9d03dce1d1087f266fdcc0fa12803f78.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Enterprise Project Management & PMO By Khurrum Ghori PMP, MCTS Microsoft EPM Technology Specialist (MCTS) Microsoft Certified Solution Architect (MCSD. NET) PMI Certified Project Management Professional (PMP)

AGENDA • • • Introduction The Emergence of the Enterprise View What is Enterprise Project Management? Enterprise Project Management as a Solution PMO (Project Management Office). PMO Goals & Responsibilities PMO Key Processes How to Setup & implement PMO EPM Solution- Microsoft Office Project 2007 family • Lessons Learned from Industry
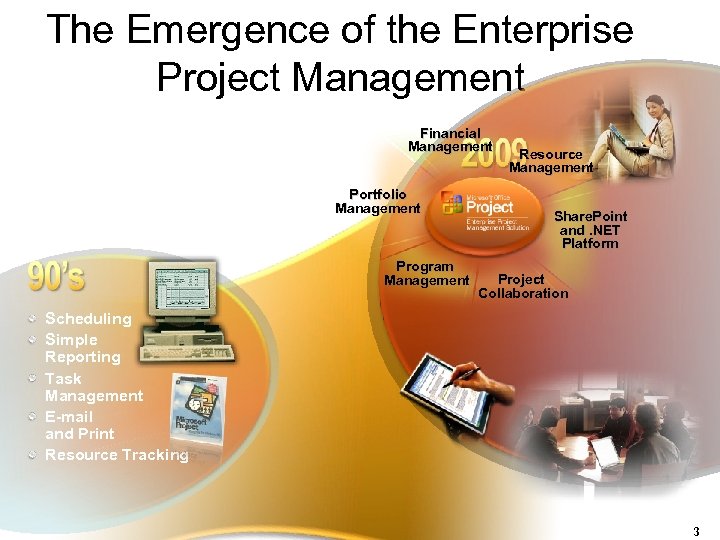
The Emergence of the Enterprise Project Management Financial Management Portfolio Management Program Management Resource Management Share. Point and. NET Platform Project Collaboration Scheduling Simple Reporting Task Management E-mail and Print Resource Tracking 3
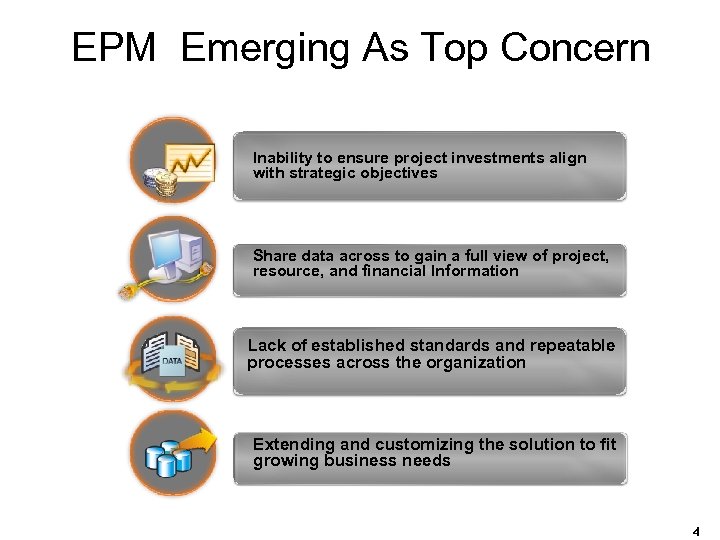
EPM Emerging As Top Concern Inability to ensure project investments align with strategic objectives Share data across to gain a full view of project, resource, and financial Information Lack of established standards and repeatable processes across the organization Extending and customizing the solution to fit growing business needs 4
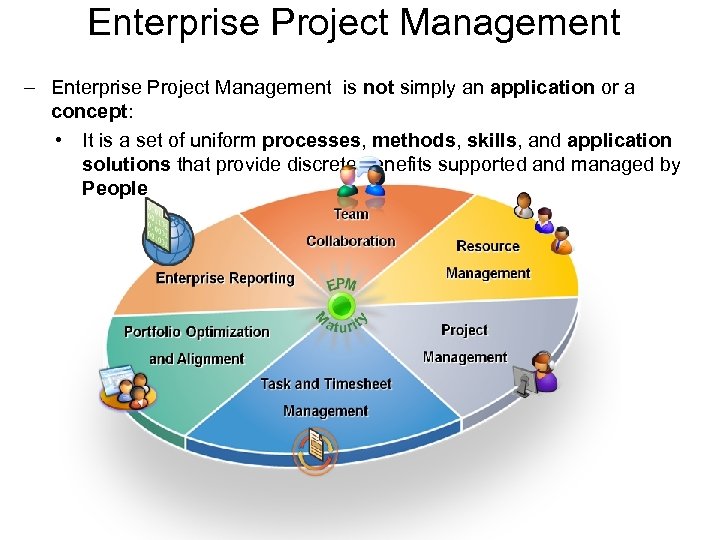
Enterprise Project Management – Enterprise Project Management is not simply an application or a concept: • It is a set of uniform processes, methods, skills, and application solutions that provide discrete benefits supported and managed by People
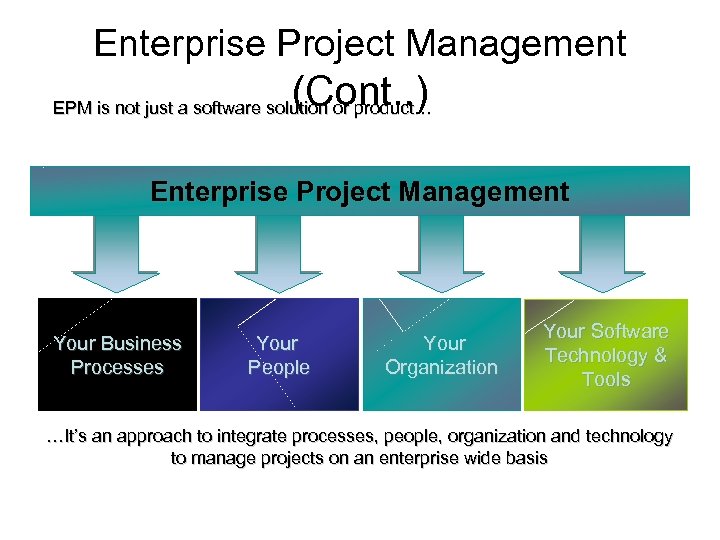
Enterprise Project Management (Cont. . ) EPM is not just a software solution or product… Enterprise Project Management Your Business Processes Your People Your Organization Your Software Technology & Tools …It’s an approach to integrate processes, people, organization and technology to manage projects on an enterprise wide basis

