delivery CRM Enterprise EAI Manufacturing Shared Database Front Office Back office EAI SCM EAI WMS Inventory and Supply Service HRMS APO EAI Employees EAI BI & Reporting Tools Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 55
Typical ERP Integration with legacy Applications Managers & Stakeholders Banks EDI/ Gateway EAI Legacy ERP System Planning Finance Sales & Delivery CRM Enterprise EAI Manufacturing Shared Database Front Office Back office EAI SCM EAI WMS Inventory and Supply Service HRMS APO EAI Employees EAI BI & Reporting Tools Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 55
 Typical ERP Modules Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 56
Typical ERP Modules Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 56
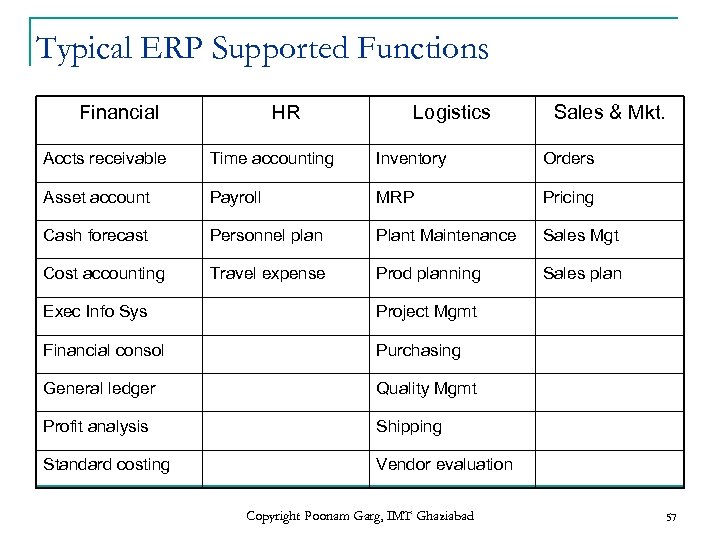 Typical ERP Supported Functions Financial HR Logistics Sales & Mkt. Accts receivable Time accounting Inventory Orders Asset account Payroll MRP Pricing Cash forecast Personnel plan Plant Maintenance Sales Mgt Cost accounting Travel expense Prod planning Sales plan Exec Info Sys Project Mgmt Financial consol Purchasing General ledger Quality Mgmt Profit analysis Shipping Standard costing Vendor evaluation Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 57
Typical ERP Supported Functions Financial HR Logistics Sales & Mkt. Accts receivable Time accounting Inventory Orders Asset account Payroll MRP Pricing Cash forecast Personnel plan Plant Maintenance Sales Mgt Cost accounting Travel expense Prod planning Sales plan Exec Info Sys Project Mgmt Financial consol Purchasing General ledger Quality Mgmt Profit analysis Shipping Standard costing Vendor evaluation Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 57
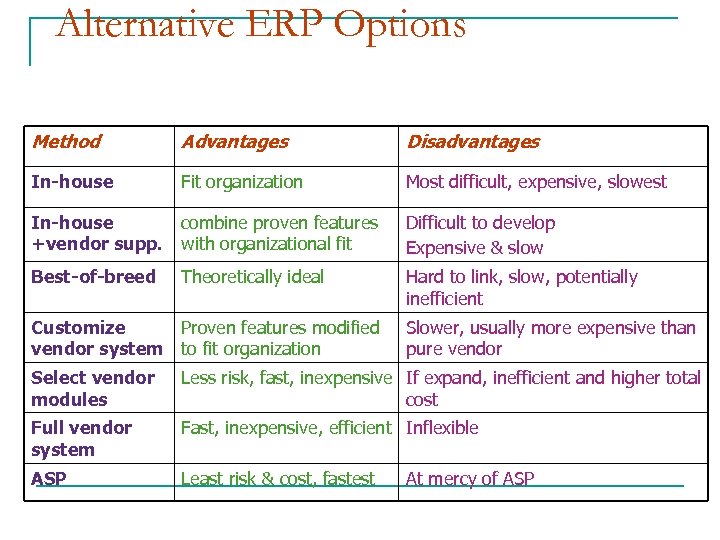 Alternative ERP Options Method Advantages Disadvantages In-house Fit organization Most difficult, expensive, slowest In-house +vendor supp. combine proven features with organizational fit Difficult to develop Expensive & slow Best-of-breed Theoretically ideal Hard to link, slow, potentially inefficient Customize Proven features modified vendor system to fit organization Slower, usually more expensive than pure vendor Select vendor modules Less risk, fast, inexpensive If expand, inefficient and higher total cost Full vendor system Fast, inexpensive, efficient Inflexible ASP Least risk & cost, fastest At mercy of ASP
Alternative ERP Options Method Advantages Disadvantages In-house Fit organization Most difficult, expensive, slowest In-house +vendor supp. combine proven features with organizational fit Difficult to develop Expensive & slow Best-of-breed Theoretically ideal Hard to link, slow, potentially inefficient Customize Proven features modified vendor system to fit organization Slower, usually more expensive than pure vendor Select vendor modules Less risk, fast, inexpensive If expand, inefficient and higher total cost Full vendor system Fast, inexpensive, efficient Inflexible ASP Least risk & cost, fastest At mercy of ASP
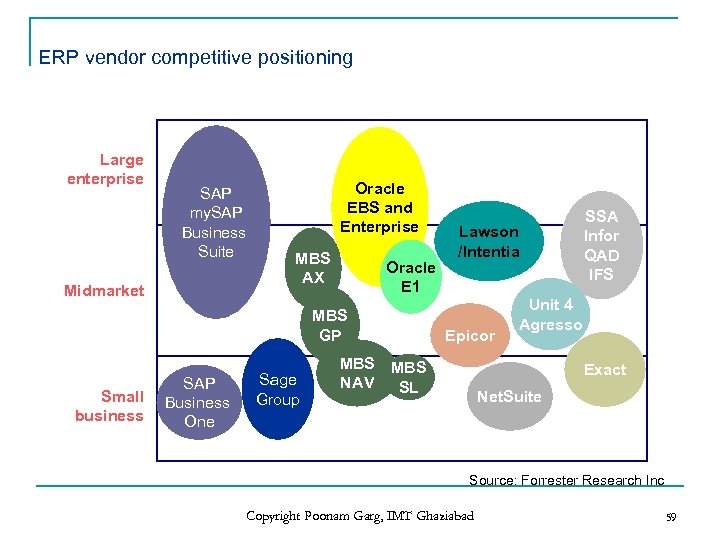 ERP vendor competitive positioning Large enterprise SAP my. SAP Business Suite Midmarket Oracle EBS and Enterprise MBS AX Oracle E 1 MBS GP Small business SAP Business One Sage Group Lawson /Intentia Epicor MBS NAV SL SSA Infor QAD IFS Unit 4 Agresso Exact Net. Suite Source: Forrester Research Inc Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 59
ERP vendor competitive positioning Large enterprise SAP my. SAP Business Suite Midmarket Oracle EBS and Enterprise MBS AX Oracle E 1 MBS GP Small business SAP Business One Sage Group Lawson /Intentia Epicor MBS NAV SL SSA Infor QAD IFS Unit 4 Agresso Exact Net. Suite Source: Forrester Research Inc Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 59
