 Enhanced Static Gradient Survey (ESGS) Short overview TCO Reservour Management 1
Enhanced Static Gradient Survey (ESGS) Short overview TCO Reservour Management 1
 Contents What is SGS? u Why do we run SGS? u Differences between SGS and ESGS u Usual SGS interpretation u ESGS interpretation u Conclusions u TCO Reservour Management 2
Contents What is SGS? u Why do we run SGS? u Differences between SGS and ESGS u Usual SGS interpretation u ESGS interpretation u Conclusions u TCO Reservour Management 2
 What is SGS ? u Static Gradient Survey – Downhole temperature and pressure when the well is shut-in – The data is recorded by Schlumberger slickline WCQR memory gauges at depths specified in the program TCO Reservour Management 3
What is SGS ? u Static Gradient Survey – Downhole temperature and pressure when the well is shut-in – The data is recorded by Schlumberger slickline WCQR memory gauges at depths specified in the program TCO Reservour Management 3
 Why do we run SGS? The contract between Ro. K agencies and TCO stipulates that the TCO provides static reservoir pressure reports. No less than 50% of total operating wells must be surveyed per year according to the contract requirements. u To monitor changes in reservoir pressures during the life of the reservoir u TCO Reservour Management 4
Why do we run SGS? The contract between Ro. K agencies and TCO stipulates that the TCO provides static reservoir pressure reports. No less than 50% of total operating wells must be surveyed per year according to the contract requirements. u To monitor changes in reservoir pressures during the life of the reservoir u TCO Reservour Management 4
 Differences between SGS and ESGS Ø Infrequent stops Ø Stop at MPP for 30 min Ø Pressure and temperature gradient calculations ESGS Ø Stops every 10 meters from TD to 50 m above the top of Bash with 60 min stop at MPP Ø Pressure and temperature gradient calculations Ø Studying of inflow & crossflow locations Ø Identification of fluid contact using density computed from pressure gradient TCO Reservour Management 5
