e144fb316dafdcfa4976f4e04a579d8e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Enterprise Logistics and Integration into Global Supply Networks Nimish Jhaveri CARANA Corporation Consultant World Bank Knowledge Economy Forum April 2007 1 a

Overview • The Relevance of Transport & Logistics • Challenges • Successes • Considerations 2
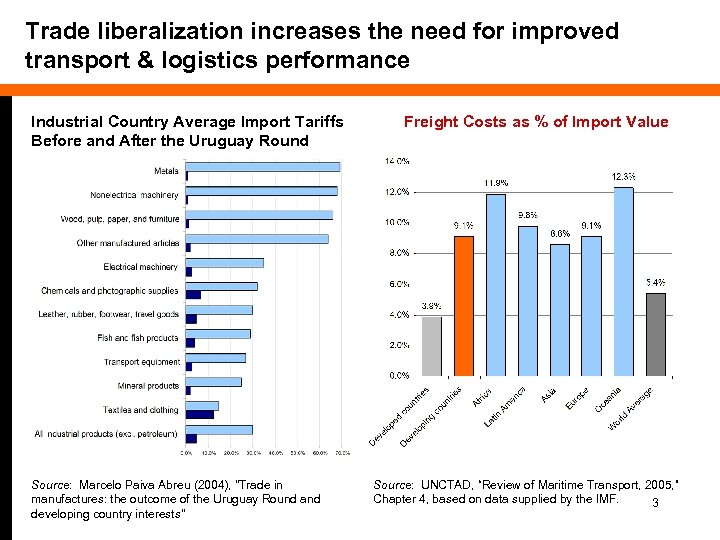
Trade liberalization increases the need for improved transport & logistics performance Industrial Country Average Import Tariffs Before and After the Uruguay Round Source: Marcelo Paiva Abreu (2004), "Trade in manufactures: the outcome of the Uruguay Round and developing country interests" Freight Costs as % of Import Value Source: UNCTAD, “Review of Maritime Transport, 2005, ” Chapter 4, based on data supplied by the IMF. 3
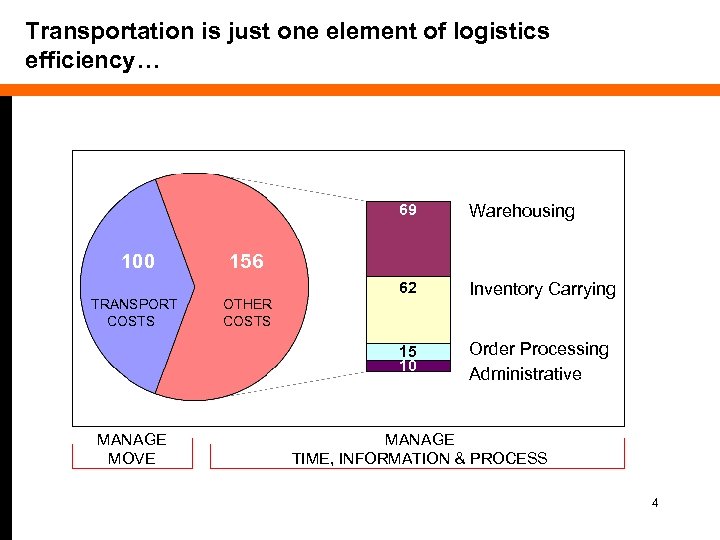
Transportation is just one element of logistics efficiency… 69 62 TRANSPORT COSTS MANAGE MOVE Inventory Carrying 15 10 100 Warehousing Order Processing Administrative 156 OTHER COSTS MANAGE TIME, INFORMATION & PROCESS 4
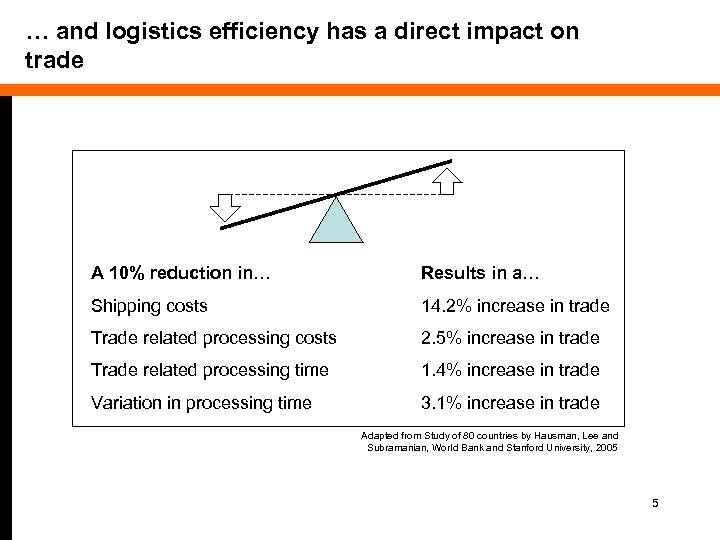