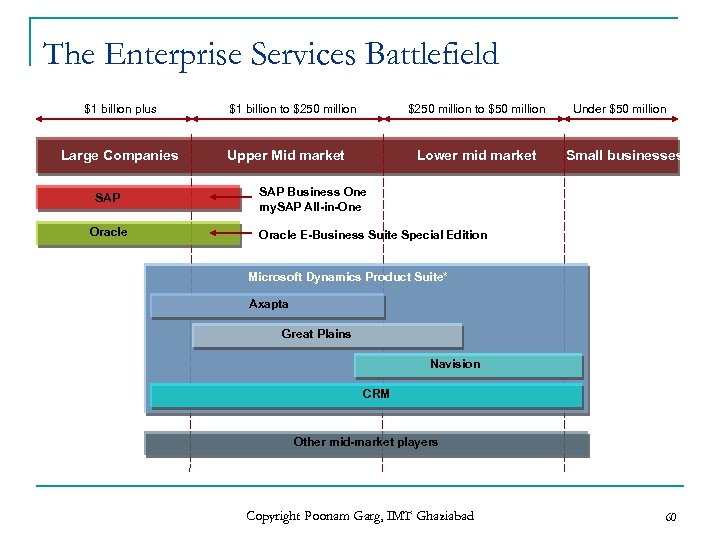 The Enterprise Services Battlefield $1 billion plus Large Companies SAP Oracle $1 billion to $250 million to $50 million Upper Mid market Lower mid market Under $50 million Small businesses SAP Business One my. SAP All-in-One Oracle E-Business Suite Special Edition Microsoft Dynamics Product Suite* Axapta Great Plains Navision CRM Other mid-market players Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 60
The Enterprise Services Battlefield $1 billion plus Large Companies SAP Oracle $1 billion to $250 million to $50 million Upper Mid market Lower mid market Under $50 million Small businesses SAP Business One my. SAP All-in-One Oracle E-Business Suite Special Edition Microsoft Dynamics Product Suite* Axapta Great Plains Navision CRM Other mid-market players Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 60
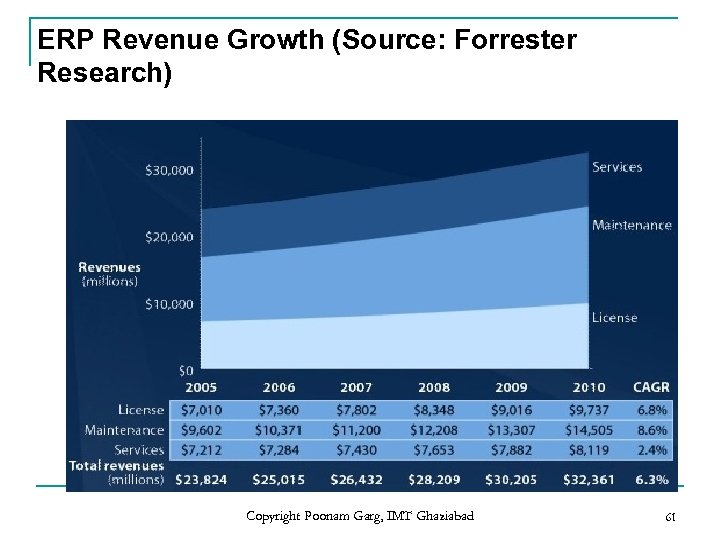 ERP Revenue Growth (Source: Forrester Research) Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 61
ERP Revenue Growth (Source: Forrester Research) Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 61
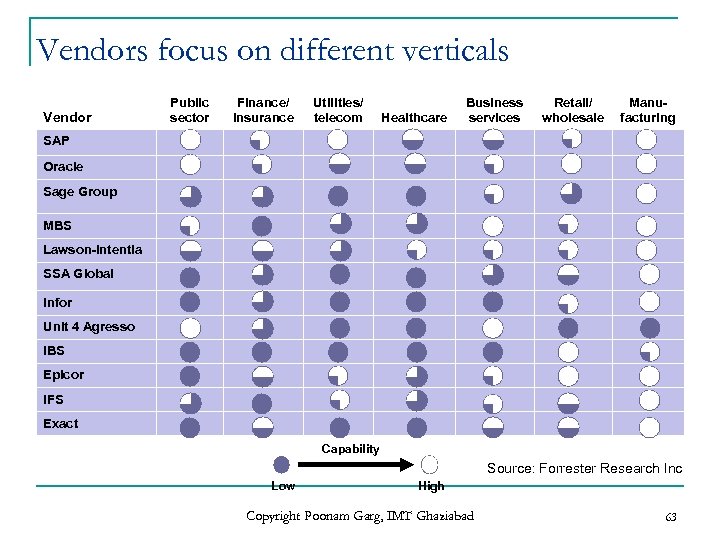 Vendors focus on different verticals Vendor Public sector Finance/ insurance Utilities/ telecom Healthcare Business services Retail/ wholesale Manufacturing SAP Oracle Sage Group MBS Lawson-Intentia SSA Global Infor Unit 4 Agresso IBS Epicor IFS Exact Capability Source: Forrester Research Inc Low High Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 63
Vendors focus on different verticals Vendor Public sector Finance/ insurance Utilities/ telecom Healthcare Business services Retail/ wholesale Manufacturing SAP Oracle Sage Group MBS Lawson-Intentia SSA Global Infor Unit 4 Agresso IBS Epicor IFS Exact Capability Source: Forrester Research Inc Low High Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 63
 ERP Vendors n n n There were five dominating ERP software suppliers: SAP, Oracle, People. Soft, Baan and J. D. Edwards. They controlled more than 60% of the multi- billion dollar global market. Each vendor had a specialty in one particular module area such as q q Baan in manufacturing, People. Soft in human resources management, SAP in logistics, and Oracle in financials ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 64 64
ERP Vendors n n n There were five dominating ERP software suppliers: SAP, Oracle, People. Soft, Baan and J. D. Edwards. They controlled more than 60% of the multi- billion dollar global market. Each vendor had a specialty in one particular module area such as q q Baan in manufacturing, People. Soft in human resources management, SAP in logistics, and Oracle in financials ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 64 64
 SAP AG n n n SAP AG (“Systeme, Anwendungen, und Produkte in Datenverarbeitung”), or Systems, Applications and Products in Data Processing In 1979, SAP launched SAP R/2, a mainframe-based ERP In 1992 SAP R/3 was launched based on client/server By 1999 SAP became third largest software vendor in the world and the largest in the ERP sector with a market share of about 36% serving over 17, 000 customers in over 100 countries. In 1999 SAP extended the ERP functions by adding CRM, SCM, sales-force automation and data warehousing. SAP’s Internet-enabled ERP solutions are provided by the recently launched ERP product called my. SAP. COM ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 65 65
SAP AG n n n SAP AG (“Systeme, Anwendungen, und Produkte in Datenverarbeitung”), or Systems, Applications and Products in Data Processing In 1979, SAP launched SAP R/2, a mainframe-based ERP In 1992 SAP R/3 was launched based on client/server By 1999 SAP became third largest software vendor in the world and the largest in the ERP sector with a market share of about 36% serving over 17, 000 customers in over 100 countries. In 1999 SAP extended the ERP functions by adding CRM, SCM, sales-force automation and data warehousing. SAP’s Internet-enabled ERP solutions are provided by the recently launched ERP product called my. SAP. COM ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 65 65
