Consonants.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 English Phonetics Consonants in English
English Phonetics Consonants in English
 Consonants in English § (a) kind of obstruction which is formed in the mouth when they are produced; § (b) sort of articulatory peculiarities they have; § (c) if the work of vocal cords is involved § (1) plosives -p b t d k g; § (2) affricates - tς, tr § § dr; (3) fricatives - v θ ð s z ς, ζ h; (4) nasals - m n ŋ ; (5) lateral and frictionless consonants -l r; (6) semi-vowels - w j.
Consonants in English § (a) kind of obstruction which is formed in the mouth when they are produced; § (b) sort of articulatory peculiarities they have; § (c) if the work of vocal cords is involved § (1) plosives -p b t d k g; § (2) affricates - tς, tr § § dr; (3) fricatives - v θ ð s z ς, ζ h; (4) nasals - m n ŋ ; (5) lateral and frictionless consonants -l r; (6) semi-vowels - w j.
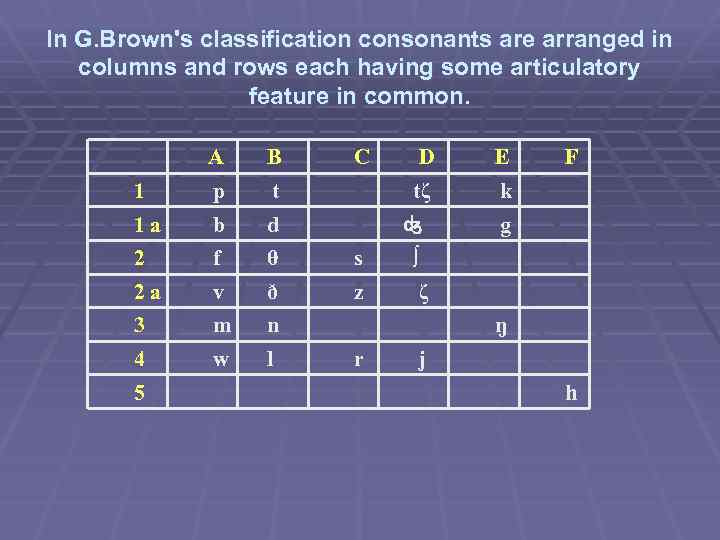 In G. Brown's classification consonants are arranged in columns and rows each having some articulatory feature in common. A B 1 p 1 a D E t tζ k b d g 2 f θ s ∫ 2 a v ð z ζ 3 m n 4 w l 5 C F ŋ r j h
In G. Brown's classification consonants are arranged in columns and rows each having some articulatory feature in common. A B 1 p 1 a D E t tζ k b d g 2 f θ s ∫ 2 a v ð z ζ 3 m n 4 w l 5 C F ŋ r j h
 consonants § A consonant may be defined as a speech sound in the production of which an obstruction (complete or incomplete) is formed in the mouth cavity.
consonants § A consonant may be defined as a speech sound in the production of which an obstruction (complete or incomplete) is formed in the mouth cavity.
 Consonants type of obsruction § A contains all phonemes with the similar features the lower lip is involved in its articulation. Theу are all labial.
Consonants type of obsruction § A contains all phonemes with the similar features the lower lip is involved in its articulation. Theу are all labial.
 Consonants type of obsruction § В contains the consonants which are formed by a closure between the tongue tip or blade and the dental ridge or the upper teeth. They are dental/alveolar.
Consonants type of obsruction § В contains the consonants which are formed by a closure between the tongue tip or blade and the dental ridge or the upper teeth. They are dental/alveolar.
 Consonants type of obsruction § С contains consonants which involve complete articulation with the tip/blade of the tongue opposed to some part of the dental ridge. This class can be called post dental.
Consonants type of obsruction § С contains consonants which involve complete articulation with the tip/blade of the tongue opposed to some part of the dental ridge. This class can be called post dental.
 consonants type of obsruction § D contains consonants which involve articulation further back in the oral cavity than other consonants. They are called palatal.
consonants type of obsruction § D contains consonants which involve articulation further back in the oral cavity than other consonants. They are called palatal.
 consonants type of obsruction § E contains consonants which are formed with back of the tongue making a closure against the soft palate or velum. They are called velar.
consonants type of obsruction § E contains consonants which are formed with back of the tongue making a closure against the soft palate or velum. They are called velar.
 consonants type of obsruction § F contains only one phoneme ‘h’. It is a glottal or pharyngal fricative.
consonants type of obsruction § F contains only one phoneme ‘h’. It is a glottal or pharyngal fricative.
