53c137fe450efef27728a91646a42b20.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 Enterprise Cost of Risk (ECOR) ERM 002 Presented by: Scot Schwarting Director of Risk Management Whirlpool Linda Conrad Director of Strategic Business Risk Zurich North America Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 1
Enterprise Cost of Risk (ECOR) ERM 002 Presented by: Scot Schwarting Director of Risk Management Whirlpool Linda Conrad Director of Strategic Business Risk Zurich North America Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 1
 • Linda Conrad - Director of Strategic Business Risk; Zurich Linda leads a global team responsible for delivering tactical solutions to strategic issues like business resilience, supply chain risk, Enterprise Risk Management, Total Risk Profiling. Linda addresses enterprise resiliency issues in print and television appearances, including CNBC and Fox Business News, and a Wall Street Journal Microsite. Linda is on the RIMS ERM Committee and Supply Chain Risk Leadership Council. Linda holds a Specialist designation in ERM, and serves on the Educational Board of the Institute of Risk Management in London. • Scot Schwarting -Director of Risk Management Whirlpool Scot Schwarting joined Whirlpool Corporation as director of Risk Management in 2007. He is responsible for the company’s risk management activities, including actions to further embed Enterprise Risk Management into corporate strategy. Prior to joining Whirlpool, Schwarting held various progressive risk management positions at OSI Industries, Inc. , including serving as assistant vice president of Insurance. Schwarting earned a master’s degree in management from North Park University’s School of Business and a bachelor’s degree from North Central College. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 2
• Linda Conrad - Director of Strategic Business Risk; Zurich Linda leads a global team responsible for delivering tactical solutions to strategic issues like business resilience, supply chain risk, Enterprise Risk Management, Total Risk Profiling. Linda addresses enterprise resiliency issues in print and television appearances, including CNBC and Fox Business News, and a Wall Street Journal Microsite. Linda is on the RIMS ERM Committee and Supply Chain Risk Leadership Council. Linda holds a Specialist designation in ERM, and serves on the Educational Board of the Institute of Risk Management in London. • Scot Schwarting -Director of Risk Management Whirlpool Scot Schwarting joined Whirlpool Corporation as director of Risk Management in 2007. He is responsible for the company’s risk management activities, including actions to further embed Enterprise Risk Management into corporate strategy. Prior to joining Whirlpool, Schwarting held various progressive risk management positions at OSI Industries, Inc. , including serving as assistant vice president of Insurance. Schwarting earned a master’s degree in management from North Park University’s School of Business and a bachelor’s degree from North Central College. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 2
 ECOR Session Objectives 1. Define Traditional Cost of Risk (TCOR) and Enterprise Cost of Risk (ECOR) across entire organization – both insurable and uninsurable exposures 2. Understand risks that could cost the company money 3. Determine how a Risk Manager can address ECOR and establish a risk dashboard to identify and monitor risk expenses Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 3
ECOR Session Objectives 1. Define Traditional Cost of Risk (TCOR) and Enterprise Cost of Risk (ECOR) across entire organization – both insurable and uninsurable exposures 2. Understand risks that could cost the company money 3. Determine how a Risk Manager can address ECOR and establish a risk dashboard to identify and monitor risk expenses Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 3
 ECOR Background • Scot Schwarting and Linda Conrad both serve on the RIMS ERM Committee led by Carol Fox • On a Q 4 2013 call of RIMS ERM Committee, Linda objected to the use of the term TOTAL in TCOR, since it only includes costs of insurable risk. • Linda suggested that we redefine the term from an enterprise perspective, to include other costs of risks hidden in the organization • Linda proposed that we call this ECOR for Enterprise Cost of Risk Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 4
ECOR Background • Scot Schwarting and Linda Conrad both serve on the RIMS ERM Committee led by Carol Fox • On a Q 4 2013 call of RIMS ERM Committee, Linda objected to the use of the term TOTAL in TCOR, since it only includes costs of insurable risk. • Linda suggested that we redefine the term from an enterprise perspective, to include other costs of risks hidden in the organization • Linda proposed that we call this ECOR for Enterprise Cost of Risk Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 4
 ECOR in the media Subsequently in 2014, Carol Fox began promoting this broader concept in an article for CFO. com article called ‘Total Cost of Risk’ Redefined Author Caroline Mc. Donald writes: “Risk managers, often seen mostly as insurance buyers, have work to do in expanding their view of risk to match those of senior executives and board members…. Today, senior executives and boards think of risk in much broader terms, and risk managers need to see themselves as more than insurance buyers. ” Carol Fox, director, strategic and enterprise risk practice at the Risk and Insurance Management Society, agreed: “CFOs don’t think of total cost of risk as what we’re measuring. ” While insurance remains important for transferring risk and protecting the balance sheet, Fox said, companies are trying to strengthen their overall risk-management capabilities with an eye to overcoming obstacles to reaching organizational goals. “They’re looking at what their strategic plans are and how those play into risk scenarios, ” she said Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 5
