eebb3c1532b14b9a30fab6182c3c8bb2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 86
 Engineering 245 The Lean Launch. Pad Session 1: Overview/Business Models/Customer Development Professors Steve Blank, Ann Miura-Ko, Jon Feiber http: //e 245. stanford. edu/
Engineering 245 The Lean Launch. Pad Session 1: Overview/Business Models/Customer Development Professors Steve Blank, Ann Miura-Ko, Jon Feiber http: //e 245. stanford. edu/
 Agenda “Is This the Right Course for Me? ” • • Course Objectives/teams/project Introductions Class Logistics Building a “Lean Startup” – – Idea Sizing the Opportunity Business Models Customer Development • Break: Stay If You Want to Be in the Class • Class “Culture” and Next Steps
Agenda “Is This the Right Course for Me? ” • • Course Objectives/teams/project Introductions Class Logistics Building a “Lean Startup” – – Idea Sizing the Opportunity Business Models Customer Development • Break: Stay If You Want to Be in the Class • Class “Culture” and Next Steps
 Course Objectives • Understand the real world aspects of Entrepreneurship by getting out of the building – – Analyze and assess an opportunity Build the product Get orders Work with a team • Learn whether entrepreneurship is for you
Course Objectives • Understand the real world aspects of Entrepreneurship by getting out of the building – – Analyze and assess an opportunity Build the product Get orders Work with a team • Learn whether entrepreneurship is for you
 What Will you Learn? • • Opportunity evaluation Search for a Business Model Customer Discovery and Validation Operating and decision making in chaos with insufficient data • Teamwork
What Will you Learn? • • Opportunity evaluation Search for a Business Model Customer Discovery and Validation Operating and decision making in chaos with insufficient data • Teamwork
 The Course ‘By the Numbers’ • • • 3/4 Units of Credit 3 Instructors, 2 CAs, 25+ Mentors, 8 Lectures 8 Weekly 10 -minute presentations 1 Final 30 minute presentation 3 Textbooks 5 -10 hours of work a week outside the classroom
The Course ‘By the Numbers’ • • • 3/4 Units of Credit 3 Instructors, 2 CAs, 25+ Mentors, 8 Lectures 8 Weekly 10 -minute presentations 1 Final 30 minute presentation 3 Textbooks 5 -10 hours of work a week outside the classroom
 Course Reading • Business Model Generation • Four Steps to the Epiphany • Founders at Work copies available at the bookstore
Course Reading • Business Model Generation • Four Steps to the Epiphany • Founders at Work copies available at the bookstore
 This Class is Hard • You can’t pass by attending the class • Your grade is determined by the work you do outside the class • There’s a lot of it • You are dependent on teamwork and teammates – communication is critical
This Class is Hard • You can’t pass by attending the class • Your grade is determined by the work you do outside the class • There’s a lot of it • You are dependent on teamwork and teammates – communication is critical
 Teams • Suggested team size is 4 people – Deadline for team formation is Jan 6 th – Must contact your mentors by Jan 7 th • Present Weekly and for Final – Weekly lessons learned – Final is demo and summary • Class is about teamwork, discovery and fast iteration
Teams • Suggested team size is 4 people – Deadline for team formation is Jan 6 th – Must contact your mentors by Jan 7 th • Present Weekly and for Final – Weekly lessons learned – Final is demo and summary • Class is about teamwork, discovery and fast iteration
 Team Projects • Any for-profit scalable startup • If you are a domain expert, that’s your best bet (but not required) • If you pick a web project, you have to build it (and there needs to be some novelty)
Team Projects • Any for-profit scalable startup • If you are a domain expert, that’s your best bet (but not required) • If you pick a web project, you have to build it (and there needs to be some novelty)
 Team Deliverables • Each Week – Lessons Learned presentation 10 minutes – Updated blog/wiki – 10’s of hours of “outside the building” progress • Final Presentation – 30 minute Lessons Learned Summary
Team Deliverables • Each Week – Lessons Learned presentation 10 minutes – Updated blog/wiki – 10’s of hours of “outside the building” progress • Final Presentation – 30 minute Lessons Learned Summary
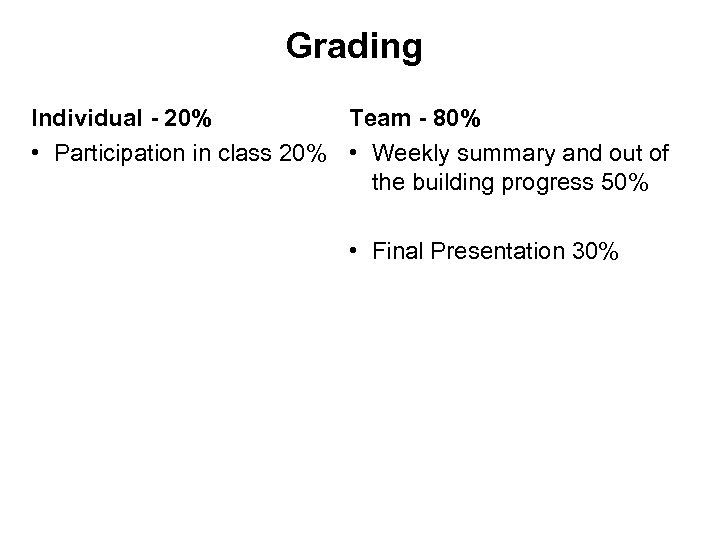 Grading Individual - 20% Team - 80% • Participation in class 20% • Weekly summary and out of the building progress 50% • Final Presentation 30%
Grading Individual - 20% Team - 80% • Participation in class 20% • Weekly summary and out of the building progress 50% • Final Presentation 30%
 Introductions
Introductions
 Steve Blank, Ann-Miura-Ko, Jon Feiber 8 startups in Silicon Valley • Semiconductors • Supercomputers • Consumer electronics • Video games • Enterprise software • Military intelligence sblank@kandsranch. com twitter sgblank www. steveblank. com • • • Yale BS EE Mc. Kinsey and Co. Charles River Ventures Stanford Ph. D MS&E TA: E 145, Mayfield Fellows, MS&E 273 V. C. @ Floodgate ann@floodgate. com @annimaniac • • • BS CS/Astro Physics U of Colorado VP Networking SUN V. C. @ MDV since 1991
Steve Blank, Ann-Miura-Ko, Jon Feiber 8 startups in Silicon Valley • Semiconductors • Supercomputers • Consumer electronics • Video games • Enterprise software • Military intelligence sblank@kandsranch. com twitter sgblank www. steveblank. com • • • Yale BS EE Mc. Kinsey and Co. Charles River Ventures Stanford Ph. D MS&E TA: E 145, Mayfield Fellows, MS&E 273 V. C. @ Floodgate ann@floodgate. com @annimaniac • • • BS CS/Astro Physics U of Colorado VP Networking SUN V. C. @ MDV since 1991
 Steve Blank, Ann-Miura-Ko, Jon Feiber 8 startups - 32 years in Silicon Valley • Semiconductors • Supercomputers • Consumer electronics • Video games • Enterprise software • Military intelligence • • • Yale BS EE Mc. Kinsey and Co. Charles River Ventures Stanford Ph. D MS&E V. C. @ Floodgate Teach: Stanford, Berkeley, Columbia Details at www. steveblank. com ann@floodgate. com @annimaniac • • • BS CS/Astro Physics U of Colorado VP Networking SUN V. C. @ MDV since 1991
Steve Blank, Ann-Miura-Ko, Jon Feiber 8 startups - 32 years in Silicon Valley • Semiconductors • Supercomputers • Consumer electronics • Video games • Enterprise software • Military intelligence • • • Yale BS EE Mc. Kinsey and Co. Charles River Ventures Stanford Ph. D MS&E V. C. @ Floodgate Teach: Stanford, Berkeley, Columbia Details at www. steveblank. com ann@floodgate. com @annimaniac • • • BS CS/Astro Physics U of Colorado VP Networking SUN V. C. @ MDV since 1991
 Steve Blank, Ann-Miura-Ko, Jon Feiber 8 startups - 32 years in Silicon Valley • Semiconductors • Supercomputers • Consumer electronics • Video games • Enterprise software • Military intelligence Teach: Stanford, Berkeley, Columbia Details at www. steveblank. com • • • Yale BS EE Mc. Kinsey and Co. Charles River Ventures Stanford Ph. D MS&E V. C. @ Floodgate ann@floodgate. com @annimaniac • BS CS/Astro Physics U of Colorado • 50 th employee, VP Networking @ Sun • V. C. @ MDV since 1991 • jdf@mdv. com
Steve Blank, Ann-Miura-Ko, Jon Feiber 8 startups - 32 years in Silicon Valley • Semiconductors • Supercomputers • Consumer electronics • Video games • Enterprise software • Military intelligence Teach: Stanford, Berkeley, Columbia Details at www. steveblank. com • • • Yale BS EE Mc. Kinsey and Co. Charles River Ventures Stanford Ph. D MS&E V. C. @ Floodgate ann@floodgate. com @annimaniac • BS CS/Astro Physics U of Colorado • 50 th employee, VP Networking @ Sun • V. C. @ MDV since 1991 • jdf@mdv. com
 Course Assistant (CA’s) Thomas Haymore • B. A. in Political Science • Stanford Law (‘ 06) • J. D. Stanford Law (‘ 12) thomas. haymore@gmail. com Felix Huber • MS MS&E 2010 • Google Translate Product Mgr huberfelix@gmail. com • CA’s role: Class/lecture questions, Grading and attendance
Course Assistant (CA’s) Thomas Haymore • B. A. in Political Science • Stanford Law (‘ 06) • J. D. Stanford Law (‘ 12) thomas. haymore@gmail. com Felix Huber • MS MS&E 2010 • Google Translate Product Mgr huberfelix@gmail. com • CA’s role: Class/lecture questions, Grading and attendance
 Volunteer Course Assistant (CA’s) Thomas Haymore B. A. in Political Science • Stanford Law (‘ 06) • J. D. Stanford Law (‘ 12) thomas. haymore@gmail. com Felix Huber • MS MS&E 2010 • Google Translate Product Mgr huberfelix@gmail. com • CA’s role: Class/lecture questions, Grading and attendance
Volunteer Course Assistant (CA’s) Thomas Haymore B. A. in Political Science • Stanford Law (‘ 06) • J. D. Stanford Law (‘ 12) thomas. haymore@gmail. com Felix Huber • MS MS&E 2010 • Google Translate Product Mgr huberfelix@gmail. com • CA’s role: Class/lecture questions, Grading and attendance
 Mentors • Mentors are Venture Capitalists or Entrepreneurs • Mentors role is to: – – Help you “Get you out of the building” Share contacts Offer “Real-world” entrepreneurial advice Critical feedback • You arrange your schedule for the mentors, not the other way around
Mentors • Mentors are Venture Capitalists or Entrepreneurs • Mentors role is to: – – Help you “Get you out of the building” Share contacts Offer “Real-world” entrepreneurial advice Critical feedback • You arrange your schedule for the mentors, not the other way around
 Class Logistics
Class Logistics
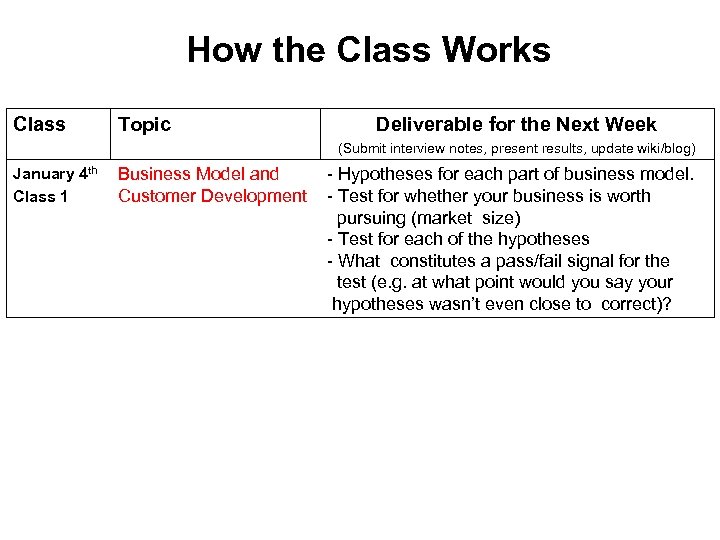 How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog) January 4 th Business Model and Class 1 Customer Development - Hypotheses for each part of business model. - Test for whether your business is worth pursuing (market size) - Test for each of the hypotheses - What constitutes a pass/fail signal for the test (e. g. at what point would you say your hypotheses wasn’t even close to correct)?
