f5eb730516e5edc3dfbcf4efe18231ed.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 English Moods Alexander Strelnikov © Municipal Resource Centre for Foreign Languages Nizhniy Tagil, Jan. 13, 2014
English Moods Alexander Strelnikov © Municipal Resource Centre for Foreign Languages Nizhniy Tagil, Jan. 13, 2014
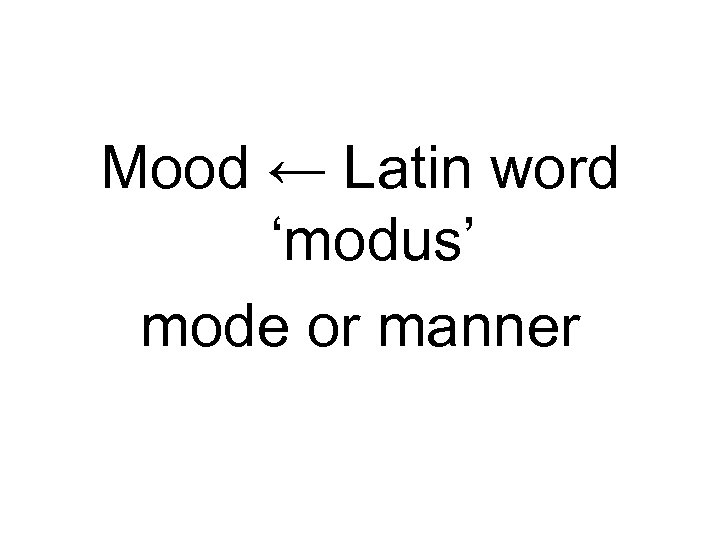 Mood ← Latin word ‘modus’ mode or manner
Mood ← Latin word ‘modus’ mode or manner
 Mood expresses the character of connections between the process denoted by the verb and actual reality
Mood expresses the character of connections between the process denoted by the verb and actual reality
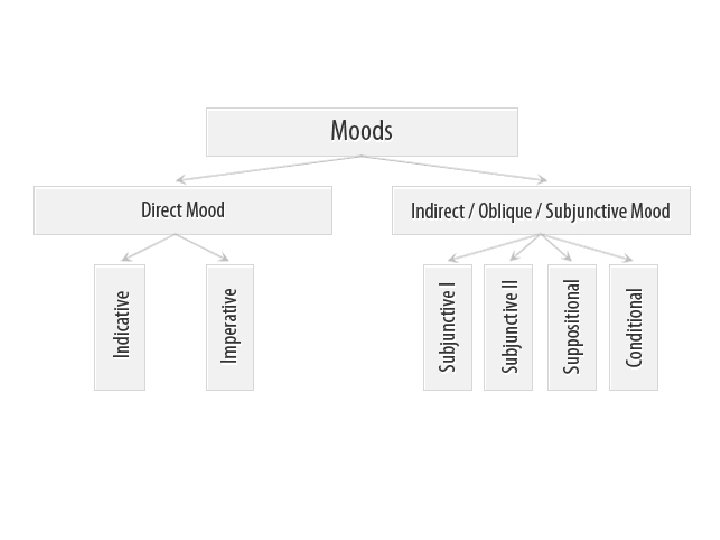