 Oracle Corporation n n founded in 1977 in the USA, is best-known for its database software and related applications and is the second largest software company in the world after Microsoft. second to SAP in the enterprise systems category with over 5, 000 customers in 140 countries. Oracles ERP system is known as Oracle Applications, having more than 50 different modules in six major categories: finance, accounts payable, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, projects and front office. Now taken over People. Soft and JD Edwards ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 66 66
Oracle Corporation n n founded in 1977 in the USA, is best-known for its database software and related applications and is the second largest software company in the world after Microsoft. second to SAP in the enterprise systems category with over 5, 000 customers in 140 countries. Oracles ERP system is known as Oracle Applications, having more than 50 different modules in six major categories: finance, accounts payable, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, projects and front office. Now taken over People. Soft and JD Edwards ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 66 66
 People. Soft Inc. n n Started in 1987 in California, with specialization in human resource management and financial services modules. Enterprise solutions from People. Soft include modules for manufacturing, materials management, distribution, finance, human resources and supply chain planning. One of the strengths of People. Soft is the recognition by its customers that it is flexible and collaborative In 2005 People. Soft became a part of Oracle offering People. Soft 9 ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 67 67
People. Soft Inc. n n Started in 1987 in California, with specialization in human resource management and financial services modules. Enterprise solutions from People. Soft include modules for manufacturing, materials management, distribution, finance, human resources and supply chain planning. One of the strengths of People. Soft is the recognition by its customers that it is flexible and collaborative In 2005 People. Soft became a part of Oracle offering People. Soft 9 ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 67 67
 J. D. Edwards n n founded in 1977 in Denver (cofounded by Jack Thompson, Dan Gregory and C. Edward Mc. Vaney) with long experience of supplying software for the AS/400 market. Its ERP product called One. World is “capable of running on multiple platforms and with multiple databases, . . . [and] revolutionizes enterprise software by liberating users from inflexible, static technologies The product includes modules for finance, manufacturing, distribution/logistics and human resources, quality management, maintenance management, data warehousing, customer support and after-sales service Now a part of Oracle offering JD Edwards Enterprise. One and JD Edwards World ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 68 68
J. D. Edwards n n founded in 1977 in Denver (cofounded by Jack Thompson, Dan Gregory and C. Edward Mc. Vaney) with long experience of supplying software for the AS/400 market. Its ERP product called One. World is “capable of running on multiple platforms and with multiple databases, . . . [and] revolutionizes enterprise software by liberating users from inflexible, static technologies The product includes modules for finance, manufacturing, distribution/logistics and human resources, quality management, maintenance management, data warehousing, customer support and after-sales service Now a part of Oracle offering JD Edwards Enterprise. One and JD Edwards World ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 68 68
