9fbd7b2b3bafba9c7a57295ff0fbc083.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Enriching OWL with Instance Recognition Semantics for Automated Semantic Annotation Stephen W. Liddle Information Systems Department Yihong Ding & David W. Embley Computer Science Department Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah
Enriching OWL with Instance Recognition Semantics for Automated Semantic Annotation Stephen W. Liddle Information Systems Department Yihong Ding & David W. Embley Computer Science Department Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah
 Outline n Background n Instance recognition semantics n Automated semantic annotation n OWL-AA: OWL for Automated Annotation n Related work n Conclusion 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 2 of 20
Outline n Background n Instance recognition semantics n Automated semantic annotation n OWL-AA: OWL for Automated Annotation n Related work n Conclusion 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 2 of 20
 Motivation n Big Hairy Audacious Goal: deliver a machine- processable semantic web that will let us build agents to work intelligently on our behalf n Realistic Shorter-term Goal: provide automatic semantic annotation machinery that turns ordinary web pages into semantic web pages by adding appropriate metadata n Goal of this Paper: Show that we can extend OWL with epistemological declarations that let us use our data extraction engine to provide a solid automatic annotator that works with standard ontologies 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 3 of 20
Motivation n Big Hairy Audacious Goal: deliver a machine- processable semantic web that will let us build agents to work intelligently on our behalf n Realistic Shorter-term Goal: provide automatic semantic annotation machinery that turns ordinary web pages into semantic web pages by adding appropriate metadata n Goal of this Paper: Show that we can extend OWL with epistemological declarations that let us use our data extraction engine to provide a solid automatic annotator that works with standard ontologies 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 3 of 20
 Typical Approach n Typical approach to automatic annotation: n Use existing data extraction engine to wrap and annotate pages n BUT these approaches do not match extracted data with an ontology n Main drawback: n Post-processing step to map extracted data to the ontology 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 4 of 20
Typical Approach n Typical approach to automatic annotation: n Use existing data extraction engine to wrap and annotate pages n BUT these approaches do not match extracted data with an ontology n Main drawback: n Post-processing step to map extracted data to the ontology 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 4 of 20
 Our Approach n Our data extraction engine is ontology based and does not need a post-processing alignment step We have demonstrated that our approach works (Ding/Embley/Liddle 2006, LNCS 4185) n But our ontology language is not a W 3 C standard n n OWL is a standard (W 3 C recommendation) n But lacks sufficient declarative instancerecognition semantics for automatic annotation 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 5 of 20
Our Approach n Our data extraction engine is ontology based and does not need a post-processing alignment step We have demonstrated that our approach works (Ding/Embley/Liddle 2006, LNCS 4185) n But our ontology language is not a W 3 C standard n n OWL is a standard (W 3 C recommendation) n But lacks sufficient declarative instancerecognition semantics for automatic annotation 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 5 of 20
