f89e66b77ef3bc588cd37ee62d981380.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 164

 Energy, Force, and Motion identifying energy transformations; Identifying and analyzing the transfer of heat energy by conduction, convection, and radiation interpreting a phase diagram; describing and calculating velocity and acceleration; comparing Newton’s three laws; calculating mechanical advantage; understanding the work of simple machines Waves, Electricity, and Magnetism investigating light and sound phenomena and comparing light to sound; Doppler effect; describing the causes of static electricity; constructing and analyzing series and parallel circuits; describing the relationship between voltage, current and resistance and relating electricity and magnetism and common applications
Energy, Force, and Motion identifying energy transformations; Identifying and analyzing the transfer of heat energy by conduction, convection, and radiation interpreting a phase diagram; describing and calculating velocity and acceleration; comparing Newton’s three laws; calculating mechanical advantage; understanding the work of simple machines Waves, Electricity, and Magnetism investigating light and sound phenomena and comparing light to sound; Doppler effect; describing the causes of static electricity; constructing and analyzing series and parallel circuits; describing the relationship between voltage, current and resistance and relating electricity and magnetism and common applications
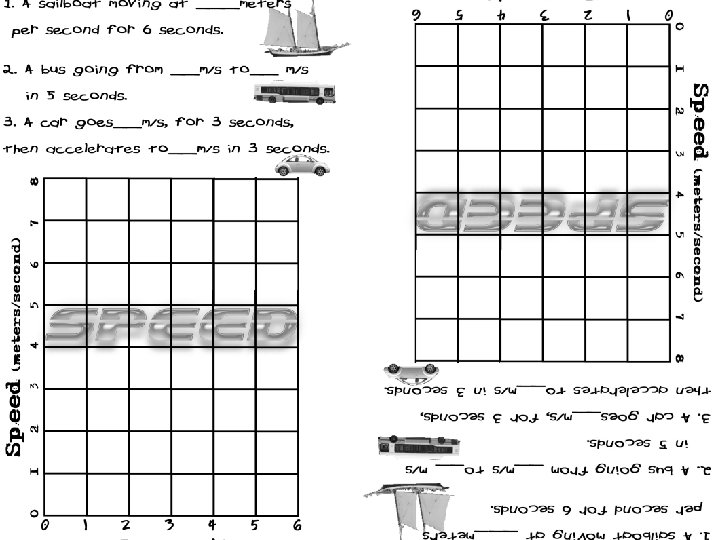
 SPEED Describes how fast an object is moving.
SPEED Describes how fast an object is moving.
 distance Average Speed = time
distance Average Speed = time

















































 Velocity The speed of an object in a certain direction.
Velocity The speed of an object in a certain direction.
 Velocity d V = t speed of an object in a certain direction. V = velocity (meters/second) d = distance (meters) t = time (seconds)
Velocity d V = t speed of an object in a certain direction. V = velocity (meters/second) d = distance (meters) t = time (seconds)
 Velocity speed of an object in a certain direction. 0 3 seconds 1 2
Velocity speed of an object in a certain direction. 0 3 seconds 1 2
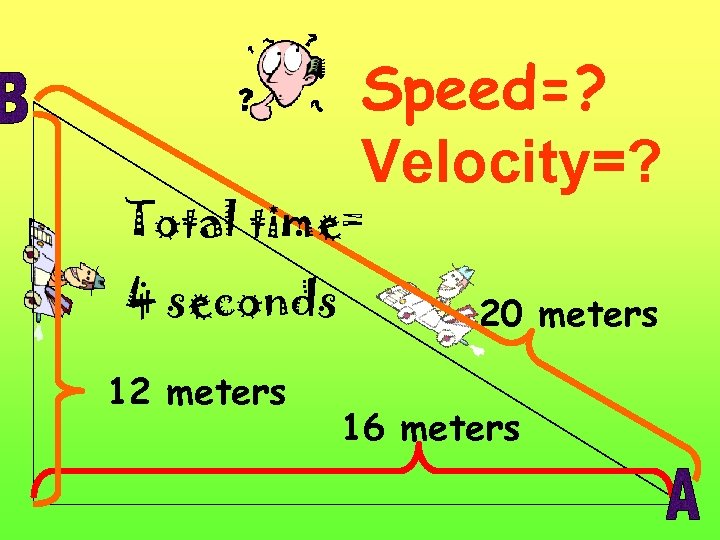 Speed=? Velocity=? Total time= 4 seconds 12 meters 20 meters 16 meters
Speed=? Velocity=? Total time= 4 seconds 12 meters 20 meters 16 meters
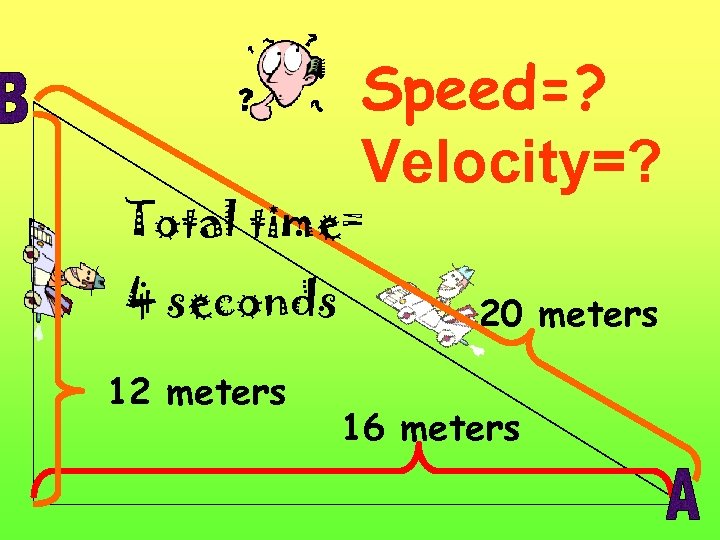 Speed=? Velocity=? Total time= 4 seconds 12 meters 20 meters 16 meters
Speed=? Velocity=? Total time= 4 seconds 12 meters 20 meters 16 meters
 Numerator Denominator 5 12
Numerator Denominator 5 12
 Acceleration
Acceleration
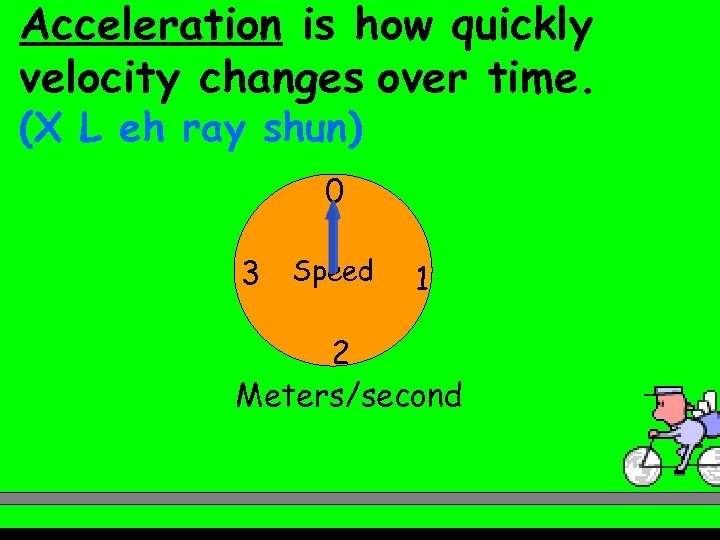 Acceleration is how quickly velocity changes over time. (X L eh ray shun) 0 3 Speed 1 2 Meters/second
Acceleration is how quickly velocity changes over time. (X L eh ray shun) 0 3 Speed 1 2 Meters/second
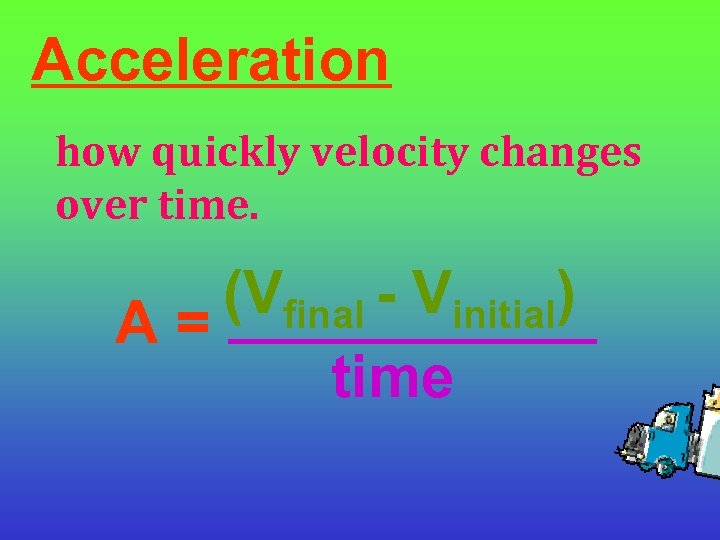 Acceleration how quickly velocity changes over time. (Vfinal - Vinitial) A = ______ time
Acceleration how quickly velocity changes over time. (Vfinal - Vinitial) A = ______ time
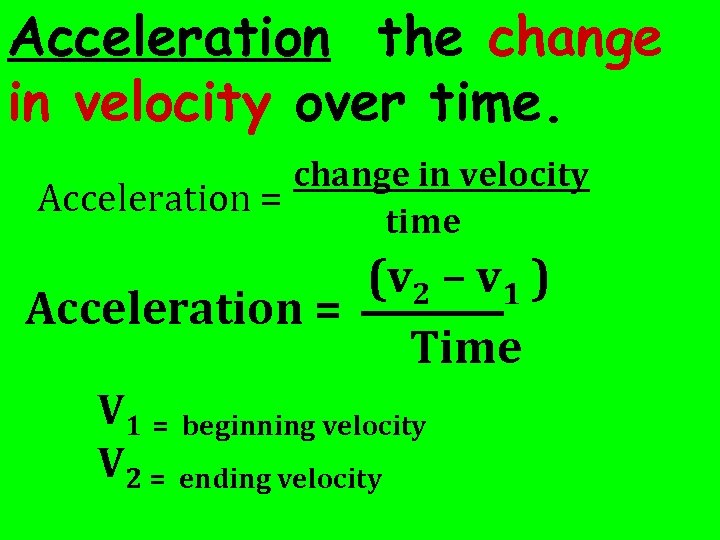 Acceleration the change in velocity over time. change in velocity Acceleration = time (v 2 – v 1 ) ____ Acceleration = Time V 1 = beginning velocity V 2 = ending velocity
Acceleration the change in velocity over time. change in velocity Acceleration = time (v 2 – v 1 ) ____ Acceleration = Time V 1 = beginning velocity V 2 = ending velocity
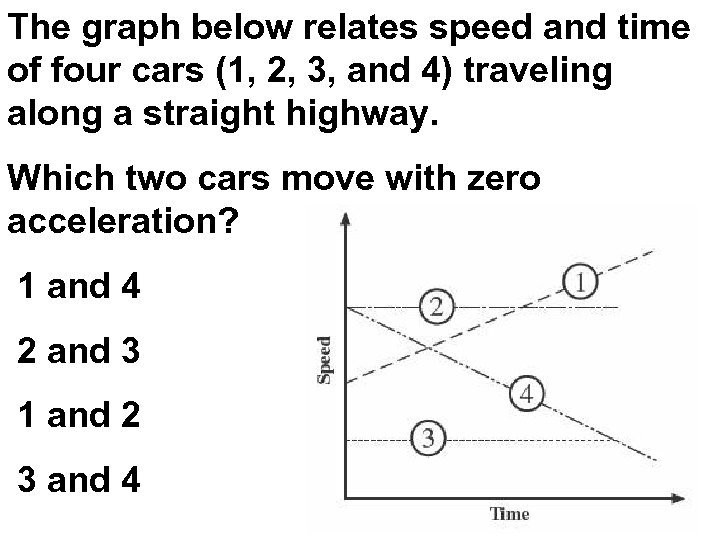 The graph below relates speed and time of four cars (1, 2, 3, and 4) traveling along a straight highway. Which two cars move with zero acceleration? 1 and 4 2 and 3 1 and 2 3 and 4
The graph below relates speed and time of four cars (1, 2, 3, and 4) traveling along a straight highway. Which two cars move with zero acceleration? 1 and 4 2 and 3 1 and 2 3 and 4
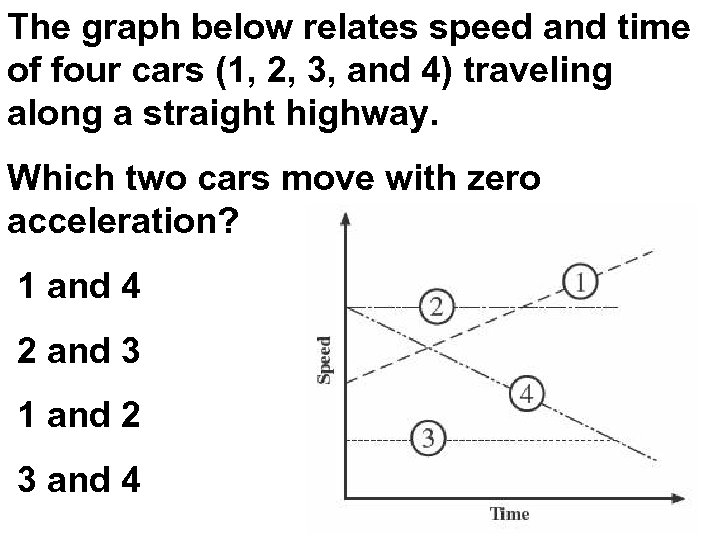 The graph below relates speed and time of four cars (1, 2, 3, and 4) traveling along a straight highway. Which two cars move with zero acceleration? 1 and 4 2 and 3 1 and 2 3 and 4