In Short… Enterprise Project Management is a discipline of getting the right information; to the right people; at the right time. This matters as the information provided affects the short and long-term strategic plans for the organization (enterprise)

So, How do you Begin? “The development & implementation of Enterprise Project Management (EPM) Solution in your Organization is a Journey… not simply a Destination”

The Journey…. People/0 rganizational Change Management and Concepts of how you will implement & Integrate EPM Solution into your organization is fundamental to success Most importantly – You have to align People, Process, and Tools into a seamless and homogenous solution The Tools should compliment the Process The Process should compliment the Tools The Tools and Process need to support the People You can reach your Destination in this journey through Strong Project Management Office (PMO)

What is a PMO? A Project Management Office (PMO) is an organizational unit designed to coordinate the management of projects within its domain. (PMBOK-3 rd Edition P-17) It may be called a: • Project Management Office • Project Support Office • Program Management Office • Project Management Group • Project Management Center of Excellence • Directorate of Project Management The PMO strives to standardize and introduce repeatable project delivery process & and can be a source for documentation, guidance, and metrics on the practice of project management and execution.

PMO Goals & Responsibilities • Facilitate effective project management across all projects & programs • Project Management Mentoring, consulting & Coaching to Project Heads/Leads/teams across organization • Customized projects’ health Report for Management (e. g. project status & Progress report) • Software Process & Project Management Templates Development & Deployment across all organization • Collect, organize, and integrate project data for the entire organization. • Centralized Project documents repository for project collaboration. • Analyze, develop and implement new process as required for departments improvement • Monitoring, controlling, Audits (e. g. process, risk, quality) & Tool Selection • Support Program management & Portfolio management

