КИС -9-engl.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 43

Enterprise Information Systems E-Business & E-Commerce

E-business and E-commerce

E-business: Applications for e-business e-Business — бизнес-модель, в которой бизнес-процессы, обмен информацией и реализуются с использованием Web-сервисов. Web- сервисы используются во всей цепочке создания добавленной стоимости предприятия.

E-business Преимущества WEB – сервисов в e-Business: • Снижение издержек на оплату труда; • Отсутствие рисков, связанных с человеческим фактором (ошибки, утечка информации, воровство, больничные и т. п. ); • Увеличение скорости выполнения операций, а как следствие – скорости самого бизнеса (зарабатывания денег); • Сокращение, а в ряде моделей бизнеса и полное отсутствие материальных активов организации (весь бизнес распределен в киберпространстве — нет ни офиса, ни сотрудников, ни материальных товаров); • Высокая скорость масштабирования бизнеса. Информация в электронном виде может копироваться по заданным алгоритмам со скоростью света; • Исчезновение расстояний между продавцом и покупателем. Находясь в самолете над Австралией можно с легкостью продать лыжи покупателю из Канады; • Возможность даже небольшим организациям конкурировать с гигантами в своей отрасли.

E-business

E-business

Sorts of E -…

E-business: Applications for e-business

E-business: e-Procurement and e-Commerce • Service Exchange Process = Procurement or Sales process • E-Procurement (Supplier Exchange) • Use of information and communication technologies to electronically support procurement processes and their integration into the workflow of a company. • E-commerce (Sales Aspect of E-Business) • Any form of business information, communication or transaction in the sales area (sales process) of companies using electronic media

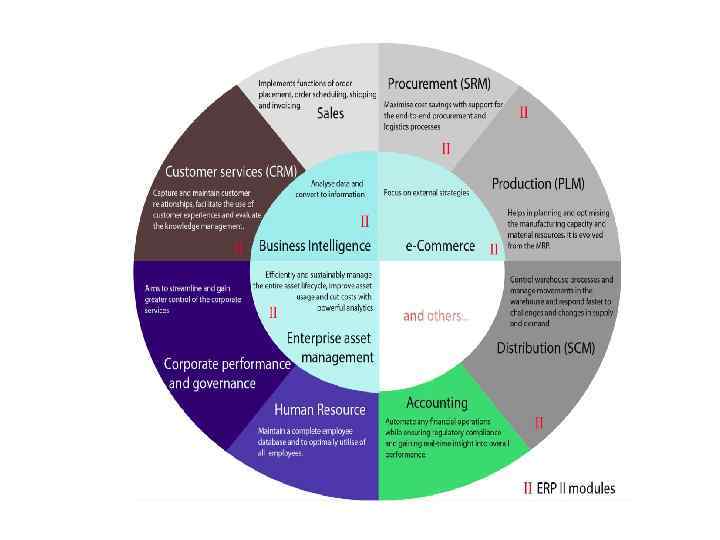
E-business: Relationship to ERP system

E-business: Relations between different actors

E-business: Relations between different actors

E-business: Business-to-Consumer • • • Implies online trading between companies and customers The relationship is characterized by a short-term market contact and small to medium transaction amounts The key focus is on the product selection, ordering and payment B 2 C platforms are mainly e-shop and e-marketplace Example: amazon. com

E-business: Business-to-Business • Service relationship between companies or companies groups • In contrast to B 2 C is characterized by a long-term business relationship and complex value creation chains • B 2 B platforms are mainly e-company, e-procurement and emarketplace • Example: supplyon. de

E-business: Business areas • Government-to-Business • Service exchange between public administration and company • Refers mainly to transactions in the field of public procurement, particularly in formal tendering procedures • Government-to-Government • Service exchange between states, public institutions or departments • Intends to support organizations in trading • Government-to-Consumer • Includes services for citizens, such as provision of information and forms, car registration, residence registration or change

E-business: Platforms in e-business • E-Procurement • Electronic procurement of products or services • E-Shop • Electronic sale of products and services by a company over digital networks • E-Market Place • Represent virtual trading platforms in the B 2 B or B 2 C sector, as opposed to e-shops there are several providers

E-business: Platforms in e-business • E-community • Organized exchange of information / communication within an electronic network of contacts • Relationship between actors can be thematically determined by communication contents, but also through the social or professional status of community participants • E-Company • Linking companies for the purpose of cooperation, thereby creating a common joint, via digital value-networks transaction

