63496df22f01535215ba8410afb2ff0a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Energy Part 2 – Fossil Fuels
Energy Part 2 – Fossil Fuels
 Types: Coal n q q q Lignite – soft, lowest heat content Bituminous – soft, high sulfur content, 50% of US reserves Anthracite – hard, high heat content, low sulfur, 2% of US reserves
Types: Coal n q q q Lignite – soft, lowest heat content Bituminous – soft, high sulfur content, 50% of US reserves Anthracite – hard, high heat content, low sulfur, 2% of US reserves
 Coal n n Supplies 25% of world energy China and the US consuming the most 87% of coal in the US is used to produce electricity Clean Air Act: requires a 90% reduction of sulfur-containing gases from coal combustion
Coal n n Supplies 25% of world energy China and the US consuming the most 87% of coal in the US is used to produce electricity Clean Air Act: requires a 90% reduction of sulfur-containing gases from coal combustion
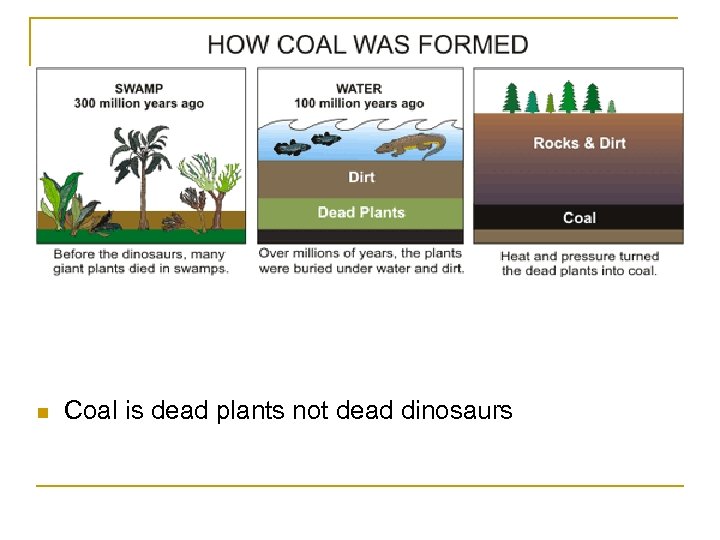 n Coal is dead plants not dead dinosaurs
n Coal is dead plants not dead dinosaurs
 Extraction and Purification of Coal n Extraction methods: q q n Surface mining Underground mining Purification q q Removes foreign materials Screens for size Crushes and washes coal to remove contaminants May convert coal to liquid through clean coal technologies
Extraction and Purification of Coal n Extraction methods: q q n Surface mining Underground mining Purification q q Removes foreign materials Screens for size Crushes and washes coal to remove contaminants May convert coal to liquid through clean coal technologies
 Clean Coal n Process to reduce the negative impacts on the environment from burning coal q q n Washing coal to remove minerals and impurities Capturing sulfur and carbon dioxide from flue gases Others: q q using natural gas Microbial fuel cells charged with biomass or sewage
Clean Coal n Process to reduce the negative impacts on the environment from burning coal q q n Washing coal to remove minerals and impurities Capturing sulfur and carbon dioxide from flue gases Others: q q using natural gas Microbial fuel cells charged with biomass or sewage
 Steps of Clean Coal Technology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Oxygen is introduced to burn coal completely Coal is pulverized to burn more completely Ash is removed using electrostatic precipitators Steam is condensed and returned to the boiler CO 2 is removed using live and then sequestered
Steps of Clean Coal Technology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Oxygen is introduced to burn coal completely Coal is pulverized to burn more completely Ash is removed using electrostatic precipitators Steam is condensed and returned to the boiler CO 2 is removed using live and then sequestered