ECOR in the media Subsequently in 2014, Carol Fox began promoting this broader concept in an article for CFO. com article called ‘Total Cost of Risk’ Redefined Author Caroline Mc. Donald writes: “Risk managers, often seen mostly as insurance buyers, have work to do in expanding their view of risk to match those of senior executives and board members…. Today, senior executives and boards think of risk in much broader terms, and risk managers need to see themselves as more than insurance buyers. ” Carol Fox, director, strategic and enterprise risk practice at the Risk and Insurance Management Society, agreed: “CFOs don’t think of total cost of risk as what we’re measuring. ” While insurance remains important for transferring risk and protecting the balance sheet, Fox said, companies are trying to strengthen their overall risk-management capabilities with an eye to overcoming obstacles to reaching organizational goals. “They’re looking at what their strategic plans are and how those play into risk scenarios, ” she said Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 5
 ECOR in the media In the same article, we hear from Rich Sarnie, vice president of risk management at the Great Atlantic & Pacific Tea Co. “We need to expand it and make sure it includes all the risks and the costs associated with those risks, not just the insurable ones. ” Mr. Sarnie says, “Executives are much more focused on risk management these days, but “it’s not the insurable risks that are keeping them up at night. It’s other risks, ” said Sarnie. Such risks include the availability of affordable financing, reputational risk, supply-chain risk, and technology or social-media risk. Boards “want to know how we are identifying those risks and how we are managing them, plain and simple. ” http: //ww 2. cfo. com/risk-management/2012/07/total-cost-of-risk-redefined/ Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 6
ECOR in the media In the same article, we hear from Rich Sarnie, vice president of risk management at the Great Atlantic & Pacific Tea Co. “We need to expand it and make sure it includes all the risks and the costs associated with those risks, not just the insurable ones. ” Mr. Sarnie says, “Executives are much more focused on risk management these days, but “it’s not the insurable risks that are keeping them up at night. It’s other risks, ” said Sarnie. Such risks include the availability of affordable financing, reputational risk, supply-chain risk, and technology or social-media risk. Boards “want to know how we are identifying those risks and how we are managing them, plain and simple. ” http: //ww 2. cfo. com/risk-management/2012/07/total-cost-of-risk-redefined/ Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 6
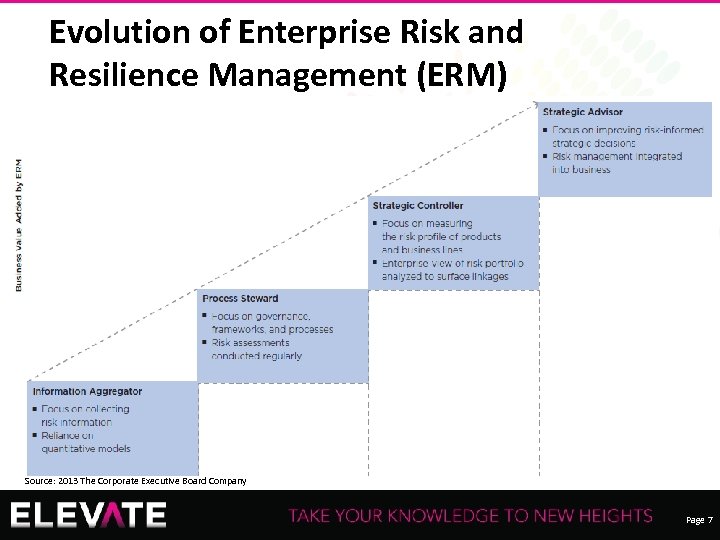 Evolution of Enterprise Risk and Resilience Management (ERM) Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Source: 2013 The Corporate Executive Board Company Page 7
Evolution of Enterprise Risk and Resilience Management (ERM) Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Source: 2013 The Corporate Executive Board Company Page 7
 Session Objectives 1. Define ECOR across entire organization – both insurable and uninsurable – including “hidden” 2. Understand risk exposures that could cost the company money and how a Risk Manager can address them 3. Establish a risk dashboard to identify and monitor risk expenses Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 8
Session Objectives 1. Define ECOR across entire organization – both insurable and uninsurable – including “hidden” 2. Understand risk exposures that could cost the company money and how a Risk Manager can address them 3. Establish a risk dashboard to identify and monitor risk expenses Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 8
 Total Cost of Risk (TCOR) • What is TCOR? • It is a company’s Total Cost of Risk to insure its organization • What does TCOR include? • Risk Transfer Premium • Retained Losses • Risk Management Admin (Staff) • Claims Costs (Internal and External) • Loss Control (Internal and External) • Collateral Costs • Risk management teams can also measure incidents and claims versus real operational yardsticks, such as employee hours worked, customer traffic in stores or miles driven for employees. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 9
Total Cost of Risk (TCOR) • What is TCOR? • It is a company’s Total Cost of Risk to insure its organization • What does TCOR include? • Risk Transfer Premium • Retained Losses • Risk Management Admin (Staff) • Claims Costs (Internal and External) • Loss Control (Internal and External) • Collateral Costs • Risk management teams can also measure incidents and claims versus real operational yardsticks, such as employee hours worked, customer traffic in stores or miles driven for employees. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 9
 Total Cost of Risk (TCOR) • What is NOT in TCOR? • Uninsurable and non-hazard risk • What else does Senior Management and the Board need to manage? • What is the opportunity to redefine and expand our view of risk? Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 10
