e7e5ded8bc9622c7c8ff616cda4ac8c2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Energy Innovation, Science and Technology: Pathway to Progress in a North American Market? Washington, DC 8 th March, 2007 Dr. M. Raymont, Energy. INet Inc.
Energy Innovation, Science and Technology: Pathway to Progress in a North American Market? Washington, DC 8 th March, 2007 Dr. M. Raymont, Energy. INet Inc.
 Is Energy Innovation the Key? Energy Innovation is essential but insufficient Many other inputs must be coordinated if we are to successfully address our energy challenges, and implement solutions – Capital, capital stock, tax, payment and other financial – Regulatory – balance protection and incentives – Infrastructure – huge existing distribution network – Human skills – do we have the people? – Risk – who, and how to share? – Transition – timeframe, scale, collateral resource availability Innovation must be set in a much broader context of where we’re trying to go, why and how. It must be pragmatic and commercially focused (Future. Gen vs. western coals/China/India? grain ethanol? heavy oil upgraders? )
Is Energy Innovation the Key? Energy Innovation is essential but insufficient Many other inputs must be coordinated if we are to successfully address our energy challenges, and implement solutions – Capital, capital stock, tax, payment and other financial – Regulatory – balance protection and incentives – Infrastructure – huge existing distribution network – Human skills – do we have the people? – Risk – who, and how to share? – Transition – timeframe, scale, collateral resource availability Innovation must be set in a much broader context of where we’re trying to go, why and how. It must be pragmatic and commercially focused (Future. Gen vs. western coals/China/India? grain ethanol? heavy oil upgraders? )
 Have we got the Right Topic? ! Do we have the innovative technologies today to deal with the energy challenges we face? -- If not what are the challenges we face and what solutions do we need? How do we move to an implementation agenda? How do we drastically accelerate implementation? How do we fairly apportion costs and consequences? How do we coordinate global action? How do we ensure that the public is informed and supportive?
Have we got the Right Topic? ! Do we have the innovative technologies today to deal with the energy challenges we face? -- If not what are the challenges we face and what solutions do we need? How do we move to an implementation agenda? How do we drastically accelerate implementation? How do we fairly apportion costs and consequences? How do we coordinate global action? How do we ensure that the public is informed and supportive?