Why introduce PMO? Some typical issues • Projects are not effectively prioritised • Limited understanding of resource capacity • Projects happen without authorisation • Lack of control of project Schedule • No definitive list of project’s tasks • Project risks are not captured and mitigated • Project benefits are not managed or realised • Inconsistent approaches • No visibility of progress • Minimal control of project documentation
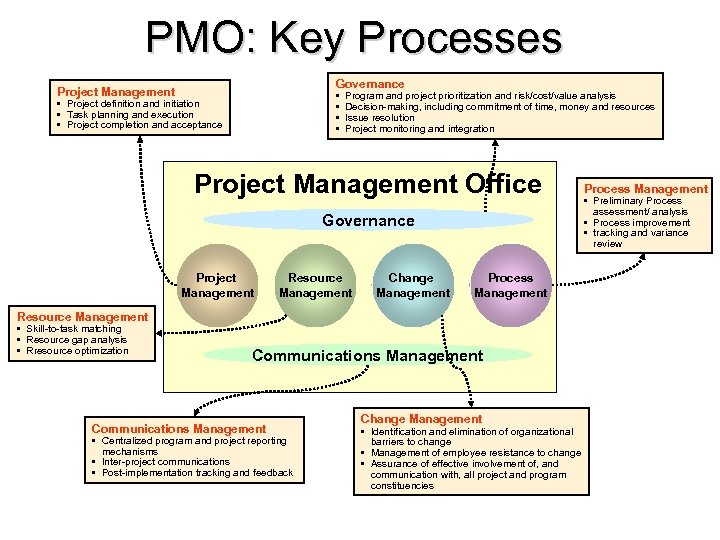
PMO: Key Processes Governance Project Management • • • Project definition and initiation • Task planning and execution • Project completion and acceptance Program and project prioritization and risk/cost/value analysis Decision-making, including commitment of time, money and resources Issue resolution Project monitoring and integration Project Management Office Governance Project Management Resource Management Change Management Process Management Resource Management • Skill-to-task matching • Resource gap analysis • Rresource optimization Communications Management • Centralized program and project reporting mechanisms • Inter-project communications • Post-implementation tracking and feedback Change Management • Identification and elimination of organizational barriers to change • Management of employee resistance to change • Assurance of effective involvement of, and communication with, all project and program constituencies Process Management • Preliminary Process assessment/ analysis • Process improvement • tracking and variance review
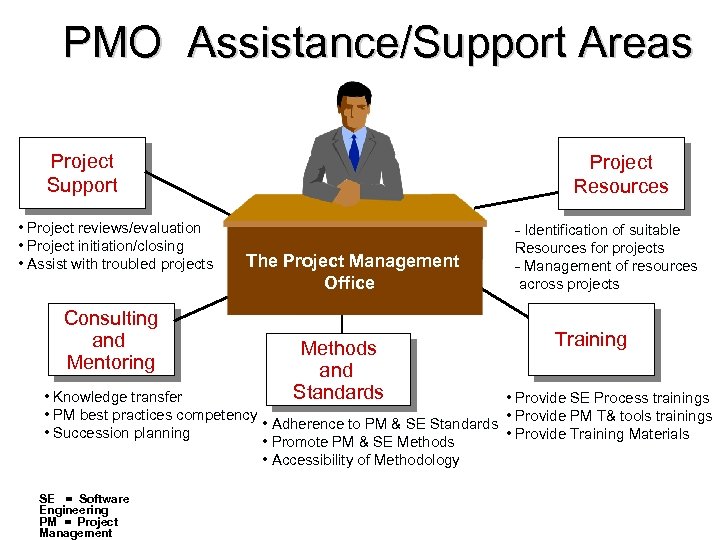
PMO Assistance/Support Areas Project Support • Project reviews/evaluation • Project initiation/closing • Assist with troubled projects Consulting and Mentoring Project Resources The Project Management Office Methods and Standards - Identification of suitable Resources for projects - Management of resources across projects Training • Knowledge transfer • Provide SE Process trainings • PM best practices competency • Provide PM T& tools trainings • Adherence to PM & SE Standards • Succession planning • Provide Training Materials • Promote PM & SE Methods • Accessibility of Methodology SE = Software Engineering PM = Project Management

Types of PMO Early on in PMO history, the Gartner Group identified three PMO models as flourishing: Project Repository Model, Project Coach Model & Enterprise PMO Model There are Many types of PMO Models defined in various books but I PMO categorize in 3 types: • The Supportive/Reporting PMO (Project Management Office). This is the most common type of PMO. It doesn't control or direct projects. Instead it supports projects by offering training, mentoring, administration and reporting to the stakeholders. • The Controlling PMO (Project Management Office). Supportive services may not be enough to put projects back on track. By offering controlling services (such as project reviews, audits and assessments), the PMO can influence project delivery. • The Directive/Enterprise (Project Management Office). The least common, but sometimes most effective type of PMO, is one that directs projects.

your Organization? • If you're implementing a PMO (Project Management Office) for the first time, then the "Supportive/ Reporting" model is best. It helps you add value to projects by offering reporting, training and monitoring services, without taking on the responsibility for the projects themselves. • If you have an established PMO (Project Management Office) and you want to ensure that projects are independently assessed, then the "Controlling" model is best. You can directly influence the success of projects, as well as implement best practices, standards, and tools. • If your organization has a set of high risk projects & drives you business, then usually the "Directive/Enterprise" model is best.