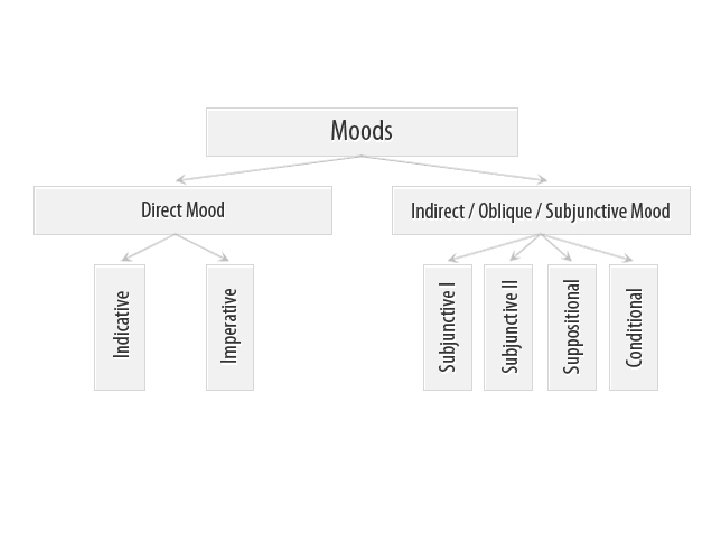
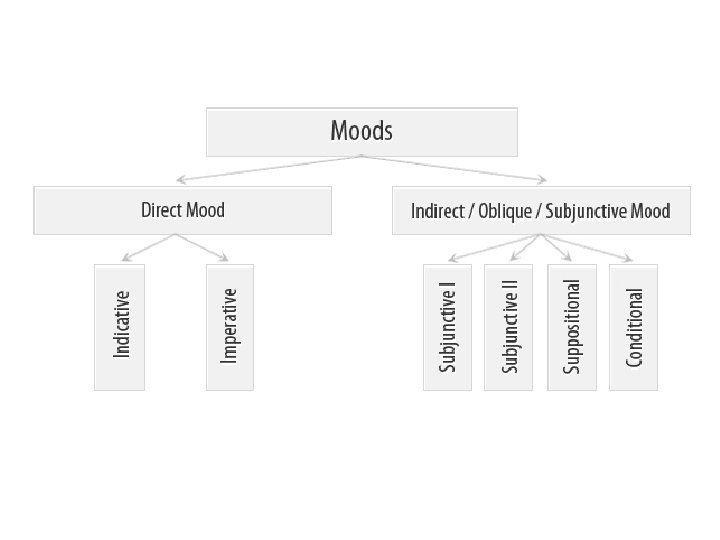
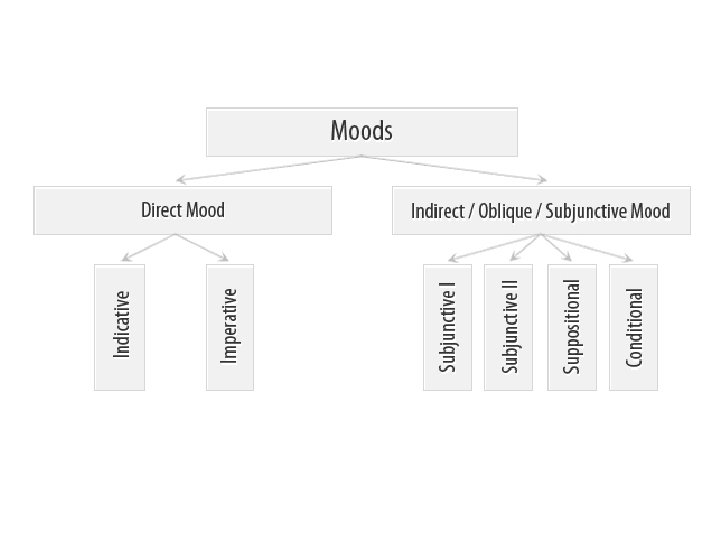
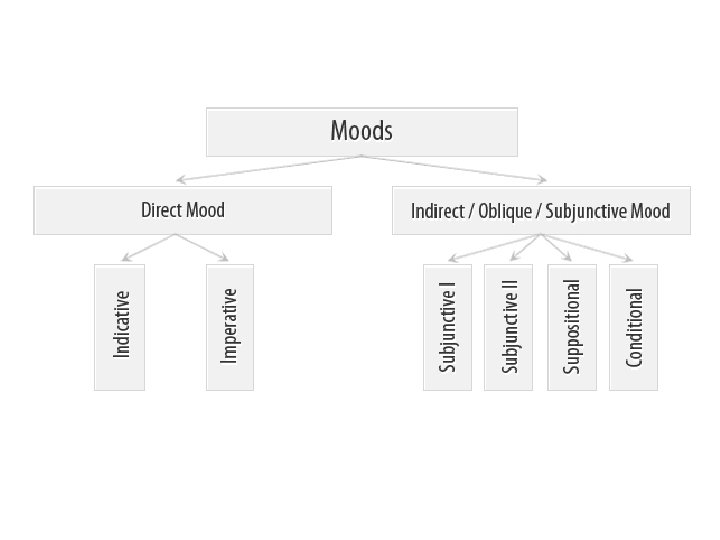
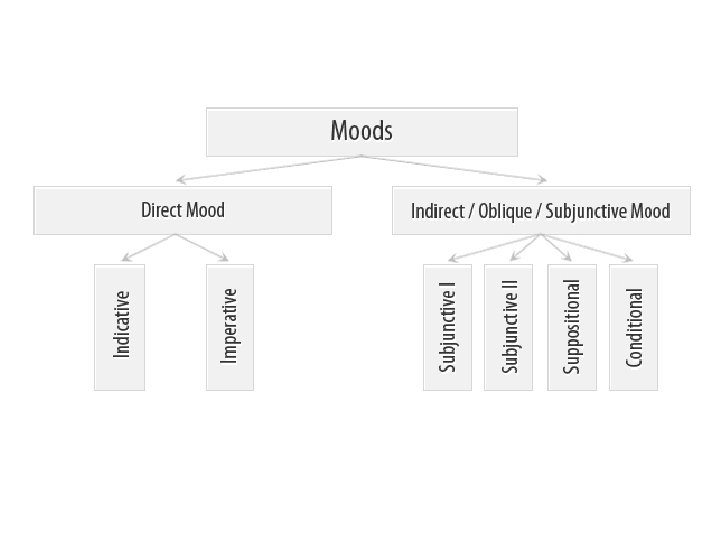
 Classification of moods Different scholars define different number of moods: 0 ↔ 16
Classification of moods Different scholars define different number of moods: 0 ↔ 16
 Classification of moods • Direct (indicative, imperative) mood shows that the process is real, i. e. that it took place in the past, takes place in the present, or will take place in future. • Indirect (oblique) moods show that the process is unreal, imaginary (hypothetical, possible or impossible, desired, etc. ).
