fbdb492908ae5104c285e534ea07a8b3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Enhancing TVET Graduates' 21 st Century Skills Through An Integrated Curriculum - the Malaysian Polytechnics' Experience Dr. Helen Teh Sultan Haji Ahmad Shah Polytechnic Department of Polytechnic Education Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia E-mail: helenteh@polisas. edu. my 2
Enhancing TVET Graduates' 21 st Century Skills Through An Integrated Curriculum - the Malaysian Polytechnics' Experience Dr. Helen Teh Sultan Haji Ahmad Shah Polytechnic Department of Polytechnic Education Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia E-mail: helenteh@polisas. edu. my 2
 THE AUTHORS Dr Noreen Kamarudin 1 Principal Assistant Director, Curriculum Development Division (CDD), Dept of Polytechnic Education (DPE), Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (Mo. HE). Projects: CDIO No. U (DPE-Singapore Polytechnic-Temasek Foundation: 2014 -2015), Design Thinking (DPE-Genovasi: 2016), Learning Express Mo. U (DPE-Singapore Polytechnic: 20172019) Integrated Curriculum (11 th Malaysian Plan Curriculum Development Funding: 2016 -2020) Dr Helen Teh Bee Lean 2 Job scope: curriculum development, Ahmad Shah (POLISAS), Ministry Principal Lecturer, Politeknik Sultan Hj evaluation, review and innovation. of Higher Education Malaysia (Mo. HE), Malaysia. CDIO Master Trainer Design Thinking Innovation Ambassador Diploma in Chemical Technology Program Lead Developer Researcher (Fundamental Research Grant Scheme) DPE Career Path Competency Matrix Course Facilitator for Design Thinking Job scope: teaching, curriculum development, program evaluation, needs assessment, curriculum review, research and
THE AUTHORS Dr Noreen Kamarudin 1 Principal Assistant Director, Curriculum Development Division (CDD), Dept of Polytechnic Education (DPE), Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (Mo. HE). Projects: CDIO No. U (DPE-Singapore Polytechnic-Temasek Foundation: 2014 -2015), Design Thinking (DPE-Genovasi: 2016), Learning Express Mo. U (DPE-Singapore Polytechnic: 20172019) Integrated Curriculum (11 th Malaysian Plan Curriculum Development Funding: 2016 -2020) Dr Helen Teh Bee Lean 2 Job scope: curriculum development, Ahmad Shah (POLISAS), Ministry Principal Lecturer, Politeknik Sultan Hj evaluation, review and innovation. of Higher Education Malaysia (Mo. HE), Malaysia. CDIO Master Trainer Design Thinking Innovation Ambassador Diploma in Chemical Technology Program Lead Developer Researcher (Fundamental Research Grant Scheme) DPE Career Path Competency Matrix Course Facilitator for Design Thinking Job scope: teaching, curriculum development, program evaluation, needs assessment, curriculum review, research and
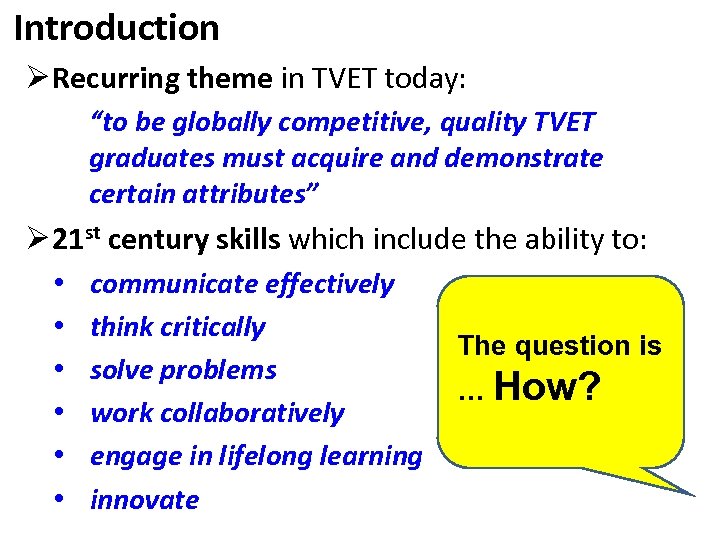 Introduction Ø Recurring theme in TVET today: “to be globally competitive, quality TVET graduates must acquire and demonstrate certain attributes” Ø 21 st century skills which include the ability to: • • • communicate effectively think critically solve problems work collaboratively engage in lifelong learning innovate The question is … How?
