6d78e43c1c38f74ad646d0c8acfa395a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Ensuring Qo. S in Your Vo. IP Development Choon Shim CTO and Senior VP of Engineering choon@qovia. com , http: //www. qovia. com
Ensuring Qo. S in Your Vo. IP Development Choon Shim CTO and Senior VP of Engineering choon@qovia. com , http: //www. qovia. com
 Vo. IP problems l l Outage: - Infrastructure: switch, router, bridge, UPS, etc - Vo. IP element: call server, SIP server, GW, GK, MCU, handsets. - Carrier: T 1/E 1, analog signal trunk lines. Voice Quality: - Delay: network bandwidth, processing power - Echo: hybrid, acoustic - Jitter: jitter buffer calculation, variable delay - Packet loss: sender base, receiver base - Out of order: complex topology
Vo. IP problems l l Outage: - Infrastructure: switch, router, bridge, UPS, etc - Vo. IP element: call server, SIP server, GW, GK, MCU, handsets. - Carrier: T 1/E 1, analog signal trunk lines. Voice Quality: - Delay: network bandwidth, processing power - Echo: hybrid, acoustic - Jitter: jitter buffer calculation, variable delay - Packet loss: sender base, receiver base - Out of order: complex topology
 Roots of the problems l l l IP is not designed for carrying real-time media stream. Management was not considered by System/Elements Vendors. Too many moving parts. Too many protocol layers. Too many API layers. Multi vendor products.
Roots of the problems l l l IP is not designed for carrying real-time media stream. Management was not considered by System/Elements Vendors. Too many moving parts. Too many protocol layers. Too many API layers. Multi vendor products.
 Vo. IP ready network l l l Fast network: low latency and jitter Clean network: few packet loss and retransmit Qo. S ready network: Voice packet has priority Fault tolerant network: redundancy and backup Manageable network: monitoring and management
Vo. IP ready network l l l Fast network: low latency and jitter Clean network: few packet loss and retransmit Qo. S ready network: Voice packet has priority Fault tolerant network: redundancy and backup Manageable network: monitoring and management