… and logistics efficiency has a direct impact on trade A 10% reduction in… Results in a… Shipping costs 14. 2% increase in trade Trade related processing costs 2. 5% increase in trade Trade related processing time 1. 4% increase in trade Variation in processing time 3. 1% increase in trade Adapted from Study of 80 countries by Hausman, Lee and Subramanian, World Bank and Stanford University, 2005 5
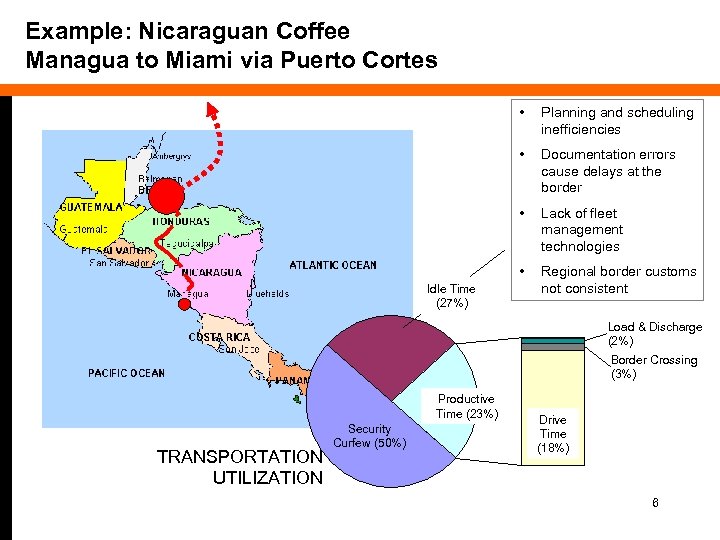
Example: Nicaraguan Coffee Managua to Miami via Puerto Cortes • • Documentation errors cause delays at the border • Lack of fleet management technologies • Idle Time (27%) Planning and scheduling inefficiencies Regional border customs not consistent Load & Discharge (2%) Border Crossing (3%) Productive Time (23%) TRANSPORTATION UTILIZATION Security Curfew (50%) Drive Time (18%) 6
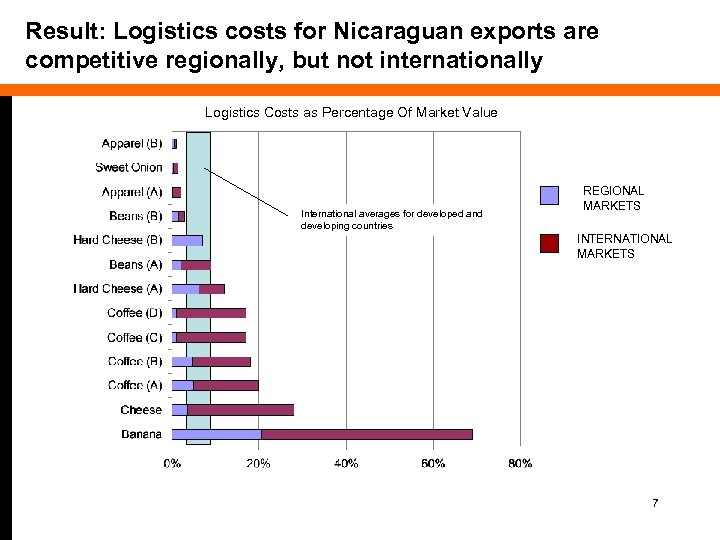
Result: Logistics costs for Nicaraguan exports are competitive regionally, but not internationally Logistics Costs as Percentage Of Market Value International averages for developed and developing countries REGIONAL MARKETS INTERNATIONAL MARKETS 7
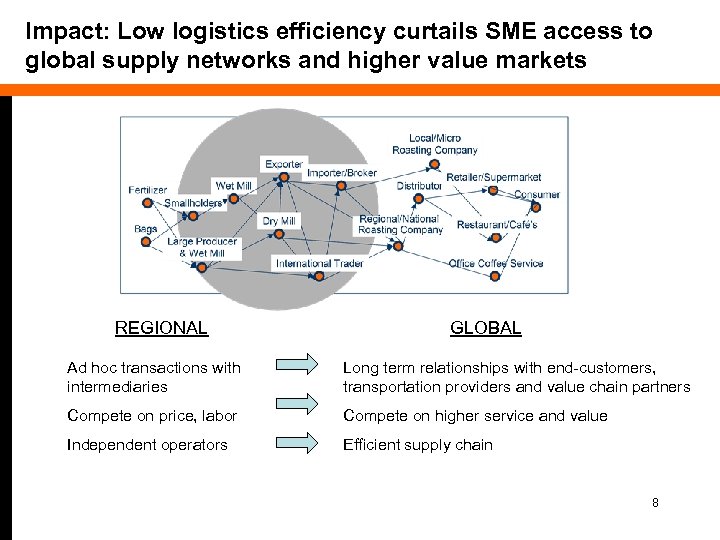
Impact: Low logistics efficiency curtails SME access to global supply networks and higher value markets REGIONAL GLOBAL Ad hoc transactions with intermediaries Long term relationships with end-customers, transportation providers and value chain partners Compete on price, labor Compete on higher service and value Independent operators Efficient supply chain 8