Introduction Ø Recurring theme in TVET today: “to be globally competitive, quality TVET graduates must acquire and demonstrate certain attributes” Ø 21 st century skills which include the ability to: • • • communicate effectively think critically solve problems work collaboratively engage in lifelong learning innovate The question is … How?
 My presentation will follow the following points: TVET context – the Malaysian Polytechnics Background of the Problem CDIO & the CDIO Integrated Curriculum The Malaysian Polytechnic’s Integrated Curriculum Models • The Implementation of the Models in selected programmes • Summary of Findings • Conclusion • •
My presentation will follow the following points: TVET context – the Malaysian Polytechnics Background of the Problem CDIO & the CDIO Integrated Curriculum The Malaysian Polytechnic’s Integrated Curriculum Models • The Implementation of the Models in selected programmes • Summary of Findings • Conclusion • •
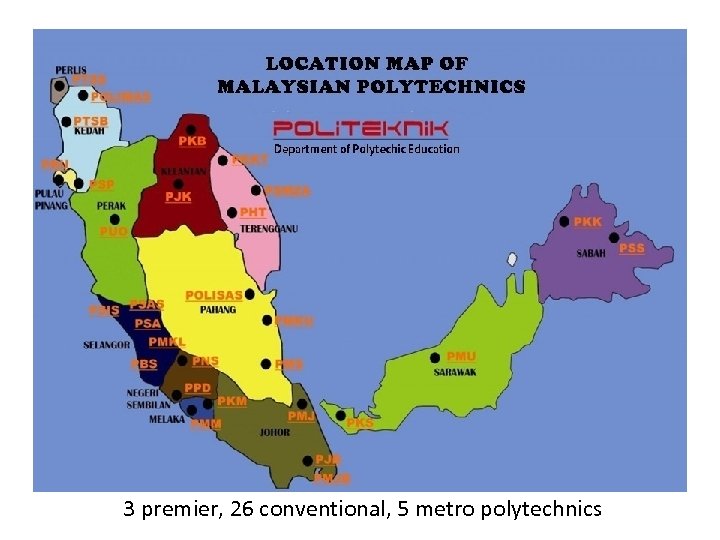 3 premier, 26 conventional, 5 metro polytechnics
3 premier, 26 conventional, 5 metro polytechnics
 Dublin Accord accredited programmes: üDiploma in Electrical Engineering üDiploma in Civil Engineering
Dublin Accord accredited programmes: üDiploma in Electrical Engineering üDiploma in Civil Engineering
 What is CDIO? • Innovative educational framework • applied in engineering and nonengineering education programmes • based on fundamentals of: • real world systems and products • to produce next generation engineers
What is CDIO? • Innovative educational framework • applied in engineering and nonengineering education programmes • based on fundamentals of: • real world systems and products • to produce next generation engineers
 Who are the initiators? Edward Crawley, Professor in Aeronautics & Astronautics, MIT, Founding CDIO Past Co-Director • CDIO approach: late 1990 s Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) • CDIO initiative: 2000 MIT in collaboration with 3 Swedish Institutions: Chalmers University of Technology, Linkoping University Royal Institute of Technology Johan Malmqvist, Professor in Product Development, Chalmers University Past CDIO Co. Director Ron Hugo, Professor in Mechanical Engineering & Manufacturing, University of Calgary CDIO Co-Director