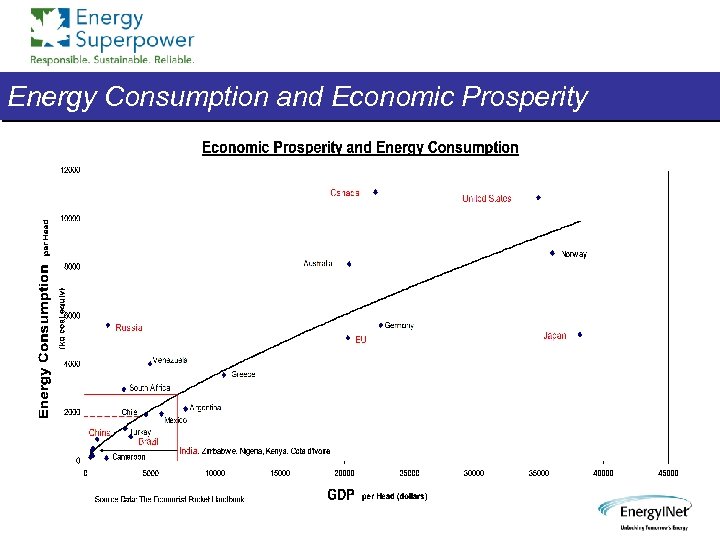 Energy Consumption and Economic Prosperity
Energy Consumption and Economic Prosperity
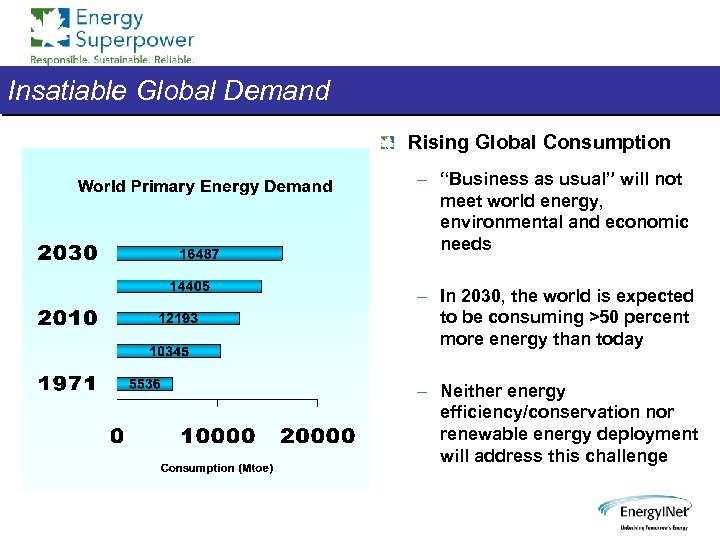 Insatiable Global Demand Rising Global Consumption – “Business as usual” will not meet world energy, environmental and economic needs – In 2030, the world is expected to be consuming >50 percent more energy than today – Neither energy efficiency/conservation nor renewable energy deployment will address this challenge
Insatiable Global Demand Rising Global Consumption – “Business as usual” will not meet world energy, environmental and economic needs – In 2030, the world is expected to be consuming >50 percent more energy than today – Neither energy efficiency/conservation nor renewable energy deployment will address this challenge
 Energy -- Bain or Boon? Energy consumption correlates very strongly to GDP and living standards, and an abundant energy supply is a major economic driver Energy production and consumption per se do not contribute meaningfully to climate change; by-products do Therefore, increased energy usage is not axiomatically problematic, and not contrary to responsible usage and sustainability Indeed, energy helps solve many global social and environmental challenges (desalination, CO 2 sequestration, food production, etc) So we should actively accelerate energy production technologies which mitigate by-products of production and use, covering both fossil fuels and alternate/renewable sources Appropriate efficiency and conservation measures will also help reduce energy by-product impacts, and extend supply
Energy -- Bain or Boon? Energy consumption correlates very strongly to GDP and living standards, and an abundant energy supply is a major economic driver Energy production and consumption per se do not contribute meaningfully to climate change; by-products do Therefore, increased energy usage is not axiomatically problematic, and not contrary to responsible usage and sustainability Indeed, energy helps solve many global social and environmental challenges (desalination, CO 2 sequestration, food production, etc) So we should actively accelerate energy production technologies which mitigate by-products of production and use, covering both fossil fuels and alternate/renewable sources Appropriate efficiency and conservation measures will also help reduce energy by-product impacts, and extend supply
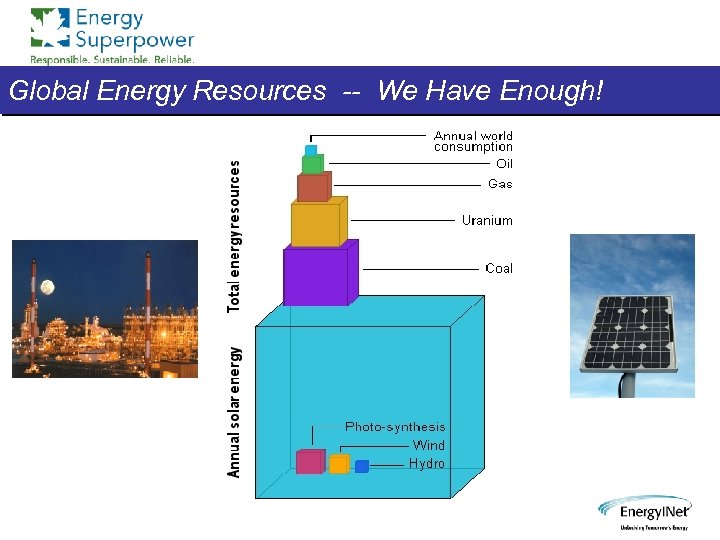 Global Energy Resources -- We Have Enough!
Global Energy Resources -- We Have Enough!