 A Solution n Extend OWL with declarative instance- recognition semantics n Call this OWL for Automated Annotation (OWL -AA) n OWL-AA extension is epistemological in nature Ontological definitions should be independent of the form of knowledge representation n Epistemological definitions may be sensitive to the form of knowledge representation n 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 6 of 20
A Solution n Extend OWL with declarative instance- recognition semantics n Call this OWL for Automated Annotation (OWL -AA) n OWL-AA extension is epistemological in nature Ontological definitions should be independent of the form of knowledge representation n Epistemological definitions may be sensitive to the form of knowledge representation n 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 6 of 20
 Our Contributions n OWL-AA extends OWL to provide for automated semantic annotation that Embeds instance-recognition semantics declarations in ontologies and data extraction tools n Provides enhanced knowledge sharing and reuse via semantic web n Separates domain knowledge creation from semantic annotation process n n 6 November 2007 Thus maintaining separation between concerns of domain experts and software developers ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 7 of 20
Our Contributions n OWL-AA extends OWL to provide for automated semantic annotation that Embeds instance-recognition semantics declarations in ontologies and data extraction tools n Provides enhanced knowledge sharing and reuse via semantic web n Separates domain knowledge creation from semantic annotation process n n 6 November 2007 Thus maintaining separation between concerns of domain experts and software developers ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 7 of 20
 Instance Recognition Semantics n Instance Semantics Recognizers (ISR’s) n Formal specifications that identify instances of a concept in unstructured, semistructured, or structured text n Example: n Concept: Phone. Number n Text: “Call me at 555 -1212. ” n ISR should recognize that 555 -1212 in the text has the intensional meaning of Phone. Number. 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 8 of 20
Instance Recognition Semantics n Instance Semantics Recognizers (ISR’s) n Formal specifications that identify instances of a concept in unstructured, semistructured, or structured text n Example: n Concept: Phone. Number n Text: “Call me at 555 -1212. ” n ISR should recognize that 555 -1212 in the text has the intensional meaning of Phone. Number. 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 8 of 20
![ISR Declarations in Data Frames Bedroom. Nr internal representation: Integer external representation: [1 -9]|10 ISR Declarations in Data Frames Bedroom. Nr internal representation: Integer external representation: [1 -9]|10](https://present5.com/presentation/9fbd7b2b3bafba9c7a57295ff0fbc083/image-9.jpg) ISR Declarations in Data Frames Bedroom. Nr internal representation: Integer external representation: [1 -9]|10 left context phrase: b right context phrase: . *r(oo)? ms? exception phrase: s. *ba(th)? s? b. *r(oo)? ms? context keywords: b(r|d)s? |bdrms? |bed(rooms? )? . . . Less. Than(p 1: Price, p 2: Price) returns (Boolean) context keywords: less than|<|or less|fewer|. . . end Feature external representation: Apartment. Feature. lexicon. . . end 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 9 of 20
ISR Declarations in Data Frames Bedroom. Nr internal representation: Integer external representation: [1 -9]|10 left context phrase: b right context phrase: . *r(oo)? ms? exception phrase: s. *ba(th)? s? b. *r(oo)? ms? context keywords: b(r|d)s? |bdrms? |bed(rooms? )? . . . Less. Than(p 1: Price, p 2: Price) returns (Boolean) context keywords: less than|<|or less|fewer|. . . end Feature external representation: Apartment. Feature. lexicon. . . end 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 9 of 20