Who are the initiators? Edward Crawley, Professor in Aeronautics & Astronautics, MIT, Founding CDIO Past Co-Director • CDIO approach: late 1990 s Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) • CDIO initiative: 2000 MIT in collaboration with 3 Swedish Institutions: Chalmers University of Technology, Linkoping University Royal Institute of Technology Johan Malmqvist, Professor in Product Development, Chalmers University Past CDIO Co. Director Ron Hugo, Professor in Mechanical Engineering & Manufacturing, University of Calgary CDIO Co-Director
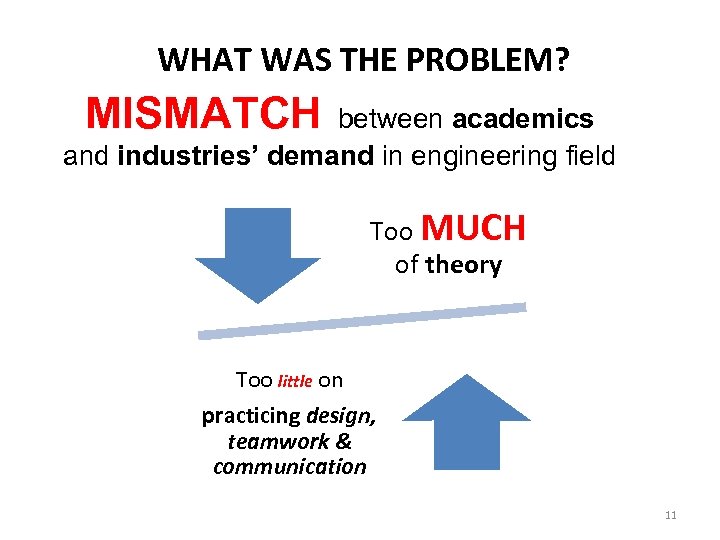 WHAT WAS THE PROBLEM? MISMATCH between academics and industries’ demand in engineering field Too MUCH of theory Too little on practicing design, teamwork & communication 11
WHAT WAS THE PROBLEM? MISMATCH between academics and industries’ demand in engineering field Too MUCH of theory Too little on practicing design, teamwork & communication 11
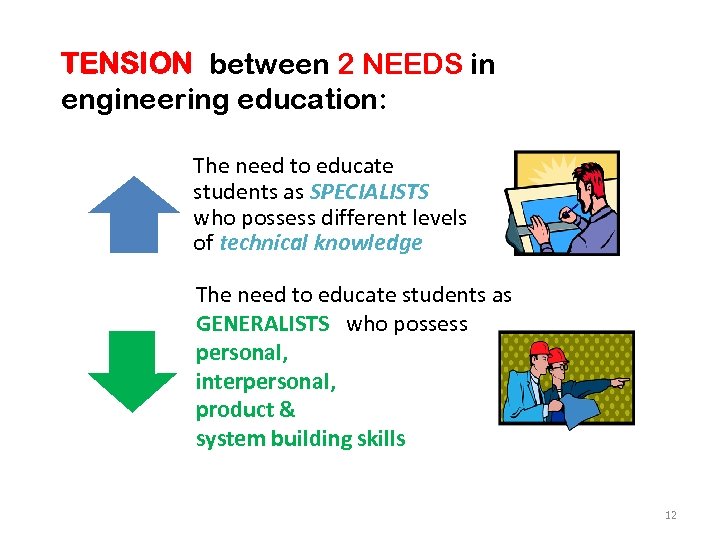 TENSION between 2 NEEDS in engineering education: The need to educate students as SPECIALISTS who possess different levels of technical knowledge The need to educate students as GENERALISTS who possess personal, interpersonal, product & system building skills 12
TENSION between 2 NEEDS in engineering education: The need to educate students as SPECIALISTS who possess different levels of technical knowledge The need to educate students as GENERALISTS who possess personal, interpersonal, product & system building skills 12
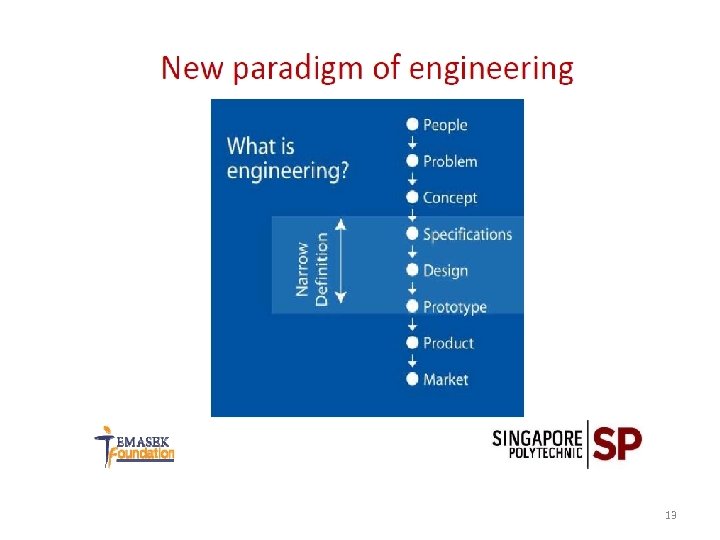 13
13
 CDIO in Malaysian Education Blueprint Shift 1: Holistic, entrepreneurial & balanced graduate 15
CDIO in Malaysian Education Blueprint Shift 1: Holistic, entrepreneurial & balanced graduate 15
 CDIO standards and syllabus 12 CDIO STANDARDS http: //www. cdio. org/implem enting-cdio/standards/12 cdio-standards 1. CDIO as the context 2. Learning Outcomes 3. Integrated Curriculum 4. Introduction to Engineering 5. Design-implement experience 6. Engineering workspaces 7. Integrated learning experiences 8. Active Learning 9. Enhancement of faculty CDIO competence 10. Enhancement of faculty teaching competence 11. Learning assessment 12. Programme Evaluation http: //www. cdio. org/frameworkbenefits/cdio-syllabus