How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog) January 4 th Business Model and Class 1 Customer Development - Hypotheses for each part of business model. - Test for whether your business is worth pursuing (market size) - Test for each of the hypotheses - What constitutes a pass/fail signal for the test (e. g. at what point would you say your hypotheses wasn’t even close to correct)?
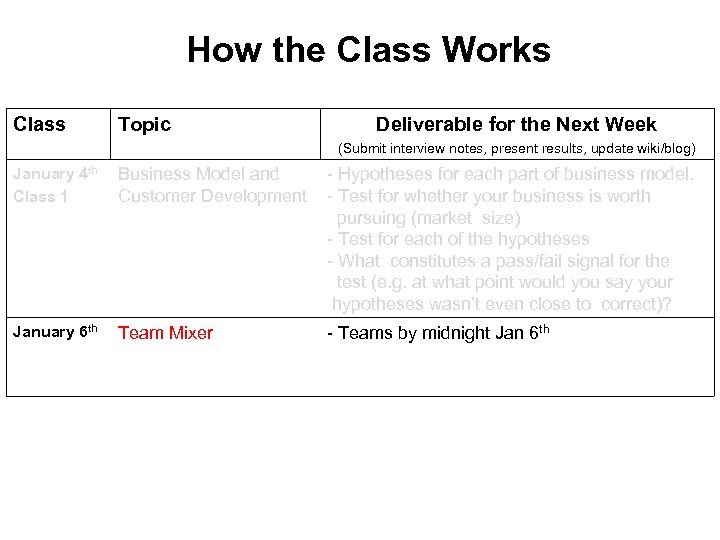 How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog) January 4 th Business Model and Class 1 Customer Development - Hypotheses for each part of business model. - Test for whether your business is worth pursuing (market size) - Test for each of the hypotheses - What constitutes a pass/fail signal for the test (e. g. at what point would you say your hypotheses wasn’t even close to correct)? January 6 th Team Mixer - Teams by midnight Jan 6 th
How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog) January 4 th Business Model and Class 1 Customer Development - Hypotheses for each part of business model. - Test for whether your business is worth pursuing (market size) - Test for each of the hypotheses - What constitutes a pass/fail signal for the test (e. g. at what point would you say your hypotheses wasn’t even close to correct)? January 6 th Team Mixer - Teams by midnight Jan 6 th
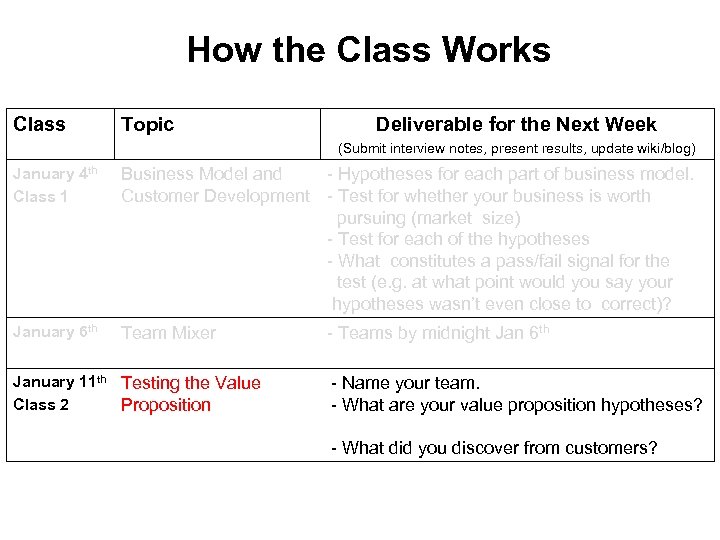 How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog) January 4 th Class 1 Business Model and - Hypotheses for each part of business model. Customer Development - Test for whether your business is worth pursuing (market size) - Test for each of the hypotheses - What constitutes a pass/fail signal for the test (e. g. at what point would you say your hypotheses wasn’t even close to correct)? January 6 th Team Mixer January 11 th Testing the Value Class 2 Proposition - Teams by midnight Jan 6 th -- Name your team. -- What are your value proposition hypotheses? -- What did you discover from customers?
How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog) January 4 th Class 1 Business Model and - Hypotheses for each part of business model. Customer Development - Test for whether your business is worth pursuing (market size) - Test for each of the hypotheses - What constitutes a pass/fail signal for the test (e. g. at what point would you say your hypotheses wasn’t even close to correct)? January 6 th Team Mixer January 11 th Testing the Value Class 2 Proposition - Teams by midnight Jan 6 th -- Name your team. -- What are your value proposition hypotheses? -- What did you discover from customers?
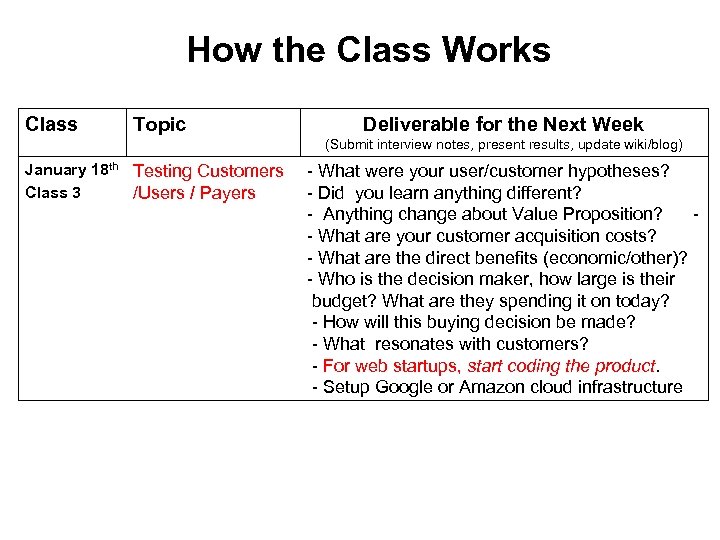 How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog) January 18 th Testing Customers Class 3 /Users / Payers - What were your user/customer hypotheses? - Did you learn anything different? - Anything change about Value Proposition? - - What are your customer acquisition costs? - What are the direct benefits (economic/other)? - Who is the decision maker, how large is their budget? What are they spending it on today? - - How will this buying decision be made? - - What resonates with customers? - - For web startups, start coding the product. - - Setup Google or Amazon cloud infrastructure
How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog) January 18 th Testing Customers Class 3 /Users / Payers - What were your user/customer hypotheses? - Did you learn anything different? - Anything change about Value Proposition? - - What are your customer acquisition costs? - What are the direct benefits (economic/other)? - Who is the decision maker, how large is their budget? What are they spending it on today? - - How will this buying decision be made? - - What resonates with customers? - - For web startups, start coding the product. - - Setup Google or Amazon cloud infrastructure
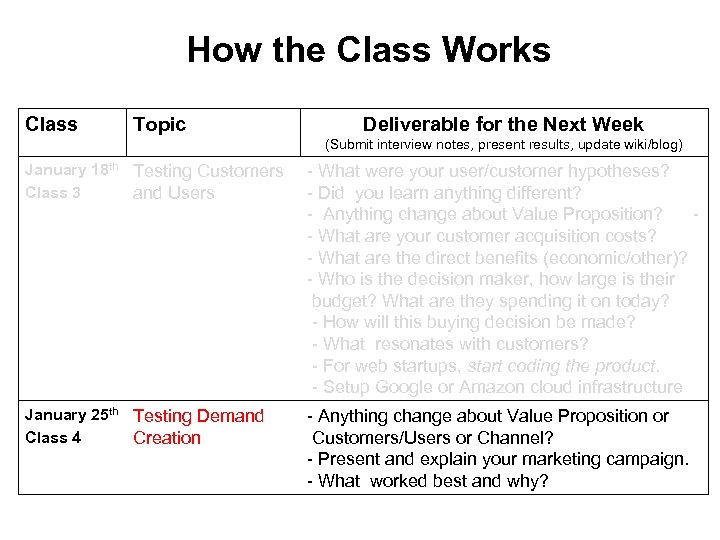 How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog) January 18 th Testing Customers Class 3 and Users - What were your user/customer hypotheses? - Did you learn anything different? - Anything change about Value Proposition? - - What are your customer acquisition costs? - What are the direct benefits (economic/other)? - Who is the decision maker, how large is their budget? What are they spending it on today? - - How will this buying decision be made? - - What resonates with customers? - - For web startups, start coding the product. - - Setup Google or Amazon cloud infrastructure January 25 th Testing Demand Class 4 Creation - Anything change about Value Proposition or Customers/Users or Channel? - Present and explain your marketing campaign. - What worked best and why?
How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog) January 18 th Testing Customers Class 3 and Users - What were your user/customer hypotheses? - Did you learn anything different? - Anything change about Value Proposition? - - What are your customer acquisition costs? - What are the direct benefits (economic/other)? - Who is the decision maker, how large is their budget? What are they spending it on today? - - How will this buying decision be made? - - What resonates with customers? - - For web startups, start coding the product. - - Setup Google or Amazon cloud infrastructure January 25 th Testing Demand Class 4 Creation - Anything change about Value Proposition or Customers/Users or Channel? - Present and explain your marketing campaign. - What worked best and why?
 How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog) Feb 1 st Class 5 Testing Sales Channel For web teams: Get working website/analytics up. - Track where visitors are coming from, how behavior differs. - What were your hypotheses about site results? - Anything in Value Proposition or Customers/Users? For non-web teams: Interview 10 people in channel - Anything change in Value Proposition, Channel or Customers/Users? - Does your product extend/replace existing channel revenue? - What’s the “cost” of your channel/ it’s efficiency vs. product selling price. For Everyone: What is your customer lifetime value? - What feedback did you receive from your users? - What are the entry barriers?