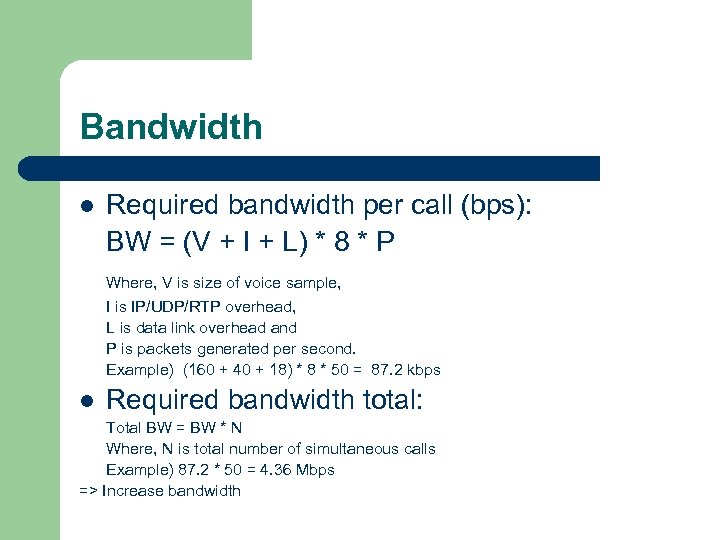 Bandwidth l Required bandwidth per call (bps): BW = (V + I + L) * 8 * P Where, V is size of voice sample, I is IP/UDP/RTP overhead, L is data link overhead and P is packets generated per second. Example) (160 + 40 + 18) * 8 * 50 = 87. 2 kbps l Required bandwidth total: Total BW = BW * N Where, N is total number of simultaneous calls Example) 87. 2 * 50 = 4. 36 Mbps => Increase bandwidth
Bandwidth l Required bandwidth per call (bps): BW = (V + I + L) * 8 * P Where, V is size of voice sample, I is IP/UDP/RTP overhead, L is data link overhead and P is packets generated per second. Example) (160 + 40 + 18) * 8 * 50 = 87. 2 kbps l Required bandwidth total: Total BW = BW * N Where, N is total number of simultaneous calls Example) 87. 2 * 50 = 4. 36 Mbps => Increase bandwidth
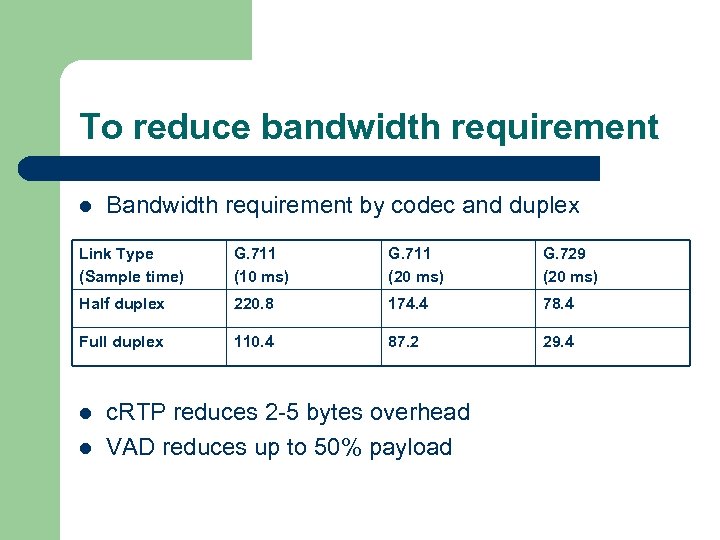 To reduce bandwidth requirement l Bandwidth requirement by codec and duplex Link Type (Sample time) G. 711 (10 ms) G. 711 (20 ms) G. 729 (20 ms) Half duplex 220. 8 174. 4 78. 4 Full duplex 110. 4 87. 2 29. 4 l l c. RTP reduces 2 -5 bytes overhead VAD reduces up to 50% payload
To reduce bandwidth requirement l Bandwidth requirement by codec and duplex Link Type (Sample time) G. 711 (10 ms) G. 711 (20 ms) G. 729 (20 ms) Half duplex 220. 8 174. 4 78. 4 Full duplex 110. 4 87. 2 29. 4 l l c. RTP reduces 2 -5 bytes overhead VAD reduces up to 50% payload
 Clean network l l l Reduce hop counts Reduce complexity of network topology Remove duplex mismatch Remove black hole and loop Avoid half duplex link Use common sense for cabling
Clean network l l l Reduce hop counts Reduce complexity of network topology Remove duplex mismatch Remove black hole and loop Avoid half duplex link Use common sense for cabling
 Qo. S ready network l Layer 3: - l Type of Service (TOS) RSVP signaling (RFC 2205) Diff. Serv (RFC 2474) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 2: - 802. 1 p and 802. 1 q - Ethernet Class of Service (COS)
Qo. S ready network l Layer 3: - l Type of Service (TOS) RSVP signaling (RFC 2205) Diff. Serv (RFC 2474) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 2: - 802. 1 p and 802. 1 q - Ethernet Class of Service (COS)
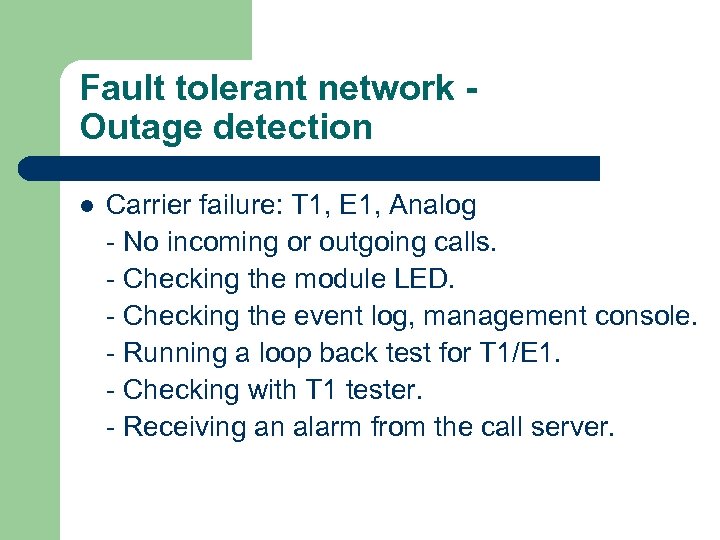 Fault tolerant network Outage detection l Carrier failure: T 1, E 1, Analog - No incoming or outgoing calls. - Checking the module LED. - Checking the event log, management console. - Running a loop back test for T 1/E 1. - Checking with T 1 tester. - Receiving an alarm from the call server.