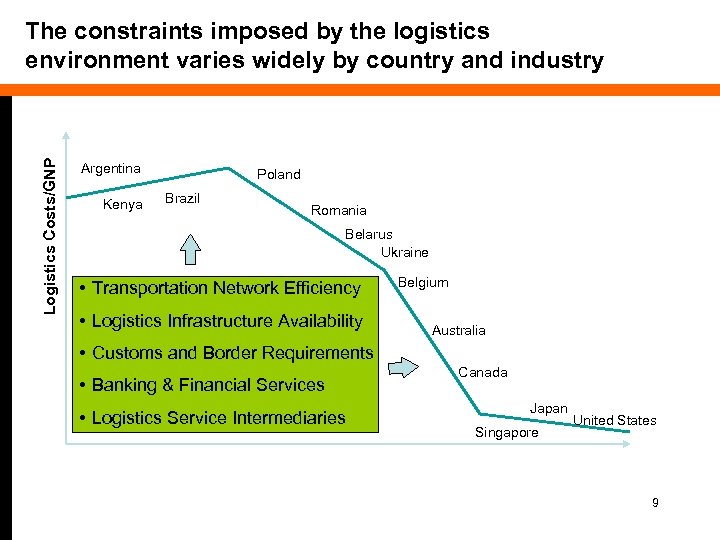
Logistics Costs/GNP The constraints imposed by the logistics environment varies widely by country and industry Argentina Kenya Poland Brazil Romania Belarus Ukraine • Transportation Network Efficiency • Logistics Infrastructure Availability Belgium Australia • Customs and Border Requirements • Banking & Financial Services • Logistics Service Intermediaries Canada Japan Singapore United States 9
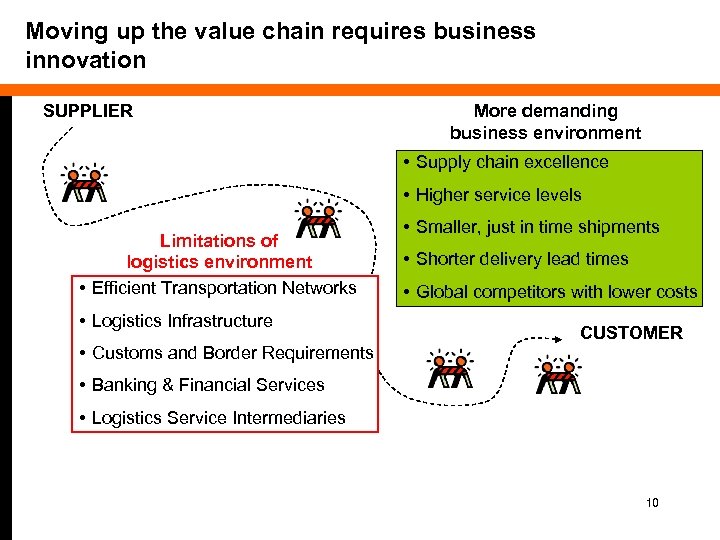
Moving up the value chain requires business innovation SUPPLIER More demanding business environment • Supply chain excellence • Higher service levels Limitations of logistics environment • Efficient Transportation Networks • Logistics Infrastructure • Customs and Border Requirements • Smaller, just in time shipments • Shorter delivery lead times • Global competitors with lower costs CUSTOMER • Banking & Financial Services • Logistics Service Intermediaries 10
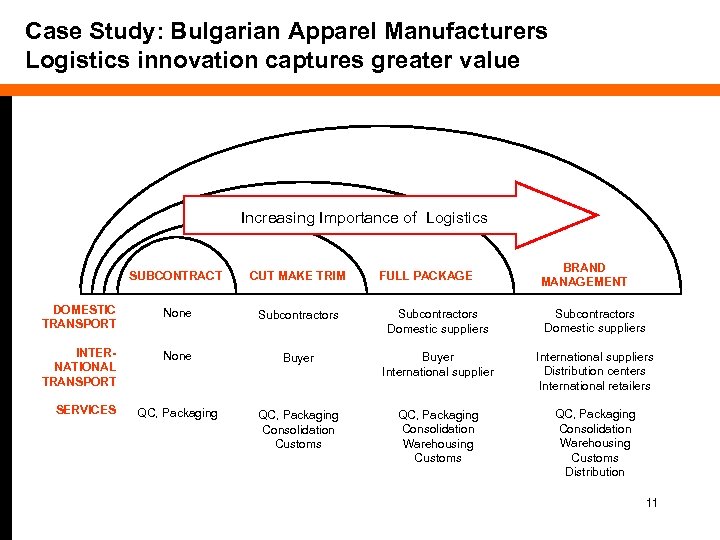