CDIO standards and syllabus 12 CDIO STANDARDS http: //www. cdio. org/implem enting-cdio/standards/12 cdio-standards 1. CDIO as the context 2. Learning Outcomes 3. Integrated Curriculum 4. Introduction to Engineering 5. Design-implement experience 6. Engineering workspaces 7. Integrated learning experiences 8. Active Learning 9. Enhancement of faculty CDIO competence 10. Enhancement of faculty teaching competence 11. Learning assessment 12. Programme Evaluation http: //www. cdio. org/frameworkbenefits/cdio-syllabus

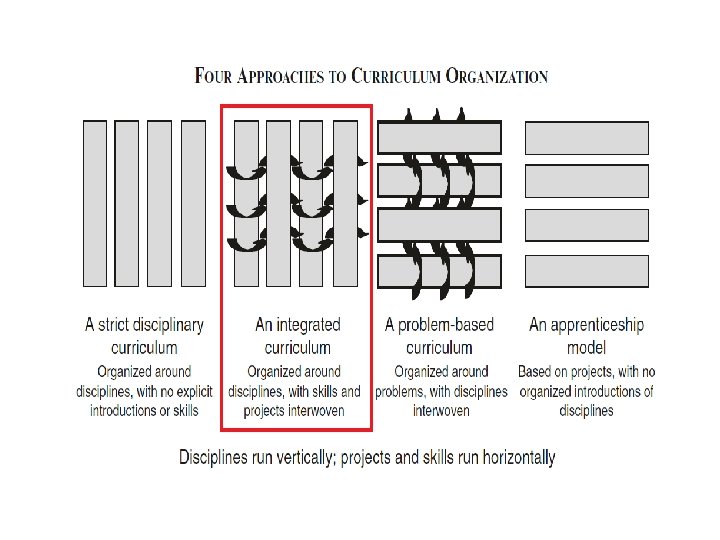
 Existing Curriculum Drawbacks: Students’ Problems: Ø Too many assessments Ø Spending too much time on various assessments Ø Unable to relate between courses Lecturers’ Problems: Ø Courses are taught in silo Benefits of integrated Curriculum ü Incorporating a few courses’ assessment into one project ü Faculty plan, do and assess project tasks & assessment together ü Active and experiential learning for students ü Real projects based on community and industry needs
Existing Curriculum Drawbacks: Students’ Problems: Ø Too many assessments Ø Spending too much time on various assessments Ø Unable to relate between courses Lecturers’ Problems: Ø Courses are taught in silo Benefits of integrated Curriculum ü Incorporating a few courses’ assessment into one project ü Faculty plan, do and assess project tasks & assessment together ü Active and experiential learning for students ü Real projects based on community and industry needs
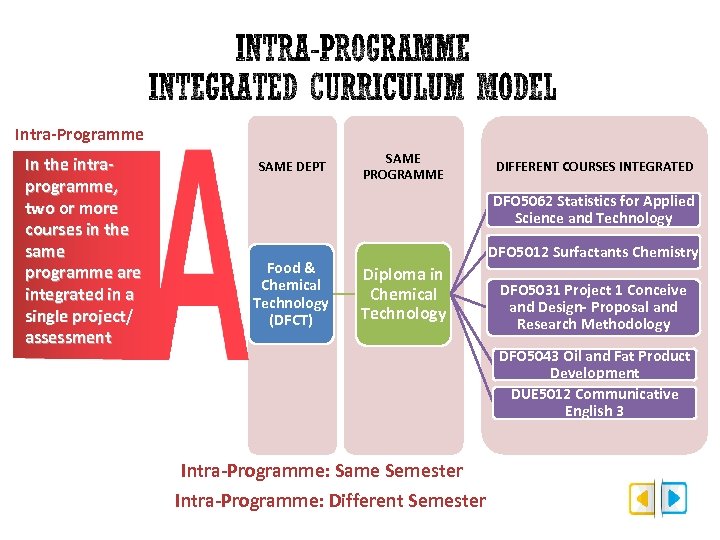 Intra-Programme In the intraprogramme, two or more courses in the same programme are integrated in a single project/ assessment SAME DEPT SAME PROGRAMME DIFFERENT COURSES INTEGRATED DFO 5062 Statistics for Applied Science and Technology Food & Chemical Technology (DFCT) DFO 5012 Surfactants Chemistry Diploma in Chemical Technology DFO 5031 Project 1 Conceive and Design- Proposal and Research Methodology DFO 5043 Oil and Fat Product Development DUE 5012 Communicative English 3 Intra-Programme: Same Semester Intra-Programme: Different Semester
Intra-Programme In the intraprogramme, two or more courses in the same programme are integrated in a single project/ assessment SAME DEPT SAME PROGRAMME DIFFERENT COURSES INTEGRATED DFO 5062 Statistics for Applied Science and Technology Food & Chemical Technology (DFCT) DFO 5012 Surfactants Chemistry Diploma in Chemical Technology DFO 5031 Project 1 Conceive and Design- Proposal and Research Methodology DFO 5043 Oil and Fat Product Development DUE 5012 Communicative English 3 Intra-Programme: Same Semester Intra-Programme: Different Semester