The graph below relates speed and time of four cars (1, 2, 3, and 4) traveling along a straight highway. Which two cars move with zero acceleration? 1 and 4 2 and 3 1 and 2 3 and 4
 Which of the following is certain to change as a ball accelerates? mass of the ball inertia of the ball velocity of the ball force acting on the ball
Which of the following is certain to change as a ball accelerates? mass of the ball inertia of the ball velocity of the ball force acting on the ball
 Which of the following is certain to change as a ball accelerates? mass of the ball inertia of the ball velocity of the ball force acting on the ball
Which of the following is certain to change as a ball accelerates? mass of the ball inertia of the ball velocity of the ball force acting on the ball
 What must happen to an object in order to accelerate it? A net force must be applied. Some weight must be removed. Its frictional coefficient must be reduced. It must contain momentum.
What must happen to an object in order to accelerate it? A net force must be applied. Some weight must be removed. Its frictional coefficient must be reduced. It must contain momentum.
 What must happen to an object in order to accelerate it? A net force must be applied. Some weight must be removed. Its frictional coefficient must be reduced. It must contain momentum.
What must happen to an object in order to accelerate it? A net force must be applied. Some weight must be removed. Its frictional coefficient must be reduced. It must contain momentum.
 Which of these describes the object with the largest acceleration ? An object with a small change in velocity over a small change in time An object with a small change in velocity over a large change in time An object with a large change in velocity over a small change in time An object with a large change in velocity over a large change in time
Which of these describes the object with the largest acceleration ? An object with a small change in velocity over a small change in time An object with a small change in velocity over a large change in time An object with a large change in velocity over a small change in time An object with a large change in velocity over a large change in time
 Which of these describes the object with the largest acceleration ? An object with a small change in velocity over a small change in time An object with a small change in velocity over a large change in time An object with a large change in velocity over a small change in time An object with a large change in velocity over a large change in time
Which of these describes the object with the largest acceleration ? An object with a small change in velocity over a small change in time An object with a small change in velocity over a large change in time An object with a large change in velocity over a small change in time An object with a large change in velocity over a large change in time
 Scalar a measurement that does NOT contain direction. Egg sample: Speed Vector a measurement that contains direction. Egg sample: Velocity
Scalar a measurement that does NOT contain direction. Egg sample: Speed Vector a measurement that contains direction. Egg sample: Velocity
 Forces of Nature Gravitational Magnetic
Forces of Nature Gravitational Magnetic
 Mass and Inertia The universe consists of matter in motion
Mass and Inertia The universe consists of matter in motion
 The greater the mass the harder it is to move. And. . . the harder it is to stop moving.
The greater the mass the harder it is to move. And. . . the harder it is to stop moving.
 Lower mass objects are easier to move. . . and to stop moving.
Lower mass objects are easier to move. . . and to stop moving.
 NEWTON’s Laws 1 st Law of Motion : An object remains at a constant speed in astraight path , until a net force acts on it.
NEWTON’s Laws 1 st Law of Motion : An object remains at a constant speed in astraight path , until a net force acts on it.
 NEWTON’s 1 st Law of Motion is the law of An object will remain at a constant speed (unless disturbed).
NEWTON’s 1 st Law of Motion is the law of An object will remain at a constant speed (unless disturbed).