How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog) Feb 1 st Class 5 Testing Sales Channel For web teams: Get working website/analytics up. - Track where visitors are coming from, how behavior differs. - What were your hypotheses about site results? - Anything in Value Proposition or Customers/Users? For non-web teams: Interview 10 people in channel - Anything change in Value Proposition, Channel or Customers/Users? - Does your product extend/replace existing channel revenue? - What’s the “cost” of your channel/ it’s efficiency vs. product selling price. For Everyone: What is your customer lifetime value? - What feedback did you receive from your users? - What are the entry barriers?
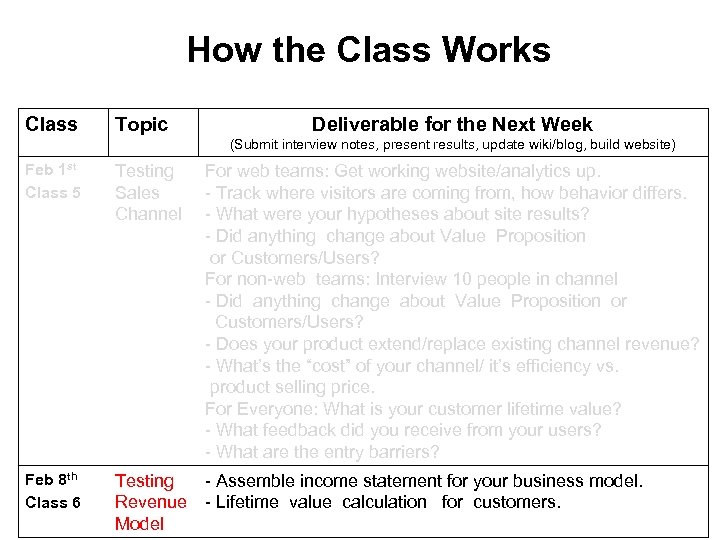 How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog, build website) Feb 1 st Class 5 Testing Sales Channel Feb 8 th Class 6 Testing - Assemble income statement for your business model. Revenue - Lifetime value calculation for customers. Model For web teams: Get working website/analytics up. - Track where visitors are coming from, how behavior differs. - What were your hypotheses about site results? - Did anything change about Value Proposition or Customers/Users? For non-web teams: Interview 10 people in channel - Did anything change about Value Proposition or Customers/Users? - Does your product extend/replace existing channel revenue? - What’s the “cost” of your channel/ it’s efficiency vs. product selling price. For Everyone: What is your customer lifetime value? - What feedback did you receive from your users? - What are the entry barriers?
How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog, build website) Feb 1 st Class 5 Testing Sales Channel Feb 8 th Class 6 Testing - Assemble income statement for your business model. Revenue - Lifetime value calculation for customers. Model For web teams: Get working website/analytics up. - Track where visitors are coming from, how behavior differs. - What were your hypotheses about site results? - Did anything change about Value Proposition or Customers/Users? For non-web teams: Interview 10 people in channel - Did anything change about Value Proposition or Customers/Users? - Does your product extend/replace existing channel revenue? - What’s the “cost” of your channel/ it’s efficiency vs. product selling price. For Everyone: What is your customer lifetime value? - What feedback did you receive from your users? - What are the entry barriers?
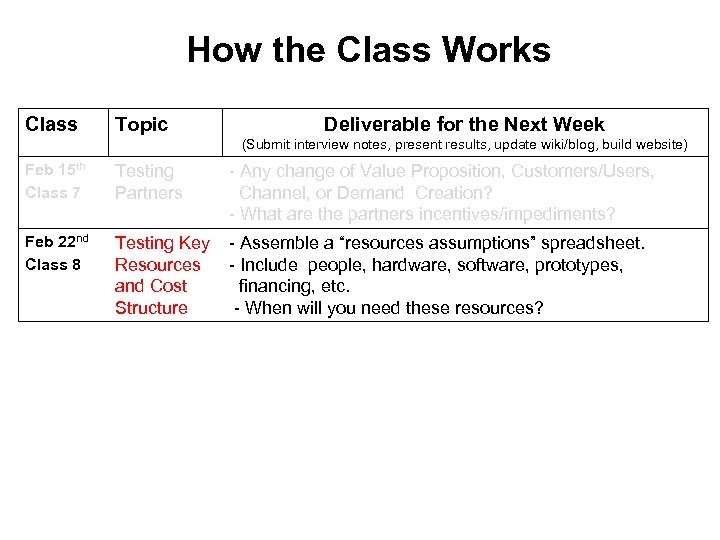
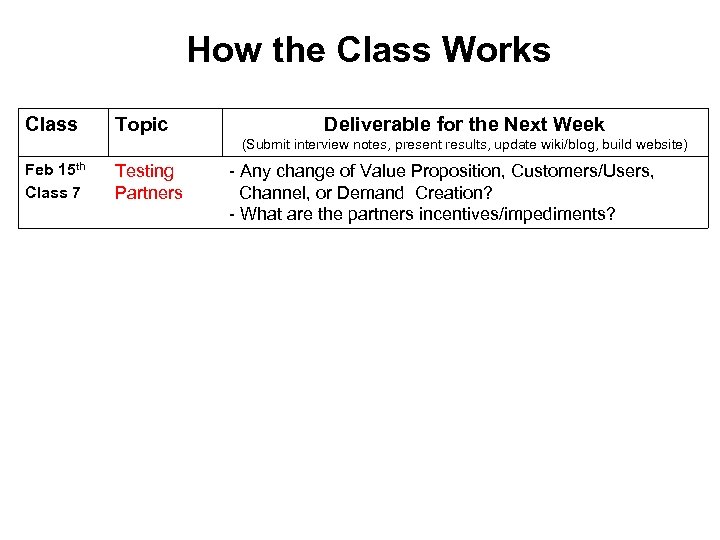 How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog, build website) Feb 15 th Class 7 Testing Partners - Any change of Value Proposition, Customers/Users, Channel, or Demand Creation? - What are the partners incentives/impediments?
How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog, build website) Feb 15 th Class 7 Testing Partners - Any change of Value Proposition, Customers/Users, Channel, or Demand Creation? - What are the partners incentives/impediments?
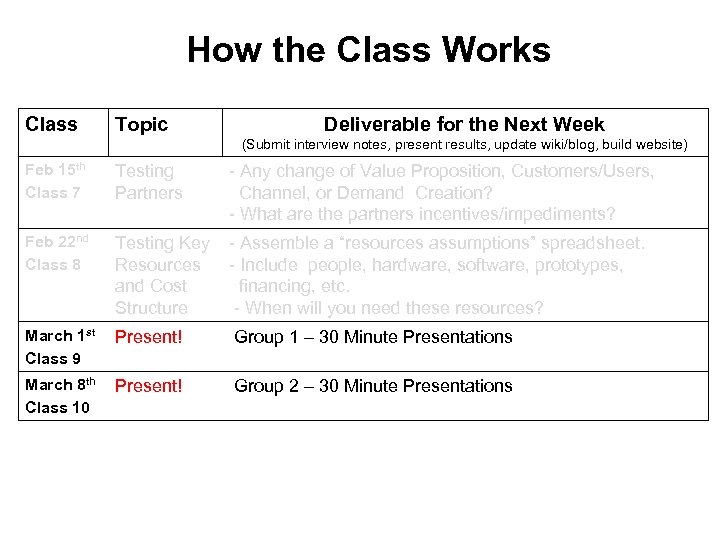
 How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog, build website) Feb 15 th Class 7 Testing Partners Feb 22 nd Class 8 Testing Key - Assemble a “resources assumptions” spreadsheet. Resources - Include people, hardware, software, prototypes, and Cost financing, etc. Structure - - When will you need these resources? - Any change of Value Proposition, Customers/Users, Channel, or Demand Creation? - What are the partners incentives/impediments?
How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog, build website) Feb 15 th Class 7 Testing Partners Feb 22 nd Class 8 Testing Key - Assemble a “resources assumptions” spreadsheet. Resources - Include people, hardware, software, prototypes, and Cost financing, etc. Structure - - When will you need these resources? - Any change of Value Proposition, Customers/Users, Channel, or Demand Creation? - What are the partners incentives/impediments?
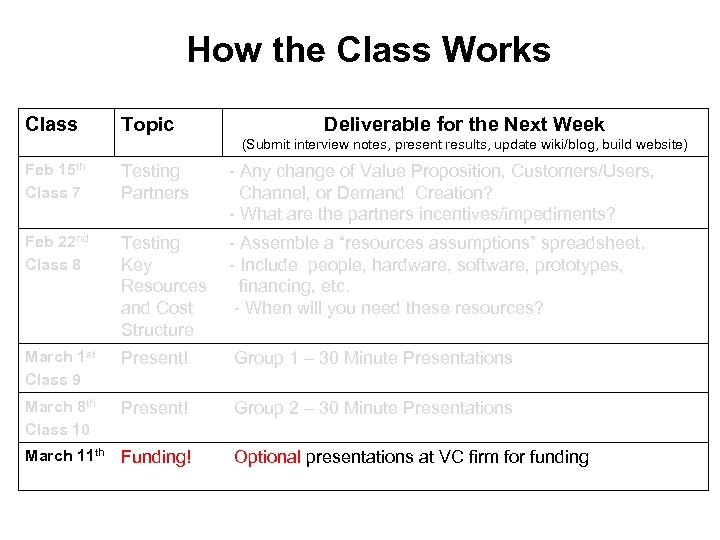
 How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog, build website) Feb 15 th Class 7 Testing Partners Feb 22 nd Class 8 Testing Key - Assemble a “resources assumptions” spreadsheet. Resources - Include people, hardware, software, prototypes, and Cost financing, etc. Structure - - When will you need these resources? March 1 st Class 9 Present! - Group 1 – 30 Minute Presentations March 8 th Class 10 Present! - Group 2 – 30 Minute Presentations - Any change of Value Proposition, Customers/Users, Channel, or Demand Creation? - What are the partners incentives/impediments?
How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog, build website) Feb 15 th Class 7 Testing Partners Feb 22 nd Class 8 Testing Key - Assemble a “resources assumptions” spreadsheet. Resources - Include people, hardware, software, prototypes, and Cost financing, etc. Structure - - When will you need these resources? March 1 st Class 9 Present! - Group 1 – 30 Minute Presentations March 8 th Class 10 Present! - Group 2 – 30 Minute Presentations - Any change of Value Proposition, Customers/Users, Channel, or Demand Creation? - What are the partners incentives/impediments?