Tools for PMO To set up and run a PMO (Project Management Office), you need three types of tools. Templates Provide your Project Managers with templates to help them complete project documents faster and more efficiently. Methodology Implement a Methodology for managing projects. The methodology helps guide your projects towards completion. Software Use EPM software for the day-to-day effective planning, tracking and reporting of projects. Right People Right Data

PMO Setup & Implementation Strategy

Five Steps to Set-up PMO 1 Nominate and Confirm PMO Team 2 Set-up PMO 3 1. Nominate and confirm PMO team: 4 Identify, nominate and obtain approval for the PMO leadership from senior management as identified in PMO organogram 2. Setup PMO: 4 Determine relevant stakeholders, participants and structure PMO appropriately 4 Communicate key interested officers’ required involvement and PMO expectations Prepare Tools, Processes & Templates 3. Prepare tools, processes and templates: 4 Prepare all required tools, processes and templates 4 Prepare project reporting, issue management, change management, and planning and communication management processes Develop PMO Master Plan 4. Develop PMO master plan: 4 Conduct interviews, meetings, and workshops with key interested stakeholders 4 Prioritize work initiatives and conduct high-level review of any dependencies, overlaps, and issues 4 Consolidate tentative work initiative project plans into a consolidated master plan 4 5 Conduct First PMO Session 5. Conduct first PMO session: 4 Conduct first basic PMO workshop, communicate timing and agenda of first PMO session to all stake holders 4 Discuss issues, dependencies, project plan recommendations, role of PM Going forward