 Our Energy Challenges • Energy, environment, and economy inexorably linked in ways we can no longer ignore, with global, as well as national implications • Sufficient energy resources for global needs for several hundred years, perhaps indefinitely, but extraction and usage technologies are major issues • No “Magic Bullet” supply solution; every energy source will be needed • Carbon/fossil energy sources will still supply most of the world’s energy needs for the foreseeable future • Renewable energy sources will grow rapidly, but, even with accelerated effort, they will comprise no more than 20% of world supply in 2050 • Thus, triaging the impact of fossil fuels, and managing the transition to new energy paradigms are the most critical energy issues facing the planet in the next 100 years or more • Solutions will come from using an “Energy Systems” approach to ensure we end up with a truly integrated energy economy, balancing economic, environmental and social needs
Our Energy Challenges • Energy, environment, and economy inexorably linked in ways we can no longer ignore, with global, as well as national implications • Sufficient energy resources for global needs for several hundred years, perhaps indefinitely, but extraction and usage technologies are major issues • No “Magic Bullet” supply solution; every energy source will be needed • Carbon/fossil energy sources will still supply most of the world’s energy needs for the foreseeable future • Renewable energy sources will grow rapidly, but, even with accelerated effort, they will comprise no more than 20% of world supply in 2050 • Thus, triaging the impact of fossil fuels, and managing the transition to new energy paradigms are the most critical energy issues facing the planet in the next 100 years or more • Solutions will come from using an “Energy Systems” approach to ensure we end up with a truly integrated energy economy, balancing economic, environmental and social needs
 Options “Business as Usual” – – Increasing geopolitical tensions Supply disruptions Deteriorating environmental/climate change issues Increased market and price instability An Era of Responsible, Sustainable Energy Supply – Responsible development of “conventional” (especially fossil) energy sources with particular emphasis on lower carbon footprint and reduced collateral resource requirements – Integration of energy sources, distribution and markets; “systems thinking” – Accelerated development of unconventional/alternate energy sources – Emphasis on technology development and deployment – Responsive and encouraging regulatory environment – More certain and stable business environment
Options “Business as Usual” – – Increasing geopolitical tensions Supply disruptions Deteriorating environmental/climate change issues Increased market and price instability An Era of Responsible, Sustainable Energy Supply – Responsible development of “conventional” (especially fossil) energy sources with particular emphasis on lower carbon footprint and reduced collateral resource requirements – Integration of energy sources, distribution and markets; “systems thinking” – Accelerated development of unconventional/alternate energy sources – Emphasis on technology development and deployment – Responsive and encouraging regulatory environment – More certain and stable business environment
 The Challenge and the Opportunity Challenge -- How to Unleash Technology Innovation in order to Increase Energy Supply, Security and Availability while Reducing Absolute Environmental Impacts, particularly GHG’s Solution -- To Integrate and Balance the Innovation Supply Chain for Effective Solutions Delivery so that we get Innovative Solutions Implemented Innovation Supply Chain – What’s That?
The Challenge and the Opportunity Challenge -- How to Unleash Technology Innovation in order to Increase Energy Supply, Security and Availability while Reducing Absolute Environmental Impacts, particularly GHG’s Solution -- To Integrate and Balance the Innovation Supply Chain for Effective Solutions Delivery so that we get Innovative Solutions Implemented Innovation Supply Chain – What’s That?