Differences between SGS and ESGS Ø Infrequent stops Ø Stop at MPP for 30 min Ø Pressure and temperature gradient calculations ESGS Ø Stops every 10 meters from TD to 50 m above the top of Bash with 60 min stop at MPP Ø Pressure and temperature gradient calculations Ø Studying of inflow & crossflow locations Ø Identification of fluid contact using density computed from pressure gradient TCO Reservour Management 5
 Usual Static Gradient Survey interpretation u u FPE reviews raw data provided by SLB: depth, temperature and pressure. Using these data Field PE: – builds pressure gradient plots – builds temperature gradient plots – calculates pressures at mid-point of perforations (MPP), Datum pressures and gradients TCO Reservour Management 6
Usual Static Gradient Survey interpretation u u FPE reviews raw data provided by SLB: depth, temperature and pressure. Using these data Field PE: – builds pressure gradient plots – builds temperature gradient plots – calculates pressures at mid-point of perforations (MPP), Datum pressures and gradients TCO Reservour Management 6
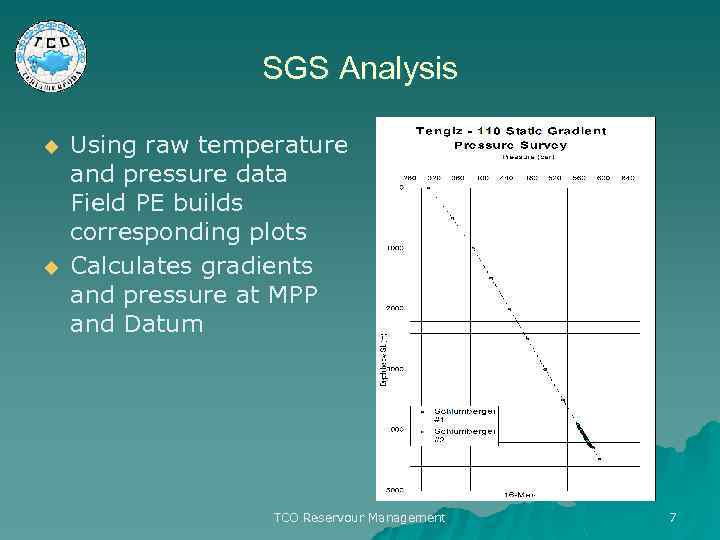 SGS Analysis u u Using raw temperature and pressure data Field PE builds corresponding plots Calculates gradients and pressure at MPP and Datum TCO Reservour Management 7
SGS Analysis u u Using raw temperature and pressure data Field PE builds corresponding plots Calculates gradients and pressure at MPP and Datum TCO Reservour Management 7
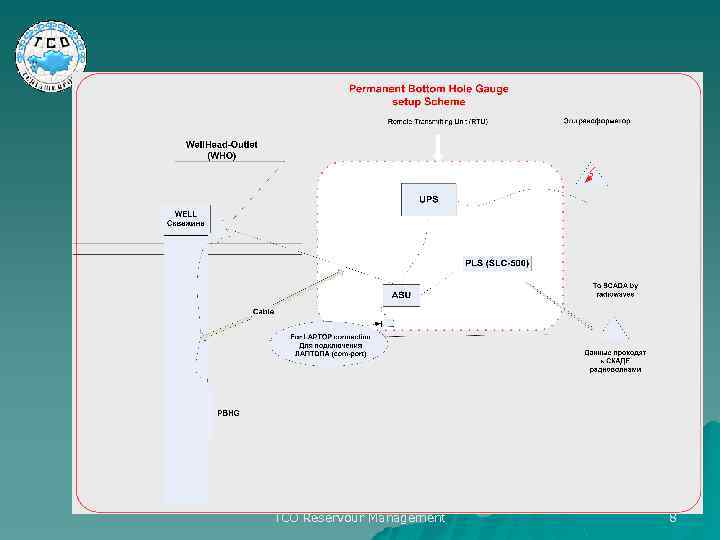 TCO Reservour Management 8
TCO Reservour Management 8
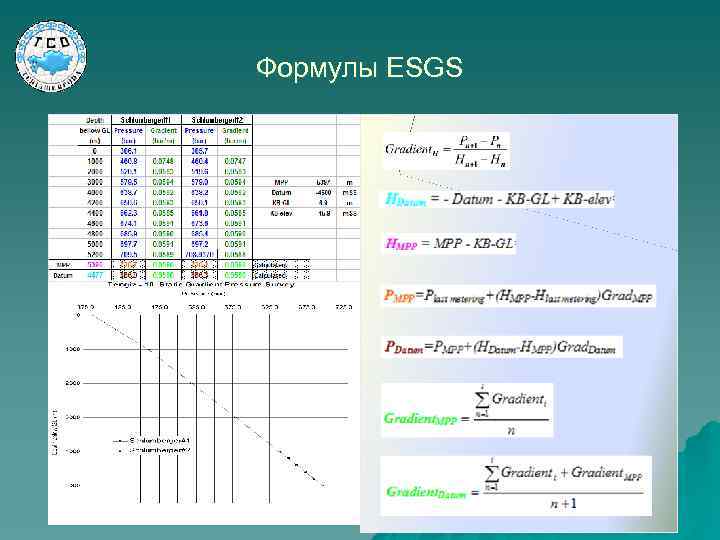 Формулы ЕSGS TCO Reservour Management 9
Формулы ЕSGS TCO Reservour Management 9
 Enhanced SGS interpretation Field PE calculates pressure and temperature gradients as in usual SGS. u These gradients are used to identify crossflow zones, fluid densities, and types u Compares ESGS temperature and density data with last PLT in Emeraude u TCO Reservour Management 10