 Baan n Found in 1978 with expertise in software for the manufacturing industry ERP solution areas that Baan covers include finance, procurement, manufacturing, distribution, integration and implementation, planning, sales, service and maintenance, business portals, collaborative commerce and business intelligence. Bought by Infor in 2006 ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 69 69
Baan n Found in 1978 with expertise in software for the manufacturing industry ERP solution areas that Baan covers include finance, procurement, manufacturing, distribution, integration and implementation, planning, sales, service and maintenance, business portals, collaborative commerce and business intelligence. Bought by Infor in 2006 ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 69 69
 Current Situation n n JD Edwards was merged with People. Soft Then People. Soft was merged with Oracle in 2005 Baan was bought by Invensys (in 2000), then SSA Global Technologies (in 2003) and changed the name to SSA ERP was acquired by Infor in 2006 Now 3 largest ERP companies: q q q SAP : logistics Oracle : financial, HRM Infor: manufacturing ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 70 70
Current Situation n n JD Edwards was merged with People. Soft Then People. Soft was merged with Oracle in 2005 Baan was bought by Invensys (in 2000), then SSA Global Technologies (in 2003) and changed the name to SSA ERP was acquired by Infor in 2006 Now 3 largest ERP companies: q q q SAP : logistics Oracle : financial, HRM Infor: manufacturing ITEC 6620 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 70 70
 ERP Product evaluation criteria
ERP Product evaluation criteria
 Tailor-made ERP solutions ERP Product evaluation criteria ü Functional fit with the company’s Business processes ü Degree of integration between the various components of the ERP systems ü flexibility and scalability ü complexity; user friendliness ü Reputation of the ERP product ü Quick implementation; shortened ROI period ü Ability to support multi site planning and control ü technology; client/server capabilities, database independence, security
Tailor-made ERP solutions ERP Product evaluation criteria ü Functional fit with the company’s Business processes ü Degree of integration between the various components of the ERP systems ü flexibility and scalability ü complexity; user friendliness ü Reputation of the ERP product ü Quick implementation; shortened ROI period ü Ability to support multi site planning and control ü technology; client/server capabilities, database independence, security
 ERP Product evaluation criteria ü ü ü Availability of regular updates availability of reference sites Total cost, including cost of license, training, implementation, maintenance, customization, and hardware requirement.
ERP Product evaluation criteria ü ü ü Availability of regular updates availability of reference sites Total cost, including cost of license, training, implementation, maintenance, customization, and hardware requirement.
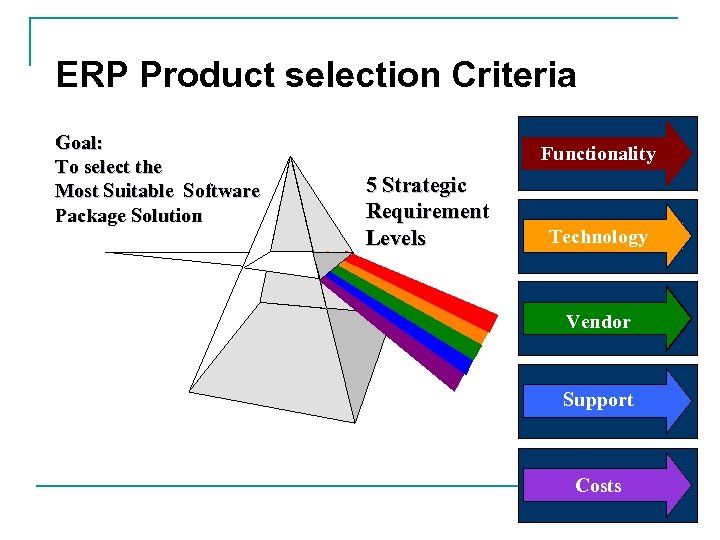 ERP Product selection Criteria Goal: To select the Most Suitable Software Package Solution Functionality 5 Strategic Requirement Levels Technology Vendor Support Costs
ERP Product selection Criteria Goal: To select the Most Suitable Software Package Solution Functionality 5 Strategic Requirement Levels Technology Vendor Support Costs
 Technology requirements/ Infrastructure n n n Assessment of existing systems during the pre-implementation planning Layout, configuration, setup and interoperability of hardware components Networking issues Ver. 1. 0 Slide 75
Technology requirements/ Infrastructure n n n Assessment of existing systems during the pre-implementation planning Layout, configuration, setup and interoperability of hardware components Networking issues Ver. 1. 0 Slide 75
 Pre requisites for effective ERP implementation n Business Process Reengineering (BPR) q A fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business processes to bring about dramatic improvements in performance – Michael Hammer Ver. 1. 0 Slide 76