Total Cost of Risk (TCOR) • What is NOT in TCOR? • Uninsurable and non-hazard risk • What else does Senior Management and the Board need to manage? • What is the opportunity to redefine and expand our view of risk? Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 10
 Enterprise Cost of Risk (ECOR) • What is ECOR? • It is a company’s Enterprise Cost of Risk to manage its organization • What does ECOR include? • Risk expenses that derive from other business activities which are ‘less insurable” but no less costly to the organization • Sound risk stewardship now demands an enterprise risk management approach that addresses exposures and opportunities from all angles • Risk managers can search for emerging issues, risk costs and unexpected interconnections – concentration and correlations – which may not be as visible from a decentralized viewpoint. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 11
Enterprise Cost of Risk (ECOR) • What is ECOR? • It is a company’s Enterprise Cost of Risk to manage its organization • What does ECOR include? • Risk expenses that derive from other business activities which are ‘less insurable” but no less costly to the organization • Sound risk stewardship now demands an enterprise risk management approach that addresses exposures and opportunities from all angles • Risk managers can search for emerging issues, risk costs and unexpected interconnections – concentration and correlations – which may not be as visible from a decentralized viewpoint. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 11
 How to determine ECOR • Break the cost into buckets to see what we do and do not yet know • What might these buckets include and their sources: • Hazard Total Cost of Risk – insured and non insured insurable losses • Financial risks – Balance sheet reserves – Liabilities – short & long term • Shareholder risks – 8 K reportable events, they are material and unexpected • What are we left with? • Drivers of risk that are part of strategy and are soft measures • Example HR – open positions, by level, by band, by discipline • Can we put a number to these? Department’s contribution to Sales example or profit? • What are the opportunities to measure Enterprise Cost of Risk • CEB and other studies show strategy is biggest risk? How quantified? • 68% of risk to shareholder value is therefore the opportunity space for risk management of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Recording Page 12
How to determine ECOR • Break the cost into buckets to see what we do and do not yet know • What might these buckets include and their sources: • Hazard Total Cost of Risk – insured and non insured insurable losses • Financial risks – Balance sheet reserves – Liabilities – short & long term • Shareholder risks – 8 K reportable events, they are material and unexpected • What are we left with? • Drivers of risk that are part of strategy and are soft measures • Example HR – open positions, by level, by band, by discipline • Can we put a number to these? Department’s contribution to Sales example or profit? • What are the opportunities to measure Enterprise Cost of Risk • CEB and other studies show strategy is biggest risk? How quantified? • 68% of risk to shareholder value is therefore the opportunity space for risk management of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Recording Page 12
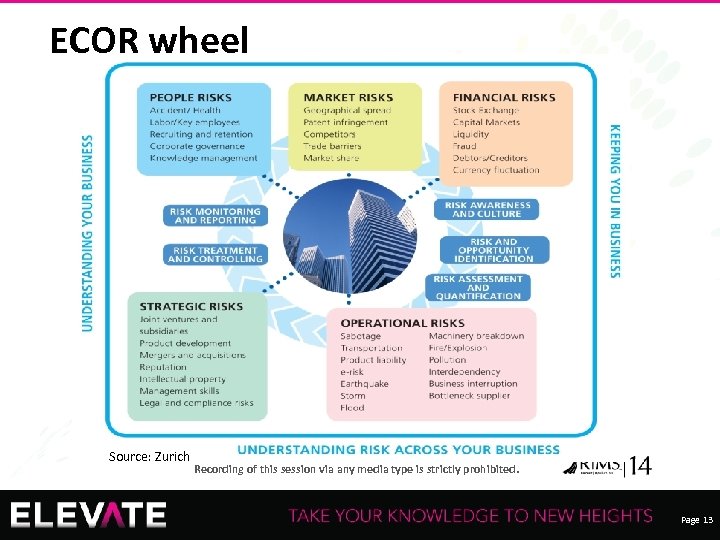 ECOR wheel Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 13
ECOR wheel Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 13
 Enterprise Resilience Challenges Source: Gary Larson Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 14
Enterprise Resilience Challenges Source: Gary Larson Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 14
 Session Objectives 1. Define ECOR across entire organization – both insurable and uninsurable – including "hidden“ 2. Understand risk exposures that could cost the company money and how a Risk Manager can address them 3. Establish a risk dashboard to identify and monitor risk expenses Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 15
Session Objectives 1. Define ECOR across entire organization – both insurable and uninsurable – including "hidden“ 2. Understand risk exposures that could cost the company money and how a Risk Manager can address them 3. Establish a risk dashboard to identify and monitor risk expenses Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 15
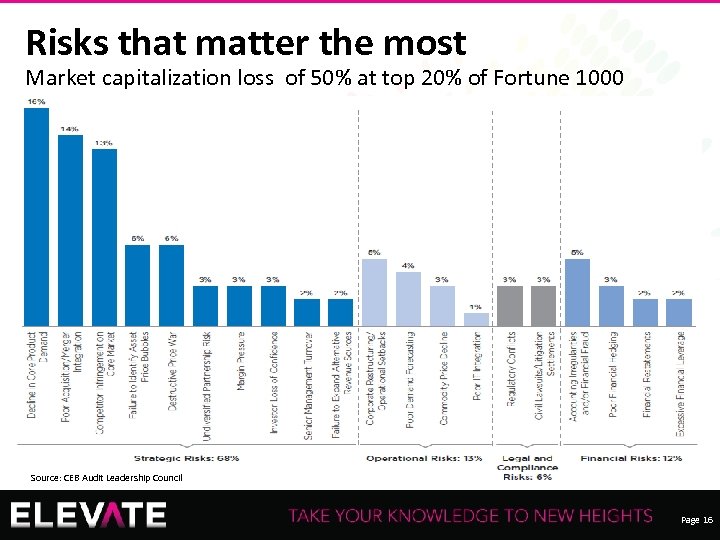 Risks that matter the most Market capitalization loss of 50% at top 20% of Fortune 1000 Source: CEB Audit Leadership Council Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 16
Risks that matter the most Market capitalization loss of 50% at top 20% of Fortune 1000 Source: CEB Audit Leadership Council Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 16
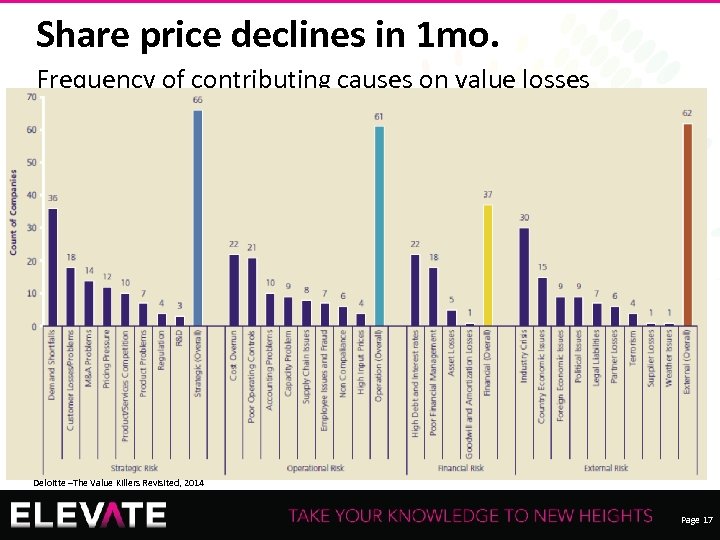 Share price declines in 1 mo. Frequency of contributing causes on value losses Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Deloitte –The Value Killers Revisited, 2014 Page 17
Share price declines in 1 mo. Frequency of contributing causes on value losses Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Deloitte –The Value Killers Revisited, 2014 Page 17
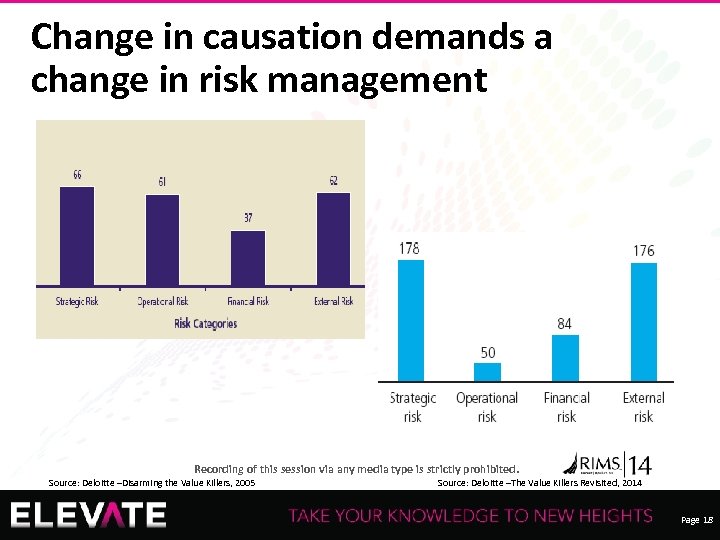 Change in causation demands a change in risk management Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Source: Deloitte –Disarming the Value Killers, 2005 Source: Deloitte –The Value Killers Revisited, 2014 Page 18