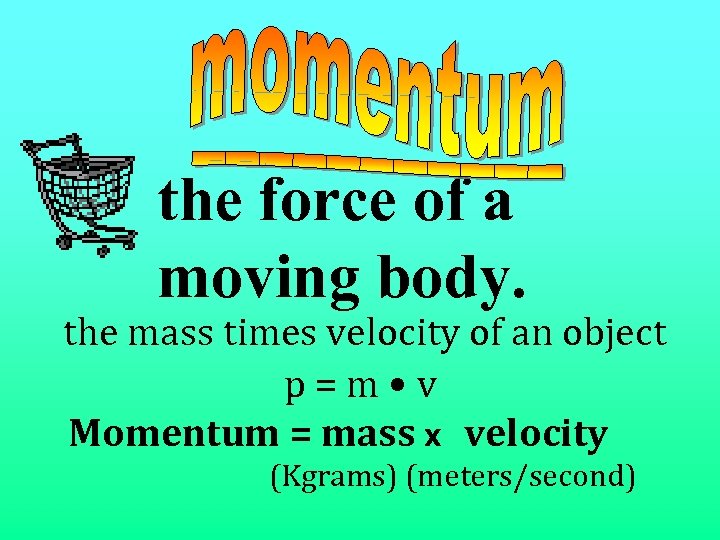 the force of a moving body. the mass times velocity of an object p=m • v Momentum = mass x velocity (Kgrams) (meters/second)
the force of a moving body. the mass times velocity of an object p=m • v Momentum = mass x velocity (Kgrams) (meters/second)
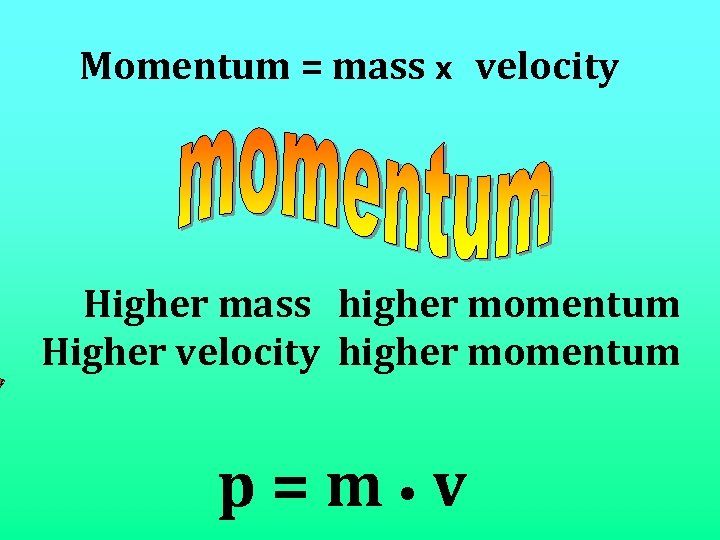 Momentum = mass x velocity Higher mass higher momentum Higher velocity higher momentum p=m • v
Momentum = mass x velocity Higher mass higher momentum Higher velocity higher momentum p=m • v
 includes velocity. So, it has direction. Momentum points in the direction of motion.
includes velocity. So, it has direction. Momentum points in the direction of motion.
 Conservation of momentum When objects collide, all of the momentum goes somewhere.
Conservation of momentum When objects collide, all of the momentum goes somewhere.
 Conservation of momentum When objects collide, all of the momentum goes somewhere.
Conservation of momentum When objects collide, all of the momentum goes somewhere.
 Conservation of momentum When objects collide, all of the momentum goes somewhere.
Conservation of momentum When objects collide, all of the momentum goes somewhere.
 Conservation of momentum When objects collide, all of the momentum goes somewhere.
Conservation of momentum When objects collide, all of the momentum goes somewhere.
 NEWTON’s nd Law of Motion : 2 An object that has a force acting on it will change its speed (accelerate).
NEWTON’s nd Law of Motion : 2 An object that has a force acting on it will change its speed (accelerate).
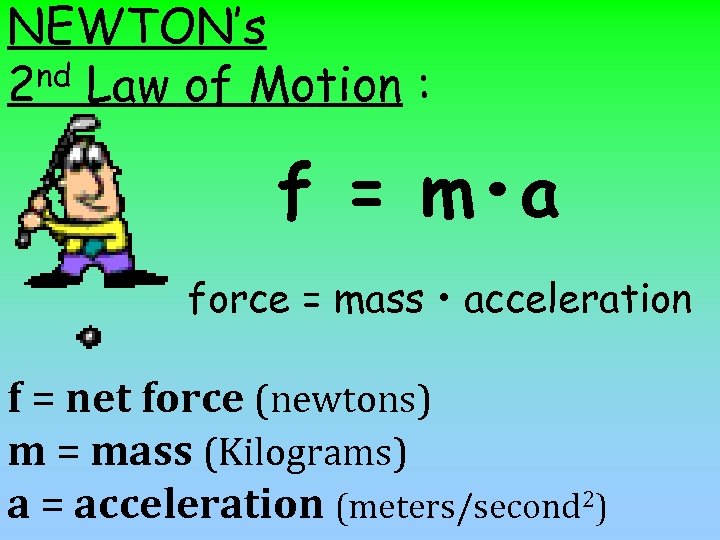 NEWTON’s nd Law of Motion : 2 f = m • a force = mass • acceleration f = net force (newtons) m = mass (Kilograms) a = acceleration (meters/second 2)
NEWTON’s nd Law of Motion : 2 f = m • a force = mass • acceleration f = net force (newtons) m = mass (Kilograms) a = acceleration (meters/second 2)
 NEWTON’s nd Law of Motion : f 2 mass of the club = m • a acceleration of the club force of the club
NEWTON’s nd Law of Motion : f 2 mass of the club = m • a acceleration of the club force of the club
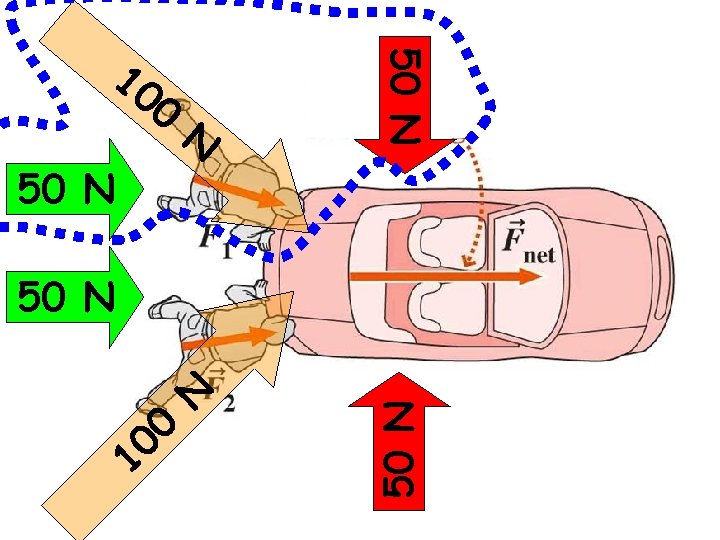
 Net force is the total amount of Force (minus the forces that cancel each other out). Force of gravity Force of muscles Net force
Net force is the total amount of Force (minus the forces that cancel each other out). Force of gravity Force of muscles Net force
 When the net force is Zero. -> NO movement When the net force is NOT Zero. -> movement
When the net force is Zero. -> NO movement When the net force is NOT Zero. -> movement
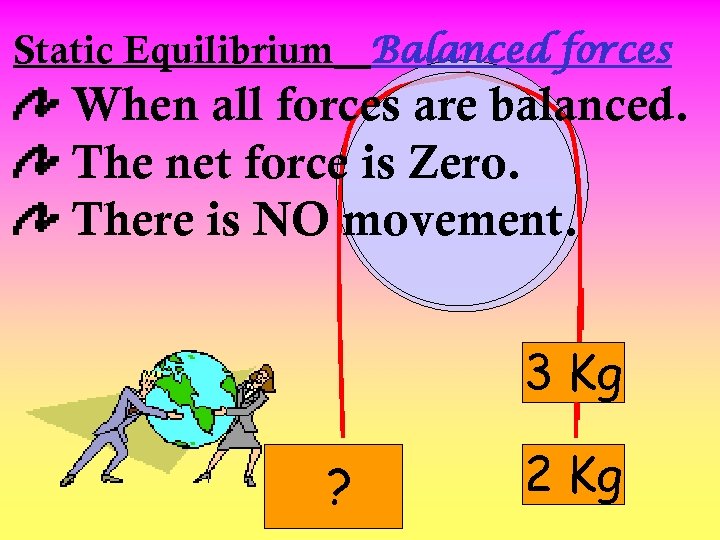 Static Equilibrium Balanced forces When all forces are balanced. The net force is Zero. There is NO movement. 3 Kg ? 2 Kg
Static Equilibrium Balanced forces When all forces are balanced. The net force is Zero. There is NO movement. 3 Kg ? 2 Kg
 N 50 N 10 0 N 50 N
N 50 N 10 0 N 50 N
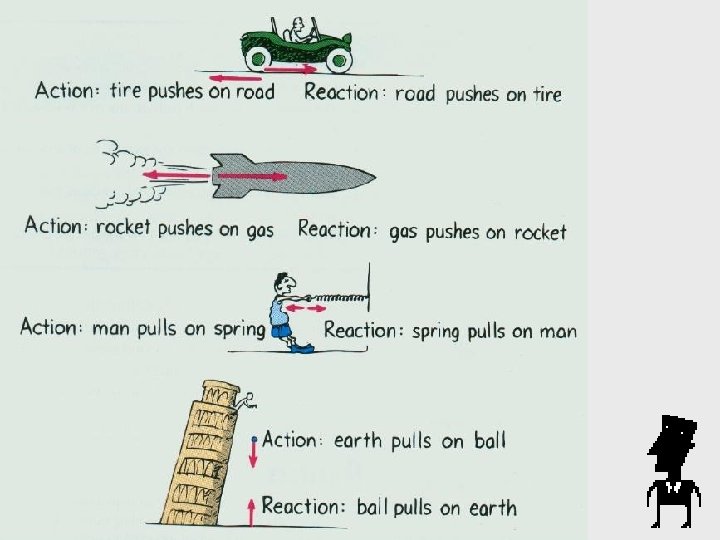
 NEWTON’s 3 rd Law of Motion: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
NEWTON’s 3 rd Law of Motion: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
 NEWTON’s 3 rd Law of Motion: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
NEWTON’s 3 rd Law of Motion: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
 NEWTON’s 3 rd Law of Motion: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
NEWTON’s 3 rd Law of Motion: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
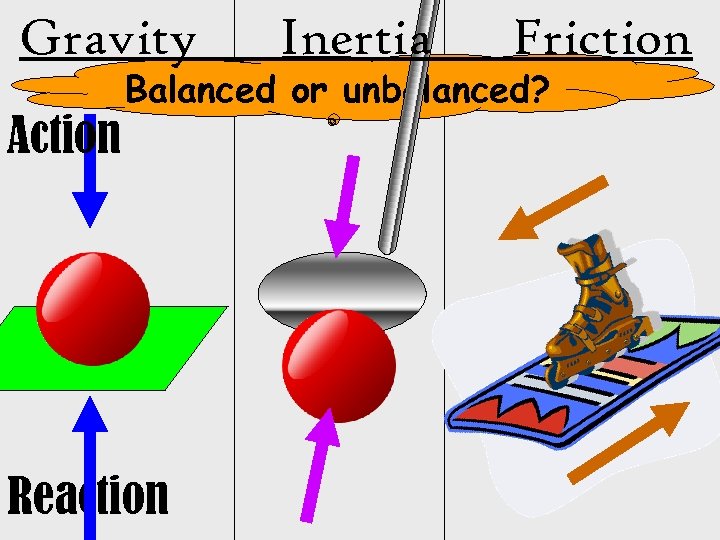 Gravity Action Inertia Friction Balanced or unbalanced? Reaction
Gravity Action Inertia Friction Balanced or unbalanced? Reaction
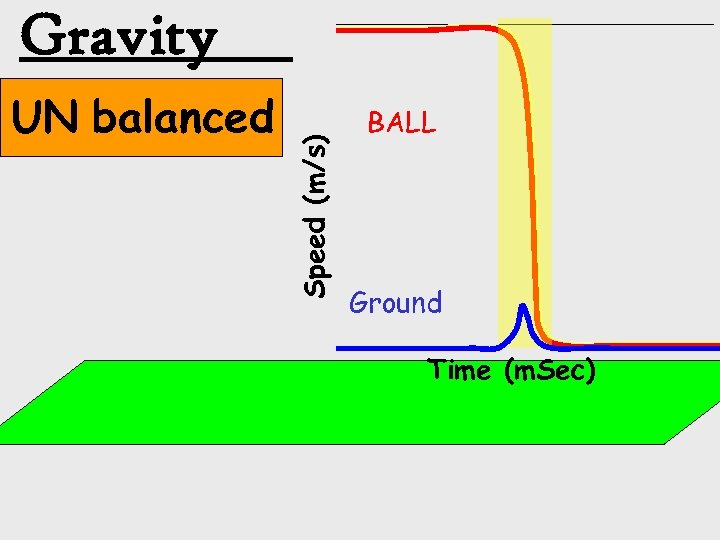 UN balanced Speed (m/s) Gravity BALL Ground Time (m. Sec)
UN balanced Speed (m/s) Gravity BALL Ground Time (m. Sec)
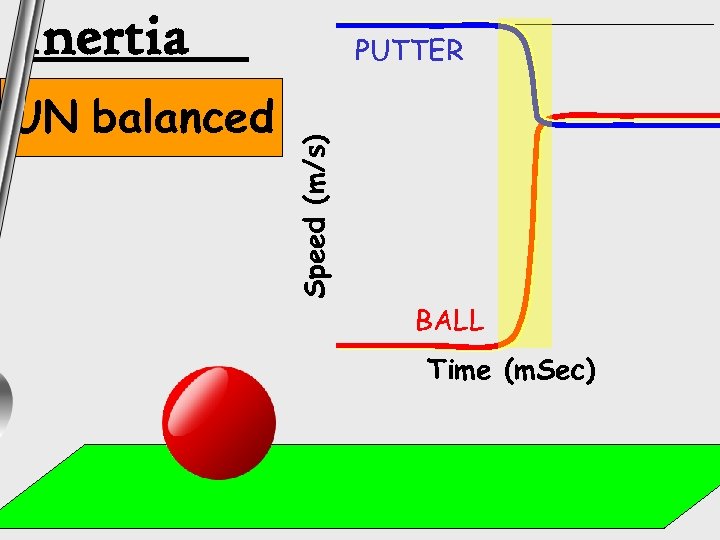 Inertia Speed (m/s) UN balanced PUTTER BALL Time (m. Sec)
Inertia Speed (m/s) UN balanced PUTTER BALL Time (m. Sec)
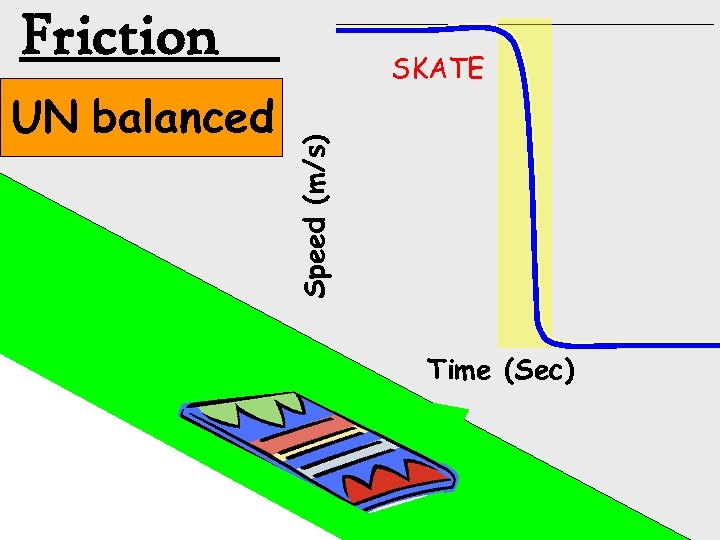 Friction Speed (m/s) UN balanced SKATE Time (Sec)
Friction Speed (m/s) UN balanced SKATE Time (Sec)
 A car is traveling down a hill. Which of the following will affect the amount of energy the car has? how long the car is the time of day how much the car weighs the color of the car
A car is traveling down a hill. Which of the following will affect the amount of energy the car has? how long the car is the time of day how much the car weighs the color of the car