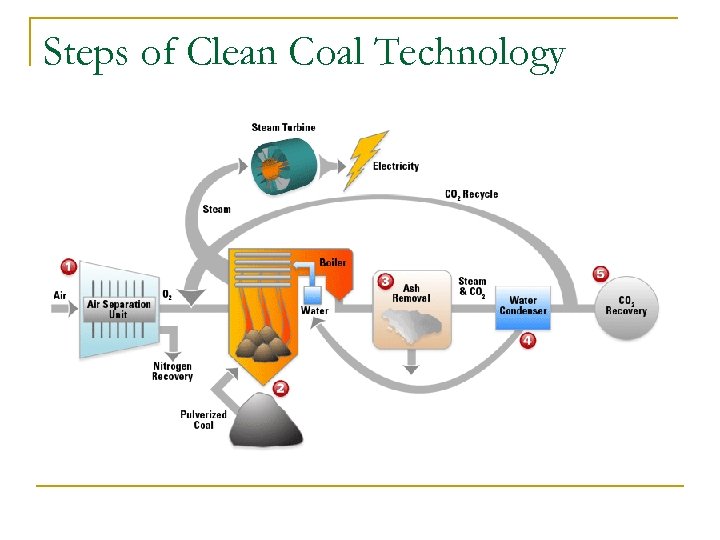 Steps of Clean Coal Technology
Steps of Clean Coal Technology
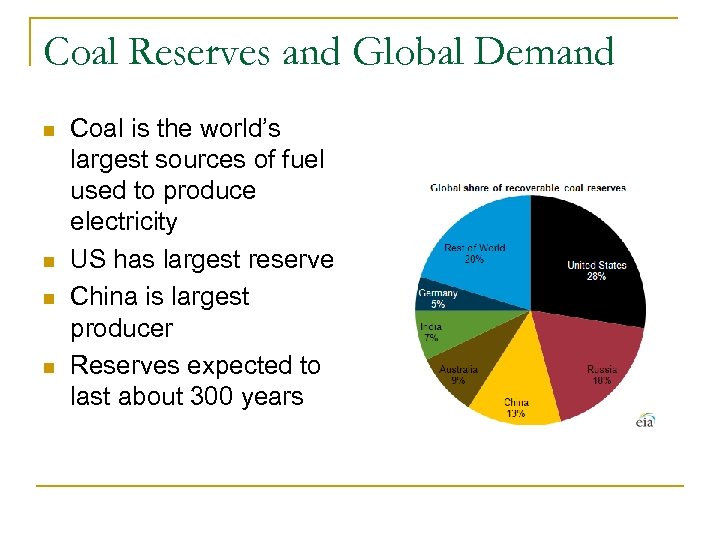 Coal Reserves and Global Demand n n Coal is the world’s largest sources of fuel used to produce electricity US has largest reserve China is largest producer Reserves expected to last about 300 years
Coal Reserves and Global Demand n n Coal is the world’s largest sources of fuel used to produce electricity US has largest reserve China is largest producer Reserves expected to last about 300 years
 Coal Pros n Abundant, known reserves (300 years worth) n Unidentified reserves (1, 000 years worth) n US reserves will last 300 years n Relatively high net-energy yield n US government subsidies keep prices low n Stable, non-explosive; not harmful if spilled Cons n Extraction methods disrupt environment and lead to pollution n Underground mining is dangerous and unhealthy n Up to 20% ends up as fly ash, boiler slag, sludge n Releases mercury, sulfur, and radioactive particles into the air n 35% of CO 2 pollution n 30% of NOx pollution n Expensive to process and transport n Pollution causes global warming n Pollution controls are expensive
Coal Pros n Abundant, known reserves (300 years worth) n Unidentified reserves (1, 000 years worth) n US reserves will last 300 years n Relatively high net-energy yield n US government subsidies keep prices low n Stable, non-explosive; not harmful if spilled Cons n Extraction methods disrupt environment and lead to pollution n Underground mining is dangerous and unhealthy n Up to 20% ends up as fly ash, boiler slag, sludge n Releases mercury, sulfur, and radioactive particles into the air n 35% of CO 2 pollution n 30% of NOx pollution n Expensive to process and transport n Pollution causes global warming n Pollution controls are expensive
 Energy Crisis n Shortages of fuel in the world market q n OPEC (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries) q q n Mainly petroleum Control world Petroleum supply OPEC decrease production to increase cost of oil or increase production to decrease the cost of oil As prices for oil increase tar sands and oil shale become profitable sources of oil
Energy Crisis n Shortages of fuel in the world market q n OPEC (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries) q q n Mainly petroleum Control world Petroleum supply OPEC decrease production to increase cost of oil or increase production to decrease the cost of oil As prices for oil increase tar sands and oil shale become profitable sources of oil