Pre requisites for effective ERP implementation n Business Process Reengineering (BPR) q A fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business processes to bring about dramatic improvements in performance – Michael Hammer Ver. 1. 0 Slide 76
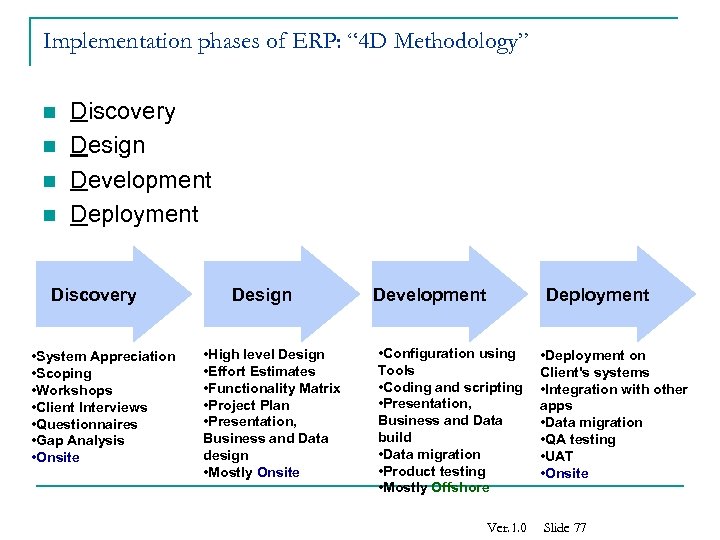 Implementation phases of ERP: “ 4 D Methodology” n n Discovery Design Development Deployment Discovery • System Appreciation • Scoping • Workshops • Client Interviews • Questionnaires • Gap Analysis • Onsite Design • High level Design • Effort Estimates • Functionality Matrix • Project Plan • Presentation, Business and Data design • Mostly Onsite Development Deployment • Configuration using Tools • Coding and scripting • Presentation, Business and Data build • Data migration • Product testing • Mostly Offshore Ver. 1. 0 • Deployment on Client's systems • Integration with other apps • Data migration • QA testing • UAT • Onsite Slide 77
Implementation phases of ERP: “ 4 D Methodology” n n Discovery Design Development Deployment Discovery • System Appreciation • Scoping • Workshops • Client Interviews • Questionnaires • Gap Analysis • Onsite Design • High level Design • Effort Estimates • Functionality Matrix • Project Plan • Presentation, Business and Data design • Mostly Onsite Development Deployment • Configuration using Tools • Coding and scripting • Presentation, Business and Data build • Data migration • Product testing • Mostly Offshore Ver. 1. 0 • Deployment on Client's systems • Integration with other apps • Data migration • QA testing • UAT • Onsite Slide 77
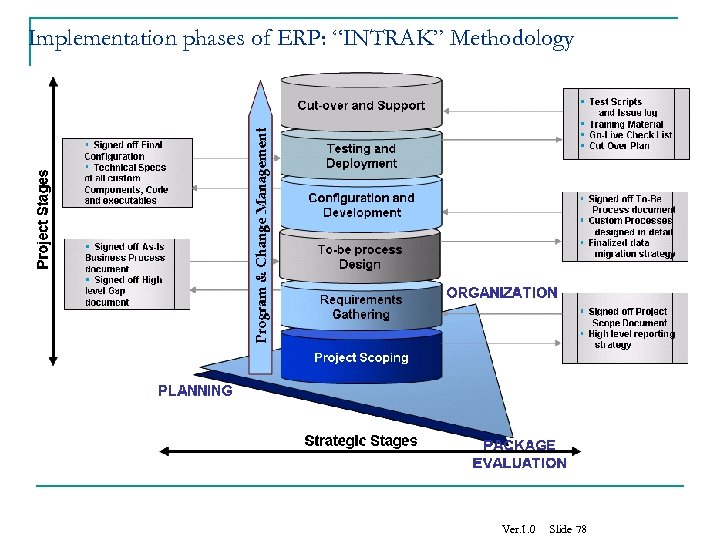 Implementation phases of ERP: “INTRAK” Methodology Ver. 1. 0 Slide 78
Implementation phases of ERP: “INTRAK” Methodology Ver. 1. 0 Slide 78
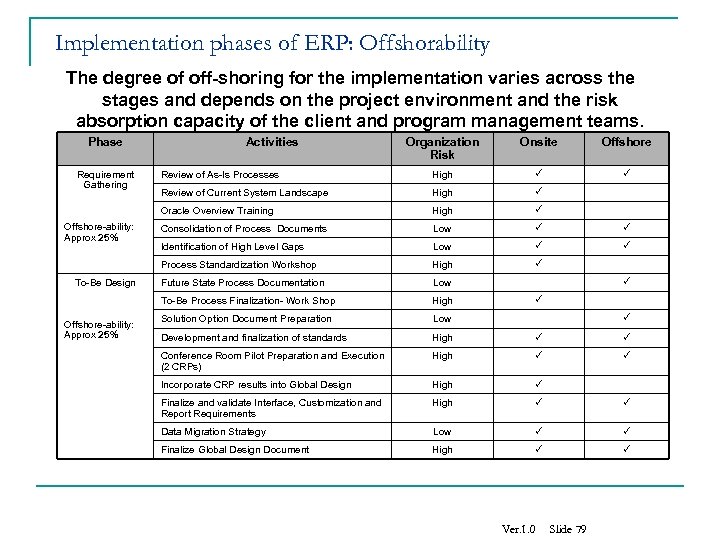 Implementation phases of ERP: Offshorability The degree of off-shoring for the implementation varies across the stages and depends on the project environment and the risk absorption capacity of the client and program management teams. Phase Offshore-ability: Approx 25% Offshore Review of As-Is Processes High Review of Current System Landscape High Consolidation of Process Documents Low Identification of High Level Gaps Low High Future State Process Documentation Low To-Be Process Finalization- Work Shop To-Be Design Onsite Process Standardization Workshop Offshore-ability: Approx 25% Organization Risk Oracle Overview Training Requirement Gathering Activities High Solution Option Document Preparation Low Development and finalization of standards High Conference Room Pilot Preparation and Execution (2 CRPs) High Incorporate CRP results into Global Design High Finalize and validate Interface, Customization and Report Requirements High Data Migration Strategy Low Finalize Global Design Document High Ver. 1. 0 Slide 79
Implementation phases of ERP: Offshorability The degree of off-shoring for the implementation varies across the stages and depends on the project environment and the risk absorption capacity of the client and program management teams. Phase Offshore-ability: Approx 25% Offshore Review of As-Is Processes High Review of Current System Landscape High Consolidation of Process Documents Low Identification of High Level Gaps Low High Future State Process Documentation Low To-Be Process Finalization- Work Shop To-Be Design Onsite Process Standardization Workshop Offshore-ability: Approx 25% Organization Risk Oracle Overview Training Requirement Gathering Activities High Solution Option Document Preparation Low Development and finalization of standards High Conference Room Pilot Preparation and Execution (2 CRPs) High Incorporate CRP results into Global Design High Finalize and validate Interface, Customization and Report Requirements High Data Migration Strategy Low Finalize Global Design Document High Ver. 1. 0 Slide 79