 Resiliency n There are no document layout dependencies in our ISR declarations n Other approaches typically use page layout information for extraction n Layout independence (resiliency) is a major benefit Page layouts change periodically on the web n Different publishers in the same domain generally use different page layouts n Rewriting wrappers is costly n 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 10 of 20
Resiliency n There are no document layout dependencies in our ISR declarations n Other approaches typically use page layout information for extraction n Layout independence (resiliency) is a major benefit Page layouts change periodically on the web n Different publishers in the same domain generally use different page layouts n Rewriting wrappers is costly n 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 10 of 20
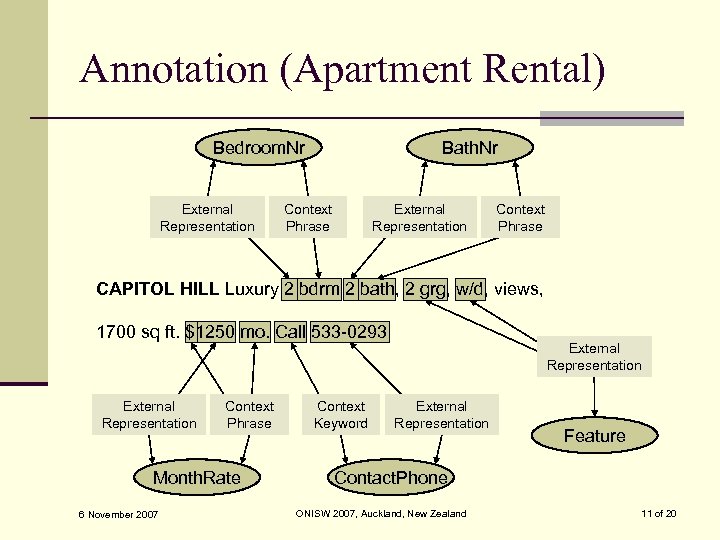 Annotation (Apartment Rental) Bedroom. Nr External Representation Bath. Nr Context Phrase External Representation Context Phrase CAPITOL HILL Luxury 2 bdrm 2 bath, 2 grg, w/d, views, 1700 sq ft. $1250 mo. Call 533 -0293 External Representation Context Phrase Month. Rate 6 November 2007 Context Keyword External Representation Feature Contact. Phone ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 11 of 20
Annotation (Apartment Rental) Bedroom. Nr External Representation Bath. Nr Context Phrase External Representation Context Phrase CAPITOL HILL Luxury 2 bdrm 2 bath, 2 grg, w/d, views, 1700 sq ft. $1250 mo. Call 533 -0293 External Representation Context Phrase Month. Rate 6 November 2007 Context Keyword External Representation Feature Contact. Phone ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 11 of 20
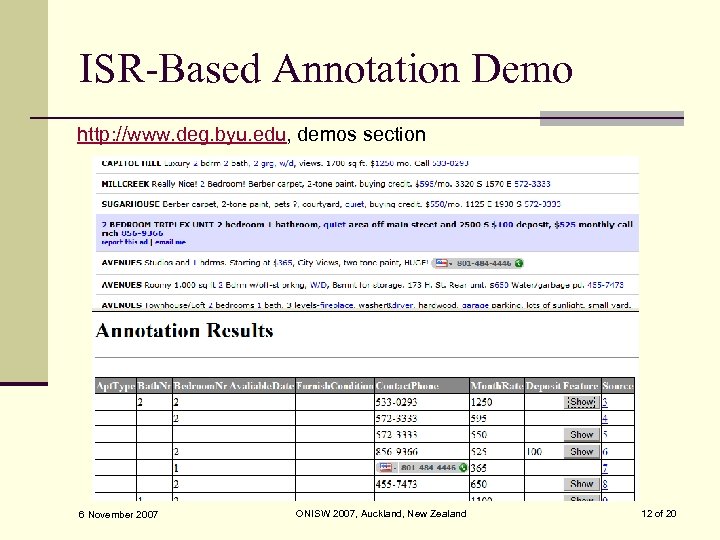 ISR-Based Annotation Demo http: //www. deg. byu. edu, demos section 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 12 of 20
ISR-Based Annotation Demo http: //www. deg. byu. edu, demos section 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 12 of 20
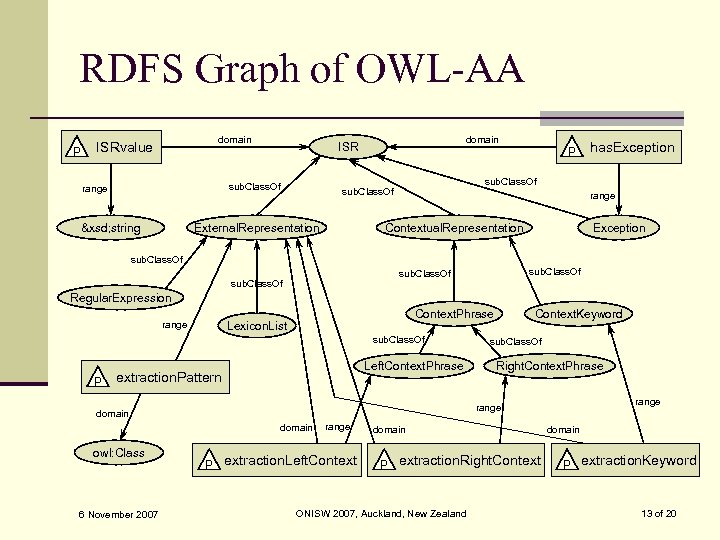 RDFS Graph of OWL-AA P domain ISRvalue sub. Class. Of range &xsd; string domain ISR has. Exception sub. Class. Of External. Representation P range Exception Contextual. Representation sub. Class. Of Regular. Expression Context. Phrase Lexicon. List range sub. Class. Of P Left. Context. Phrase extraction. Pattern domain 6 November 2007 sub. Class. Of Right. Context. Phrase range domain owl: Class Context. Keyword range P extraction. Left. Context domain P extraction. Right. Context ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand domain P extraction. Keyword 13 of 20
RDFS Graph of OWL-AA P domain ISRvalue sub. Class. Of range &xsd; string domain ISR has. Exception sub. Class. Of External. Representation P range Exception Contextual. Representation sub. Class. Of Regular. Expression Context. Phrase Lexicon. List range sub. Class. Of P Left. Context. Phrase extraction. Pattern domain 6 November 2007 sub. Class. Of Right. Context. Phrase range domain owl: Class Context. Keyword range P extraction. Left. Context domain P extraction. Right. Context ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand domain P extraction. Keyword 13 of 20
 OWL-AA Details (1) n Add namespace xmlns: owlaa=“http: //www. deg. byu. edu/OWL-AA#” n Add properties to OWL classes associating ISR declarations
OWL-AA Details (1) n Add namespace xmlns: owlaa=“http: //www. deg. byu. edu/OWL-AA#” n Add properties to OWL classes associating ISR declarations
