4434dd95df279d67a799a8129c1a7c6c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Engineering Process at Microsoft Dmitri Gavrilov Principal Software Development Lead Exchange Server
Engineering Process at Microsoft Dmitri Gavrilov Principal Software Development Lead Exchange Server
 Agenda Roles Career paths Product release cycle Tools
Agenda Roles Career paths Product release cycle Tools
 Roles Three main roles: dev, test, product management Product Manager (PM): Owns scenarios Does not write code Interaction with customers, other teams Writes functional specs Dev (SDE): Owns product code Fixes product bugs Writes design specs Test (SDET): Owns product quality Writes test code and fixes test bugs Writes test specs
Roles Three main roles: dev, test, product management Product Manager (PM): Owns scenarios Does not write code Interaction with customers, other teams Writes functional specs Dev (SDE): Owns product code Fixes product bugs Writes design specs Test (SDET): Owns product quality Writes test code and fixes test bugs Writes test specs
 Additional Roles Managers Lead, Manager, Director/PUM/GM Executive (a hierarchy of VPs) Architects Super-smart individual contributors Contractors Manual testing/deployment/operations Hourly pay, can only work 9 months out of 12.
Additional Roles Managers Lead, Manager, Director/PUM/GM Executive (a hierarchy of VPs) Architects Super-smart individual contributors Contractors Manual testing/deployment/operations Hourly pay, can only work 9 months out of 12.
 More Additional Roles User Experience/docs/help writers Support Escalation Engineers (frontline support, mostly in India, answer FAQs) Support Engineers (second line of defence, know product well, can solve most problems) Critical Problem Resolution Engineers (virtuoso debuggers) Premier Field Engineers (dedicated to important customers) Product Marketing Sales
More Additional Roles User Experience/docs/help writers Support Escalation Engineers (frontline support, mostly in India, answer FAQs) Support Engineers (second line of defence, know product well, can solve most problems) Critical Problem Resolution Engineers (virtuoso debuggers) Premier Field Engineers (dedicated to important customers) Product Marketing Sales
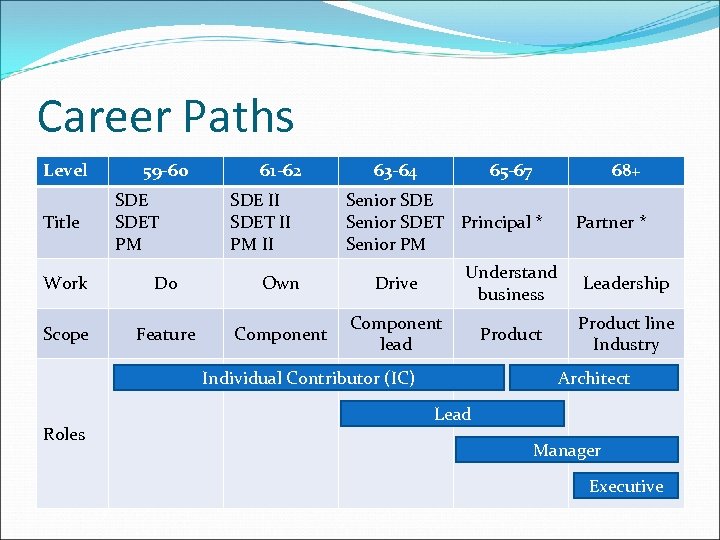 Career Paths Level Title 59 -60 SDET PM 61 -62 SDE II SDET II PM II 63 -64 65 -67 68+ Senior SDET Principal * Senior PM Partner * Work Do Own Drive Understand business Leadership Scope Feature Component lead Product line Industry Individual Contributor (IC) Roles Architect Lead Manager Executive
Career Paths Level Title 59 -60 SDET PM 61 -62 SDE II SDET II PM II 63 -64 65 -67 68+ Senior SDET Principal * Senior PM Partner * Work Do Own Drive Understand business Leadership Scope Feature Component lead Product line Industry Individual Contributor (IC) Roles Architect Lead Manager Executive
 Product Release Cycle Milestones (6 -9 months) MQ (quality) Dev/Test: fix postponed items from prev release PM: Prioritize scenarios M 1 -Mn (dev milestones) Dev/Test/PM: Implement features MP (polish) Later milestones are released to external testers: Internal testing (dogfooding) Public Betas Release Candidate RTM/RTW (release to manufacturing/web) SE (Support Engineering): hotfixes, service packs
Product Release Cycle Milestones (6 -9 months) MQ (quality) Dev/Test: fix postponed items from prev release PM: Prioritize scenarios M 1 -Mn (dev milestones) Dev/Test/PM: Implement features MP (polish) Later milestones are released to external testers: Internal testing (dogfooding) Public Betas Release Candidate RTM/RTW (release to manufacturing/web) SE (Support Engineering): hotfixes, service packs
 Bug Bar Criteria for taking/not taking bug fixes There always more bugs in the product Do you fix them now or in the next milestone/release? Bug bar is raised towards the end of milestone Highest setting just before RTM After RTM, the bar goes down somewhat Safer to release a hotfix to a set of customers that need it Hotfixes are rolled into service packs When bar is high, bugs are triaged/approved by the War Team (release management people) You come to war and defend your bug: prove why it meets the bar.