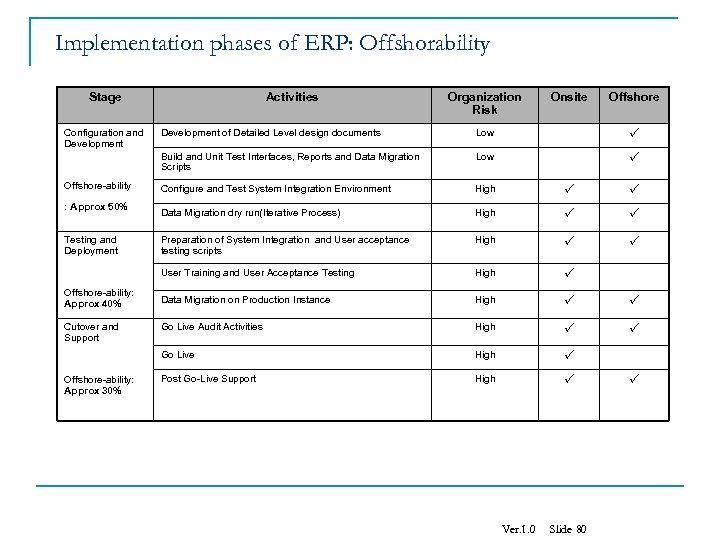 Implementation phases of ERP: Offshorability Stage Configuration and Development Activities Organization Risk Onsite Offshore-ability: Approx 40% Cutover and Support Offshore-ability: Approx 30% Low Configure and Test System Integration Environment High Data Migration dry run(Iterative Process) High Preparation of System Integration and User acceptance testing scripts High Data Migration on Production Instance High Go Live Audit Activities High Go Live Testing and Deployment User Training and User Acceptance Testing : Approx 50% Low Build and Unit Test Interfaces, Reports and Data Migration Scripts Offshore-ability Development of Detailed Level design documents High Post Go-Live Support High Ver. 1. 0 Slide 80
Implementation phases of ERP: Offshorability Stage Configuration and Development Activities Organization Risk Onsite Offshore-ability: Approx 40% Cutover and Support Offshore-ability: Approx 30% Low Configure and Test System Integration Environment High Data Migration dry run(Iterative Process) High Preparation of System Integration and User acceptance testing scripts High Data Migration on Production Instance High Go Live Audit Activities High Go Live Testing and Deployment User Training and User Acceptance Testing : Approx 50% Low Build and Unit Test Interfaces, Reports and Data Migration Scripts Offshore-ability Development of Detailed Level design documents High Post Go-Live Support High Ver. 1. 0 Slide 80
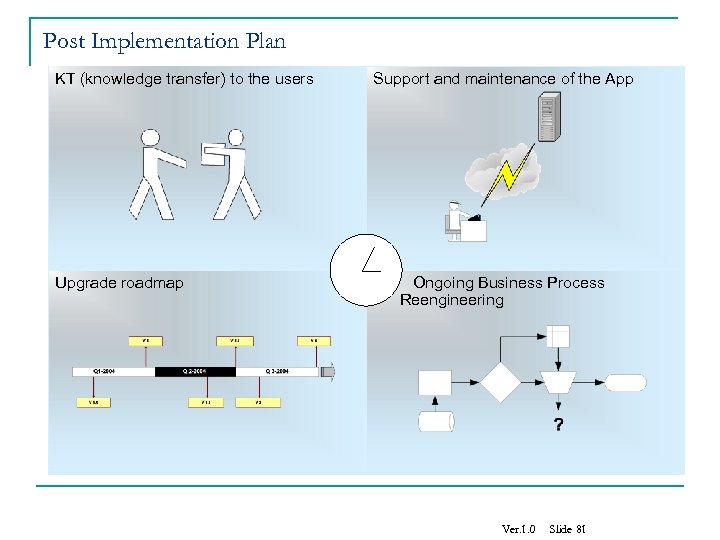 Post Implementation Plan KT (knowledge transfer) to the users Upgrade roadmap Support and maintenance of the App Ongoing Business Process Reengineering Ver. 1. 0 Slide 81
Post Implementation Plan KT (knowledge transfer) to the users Upgrade roadmap Support and maintenance of the App Ongoing Business Process Reengineering Ver. 1. 0 Slide 81
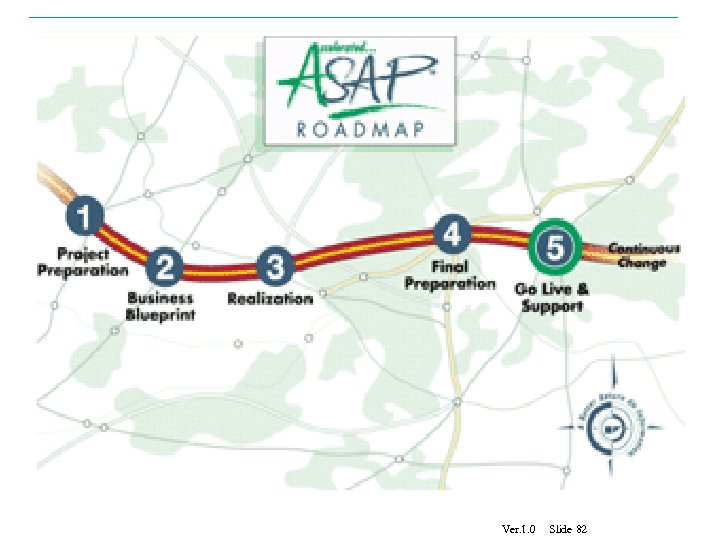 Ver. 1. 0 Slide 82
Ver. 1. 0 Slide 82
 1. Project Preparation, in which the project team is identified and mobilized, the project standards are defined, and the project work environment is set up; 2. Blueprint, in which the business processes are defined and the business blueprint document is designed; 3. Realization, in which the system is configured, knowledge transfer occurs, extensive unit testing is completed, and data mappings and data requirements for migration are defined; 4. Final Preparation, in which final integration testing, stress testing, and conversion testing are conducted, and all end users are trained; and 5. Go-Live and Support, in which the data is migrated from the legacy systems, the new system is activated, and postimplementation support is provided. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 83
1. Project Preparation, in which the project team is identified and mobilized, the project standards are defined, and the project work environment is set up; 2. Blueprint, in which the business processes are defined and the business blueprint document is designed; 3. Realization, in which the system is configured, knowledge transfer occurs, extensive unit testing is completed, and data mappings and data requirements for migration are defined; 4. Final Preparation, in which final integration testing, stress testing, and conversion testing are conducted, and all end users are trained; and 5. Go-Live and Support, in which the data is migrated from the legacy systems, the new system is activated, and postimplementation support is provided. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 83
 Benefits of ERP n Decreased cost q q n Reduced cycle times Optimum utilization of resources Increased Profit q q Better planning Business Intelligence Acquisition of customers thru integration with CRM n Channel management n Sales force automation Retention of customers n more share of wallet n Better service and quick response time Ver. 1. 0 Slide 84