Change in causation demands a change in risk management Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Source: Deloitte –Disarming the Value Killers, 2005 Source: Deloitte –The Value Killers Revisited, 2014 Page 18
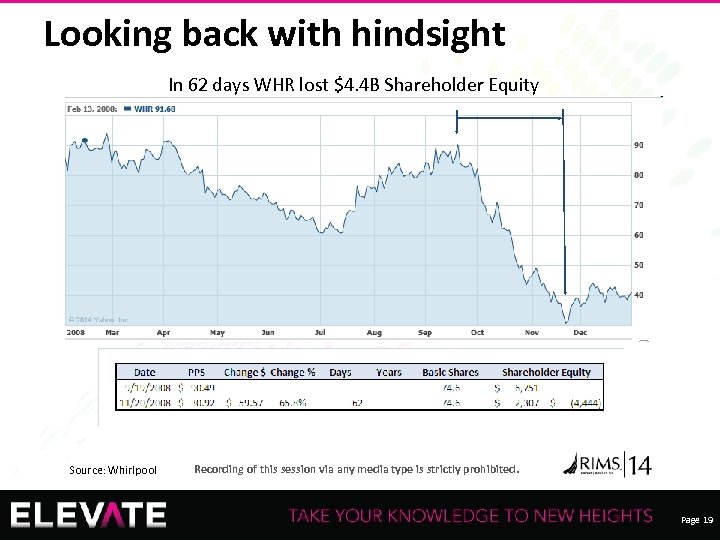 Looking back with hindsight In 62 days WHR lost $4. 4 B Shareholder Equity Source: Whirlpool 19 Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 19
Looking back with hindsight In 62 days WHR lost $4. 4 B Shareholder Equity Source: Whirlpool 19 Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 19
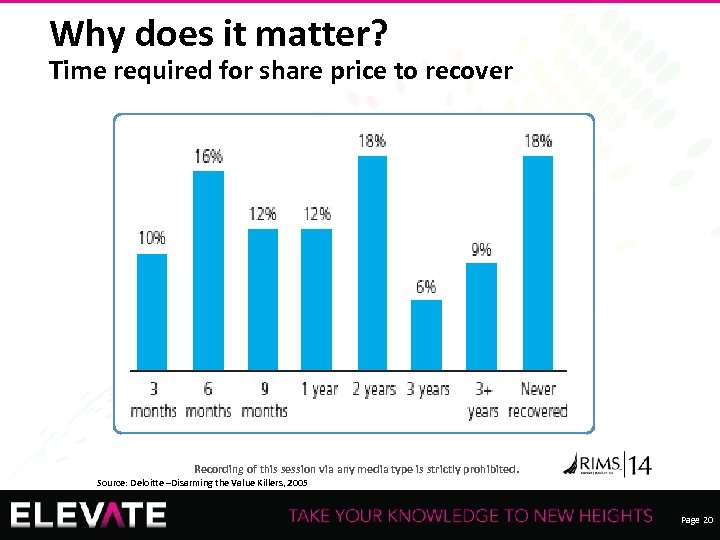 Why does it matter? Time required for share price to recover Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Source: Deloitte –Disarming the Value Killers, 2005 Page 20
Why does it matter? Time required for share price to recover Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Source: Deloitte –Disarming the Value Killers, 2005 Page 20
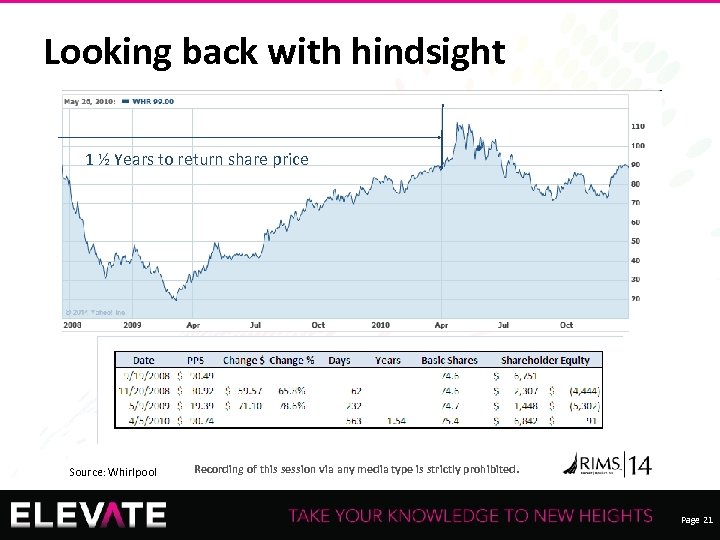 Looking back with hindsight 1 ½ Years to return share price Source: Whirlpool 21 Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 21
Looking back with hindsight 1 ½ Years to return share price Source: Whirlpool 21 Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 21
 What Does ECOR Include? • Results from discontinued operations • Mergers, acquisitions & divestitures - in notes to financial statement and balance sheet and income statement • S&P rating reviews - example: extreme event management - could impact rating and cost of capital • Gains & losses from Foreign currency - line item on Profit & Loss Statement • Intellectual capital –copyright infringement • HR and key executive management - talent risk - could be on lots of line items on balance sheet and income statements: level of premium you write / sales, amount of losses because of bad pricing. Also difficult to attract people, finders fees - cost of operations or Human Resources • Simulating how different risks may happen at different times (multiple lines occur at different times across calendar year) • Goodwill - calculated but not reflected Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 22
What Does ECOR Include? • Results from discontinued operations • Mergers, acquisitions & divestitures - in notes to financial statement and balance sheet and income statement • S&P rating reviews - example: extreme event management - could impact rating and cost of capital • Gains & losses from Foreign currency - line item on Profit & Loss Statement • Intellectual capital –copyright infringement • HR and key executive management - talent risk - could be on lots of line items on balance sheet and income statements: level of premium you write / sales, amount of losses because of bad pricing. Also difficult to attract people, finders fees - cost of operations or Human Resources • Simulating how different risks may happen at different times (multiple lines occur at different times across calendar year) • Goodwill - calculated but not reflected Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 22
 What Does ECOR Include? • Legal costs - settlements, judgments - in operating costs (whether HR related, trade sanctions, bad faith, D & O etc. ) - what are the counter measures, actions to mitigate have costs • Fines, penalties - OFAC, Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) - may go as operations expense to company or a business unit • Manual workarounds – how to estimate costs • Project risk and initiatives - project budget, cost overruns, opportunity cost if not ready on time, • Concentration risk (Letters of credit to secure assets, diversify banks, have limits and use highly rated risks) - purchase fee and recovery shown in bad debt expense line item on income statement) • Concentration risk by country, by category of investment, by banking, by counterparty, by asset classes (like mortgage backed security), etc. how much foreign securities you can hold (ex 10% of net worth as set by NY insurance code)- if some investments permanently lose value it will show as investment loss on income statement Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 23
What Does ECOR Include? • Legal costs - settlements, judgments - in operating costs (whether HR related, trade sanctions, bad faith, D & O etc. ) - what are the counter measures, actions to mitigate have costs • Fines, penalties - OFAC, Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) - may go as operations expense to company or a business unit • Manual workarounds – how to estimate costs • Project risk and initiatives - project budget, cost overruns, opportunity cost if not ready on time, • Concentration risk (Letters of credit to secure assets, diversify banks, have limits and use highly rated risks) - purchase fee and recovery shown in bad debt expense line item on income statement) • Concentration risk by country, by category of investment, by banking, by counterparty, by asset classes (like mortgage backed security), etc. how much foreign securities you can hold (ex 10% of net worth as set by NY insurance code)- if some investments permanently lose value it will show as investment loss on income statement Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 23