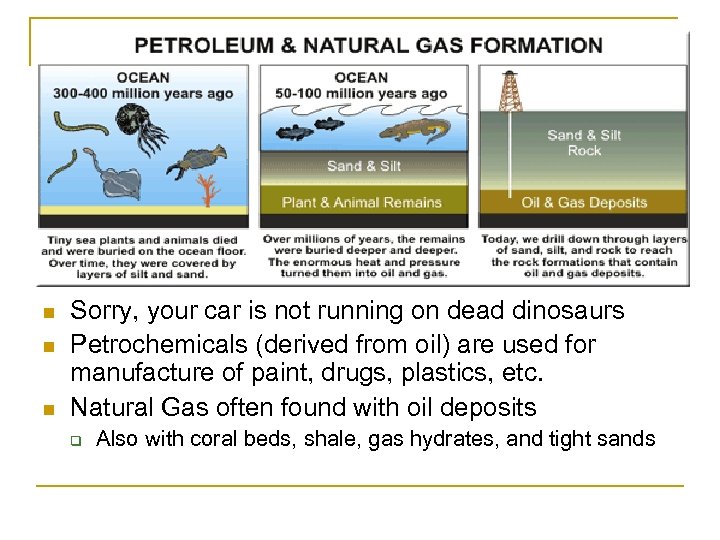 n n n Sorry, your car is not running on dead dinosaurs Petrochemicals (derived from oil) are used for manufacture of paint, drugs, plastics, etc. Natural Gas often found with oil deposits q Also with coral beds, shale, gas hydrates, and tight sands
n n n Sorry, your car is not running on dead dinosaurs Petrochemicals (derived from oil) are used for manufacture of paint, drugs, plastics, etc. Natural Gas often found with oil deposits q Also with coral beds, shale, gas hydrates, and tight sands
 Oil Extraction and Purification n Extraction: q q q n Drill down to the oil, usually trapped in porous sandstone Oil under pressure flows out naturally Low pressure wells must be pumped Purification: q q q Crude oil is sent to a refinery and “cracked” Cracking = separating the components by boiling point Produces: gasoline, heating oil, diesel oil, asphalt, etc.
Oil Extraction and Purification n Extraction: q q q n Drill down to the oil, usually trapped in porous sandstone Oil under pressure flows out naturally Low pressure wells must be pumped Purification: q q q Crude oil is sent to a refinery and “cracked” Cracking = separating the components by boiling point Produces: gasoline, heating oil, diesel oil, asphalt, etc.
 Natural Gas Extraction and Purification n Extraction: q q Usually present below non porous areas and above the oil Extraction similar to oil extraction Flows from well under own pressure and pumped into gas pipelines 560 billion m 3 produced in the US each year
Natural Gas Extraction and Purification n Extraction: q q Usually present below non porous areas and above the oil Extraction similar to oil extraction Flows from well under own pressure and pumped into gas pipelines 560 billion m 3 produced in the US each year
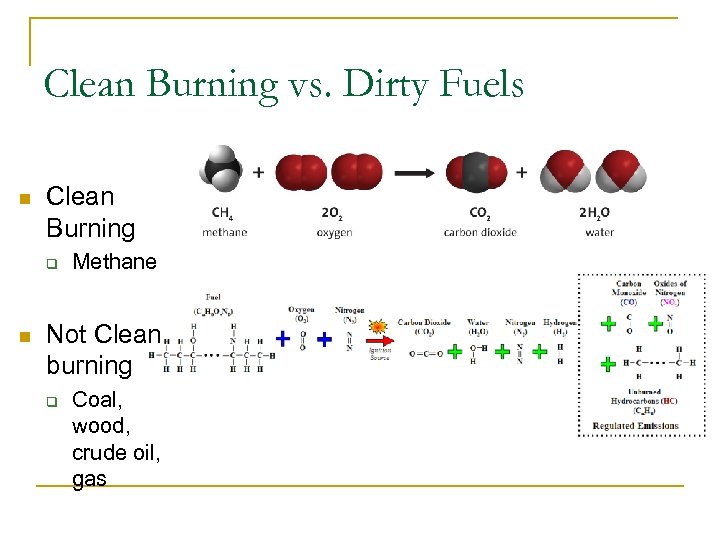 Clean Burning vs. Dirty Fuels n Clean Burning q n Methane Not Clean burning q Coal, wood, crude oil, gas
Clean Burning vs. Dirty Fuels n Clean Burning q n Methane Not Clean burning q Coal, wood, crude oil, gas
 Methane Hydrates n Methane locked in ice q q n Natural gas uses expected to increase q q n Located in permafrost regions At water depths greater than 1, 640 feet (500 m) Natural gas is clean burning Natural gas plants are relatively cheap to build US Natural gas consumption is expected to increase 40% q q Due to use in transportation Alternative liquid fuel
Methane Hydrates n Methane locked in ice q q n Natural gas uses expected to increase q q n Located in permafrost regions At water depths greater than 1, 640 feet (500 m) Natural gas is clean burning Natural gas plants are relatively cheap to build US Natural gas consumption is expected to increase 40% q q Due to use in transportation Alternative liquid fuel