 KEY A car is traveling down a hill. Which of the following will affect the amount of energy the car has? how long the car is the time of day how much the car weighs the color of the car
KEY A car is traveling down a hill. Which of the following will affect the amount of energy the car has? how long the car is the time of day how much the car weighs the color of the car
 Friction the resistive force that occurs when two surfaces travel past each other. causes physical deformation generates heat
Friction the resistive force that occurs when two surfaces travel past each other. causes physical deformation generates heat
 Friction the resistive force that occurs when two surfaces contact each other.
Friction the resistive force that occurs when two surfaces contact each other.
 Oliver the dog doesn't want to walk in the rain. He can make his owner pull harder on the leash to get him out the door by: A. sitting on the vinyl floor. B. sitting on the tile floor. C. sitting on the carpeted floor. D. sitting on the wood floor.
Oliver the dog doesn't want to walk in the rain. He can make his owner pull harder on the leash to get him out the door by: A. sitting on the vinyl floor. B. sitting on the tile floor. C. sitting on the carpeted floor. D. sitting on the wood floor.
 KEY Oliver the dog doesn't want to walk in the rain. He can make his owner pull harder on the leash to get him out the door by: A. sitting on the vinyl floor. B. sitting on the tile floor. C. sitting on the carpeted floor. D. sitting on the wood floor.
KEY Oliver the dog doesn't want to walk in the rain. He can make his owner pull harder on the leash to get him out the door by: A. sitting on the vinyl floor. B. sitting on the tile floor. C. sitting on the carpeted floor. D. sitting on the wood floor.
 Pauline needs to measure the sliding friction of a brick. How should she go about doing this? A. attach the brick to a string and then to a spring scale and read the force needed to quickly lift the brick off the ground B. drag the brick by a string attached to a spring scale so that it gradually speeds up C. drag the brick by a string attached to a spring scale along the surface of a table at a constant speed and read the force D. hang the brick from a string attached to a spring scale and read the force
Pauline needs to measure the sliding friction of a brick. How should she go about doing this? A. attach the brick to a string and then to a spring scale and read the force needed to quickly lift the brick off the ground B. drag the brick by a string attached to a spring scale so that it gradually speeds up C. drag the brick by a string attached to a spring scale along the surface of a table at a constant speed and read the force D. hang the brick from a string attached to a spring scale and read the force
 KEY Pauline needs to measure the sliding friction of a brick. How should she go about doing this? A. attach the brick to a string and then to a spring scale and read the force needed to quickly lift the brick off the ground B. drag the brick by a string attached to a spring scale so that it gradually speeds up C. drag the brick by a string attached to a spring scale along the surface of a table at a constant speed and read the force D. hang the brick from a string attached to a spring scale and read the force
KEY Pauline needs to measure the sliding friction of a brick. How should she go about doing this? A. attach the brick to a string and then to a spring scale and read the force needed to quickly lift the brick off the ground B. drag the brick by a string attached to a spring scale so that it gradually speeds up C. drag the brick by a string attached to a spring scale along the surface of a table at a constant speed and read the force D. hang the brick from a string attached to a spring scale and read the force
 Sliding frictionthe drag force created when the surface of one object slides across the surface of another object. Sliding Friction Lab Object Surface force (Newstons)
Sliding frictionthe drag force created when the surface of one object slides across the surface of another object. Sliding Friction Lab Object Surface force (Newstons)
 terminal velocity gravity will accelerate an object until air resistance (friction) does not allow it to go any faster.
terminal velocity gravity will accelerate an object until air resistance (friction) does not allow it to go any faster.