 What Does ECOR Include? • Opportunity cost? - income statement shows what did happen but does not show what could happen. When we do project proposals, we try to anticipate opportunity cost as Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA), and it is implicit in our prioritization of initiatives / projects. Every project we don’t do, we lose the potential benefit. Do you validate project assumptions and benefit "promises"? Do you go to quantify success? • Example: remote workspace can be purchased for 100 K /year for 10 years. Business Interruption (BI) could be impact on inability to do business (at x $ per day) • Example: TCOR willing to spend a million per year to reduce WC costs by 25 mil, and cost is recovered. Defense costs, medical cost containment, prescription controls • Claims settlement : Marine example of value of goods shipped, but do you capture the administrative time to process? • Strategic planning - missed targets, EPS, sales • Ways to be green: fleet or light bulbs - loss of customers if you are not? Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 24
What Does ECOR Include? • Opportunity cost? - income statement shows what did happen but does not show what could happen. When we do project proposals, we try to anticipate opportunity cost as Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA), and it is implicit in our prioritization of initiatives / projects. Every project we don’t do, we lose the potential benefit. Do you validate project assumptions and benefit "promises"? Do you go to quantify success? • Example: remote workspace can be purchased for 100 K /year for 10 years. Business Interruption (BI) could be impact on inability to do business (at x $ per day) • Example: TCOR willing to spend a million per year to reduce WC costs by 25 mil, and cost is recovered. Defense costs, medical cost containment, prescription controls • Claims settlement : Marine example of value of goods shipped, but do you capture the administrative time to process? • Strategic planning - missed targets, EPS, sales • Ways to be green: fleet or light bulbs - loss of customers if you are not? Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 24
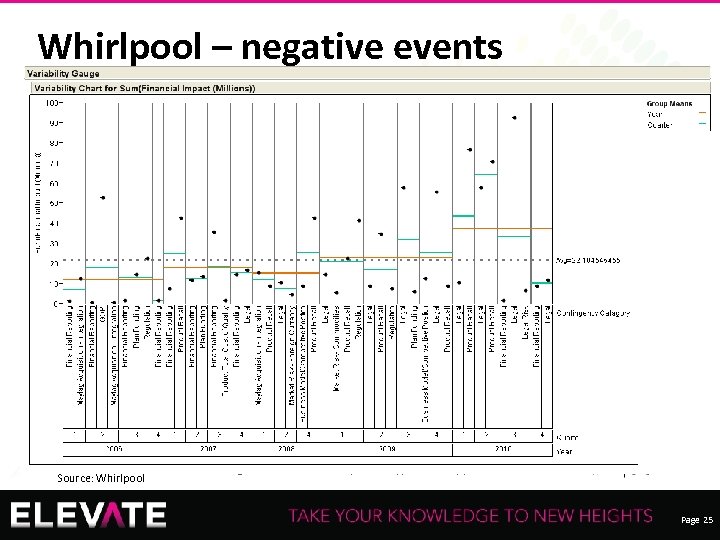 Whirlpool – negative events Source: Whirlpool Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 25
Whirlpool – negative events Source: Whirlpool Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 25
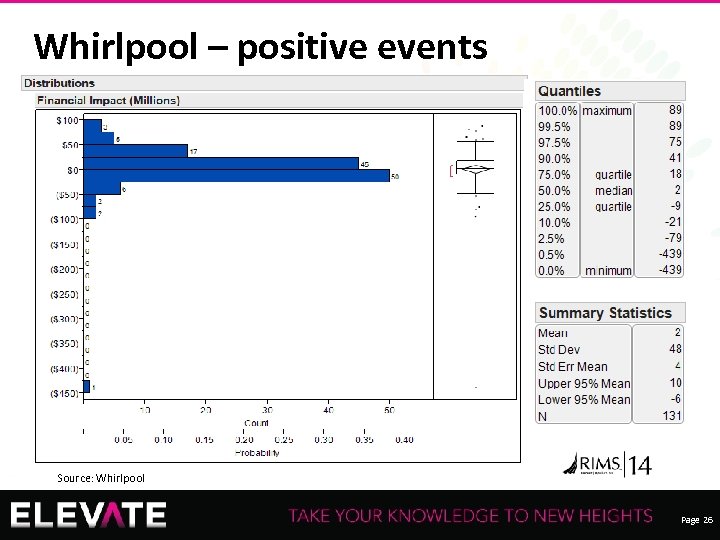 Whirlpool – positive events Source: Whirlpool Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 26
Whirlpool – positive events Source: Whirlpool Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 26
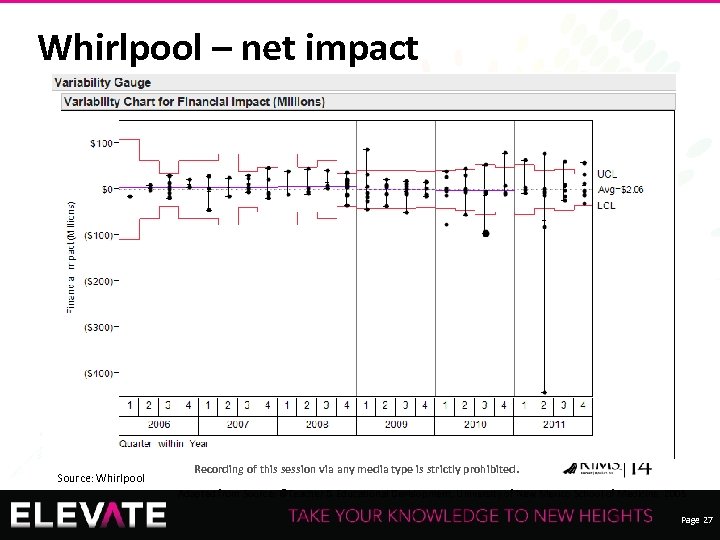 Whirlpool – net impact Source: Whirlpool Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Adapted from Source: ©Teacher & Educational Development, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, 2005 Page 27
Whirlpool – net impact Source: Whirlpool Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Adapted from Source: ©Teacher & Educational Development, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, 2005 Page 27
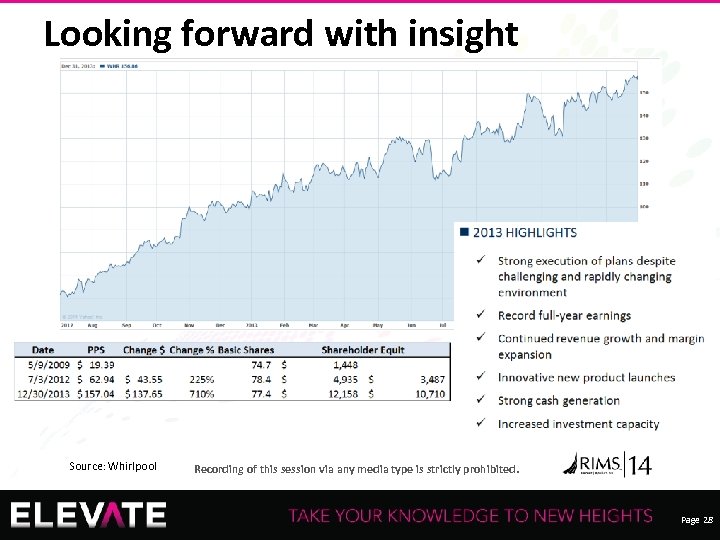 Looking forward with insight Source: Whirlpool 28 Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 28
Looking forward with insight Source: Whirlpool 28 Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 28
 Session Objectives 1. Define ECOR across entire organization – both insurable and uninsurable – including "hidden“ 2. Understand risk exposures that could cost the company money and how a Risk Manager can address them 3. Establish a risk dashboard to identify and monitor risk expenses Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 29
Session Objectives 1. Define ECOR across entire organization – both insurable and uninsurable – including "hidden“ 2. Understand risk exposures that could cost the company money and how a Risk Manager can address them 3. Establish a risk dashboard to identify and monitor risk expenses Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 29
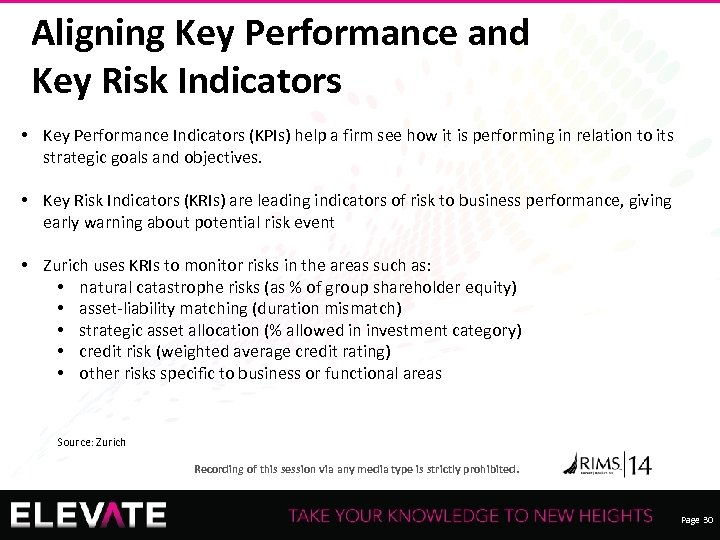 Aligning Key Performance and Key Risk Indicators • Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) help a firm see how it is performing in relation to its strategic goals and objectives. • Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) are leading indicators of risk to business performance, giving early warning about potential risk event • Zurich uses KRIs to monitor risks in the areas such as: • natural catastrophe risks (as % of group shareholder equity) • asset-liability matching (duration mismatch) • strategic asset allocation (% allowed in investment category) • credit risk (weighted average credit rating) • other risks specific to business or functional areas Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 30
Aligning Key Performance and Key Risk Indicators • Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) help a firm see how it is performing in relation to its strategic goals and objectives. • Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) are leading indicators of risk to business performance, giving early warning about potential risk event • Zurich uses KRIs to monitor risks in the areas such as: • natural catastrophe risks (as % of group shareholder equity) • asset-liability matching (duration mismatch) • strategic asset allocation (% allowed in investment category) • credit risk (weighted average credit rating) • other risks specific to business or functional areas Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 30
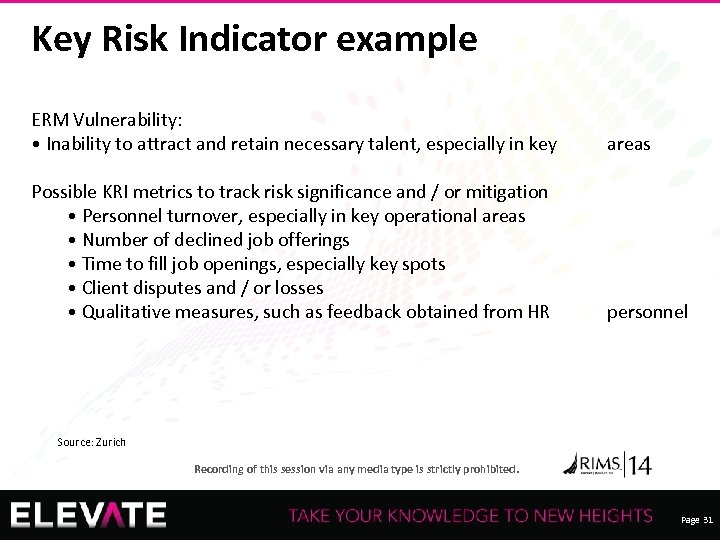 Key Risk Indicator example ERM Vulnerability: • Inability to attract and retain necessary talent, especially in key areas Possible KRI metrics to track risk significance and / or mitigation • Personnel turnover, especially in key operational areas • Number of declined job offerings • Time to fill job openings, especially key spots • Client disputes and / or losses • Qualitative measures, such as feedback obtained from HR personnel Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 31