 Oil Shale n Contains kerogen q n 3 trillion barrels of recoverable oil from oil shale in the world q n Heating oil shale in the absence of air turns kerogen into oil 750 billion located in the United States Largest reserves: Estonia, Australia, Germany, Israel, Jordan q In US Wyoming, Utah, Colorado
Oil Shale n Contains kerogen q n 3 trillion barrels of recoverable oil from oil shale in the world q n Heating oil shale in the absence of air turns kerogen into oil 750 billion located in the United States Largest reserves: Estonia, Australia, Germany, Israel, Jordan q In US Wyoming, Utah, Colorado
 Oil Shale Mining n In suti – heat oil shale in the ground to extract oil and gas via pumping q n Potential to affect aquifers Surface Mining q q Destroys environment Moderate net energy yield due to high inputs required to extract oil and repair environment
Oil Shale Mining n In suti – heat oil shale in the ground to extract oil and gas via pumping q n Potential to affect aquifers Surface Mining q q Destroys environment Moderate net energy yield due to high inputs required to extract oil and repair environment
 Tar Sands n Contain Bitumen – semisolid form of oil q n n Represent about 2/3 of world oil reserves Most in Canada and Venezuela q n High in sulfur (~5%) = dirty oil Keystone Pipeline Moderate net-energy yield due to high inputs q q Strip-mining In suti recovery
Tar Sands n Contain Bitumen – semisolid form of oil q n n Represent about 2/3 of world oil reserves Most in Canada and Venezuela q n High in sulfur (~5%) = dirty oil Keystone Pipeline Moderate net-energy yield due to high inputs q q Strip-mining In suti recovery
 Hydrofracking n n Removes natural gas that was previously urecoverable Process: q q q n Chemicals are mixed with large quantities of water and sand Mixture is injected into wells at extremely high pressure to create fractures in rock Oil and natural gas to flow out of the well Estimates 80% of natural gas wells will be with hydraulic fracking
Hydrofracking n n Removes natural gas that was previously urecoverable Process: q q q n Chemicals are mixed with large quantities of water and sand Mixture is injected into wells at extremely high pressure to create fractures in rock Oil and natural gas to flow out of the well Estimates 80% of natural gas wells will be with hydraulic fracking
 Hydrofracking Pros n Process of bringing well to completion is short n Well can be in production 20 – 40 years n Makes it possible to access new reserves of oil and natural gas n Stimulates the economy n Allows independence from foreign sources of oil Cons n Dangerous chemicals used in the process can enter the water supply n Toxic, radioactive, caustic liquids pose storage problems n Currently no regulations for fracking n Results in contaminated water, air pollution, destroyed streams, and negative environmental impacts