Implementing a PMO: Basic Stages Assessment Definition Assess current environment: PMO Need Assessment, Current Projects Assessment, ROI and Cost Model Assessment Define Program Management Office (PMO): PMO Strategy and Mission Document Commitment Gain Executive Commitment to Build and Maintain PMO Initiation Initiate PMO Project: Governance Process, Business Case Development and Sign-off Plan PMO Implementation: PMO Manual, PMO Project Plan Sign-off Planning Build and Implement the PMO: Initiate Training, Support, PMO Processes to Client, Shutdown Hand-over Transition Close. Project: Plan, Review Execution / Control Transition / PMO Improvements PMO Maturity Level: Assessme & improvement
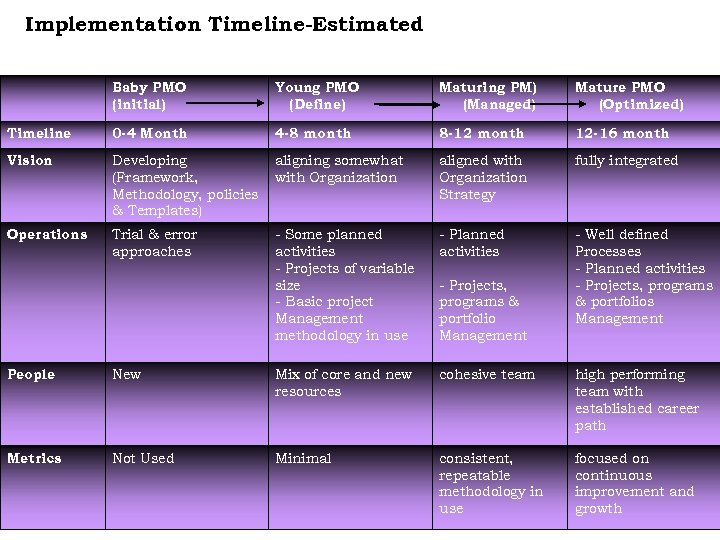
Implementation Timeline-Estimated Baby PMO (initial) Young PMO (Define) Maturing PM) (Managed) Mature PMO (Optimized) Timeline 0 -4 Month 4 -8 month 8 -12 month 12 -16 month Vision Developing (Framework, Methodology, policies & Templates) aligning somewhat with Organization aligned with Organization Strategy fully integrated Operations Trial & error approaches - Some planned activities - Projects of variable size - Basic project Management methodology in use - Planned activities - Well defined Processes - Planned activities - Projects, programs & portfolios Management - Projects, programs & portfolio Management People New Mix of core and new resources cohesive team high performing team with established career path Metrics Not Used Minimal consistent, repeatable methodology in use focused on continuous improvement and growth
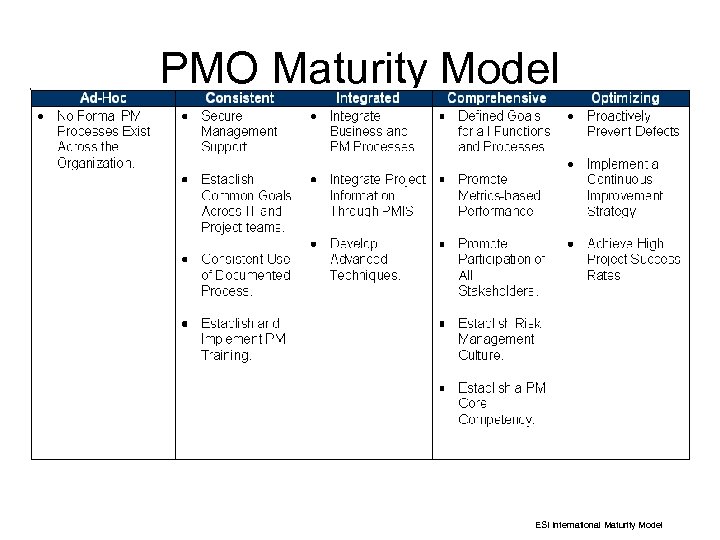
PMO Maturity Model Tactical Strategic ESI International Maturity Model
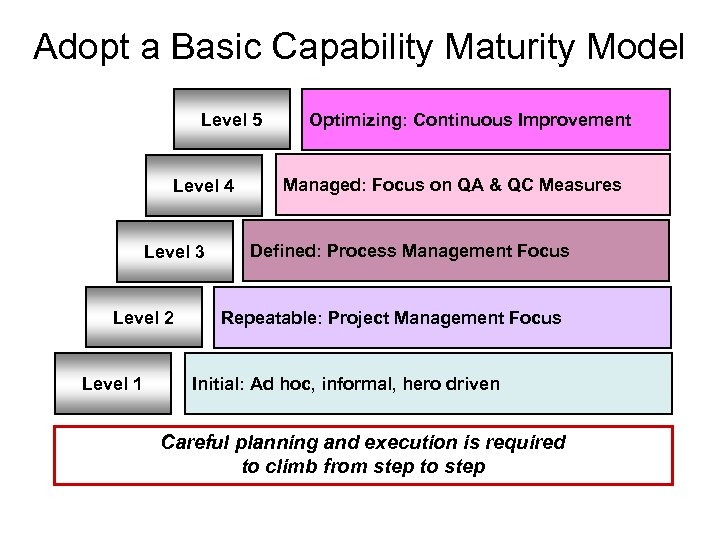
Adopt a Basic Capability Maturity Model Level 5 Level 4 Level 3 Level 2 Level 1 Optimizing: Continuous Improvement Managed: Focus on QA & QC Measures Defined: Process Management Focus Repeatable: Project Management Focus Initial: Ad hoc, informal, hero driven Careful planning and execution is required to climb from step to step