 OWL-AA Details (2) n Declare ISR value and contextual restriction
OWL-AA Details (2) n Declare ISR value and contextual restriction
 OWL-AA Details (3) n Add context phrases, context keywords, and exceptions
OWL-AA Details (3) n Add context phrases, context keywords, and exceptions
 OWL-AA Features n Syntactically, OWL-AA is attachment- independent w. r. t. OWL n No need to change a single line of existing OWL ontologies n Semantically, OWL-AA is also attachment- independent w. r. t. OWL n ISR declarations do not change meaning of existing ontology concepts at conceptual level n Prototype implementation translates OWL-AA to our own internal format for processing 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 17 of 20
OWL-AA Features n Syntactically, OWL-AA is attachment- independent w. r. t. OWL n No need to change a single line of existing OWL ontologies n Semantically, OWL-AA is also attachment- independent w. r. t. OWL n ISR declarations do not change meaning of existing ontology concepts at conceptual level n Prototype implementation translates OWL-AA to our own internal format for processing 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 17 of 20
 Related Work n We aren’t the first to work on ISR declarations n IBM’s Unstructured Information Management Architecture n There are many proposals for extending OWL n Two extensions related to ours n Context OWL (C-OWL) n Extension for ontology mapping that localizes ontology content for global visibility n OWL-Eu n Extension that enriches OWL with customized datatypes, a significant need n Not attachment-independent, unfortunately n But our approach is compatible with OWL-Eu too 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 18 of 20
Related Work n We aren’t the first to work on ISR declarations n IBM’s Unstructured Information Management Architecture n There are many proposals for extending OWL n Two extensions related to ours n Context OWL (C-OWL) n Extension for ontology mapping that localizes ontology content for global visibility n OWL-Eu n Extension that enriches OWL with customized datatypes, a significant need n Not attachment-independent, unfortunately n But our approach is compatible with OWL-Eu too 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 18 of 20
 Conclusion n Automated semantic annotation is an important and fundamental problem for the semantic web n Key to automated annotation is ISR declaration n Our epistemological OWL-AA extension augments OWL to formalize ISR declarations 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 19 of 20
Conclusion n Automated semantic annotation is an important and fundamental problem for the semantic web n Key to automated annotation is ISR declaration n Our epistemological OWL-AA extension augments OWL to formalize ISR declarations 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 19 of 20
 Conclusion (cont. ) n OWL-AA is fully compatible with ordinary OWL n Attachable/detachable n OWL-AA does not introduce complexity or decidability issues into OWL n Prototype implementation demonstrates that our approach works well n Embedding epistemological declarations in OWL is a fruitful area meriting further research 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 20 of 20
Conclusion (cont. ) n OWL-AA is fully compatible with ordinary OWL n Attachable/detachable n OWL-AA does not introduce complexity or decidability issues into OWL n Prototype implementation demonstrates that our approach works well n Embedding epistemological declarations in OWL is a fruitful area meriting further research 6 November 2007 ONISW 2007, Auckland, New Zealand 20 of 20