 How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog, build website) Feb 15 th Class 7 Testing Partners Feb 22 nd Class 8 Testing - Assemble a “resources assumptions” spreadsheet. Key - Include people, hardware, software, prototypes, Resources financing, etc. and Cost - - When will you need these resources? Structure March 1 st Class 9 Present! - Group 1 – 30 Minute Presentations March 8 th Class 10 Present! - Group 2 – 30 Minute Presentations March 11 th Funding! - Any change of Value Proposition, Customers/Users, Channel, or Demand Creation? - What are the partners incentives/impediments? - Optional presentations at VC firm for funding
How the Class Works Class Topic Deliverable for the Next Week (Submit interview notes, present results, update wiki/blog, build website) Feb 15 th Class 7 Testing Partners Feb 22 nd Class 8 Testing - Assemble a “resources assumptions” spreadsheet. Key - Include people, hardware, software, prototypes, Resources financing, etc. and Cost - - When will you need these resources? Structure March 1 st Class 9 Present! - Group 1 – 30 Minute Presentations March 8 th Class 10 Present! - Group 2 – 30 Minute Presentations March 11 th Funding! - Any change of Value Proposition, Customers/Users, Channel, or Demand Creation? - What are the partners incentives/impediments? - Optional presentations at VC firm for funding
 How to Build A Startup Idea Size Opportunity Business Model Customer Development
How to Build A Startup Idea Size Opportunity Business Model Customer Development
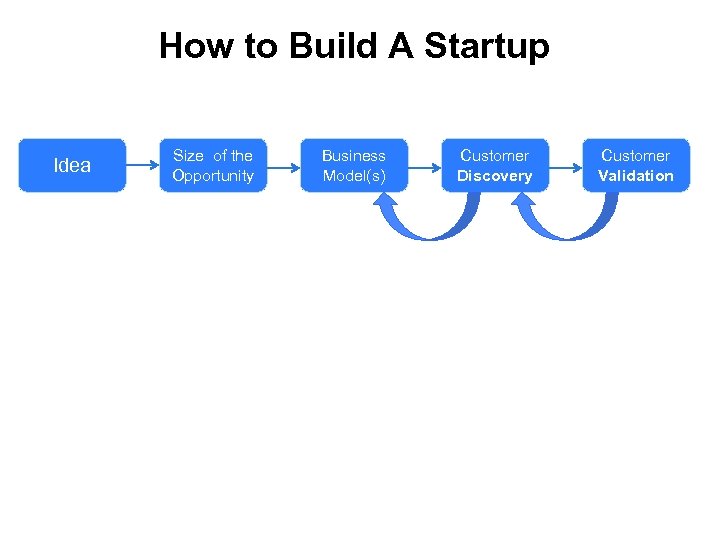 How to Build A Startup Idea Size of the Opportunity Business Model(s) Customer Discovery Customer Validation
How to Build A Startup Idea Size of the Opportunity Business Model(s) Customer Discovery Customer Validation
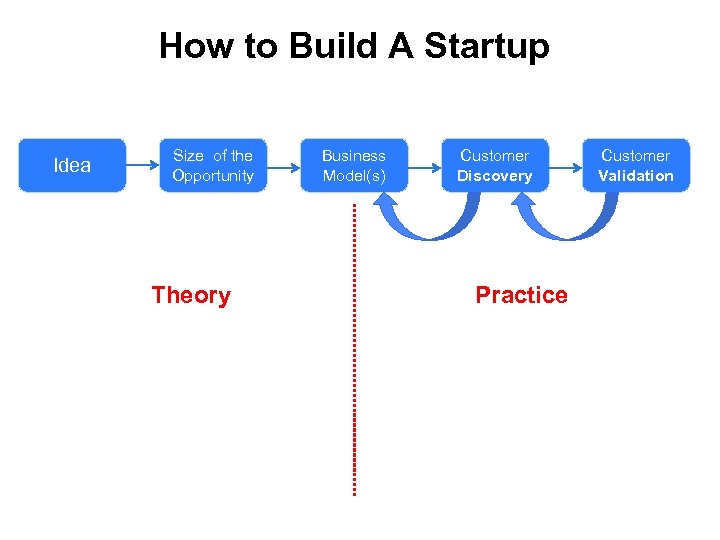 How to Build A Startup Idea Size of the Opportunity Theory Business Model(s) Customer Discovery Practice Customer Validation
How to Build A Startup Idea Size of the Opportunity Theory Business Model(s) Customer Discovery Practice Customer Validation
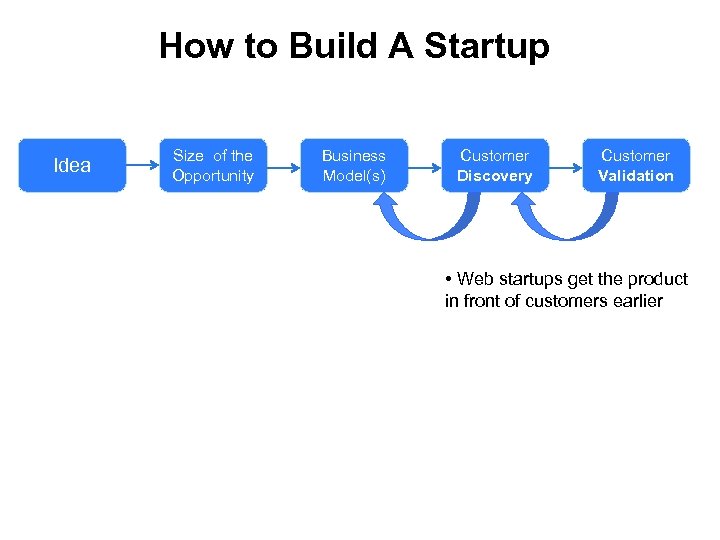 How to Build A Startup Idea Size of the Opportunity Business Model(s) Customer Discovery Customer Validation • Web startups get the product in front of customers earlier
How to Build A Startup Idea Size of the Opportunity Business Model(s) Customer Discovery Customer Validation • Web startups get the product in front of customers earlier
 How to Build A Startup Idea Size of the Opportunity Business Model(s) Customer Discovery Customer Validation
How to Build A Startup Idea Size of the Opportunity Business Model(s) Customer Discovery Customer Validation
 Idea
Idea
 We’re Engineers Darn It! Stanford • • Aren’t companies all about product? I have a great technology idea Teach me how to make a company around it Just like Facebook and Google (or Intel or Apple)
We’re Engineers Darn It! Stanford • • Aren’t companies all about product? I have a great technology idea Teach me how to make a company around it Just like Facebook and Google (or Intel or Apple)
 Sources of Startup Ideas? • Technology shifts – Moore’s Law – Disruptive tech – Research • Market changes • Dinosaur factor – Arrogance – Deadened reflexes • Irrational exuberance – Undervalued assets – Value chain disruption – Deregulation • Societal changes – Changes in ways we live, learn, work, etc. – The world is flat (outsourcing)
Sources of Startup Ideas? • Technology shifts – Moore’s Law – Disruptive tech – Research • Market changes • Dinosaur factor – Arrogance – Deadened reflexes • Irrational exuberance – Undervalued assets – Value chain disruption – Deregulation • Societal changes – Changes in ways we live, learn, work, etc. – The world is flat (outsourcing)
 An Idea is _Not_ a Company
An Idea is _Not_ a Company
 Size of Opportunity
Size of Opportunity
 This Class is about Scalable Startups n n Not all startups are designed to scale Small business startups have different goals u n Scalable startups are designed to grow big u n They are done by normal people Typically require venture capital This means the size of the opportunity needs to be $100’s of millions to billions