Fault tolerant network Outage detection l Carrier failure: T 1, E 1, Analog - No incoming or outgoing calls. - Checking the module LED. - Checking the event log, management console. - Running a loop back test for T 1/E 1. - Checking with T 1 tester. - Receiving an alarm from the call server.
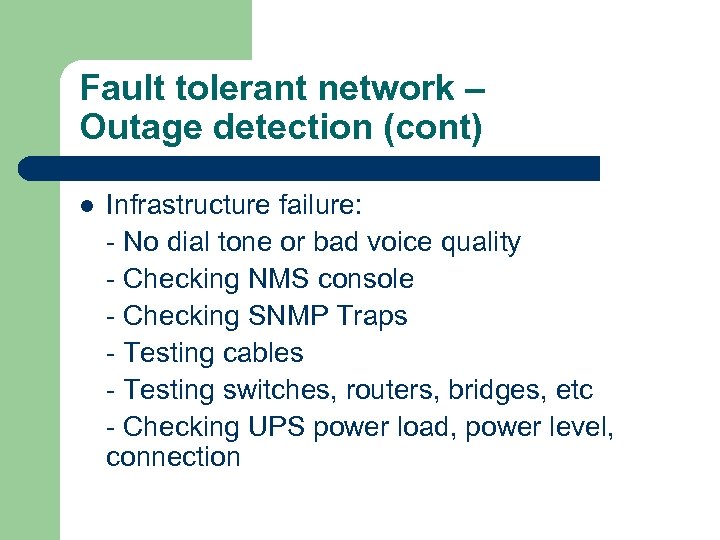 Fault tolerant network – Outage detection (cont) l Infrastructure failure: - No dial tone or bad voice quality - Checking NMS console - Checking SNMP Traps - Testing cables - Testing switches, routers, bridges, etc - Checking UPS power load, power level, connection
Fault tolerant network – Outage detection (cont) l Infrastructure failure: - No dial tone or bad voice quality - Checking NMS console - Checking SNMP Traps - Testing cables - Testing switches, routers, bridges, etc - Checking UPS power load, power level, connection
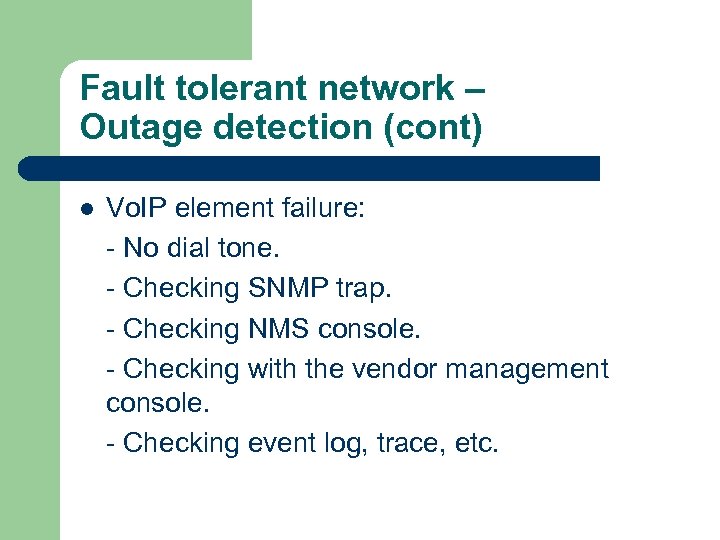 Fault tolerant network – Outage detection (cont) l Vo. IP element failure: - No dial tone. - Checking SNMP trap. - Checking NMS console. - Checking with the vendor management console. - Checking event log, trace, etc.
Fault tolerant network – Outage detection (cont) l Vo. IP element failure: - No dial tone. - Checking SNMP trap. - Checking NMS console. - Checking with the vendor management console. - Checking event log, trace, etc.