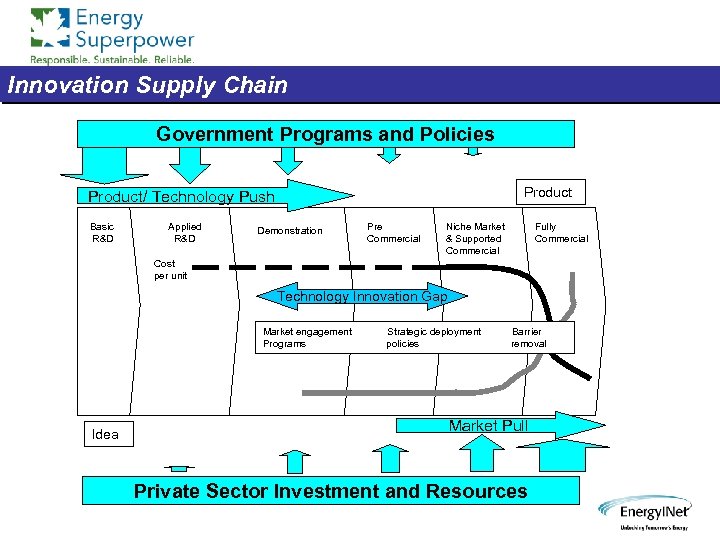 Innovation Supply Chain Government Programs and Policies Product/ Technology Push Basic R&D Applied R&D Demonstration Pre Commercial Niche Market & Supported Commercial Fully Commercial Cost per unit Technology Innovation Gap Market engagement Programs Idea Strategic deployment policies Barrier removal Market Pull Private Sector Investment and Resources
Innovation Supply Chain Government Programs and Policies Product/ Technology Push Basic R&D Applied R&D Demonstration Pre Commercial Niche Market & Supported Commercial Fully Commercial Cost per unit Technology Innovation Gap Market engagement Programs Idea Strategic deployment policies Barrier removal Market Pull Private Sector Investment and Resources
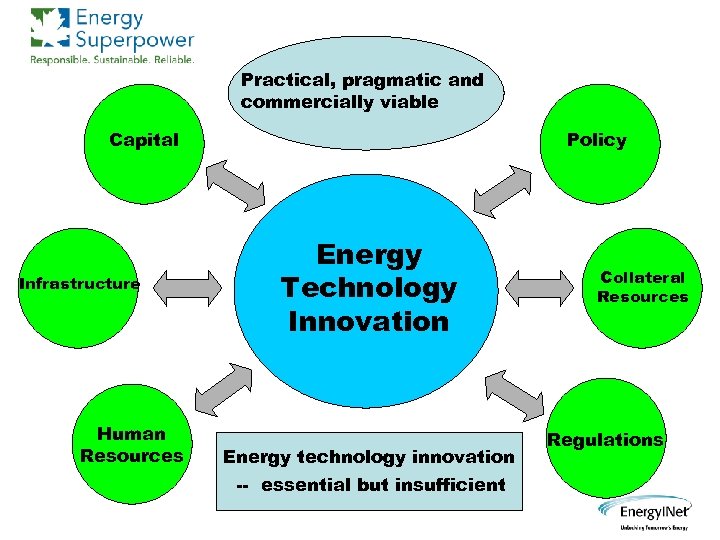 Practical, pragmatic and commercially viable Capital Infrastructure Human Resources Policy Energy Technology Innovation Energy technology innovation -- essential but insufficient Collateral Resources Regulations
Practical, pragmatic and commercially viable Capital Infrastructure Human Resources Policy Energy Technology Innovation Energy technology innovation -- essential but insufficient Collateral Resources Regulations
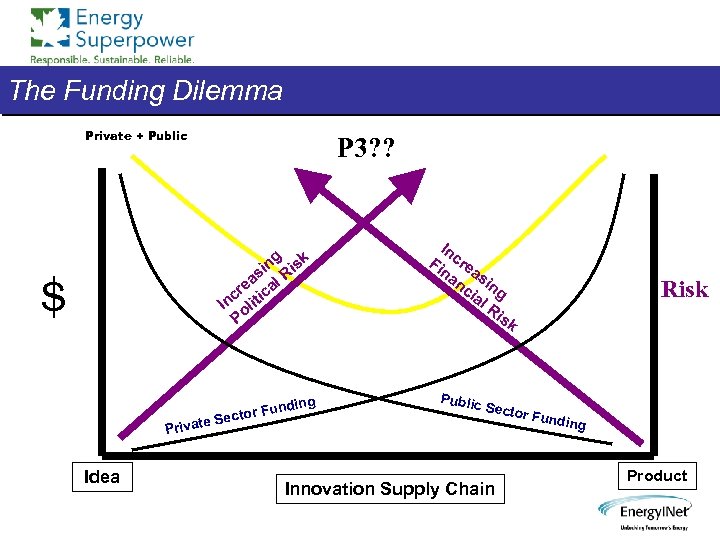 The Funding Dilemma Private + Public P 3? ? g k in Ris s ea cal r nc liti I o P S ate Se Priv Idea undi ctor F ng In Fi cre na as nc ing ia l. R is k Public Risk Secto r Fund Innovation Supply Chain ing Product
The Funding Dilemma Private + Public P 3? ? g k in Ris s ea cal r nc liti I o P S ate Se Priv Idea undi ctor F ng In Fi cre na as nc ing ia l. R is k Public Risk Secto r Fund Innovation Supply Chain ing Product
 What Should Government Do? Show leadership -- embrace and lead a vision of integrated, innovative energy production and usage with minimal carbon releases Provide increased certainty for investment decisions -clearer, long-term policy frameworks Accelerate the implementation of responsive, simplified, coordinated and supportive regulations Share technology innovation and implementation risks Strengthen our innovation supply chains to improve the outputs of technological innovation
What Should Government Do? Show leadership -- embrace and lead a vision of integrated, innovative energy production and usage with minimal carbon releases Provide increased certainty for investment decisions -clearer, long-term policy frameworks Accelerate the implementation of responsive, simplified, coordinated and supportive regulations Share technology innovation and implementation risks Strengthen our innovation supply chains to improve the outputs of technological innovation
 Some Energy. INet Project Areas Implementing clean carbon technologies Do we need a hydrogen economy, electricity economy or both? Large and small scale electricity storage Community energy planning and green energy buildings GHG friendly transportation options Reducing water usage in the energy sector Applying nuclear technology to fossil fuel extraction/processing Ocean energy commercial evaluation Non-volcanic deep geothermal Bioenergy from non-food sources Advanced CO 2 management demonstration sites Integrating renewable energy into conventional distribution infrastructure