This Class is about Scalable Startups n n Not all startups are designed to scale Small business startups have different goals u n Scalable startups are designed to grow big u n They are done by normal people Typically require venture capital This means the size of the opportunity needs to be $100’s of millions to billions
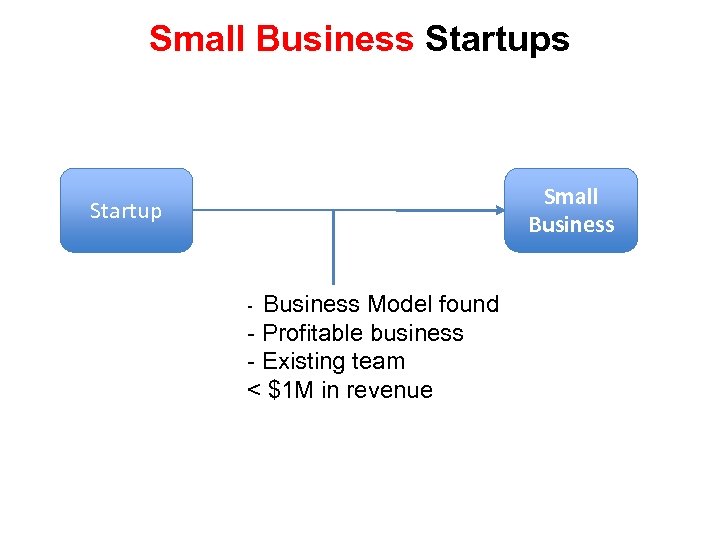 Small Business Startups Small Business Startup - Business Model found - Profitable business - Existing team < $1 M in revenue
Small Business Startups Small Business Startup - Business Model found - Profitable business - Existing team < $1 M in revenue
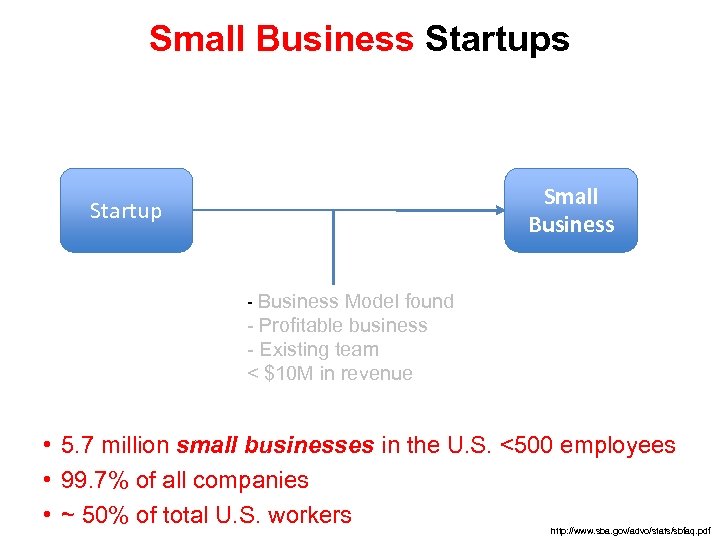 Small Business Startups Small Business Startup - Business Model found - Profitable business - Existing team < $10 M in revenue • 5. 7 million small businesses in the U. S. <500 employees • 99. 7% of all companies • ~ 50% of total U. S. workers http: //www. sba. gov/advo/stats/sbfaq. pdf
Small Business Startups Small Business Startup - Business Model found - Profitable business - Existing team < $10 M in revenue • 5. 7 million small businesses in the U. S. <500 employees • 99. 7% of all companies • ~ 50% of total U. S. workers http: //www. sba. gov/advo/stats/sbfaq. pdf
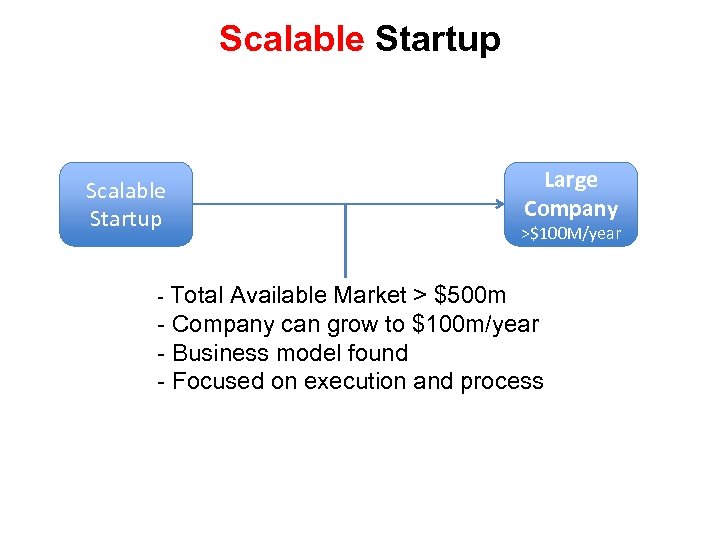 Scalable Startup Large Company >$100 M/year - Total Available Market > $500 m - Company can grow to $100 m/year - Business model found - Focused on execution and process
Scalable Startup Large Company >$100 M/year - Total Available Market > $500 m - Company can grow to $100 m/year - Business model found - Focused on execution and process
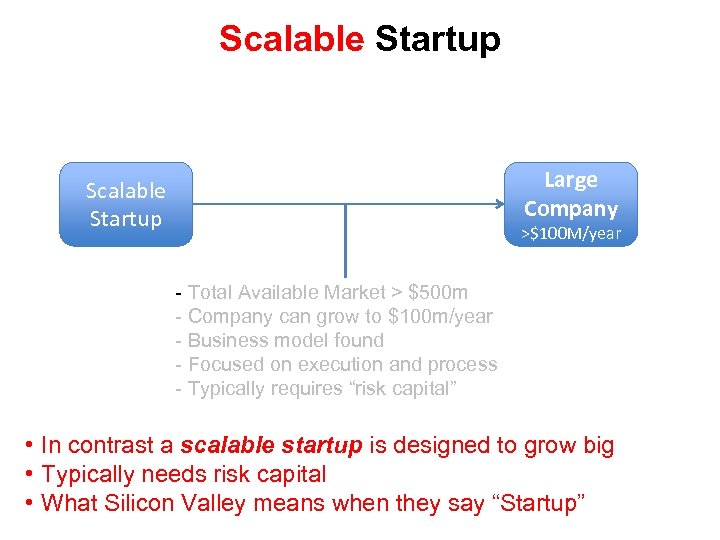 Scalable Startup Large Company Scalable Startup >$100 M/year - Total Available Market > $500 m - Company can grow to $100 m/year - Business model found - Focused on execution and process - Typically requires “risk capital” • In contrast a scalable startup is designed to grow big • Typically needs risk capital • What Silicon Valley means when they say “Startup”
Scalable Startup Large Company Scalable Startup >$100 M/year - Total Available Market > $500 m - Company can grow to $100 m/year - Business model found - Focused on execution and process - Typically requires “risk capital” • In contrast a scalable startup is designed to grow big • Typically needs risk capital • What Silicon Valley means when they say “Startup”
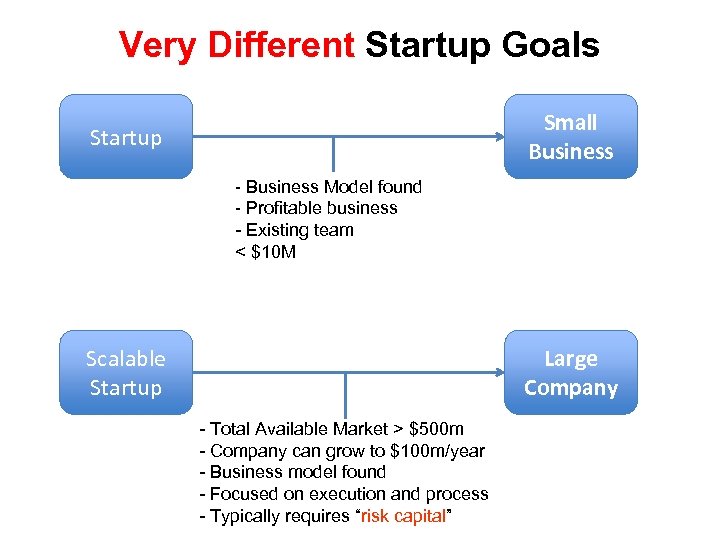 Very Different Startup Goals Small Business Startup - Business Model found - Profitable business - Existing team < $10 M Scalable Startup Large Company - Total Available Market > $500 m - Company can grow to $100 m/year - Business model found - Focused on execution and process - Typically requires “risk capital”
Very Different Startup Goals Small Business Startup - Business Model found - Profitable business - Existing team < $10 M Scalable Startup Large Company - Total Available Market > $500 m - Company can grow to $100 m/year - Business model found - Focused on execution and process - Typically requires “risk capital”
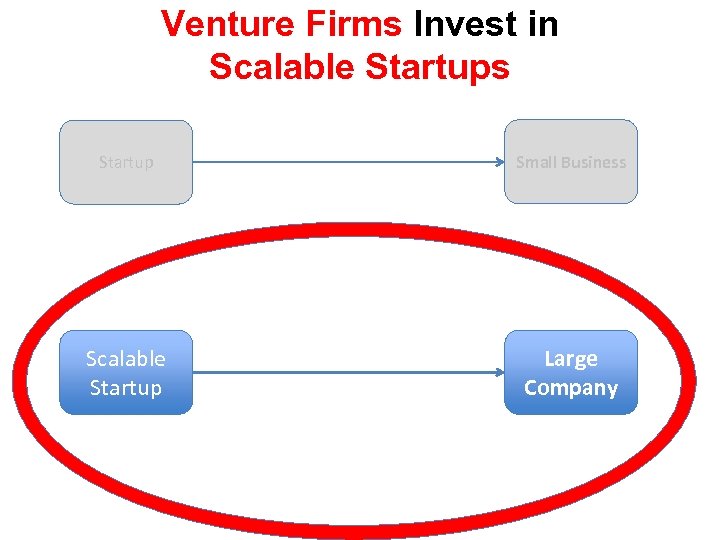 Venture Firms Invest in Scalable Startups Startup Small Business Scalable Startup Large Company
Venture Firms Invest in Scalable Startups Startup Small Business Scalable Startup Large Company
 Market/Opportunity Analysis How Big is It? : Market/Opportunity Analysis u u Identify a Customer and Market Need Size the Market Competitors Growth Potential
Market/Opportunity Analysis How Big is It? : Market/Opportunity Analysis u u Identify a Customer and Market Need Size the Market Competitors Growth Potential
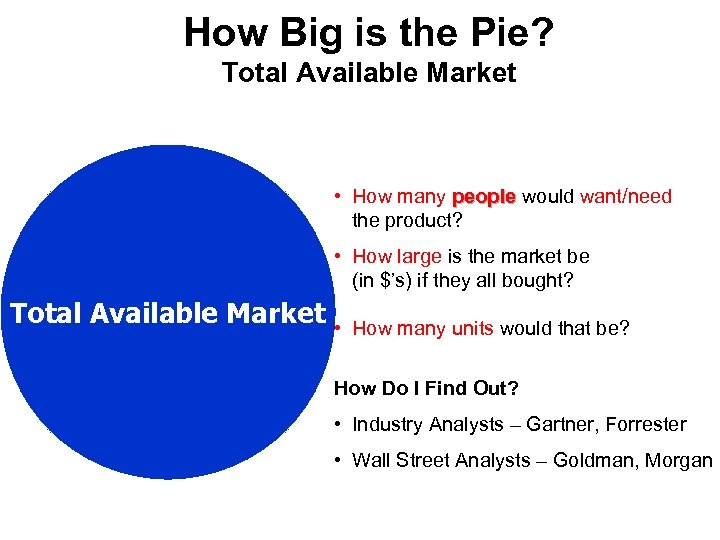 How Big is the Pie? Total Available Market • How many people would want/need people the product? • How large is the market be (in $’s) if they all bought? Total Available Market • How many units would that be? How Do I Find Out? • Industry Analysts – Gartner, Forrester • Wall Street Analysts – Goldman, Morgan
How Big is the Pie? Total Available Market • How many people would want/need people the product? • How large is the market be (in $’s) if they all bought? Total Available Market • How many units would that be? How Do I Find Out? • Industry Analysts – Gartner, Forrester • Wall Street Analysts – Goldman, Morgan