PMO Trend “The trend is rising within the IT function to create a PMO to drive an effective project management. By 2009, 60 percent of Global 2000 enterprises will adopt an enterprise portfolio management approach to strategically and tactically deliver business value, optimize all enterprise investments, and lay the groundwork for a technologically sophisticated business strategy. ” – META Group, 2005
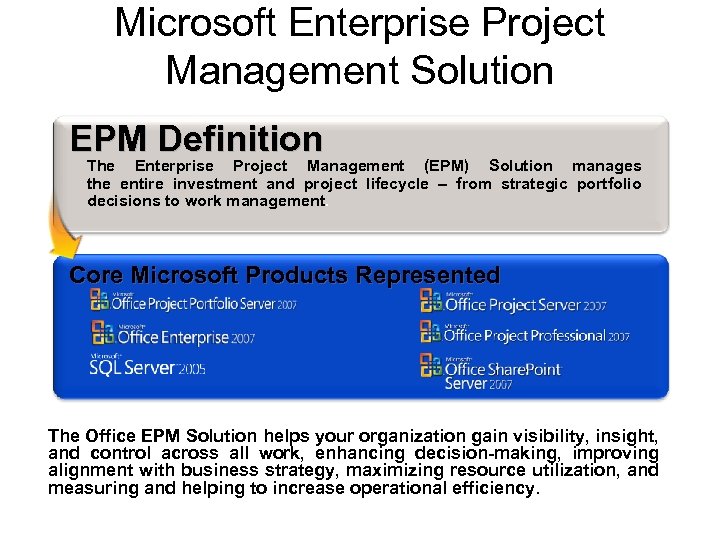
Microsoft Enterprise Project Management Solution EPM Definition The Enterprise Project Management (EPM) Solution manages the entire investment and project lifecycle – from strategic portfolio decisions to work management. Core Microsoft Products Represented The Office EPM Solution helps your organization gain visibility, insight, and control across all work, enhancing decision-making, improving alignment with business strategy, maximizing resource utilization, and measuring and helping to increase operational efficiency.
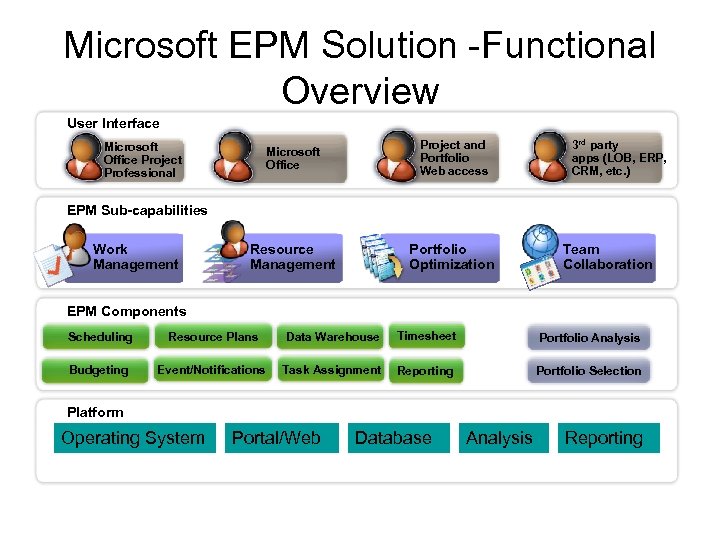
Microsoft EPM Solution -Functional Overview User Interface Microsoft Office Project and Portfolio Web access Resource Management Portfolio Optimization Microsoft Office Project Professional 3 rd party apps (LOB, ERP, CRM, etc. ) EPM Sub-capabilities Work Management Team Collaboration EPM Components Scheduling Resource Plans Data Warehouse Timesheet Portfolio Analysis Budgeting Event/Notifications Task Assignment Reporting Portfolio Selection Platform Operating System Portal/Web Database Analysis Reporting

Microsoft EPM Solution Technical Overview LOB: Frontend • ERP • CRM Project Portfolio Server Services Capabilities Scheduling Timesheet Portfolio Gov Resource Plans Event/Notifications Reporting Portfolio Selection Data Warehouse Platform Task Assignment Budgeting Security Capacity Planning
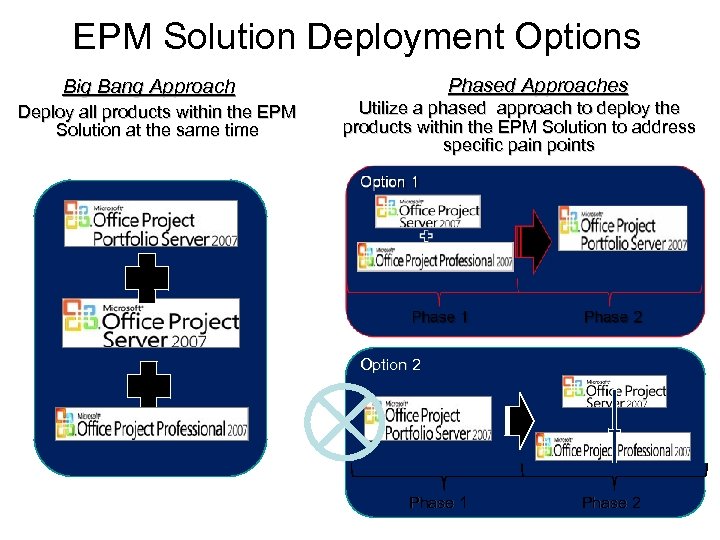
EPM Solution Deployment Options Phased Approaches Big Bang Approach Deploy all products within the EPM Solution at the same time Utilize a phased approach to deploy the products within the EPM Solution to address specific pain points Option 2 Phase 1 Phase 2