 In the absence of air resistance, which of these objects will fall at the fastest rate when dropped? the ball with a mass of 75 kg the ball with a mass of 25 kg the ball with a mass of 10 kg They all fall at the same rate.
In the absence of air resistance, which of these objects will fall at the fastest rate when dropped? the ball with a mass of 75 kg the ball with a mass of 25 kg the ball with a mass of 10 kg They all fall at the same rate.
 In the absence of air resistance, KEY which of these objects will fall at the fastest rate when dropped? the ball with a mass of 75 kg the ball with a mass of 25 kg the ball with a mass of 10 kg They all fall at the same rate.
In the absence of air resistance, KEY which of these objects will fall at the fastest rate when dropped? the ball with a mass of 75 kg the ball with a mass of 25 kg the ball with a mass of 10 kg They all fall at the same rate.
 Pressure is the amount of force exerted over a certain area. Pressure = Force Area
Pressure is the amount of force exerted over a certain area. Pressure = Force Area
 Pressure = Force (newtons) Area (m 2) 1 Pascal = 1 Newton/meter 2
Pressure = Force (newtons) Area (m 2) 1 Pascal = 1 Newton/meter 2

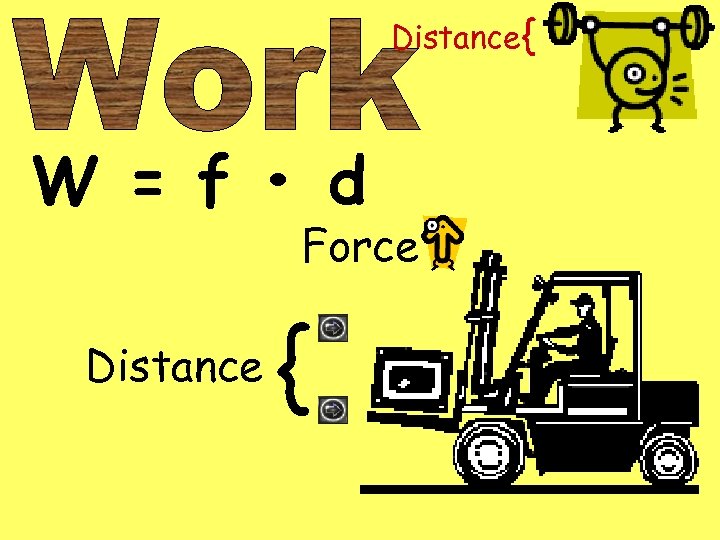 Distance { W = f • d Force Distance {
Distance { W = f • d Force Distance {
 Gravitational force
Gravitational force
 Gravitational force
Gravitational force
 Gravitational force o INCREASES with Mass o DECREASES with Distance
Gravitational force o INCREASES with Mass o DECREASES with Distance
 All objects in the universe are attracted to each other by the force of effort. friction. gravity. inertia.
All objects in the universe are attracted to each other by the force of effort. friction. gravity. inertia.
 All objects in the universe are attracted to each other by the force of effort. friction. gravity. inertia.
All objects in the universe are attracted to each other by the force of effort. friction. gravity. inertia.
 Four pairs of objects have the masses shown below. If the objects in each pair are the same distance apart, the gravitational force between the objects in which pair is greatest? 1 kilogram and 2 kilograms and 1 kilogram 2 kilograms and 2 kilograms
Four pairs of objects have the masses shown below. If the objects in each pair are the same distance apart, the gravitational force between the objects in which pair is greatest? 1 kilogram and 2 kilograms and 1 kilogram 2 kilograms and 2 kilograms
 Four pairs of objects have the masses shown below. If the objects in each pair are the same distance apart, the gravitational force between the objects in which pair is greatest? 1 kilogram and 2 kilograms and 1 kilogram 2 kilograms and 2 kilograms
Four pairs of objects have the masses shown below. If the objects in each pair are the same distance apart, the gravitational force between the objects in which pair is greatest? 1 kilogram and 2 kilograms and 1 kilogram 2 kilograms and 2 kilograms
 As an astronaut travels from Earth to a space station orbiting Earth, what happens to her mass and weight? Her mass decreases, but her weight remains the same. Her mass increases as her weight decreases. Her mass remains the same, but her weight decreases. Her mass decreases and her weight also decreases.
As an astronaut travels from Earth to a space station orbiting Earth, what happens to her mass and weight? Her mass decreases, but her weight remains the same. Her mass increases as her weight decreases. Her mass remains the same, but her weight decreases. Her mass decreases and her weight also decreases.
 As an astronaut travels from Earth to a space station orbiting Earth, what happens to her mass and weight? Her mass decreases, but her weight remains the same. Her mass increases as her weight decreases. Her mass remains the same, but her weight decreases. Her mass decreases and her weight also decreases.
As an astronaut travels from Earth to a space station orbiting Earth, what happens to her mass and weight? Her mass decreases, but her weight remains the same. Her mass increases as her weight decreases. Her mass remains the same, but her weight decreases. Her mass decreases and her weight also decreases.
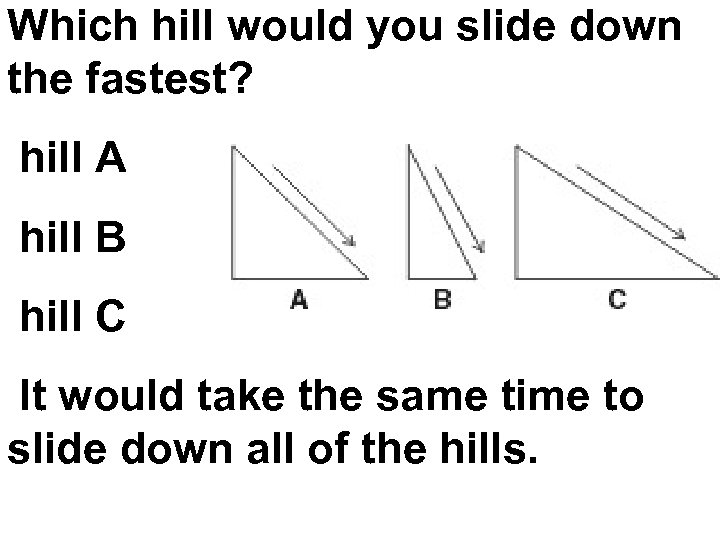 Which hill would you slide down the fastest? hill A hill B hill C It would take the same time to slide down all of the hills.
Which hill would you slide down the fastest? hill A hill B hill C It would take the same time to slide down all of the hills.
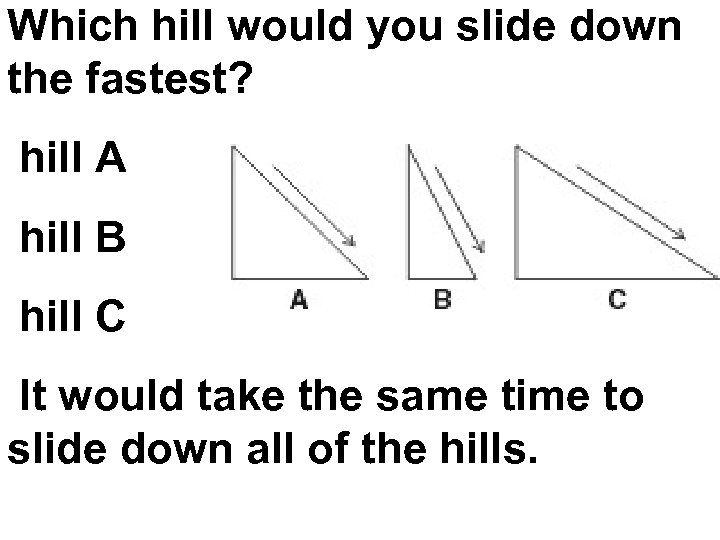 Which hill would you slide down the fastest? hill A hill B hill C It would take the same time to slide down all of the hills.
Which hill would you slide down the fastest? hill A hill B hill C It would take the same time to slide down all of the hills.