Classification of moods • Direct (indicative, imperative) mood shows that the process is real, i. e. that it took place in the past, takes place in the present, or will take place in future. • Indirect (oblique) moods show that the process is unreal, imaginary (hypothetical, possible or impossible, desired, etc. ).
 The indicative mood Used to make a simple statement or to ask a question or to make a possible supposition. I wake up early in the morning. (Statement) Sun rises in the east. (Statement) Barking dogs seldom bite. (Statement) Milk is sweet. (Statement) What is your name? (Question) Is that your husband? (Question) If you ask him, he will help you. (Possible supposition)
The indicative mood Used to make a simple statement or to ask a question or to make a possible supposition. I wake up early in the morning. (Statement) Sun rises in the east. (Statement) Barking dogs seldom bite. (Statement) Milk is sweet. (Statement) What is your name? (Question) Is that your husband? (Question) If you ask him, he will help you. (Possible supposition)
 Note! Terminology Tenses (indicative) ↕ Forms of the verb (oblique)
Note! Terminology Tenses (indicative) ↕ Forms of the verb (oblique)
 The Imperative mood • Used to express a command, request or advice. Go at once. (Command) Sit down. (Command) Excuse me. (Request) Keep quiet. (Order) Work hard. (Advice) Don’t be silly. (Advice) “You” is usually omitted.
The Imperative mood • Used to express a command, request or advice. Go at once. (Command) Sit down. (Command) Excuse me. (Request) Keep quiet. (Order) Work hard. (Advice) Don’t be silly. (Advice) “You” is usually omitted.
 Subjunctive I • Expresses various attitudes of the speaker: desire, consideration (supposition, suggestion, hypothesis), inducement (recommendation, request, command, order), etc.
Subjunctive I • Expresses various attitudes of the speaker: desire, consideration (supposition, suggestion, hypothesis), inducement (recommendation, request, command, order), etc.
 Subjunctive I • has a certain formal, and even archaic stylistic flavor
Subjunctive I • has a certain formal, and even archaic stylistic flavor
 Subjunctive I has a certain formal and even archaic stylistic flavor Infinitive without “to” Long Live Revolution! Long live October day! God bless you! God save the Queen! Success attend you!
Subjunctive I has a certain formal and even archaic stylistic flavor Infinitive without “to” Long Live Revolution! Long live October day! God bless you! God save the Queen! Success attend you!
 Subjunctive II • All the meanings imply unreal conditions of some sort.
Subjunctive II • All the meanings imply unreal conditions of some sort.
 Subjunctive II • • • V 2 (to be – were) I wish he were here. If I were at home now! She behaves as if (as though) she were right. It’s high time she tried to change the situation. If only he had the tickets!
Subjunctive II • • • V 2 (to be – were) I wish he were here. If I were at home now! She behaves as if (as though) she were right. It’s high time she tried to change the situation. If only he had the tickets!
 The suppositional mood • Expresses supposition, suggestion, recommendation, inducements of various types and degrees of intensity.
The suppositional mood • Expresses supposition, suggestion, recommendation, inducements of various types and degrees of intensity.
 The suppositional mood should + infinitive after necessary Important desirable requested demanded advisable arranged ordered commanded
The suppositional mood should + infinitive after necessary Important desirable requested demanded advisable arranged ordered commanded
 The suppositional mood • It is obligatory that she should be present at the meeting. • It is necessary that he should go there at once. • It is needed that she should say that at once. • It was important that he should stay at school. • Harris proposed that we should have eggs for breakfast. • By the evening he looked so bad that she suggested that he should go to bed. • I insist that I should be freed.