Successful PMO Using Microsoft EPM Solution Project Managers Senior Management Resource Managers Team Members

Benefits from EPM Solution? • • • Optimum Experience for Portfolio, Program, Project & Resource Managers Clearly Understand Responsibilities. Dashboard view of ownership Increase Visibility, better Control & accomplish More Effectively Participation- Collaborate with other project team members & Contribute to multiple projects Extensive reporting yielding better business insight Increases Business Awareness- Assure that projects align with overall business objectives Executives Project Managers Resource Managers Team Members IT Admins
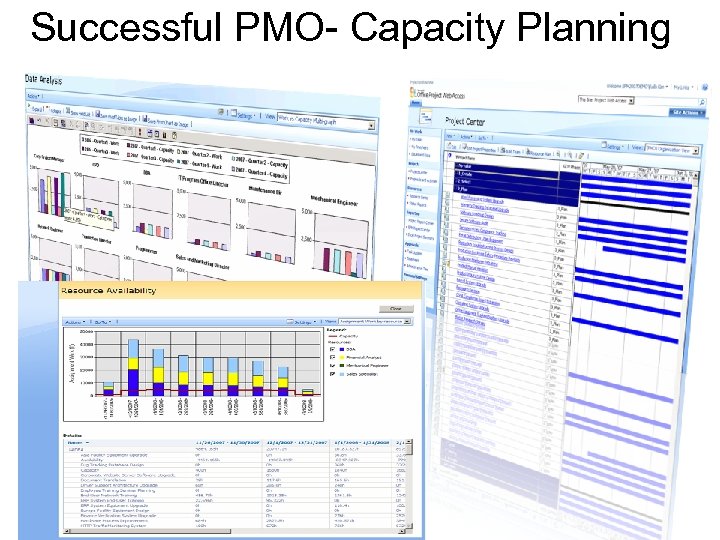
Successful PMO- Capacity Planning
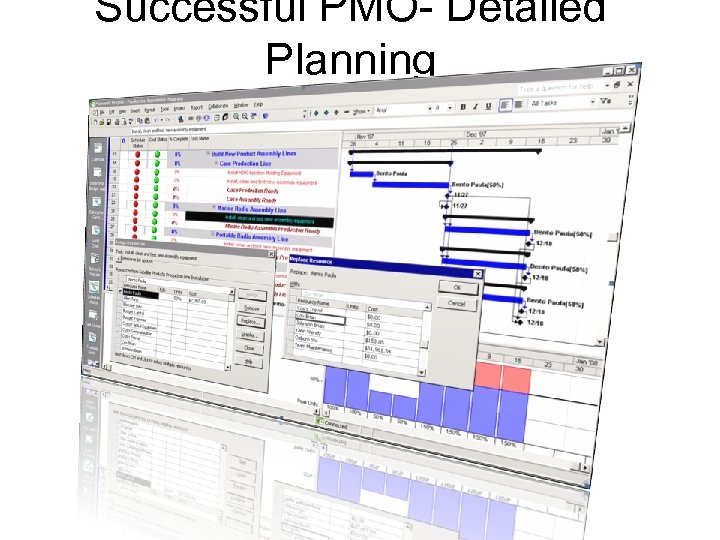
Successful PMO- Detailed Planning
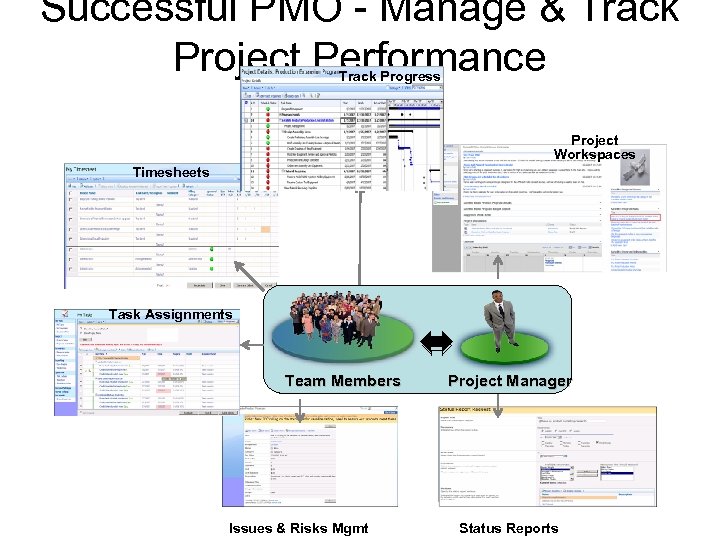
Successful PMO - Manage & Track Project Performance Track Progress Project Workspaces Timesheets Task Assignments Timesheets Team Members Issues & Risks Mgmt Project Manager Status Reports
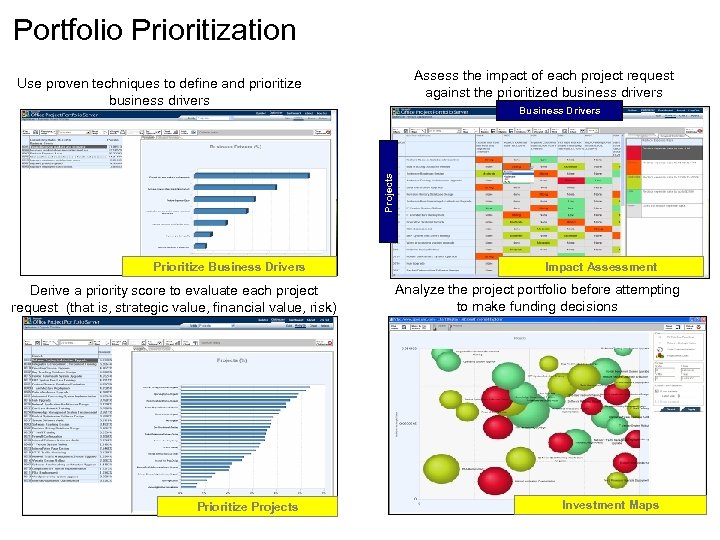