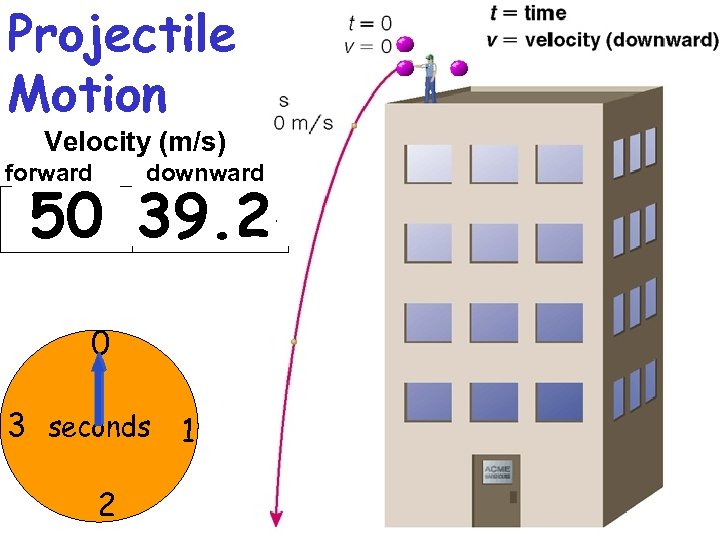 Projectile Motion Velocity (m/s) forward downward 50 19. 6 39. 2 29. 4 9. 8 0 0 3 seconds 1 2
Projectile Motion Velocity (m/s) forward downward 50 19. 6 39. 2 29. 4 9. 8 0 0 3 seconds 1 2
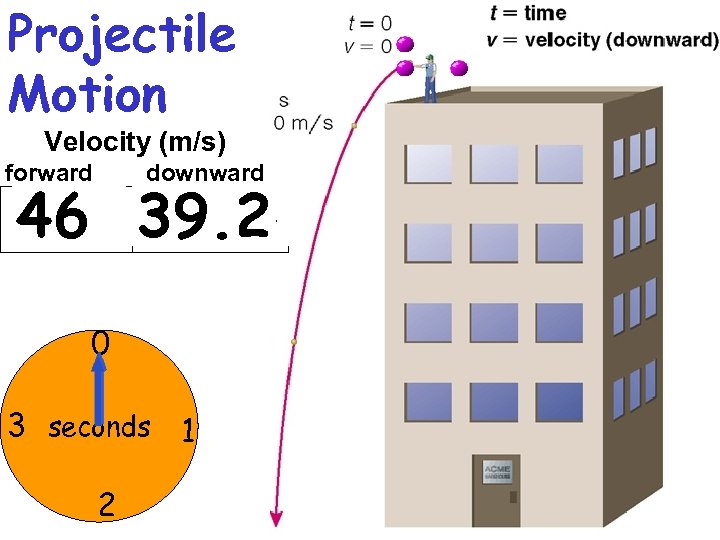 Projectile Motion Velocity (m/s) forward downward 46 29. 4 47 39. 2 48 19. 6 49 9. 8 50 0 0 3 seconds 1 2
Projectile Motion Velocity (m/s) forward downward 46 29. 4 47 39. 2 48 19. 6 49 9. 8 50 0 0 3 seconds 1 2
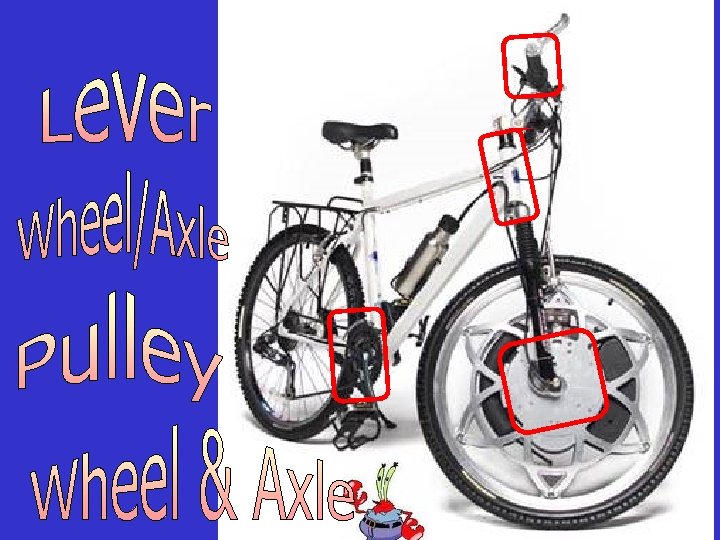
 Simple Machines and work Lever Inclined plane Pulley Wedge Screw Wheel and axle
Simple Machines and work Lever Inclined plane Pulley Wedge Screw Wheel and axle
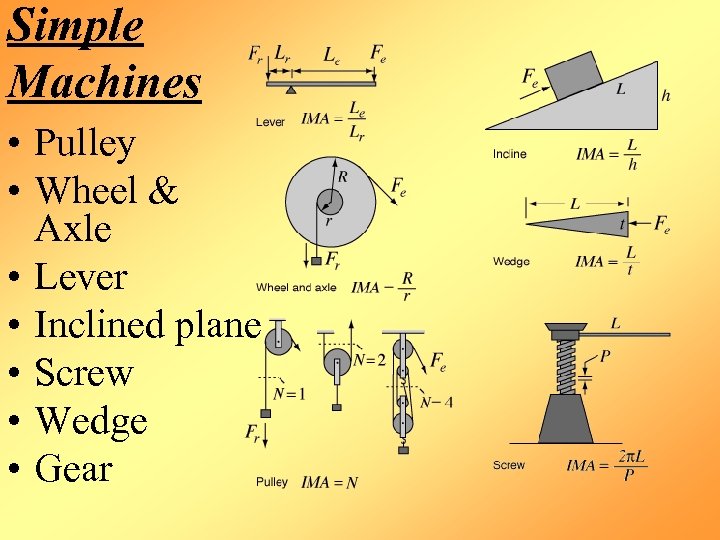 Simple Machines • Pulley • Wheel & Axle • Lever • Inclined plane • Screw • Wedge • Gear
Simple Machines • Pulley • Wheel & Axle • Lever • Inclined plane • Screw • Wedge • Gear
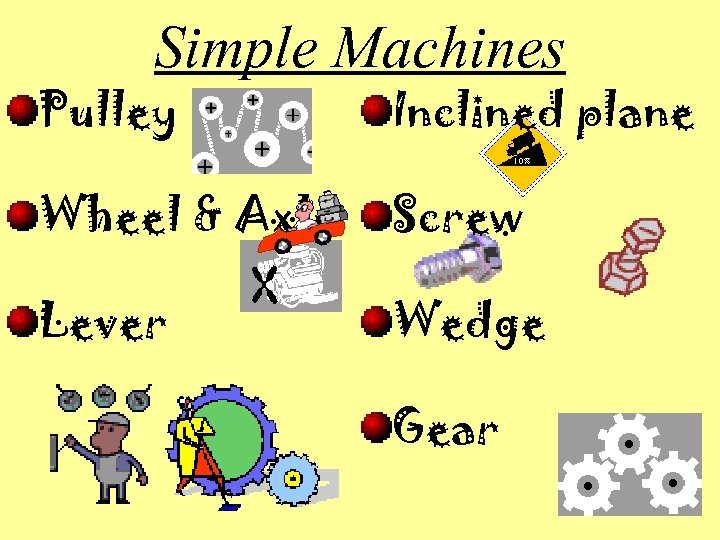 Simple Machines Pulley Inclined plane Wheel & Axle Screw Lever Wedge Gear
Simple Machines Pulley Inclined plane Wheel & Axle Screw Lever Wedge Gear
 Which activity involves the use of a simple machine? riding on a seesaw flying a kite listening to a radio skiing down a hill
Which activity involves the use of a simple machine? riding on a seesaw flying a kite listening to a radio skiing down a hill
 Which activity involves the use of a simple machine? riding on a seesaw flying a kite listening to a radio skiing down a hill
Which activity involves the use of a simple machine? riding on a seesaw flying a kite listening to a radio skiing down a hill

 Simple Machine A mechanism that lowers the amount of force needed to do work, by increasing the distance.
Simple Machine A mechanism that lowers the amount of force needed to do work, by increasing the distance.
 On which simple machine is a fulcrum found? pulley wheel axle lever
On which simple machine is a fulcrum found? pulley wheel axle lever
 On which simple machine is a fulcrum found? pulley wheel axle lever
On which simple machine is a fulcrum found? pulley wheel axle lever
 ALL Simple Machines work the same way
ALL Simple Machines work the same way
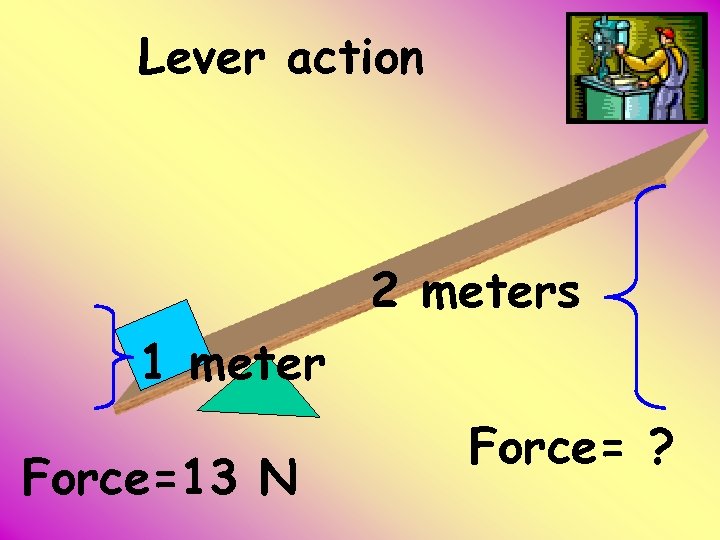 Lever action 2 meters 1 meter Force=13 N Force= ?