The suppositional mood • It is obligatory that she should be present at the meeting. • It is necessary that he should go there at once. • It is needed that she should say that at once. • It was important that he should stay at school. • Harris proposed that we should have eggs for breakfast. • By the evening he looked so bad that she suggested that he should go to bed. • I insist that I should be freed.
 The suppositional mood Various tenses in the main clause. • He demands (demanded, will demand) that we should be attentive. • She insists (insisted, will insist) that he should be careful.
The suppositional mood Various tenses in the main clause. • He demands (demanded, will demand) that we should be attentive. • She insists (insisted, will insist) that he should be careful.
 The suppositional mood to fear to worry to be afraid + LEST • Mary feared lest he should come in. • She closed the window lest the children should catch cold. • She put her hand of the railing lest she should fall.
The suppositional mood to fear to worry to be afraid + LEST • Mary feared lest he should come in. • She closed the window lest the children should catch cold. • She put her hand of the railing lest she should fall.
 The suppositional mood • Does not exist in American grammar. • Subjunctive I is used instead. It is obligatory that she be present at the meeting. It is necessary that he go there at once.
The suppositional mood • Does not exist in American grammar. • Subjunctive I is used instead. It is obligatory that she be present at the meeting. It is necessary that he go there at once.
 Conditionals main clause + if-clause or if-clause + main clause The conjunction “IF” occupies # 55 in the list of most frequently used English words.
Conditionals main clause + if-clause or if-clause + main clause The conjunction “IF” occupies # 55 in the list of most frequently used English words.
 Using commas in conditional sentences if-clause , main clause if-clause If you swallow some of the cleaning fluid, it will kill you. It will kill you if you swallow some of the cleaning fluid.
Using commas in conditional sentences if-clause , main clause if-clause If you swallow some of the cleaning fluid, it will kill you. It will kill you if you swallow some of the cleaning fluid.
 INDICATIVE! • If I have money, I will buy a car. • If the weather is fine, we will go to the park. • If my friend is not late, we will go to the cinema. • Variation: • If a man has cheated before, he will do it again.
INDICATIVE! • If I have money, I will buy a car. • If the weather is fine, we will go to the park. • If my friend is not late, we will go to the cinema. • Variation: • If a man has cheated before, he will do it again.
 INDICATIVE! General truth. • If you heat ice, it melts. • If you don’t understand, you are a fool. • If somebody hits me, I hit back. • If the boss finds out, he will be angry.
INDICATIVE! General truth. • If you heat ice, it melts. • If you don’t understand, you are a fool. • If somebody hits me, I hit back. • If the boss finds out, he will be angry.
 Types of conditionals Russian БЫ is used in translation. Real Unreal Mixed types: Real – unreal Unreal – real
Types of conditionals Russian БЫ is used in translation. Real Unreal Mixed types: Real – unreal Unreal – real
 Real conditions • If I were rich, I would give i. Phones to everyone. • If I had money I would go to the seaside. • If today were Saturday, we could go to the beach.
Real conditions • If I were rich, I would give i. Phones to everyone. • If I had money I would go to the seaside. • If today were Saturday, we could go to the beach.
 Unreal conditions • Refer to the past • The probability is 0 %. • If I had known that you were there, I would have written you a letter. • Had I known that you were there, I would have written you a letter. • If you hadn’t been here, I would have made up a love for myself.
Unreal conditions • Refer to the past • The probability is 0 %. • If I had known that you were there, I would have written you a letter. • Had I known that you were there, I would have written you a letter. • If you hadn’t been here, I would have made up a love for myself.
 Mixed types of conditionals REAL - UNREAL Real (main clause) – Unreal (if-clause) • I would be a general’s wife if I had married a general. • I wouldn’t be so aggressive now if I hadn’t forgotten to take my pills yesterday.
Mixed types of conditionals REAL - UNREAL Real (main clause) – Unreal (if-clause) • I would be a general’s wife if I had married a general. • I wouldn’t be so aggressive now if I hadn’t forgotten to take my pills yesterday.
 Mixed types of conditionals UNREAL - REAL Unreal (main clause) – Real (if-clause) • You would have passed the exam yesterday if you were more attentive. • I would have become a basketball player if I were taller. • I would have worked as Santa last Christmas if I were kinder.
Mixed types of conditionals UNREAL - REAL Unreal (main clause) – Real (if-clause) • You would have passed the exam yesterday if you were more attentive. • I would have become a basketball player if I were taller. • I would have worked as Santa last Christmas if I were kinder.