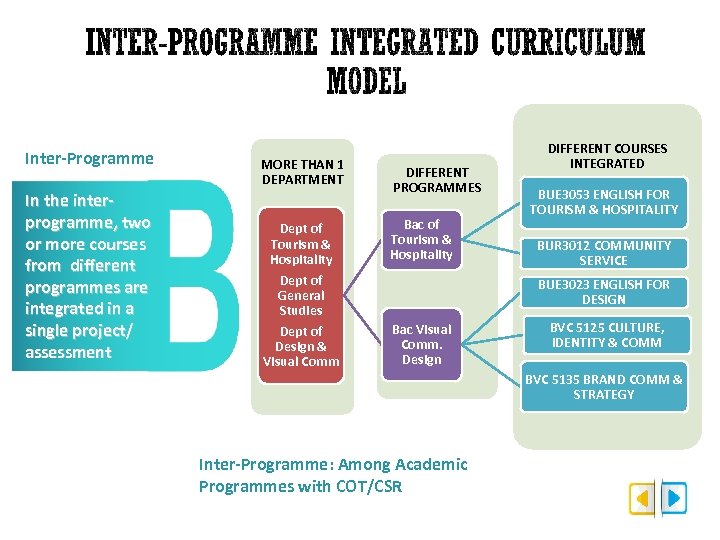 Inter-Programme In the interprogramme, two or more courses from different programmes are integrated in a single project/ assessment MORE THAN 1 DEPARTMENT Dept of Tourism & Hospitality Dept of General Studies Dept of Design & Visual Comm DIFFERENT PROGRAMMES Bac of Tourism & Hospitality DIFFERENT COURSES INTEGRATED BUE 3053 ENGLISH FOR TOURISM & HOSPITALITY BUR 3012 COMMUNITY SERVICE BUE 3023 ENGLISH FOR DESIGN Bac Visual Comm. Design BVC 5125 CULTURE, IDENTITY & COMM BVC 5135 BRAND COMM & STRATEGY Inter-Programme: Among Academic Programmes with COT/CSR
Inter-Programme In the interprogramme, two or more courses from different programmes are integrated in a single project/ assessment MORE THAN 1 DEPARTMENT Dept of Tourism & Hospitality Dept of General Studies Dept of Design & Visual Comm DIFFERENT PROGRAMMES Bac of Tourism & Hospitality DIFFERENT COURSES INTEGRATED BUE 3053 ENGLISH FOR TOURISM & HOSPITALITY BUR 3012 COMMUNITY SERVICE BUE 3023 ENGLISH FOR DESIGN Bac Visual Comm. Design BVC 5125 CULTURE, IDENTITY & COMM BVC 5135 BRAND COMM & STRATEGY Inter-Programme: Among Academic Programmes with COT/CSR
 INTRA-PROGRAMME INTEGRATED LEARNING EXPERIENCES (STANDARD 7 & STANDARD 11) BACHELOR IN CIVIL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY a. IP-ILE-SEM 3 b. IP-ILE-SEM 5 c. IP-ILE-SEM 7 (WBL)
INTRA-PROGRAMME INTEGRATED LEARNING EXPERIENCES (STANDARD 7 & STANDARD 11) BACHELOR IN CIVIL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY a. IP-ILE-SEM 3 b. IP-ILE-SEM 5 c. IP-ILE-SEM 7 (WBL)



 First batch of Bach in Civil Engineering Technology (BCT) graduates of PUO who recently graduated 100 % EMPLOYABILITY RATE The Director General of DPE with PUO’s BCT staff
First batch of Bach in Civil Engineering Technology (BCT) graduates of PUO who recently graduated 100 % EMPLOYABILITY RATE The Director General of DPE with PUO’s BCT staff

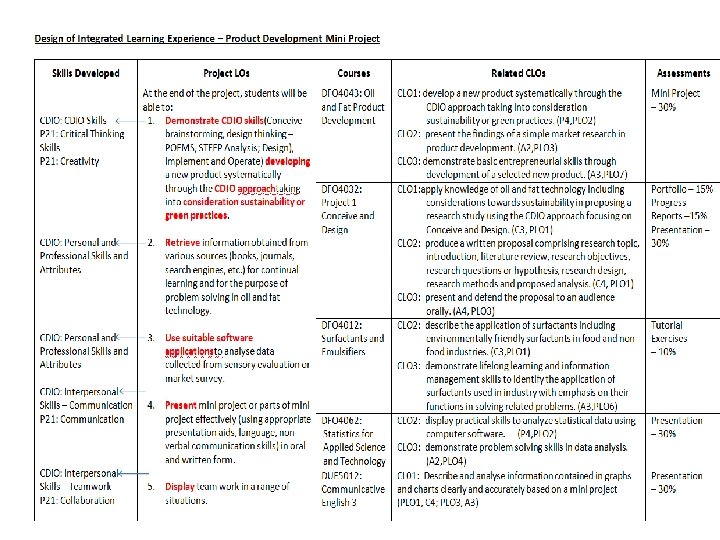

 INTER-PROGRAMME INTEGRATED LEARNING EXPERIENCE BVC-BTH-ENGLISH-CDEC PIS-Kg. Parit Bugis
INTER-PROGRAMME INTEGRATED LEARNING EXPERIENCE BVC-BTH-ENGLISH-CDEC PIS-Kg. Parit Bugis

 THE PROJECT BRIEF Designing the Integrated Curriculum Objective & Expected Outcomes
THE PROJECT BRIEF Designing the Integrated Curriculum Objective & Expected Outcomes