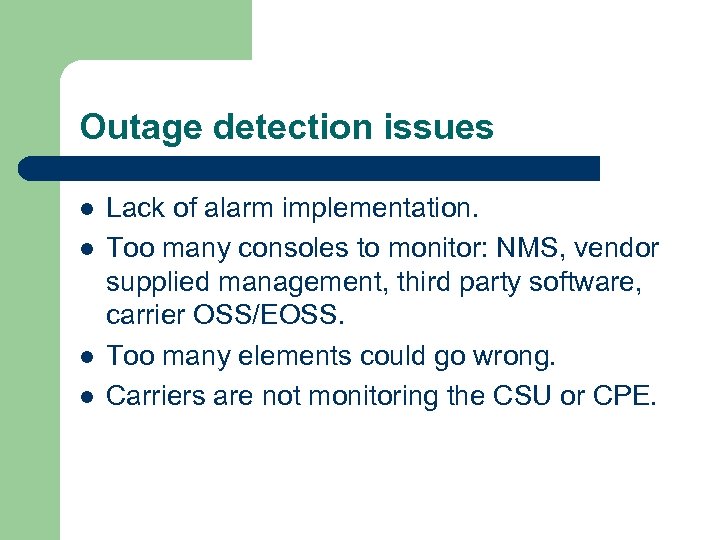 Outage detection issues l l Lack of alarm implementation. Too many consoles to monitor: NMS, vendor supplied management, third party software, carrier OSS/EOSS. Too many elements could go wrong. Carriers are not monitoring the CSU or CPE.
Outage detection issues l l Lack of alarm implementation. Too many consoles to monitor: NMS, vendor supplied management, third party software, carrier OSS/EOSS. Too many elements could go wrong. Carriers are not monitoring the CSU or CPE.
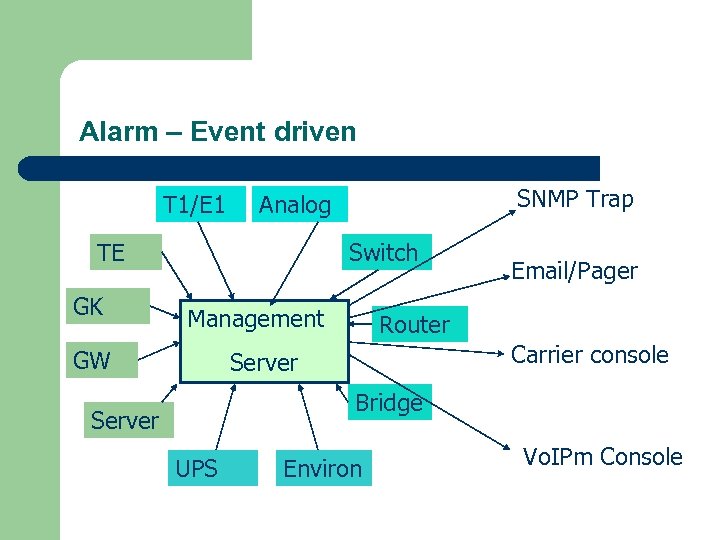 Alarm – Event driven T 1/E 1 TE GK SNMP Trap Analog Switch Management GW Email/Pager Router Carrier console Server Bridge Server UPS Environ Vo. IPm Console
Alarm – Event driven T 1/E 1 TE GK SNMP Trap Analog Switch Management GW Email/Pager Router Carrier console Server Bridge Server UPS Environ Vo. IPm Console
 Checking vital signs l l Blind polling: send a ping to every elements every x minutes. It triggers extra network traffics. Total number of packets per hour N = e * x / 60, where e = number of elements, x is minutes. Severity base polling: send a ping to critical elements more often. For example) GW: every 5 mins, GK: every 6 mins, Switch: every 10 mins, Terminal element: 30 mins, etc. Dynamic polling: recalculates number of pings based on the previous faults, traffic or volume. Number of packets N = f(1). . f(e), where f is the function being used for calculating faults, traffic and volume.
Checking vital signs l l Blind polling: send a ping to every elements every x minutes. It triggers extra network traffics. Total number of packets per hour N = e * x / 60, where e = number of elements, x is minutes. Severity base polling: send a ping to critical elements more often. For example) GW: every 5 mins, GK: every 6 mins, Switch: every 10 mins, Terminal element: 30 mins, etc. Dynamic polling: recalculates number of pings based on the previous faults, traffic or volume. Number of packets N = f(1). . f(e), where f is the function being used for calculating faults, traffic and volume.