Some Energy. INet Project Areas Implementing clean carbon technologies Do we need a hydrogen economy, electricity economy or both? Large and small scale electricity storage Community energy planning and green energy buildings GHG friendly transportation options Reducing water usage in the energy sector Applying nuclear technology to fossil fuel extraction/processing Ocean energy commercial evaluation Non-volcanic deep geothermal Bioenergy from non-food sources Advanced CO 2 management demonstration sites Integrating renewable energy into conventional distribution infrastructure

 Innovation’s International Connection Many countries face similar challenges – innovation is a global concern; supply chains are international and integrating rapidly Canada develops only three percent of the world’s S&T, so the rest must be developed outside Canada – Technology is an international commodity, and technologies need to be sourced internationally. We cannot afford the time or money to “reinvent the wheel” International technology intelligence and awareness International consortiums make sense for international challenges Think outside the US/EU “box”; e. g. China (HTGC pebble bed reactors), Brazil (biomass ethanol), Russia (PV’s), Taiwan, S. Korea, etc Shared investment reduces costs and risks
Innovation’s International Connection Many countries face similar challenges – innovation is a global concern; supply chains are international and integrating rapidly Canada develops only three percent of the world’s S&T, so the rest must be developed outside Canada – Technology is an international commodity, and technologies need to be sourced internationally. We cannot afford the time or money to “reinvent the wheel” International technology intelligence and awareness International consortiums make sense for international challenges Think outside the US/EU “box”; e. g. China (HTGC pebble bed reactors), Brazil (biomass ethanol), Russia (PV’s), Taiwan, S. Korea, etc Shared investment reduces costs and risks
 Other Benefits from Energy Innovation Energy sector is one of the world’s biggest economic drivers Abundant, secure supplies of energy are vital for the rest of the economy Energy technology companies have local customers and demonstration opportunities Investors understand energy technologies Technologies will build a more competitive energy sector Huge export opportunities exist for energy technologies If we focus on innovative, integrated approaches to responsible energy development, we have a huge opportunity to contribute to global sustainability, while enjoying economic growth.
Other Benefits from Energy Innovation Energy sector is one of the world’s biggest economic drivers Abundant, secure supplies of energy are vital for the rest of the economy Energy technology companies have local customers and demonstration opportunities Investors understand energy technologies Technologies will build a more competitive energy sector Huge export opportunities exist for energy technologies If we focus on innovative, integrated approaches to responsible energy development, we have a huge opportunity to contribute to global sustainability, while enjoying economic growth.