 THE PROJECT BRIEF Designing the Integrated Curriculum Objective & Expected Outcomes
THE PROJECT BRIEF Designing the Integrated Curriculum Objective & Expected Outcomes
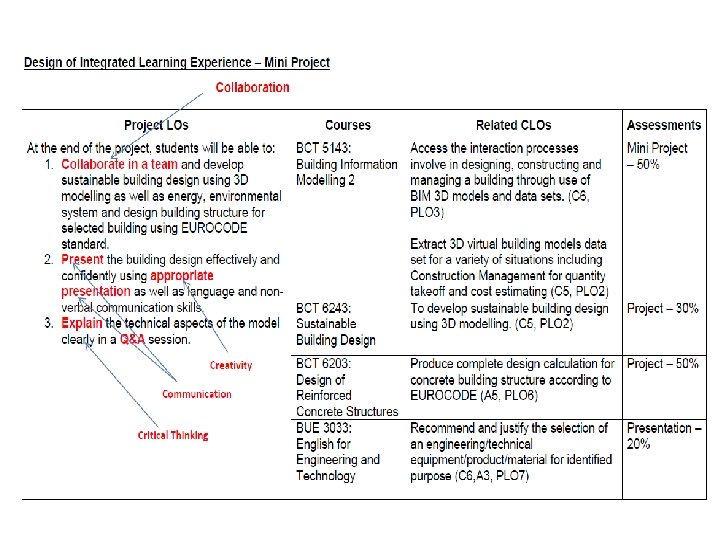
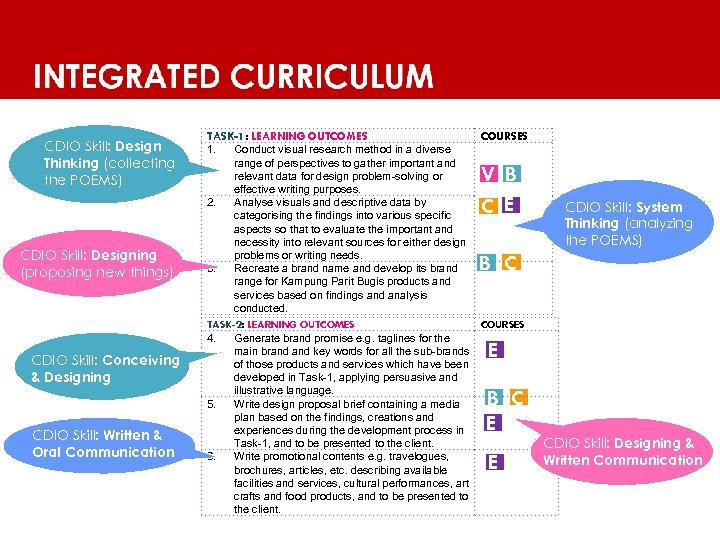 INTEGRATED CURRICULUM CDIO Skill: Design Thinking (collecting the POEMS) CDIO Skill: Designing (proposing new things) CDIO Skill: Conceiving & Designing CDIO Skill: Written & Oral Communication TASK-1: LEARNING OUTCOMES Conduct visual research method in a diverse range of perspectives to gather important and relevant data for design problem-solving or effective writing purposes. 2. Analyse visuals and descriptive data by categorising the findings into various specific aspects so that to evaluate the important and necessity into relevant sources for either design problems or writing needs. 3. Recreate a brand name and develop its brand range for Kampung Parit Bugis products and services based on findings and analysis conducted. TASK-2: LEARNING OUTCOMES 4. Generate brand promise e. g. taglines for the main brand key words for all the sub-brands of those products and services which have been developed in Task-1, applying persuasive and illustrative language. 5. Write design proposal brief containing a media plan based on the findings, creations and experiences during the development process in Task-1, and to be presented to the client. 6. Write promotional contents e. g. travelogues, brochures, articles, etc. describing available facilities and services, cultural performances, art crafts and food products, and to be presented to the client. COURSES 1. V B C E CDIO Skill: System Thinking (analyzing the POEMS) B C COURSES E B C E E CDIO Skill: Designing & Written Communication
INTEGRATED CURRICULUM CDIO Skill: Design Thinking (collecting the POEMS) CDIO Skill: Designing (proposing new things) CDIO Skill: Conceiving & Designing CDIO Skill: Written & Oral Communication TASK-1: LEARNING OUTCOMES Conduct visual research method in a diverse range of perspectives to gather important and relevant data for design problem-solving or effective writing purposes. 2. Analyse visuals and descriptive data by categorising the findings into various specific aspects so that to evaluate the important and necessity into relevant sources for either design problems or writing needs. 