Key Risk Indicator example ERM Vulnerability: • Inability to attract and retain necessary talent, especially in key areas Possible KRI metrics to track risk significance and / or mitigation • Personnel turnover, especially in key operational areas • Number of declined job offerings • Time to fill job openings, especially key spots • Client disputes and / or losses • Qualitative measures, such as feedback obtained from HR personnel Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 31
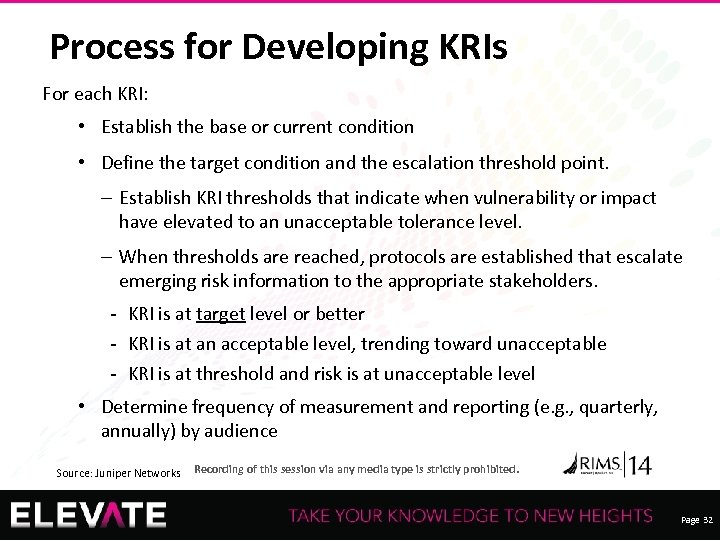 Process for Developing KRIs For each KRI: • Establish the base or current condition • Define the target condition and the escalation threshold point. ‒ Establish KRI thresholds that indicate when vulnerability or impact have elevated to an unacceptable tolerance level. ‒ When thresholds are reached, protocols are established that escalate emerging risk information to the appropriate stakeholders. - KRI is at target level or better - KRI is at an acceptable level, trending toward unacceptable - KRI is at threshold and risk is at unacceptable level • Determine frequency of measurement and reporting (e. g. , quarterly, annually) by audience Source: Juniper Networks Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 32
Process for Developing KRIs For each KRI: • Establish the base or current condition • Define the target condition and the escalation threshold point. ‒ Establish KRI thresholds that indicate when vulnerability or impact have elevated to an unacceptable tolerance level. ‒ When thresholds are reached, protocols are established that escalate emerging risk information to the appropriate stakeholders. - KRI is at target level or better - KRI is at an acceptable level, trending toward unacceptable - KRI is at threshold and risk is at unacceptable level • Determine frequency of measurement and reporting (e. g. , quarterly, annually) by audience Source: Juniper Networks Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 32
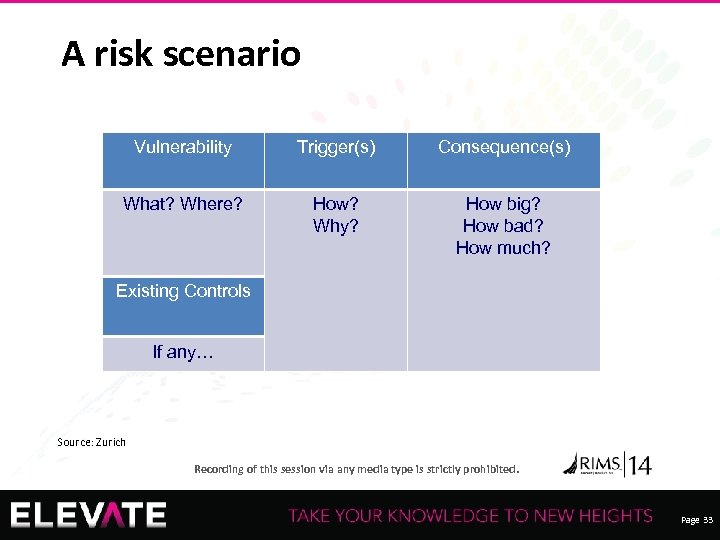 A risk scenario Vulnerability Trigger(s) Consequence(s) What? Where? How? Why? How big? How bad? How much? Existing Controls If any… Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 33
A risk scenario Vulnerability Trigger(s) Consequence(s) What? Where? How? Why? How big? How bad? How much? Existing Controls If any… Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 33
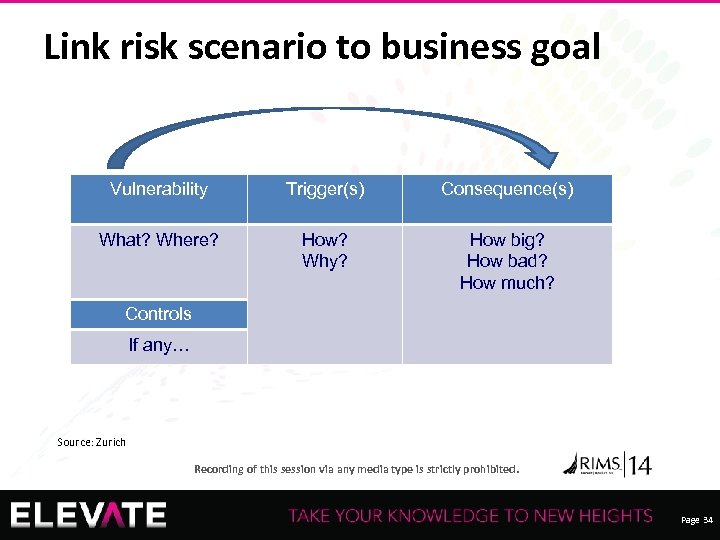 Link risk scenario to business goal Vulnerability Trigger(s) Consequence(s) What? Where? How? Why? How big? How bad? How much? Controls If any… Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 34
Link risk scenario to business goal Vulnerability Trigger(s) Consequence(s) What? Where? How? Why? How big? How bad? How much? Controls If any… Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 34
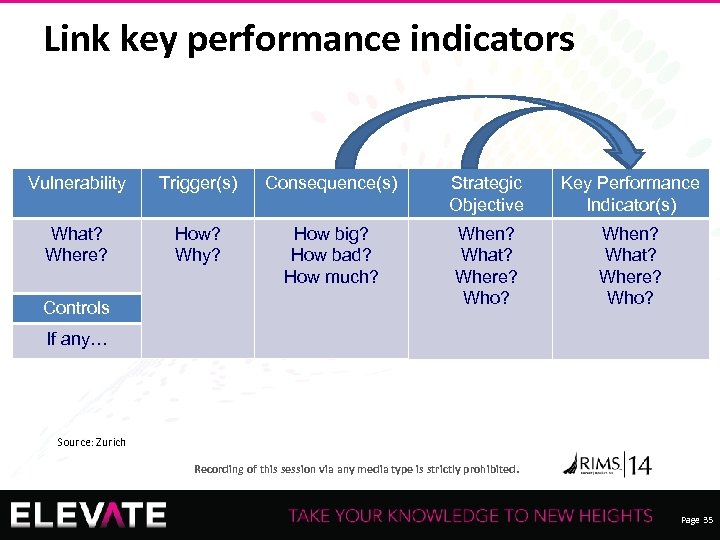 Link key performance indicators Vulnerability Trigger(s) Consequence(s) Strategic Objective Key Performance Indicator(s) What? Where? How? Why? How big? How bad? How much? When? What? Where? Who? Controls If any… Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 35
Link key performance indicators Vulnerability Trigger(s) Consequence(s) Strategic Objective Key Performance Indicator(s) What? Where? How? Why? How big? How bad? How much? When? What? Where? Who? Controls If any… Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 35
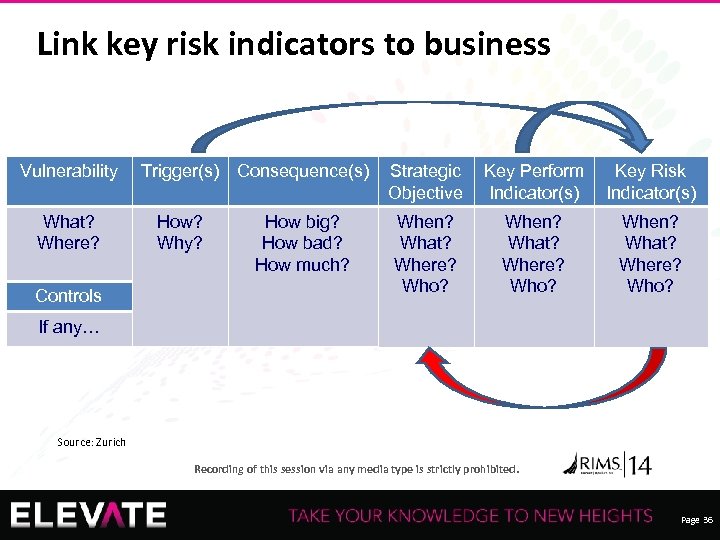 Link key risk indicators to business Vulnerability What? Where? Controls Trigger(s) Consequence(s) How? Why? How big? How bad? How much? Strategic Objective Key Perform Indicator(s) Key Risk Indicator(s) When? What? Where? Who? If any… Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 36
Link key risk indicators to business Vulnerability What? Where? Controls Trigger(s) Consequence(s) How? Why? How big? How bad? How much? Strategic Objective Key Perform Indicator(s) Key Risk Indicator(s) When? What? Where? Who? If any… Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 36
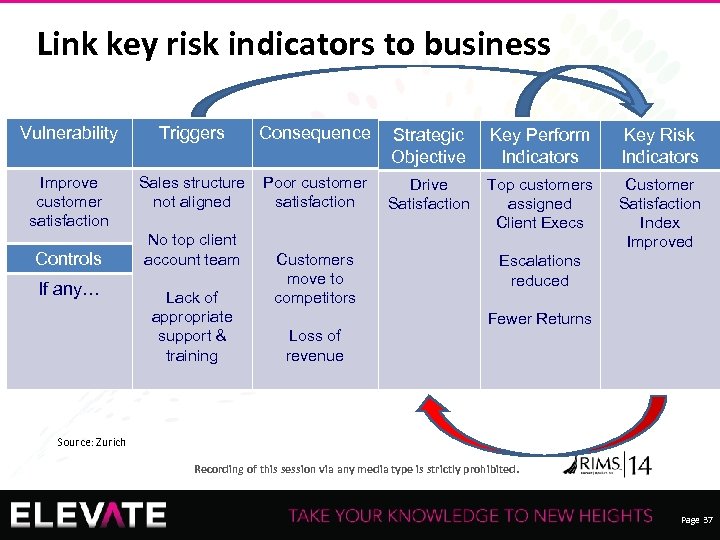 Link key risk indicators to business Vulnerability Triggers Consequence Strategic Objective Key Perform Indicators Key Risk Indicators Improve customer satisfaction Sales structure not aligned Poor customer satisfaction Drive Satisfaction Top customers assigned Client Execs Customer Satisfaction Index Improved Controls If any… No top client account team Lack of appropriate support & training Customers move to competitors Loss of revenue Escalations reduced Fewer Returns Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 37
Link key risk indicators to business Vulnerability Triggers Consequence Strategic Objective Key Perform Indicators Key Risk Indicators Improve customer satisfaction Sales structure not aligned Poor customer satisfaction Drive Satisfaction Top customers assigned Client Execs Customer Satisfaction Index Improved Controls If any… No top client account team Lack of appropriate support & training Customers move to competitors Loss of revenue Escalations reduced Fewer Returns Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 37
 What you need to report & manage KRIs Operational units held responsible or accountable Source: Juniper Networks Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 38
What you need to report & manage KRIs Operational units held responsible or accountable Source: Juniper Networks Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 38