 The horizontal division is based on manner of articulation. § Row 1 contains consonants which are formed by a complete obstruction of the air stream: p, t, k, b, d, g are called stops or plosives; tς, - affricated stops. This group also has voice distinctions between its members: p b, t d, k g, tς
The horizontal division is based on manner of articulation. § Row 1 contains consonants which are formed by a complete obstruction of the air stream: p, t, k, b, d, g are called stops or plosives; tς, - affricated stops. This group also has voice distinctions between its members: p b, t d, k g, tς
 The horizontal division is based on manner of articulation. § Row 2 contains f, θ , s, ∫, v, ð , z, ζ which, are called fricatives. There is no complete obstruction of the air stream which results in hissing sound. The fricatives in columns A and В are much less fricative than those in columns C, D.
The horizontal division is based on manner of articulation. § Row 2 contains f, θ , s, ∫, v, ð , z, ζ which, are called fricatives. There is no complete obstruction of the air stream which results in hissing sound. The fricatives in columns A and В are much less fricative than those in columns C, D.
 The horizontal division is based on manner of articulation. § Row 3 contains the nasal consonants m, n, n. During the articulation of nasal consonants the released air passes through nasal cavities and sets up resonance there.
The horizontal division is based on manner of articulation. § Row 3 contains the nasal consonants m, n, n. During the articulation of nasal consonants the released air passes through nasal cavities and sets up resonance there.
 The horizontal division is based on manner of articulation. § Row 4 contains a set of consonants which is indeed an as sorted set. They are realized neither by complete obstruction nor by incomplete obstruction. They have much more vowel like articulation. All of them, if prolonged, sound like vowels. But they should be regarded as consonants since they can all precede a vowel (‘wet, yes, let, red’ ).
The horizontal division is based on manner of articulation. § Row 4 contains a set of consonants which is indeed an as sorted set. They are realized neither by complete obstruction nor by incomplete obstruction. They have much more vowel like articulation. All of them, if prolonged, sound like vowels. But they should be regarded as consonants since they can all precede a vowel (‘wet, yes, let, red’ ).
 The horizontal division is based on manner of articulation. § Row 5 contains ‘h’ with a wide variety of realization; all of them are breathy onsets to following vowels.
The horizontal division is based on manner of articulation. § Row 5 contains ‘h’ with a wide variety of realization; all of them are breathy onsets to following vowels.
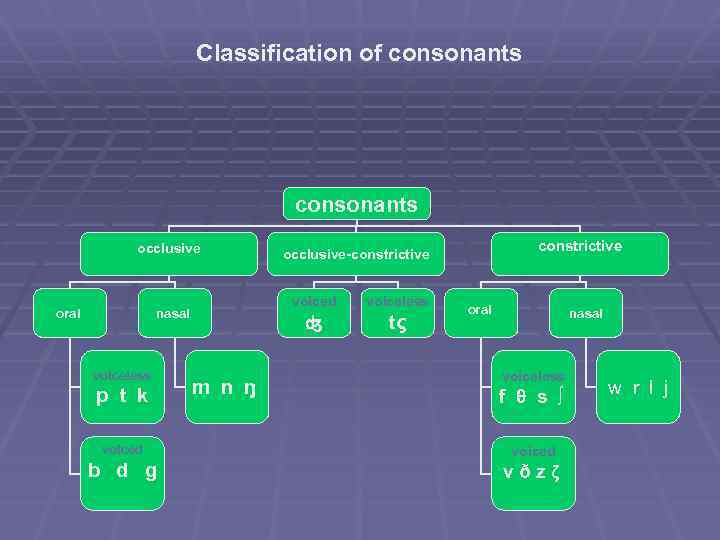 Classification of consonants occlusive oral voiced voiceless p t k voiced b d g m n ŋ voiceless nasal constrictive occlusive-constrictive tς oral nasal voiceless f θ s ∫ voiced vðzζ w r l j
Classification of consonants occlusive oral voiced voiceless p t k voiced b d g m n ŋ voiceless nasal constrictive occlusive-constrictive tς oral nasal voiceless f θ s ∫ voiced vðzζ w r l j


