e5a6a40de34d57aba8a900b895b0f525.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Entering Engineering Today… for a Better World Tomorrow Jane Simmons, BSc Geological Engineering University of New Brunswick January 15, 2008

Introductions Jane Simmons Geo-Environmental Engineering President Engineers Without Borders – UNB Chapter Hometown: Hensall, ON (pop 1400)

Engineering? Why me… The THREE reasons I’m here today: q Town Water Meeting q A Torque Wrench q Three Extraordinary Women

Hensall, ON (pop 1200)

Missing Designs? $4 Eyeglasses + Effective global distribution and marketing system = Better vision 1 billion people could afford to buy A Torque Wrench for Women

An Inspiration… q UNB Chemical Engineering Graduate Lived in Monze, Zambia for 3 years q q Water. Aid q NOW…Working on Poverty Reduction Strategies in NB

The Engineering Design Process: A way to solve all just about any problem Jane Simmons, BSc Geological Engineering University of New Brunswick January 15, 2008

If the only tool you have is a hammer, you tend to see every problem as a nail. Abraham Maslow

Learning Goals Recognize the steps of the Engineering Design Process in a real life example.

Why do we need a process?

Why do I need a process? 1. Increase the size of our toolbox. 2. Problems are complex! 3. Increase our odds of developing a solution that will work.
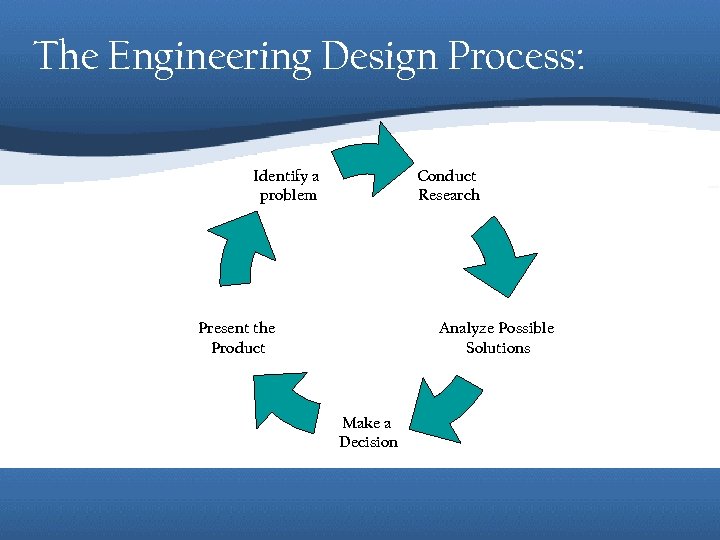
The Engineering Design Process: Identify a problem Conduct Research Present the Product Analyze Possible Solutions Make a Decision

Step 1: Identify a Problem Society identifies needs and engineers must figure out what the problem is in order to improve the situation. Identify a problem Conduct Research Present the Product Analyze Possible Solutions Make a Decision What is something you need?

Conduct Research Answer Questions: -What is good about how it is being done? -What is wrong with the way it is being done? -What has been written about this? -Does a solution already exist? Narrow the research – eliminate extreme solutions Identify a problem Conduct Research Present the Product Analyze Possible Solutions Make a Decision Where would we do our research?

Analyze Possible Solutions Analyze Set Criteria – Determine the relative importance of each characteristic desired by the client (i. e. low cost and durability) Finding Alternative Solutions – Brainstorming! Analyzing Possible Solutions Identify a problem Conduct Research Present the Product – Use criteria to “grade” brainstorming results What’s most important to us? Analyze Possible Solutions Make a Decision
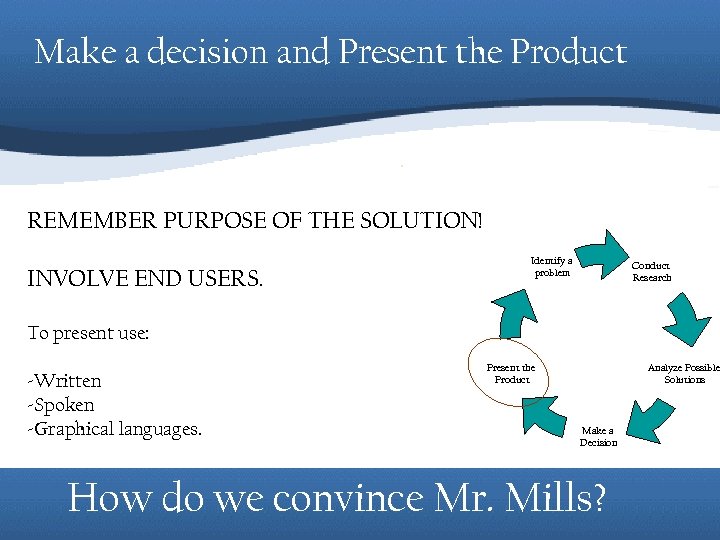
Make a decision and Present the Product REMEMBER PURPOSE OF THE SOLUTION! INVOLVE END USERS. Identify a problem Conduct Research To present use: -Written -Spoken -Graphical languages. Present the Product Analyze Possible Solutions Make a Decision How do we convince Mr. Mills?