Portfolio Prioritization Assess the impact of each project request against the prioritized business drivers Use proven techniques to define and prioritize business drivers Projects Business Drivers Prioritize Business Drivers Derive a priority score to evaluate each project request (that is, strategic value, financial value, risk) Prioritize Projects Impact Assessment Analyze the project portfolio before attempting to make funding decisions Investment Maps
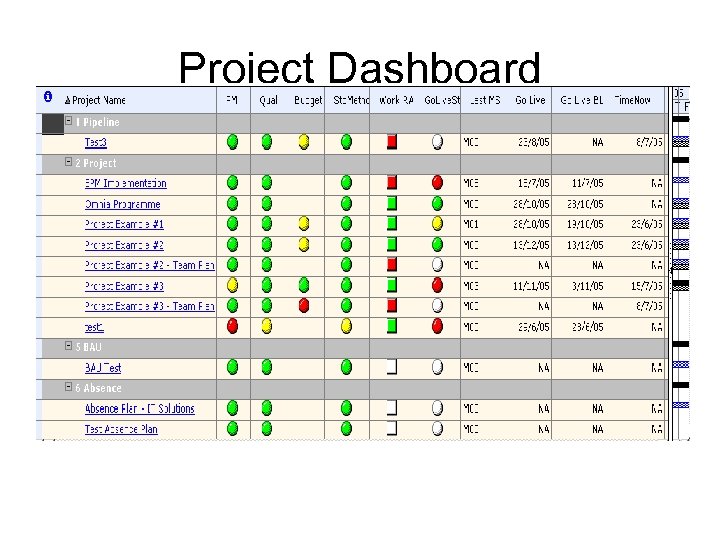
Project Dashboard

Lessons Learned from Industry Critical success factors in implementing a PMO Developing a Multidisciplinary & Focus team Actively engage your stakeholders & organization’s Executives. Develop a Strong Business Case for the EPM Initiative -Clear and complete business goals, requirements, and usage scenarios Focus on Groundwork/Up-Front Time Define PMO Structure - The Organizational Structure Can Facilitate or Hinder the “Project Culture” Effective & Continuous communication at all levels. Make your PMO Test Bench/Test Drive ready for testing & deployment before Installed in real environment Train the users at all Experience/usage Levels–Using Customized Instructions Fostering a project management culture Change Takes Patience & Perseverance Project Management is not for the Faint of Heart -The Project Management Role Requires True Leadership
9d03dce1d1087f266fdcc0fa12803f78.ppt