Lever action 2 meters 1 meter Force=13 N Force= ?
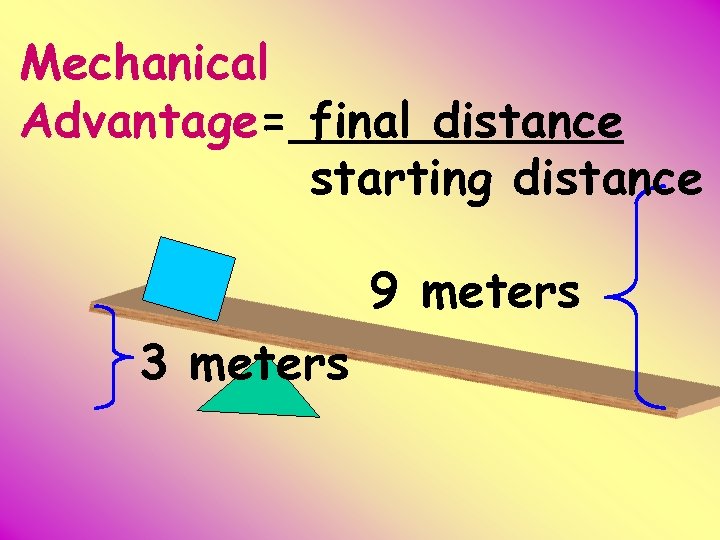 Mechanical Advantage= final distance starting distance 9 meters 3 meters
Mechanical Advantage= final distance starting distance 9 meters 3 meters
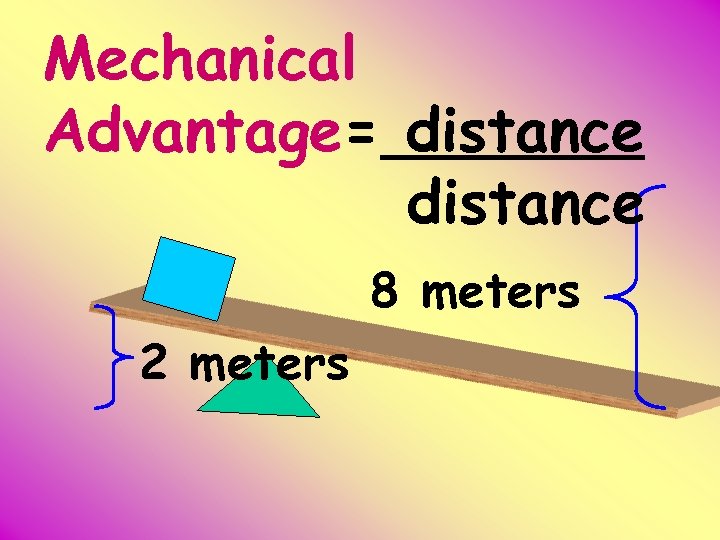 Mechanical Advantage= distance 8 meters 2 meters
Mechanical Advantage= distance 8 meters 2 meters
 Which of the following is often used as a lever? file nail saw crowbar
Which of the following is often used as a lever? file nail saw crowbar
 Which of the following is often used as a lever? file nail saw crowbar
Which of the following is often used as a lever? file nail saw crowbar
 The Wedge
The Wedge
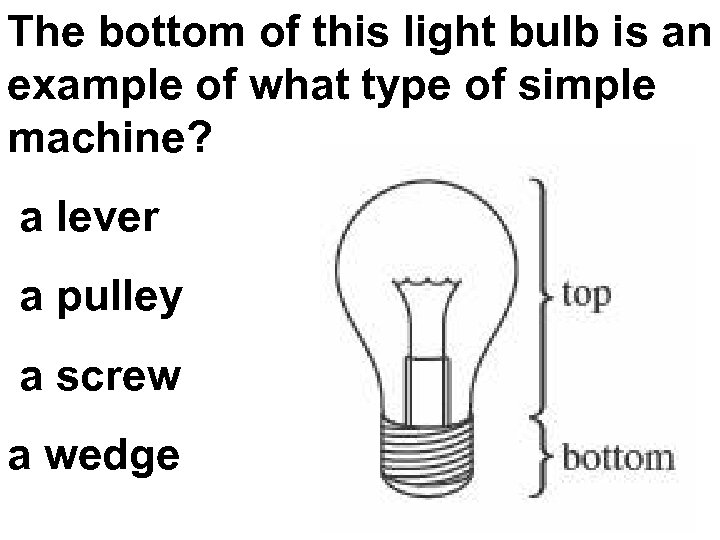 The bottom of this light bulb is an example of what type of simple machine? a lever a pulley a screw a wedge
The bottom of this light bulb is an example of what type of simple machine? a lever a pulley a screw a wedge
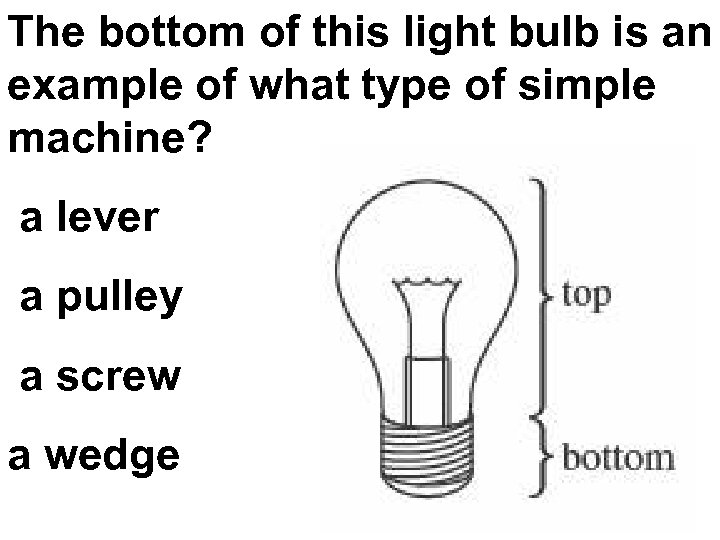 The bottom of this light bulb is an example of what type of simple machine? a lever a pulley a screw a wedge
The bottom of this light bulb is an example of what type of simple machine? a lever a pulley a screw a wedge
 What type of simple machine is used to split things apart? screw wheel and axle wedge inclined plane
What type of simple machine is used to split things apart? screw wheel and axle wedge inclined plane
 What type of simple machine is used to pull a flag up to the top of a flagpole? screw wheel and axle inclined plane pulley
What type of simple machine is used to pull a flag up to the top of a flagpole? screw wheel and axle inclined plane pulley
 What type of simple machine is used to pull a flag up to the top of a flagpole? screw wheel and axle inclined plane pulley
What type of simple machine is used to pull a flag up to the top of a flagpole? screw wheel and axle inclined plane pulley
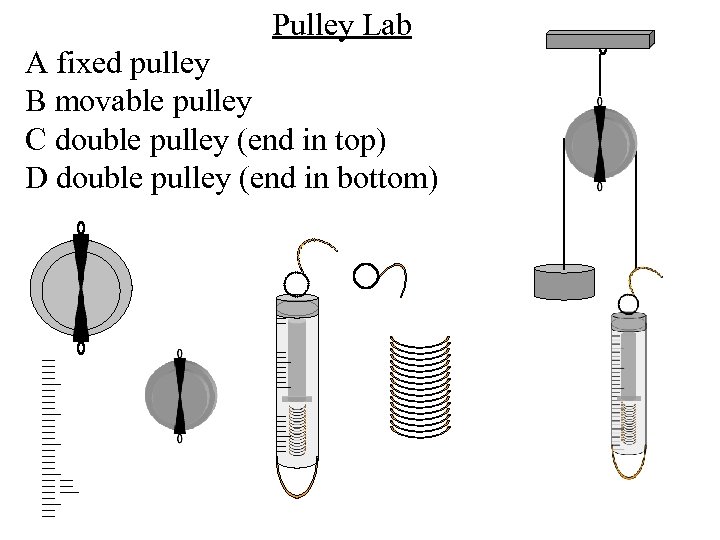 Pulley Lab A fixed pulley B movable pulley C double pulley (end in top) D double pulley (end in bottom)
Pulley Lab A fixed pulley B movable pulley C double pulley (end in top) D double pulley (end in bottom)
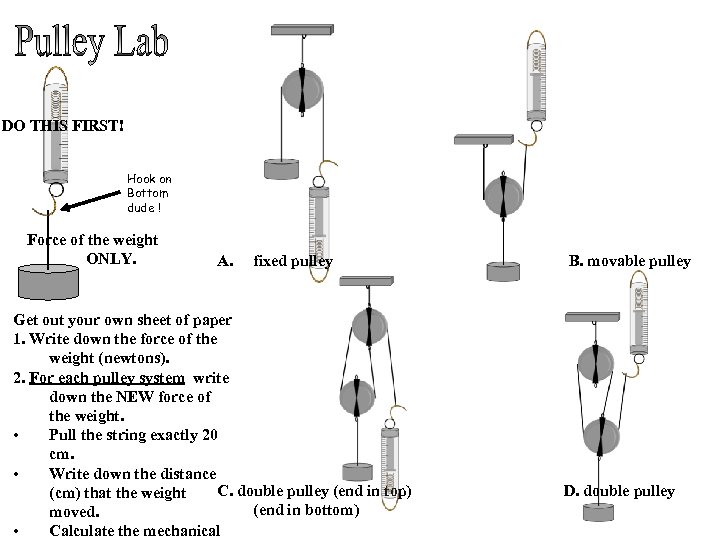 DO THIS FIRST! Hook on Bottom dude ! Force of the weight ONLY. A. fixed pulley B. movable pulley Get out your own sheet of paper 1. Write down the force of the weight (newtons). 2. For each pulley system write down the NEW force of the weight. • Pull the string exactly 20 cm. • Write down the distance C. double pulley (end in top) D. double pulley (cm) that the weight (end in bottom) moved. • Calculate the mechanical
DO THIS FIRST! Hook on Bottom dude ! Force of the weight ONLY. A. fixed pulley B. movable pulley Get out your own sheet of paper 1. Write down the force of the weight (newtons). 2. For each pulley system write down the NEW force of the weight. • Pull the string exactly 20 cm. • Write down the distance C. double pulley (end in top) D. double pulley (cm) that the weight (end in bottom) moved. • Calculate the mechanical
 BIG Teeth=16 small Teeth =8 16: 8 2: 1 So, the small gear spins TWICE AS FAST as the big gear.