 Manageable Vo. IP Network – Voice quality measurement l MOS (Mean Opinion Score): - Subjective measurement of Vo. IP. - Pre selected voice sample over different media, replayed to mixed group of men and woman, who rate them from 1 to 5. 4 – 5: Toll Quality 3 – 4: Communication quality < 3 : Synthetic quality
Manageable Vo. IP Network – Voice quality measurement l MOS (Mean Opinion Score): - Subjective measurement of Vo. IP. - Pre selected voice sample over different media, replayed to mixed group of men and woman, who rate them from 1 to 5. 4 – 5: Toll Quality 3 – 4: Communication quality < 3 : Synthetic quality
 Voice quality measurement l PSQM (Perceptual Speech Quality Measurement, ITU-T P. 861): - Automated scoring process using an algorithm that enables computer-derived scores to correlate to MOS scores. - Designed for circuit-switched network and does not take into effect important parameters such as jitter and packet loss, which affect voice quality on a VOIP network adversely.
Voice quality measurement l PSQM (Perceptual Speech Quality Measurement, ITU-T P. 861): - Automated scoring process using an algorithm that enables computer-derived scores to correlate to MOS scores. - Designed for circuit-switched network and does not take into effect important parameters such as jitter and packet loss, which affect voice quality on a VOIP network adversely.
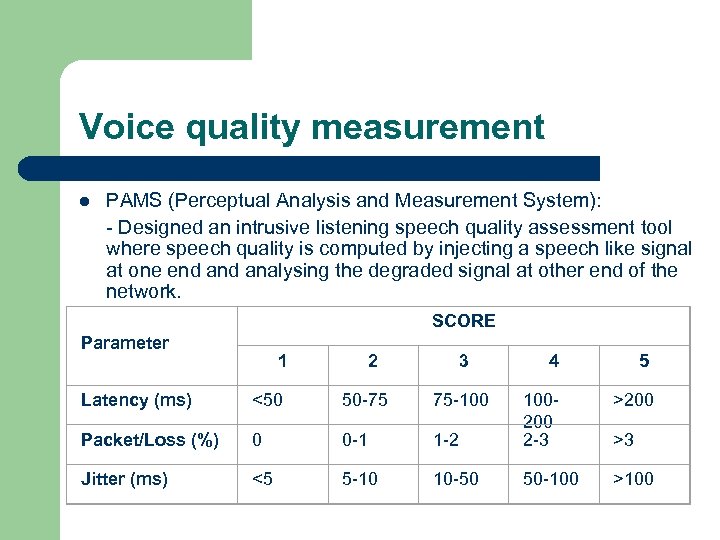 Voice quality measurement l PAMS (Perceptual Analysis and Measurement System): - Designed an intrusive listening speech quality assessment tool where speech quality is computed by injecting a speech like signal at one end analysing the degraded signal at other end of the network. SCORE Parameter 1 2 3 4 5 >200 >100 Latency (ms) <50 50 -75 75 -100 Packet/Loss (%) 0 0 -1 1 -2 100200 2 -3 Jitter (ms) <5 5 -10 10 -50 50 -100 >3
Voice quality measurement l PAMS (Perceptual Analysis and Measurement System): - Designed an intrusive listening speech quality assessment tool where speech quality is computed by injecting a speech like signal at one end analysing the degraded signal at other end of the network. SCORE Parameter 1 2 3 4 5 >200 >100 Latency (ms) <50 50 -75 75 -100 Packet/Loss (%) 0 0 -1 1 -2 100200 2 -3 Jitter (ms) <5 5 -10 10 -50 50 -100 >3
 Voice quality measurement l PESQ: PESQ (ITU–T P. 862): - The latest standard for assessing voice quality and is expected to eventually replace PSQM. - It builds on the PSQM and PAMS algorithms by adding additional processing steps to account for signal-level differences and the identification of errors associated with packet loss.