Enhanced SGS interpretation Field PE calculates pressure and temperature gradients as in usual SGS. u These gradients are used to identify crossflow zones, fluid densities, and types u Compares ESGS temperature and density data with last PLT in Emeraude u TCO Reservour Management 10
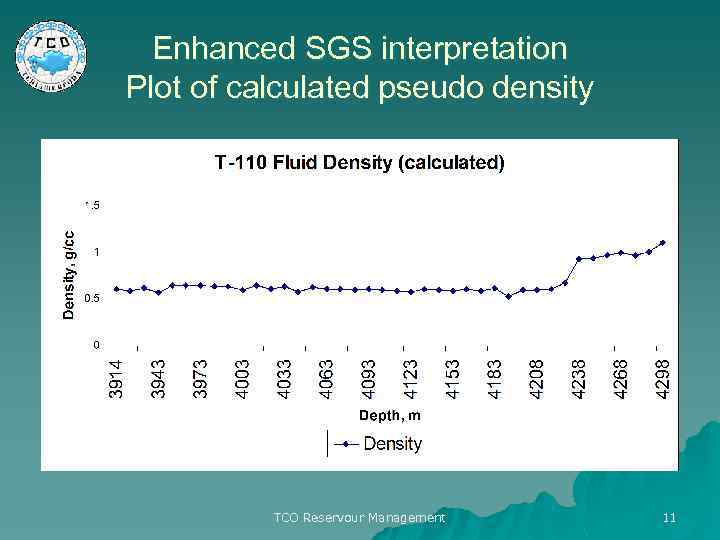 Enhanced SGS interpretation Plot of calculated pseudo density TCO Reservour Management 11
Enhanced SGS interpretation Plot of calculated pseudo density TCO Reservour Management 11
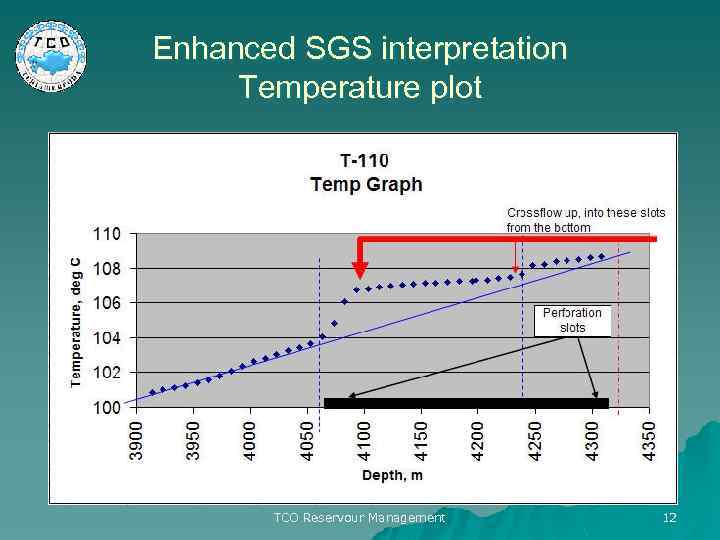 Enhanced SGS interpretation Temperature plot TCO Reservour Management 12
Enhanced SGS interpretation Temperature plot TCO Reservour Management 12
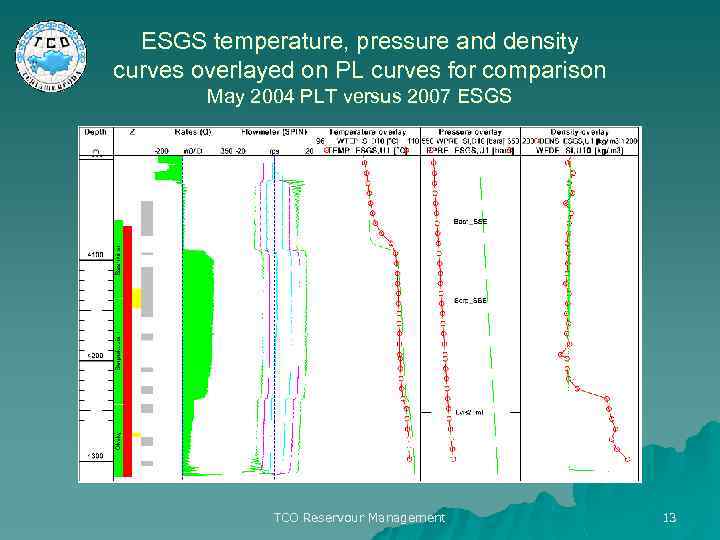 ESGS temperature, pressure and density curves overlayed on PL curves for comparison May 2004 PLT versus 2007 ESGS TCO Reservour Management 13
ESGS temperature, pressure and density curves overlayed on PL curves for comparison May 2004 PLT versus 2007 ESGS TCO Reservour Management 13
 Enhanced SGS interpretation An ESGS interpretation also includes – Wellbook log display, – Wellbore diagram, – Well utility plan, – Slickline report, – Tubing caliper log u Finally, we upload interpreted data into Bottomhole pressure database PressureGeneralGradient_Bhpdbase. xls TCO Reservour Management 14
Enhanced SGS interpretation An ESGS interpretation also includes – Wellbook log display, – Wellbore diagram, – Well utility plan, – Slickline report, – Tubing caliper log u Finally, we upload interpreted data into Bottomhole pressure database PressureGeneralGradient_Bhpdbase. xls TCO Reservour Management 14
 Conclusions Quality control of pressure data by identifying crossflow u Good in reservoir surveillance and Pre-PLT analysis u Supports in all RMG spheres u TCO Reservour Management 15
Conclusions Quality control of pressure data by identifying crossflow u Good in reservoir surveillance and Pre-PLT analysis u Supports in all RMG spheres u TCO Reservour Management 15
 Questions TCO Reservour Management 16
Questions TCO Reservour Management 16