BIG Teeth=16 small Teeth =8 16: 8 2: 1 So, the small gear spins TWICE AS FAST as the big gear.
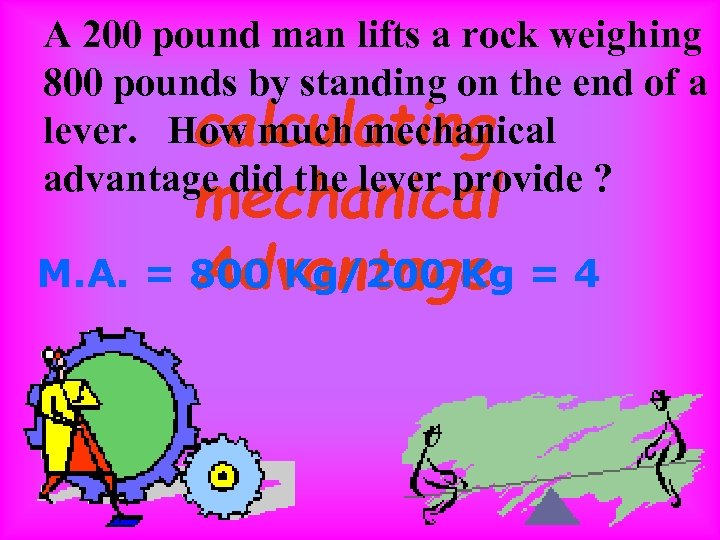 A 200 pound man lifts a rock weighing 800 pounds by standing on the end of a lever. How much mechanical calculating advantage did the lever provide ? mechanical M. A. = 800 Kg/200 Kg = 4 Advantage
A 200 pound man lifts a rock weighing 800 pounds by standing on the end of a lever. How much mechanical calculating advantage did the lever provide ? mechanical M. A. = 800 Kg/200 Kg = 4 Advantage
 If you wuz ‘n a Merry-go-round & yuz let go, Which wayz wud yu go?
If you wuz ‘n a Merry-go-round & yuz let go, Which wayz wud yu go?
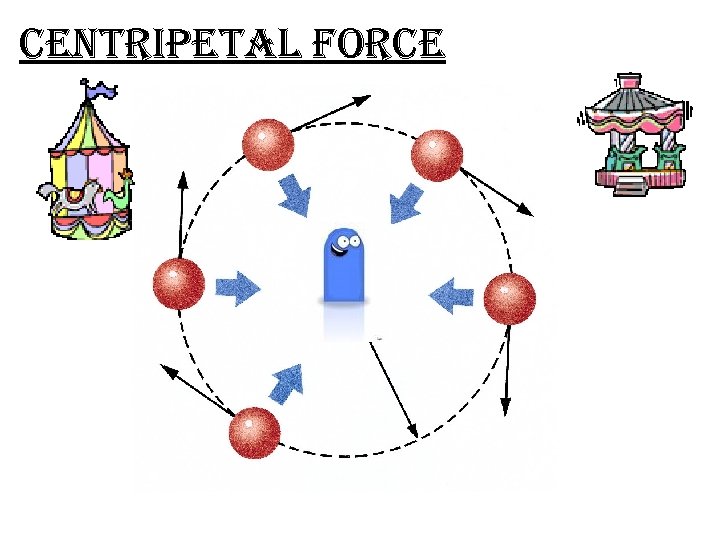
 centripetal force The inward force on a spinning object, that stops it from going in a straight line. Perpendicular
centripetal force The inward force on a spinning object, that stops it from going in a straight line. Perpendicular
 centripetal force
centripetal force
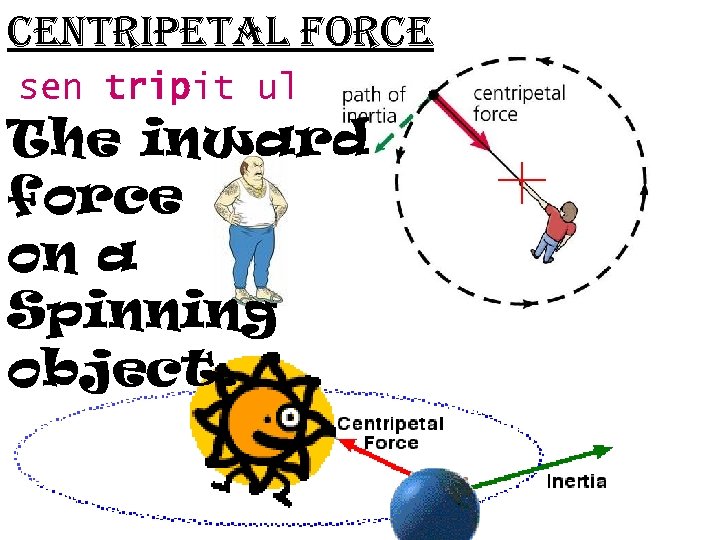 centripetal force sen tripit ul The inward force on a Spinning object.
centripetal force sen tripit ul The inward force on a Spinning object.
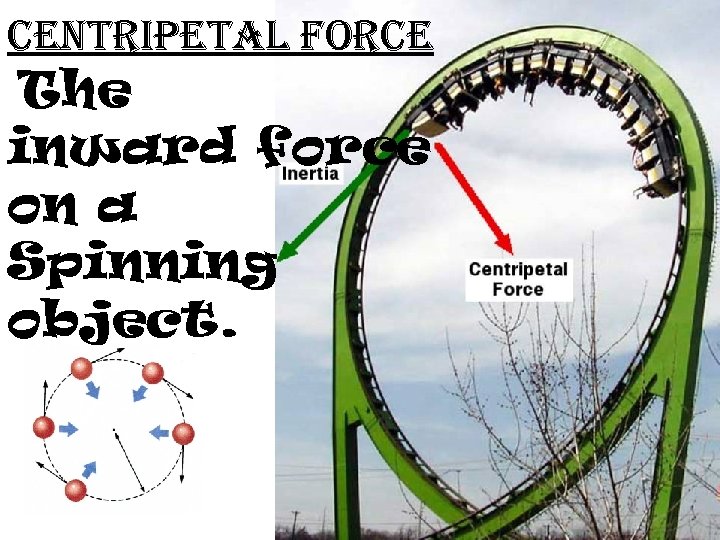 centripetal force The inward force on a Spinning object.
centripetal force The inward force on a Spinning object.
 Satellites stay in place as they orbit because of. . . the repeated firing of rocket boosters. the gravitational pull of Earth. a narrow path through the vacuum of space. solar panels generating energy to hold them in place
Satellites stay in place as they orbit because of. . . the repeated firing of rocket boosters. the gravitational pull of Earth. a narrow path through the vacuum of space. solar panels generating energy to hold them in place
 Satellites stay in place as they orbit because of. . . the repeated firing of rocket boosters. the gravitational pull of Earth. a narrow path through the vacuum of space. solar panels generating energy to hold them in place
Satellites stay in place as they orbit because of. . . the repeated firing of rocket boosters. the gravitational pull of Earth. a narrow path through the vacuum of space. solar panels generating energy to hold them in place
 © 2009 All rights reserved.
© 2009 All rights reserved.