Voice quality measurement l PESQ: PESQ (ITU–T P. 862): - The latest standard for assessing voice quality and is expected to eventually replace PSQM. - It builds on the PSQM and PAMS algorithms by adding additional processing steps to account for signal-level differences and the identification of errors associated with packet loss.
 Voice quality measurement l Delay guideline: ITU-T G. 114 Acceptable under conditions 0 150 Unacceptable 400 0 – 150 ms: Good quality and no echo 151 – 400 ms: Acceptable under certain conditions and echo canceling is needed 401+: Unacceptable for real-time voice traffic and planning and testing purposes only
Voice quality measurement l Delay guideline: ITU-T G. 114 Acceptable under conditions 0 150 Unacceptable 400 0 – 150 ms: Good quality and no echo 151 – 400 ms: Acceptable under certain conditions and echo canceling is needed 401+: Unacceptable for real-time voice traffic and planning and testing purposes only
 Quality problem detection l l Interpret RTCP and RTCP XR. Packet monitoring by Layer 2 switch taping or port mirroring. Probing and active monitoring by injecting a test packet. SNMP, RMON or s. Flow gathering.
Quality problem detection l l Interpret RTCP and RTCP XR. Packet monitoring by Layer 2 switch taping or port mirroring. Probing and active monitoring by injecting a test packet. SNMP, RMON or s. Flow gathering.
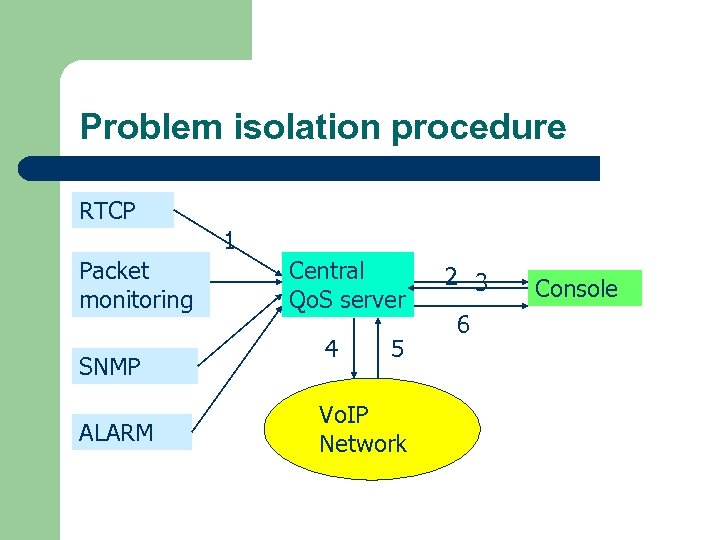 Problem isolation procedure RTCP 1 Packet monitoring SNMP ALARM Central Qo. S server 4 5 Vo. IP Network 2 3 6 Console
Problem isolation procedure RTCP 1 Packet monitoring SNMP ALARM Central Qo. S server 4 5 Vo. IP Network 2 3 6 Console
 Central Qo. S management server l l l l Discover Vo. IP components/elements dynamically. Create a topology and aggregate multiple call servers, GW, GK, MCU, SIP Servers, etc. Collect performance/delay data from various sources. Calculate variable polling period and injects an active packet. Make a statistical model to use for assign Qo. S. Organize elements/Qo. S data in the relational DBMS. Detect voice quality problem and send an alarm to console. Inject an active test packet to isolate the problem as per console.
Central Qo. S management server l l l l Discover Vo. IP components/elements dynamically. Create a topology and aggregate multiple call servers, GW, GK, MCU, SIP Servers, etc. Collect performance/delay data from various sources. Calculate variable polling period and injects an active packet. Make a statistical model to use for assign Qo. S. Organize elements/Qo. S data in the relational DBMS. Detect voice quality problem and send an alarm to console. Inject an active test packet to isolate the problem as per console.
 Console l l l Display overall call quality. Display topology and status display. Display drill down to detail elements with MOS/PESQ. Display real time status and quality changes. Trigger the problem isolation procedure.
Console l l l Display overall call quality. Display topology and status display. Display drill down to detail elements with MOS/PESQ. Display real time status and quality changes. Trigger the problem isolation procedure.
 Q&A l Thank you! Any questions?
Q&A l Thank you! Any questions?