Benefits of ERP n Decreased cost q q n Reduced cycle times Optimum utilization of resources Increased Profit q q Better planning Business Intelligence Acquisition of customers thru integration with CRM n Channel management n Sales force automation Retention of customers n more share of wallet n Better service and quick response time Ver. 1. 0 Slide 84
 Two Main ERP Applications Core applications n n n Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) transaction processing systems support the day-to-day operational activities of the business support mission-critical tasks through simple queries of operational databases include Sales and Distribution, Business Planning, Production Planning, Shop Floor Control, and Logistics modules Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 85
Two Main ERP Applications Core applications n n n Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) transaction processing systems support the day-to-day operational activities of the business support mission-critical tasks through simple queries of operational databases include Sales and Distribution, Business Planning, Production Planning, Shop Floor Control, and Logistics modules Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 85
 Two Main ERP Applications Business analysis applications n n Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) decision support tool for management-critical tasks through analytical investigation of complex data associations supplies management with “real-time” information and permits timely decisions to improve performance and achieve competitive advantage includes decision support, modeling, information retrieval, adhoc reporting/analysis. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 86
Two Main ERP Applications Business analysis applications n n Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) decision support tool for management-critical tasks through analytical investigation of complex data associations supplies management with “real-time” information and permits timely decisions to improve performance and achieve competitive advantage includes decision support, modeling, information retrieval, adhoc reporting/analysis. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 86
 OLAP n Supports management-critical tasks through analytical investigation of complex data q q q Consolidation is the aggregation or roll-up of data. Drill-down allows the user to see data in selective increasing levels of detail. Slicing and Dicing enables the user to examine data from different viewpoints often performed along a time axis to depict trends and patterns. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 87
OLAP n Supports management-critical tasks through analytical investigation of complex data q q q Consolidation is the aggregation or roll-up of data. Drill-down allows the user to see data in selective increasing levels of detail. Slicing and Dicing enables the user to examine data from different viewpoints often performed along a time axis to depict trends and patterns. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 87
 Colgate Case Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 88
Colgate Case Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 88
 Colgate Brief History n William Colgate established “Colgate” in 1806 n Mainly a starch, soap and candle business n Merger with Palmolive in 1928; Colgate. Palmolive-Peet n Corporate name changed to Colgate. Palmolive in 1956 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 89
Colgate Brief History n William Colgate established “Colgate” in 1806 n Mainly a starch, soap and candle business n Merger with Palmolive in 1928; Colgate. Palmolive-Peet n Corporate name changed to Colgate. Palmolive in 1956 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 89