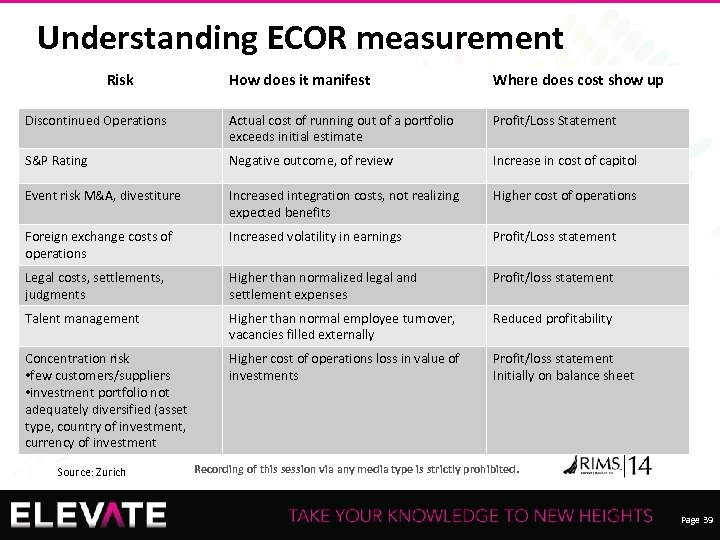 Understanding ECOR measurement Risk How does it manifest Where does cost show up Discontinued Operations Actual cost of running out of a portfolio exceeds initial estimate Profit/Loss Statement S&P Rating Negative outcome, of review Increase in cost of capitol Event risk M&A, divestiture Increased integration costs, not realizing expected benefits Higher cost of operations Foreign exchange costs of operations Increased volatility in earnings Profit/Loss statement Legal costs, settlements, judgments Higher than normalized legal and settlement expenses Profit/loss statement Talent management Higher than normal employee turnover, vacancies filled externally Reduced profitability Concentration risk Higher cost of operations loss in value of • few customers/suppliers investments • investment portfolio not adequately diversified (asset type, country of investment, currency of investment Source: Zurich Profit/loss statement Initially on balance sheet Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 39
Understanding ECOR measurement Risk How does it manifest Where does cost show up Discontinued Operations Actual cost of running out of a portfolio exceeds initial estimate Profit/Loss Statement S&P Rating Negative outcome, of review Increase in cost of capitol Event risk M&A, divestiture Increased integration costs, not realizing expected benefits Higher cost of operations Foreign exchange costs of operations Increased volatility in earnings Profit/Loss statement Legal costs, settlements, judgments Higher than normalized legal and settlement expenses Profit/loss statement Talent management Higher than normal employee turnover, vacancies filled externally Reduced profitability Concentration risk Higher cost of operations loss in value of • few customers/suppliers investments • investment portfolio not adequately diversified (asset type, country of investment, currency of investment Source: Zurich Profit/loss statement Initially on balance sheet Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 39
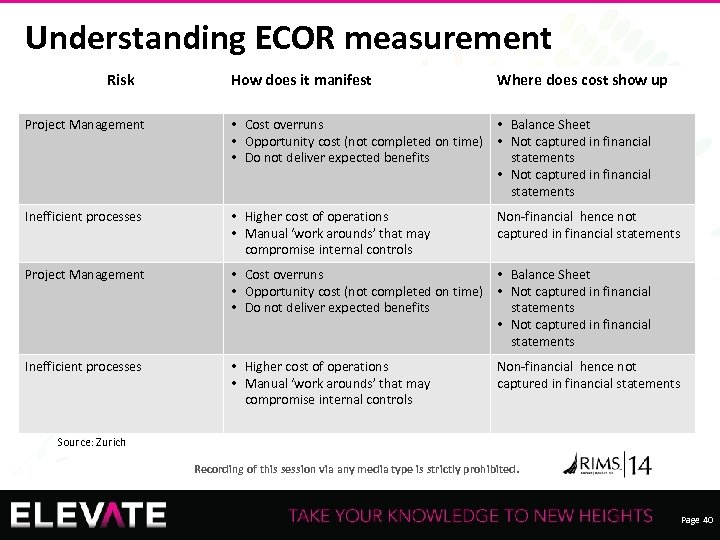 Understanding ECOR measurement Risk How does it manifest Where does cost show up Project Management • Cost overruns • Balance Sheet • Opportunity cost (not completed on time) • Not captured in financial • Do not deliver expected benefits statements • Not captured in financial statements Inefficient processes • Higher cost of operations • Manual ‘work arounds’ that may compromise internal controls Non-financial hence not captured in financial statements Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 40
Understanding ECOR measurement Risk How does it manifest Where does cost show up Project Management • Cost overruns • Balance Sheet • Opportunity cost (not completed on time) • Not captured in financial • Do not deliver expected benefits statements • Not captured in financial statements Inefficient processes • Higher cost of operations • Manual ‘work arounds’ that may compromise internal controls Non-financial hence not captured in financial statements Source: Zurich Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 40
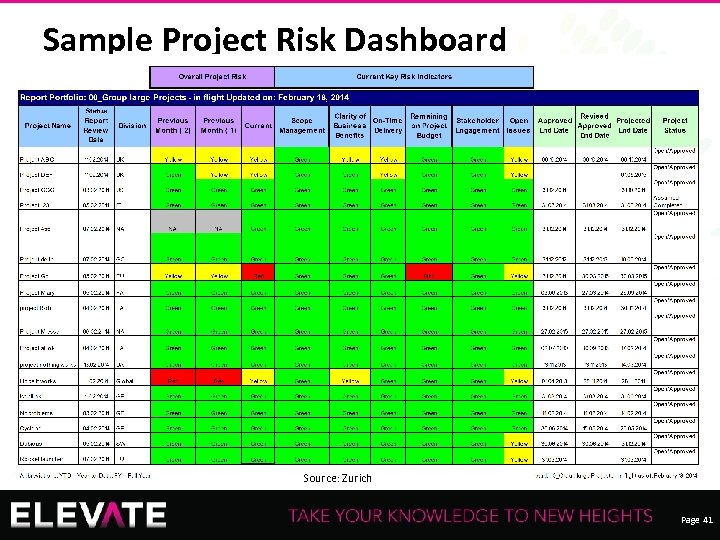 Sample Project Risk Dashboard Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Source: Zurich Page 41
Sample Project Risk Dashboard Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Source: Zurich Page 41
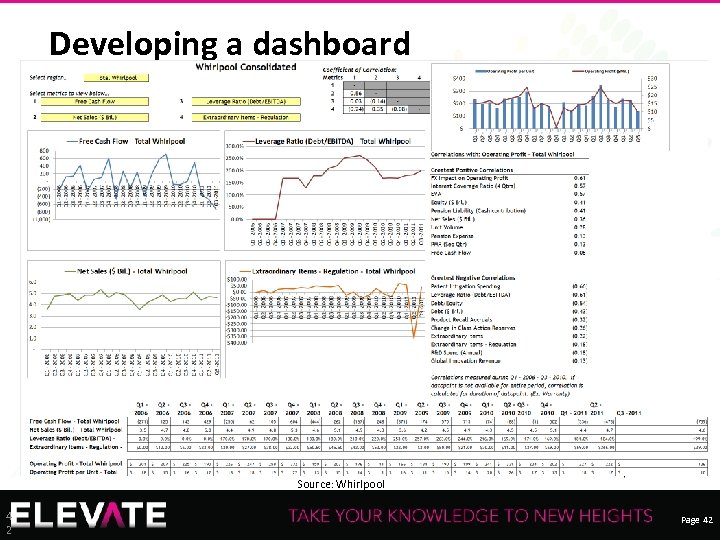 Developing a dashboard Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Source: Whirlpool 4 2 Page 42
Developing a dashboard Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Source: Whirlpool 4 2 Page 42
 How can ECOR help business? Robust risk culture and ERM can yield greater enterprise resilience: 59% Increased profitability 62% Reduced earnings volatility 86% Better risk - based decisions (learn from risk information + mistakes) 80% Increased management accountability (shareholder confidence) 79% Aligned governance practices Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 43
How can ECOR help business? Robust risk culture and ERM can yield greater enterprise resilience: 59% Increased profitability 62% Reduced earnings volatility 86% Better risk - based decisions (learn from risk information + mistakes) 80% Increased management accountability (shareholder confidence) 79% Aligned governance practices Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 43
 Linking risk culture and results A 2012 Federation of European Risk Managers Association (FERMA) study found firms demonstrating a more mature approach to Risk Management have better financial results • EBITDA growth of over 10% was generated by 28% of companies with “advanced” risk management practices, compared with just 16% of firms with “emerging” practices • Revenue growth of 10% was shown by 29% of companies with “advanced” practices, compared with 18% of companies with “emerging” practices Creating an active risk culture can be correlated with higher growth, as organization becomes more aware and accountable for risk. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 44
Linking risk culture and results A 2012 Federation of European Risk Managers Association (FERMA) study found firms demonstrating a more mature approach to Risk Management have better financial results • EBITDA growth of over 10% was generated by 28% of companies with “advanced” risk management practices, compared with just 16% of firms with “emerging” practices • Revenue growth of 10% was shown by 29% of companies with “advanced” practices, compared with 18% of companies with “emerging” practices Creating an active risk culture can be correlated with higher growth, as organization becomes more aware and accountable for risk. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 44