3. Recreate a brand name and develop its brand range for Kampung Parit Bugis products and services based on findings and analysis conducted. TASK-2: LEARNING OUTCOMES 4. Generate brand promise e. g. taglines for the main brand key words for all the sub-brands of those products and services which have been developed in Task-1, applying persuasive and illustrative language. 5. Write design proposal brief containing a media plan based on the findings, creations and experiences during the development process in Task-1, and to be presented to the client. 6. Write promotional contents e. g. travelogues, brochures, articles, etc. describing available facilities and services, cultural performances, art crafts and food products, and to be presented to the client. COURSES 1. V B C E CDIO Skill: System Thinking (analyzing the POEMS) B C COURSES E B C E E CDIO Skill: Designing & Written Communication
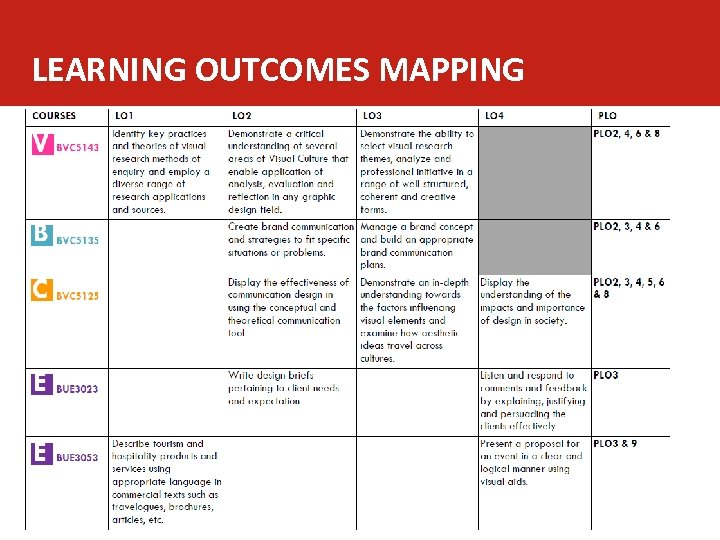 LEARNING OUTCOMES MAPPING
LEARNING OUTCOMES MAPPING
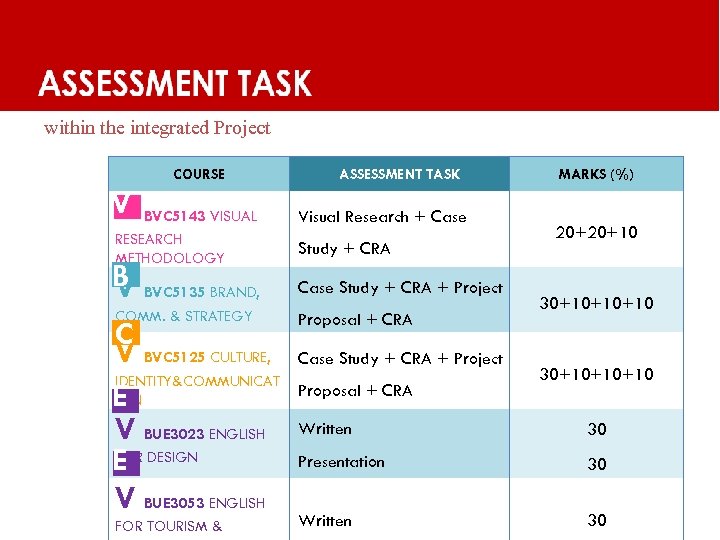 ASSESSMENT TASK within the integrated Project COURSE V BVC 5143 VISUAL V RESEARCH METHODOLOGY B BVC 5135 BRAND, V COMM. & STRATEGY C V BVC 5125 CULTURE, IDENTITY&COMMUNICAT ION E V BUE 3023 ENGLISH FOR E DESIGN V BUE 3053 ENGLISH FOR TOURISM & ASSESSMENT TASK Visual Research + Case Study + CRA + Project Proposal + CRA MARKS (%) 20+20+10 30+10+10+10 Written 30 Presentation 30 Written 30
ASSESSMENT TASK within the integrated Project COURSE V BVC 5143 VISUAL V RESEARCH METHODOLOGY B BVC 5135 BRAND, V COMM. & STRATEGY C V BVC 5125 CULTURE, IDENTITY&COMMUNICAT ION E V BUE 3023 ENGLISH FOR E DESIGN V BUE 3053 ENGLISH FOR TOURISM & ASSESSMENT TASK Visual Research + Case Study + CRA + Project Proposal + CRA MARKS (%) 20+20+10 30+10+10+10 Written 30 Presentation 30 Written 30
 Comments from DPE Curriculum Council Advisors in 2016 “Saya bagi kredit kepada JPP kerana fikir lebih dari apa kita (IPT) dok fikir … di bawah CDIO… intra dan inter-program…” “…Polyhome is CDIO…” Prof. Emeritus Dato Ir Dr Zainai Mohamed, Prof. Dr Pradeep Kumar Nair, Razak School, UTM Deputy VC, Taylor’s University
Comments from DPE Curriculum Council Advisors in 2016 “Saya bagi kredit kepada JPP kerana fikir lebih dari apa kita (IPT) dok fikir … di bawah CDIO… intra dan inter-program…” “…Polyhome is CDIO…” Prof. Emeritus Dato Ir Dr Zainai Mohamed, Prof. Dr Pradeep Kumar Nair, Razak School, UTM Deputy VC, Taylor’s University