 Colgate Brief History (cont) n Continuous growth n Today $9. 9 Billion company (2003) n Operations in more than 200 countries and territories n Colgate is now recognized as one of the leading manufacturers of oral care, dental care, household surface care, fabric care and pet nutrition products Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 90
Colgate Brief History (cont) n Continuous growth n Today $9. 9 Billion company (2003) n Operations in more than 200 countries and territories n Colgate is now recognized as one of the leading manufacturers of oral care, dental care, household surface care, fabric care and pet nutrition products Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 90
 Colgate n Divergence of operating platform q n Dozens of platforms Low IT skills/knowledge q No one understood all of the legacy systems n Each CIO for each country – very decentralized IS organization – no standards or best practices in place n No centralized operation n Decided to implement ERP software in 1999 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 91
Colgate n Divergence of operating platform q n Dozens of platforms Low IT skills/knowledge q No one understood all of the legacy systems n Each CIO for each country – very decentralized IS organization – no standards or best practices in place n No centralized operation n Decided to implement ERP software in 1999 Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 91
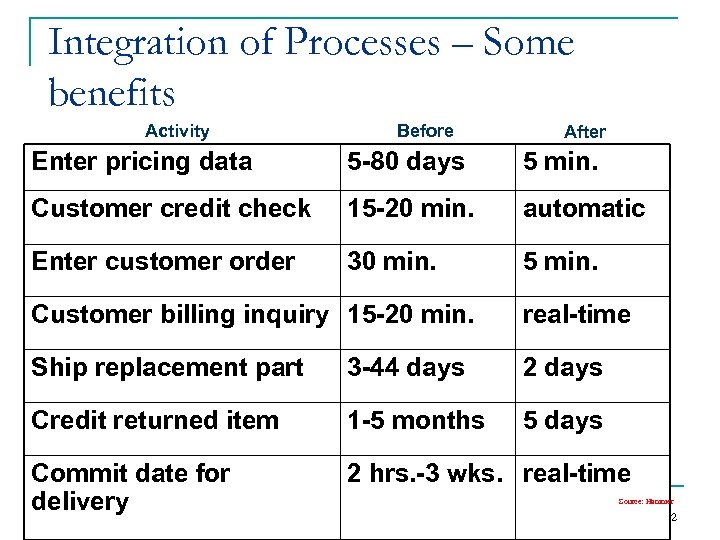 Integration of Processes – Some benefits Activity Before After Enter pricing data 5 -80 days 5 min. Customer credit check 15 -20 min. automatic Enter customer order 30 min. 5 min. Customer billing inquiry 15 -20 min. real-time Ship replacement part 3 -44 days 2 days Credit returned item 1 -5 months 5 days Commit date for delivery 2 hrs. -3 wks. real-time Source: Hammer Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 92
Integration of Processes – Some benefits Activity Before After Enter pricing data 5 -80 days 5 min. Customer credit check 15 -20 min. automatic Enter customer order 30 min. 5 min. Customer billing inquiry 15 -20 min. real-time Ship replacement part 3 -44 days 2 days Credit returned item 1 -5 months 5 days Commit date for delivery 2 hrs. -3 wks. real-time Source: Hammer Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 92
 Outcomes for Colgate n Availability of information in real time n Decision making made easy because of availability of accurate and up-todate data n Business process re-engineered and in some cases different departments consolidated into one n Improved efficiency: about 30% for the database applications and about 50% reduction in processing time Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 93
Outcomes for Colgate n Availability of information in real time n Decision making made easy because of availability of accurate and up-todate data n Business process re-engineered and in some cases different departments consolidated into one n Improved efficiency: about 30% for the database applications and about 50% reduction in processing time Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 93
 Outcomes for Colgate Cont’d n Colgate saved $225 million where as target was $125 million. n Datacenters shrinks to 1 (and one backup) from 75 n Inventory reduce by 10% n Facilitated move to e. Commerce. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 94
Outcomes for Colgate Cont’d n Colgate saved $225 million where as target was $125 million. n Datacenters shrinks to 1 (and one backup) from 75 n Inventory reduce by 10% n Facilitated move to e. Commerce. Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 94
 ERP in …. IMT ? n n Why do you think the IMT would want to implement an ERP system? What kinds of challenges would the IMT face in implementing an ERP system? Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 95
ERP in …. IMT ? n n Why do you think the IMT would want to implement an ERP system? What kinds of challenges would the IMT face in implementing an ERP system? Copyright Poonam Garg, IMT Ghaziabad 95