Case Study: Bulgarian Apparel Manufacturers Logistics innovation captures greater value Increasing Importance of Logistics BRAND MANAGEMENT SUBCONTRACT CUT MAKE TRIM DOMESTIC TRANSPORT None Subcontractors Domestic suppliers INTERNATIONAL TRANSPORT None Buyer International suppliers Distribution centers International retailers QC, Packaging Consolidation Customs QC, Packaging Consolidation Warehousing Customs Distribution SERVICES FULL PACKAGE 11
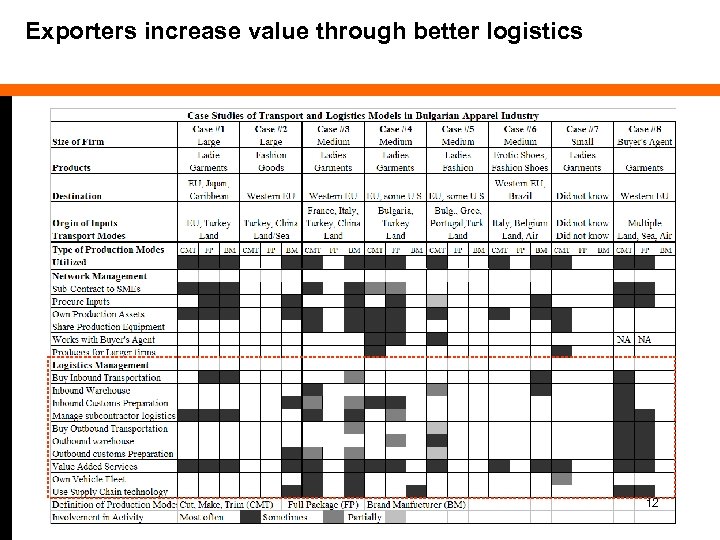
Exporters increase value through better logistics 12

Transferring Knowledge and Technology for Change Challenges • Enterprise culture – High dependence on few senior managers – Tactical, conservative mindset – Confident, entrepreneurial • Available Resources – Limited investment in plant, equipment, IT – Human resources • “Don’t know what you don’t know” – Limited exposure to leading management solutions – Limited demand for new knowledge 13
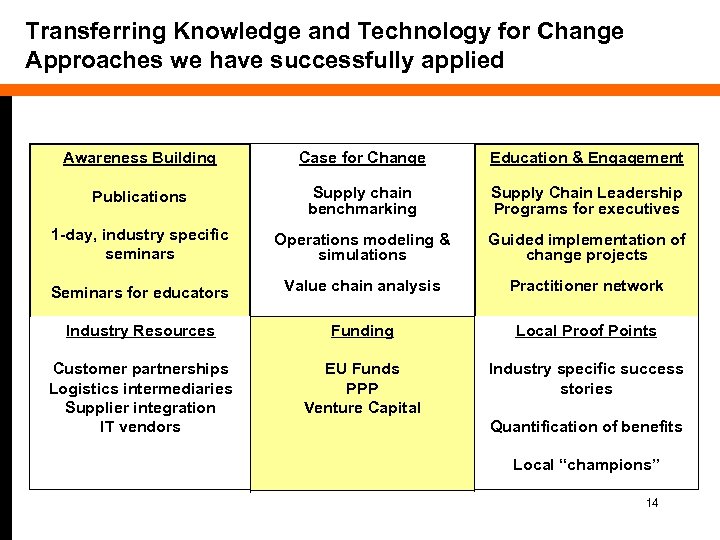
Transferring Knowledge and Technology for Change Approaches we have successfully applied Awareness Building Case for Change Education & Engagement Publications Supply chain benchmarking Supply Chain Leadership Programs for executives 1 -day, industry specific seminars Operations modeling & simulations Guided implementation of