E-business: Business Model Classification

E-business: Revenue model • Differentiation of offered services in core and secondary services • Core service: revenues are generated directly by offered products or services • Secondary services: building on the core services, additional services can be derived which generate indirect revenue • Combination of core and secondary service • Singular principle • Focus on the paid core service, secondary service is not available (e. g. , sale via the e-shop)

E-business: Revenue model • Plural principle • Paid core service (e. g. , mediation services on an e-Marketplace) is combined with marketable secondary service • Symbiosis principle • Similar to the plural principle, the focus is on both services, the core service is offered free of charge (e. g. , participation in ecommunity) in order to obtain the information for the secondary service (e. g. , personalized advertising)

E-business: Revenue systematic • Margin model • Service price is derived from the costs for service provision plus profit margin • Example: E-Shop • Commission model • If particular third-party services are mediated to the customer, a provision fee has to be paid depending on the success • Example: affiliate / partner programs • Basic fee model • Is commonly used for transaction independent services • Example: admission fee in e-community

E-business&E-commerce

E-business&E-commerce

E-commerce

E-commerce general idea

E-commerce work flow

E-commerce

E-commerce components
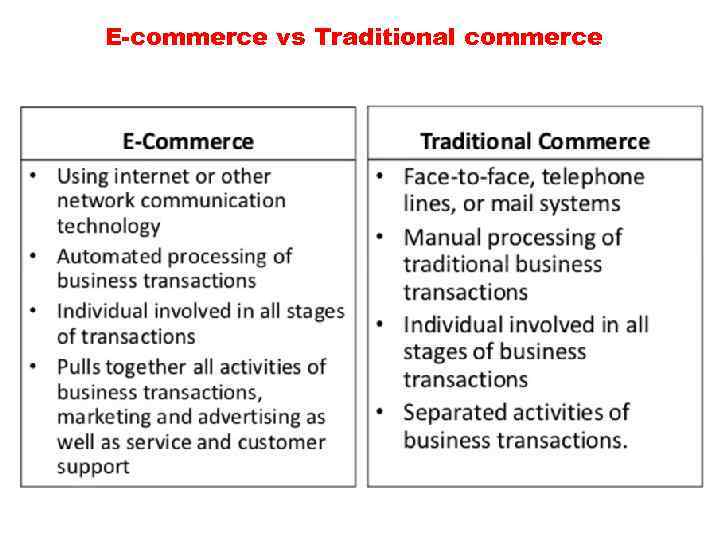
E-commerce vs Traditional commerce


E-commerce: E-Shop • Web page for electronic purchase of products or services • Shopping in an online store supports all functions included in an order process • Similar to retail stores products can be selected from a range of goods and placed in a virtual shopping basket

E-commerce: Products • Products can be physical or digital goods or services • Characteristics of digital products: • No wear and tear • Experience goods • Easy to modify • Low distribution costs • For digital products (software, music, e -books), the entire purchase process can be electronically developed

E-commerce: Product Catalog • Analogous to the classical mail order catalog an electronic product catalog contains the offered products • Visitors can get information about the goods offered in an e-shop • Connections to ERP system

E-commerce: Product basket • Contains products to be bought • Serves intermediate or control storage for product selection • Should have the following functionalities: • Add several products • Deletion or replacement of added articles • Display the product details • Subsequent adjustment of the order quantity • Gross and net pricing • Display shipping costs • Display possible payment methods

E-commerce: Process units in online-shopping

E-commerce: How do Websites work

E-commerce: Online-shopping processes • Product order (e. Sales) Process from product selection to the virtual checkout • Rule of thumb: complete the order with 3 mouse clicks • Information about where is the customer in the order process • Enter the required customer information; creation of a user account

E-commerce: Online-shopping processes (2) • Product payment (e. Payment) • Order is completed by payment • Requirements: security, usability, acceptance / dissemination, costeffectiveness • Product Delivery (e. Fulfillment) • Distinction between electronic and physical products • Shipping process for physical products by parcel service (German Post / DHL, DPD, GLS, Hermes, UPS)

E-commerce: Payment methods • Common payment methods: • Offline vs. Online • Classical methods: invoice, cash in advance, cash on delivery, direct debit, credit card • E-Payment method: paypal. com

E-commerce: Challenges in e-commerce

E-commerce: Store solutions Shop solution alone is not sufficient! - Product maintenance, fulfillment, accounting, . . .

E-business and E-commerce
КИС -9-engl.pptx