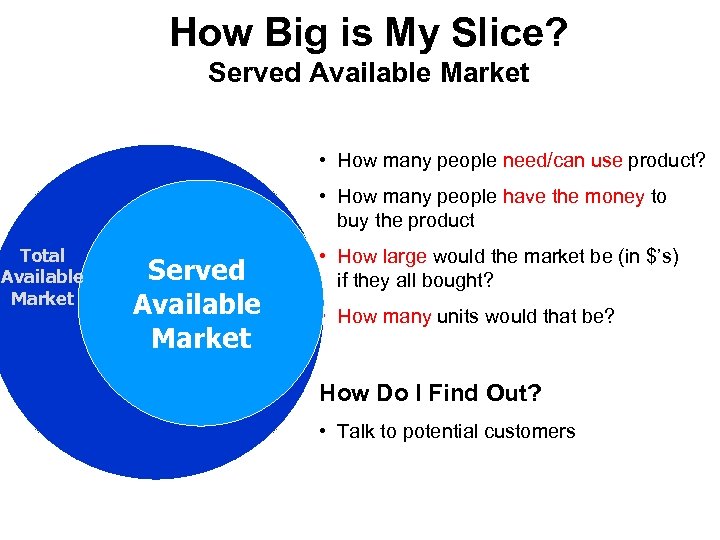 How Big is My Slice? Served Available Market • How many people need/can use product? • How many people have the money to buy the product Total Available Market Served Available Market • How large would the market be (in $’s) if they all bought? • How many units would that be? How Do I Find Out? • Talk to potential customers
How Big is My Slice? Served Available Market • How many people need/can use product? • How many people have the money to buy the product Total Available Market Served Available Market • How large would the market be (in $’s) if they all bought? • How many units would that be? How Do I Find Out? • Talk to potential customers
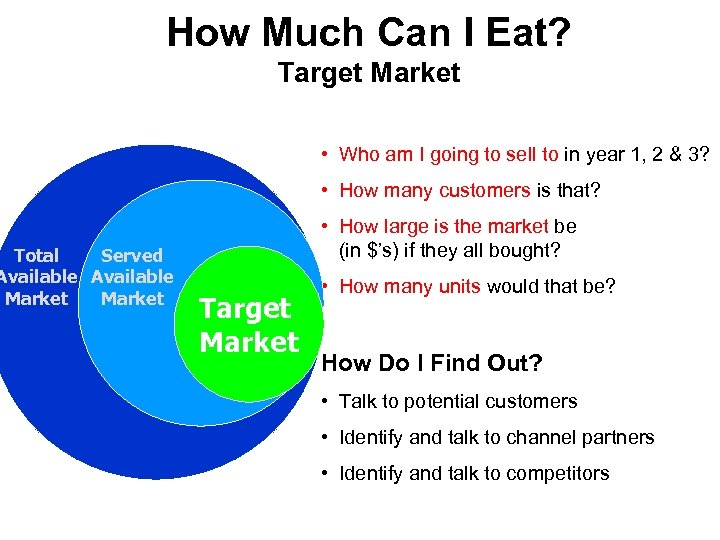 How Much Can I Eat? Total Served Available Market Target Market • Who am I going to sell to in year 1, 2 & 3? • How many customers is that? • How large is the market be (in $’s) if they all bought? Target Market • How many units would that be? How Do I Find Out? • Talk to potential customers • Identify and talk to channel partners • Identify and talk to competitors
How Much Can I Eat? Total Served Available Market Target Market • Who am I going to sell to in year 1, 2 & 3? • How many customers is that? • How large is the market be (in $’s) if they all bought? Target Market • How many units would that be? How Do I Find Out? • Talk to potential customers • Identify and talk to channel partners • Identify and talk to competitors
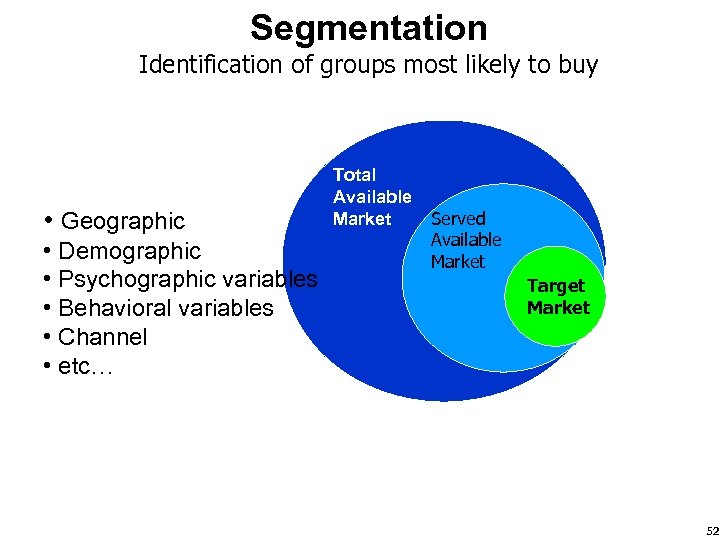 Segmentation Identification of groups most likely to buy • Geographic • Demographic • Psychographic variables • Behavioral variables • Channel • etc… Total Available Market Served Available Market Target Market 52
Segmentation Identification of groups most likely to buy • Geographic • Demographic • Psychographic variables • Behavioral variables • Channel • etc… Total Available Market Served Available Market Target Market 52
 Market Size: Summary n Market Size Questions: u How big can this market be? u How much of it can we get? u Market growth rate u Market structure (Mature or in flux? ) n Most important: Talk to Customers and Sales Channel Next important: Market size by competitive approximation n Wall Street analyst reports are great And : Market research firms Like Forester, Gartner n u
Market Size: Summary n Market Size Questions: u How big can this market be? u How much of it can we get? u Market growth rate u Market structure (Mature or in flux? ) n Most important: Talk to Customers and Sales Channel Next important: Market size by competitive approximation n Wall Street analyst reports are great And : Market research firms Like Forester, Gartner n u
 Business Model
Business Model
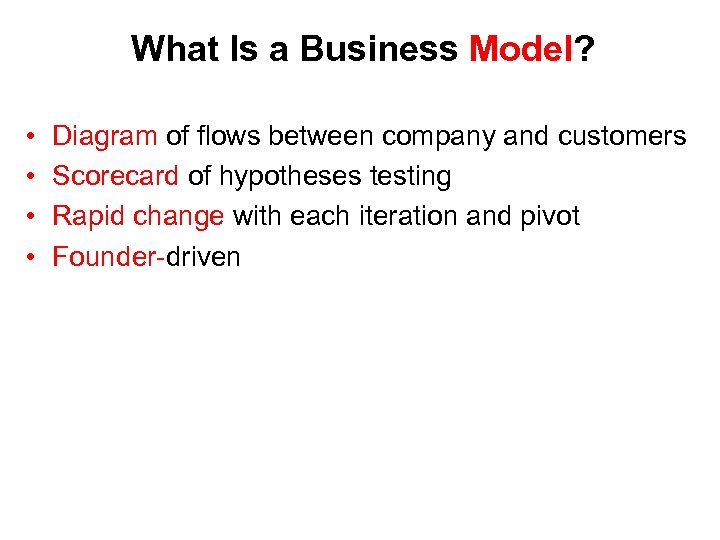 What Is a Business Model? • • Diagram of flows between company and customers Scorecard of hypotheses testing Rapid change with each iteration and pivot Founder-driven * Alex Osterwalder
What Is a Business Model? • • Diagram of flows between company and customers Scorecard of hypotheses testing Rapid change with each iteration and pivot Founder-driven * Alex Osterwalder
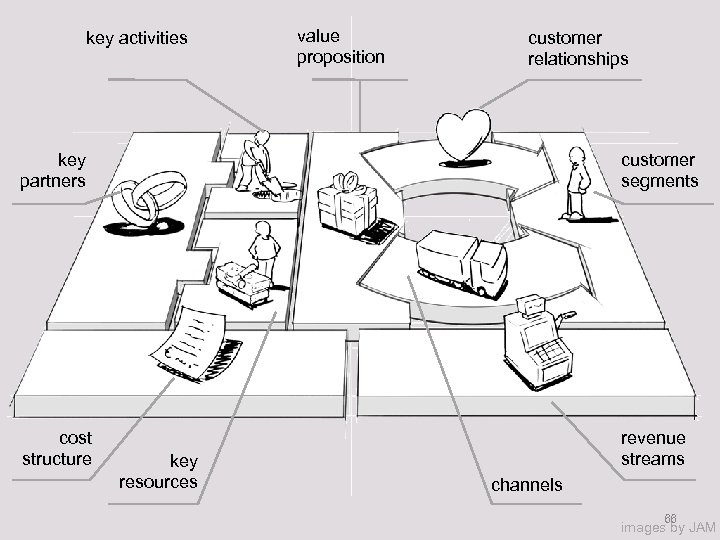
 9 building blocks of a business model:
9 building blocks of a business model:
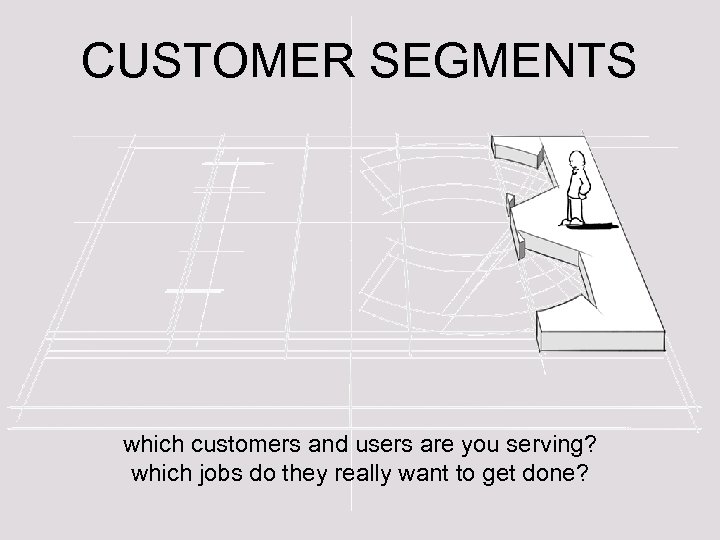 CUSTOMER SEGMENTS which customers and users are you serving? which jobs do they really want to get done?
CUSTOMER SEGMENTS which customers and users are you serving? which jobs do they really want to get done?
 VALUE PROPOSITIONS what are you offering them? what is that getting done for them? do they care?
VALUE PROPOSITIONS what are you offering them? what is that getting done for them? do they care?
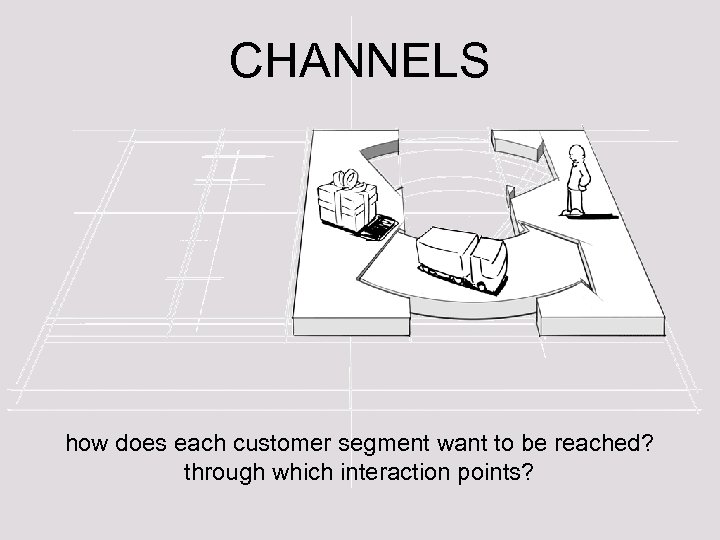 CHANNELS how does each customer segment want to be reached? through which interaction points?
CHANNELS how does each customer segment want to be reached? through which interaction points?
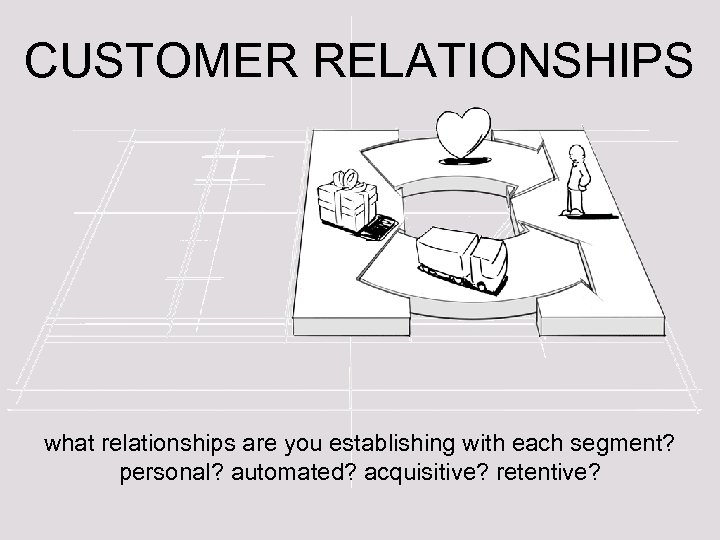 CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIPS what relationships are you establishing with each segment? personal? automated? acquisitive? retentive?
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIPS what relationships are you establishing with each segment? personal? automated? acquisitive? retentive?