Hydrofracking Pros n Process of bringing well to completion is short n Well can be in production 20 – 40 years n Makes it possible to access new reserves of oil and natural gas n Stimulates the economy n Allows independence from foreign sources of oil Cons n Dangerous chemicals used in the process can enter the water supply n Toxic, radioactive, caustic liquids pose storage problems n Currently no regulations for fracking n Results in contaminated water, air pollution, destroyed streams, and negative environmental impacts
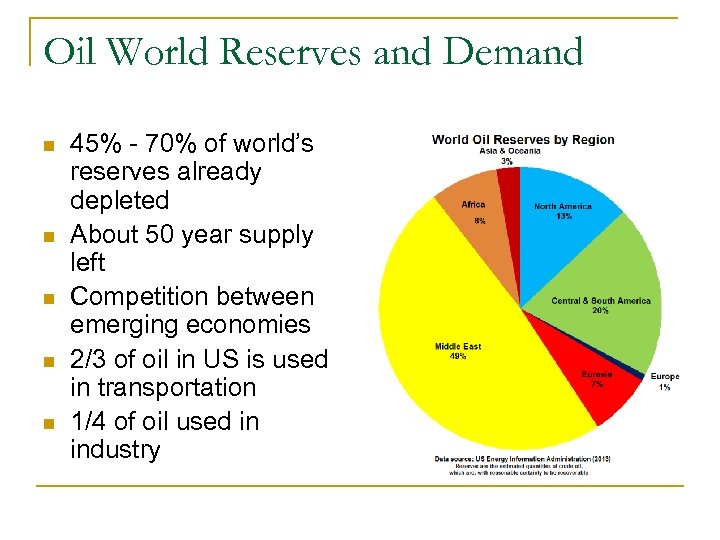 Oil World Reserves and Demand n n n 45% - 70% of world’s reserves already depleted About 50 year supply left Competition between emerging economies 2/3 of oil in US is used in transportation 1/4 of oil used in industry
Oil World Reserves and Demand n n n 45% - 70% of world’s reserves already depleted About 50 year supply left Competition between emerging economies 2/3 of oil in US is used in transportation 1/4 of oil used in industry
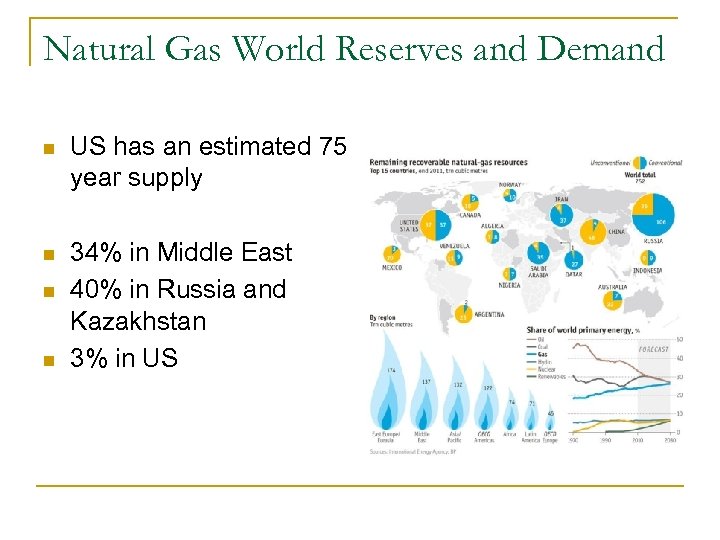 Natural Gas World Reserves and Demand n US has an estimated 75 year supply n 34% in Middle East 40% in Russia and Kazakhstan 3% in US n n
Natural Gas World Reserves and Demand n US has an estimated 75 year supply n 34% in Middle East 40% in Russia and Kazakhstan 3% in US n n
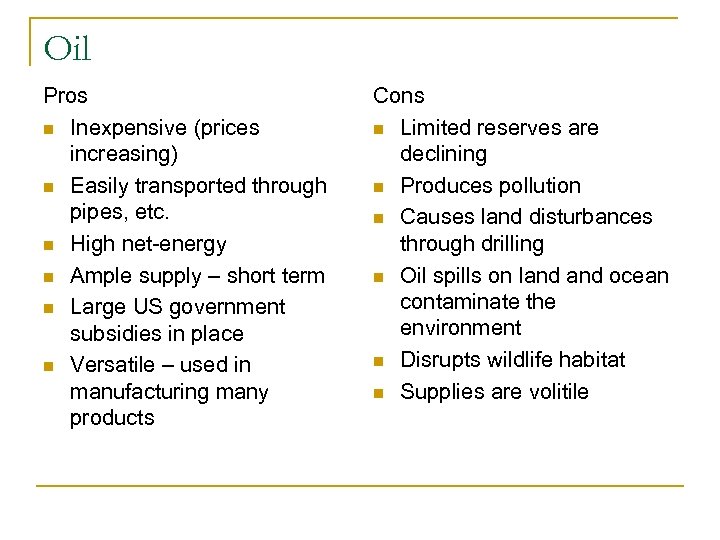 Oil Pros n Inexpensive (prices increasing) n Easily transported through pipes, etc. n High net-energy n Ample supply – short term n Large US government subsidies in place n Versatile – used in manufacturing many products Cons n Limited reserves are declining n Produces pollution n Causes land disturbances through drilling n Oil spills on land ocean contaminate the environment n Disrupts wildlife habitat n Supplies are volitile
Oil Pros n Inexpensive (prices increasing) n Easily transported through pipes, etc. n High net-energy n Ample supply – short term n Large US government subsidies in place n Versatile – used in manufacturing many products Cons n Limited reserves are declining n Produces pollution n Causes land disturbances through drilling n Oil spills on land ocean contaminate the environment n Disrupts wildlife habitat n Supplies are volitile
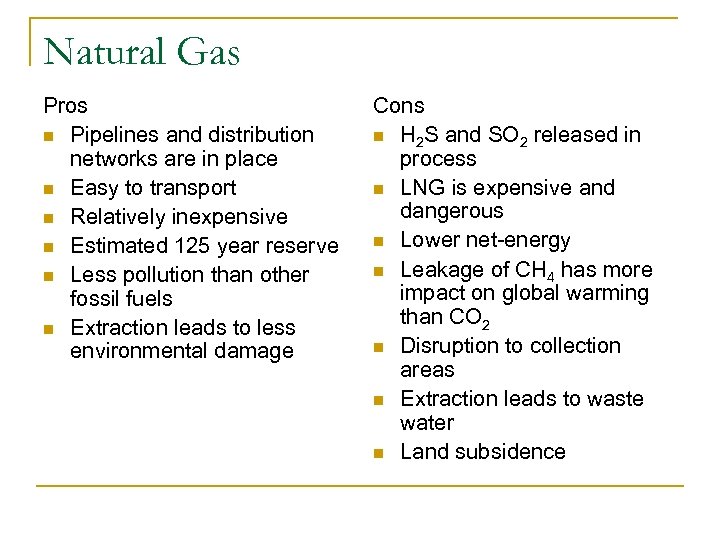 Natural Gas Pros n Pipelines and distribution networks are in place n Easy to transport n Relatively inexpensive n Estimated 125 year reserve n Less pollution than other fossil fuels n Extraction leads to less environmental damage Cons n H 2 S and SO 2 released in process n LNG is expensive and dangerous n Lower net-energy n Leakage of CH 4 has more impact on global warming than CO 2 n Disruption to collection areas n Extraction leads to waste water n Land subsidence