Moving Windmills http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=ar. D 374 MFk 4 w
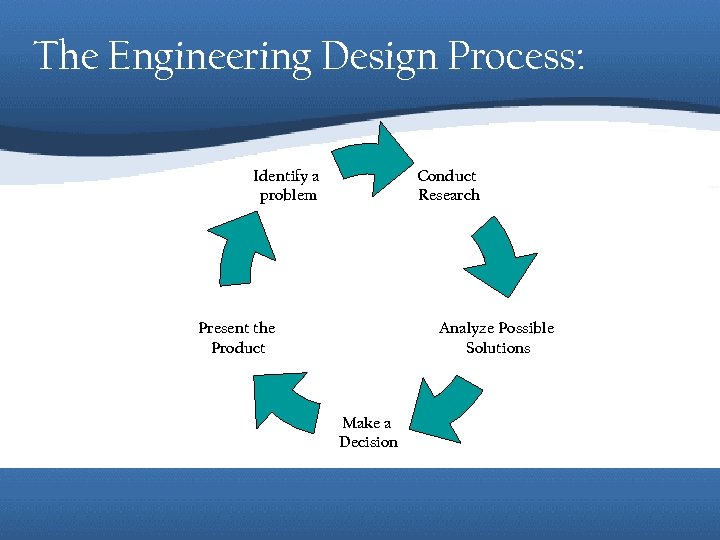
The Engineering Design Process: Identify a problem Conduct Research Present the Product Analyze Possible Solutions Make a Decision
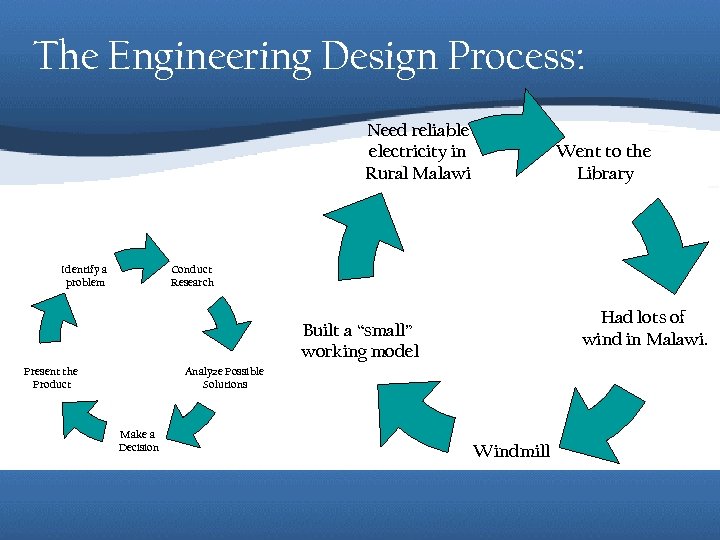
The Engineering Design Process: Need reliable electricity in Rural Malawi Identify a problem Went to the Library Conduct Research Had lots of wind in Malawi. Built a “small” working model Present the Product Analyze Possible Solutions Make a Decision Windmill

If the only tool you have is a hammer, you tend to see every problem as a nail. Abraham Maslow

Outside the Classroom Engineering Clubs and Societies • Engineers Without Borders • Engineering Undergraduate Society (EUS) • Women in Engineering Society • Departmental Societies • Design Tournaments Campus Wide • Student Union • Multicultural Clubs • Intramural Sports

…Engineering Needs You THREE Reasons to become an Engineer: q Create change in communities q Designing for EVERYONE q Be an inspiration!

QUESTIONS?
e5a6a40de34d57aba8a900b895b0f525.ppt