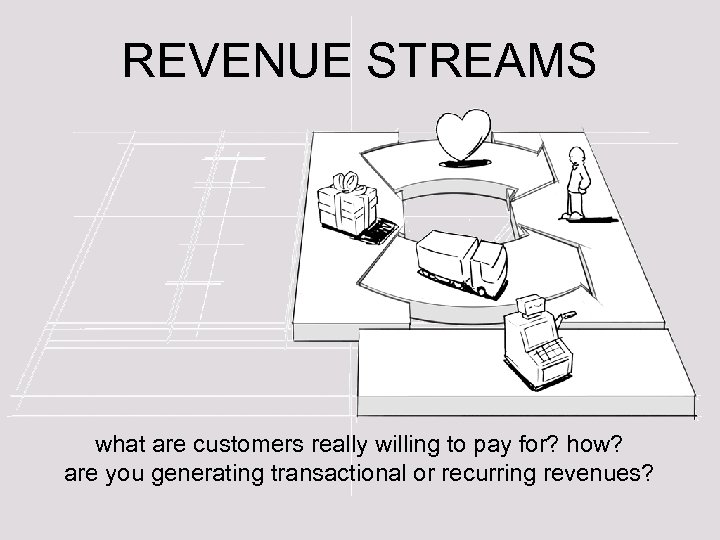 REVENUE STREAMS what are customers really willing to pay for? how? are you generating transactional or recurring revenues?
REVENUE STREAMS what are customers really willing to pay for? how? are you generating transactional or recurring revenues?
 KEY RESOURCES which resources underpin your business model? which assets are essential?
KEY RESOURCES which resources underpin your business model? which assets are essential?
 KEY ACTIVITIES which activities do you need to perform well in your business model? what is crucial? 63
KEY ACTIVITIES which activities do you need to perform well in your business model? what is crucial? 63
 KEY PARTNERS which partners and suppliers leverage your model? who do you need to rely on?
KEY PARTNERS which partners and suppliers leverage your model? who do you need to rely on?
 COST STRUCTURE what is the resulting cost structure? which key elements drive your costs?
COST STRUCTURE what is the resulting cost structure? which key elements drive your costs?
 key activities value proposition customer relationships key partners customer segments cost structure revenue streams key resources channels 66 images by JAM
key activities value proposition customer relationships key partners customer segments cost structure revenue streams key resources channels 66 images by JAM
 sketch out your business model
sketch out your business model
 building block building block g buildin block building block building block
building block building block g buildin block building block building block
 But, Realize They’re Hypotheses
But, Realize They’re Hypotheses
 9 Guesses Guess Guess Guess
9 Guesses Guess Guess Guess
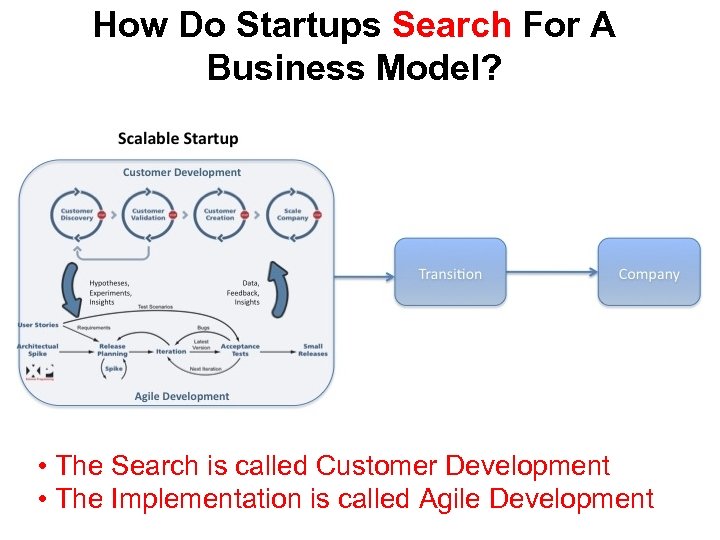 How Do Startups Search For A Business Model? • The Search is called Customer Development • The Implementation is called Agile Development
How Do Startups Search For A Business Model? • The Search is called Customer Development • The Implementation is called Agile Development
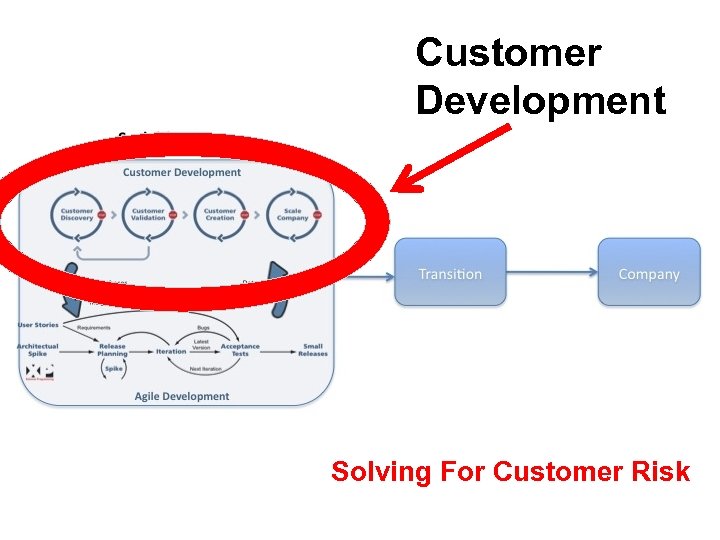 Customer Development Solving For Customer Risk
Customer Development Solving For Customer Risk
 Customer Development The founders ^ Get Out of the Building
Customer Development The founders ^ Get Out of the Building
 More startups fail from a lack of customers than from a failure of product development (focus on “who” more than “what”)
More startups fail from a lack of customers than from a failure of product development (focus on “who” more than “what”)
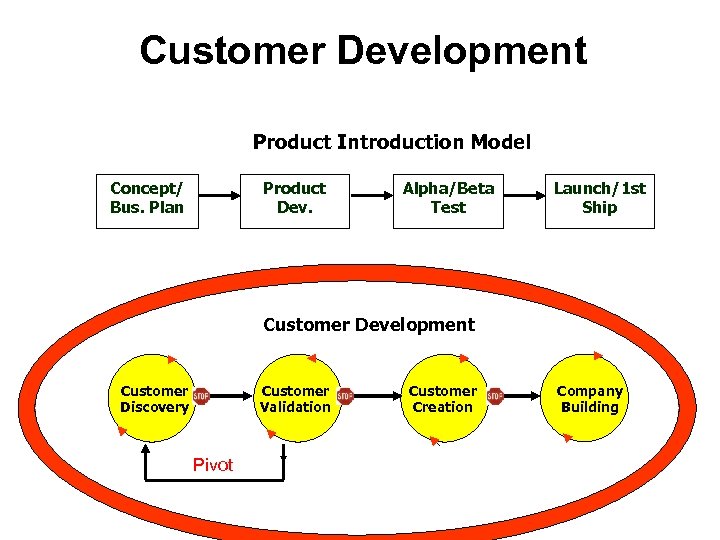 Customer Development Product Introduction Model Concept/ Bus. Plan Product Dev. Alpha/Beta Test Launch/1 st Ship Customer Development Customer Discovery Customer Validation Pivot Customer Creation Company Building
Customer Development Product Introduction Model Concept/ Bus. Plan Product Dev. Alpha/Beta Test Launch/1 st Ship Customer Development Customer Discovery Customer Validation Pivot Customer Creation Company Building
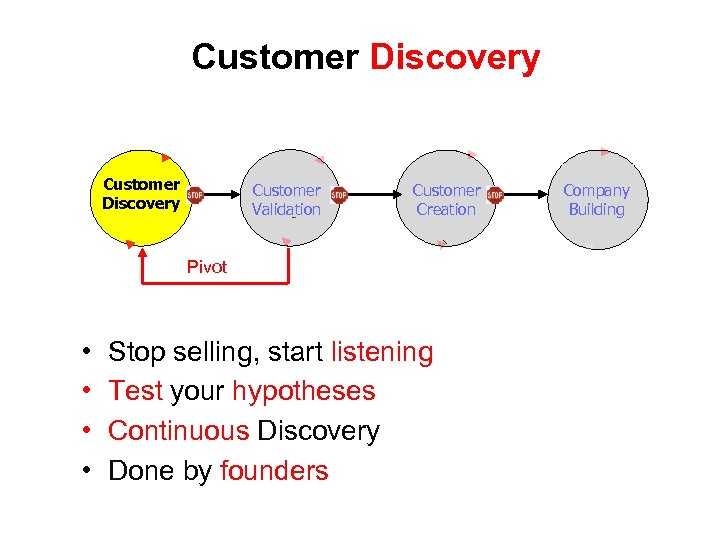 Customer Discovery Customer Validation Customer Creation Pivot • • Stop selling, start listening Test your hypotheses Continuous Discovery Done by founders Company Building
Customer Discovery Customer Validation Customer Creation Pivot • • Stop selling, start listening Test your hypotheses Continuous Discovery Done by founders Company Building
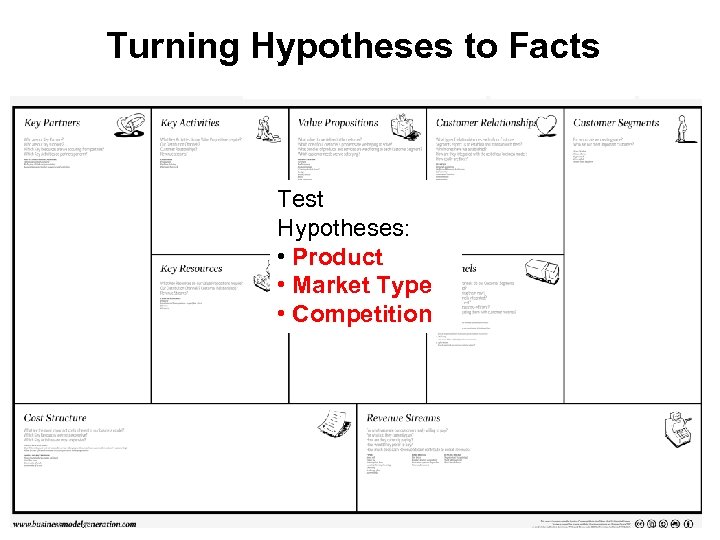 Turning Hypotheses to Facts Test Hypotheses: • Product • Market Type • Competition
Turning Hypotheses to Facts Test Hypotheses: • Product • Market Type • Competition
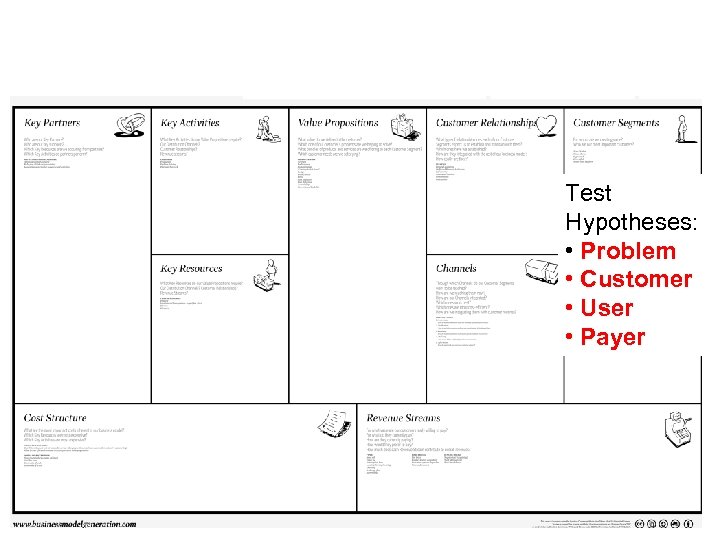 Test Hypotheses: • Problem • Customer • User • Payer
Test Hypotheses: • Problem • Customer • User • Payer
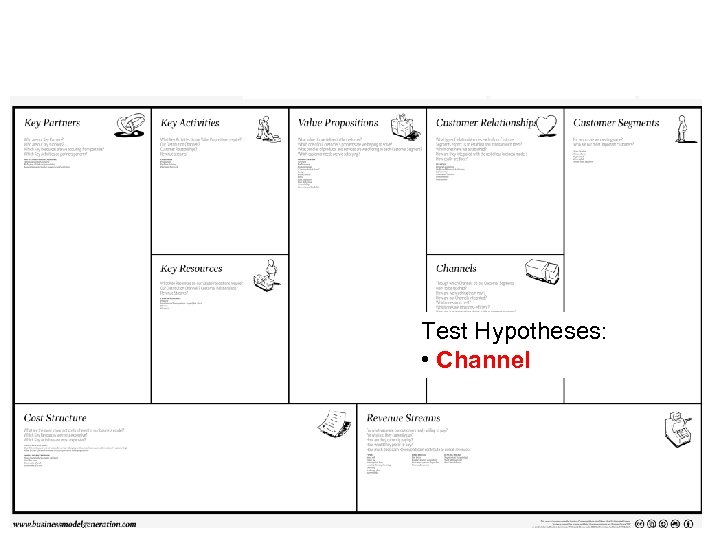 Test Hypotheses: • Channel
Test Hypotheses: • Channel
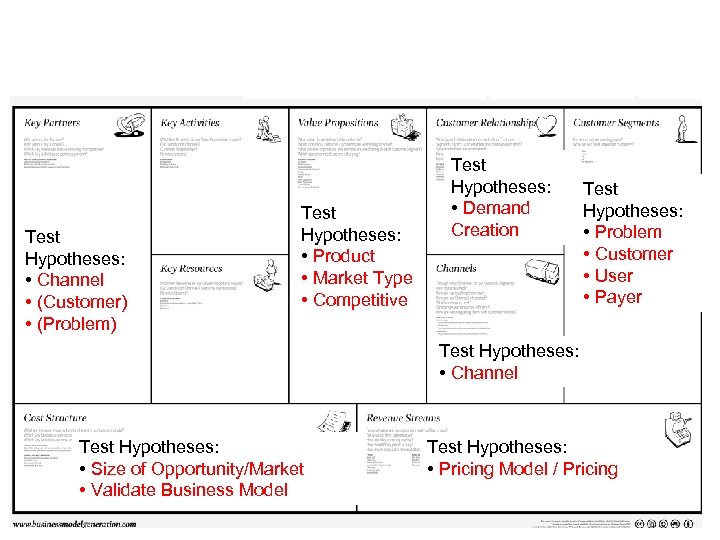 Test Hypotheses: • Channel • (Customer) • (Problem) Test Hypotheses: • Product • Market Type • Competitive Test Hypotheses: • Demand Creation Test Hypotheses: • Problem • Customer • User • Payer Test Hypotheses: • Channel Test Hypotheses: • Size of Opportunity/Market • Validate Business Model Test Hypotheses: • Pricing Model / Pricing