Bug Bar Criteria for taking/not taking bug fixes There always more bugs in the product Do you fix them now or in the next milestone/release? Bug bar is raised towards the end of milestone Highest setting just before RTM After RTM, the bar goes down somewhat Safer to release a hotfix to a set of customers that need it Hotfixes are rolled into service packs When bar is high, bugs are triaged/approved by the War Team (release management people) You come to war and defend your bug: prove why it meets the bar.
 Bug Bar Example High Medium High impact or frequent crash/hang, serious perf degradation, scale, config that will prevent production Core scenario with high impact with no reasonable workaround Data corruption or loss RC blockers or RC failures Very high impact supportability bugs that could save lots of time and money down the road High impact globalization/localization issues DOA and Test Pass blockers CPX issues that prevent from shipping (Policheck, API scan, etc) Security Issues rated as “Critical” based on the SWI guideline Low Critical partner dependency issues (including other component teams, Ex. RAP and PSS) Regressions Functional behavior that is clearly against the design Security issues rated as “Moderate” based on the SWI guideline Supportability issues Code cleanups Performance improvements beyond the stated goals DCRs that are not essential to E 12 SP 1 Branding Bug with an easy workaround
Bug Bar Example High Medium High impact or frequent crash/hang, serious perf degradation, scale, config that will prevent production Core scenario with high impact with no reasonable workaround Data corruption or loss RC blockers or RC failures Very high impact supportability bugs that could save lots of time and money down the road High impact globalization/localization issues DOA and Test Pass blockers CPX issues that prevent from shipping (Policheck, API scan, etc) Security Issues rated as “Critical” based on the SWI guideline Low Critical partner dependency issues (including other component teams, Ex. RAP and PSS) Regressions Functional behavior that is clearly against the design Security issues rated as “Moderate” based on the SWI guideline Supportability issues Code cleanups Performance improvements beyond the stated goals DCRs that are not essential to E 12 SP 1 Branding Bug with an easy workaround
 Tools: Bug Tracking Product Studio: database of bugs Tree of components Bug types: code bug, Design Change Request, Work Item, Customer Escalation, etc… Bug lifetime: Opened Triaged by component triage team, assigned to a dev Dev works on the fix Tester verifies the fix (optional) Bug is marked as Ready. To. Check. In, to be approved by war Dev checks in the fix, resolves the bug Tester verifies the bug is fixed, closes the bug Mgmt uses bug database to track progress Bug resolution: Fixed, Not. Repro, Duplicate, Wont. Fix, Postponed, External.
Tools: Bug Tracking Product Studio: database of bugs Tree of components Bug types: code bug, Design Change Request, Work Item, Customer Escalation, etc… Bug lifetime: Opened Triaged by component triage team, assigned to a dev Dev works on the fix Tester verifies the fix (optional) Bug is marked as Ready. To. Check. In, to be approved by war Dev checks in the fix, resolves the bug Tester verifies the bug is fixed, closes the bug Mgmt uses bug database to track progress Bug resolution: Fixed, Not. Repro, Duplicate, Wont. Fix, Postponed, External.
 Tools: Source Change Management Database of source code: Source Depot To work on a file, you have to check it out Multiple people can check out a file At check in, you may need to merge with other people’s changes, resolve conflicts Change history is preserved (incremental changes) Checkins are associated with bugs Branches are super powerful concept One primary product branch Code forked near milestones
Tools: Source Change Management Database of source code: Source Depot To work on a file, you have to check it out Multiple people can check out a file At check in, you may need to merge with other people’s changes, resolve conflicts Change history is preserved (incremental changes) Checkins are associated with bugs Branches are super powerful concept One primary product branch Code forked near milestones
 Tools: Automation Smoke Automated test running system Smoke must be run before checkin Builds product with your changes Deploys on multiple test topologies Runs tests Tests are prioritized, depending on which code is changed Topo. Builder Automated topology deployment Topologies: from single machine to complex multi-domain multi- machine topologies Quotas Lifetime management: machines are automatically reclaimed into the common pool after a while.
Tools: Automation Smoke Automated test running system Smoke must be run before checkin Builds product with your changes Deploys on multiple test topologies Runs tests Tests are prioritized, depending on which code is changed Topo. Builder Automated topology deployment Topologies: from single machine to complex multi-domain multi- machine topologies Quotas Lifetime management: machines are automatically reclaimed into the common pool after a while.
 Questions?
Questions?