Natural Gas Pros n Pipelines and distribution networks are in place n Easy to transport n Relatively inexpensive n Estimated 125 year reserve n Less pollution than other fossil fuels n Extraction leads to less environmental damage Cons n H 2 S and SO 2 released in process n LNG is expensive and dangerous n Lower net-energy n Leakage of CH 4 has more impact on global warming than CO 2 n Disruption to collection areas n Extraction leads to waste water n Land subsidence
 Synfuels n Any fuels produced from coal, natural gas, or biomass through chemical conversion n Creates substances the same as crude oil or processed fuel n Eg: SNG – synthetic natural gas created through coal liquification
Synfuels n Any fuels produced from coal, natural gas, or biomass through chemical conversion n Creates substances the same as crude oil or processed fuel n Eg: SNG – synthetic natural gas created through coal liquification
 Synfuel Pros and Cons Pros n Easily transported through pipelines n Produces less air pollution n Large supply of raw materials are available n Can produce gas, diesel, or kerosene without reforming or cracking Cons n Low net energy n Plants to build are expensive n Would increase depletion of coal due to inefficiencies n Product is more expensive than petroleum
Synfuel Pros and Cons Pros n Easily transported through pipelines n Produces less air pollution n Large supply of raw materials are available n Can produce gas, diesel, or kerosene without reforming or cracking Cons n Low net energy n Plants to build are expensive n Would increase depletion of coal due to inefficiencies n Product is more expensive than petroleum
 Case Studies Arctic National Wildlife Keystone Pipeline System Refuge (ANWR): n Transport synthetic crude and diluted n ANWR in NW Alaska bitumen from Canadian (19 million acres) oil sands to refineries in n Drilling debate since Illinois, distribution hubs 1977 in Oklahoma, Texas n Controversy: economics ports of oil recovery n Continuing debate over compared to costs and benefits to environmental damage US economy and environment
Case Studies Arctic National Wildlife Keystone Pipeline System Refuge (ANWR): n Transport synthetic crude and diluted n ANWR in NW Alaska bitumen from Canadian (19 million acres) oil sands to refineries in n Drilling debate since Illinois, distribution hubs 1977 in Oklahoma, Texas n Controversy: economics ports of oil recovery n Continuing debate over compared to costs and benefits to environmental damage US economy and environment