 The proof is in the results • Using Total Risk Profiling, Zurich moved from an asset-based approach to riskbased approach for operational risk quantification and capital allocation • One Zurich business unit reduced operational risk-based capital (RBC) consumption by 21. 7 percent • The business unit then identified high risk exposures, performed a deeper assessment and developed mitigation • They had an additional reduction of 28. 9 % in operational RBC consumption • Capital not consumed was then available to fund profitable growth for Zurich. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 45
The proof is in the results • Using Total Risk Profiling, Zurich moved from an asset-based approach to riskbased approach for operational risk quantification and capital allocation • One Zurich business unit reduced operational risk-based capital (RBC) consumption by 21. 7 percent • The business unit then identified high risk exposures, performed a deeper assessment and developed mitigation • They had an additional reduction of 28. 9 % in operational RBC consumption • Capital not consumed was then available to fund profitable growth for Zurich. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 45
 Another example of results After pursuing a diversified financial services strategy for several years, Zurich reported a significant financial loss in 2001, leading to changes in leadership, and a renewed focus on underwriting: • Spun off reinsurance division, sold asset management business • Appointed new CEO, new Chief Risk Officer in 2002 • Guided by a robust Risk Policy, emphasized Enterprise Risk Management and implemented processes to measure and monitor risks to earnings, capital and reputation from all sources: • Strategic • Insurance • Market • Credit • Liquidity • Operational Zurich maintained a AA S&P rating through the 2008 -2009 financial crisis and recently reported its 44 th consecutive quarter of positive net earnings. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 46
Another example of results After pursuing a diversified financial services strategy for several years, Zurich reported a significant financial loss in 2001, leading to changes in leadership, and a renewed focus on underwriting: • Spun off reinsurance division, sold asset management business • Appointed new CEO, new Chief Risk Officer in 2002 • Guided by a robust Risk Policy, emphasized Enterprise Risk Management and implemented processes to measure and monitor risks to earnings, capital and reputation from all sources: • Strategic • Insurance • Market • Credit • Liquidity • Operational Zurich maintained a AA S&P rating through the 2008 -2009 financial crisis and recently reported its 44 th consecutive quarter of positive net earnings. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 46
 The information in this presentation was compiled from sources believed to be reliable for informational purposes only. All sample policies and procedures herein should serve as a guideline, which you can use to create your own policies and procedures. We trust that you will customize these samples to reflect your own operations and believe that these samples may serve as a helpful platform for this endeavor. Any and all information contained herein is not intended to constitute legal advice and accordingly, you should consult with your own attorneys when developing programs and policies. We do not guarantee the accuracy of this information or any results and further assume no liability in connection with this presentation and sample policies and procedures, including any information, methods or safety suggestions contained herein. Moreover, Zurich reminds you that this cannot be assumed to contain every acceptable safety and compliance procedure or that additional procedures might not be appropriate under the circumstances The subject matter of this presentation is not tied to any specific insurance product nor will adopting these policies and procedures ensure coverage under any insurance policy. © 2014 The Zurich Services Corporation. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 47
The information in this presentation was compiled from sources believed to be reliable for informational purposes only. All sample policies and procedures herein should serve as a guideline, which you can use to create your own policies and procedures. We trust that you will customize these samples to reflect your own operations and believe that these samples may serve as a helpful platform for this endeavor. Any and all information contained herein is not intended to constitute legal advice and accordingly, you should consult with your own attorneys when developing programs and policies. We do not guarantee the accuracy of this information or any results and further assume no liability in connection with this presentation and sample policies and procedures, including any information, methods or safety suggestions contained herein. Moreover, Zurich reminds you that this cannot be assumed to contain every acceptable safety and compliance procedure or that additional procedures might not be appropriate under the circumstances The subject matter of this presentation is not tied to any specific insurance product nor will adopting these policies and procedures ensure coverage under any insurance policy. © 2014 The Zurich Services Corporation. Recording of this session via any media type is strictly prohibited. Page 47