 Findings Students: • see the relationship between and the relevance of different courses in solving real life problems • enjoy learning – active, innovative, experiential • focus on one big project instead of many different assignments Teachers: • “forced” in a good way to work closely with one another – no longer working in “silo” • able to “kill many birds with one stone” – meet curriculum requirements, institution’s CSR (community service), achieve KPIs, enhance image of TVET and most importantly, nurture 21 st century skills in their students. • More interaction between students, lecturers, industry and community • Employability • Higher quality innovations – winning in competitions
Findings Students: • see the relationship between and the relevance of different courses in solving real life problems • enjoy learning – active, innovative, experiential • focus on one big project instead of many different assignments Teachers: • “forced” in a good way to work closely with one another – no longer working in “silo” • able to “kill many birds with one stone” – meet curriculum requirements, institution’s CSR (community service), achieve KPIs, enhance image of TVET and most importantly, nurture 21 st century skills in their students. • More interaction between students, lecturers, industry and community • Employability • Higher quality innovations – winning in competitions
 Acknowledgement: The writers wish to thank Yong Rashidah Mat Tuselim (PUO), Dr Beh Cheng Siew (PIS), Dr Prasanna Kesavan (PIS) and Wan Izdiharuddin Wan Ishak (CDD) for their valuable input to this paper. We wish to thank CPSC- IDEB for hosting the Malaysian delegates. Finally we wish to thank CPSC and the Department of Polytechnic Education, Ministry of Higher Education for providing the funding and support for participation in this programme.
Acknowledgement: The writers wish to thank Yong Rashidah Mat Tuselim (PUO), Dr Beh Cheng Siew (PIS), Dr Prasanna Kesavan (PIS) and Wan Izdiharuddin Wan Ishak (CDD) for their valuable input to this paper. We wish to thank CPSC- IDEB for hosting the Malaysian delegates. Finally we wish to thank CPSC and the Department of Polytechnic Education, Ministry of Higher Education for providing the funding and support for participation in this programme.
 Thank you!
Thank you!