change projects Seminars for educators Value chain analysis Practitioner network Industry Resources Funding Local Proof Points Customer partnerships Logistics intermediaries Supplier integration IT vendors EU Funds PPP Venture Capital Industry specific success stories Quantification of benefits Local “champions” 14
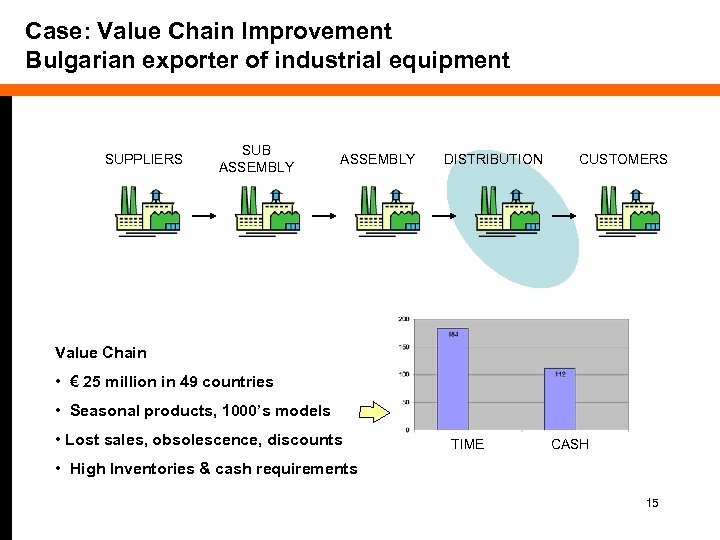
Case: Value Chain Improvement Bulgarian exporter of industrial equipment SUPPLIERS SUB ASSEMBLY DISTRIBUTION CUSTOMERS Value Chain • € 25 million in 49 countries • Seasonal products, 1000’s models • Lost sales, obsolescence, discounts TIME CASH • High Inventories & cash requirements 15
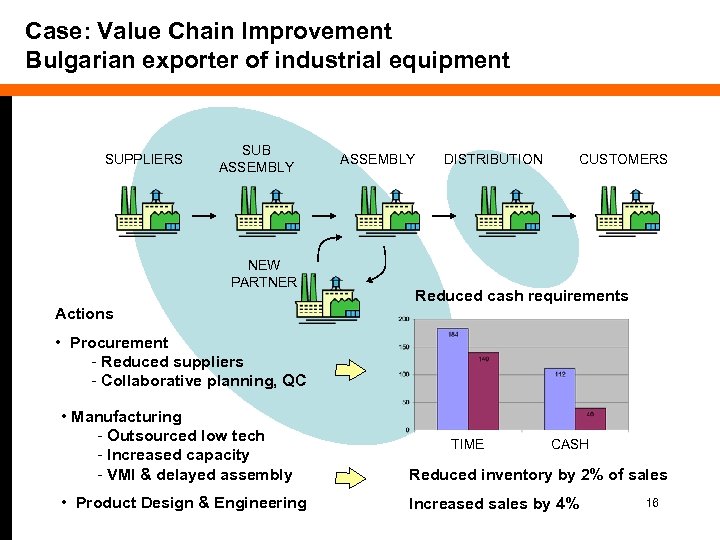
Case: Value Chain Improvement Bulgarian exporter of industrial equipment SUPPLIERS SUB ASSEMBLY NEW PARTNER ASSEMBLY DISTRIBUTION CUSTOMERS Reduced cash requirements Actions • Procurement - Reduced suppliers - Collaborative planning, QC • Manufacturing - Outsourced low tech - Increased capacity - VMI & delayed assembly Reduced inventory by 2% of sales • Product Design & Engineering Increased sales by 4% TIME CASH 16
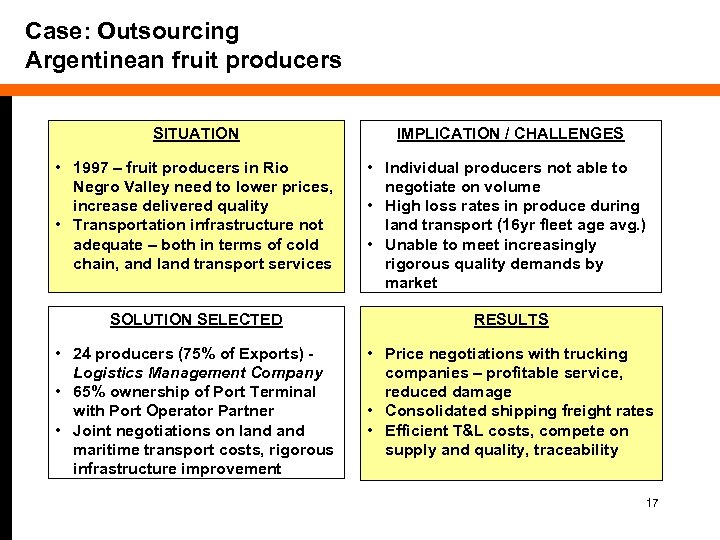
Case: Outsourcing Argentinean fruit producers SITUATION IMPLICATION / CHALLENGES • 1997 – fruit producers in Rio Negro Valley need to lower prices, increase delivered quality • Transportation infrastructure not adequate – both in terms of cold chain, and land transport services • Individual producers not able to negotiate on volume • High loss rates in produce during land transport (16 yr fleet age avg. ) • Unable to meet increasingly rigorous quality demands by market SOLUTION SELECTED RESULTS • 24 producers (75% of Exports) Logistics Management Company • 65% ownership of Port Terminal with Port Operator Partner • Joint negotiations on land maritime transport costs, rigorous infrastructure improvement • Price negotiations with trucking companies – profitable service, reduced damage • Consolidated shipping freight rates • Efficient T&L costs, compete on supply and quality, traceability 17

Final Thoughts • Supply chain innovations expand opportunities • Innovators take a risk • Knowledge & know-how • Industry structure • Supply chain partnerships • Logistics Infrastructure • Laws & Regulations • Access to capital • Performance Standards • Information availability • Identify successful innovations & adapt the system to reduce risks for followers 18

Questions? 19
e144fb316dafdcfa4976f4e04a579d8e.ppt