Test Hypotheses: • Channel • (Customer) • (Problem) Test Hypotheses: • Product • Market Type • Competitive Test Hypotheses: • Demand Creation Test Hypotheses: • Problem • Customer • User • Payer Test Hypotheses: • Channel Test Hypotheses: • Size of Opportunity/Market • Validate Business Model Test Hypotheses: • Pricing Model / Pricing
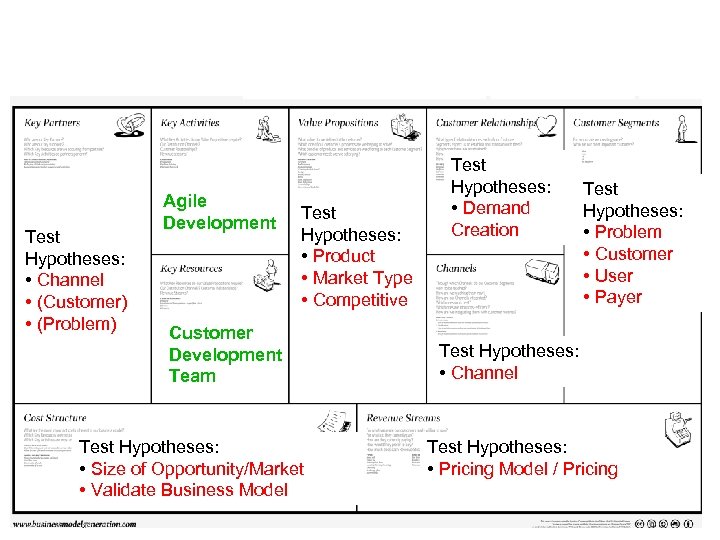 Test Hypotheses: • Channel • (Customer) • (Problem) Agile Development Test Hypotheses: • Product • Market Type • Competitive Customer Development Team Test Hypotheses: • Size of Opportunity/Market • Validate Business Model Test Hypotheses: • Demand Creation Test Hypotheses: • Problem • Customer • User • Payer Test Hypotheses: • Channel Test Hypotheses: • Pricing Model / Pricing
Test Hypotheses: • Channel • (Customer) • (Problem) Agile Development Test Hypotheses: • Product • Market Type • Competitive Customer Development Team Test Hypotheses: • Size of Opportunity/Market • Validate Business Model Test Hypotheses: • Demand Creation Test Hypotheses: • Problem • Customer • User • Payer Test Hypotheses: • Channel Test Hypotheses: • Pricing Model / Pricing
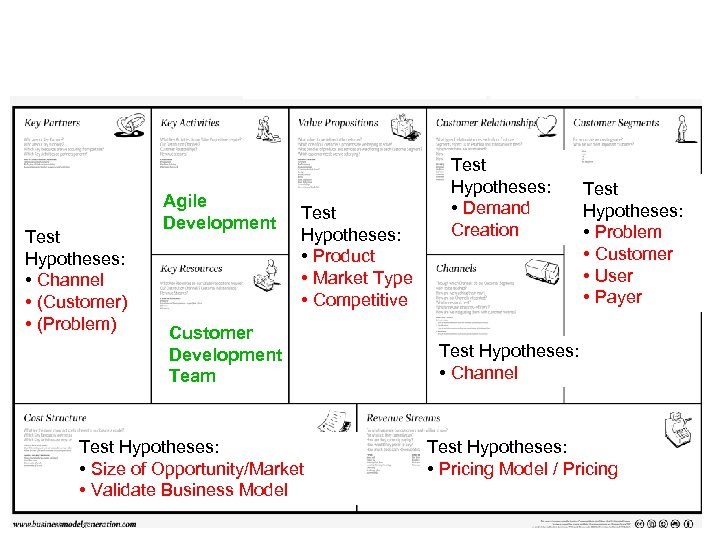 Test Hypotheses: • Channel • (Customer) • (Problem) Agile Development Test Hypotheses: • Product • Market Type • Competitive Customer Development Team Test Hypotheses: • Size of Opportunity/Market • Validate Business Model Test Hypotheses: • Demand Creation Test Hypotheses: • Problem • Customer • User • Payer Test Hypotheses: • Channel Test Hypotheses: • Pricing Model / Pricing
Test Hypotheses: • Channel • (Customer) • (Problem) Agile Development Test Hypotheses: • Product • Market Type • Competitive Customer Development Team Test Hypotheses: • Size of Opportunity/Market • Validate Business Model Test Hypotheses: • Demand Creation Test Hypotheses: • Problem • Customer • User • Payer Test Hypotheses: • Channel Test Hypotheses: • Pricing Model / Pricing
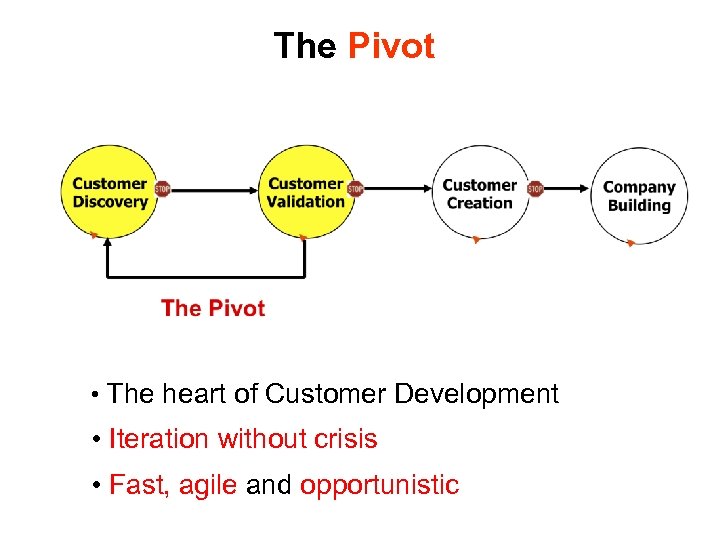 The Pivot • The heart of Customer Development • Iteration without crisis • Fast, agile and opportunistic
The Pivot • The heart of Customer Development • Iteration without crisis • Fast, agile and opportunistic
 Break
Break
 Our “Culture” for E 245 • Show up on time and stay ‘til we’re done • Keep your commitments (in class and out) • Step outside if you must call, email, skype, twitter, chat, surf the web, or do anything unrelated to E 245 • Entrepreneurship is a team sport – 80% of your grade depends on working with others
Our “Culture” for E 245 • Show up on time and stay ‘til we’re done • Keep your commitments (in class and out) • Step outside if you must call, email, skype, twitter, chat, surf the web, or do anything unrelated to E 245 • Entrepreneurship is a team sport – 80% of your grade depends on working with others
 What Lies Ahead: “To Do” List • Check web site for admission lists – attendance is mandatory in session 2 – waitlist (if any) will be cleared at beginning of class • Form full teams by Session 2 – mixer on Thursday, 5: 15 at Thornton 110 • Team deliverable by next week: Hypotheses for each part of business model. - Test for whether your business is worth pursuing (market size) - Test for each of the hypotheses - What constitutes a pass/fail signal for the test (e. g. at what point would you say your hypotheses wasn’t even close to correct)?
What Lies Ahead: “To Do” List • Check web site for admission lists – attendance is mandatory in session 2 – waitlist (if any) will be cleared at beginning of class • Form full teams by Session 2 – mixer on Thursday, 5: 15 at Thornton 110 • Team deliverable by next week: Hypotheses for each part of business model. - Test for whether your business is worth pursuing (market size) - Test for each of the hypotheses - What constitutes a pass/fail signal for the test (e. g. at what point would you say your hypotheses wasn’t even close to correct)?


